Valorization of Dextrose from Cassava Starch and Sugarcane Vinasse as Polyhydroxyalkanoates by Submerged Cultures of Cupriavidus necator: A Physicochemical–Biotechnological Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Treatment and Characterization of Raw Materials Used as a Substrate
2.2. Microorganism, Culture Media, and Cultivation Conditions
2.3. Biomass and Sugars Quantification
2.4. PHA Detection and Extraction
2.5. Material Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Treatment and Characterization of Sugarcane Vinasse
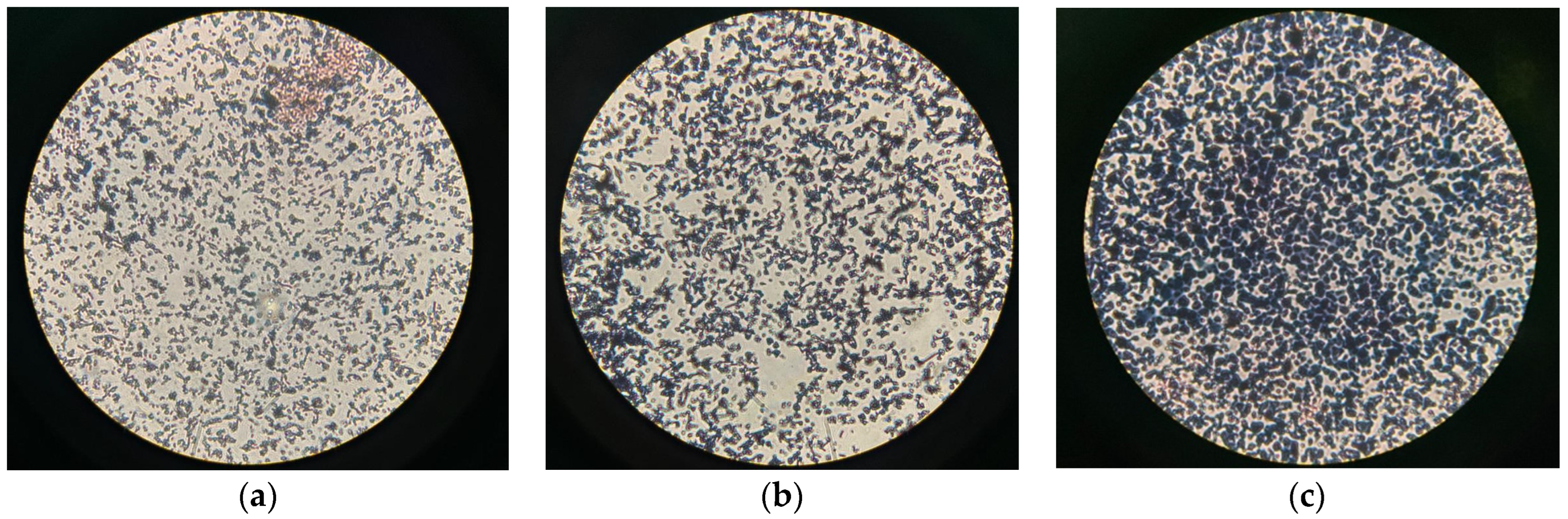
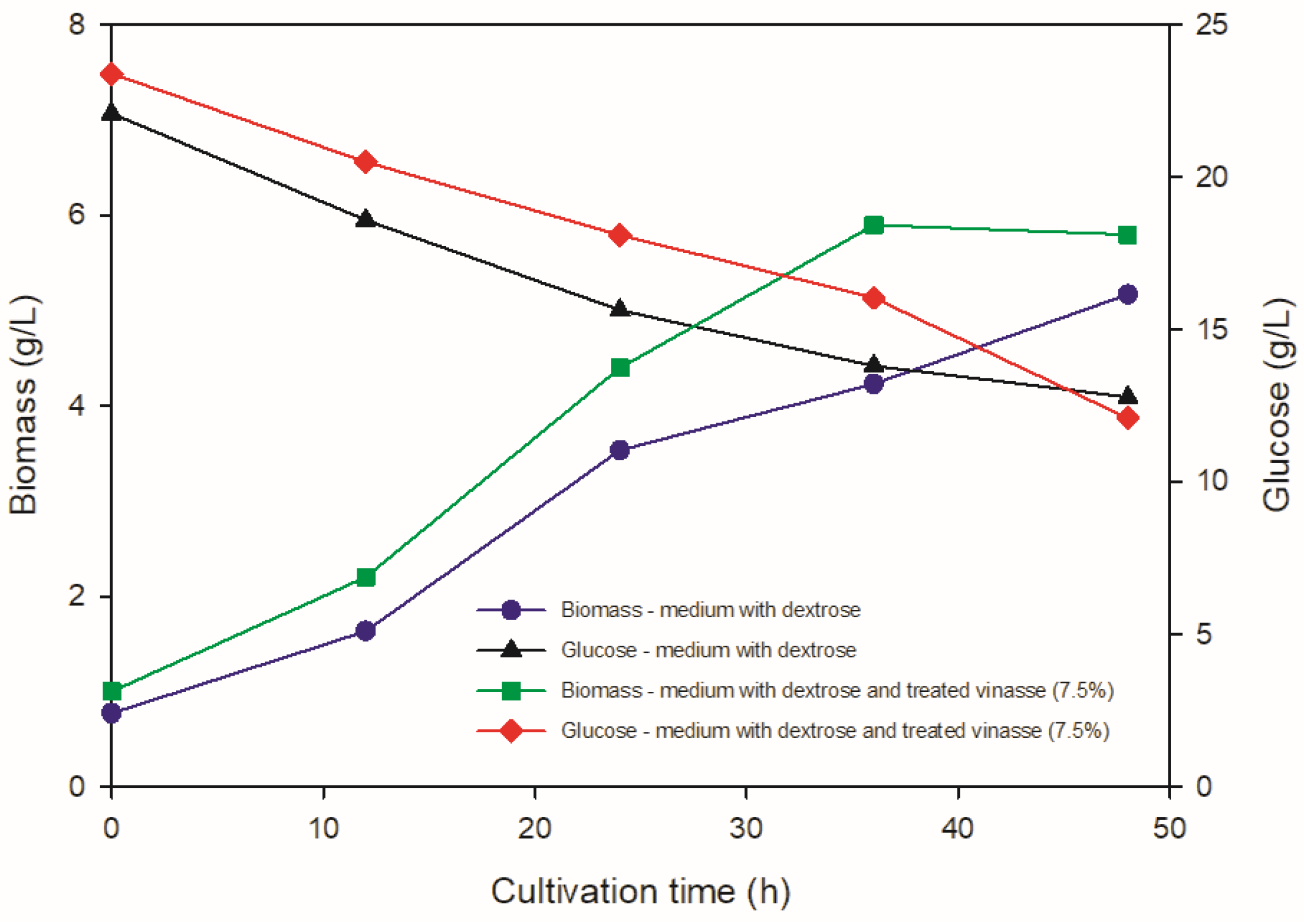
3.2. Kinetic Evaluation of C. necator in Dextrose Medium and PHB Production in Shake Flask Cultures
3.3. Evaluation of C. necator Growth and PHB Production with Dextrose from Cassava Starch and Sugarcane Vinasse as a Supplement
3.4. Biopolymer Characterization
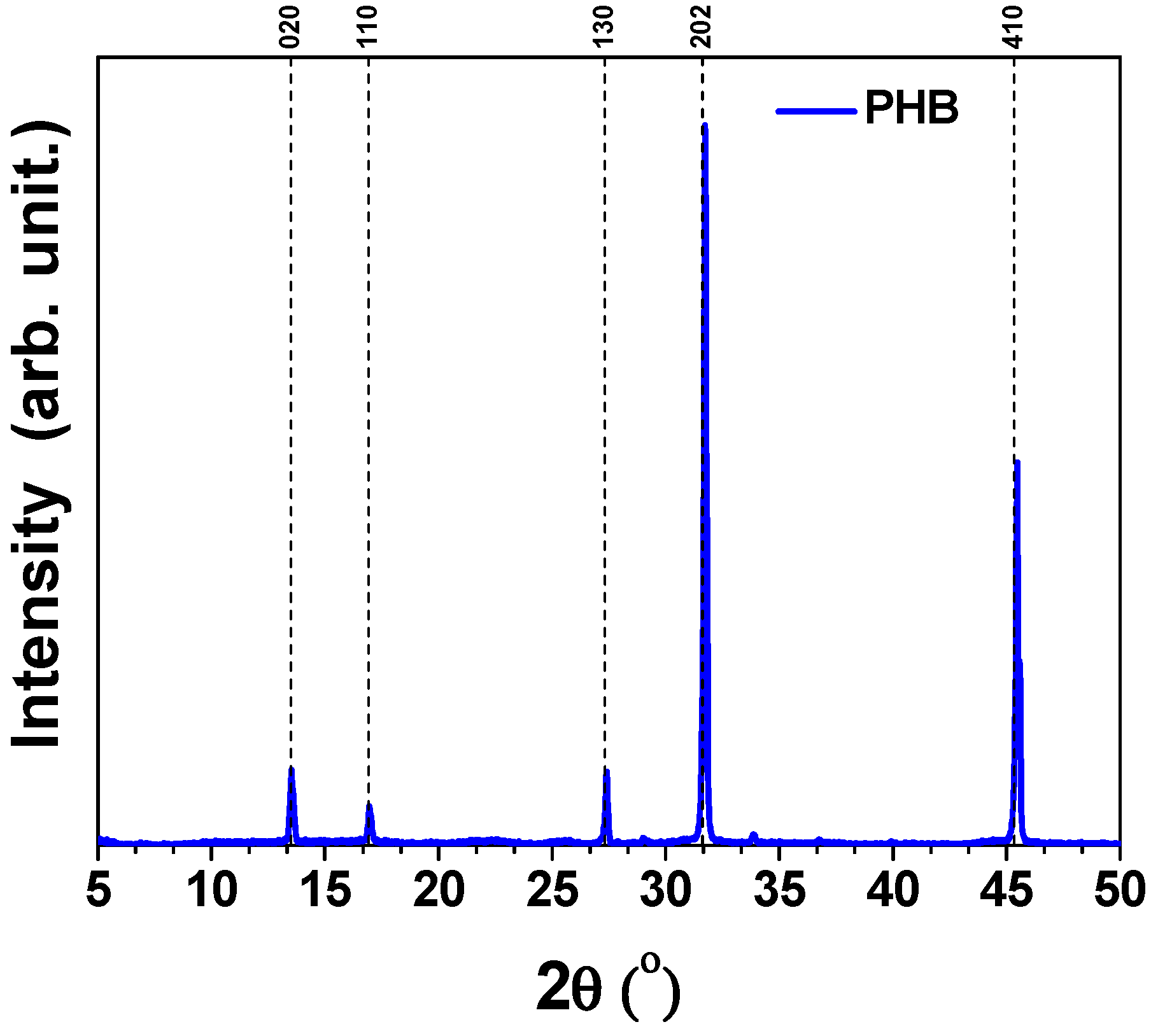
3.4.1. XRD Analysis
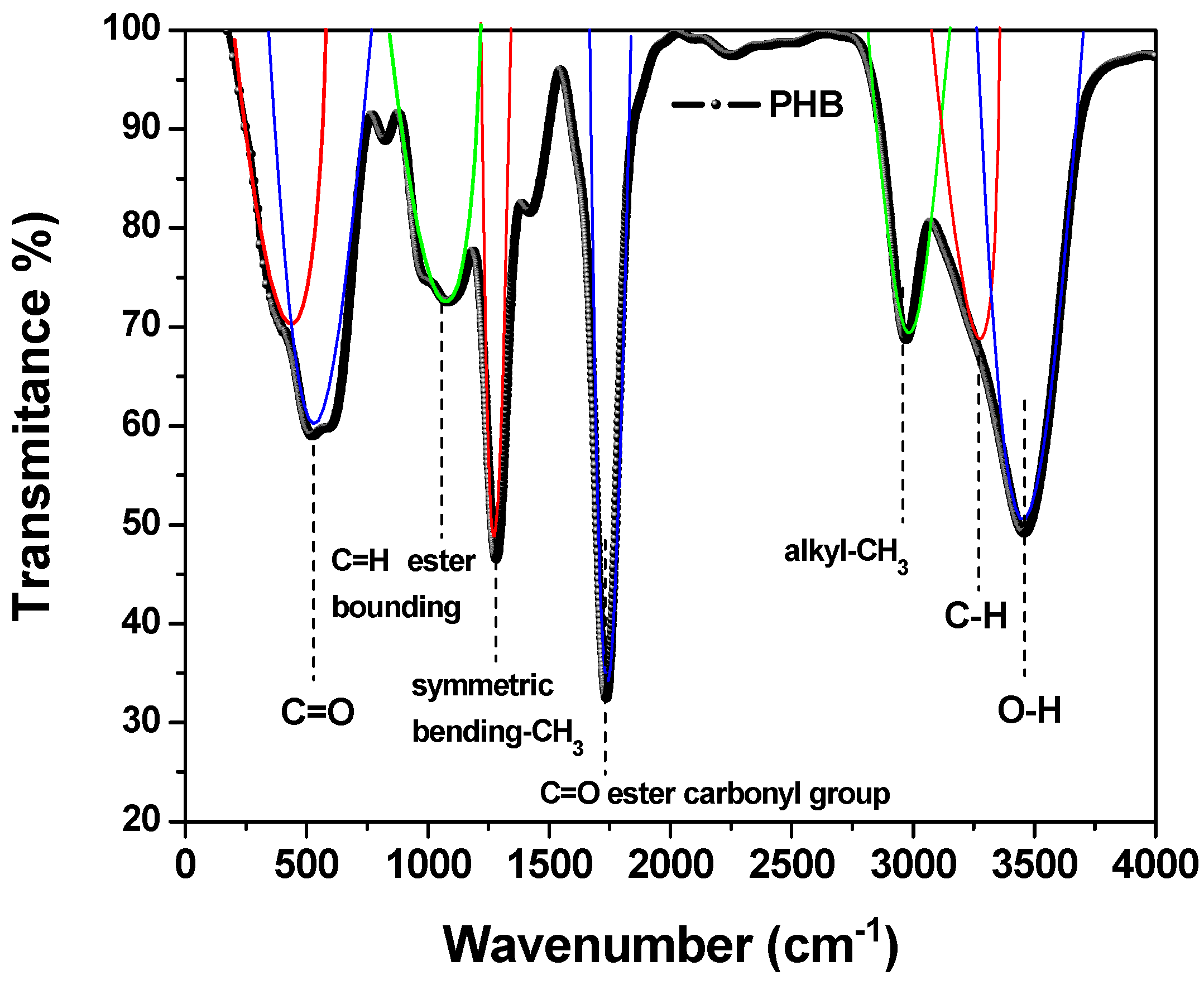
3.4.2. FTIR Spectroscopy
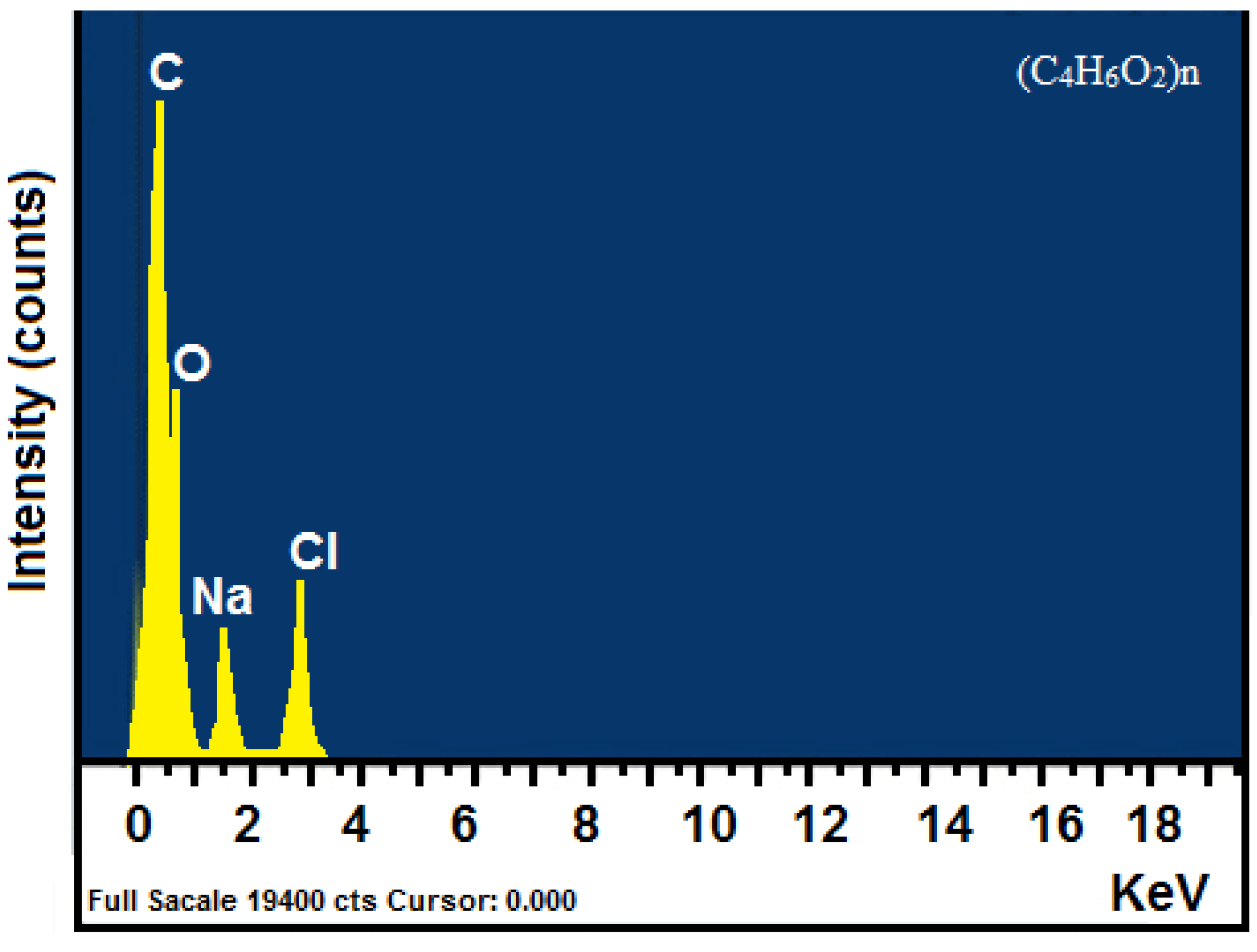
3.4.3. EDS Analysis
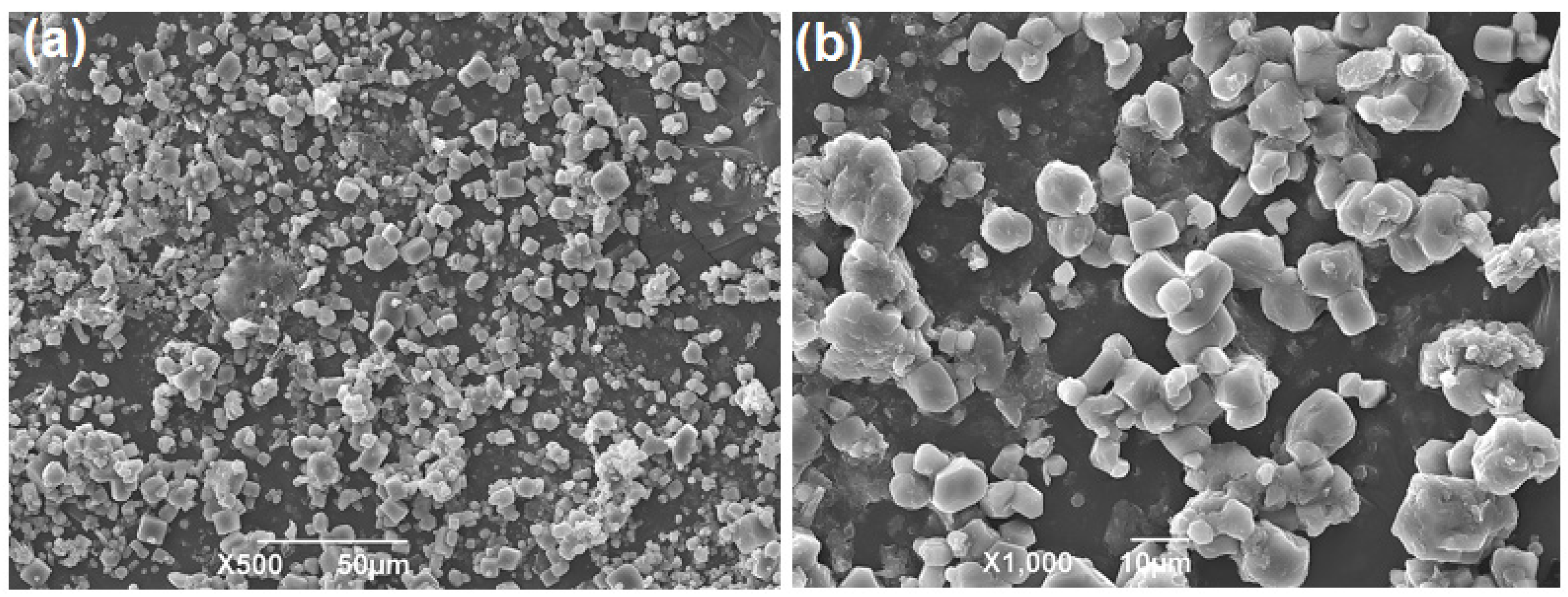
3.4.4. SEM Analysis
3.4.5. TGA Results
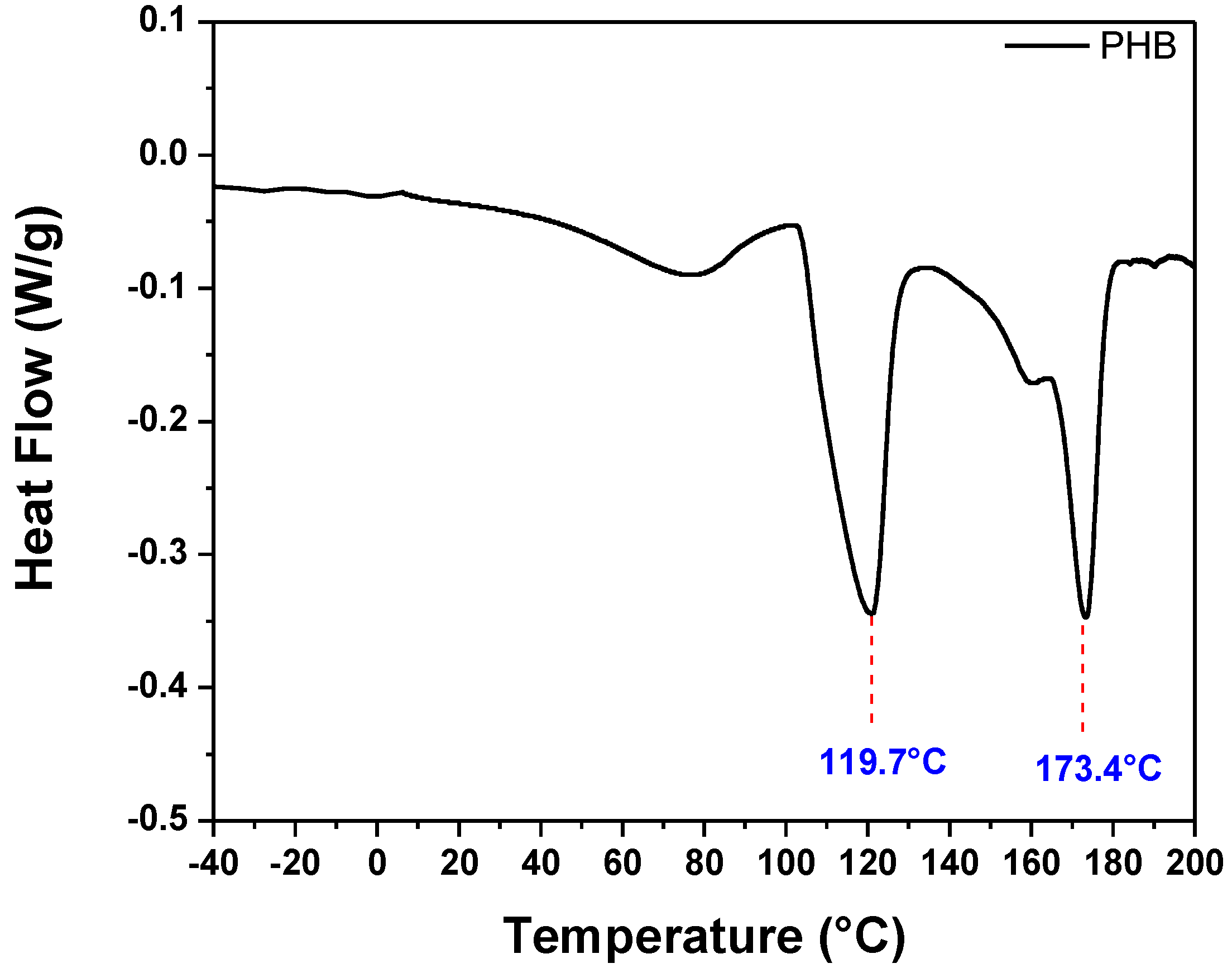
3.4.6. DSC Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costa, A.; Encarnação, T.; Tavares, R.; Bom, T.T.; Mateus, A. Bioplastics: Innovation for Green Transition. Polymers 2023, 15, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucci, D.Z.; Tavares, L.B.B.; Sell, I. PHB Packaging for the Storage of Food Products. Polym. Test. 2005, 24, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugnicourt, E.; Cinelli, P.; Lazzeri, A.; Alvarez, V. Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA): Review of Synthesis, Characteristics, Processing and Potential Applications in Packaging. Express Polym. Lett. 2014, 8, 791–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koller, M.; Braunegg, G. Advanced Approaches to Produce Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) Biopolyesters in a Sustainable and Economic Fashion. Eurobiotech J. 2018, 2, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morlino, M.S.; Serna García, R.; Savio, F.; Zampieri, G.; Morosinotto, T.; Treu, L.; Campanaro, S. Cupriavidus necator as a Platform for Polyhydroxyalkanoate Production: An Overview of Strains, Metabolism, and Modeling Approaches. Biotechnol. Adv. 2023, 69, 108264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kourmentza, C.; Plácido, J.; Venetsaneas, N.; Burniol-Figols, A.; Varrone, C.; Gavala, H.N.; Reis, M.A.M. Recent Advances and Challenges towards Sustainable Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) Production. Bioengineering 2017, 4, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koller, M.; Maršálek, L.; de Sousa Dias, M.M.; Braunegg, G. Producing Microbial Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) Biopolyesters in a Sustainable Manner. New Biotechnol. 2017, 37, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosravi-Darani, K.; Mokhtari, Z.B.; Amai, T.; Tanaka, K. Microbial Production of Poly(Hydroxybutyrate) from C1 Carbon Sources. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 1407–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesh Saratale, R.; Cho, S.K.; Dattatraya Saratale, G.; Kadam, A.A.; Ghodake, G.S.; Kumar, M.; Naresh Bharagava, R.; Kumar, G.; Su Kim, D.; Mulla, S.I.; et al. A Comprehensive Overview and Recent Advances on Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) Production Using Various Organic Waste Streams. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 325, 124685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerio de Ambiente y Desarrollo Sostenible. Plan de Acción para la Gestión Sostenible de la Biomasa Residual; Mesa Nacional de Biomasa Residual, Ed.; Ministerio de Ambiente y Desarrollo Sostenible: Bogotá, Colombia, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Liu, S.; Huang, J.; Cui, R.; Xu, Y.; Song, Z. Genetic Engineering Strategies for Sustainable Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) Production from Carbon-Rich Wastes. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 30, 103069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, S.K.; Otari, S.V.; Jeon, J.M.; Gurav, R.; Choi, Y.K.; Bhatia, R.K.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Kumar, V.; Rajesh Banu, J.; Yoon, J.J.; et al. Biowaste-to-Bioplastic (Polyhydroxyalkanoates): Conversion Technologies, Strategies, Challenges, and Perspective. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 326, 124733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ascencio-Galván, M.L.; López-Agudelo, V.A.; Gómez-Ríos, D.; Ramirez-Malule, H. A Bibliometric Landscape of Polyhydroxyalkanoates Production from Low-Cost Substrates by Cupriavidus necator and Its Perspectives for the Latin American Bioeconomy. J. Appl. Biol. Biotechnol. 2024, X, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygaard, D.; Yashchuk, O.; Hermida, É.B. Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) Production from Residual Glycerol by Wild Type Cupriavidus necator. Waste Biomass Valorization 2023, 14, 1489–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brojanigo, S.; Gronchi, N.; Cazzorla, T.; Wong, T.S.; Basaglia, M.; Favaro, L.; Casella, S. Engineering Cupriavidus necator DSM 545 for the One-Step Conversion of Starchy Waste into Polyhydroxyalkanoates. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 347, 126383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhila, N.O.; Sapozhnikova, K.Y.; Kiselev, E.G.; Vasiliev, A.D.; Nemtsev, I.V.; Shishatskaya, E.I.; Volova, T.G. Properties of Degradable Polyhydroxyalkanoates (Phas) Synthesized by a New Strain, Cupriavidus necator Ibp/Sfu-1, from Various Carbon Sources. Polymers 2021, 13, 3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya-Navarro, J.L.; Esquivel-Alfaro, M.; Jimenez-Villalta, G.; Rojas-Carrillo, O. Aprovechamiento de La Yuca Amarga (Manihot Esculenta Crantz) Para La Extracción de Almidón y La Producción de Un Material (TPS). In Memorias del I Congreso Internacional de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales de la Universidad Nacional, Costa Rica; Morales-Lopez, Y., Ed.; Universidad Nacional: Heredia, Costa Rica, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agronegocios. Familias Encuentran Producción Sostenible en la Yuca Industrial por sus Características. 2022. Available online: https://www.agronet.gov.co/Noticias/Paginas/Familias-encuentran-producci%C3%B3n-sostenible-en-la-yuca-industrial-por-sus-caracter%C3%ADsticas.aspx (accessed on 18 May 2024).
- Canales, N.; Trujilo, M. La Red de Valor de la y su Potencial en la de Colombia; Stockholm Enviroment Institute: Stockholm, Sweden, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cardona, O. Aumenta el Consumo de la Yuca Industrial en Colombia con Mejoras en Variedades. Available online: https://www.agronegocios.co/agricultura/aumenta-el-consumo-de-la-yuca-industrial-en-colombia-con-mejoras-en-variedades-2820472 (accessed on 31 May 2024).
- Velásquez, D. Análisis de la Capacidad Tecnológica de Colombia en la Producción de Bioetanol a Partir de la Caña de Azúcar Utilizando la Metodología del Benchmarking. Bachelor’s Thesis, Universidad del Valle, Cali-Valle del Cauca, Colombia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ibarra-Camacho, R.; León-Duharte, L. Caracterización Fisico-Química de Vinazas de Destilerias. Rev. Cuba. Química 2019, 31, 246–257. [Google Scholar]
- Cerón, V.Z.; Andrés, M.; Ayerbe, G. Characterization of Stillage from Sugar Cane Waste from the Production of Ethanol. Dyna 2013, 80, 124–131. [Google Scholar]
- Figaro, S.; Louisy-Louis, S.; Lambert, J.; Ehrhardt, J.J.; Ouensanga, A.; Gaspard, S. Adsorption Studies of Recalcitrant Compounds of Molasses Spentwash on Activated Carbons. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3456–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Orthofer, R.; Lamuela-Raventos, R.M. Analysis of Total Phenols and Other Oxidation Substrates and Antioxidants by Means of Folin-Ciocalteu Reagent. Methods Enzymol. 1999, 299, 152–178. [Google Scholar]
- Acosta-Cárdenas, A.; Alcaraz-Zapata, W.; Cardona-Betancur, M. Sugarcane Molasses and Vinasse as a Substrate for Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) Production. Dyna 2018, 85, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aristizábal, C. Physicochemical Characterization of a Stillage Resulting of Alcohol Production through the Use of Sugar Cane in a Liquor Industry. Ing. USBMed 2015, 6, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Franz, A.; Rehner, R.; Kienle, A.; Grammel, H. Rapid Selection of Glucose-Utilizing Variants of the Polyhydroxyalkanoate Producer Ralstonia Eutropha H16 by Incubation with High Substrate Levels. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 54, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsay, B.A.; Lomaliza, K.; Chavarie, C.; Dube, B.; Bataille, P.; Ramsay, J.A. Production of Poly-(P-hydroxybutyric-co-3-hydroxyvaleric) Acids. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 2093–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G. Use of Dinitrosalicylic Acid Reagent for Determination of Reducing Sugar. Anal. Chem. 1959, 31, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, A.; Pérez, D.; Castro, M.; Urtuvia, V.; Castillo, T.; Díaz-Barrera, A.; Espín, G.; Peña, C. Production and Recovery of Poly-3-Hydroxybutyrate [P(3HB)] of Ultra-High Molecular Weight Using Fed-Batch Cultures of Azotobacter Vinelandii OPNA Strain. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 94, 1853–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanfonato, K.; Schmidt, M.; Quines, L.K.; Gai, C.S.; Schmidell, W.; de Aragão, G.M.F. Can Vinasse Be Used as Carbon Source for Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate) Production by Cupriavidus necator DSM 545? Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 35, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronďošová, S.; Legerská, B.; Chmelová, D.; Ondrejovič, M.; Miertuš, S. Optimization of Growth Conditions to Enhance PHA Production by Cupriavidus necator. Fermentation 2022, 8, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, I.; Santolin, L.; Meyer, K.; Machatschek, R.; Bölz, U.; Tarazona, N.A.; Riedel, S.L. Microbially Synthesized Poly(Hydroxybutyrate-Co-Hydroxyhexanoate) with Low to Moderate Hydroxyhexanoate Content: Properties and Applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 263, 130188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmael, M.E.; Ibrahim, M.I.A.; Aldhumri, S.A.; Bayoumi, R.A.; Matsuo, K.; Khattab, A.M. Lipid-Membranes Interaction, Structural Assessment, and Sustainable Production of Polyhydroxyalkanoate by Priestia Filamentosa AZU-A6 from Sugarcane Molasses. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 124721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugwu, C.U.; Tokiwa, Y.; Aoyagi, H. Utilization of Broken Rice for the Production of Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate). J. Polym. Environ. 2012, 20, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, F.C.; Dias, M.L.; Castilho, L.R.; Freire, D.M.G. Characterization of Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate) Produced by Cupriavidus necator in Solid-State Fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nygaard, D.; Yashchuk, O.; Noseda, D.G.; Araoz, B.; Hermida, É.B. Improved Fermentation Strategies in a Bioreactor for Enhancing Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) Production by Wild Type Cupriavidus necator from Fructose. Heliyon 2021, 7, e05979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhila, N.; Kalacheva, G.; Volova, T. Fatty Acid Composition and Polyhydroxyalkanoates Production by Cupriavidus Eutrophus B-10646 Cells Grown on Different Carbon Sources. Process Biochem. 2015, 50, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madison, L.L.; Huisman, G.W. Metabolic Engineering of Poly(3-hydroxyalkanoates): From DNA to Plastic. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. 1999, 63, 21–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalsasso, R.R.; Pavan, F.A.; Bordignon, S.E.; de Aragão, G.M.F.; Poletto, P. Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) Production by Cupriavidus necator from Sugarcane Vinasse and Molasses as Mixed Substrate. Process Biochem. 2019, 85, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa, S.; García, C.; Alcaraz, W. Real-Time Optimization and Control for Polyhydroxybutyrate Fed-Batch Production at Pilot Plant Scale. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2020, 95, 3221–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, C.; El-Najjar, T.; Virgolini, N.; Smerilli, M.; Neureiter, M. High Cell-Density Production of Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate) in a Membrane Bioreactor. New Biotechnol. 2017, 37, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverio, M.S.; Piccoli, R.A.M.; dos Reis, J.L.M.S.; Gomez, J.G.C.; Baptista, A.S. Techno-Economic Feasibility of P(3-Hydroxybutyrate) Bioprocess with Concentrated Sugarcane Vinasse as Carbon and Minerals Source: An Experimental and in Silico Approach. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2024, 14, 2071–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grousseau, E.; Blanchet, E.; Deleris, S.; Albuquerque, M.G.E.; Paul, E.; Uribelarrea, J.-L. Impact of Sustaining a Controlled Residual Growth on Polyhydroxybutyrate Yield and Production Kinetics in Cupriavidus necator. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 148, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saratale, G.D.; Saratale, R.G.; Varjani, S.; Cho, S.K.; Ghodake, G.S.; Kadam, A.; Mulla, S.I.; Bharagava, R.N.; Kim, D.S.; Shin, H.S. Development of Ultrasound Aided Chemical Pretreatment Methods to Enrich Saccharification of Wheat Waste Biomass for Polyhydroxybutyrate Production and Its Characterization. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 150, 112425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, S.; Dikshit, P.K.; Moholkar, V.S. Production, Ultrasonic Extraction, and Characterization of Poly (3-Hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) Using Bacillus Megaterium and Cupriavidus necator. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2018, 29, 2392–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainuddin, M.Z.; Abu Bakar, A.A.; Adam, A.N.; Abdullah, S.M.; Tamchek, N.; Alauddin, M.S.; Mahat, M.M.; Wiwatcharagoses, N.; Alforidi, A.; Ghazali, M.I.M. Mechanical and Structural Properties of Polyhydroxybutyrate as Additive in Blend Material in Additive Manufacturing for Medical Applications. Polymers 2023, 15, 1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdy, S.M.; Danial, A.W.; Gad El-Rab, S.M.F.; Shoreit, A.A.M.; Hesham, A.E.L. Production and Optimization of Bioplastic (Polyhydroxybutyrate) from Bacillus Cereus Strain SH-02 Using Response Surface Methodology. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayari, S.; Severcan, F. FTIR Study of Biodegradable Biopolymers: P(3HB), P(3HB-Co-4HB) and P(3HB-Co-3HV). J. Mol. Struct. 2005, 744–747, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabarinathan, D.; Chandrika, S.P.; Venkatraman, P.; Easwaran, M.; Sureka, C.S.; Preethi, K. Production of Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) from Pseudomonas Plecoglossicida and Its Application towards Cancer Detection. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2018, 11, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, M.; Kumar, N.; Yadav, A.; Aggarwal, N.K. Production and Optimization of Polyhydroxybutyrate by Using Cupriavidus necator with Banana Peels as a Substrate. Circ. Econ. Sustain. 2023, 4, 717–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Núñez, E.; Martínez-Gutiérrez, C.A.; López-Cortés, A.; Aguirre-Macedo, M.L.; Tabasco-Novelo, C.; González-Díaz, M.O.; García-Maldonado, J.Q. Physico-Chemical Characterization of Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate) Produced by Halomonas Salina, Isolated from a Hypersaline Microbial Mat. J. Polym. Environ. 2019, 27, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopperi, H.; Amulya, K.; Venkata Mohan, S. Simultaneous Biosynthesis of Bacterial Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) and Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS): Process Optimization and Scale-Up. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 341, 125735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raju, N.N.; Sankaranarayanan, M.; Bharathiraja, B. Production of Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB), a Biodegradable Polymer from Seaweed Biomass Using Novel Bacterial Isolates. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1303, 137511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirohi, R. Sustainable Utilization of Food Waste: Production and Characterization of Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) from Damaged Wheat Grains. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirohi, R.; Pandey, J.P.; Tarafdar, A.; Agarwal, A.; Chaudhuri, S.K.; Sindhu, R. An Environmentally Sustainable Green Process for the Utilization of Damaged Wheat Grains for Poly-3-Hydroxybutyrate Production. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 21, 101271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.H.; Suh, M.J.; Cho, J.Y.; Ham, S.; Jeon, J.M.; Yoon, J.J.; Bhatia, S.K.; Gurav, R.; et al. Screening of the Strictly Xylose-Utilizing Bacillus Sp. SM01 for Polyhydroxybutyrate and Its Co-Culture with Cupriavidus necator NCIMB 11599 for Enhanced Production of PHB. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 181, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mottina, A.C.; Ayres, E.; Orefice, R.L.; Câmara, J.J.D. What Changes in Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) When Processed as Electrospun Nanofibers or Thermo-Compression Molded Film? Mater. Res. 2016, 19, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Iodine number | 850 mg/g Min |
| Ash | 15% Max |
| Humidity | 5% Max |
| Harenes | 90% Min |
| Granulometry | Mesh 8 × 30 |
| Mesh8 | 5% Max/2 mm |
| Mesh30 | 5% Max/2 mm |
| Parameter | Result | Treated Vinasse | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 h | 3 h | ||
| Total polyphenolic compounds (g/L) | 18.39 | 18.39 | 15.31 |
| Ashes (g/L) | 93.19 | ||
| pH | 4.88 ± 0.01 | ||
| °Brix | 30.0 ± 0.1 | ||
| Vinasse | Vinasse Proportion in Medium (v/v) | Biomass Concentration (g/L) | Polymer Concentration (g/L) | Polymer Accumulation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw vinasse | 2.5% | 2.97 ± 0.13 | 1.43 ± 0.06 | 48% |
| 5.0% | 3.72 ± 0.13 | 1.77 ± 0.07 | 48% | |
| 7.5% | 5.50 ± 0.13 | 2.66 ± 0.11 | 48% | |
| 25.0% | No growth | No production | 0% | |
| 50.0% | ||||
| 75.0% | ||||
| Treated vinasse | 2.5% | 3.30 ± 0.14 | 1.57 ± 0.06 | 48% |
| 5.0% | 3.87 ± 0.14 | 1.96 ± 0.08 | 51% | |
| 7.5% | 5.90 ± 0.14 | 2.98 ± 0.12 | 51% | |
| 25.0% | 1.70 ± 0.13 | 0.69 ± 0.03 | 41% | |
| 50.0% | 3.25 ± 0.13 | 1.43 ± 0.06 | 44% | |
| 75.0% | 4.44 ± 0.13 | 1.82 ± 0.08 | 41% |
| Spectrum | In Stats. | C | O | Na | Cl | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | Yes | 50.74 | 38.77 | 4.61 | 5.88 | 100.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dorado, I.; Pineda, L.; Ascencio-Galván, M.L.; López-Agudelo, V.A.; Caicedo, J.C.; Gómez-Ríos, D.; Ramírez-Malule, H. Valorization of Dextrose from Cassava Starch and Sugarcane Vinasse as Polyhydroxyalkanoates by Submerged Cultures of Cupriavidus necator: A Physicochemical–Biotechnological Approach. ChemEngineering 2024, 8, 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering8040073
Dorado I, Pineda L, Ascencio-Galván ML, López-Agudelo VA, Caicedo JC, Gómez-Ríos D, Ramírez-Malule H. Valorization of Dextrose from Cassava Starch and Sugarcane Vinasse as Polyhydroxyalkanoates by Submerged Cultures of Cupriavidus necator: A Physicochemical–Biotechnological Approach. ChemEngineering. 2024; 8(4):73. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering8040073
Chicago/Turabian StyleDorado, Isabel, Laura Pineda, Martha L. Ascencio-Galván, Víctor A. López-Agudelo, Julio C. Caicedo, David Gómez-Ríos, and Howard Ramírez-Malule. 2024. "Valorization of Dextrose from Cassava Starch and Sugarcane Vinasse as Polyhydroxyalkanoates by Submerged Cultures of Cupriavidus necator: A Physicochemical–Biotechnological Approach" ChemEngineering 8, no. 4: 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering8040073
APA StyleDorado, I., Pineda, L., Ascencio-Galván, M. L., López-Agudelo, V. A., Caicedo, J. C., Gómez-Ríos, D., & Ramírez-Malule, H. (2024). Valorization of Dextrose from Cassava Starch and Sugarcane Vinasse as Polyhydroxyalkanoates by Submerged Cultures of Cupriavidus necator: A Physicochemical–Biotechnological Approach. ChemEngineering, 8(4), 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering8040073






