Abstract
In this study, a novel chitosan–resole–pectin aerogel (CS–R–P) was created from a sol–gel reaction with a solution of Cs and P with resole by a freeze-drying technique, and this adsorbent was proposed for the removal of methylene blue (MB). In addition, with the use of an artificial intelligence technique known as an artificial neural network (ANN), this material was modeled and optimized. Its physical morphology and chemical composition were also characterized with FTIR and XPS, and its adsorption properties were analyzed. For modeling the adsorption process, three main parameters were used: the chitosan–resole–pectin concentration (45–75%), thermal treatment (6–36 h), and known concentrations of methylene blue (25–50 and 100 mg/L), established on the Box–Behnken design. The ANN was coupled with the improved gray wolf optimization (IWGO) metaheuristic algorithm, achieving a correlation coefficient of R2 = 0.99. The characterization indicates that the surface of the aerogels was micro- and mesoporous, the resole gave physical stability, and the polysaccharide base delivered the functional groups necessary for dye adsorption; the aerogels were successful dye adsorbents with a qe of 12.44 mg/g. Finally, the physical and chemical sorption was ascertainable with an adsorption that followed pseudo-second-order kinetics. The MB adsorption was clearly occurring though cation exchange and hydrogen binding as observed in the chemical composition. The ANN with the gray wolf optimizer was used for the prediction of the best operating parameters for MB removal, applying the following conditions—the CS–R–P aerogel concentration (52/30/18), the thermal treatment (9.12 h), and the initial concentration of methylene blue (37 mg/L)—achieving a 94.6% removal. These conclusions suggest that using artificial intelligence such as an ANN can provide an efficient and practical model for maximizing the removal action of new aerogels based on chitosan.
1. Introduction
An increasing population, yielding both economic growth and water pollution, requires a commitment to sustainable water management [1]. Dyes are a major class of pollutants; since the discovery of methylene blue (MB) in 1878 as one of the classified cationic dyes [2], its use has become normal in diverse industries, such as textile, paper, and tannery [3]. Its principal use is to modify the color of products, with the result that significant volumes of colorized water are generated by the different industrial processes [3]. The treatment of dye wastewater effluent is important due to its harmful impacts, such as eye burning, intoxication through inhalation, or vomiting caused by low exposures, as well as its potential threat as a human carcinogen [4]. Furthermore, it has been demonstrated in aquatic ecosystems that even with a low discharge, it can increase the chemical oxygen demand (COD) and complicate photosynthesis by decreasing the light penetration [5]. Classified as emerging pollutants that may require specific regulations and limits that are not yet present on most regulations, emerging technologies to depurate this contaminated water are needed [6].
There are known effective techniques for pollutant removal, such as chemical and physical treatment [7] or oxidation reactions [8], etc.; however, it is not easy to degrade dyes, since these molecules are very stable, and adsorption [9,10,11] is a reliable method that has the advantage of high efficiency and easy maintenance. Also, a low-cost adsorbent could be a possible approach with less secondary pollution and reusability of the adsorbents.
To achieve efficient adsorption, the material must possess specific properties such as porosity, physicochemical stability, and a high activity of functional groups on its surface [7,10]. Recently, natural polysaccharides such as chitosan (CS) have been used for their known properties such as biocompatibility, their high abundance in nature, and their abundant amine and hydroxyl groups [9,11]. CS solution is excellent as a substrate for producing 3D aerogels, and compared with other CS modifications or forms, as a powder, it presents higher adsorption and porosity, achieving CS aerogels that are effective for adsorption [12,13,14]. There are different methods to achieve aerogels, with supercritical drying and freeze drying being the most commonly used; furthermore, freeze drying may result in an aerogel with macropores and unique features such as an axial layered structure, and it has more mechanical adaptability and is more easily made compared with supercritical drying [15]. CS aerogels still exhibit low mechanical properties, and their 3D structure tends to collapse or hydrolyze on acidic media. The challenge of obtaining a highly mechanical stability with a porous material has focused on the amount of polymer concentration as the main parameter; this is crucial because it must contain enough polymer to maintain its shape, size, and swollen state during contact with the dye [16]. Diverse strategies such as nano reinforcement [17] with graphene oxide [13], montmorillonite [2], or using physical or chemical crosslinking processes [18] to overcome the instability of CS aerogel [11] have been addressed. Unfortunately, nanomaterials as enhancers are complicated to use due to their low bulk and high costs, and physical and chemical crosslinking would change the chemical disposition of the free species to ionic exchange. Therefore, we envision a cost-conscious approach using a thermosetting enforcer with a phenol/formaldehyde liquid resole reinforcement, as in a previously reported work [19], with the integration of pectin (P) as another polysaccharide chain for a 3D substrate for the sol–gel reaction with physical crosslinking in conjunction with the resole and chemical crosslinking for mechanical stability. We understand the variability of the experimental data required to find the optimal processing parameters, and to overcome this issue, we aim to propose a model. An artificial neural network (ANN) is an excellent tool to predict and model various engineering problems, regardless of the chemical, physical, or biological process under study. The ANN was inspired by the functioning of biological brains, since they consist of interconnected neurons that process and exchange information. They can also learn from relationships between the parameters and responses for nonlinear and linear systems [20,21]. These techniques have been used to model complex processes such as aerogel performance. In the literature, studies have been reported that established their various applications. Tafreshi et al. [22] proposed the application of machine learning based on ANN to model and predict the properties of organic aerogels. Abdusalamov et al. [23] demonstrated the excellent performance of this type of methodology in predicting silica aerogels’ properties, achieving a precision of the model of R2 = 0.973. Likewise, applied studies have been reported that improved the control of the porous structure of carbon aerogels [24] and, obtaining great precision, the adsorption of perfluorooctanoic acid with Cu nanoparticles and a fluorine-modified graphene aerogel [25]. This work aims to model and optimize the adsorption of MB using a chitosan–resole–pectin ANN coupled with a metaheuristic algorithm to find the optimal parameters that maximize the material adsorption capacity.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
Chitosan powder (<75% deacetylated, medium molecular weight), pectin citrus peel (>75% galacturonic acid), and methylene blue were obtained in dried powder form (Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). Phenol (99%), acetic acid (99%), sodium hydroxide (98%), and formaldehyde (37.0%) were purchased from (Golden Bell, Guadalajara, México) and (Fermont, Monterrey, México). Deionized water (DW) was required for the stock dye solutions and further diluted concentrations.
2.2. Preparation of the Chitosan, Pectin, and Resole Solution for the Sol–Gel Reaction
The CS solution and pectin solution required as the polysaccharide precursors for the sol–gel reaction were prepared with weighed chitosan and pectin powder. The CS solution at 2% w/v was created by dissolving the chitosan with DW and acetic acid, and it was left to sit for three days at room temperature. The P solution at 1% w/v was created by dissolving the pectin with DW, and it was heated at 60 °C and stirred for 1 h until gel formation. The resole (R) solution was made by dissolving phenol–formaldehyde resin (1:3.5) on NaOH at 0.1 M and stirring at 70 °C for 1 h. After that, the pH was adjusted, and the solution was placed in a rotary evaporator for 1.15 h in a water bath at 50 °C. The remaining liquid resole was removed and refrigerated. The synthesis of resole was detailed in our previous work [19].
2.2.1. Fabrication of the Chitosan–Resole–Pectin Aerogel
The CS–R–P aerogel was formulated through a standard procedure. Initially, in a syringe, the required volume percentages of the base polysaccharide solutions were measured and mixed with the amount of R solution. The mixture was then transferred to a mold and stored in an ultra-freezer at −70 °C and Freeze-Dryer (Ilshin Biobase TFD8501, Komachine, Gyeonggi-do, Korea) for 24 h. Ultimately, the dried aerogel for the crosslinking reaction was heated to 60 °C for (6, 24, and 36 h) thermal treatment.
2.2.2. Characterization of the CS–R–P Aerogel
The surface microstructure, chemical state of the surface compositions, and percentage of water retained were determined for the CS–R–P aerogel using a stereoscope (STEMI 508 Zeiss, Lein, Germany). Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) was performed using an IR spectrophotometer (Alpha II Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA), with a spectral range of 4000–400 cm−1. X-ray spectroscopy (XPS) was performed using a monochromatic Al KαX-ray source (1486.7 eV) (SPECS PHOIBOS, Berlin, Germany). Binding energies (BE) were referenced to the main C1s peak at 284.5 eV to compensate for the non-conductive samples. Also, a study of water retention and porosity [12] was conducted. To determine the percentage of water, the samples were weighed wet, then dried for 24 h at 60 °C, and re-weighed, and the result was calculated using Equation (1), with the volume of the empty spaces calculated using Equation (2).
where (g) represents the wet aerogel, and (g) corresponds to the dried aerogel.
where (cm3) represents the total volume, (cm3) represents the volume of the empty spaces, and P represents the porosity.
2.3. Artificial Neural Network Modeling
To model the removal efficiency of the MB process by applying a chitosan–resole–pectin aerogel, an experimental matrix of the Box–Behnken type with 17 experiments was developed using Design-Expert software 10.0.1 (Stat-Ease Inc., Minneapolis, MN, USA). Three principal parameters, each with three levels, were included, as shown in Table 1. The ANN modeling was accomplished by using the neural network toolbox of Matlab R2021A (Math-Works Inc., Natick, MA, USA).

Table 1.
Independent variables and their levels.
2.3.1. Adsorption Studies
Sorption experiments (with 25, 50, and 100 mg/L of MB solution in 50 mL on batches) were conducted to study the removal capacity of the MB following the experiments proposed by the experimental matrix to analyze the adsorption performance and then modeling the optimal parameters. A stock solution (1000 mg/L) of MB was prepared by dissolving (1g of MB) on 1L of DW; the stock solution was diluted to obtain the other concentrations. A piece of weighted aerogel made from a mixture of 4 mL volumes of % solution on configurations (main weights CS45/R45/P10 (0.558 g), CS60/R25/P15 (0.387 g), and CS75/R5/P20 (0.169 g)) aerogel with (6, 24, and 36 h of thermal treatment) was placed into a Falcon tube containing 50 mL of aqueous solution with known initial concentrations of MB dye and then shaken (in an orbital shaker at 400 rpm) at a constant temperature of 25 −/+ 2 °C for 3 h, in accordance with the adsorption times reported in the literature [5,7]. The pH of the diluted solutions was not adjusted. After the desired time, the aerogel was removed; these adsorption experiments were performed in triplicate for each experimental run, and the average values were reported.
2.3.2. Kinetic Studies
For the kinetic study, the experiments were performed under the same conditions (25 −/+ 2 °C for 3 h, without pH adjustment) but taking samples at six different intervals up to 24 h in 50 mL falcon tube of a 50 mg/L of MB, using samples representative of the experimental matrix as shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Kinetic experimental runs.
2.3.3. MB Adsorption
The concentration of the MB after adsorption was determined and analyzed at 665 nm [1,3] using a UV/VIS spectrophotometer (Jasco v770 spectrometer, Tokyo, Japan). The adsorption capacity of the CS–R–P aerogel [11], as the removal percentage (R%) and (qt) (mg/g), was calculated using the following Equations (3) and (4):
where m (g) symbolizes the adsorbent mass, V (L) is the volume of the solution, and C0 and Ce (mg/L) are the initial and equilibrium concentrations of the MB, respectively. For the adsorption capacity, R% symbolizes the adsorption efficiency, Y0 indicates the initial value, and Y is the final adsorption measurement.
The adsorption kinetics of the MB was studied on the CS–R–P aerogels, using pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order kinetic models, Equations (5) and (6), respectively [11,12].
where qe and qt (g·mg−1) indicate the adsorption capacities on equilibrium time t (h), k1 (min−1) is the constant rate for the pseudo-first order, and k2 (g·mg−1·min−1) is the constant rate of the pseudo-second order.
2.4. Artificial Neural Network Optimization
ANN architecture and an operating input layer with three neurons was projected (the chitosan–resole–pectin concentration, the thermal treatment time, and the initial concentration of methylene blue in mg/L), as well as an output layer and one neuron (methylene blue removal %), and a hidden layer, as presented in Figure 1. A feedforward multilayer perceptron (MLP) was harnessed employing the Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm (LM).
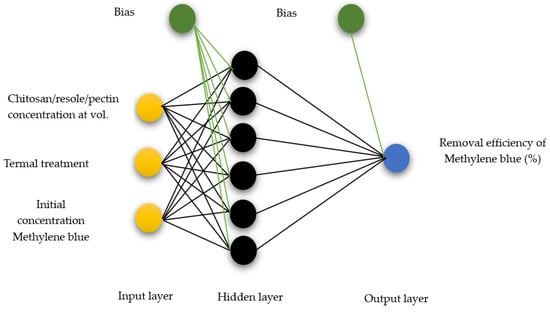
Figure 1.
Architecture for the ANN adsorption model.
The mathematical functions were taken from the literature to obtain the activation function and net input, which were (Tensig) and (Purelin). Likewise, the entire dataset was ordered into three sets: the testing group (15%), the validation group (15%), and the training group (70%), as shown in Table 3. Similarly, to find the best architecture for the ANN, a set of neural networks using 4, 6, 8, 10, and 12 hidden neurons was used [26]. The mean square error (MSE) was determined. The complete data were normalized applying Equation (7), and the ANN model was used as the fitness function [27]. The improved gray wolf optimizer (IGWO), a novel algorithm [28], was used to perfect the execution of the ANN; the results are presented later in the manuscript. The IGWO is a nature-inspired algorithm that has improvements over the original (GWO) algorithm, including a new search in three phases of initializing, moving, and selecting, established in the dimension-learning-based hunting (DLH), which sustains the efficacy of the new positions of individuals. Coupling this algorithm with the artificial neuronal network significantly reduces the half-square error of the outputs, managing to find the ideal architecture of the model.
where xi symbolizes the observed value, xmin is the minimum value, and xmax is the highest value for the variables.

Table 3.
ANN modeling for methylene blue removal.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization
For the study of the chemical structure of the CS–R–P aerogel, the FTIR (Figure 2) and XPS spectra (Figure 3) were used.
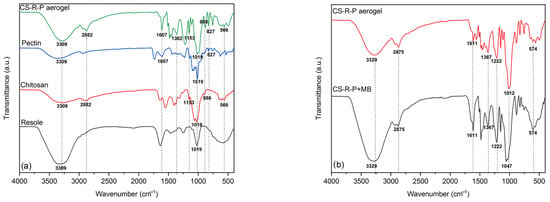
Figure 2.
FTIR spectrum comparison: (a) CS–R–P aerogel and precursors; (b) CS–R–P aerogel after adsorption of MB. CS–R–P (60-25-15) aerogel loaded with 100 mg/L of MB.
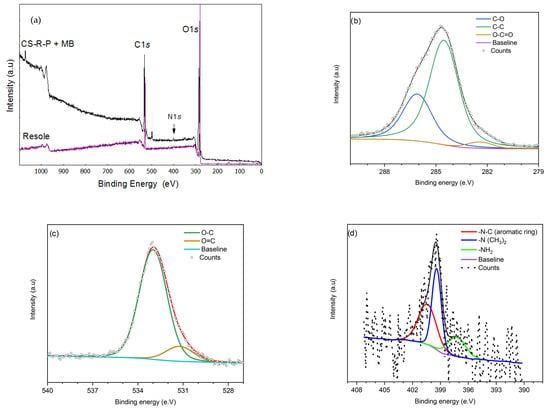
Figure 3.
XPS spectrum comparison: (a) survey spectra of the resole and CS–R–P aerogel + MB; (b) C 1s high resolution regions; (c) O 1s high resolution regions; (d) N 1s high resolution regions. The high resolutions are from the CS–R–P (60-25-15) aerogel loaded with 100 mg/L of MB.
In Figure 2a, it can be seen from the aerogel comparison that the complex was successfully crosslinked, with characteristic peaks of CS, P, and R, such as the 3309 cm−1 -OH that overlaps with the -NH of CS [11,29], appearing in all the precursors. Also, from the CS, there were peaks located at 1607 cm−1 caused by amide I, at 1379 cm−1 by amide III [11,16,30], at 1149 cm−1 by stretching of the C-N [31], and a glucosidic stretching at 884 cm−1, characteristic of polysaccharides. The R had a benzene ring at 1634 cm−1 and contributed to 1013 cm−1 with a peak, an aliphatic hydroxyl (R-OH), and ether bridge bands formation [32]. The P characteristic band of the single bond of ester 1195 cm−1 was seen as a characteristic adsorption band corresponding to a carbonyl structure at 1607 cm−1. The spectra of the CS and P shared similarities, but on the CS–R–P aerogel, they still maintained further functional groups of each added precursor [33].
In Figure 2b, the aerogel comparison can be seen after processing and being loaded with the MB dye after adsorption. Here, we can observe the peaks at 3329 cm−1 and 2875 cm−1, an increase attributed to the CH stretching. There were also notable bands corresponding to the amide I and amide III shifting and increase at 1611 cm−1 and 1367 cm−1, as well as the shift of the C-O-C carboxyl group to 1047 cm−1 and a 574 cm−1 peak increase characteristic of MB. These increasing bands could be attributed to a chemical bond formed between the MB molecules on the surface of the CS–R–P aerogel with the -NH2 groups [1,16]. According to this, we can observe that the carboxyl groups were negatively charged, which is beneficial for the adsorption of cationic dyes [11], principally because of the ease of cation exchange through hydrogen binding [11,34]. Also, Wang et al. [7] mentioned the presence of a new peak at 1342 cm−1, which in this case was also present, indicating a successful combination of the dimethyl amino groups with the CS–R–P aerogel for chemisorption.
These results were corroborated by the XPS analysis, which was performed to identify the adsorption mechanisms and the presence of the characteristic binding energies in the aerogel spectrum analysis.
Figure 3a shows the general survey spectra of the resole CS–R–P aerogel loaded with MB at 100 mg/L with concentration % volume of CS/60R/25P/15, which is version 0 or intermediate between the three levels of factors. The principal functional groups and elements were identified and confirmed as C 1s, O 1s, and N 1s, suggesting successful aerogel generation and that the MB was adsorbed with increases in C 1s and O1s. The high-resolution spectra of these main elements were determined. The deconvolution of C 1s, shown in Figure 3b, was indicated by a greater peak at 284.5 eV, assigned to C-C (51%), and two other peaks were assigned at 286.06 eV to C-O (23%) and at 282.3 eV to O-C=O (2.2%). The high-resolution O 1s in Figure 3c was deconvoluted on two peaks corresponding to the 532.9 eV O-C aliphatic (22%) and 531.2 eV O=C carboxyl groups (1.5%), which are in line with the proportion of the chemical bonding between C-O and C=O. Furthermore, these results were consistent with the calculations of the elemental chitosan/quinoa aerogel ratio in Tan et al. [18]. Also, on the high-resolution spectra of N 1s, shown in Figure 3d, representative peaks of MB were found at 400.3 eV, belonging to a C-N aromatic ring (0.4%) and at 399.2 eV (-N(CH3)2) (0.5%). This suggests that the MB molecules were combined with chemical bonding on the CS–R–P aerogel. Also, a last peak was found at 397.2 eV, corresponding to the CS amine NH2 [7].
Figure 4 shows photographs and stereoscope images of the CS–R–P aerogels in which the three-dimensional network structure formed for the polysaccharide base by the gel reaction is visible (Figure 4a,b), which is beneficial for binding with cationic dyes [11,34]. The microstructure morphology obtained by the freeze-drying process shows a highly porous structure as interconnected networks with micro- and mesoporous sizes. From Figure 4c,d, we concluded that increasing the volume of polysaccharide slightly decreased the diameter of the pores, as the precursor polysaccharide base presented a dense porous surface. The comparison of the open pores after the cross section in Figure 4c,d is recognizable in accordance with previous reports; when the amount of R limits the substrate for the structure of the three-dimensional network aerogel, although it strengthens the structure, the pores tend to increase in size [16,19]. From Figure 4d, it can also be seen that the aerogel had a flexible and porous structure with nonuniform axial growths, adjusted and controlled by the volume concentration and the crosslinking interaction between them, which determines the structure. Similar results have been seen with hydrogels [2], and directional growths are also possible with other strategies [35]. Stability after the adsorption process can also be seen, specifically on the second row of Figure 4b. Also, in Figure 4d with the cross section, the structure of the interior network of the CS–R–P aerogel was not destroyed after the adsorption of MB, which indicates the excellent stability of this material. The physical bond with the dye turned the aerogel blue and was also recognizable on the surface. The diffusion of the dye was different in the pieces observed in Figure 4b,d, with patches that probably exist because the chemical crosslinking was stronger, limiting the flexibility of the mass transfer in the aerogel [16,18]. This is in contrast with Figure 4c, which is the piece with less R, and the color transfer looks homogenous.
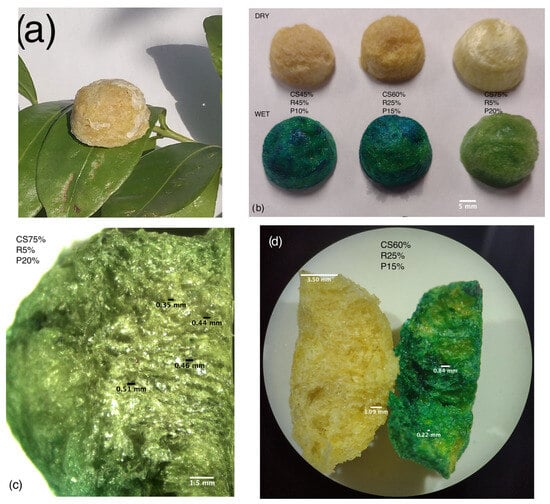
Figure 4.
Photograph and stereoscope images of the CS–R–P aerogel comparison: (a) CS–R–P aerogel; (b) CS–R–P aerogel material combinations; (c) CS–R–P after adsorption; (d) CS–R–P close up in cross section.
Table 4 shows the values calculated for the water recovery and indicates that all combinations held a considerable amount of intrinsic water, almost 50% by weight in most cases, while the value of (Ve) reflects the amount of empty space volume. This is similar to the results in El-Kousy et al. [34], who reported values of 98%, 95%, 83.5%, and 86.3% for the use of montmorillonite as a nano reinforcement to increase the water retention of the CS aerogel.

Table 4.
Water retention of the processing material.
3.2. MB Adsorption Capacity Study
The adsorption of MB was studied on the CS–R–P aerogels to evaluate the adsorbent volume concentration processing, the initial concentration of MB, and the variation in the thermal effect. The influence of these parameters combined with the experimental matrix was described. The dye concentration could be seen to decrease as the aerogel’s stability was reinforced with R, even though the improved performance could largely be due to the polymeric chain of the polysaccharide structure with a highly porous surface and with free vacant sites for chemical adsorption. Another critical parameter limitation of the mass transfer capacity was the initial concentration: the adsorption capacity results increased with the increase in dye, but the quantity and properties of the adsorbent played a crucial role also, as the literature says this tends to influence the adsorption process mechanism [3,17].
Final Thermal Effect on the Kinetic Study
The final thermal treatment, as we expected, was also another critical parameter that could influence the adsorption process due to the lack of sites available on the aerogel surface after the initial adsorption mechanism onto the many vacant sites, allowing flexibility of the adsorbent, such as swelling that increases the available remaining vacant sites and improves the adsorption capabilities. De Luna et al. [16] discussed similar results that demonstrated an increase in the adsorption capacities due to the significance of the CS aerogel processing in the final mechanical properties. Figure 5a illustrates the fitting plots corresponding to the calculated parameters from the pseudo-second-order (PSO) kinetic model with a correlation of (R2 = 0.998) and a qe 12.44 mg/g, which validate the occurrence of sorption and ion exchange. The kinetics of the remaining experiments are listed in Table 5. Also, Figure 5b shows that equilibrium was attained after >300 min, which was a longer time than the mean in previous works [16,18,34]; this explains a typical adsorption mechanism that follows the initial bulk diffusion onto the boundary layer probably due to the enhancement of the active interaction between the MB molecules and the aerogel. A diffusion of adsorbate from this layer onto the surface of the aerogel occurs due to the increase in the force of mass transfer, which is typically the slowest and reinforces the releasing of the remaining active sites on the pores. Apparently, this occurs better on the aerogel with macropores, which maintains the mechanical stability generated for the R, avoiding the loss of the 3D structure [13,35].
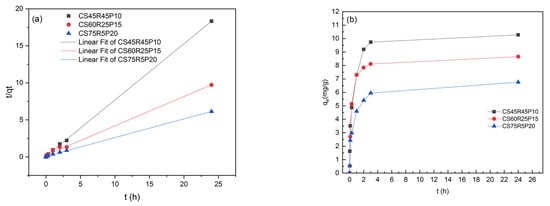
Figure 5.
Kinetic study of the CS–R–P aerogel. (a) Pseudo-second-order kinetic model of MB adsorption in the 50 mg/L known concentration; (b) adsorption time effect on the MB removal in the 50 mg/L known concentration.

Table 5.
Parameters of the methylene blue kinetics.
The results of the adsorption and the kinetic study show that the adsorption rate depends on the initial concentration of the MB together with the amount of adsorbent; in this case, the amount of polysaccharide influenced the number of free spaces for ionic adsorption, while the amount of resole added influenced the stability of the aerogel. A comparison of the maximum adsorption capacity values was made with other reported works, where we can see that these values were related to the efficiency of the adsorption capacity values, as shown in Table 6. It is worth mentioning that the pH of the original concentrations was between 5.5 and 6. The literature reports [17,18] an increase in the adsorption capacity as the temperature and pH increases (optimal 7); this aerogel’s capacity may improve in actual industry conditions.

Table 6.
Comparison with other adsorbents for MB removal.
3.3. Neural Network Modeling
The ANN was estimated, employing the methodology from [26,27]. The products of these evaluations were for a 4-neuron (MSE = 1.832), a 6-neuron (MSE = 0.111), an 8-neuron (MSE = 2.763), a 10-neuron (MSE = 0.740), and a 12-neuron (MSE = 0.902) network. From these evaluations, a hidden layer of six neurons was employed in this investigation, and 19 wolves were used as search agents for 81 iterations. Figure 6 shows the plot of the regressions (output quantities) versus (experimental) the quantities, whose R was 1 for validation, 0.9924 for testing, 0.9998 for training, and 0.9980 for the entire data group. The IGWO [28] was used to refine the execution of the ANN; these results are presented in comparison with the data generated for the Box-Behnken design in Table 7, which are the experimental runs.
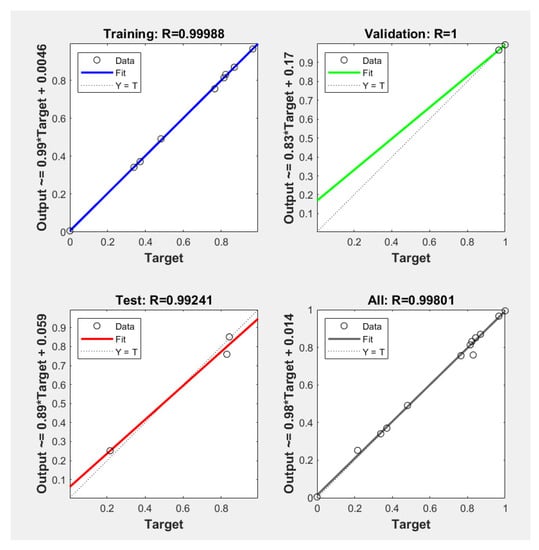
Figure 6.
Correlation plots of the predicted versus the experimental data for the ANN-IGWO model.

Table 7.
The Box–Behnken design observed and predicted values for methylene blue removal.
3.4. Evaluation of the Predictive Performance of the ANN-IGWO
In order to estimate the execution of the ANN-IGWO model, statistical equations were used from the literature [27]. The R and R2 values were evaluated to measure the proximity of the model values to the experimental values. To corroborate the proximity of the modeled line, the MSE and RMSE factors were estimated, as represented in Table 8.

Table 8.
Statistical indices for the ANN model.
3.5. Optimization Process
The ANN-IGWO is a methodology that allows optimal process parameters to be obtained to maximize the removal of methylene blue, using aerogel CS–R–P, giving results for CS–R–P concentrations by vol [%] (52/30/18), thermal treatment [hours] (9.12), and the initial concentration of methylene blue [mg/L] (37), achieving a 94.6% removal. These results were validated in triplicate in the laboratory and, compared with the findings for the 17 experiments demonstrated in Table 5, the optimization process made remarkable progress.
4. Conclusions
The goal of the present study was to highlight the relevance of the modeling and optimization in the experimental design of aerogel processing. Adsorbent technology such as CS aerogels could be a sustainable, practical, and effective option for industry wastewater treatment to improve the processing capabilities of pre-existing pollutants. The results indicate that we obtained a physical crosslinking of precursors. Also, the thermal treatment influenced the final stability of the adsorbent and adsorption capacity. We also concluded that, after adsorption, the hierarchical structure was maintained, as there was chemisorption. The kinetics occurred with the PSO, initial concentration, and adsorbent dosage being crucial for mass transfer. This study demonstrated that ANN, coupled with another artificial intelligence technique such as IGWO, can model complex systems, such as removing dyes using aerogels. Innovation and improvement of the adsorbents are required to make the separation methods convenient in real industry cases as a semicontinuous way to use CS aerogels.
Author Contributions
Methodology, J.F.-G., J.M.-R. and J.B.-F.; formal analysis, J.M.-R. and M.V.-R., writing—original draft preparation, J.F.-G. and J.M.-R.; writing—review and editing, J.F.-G., J.M.-R. and M.V.-R.; and supervision, J.F.-G. and J.B.-F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data is available by corresponding author upon request.
Acknowledgments
To the National Council of Humanity for Science and Technology (CONAHCyT) of México and the Water and Energy Institute from the University Center of Tonalá from the University of Guadalajara.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Elzahar, M.M.H. Utilization of Chitosan and Polyacrylamide Gel to Remove Direct Dyes from Wastewater. Res. Sq. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, T.; Chen, T.; Yi, H.; Rao, F.; Song, S. Removal of Methylene Blue from Water with Montmorillonite Nanosheets/Chitosan Hydrogels as Adsorbent. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 448, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafatullah, M.; Sulaiman, O.; Hashim, R.; Ahmad, A. Adsorption of methylene blue on low-cost adsorbents: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastopoulos, I.; Bhatnagar, A.; Hameed, B.H.; Ok, Y.S.; Omirou, M. A review on waste-derived adsorbents from sugar industry for pollutant removal in water and wastewater. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 240, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albis Arrieta, A.R.; López Rangel, A.J.; Romero Castilla, M.C. Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solutions Using Cassava Peel (Manihot Esculenta) Modified with Phosphoric Acid//Remoción de Azul de Metileno de Soluciones Acuosas Utilizando Cáscara de Yuca (Manihot Esculenta) Modificada Con Ácido Fosfórico. Prospectiva 2017, 15, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Somma, S.; Reverchon, E.; Baldino, L. Water Purification of Classical and Emerging Organic Pollutants: An Extensive Review. ChemEngineering 2021, 5, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Bai, H.; Zhao, Y.; Kang, S.; Yi, H.; Zhang, T.; Song, S. Synthesis of Chitosan Cross-Linked 3D Network-Structured Hydrogel for Methylene Blue Removal. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 141, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, L.S.; Almeida, A.; Nunes, C.; Henriques, B.; Coimbra, M.A.; Lopes, C.B.; Silva, C.M.; Duarte, A.C.; Pereira, E. Simple and Effective Chitosan Based Films for the Removal of Hg from Waters: Equilibrium, Kinetic and Ionic Competition. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 300, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolali, A.; Guo, W.S.; Ngo, H.H.; Chen, S.S.; Nguyen, N.C.; Tung, K.L. Typical Lignocellulosic Wastes and By-Products for Biosorption Process in Water and Wastewater Treatment: A Critical Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 160, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezakazemi, M.; Shirazian, S. Lignin-Chitosan Blend for Methylene Blue Removal: Adsorption Modeling. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 274, 778–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yu, H.; Zeng, F.; Li, X.; Sun, J.; Li, C.; Lin, H.; Su, Z. HKUST-1 Modified Ultrastability Cellulose/Chitosan Composite Aerogel for Highly Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 255, 117402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.L.; Guo, D.M.; An, Q.D.; Xiao, Z.Y.; Zhai, S.R. High-Efficacy Adsorption of Cr(VI) and Anionic Dyes onto β-Cyclodextrin/Chitosan/Hexamethylenetetramine Aerogel Beads with Task-Specific, Integrated Components. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 128, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazi, M.A.; Ghalkhani, M.; Maleki, H. Directional Freeze-Casting: A Bioinspired Method to Assemble Multifunctional Aligned Porous Structures for Advanced Applications. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2020, 22, 2000033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, I.; Gurikov, P. Aerogel Production: Current Status, Research Directions, and Future Opportunities. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2018, 134, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Z.; Liu, Z.; Hou, Y.; Jiang, H.; Li, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, X. The Rising Aerogel Fibers: Status, Challenges, and Opportunities. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2205762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luna, M.S.; Ascione, C.; Santillo, C.; Verdolotti, L.; Lavorgna, M.; Buonocore, G.G.; Ambrosio, L. Optimization of dye adsorption capacity and mechanical strength of chitosan aerogels through crosslinking strategy and graphene oxide addition. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 211, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmi; Ismaturrahmi; Mustafa, I. Methylene Blue Removal from Water Using H2SO4 Crosslinked Magnetic Chitosan Nanocomposite Beads. Microchem. J. 2019, 144, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Zheng, S.; Lv, H.; Wang, B.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, B. Rational Design and Synthesis of Chitosan-Quinoa Polysaccharide Composite Aerogel and Its Adsorption Properties for Congo Red and Methylene Blue. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 9829–9837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Gómez, J.; Romero Arellano, V.H.; Vazquez-Lepe, M.; de Martínez-Gómez, A.J.; Morales-Rivera, J. Modeling and Optimization of the Adsorption of Cr (VI) in a Chitosan-Resole Aerogel Using Response Surface Methodology. Gels 2023, 9, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ighalo, J.O.; Igwegbe, C.A.; Adeniyi, A.G.; Abdulkareem, S.A. Artificial neural network modeling of the water absorption behavior of plantain peel and bamboo fibers reinforced polystyrene composites. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 2021, 60, 472–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurczewska, J.; Cegłowski, M.; Schroeder, G. PAMAM-Halloysite Dunino Hybrid as an Effective Adsorbent of Ibuprofen and Naproxen from Aqueous Solutions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 190, 105603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafreshi, O.A.; Saadatnia, Z.; Ghaffari-Mosanenzadeh, S.; Okhovatian, S.; Park, C.B.; Naguib, H.E. Machine learning-based model for predicting the material properties of nanostructured aerogels. SPE Polym. 2023, 4, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdusalamov, R.; Pandit, P.; Milow, B.; Itskov, M.; Rege, A. Machine learning-based structure–property predictions in silica aerogels. Soft Matter 2021, 17, 7350–7358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Qiao, W.M.; Liang, X.Y. Modelling and optimization of the pore structure of carbon aerogels using an artificial neural network. New Carbon Mater. 2017, 32, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Che, N.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, C. Copper nanoparticle loading and F doping of graphene aerogel enhance its adsorption of aqueous perfluorooctanoic acid. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 7073–7085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabameri, M.; Javid, A.; Roudbari, A. Artificial neural network (ANN) modeling of COD reduction from landfill leachate by the ultrasonic process. Environ. Prot. Eng. 2017, 43, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betiku, E.; Odude, V.O.; Ishola, N.B.; Bamimore, A.; Osunleke, A.S.; Okeleye, A.A. Predictive capability evaluation of RSM, ANFIS and ANN: A case of reduction of high free fatty acid of palm kernel oil via esterification process. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 124, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadimi-Shahraki, M.H.; Taghian, S.; Mirjalili, S. An improved grey wolf optimizer for solving engineering problems. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 166, 113917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perentena, L.; Celis, B.; Valbuena, A. Síntesis de bases de schiff derivadas del quitosano por metoxibenzaldehido. Rev. Iberoam. Polímeros 2015, 16, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Sahebjamee, N.; Soltanieh, M.; Mousavi, S.M.; Heydarinasab, A. Preparation and Characterization of Porous Chitosan–Based Membrane with Enhanced Copper Ion Adsorption Performance. React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 154, 104681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuz, A.G.; Dincturk-Atalay, E.; Uygun, A.; Gode, F.; Aslan, E. A Comparison Study of Adsorption of Cr(VI) from Aqueous Solutions onto Alkyl-Substituted Polyaniline/Chitosan Composites. Desalination 2011, 279, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poljanšek, I.; Krajnc, M. Characterization of Phenol-Formaldehyde Prepolymer Resins by in Line FT-IR Spectroscopy. Acta Chim. Slov. 2005, 52, 238–244. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Wu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Shao, P. Facile fabrication of multifunctional citrus pectin aerogel fortified with cellulose nanofiber as controlled packaging of edible fungi. Food Chem. 2022, 374, 131763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Kousy, S.M.; El-Shorbagy, H.G.; El-Ghaffar, M.A.A. Chitosan/Montmorillonite Composites for Fast Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solutions. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 254, 123236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beh, J.H.; Lim, T.H.; Lew, J.H.; Lai, J.C. Cellulose Nanofibril-Based Aerogel Derived from Sago Pith Waste and Its Application on Methylene Blue Removal. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 160, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, R.; Ye, J.; Dai, W.; Yan, X.; Hu, J.; Hu, X.; Li, S.; Huang, H. Adsorptive Removal of Methyl Orange and Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution with Finger-Citron-Residue-Based Activated Carbon. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 14297–14303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaamary, E.A.S.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Hasan, H.A.; Rahim, R.A.A.; Idris, M. Rawatan Metilena Biru Dalam Air Sisa Menggunakan Scirpus Grossus. Malays. J. Anal. Sci. 2017, 21, 182–187. [Google Scholar]
- Varmazyar, A.; Sedaghat, S.; Khalaj, M. Highly Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue by a Synthesized TiO2/Montmorillonite-Albumin Nanocomposite: Kinetic and Isothermal Analysis in Water. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 37214–37219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Wei, W.; Jiang, Z.; Lu, J.; Zhu, J.; Xie, J. Removal of Cationic Dyes from Aqueous Solution by Adsorption onto Hydrophobic/Hydrophilic Silica Aerogel. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 509, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.G.; Abdel Hai, F.; Abd El-Wahab, H.; Aboelanin, H. Methylene Blue Removal Using a Novel Hydrogel Containing 3-Allyloxy-2-Hydroxy-1-Propanesulfonic Acid Sodium Salt. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2018, 37, 3561–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.G.; Elkony, A.M.; El-Bahy, S.M. Methylene Blue Uptake by Gum Arabic/Acrylic Amide/3-Allyloxy-2-Hydroxy-1-Propanesulfonic Acid Sodium Salt Semi-IPN Hydrogel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 186, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dosa, M.; Grifasi, N.; Galletti, C.; Fino, D.; Piumetti, M. Natural Zeolite Clinoptilolite Application in Wastewater Treatment: Methylene Blue, Zinc and Cadmium Abatement Tests and Kinetic Studies. Materials 2022, 15, 8191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).