Abstract
Rheological measurements under an applied magnetic field were used to investigate the changes to the internal structure and stability of an aqueous ferrofluid. The ferrofluid was prepared by dispersing 1.8 wt.% of maghemite nanoparticles with a size of d = 14 ± 3 nm and a saturation magnetization MS = 68 emu/g in water using citric acid as the surfactant. In this study, oscillatory tests were used to investigate the internal structural changes and the stability of ferrofluid under the influence of the magnetic field B. In a magnetic field of approximately 50 mT, the G′ became higher than the loss modulus G″ as the ferrofluid exhibited a gel-like character. However, at a magnetic field of approximately 200 mT, the character of the ferrofluid reverted to that of a liquid. The change in the character of the ferrofluid in this high magnetic field was associated with a gradual change from chain agglomerates to the energetically more favourable globular agglomerates, using a calculation based on a model described in a separate work. The globular agglomerates impeded the flow to a much lesser degree than the chains, causing a reduction in the viscosity. Further increase of the magnetic field resulted in sedimentation of agglomerates and loss of magneto-rheological effect.
1. Introduction
Magnetic nanoparticles are interesting for use in a variety of technologies, such as heat transfer, magnetic sealing, microfluidic pumps, medical applications, targeted drug delivery, and hyperthermia [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23]. Normally, these nanoparticles are used in the form of ferrofluids, which are colloidal suspensions of superparamagnetic nanoparticles (Co, Fe, Fe3O4, γ—Fe2O3, CoFe2O4) dispersed in a carrier liquid (water, engine oil, transformer oil, etc.) that remains stable in the presence of a magnetic field [5,6,7,8,9,10,11,23,24,25,26,27].
The magnetic properties of ferrofluids are defined by the content and the magnetic properties of the dispersed nanoparticles [8,9,10,11,28]. In addition to their magnetic properties, the colloidal stability and the rheological behaviour are very important for the use of ferrofluids, which are only applicable if they remain stable colloidal suspensions in the presence of an external magnetic field.
For the long-term colloidal stability of nanoparticles in a suspension, their agglomeration should be prevented. In general, the nanoparticles will not agglomerate when the stearic or electrostatic repulsive forces prevail over the attractive forces acting between the nanoparticles. In addition to the attractive Van der Waals forces, the magnetic dipole–dipole attractive forces must be considered when the ferrofluid is exposed to an applied magnetic field [8,29]. Therefore, the magnetic nanoparticles are coated with different molecules that provide additional electrostatic and/or steric repulsion. Shorter molecules, i.e., citric acid [30,31], provide additional electrostatic charge, which prevents agglomeration of nanoparticles. The longer molecules such as sodium oleate [32], oleic acid [28,33], and sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate [11] will provide steric repulsion and, in the case of the bilayer, also electrostatic charge.
When a ferrofluid is exposed to the external magnetic field, an increase in viscosity is observed [7,8,11,25,34]. In addition to the increase of the viscosity, the character of the ferrofluid becomes gel-like [26]. The increase of the viscosity can be explained by a phenomenon known as the magneto-rheological effect. The magneto-rheological effect is a result of the changes in the internal structure of ferrofluid and has been explained by the theoretical model [35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43]. The magnetic forces orient the nanoparticles in the ferrofluid into chain-like agglomerates, which re-orient into globular agglomerates at a higher magnetic field. The change from chain-like into globular agglomerates represents a magnetic-field-induced instability of the ferrofluid since this agglomeration is usually irreversible. The magnetic field that causes the instability depends on the repulsive forces acting between the nanoparticles and can thus be used as the measure of the colloidal stability of the ferrofluid.
In this study, rheological measurements made under an applied magnetic field were used to investigate the changes in the internal structure and the stability of a water-based ferrofluid stabilized with citric acid. We assumed that the settling of the particles caused by the irreversible change from the chain-like agglomerates to the globular agglomerates would have an influence on the rheological behaviour of the ferrofluid. This is because the dispersed nanoparticles are essential for the magneto-rheological effect. As the settling of the nanoparticles reduces the number of dispersed nanoparticles, the magneto-rheological effect should disappear. The magnetic field causing this instability is important information needed for the ferrofluid’s application, or it can be used as a measure of the ferrofluid’s stability.
The agglomeration of nanoparticles due to the van der Waals forces in aqueous suspensions is usually prevented by electrostatic repulsive forces that result from the large charge on their surfaces. This large surface charge is induced by the absorption of appropriately charged surfactant molecules, such as citric acid, onto their surfaces. In general, in addition to the van der Waals forces, the magnetic dipole–dipole interactive forces between the magnetic nanoparticles can cause agglomeration. The magnetic dipole–dipole interactions are negligible in the absence of an external magnetic field when the nanoparticles are superparamagnetic. Superparamagnetism is a phenomenon whereby the magnetic moments of ferro/ferrimagnetic nanoparticles are spontaneously relaxed when not subjected to an externally applied magnetic field [44,45]. In other words, superparamagnetic materials retain a ferromagnetic response when exposed to an external magnetic field, but unlike ferromagnetic materials, they exhibit zero remnant magnetization. This means that their behaviour with no external magnetic field resembles that of paramagnetic materials, hence the term superparamagnetic. A spontaneous relaxation of the magnetization is possible when the thermal energy (kT) prevails over the energy of the magnetic anisotropy. This is also known as Neél relaxation and can be observed in particles below a critical size. The critical volume of the nanoparticles at which this phenomenon occurs, i.e., the superparamagnetic limit, strongly depends on the effective anisotropy constant (Keff) of the material. The critical volume (Vcrit) of nanoparticles with a uniaxial magnetic anisotropy and a Neél relaxation time (τN) can be estimated using the following equations:
- k: Boltzmann constant
- T: absolute temperature.
In addition to the Neél relaxation, the magnetic moments of suspended nanoparticles can be relaxed due to Brownian motion. In this case, the nanoparticles can be larger than the superparamagnetic limit due to Neél relaxation; however, they are small enough for the kT to prevail over the magnetic dipole–dipole interactions between the individual nanoparticles. The Brownian relaxation time (τB) depends on the hydrodynamic particle volume (Vh) and on the viscosity of the media in which the nanoparticles are dispersed (η):
Without an external magnetic field, kT is higher than the magnetic dipole–dipole interaction between the nanoparticles. The Brownian motion relaxes the magnetic moments and prevents the agglomeration of the nanoparticles. Therefore, in an ideal ferrofluid, there is no agglomeration of the nanoparticles. However, partial agglomeration is present even when the ferrofluid is not exposed to an external magnetic field [36].
When the ferrofluid is exposed to an external magnetic field, the magnetic moment (m) inside the nanoparticles interacts with the external magnetic field with field strength (H), and the rotation of the particles is severely hindered. The particles start to form agglomerates when the energy of the nanoparticles in the magnetic field (EH) exceeds kT [34]
μ0: permeability of free space.
The m aligns parallel to the external magnetic field. This means that when the magnetic moments inside the nanoparticles are oriented in the same direction and placed behind each other, the dipole–dipole magnetic attractive interactions prevail over kT, and the nanoparticles form chain-like agglomerates. The dipole–dipole magnetic interaction energy (Em) between two spherical nanoparticles of the same size depends on the distance between the centres of the spheres (l) and the magnetic moment of the nanoparticles (m), which further depends on their size (d) and their magnetization (M).
The magnetic field induces a “magnetic” torque that orientates the chains parallel to the magnetic field. On the other hand, when a ferrofluid is subjected to shearing, the hydrodynamic forces cause a “hydrodynamic” torque, which tends to align the chains parallel to the flow. The lengths of the chains are determined by the two opposite forces, i.e., the magnetic dipole–dipole interactions and the hydrodynamic forces [46]. The magnetic dipole–dipole force (Fmag) of the two aligned magnetic moments keeps the nanoparticles together and causes the formation of an internal structure in the ferrofluid.
s: the thickness of the layer of surface molecules.
The hydrodynamic forces (Fhyd), which are perpendicular to the Fmag, decrease the internal order of the ferrofluid by destroying the chain-like agglomerates.
- : share rate.
- n: number of nanoparticles in the chain.
When Fmag is larger than Fhyd, the magnetic nanoparticles will remain ordered in the chain-like agglomerates, and the magneto-rheological effect will be observed. As the shearing increases, so does Fhyd, and at sufficiently large shear rates (), they become larger than Fmag. When this occurs, the magnetic interactions are too weak to have any effect on the nanoparticles, and the magneto-rheological effect disappears.
The changes in the ferrofluid’s structure with an increase in the magnetic field strength (H) can be viewed as a phase separation. The agglomeration of the nanoparticles leads to the creation of two phases, i.e., a “gas” phase and a “liquid” phase. The difference between the two phases is in the content of the nanoparticles. In the gas phase, the number of nanoparticles is substantially lower than in the liquid phase. The proposed model [35,42,43] predicts the formation of chain-like agglomerates and their transformation into globular agglomerates with the increase of the magnetic field. In a real ferrofluid, the nanoparticles are not perfect spheres, and they are polydispersed. Statistical thermodynamics shows that there is a critical size above which the interactions are strong enough to form the agglomerates. For the iron-oxide nanoparticles, this critical size is 13 nm [47]. In the model, only the interactions between these “large” nanoparticles in a single chain are considered. The interactions between the nanoparticles in different chains and the interactions between the “small” and the “large” nanoparticles are neglected. Also, it is convenient to introduce the dimensionless magnetic field (κ) and magnetization (ε).
The model predicts a change in the structure, which is formed inside the ferrofluid with the external field. First, the chain-like agglomerates start to form at a low magnetic field. As the magnetic field increases, the agglomerates go through a structural transformation from chain-like agglomerates to globular agglomerates.
The magnetic field at which the structural transformation occurs depends on the free energy of the chains (Ach) and the globules (Ag). The total free energy () of the agglomerates determine the form of the agglomerates.
If the total free energy is negative, then the chain-like agglomerates are more favourable. When the total free energy becomes positive, the globular agglomerates are favourable. The estimated free energy of the chain containing n nanoparticles is:
The total free energy of the globule is composed of three components: the free energy of the globule without the applied magnetic field (A0), the free energy of the magnetic interactions inside the globule (Am), and the free energy of the osmotic pressure between the “gas” and the “liquid” phases (As).
- : volume fraction of the nanoparticles
- .
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
We investigated the rheological properties of an aqueous ferrofluid containing 1.8 wt.% of maghemite nanoparticles stabilized in a suspension with citric acid as the surfactant. The nanoparticles were synthesized in a two-step co-precipitation process of Fe2+ and Fe3+ from an aqueous solution of sulphates with concentrated ammonia, as described in [30].
In the first step, the pH of the solution was raised to pH = 3 and kept at a constant value for 30 min. In this step, the iron hydroxides were precipitated. In the second step, the pH was raised to pH = 11.6 by the addition of a concentrated ammonia solution. During the second step, the Fe2+ was oxidized, and a spinel product was formed. The precipitated particles were washed with diluted ammonia solution.
After washing, the pH of the suspension was set to pH = 5.2, and a citric acid was added to the suspension. The suspension was heated to 80 °C and kept at a constant temperature for 90 min. The suspension was cooled down, and the pH was set to pH = 10.1.
The average grain size of the synthesized nanoparticles measured from a TEM image was d =14 ± 3 nm, with the magnetization measured at 10 kOe, where it approaches saturation MS = 68 emu/g [30].
The hydrodynamic size distribution of the nanoparticles in the ferrofluid was measured with dynamic light scattering (DLS) using a (Fritsch Analisette 12 DynaSizer, Idar-Oberstein, Germany). The measurement was performed on a thin layer of the ferrofluid and is suitable for non-transparent ferrofluids without any dilution.
2.2. Rheological Measurements
The rheological measurements were performed with a rheometer (Physica 301, Anton Paar, Graz, Austria) equipped with an MRD 180/1T magneto-rheological measuring cell. The measurements were performed with a plate-plate configuration with a 1 mm gap between the plates. The magnetic field, ranging from 0 to 400 mT, was oriented perpendicular to the flow. Both rotational and oscillatory measurements were conducted. During the rotational test, the shear rate () was varied from 0.1 to 100 s−1. The oscillatory test was performed at a constant frequency (ω) of 100s−1, while the amplitude (γ) was varied from 0.1 to 10%. At each magnetic field, five measurements were conducted with fresh suspension.
3. Results
Figure 1 shows the hydrodynamic size distribution of the nanoparticles dispersed in the ferrofluid. This size varies from 13 nm to 38 nm, with an average hydrodynamic diameter of 17 nm.
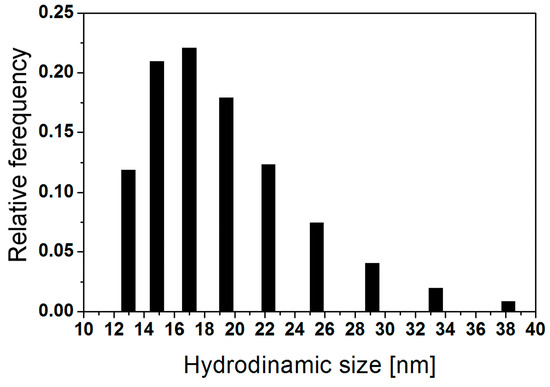
Figure 1.
DLS measurement of the hydrodynamic nanoparticle size (number–weighted distribution) in the ferrofluid.
Figure 2 shows the viscosity (η) curves of the ferrofluid measured at different magnetic fields (B). The ferrofluid exhibits a shear-thinning behaviour at all magnetic fields, as the viscosity of the ferrofluid decreases with the increasing shear rate [27,33]. As the increases, the difference in the viscosity between the different magnetic fields becomes smaller. At shear rates higher than = 10 s−1, the differences become negligible. Figure 3 shows the viscosities at a constant shear rate = 0.5 s−1 measured at different magnetic fields (B). At first, the viscosity of the ferrofluid increases with the increasing magnetic field. The viscosity increases from η = 0.15 Pas, without the applied magnetic field, to η = 0.95 Pas at B = 145 mT. The increase of the viscosity with the increasing B is expected and was observed by others [5,7,8,11,27]. At higher fields, the viscosity of the ferrofluid decreases, and at B = 280 mT, it reduces to the initial value. With a further increase of the magnetic field, the viscosity of the ferrofluid reduces below the initial value.
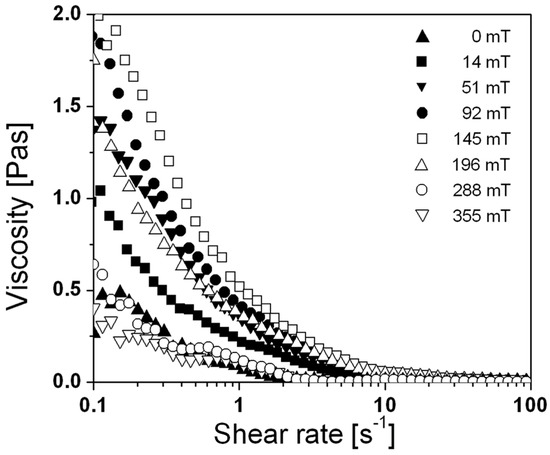
Figure 2.
Viscosity of the ferrofluid versus shear rate for different magnetic fields.
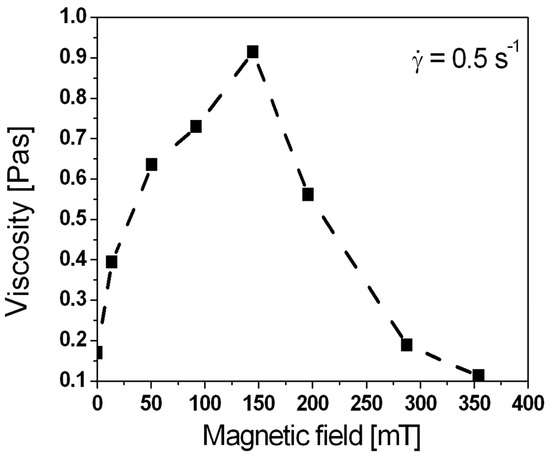
Figure 3.
Viscosity of the ferrofluid versus magnetic field at a constant shear rate.
A similar trend is observed when performing an oscillatory test. A series of amplitude sweeps at the frequency ω = 100 s−1 were conducted for different magnetic fields B. Figure 4 shows an average of five measurements of amplitude sweep at B = 90 mT. When the ferrofluid was exposed to a magnetic field of B = 90 mT, a linear viscoelastic (LVE) range was observed, which ends at γ ~ 1%. In the LVE range, the storage modulus (G′) is higher than the loss modulus (G″), proving that at B = 90 mT, the ferrofluid exhibits a gel-like character since the elastic behaviour dominates over the viscous behaviour. A comparison between the average values of G′ and G″ at γ = 0.7% (Figure 5) extracted from amplitude sweep measurements at different magnetic field strengths was used to show the changes in the character of the ferrofluid. Up to 50 mT, only G″ is observed, and the ferrofluid exhibits a liquid character. At a magnetic field B = 50 mT, the G′ becomes higher than G″ as the ferrofluid becomes gel-like. The ferrofluid retained its gel-like character up to B = 200 mT, where the character of the ferrofluid reverted to that of a liquid. At B = 400 mT, the G″ reduces to the initial value. The complex viscosity η* of the ferrofluid also varies with the applied magnetic field. The absolute value of the complex viscosity increases from η* = 0.3 Pas at B = 0 mT to η* = 1.3 Pas at B = 90 mT. With any further increase in the magnetic field, the absolute value of the complex viscosity decreases to a plateau value of approximately 0.8 Pas. The plateau stretches from B = 150 mT to B = 350 mT. At B = 400 mT, the absolute value of complex viscosity reduces to the initial value. The LVE range is shorter compared to, and the magnetic field at which the gel-like character is observed is lower compared to the ferrofluid with particles coated with oleic acid and dispersed in kerosene [26].
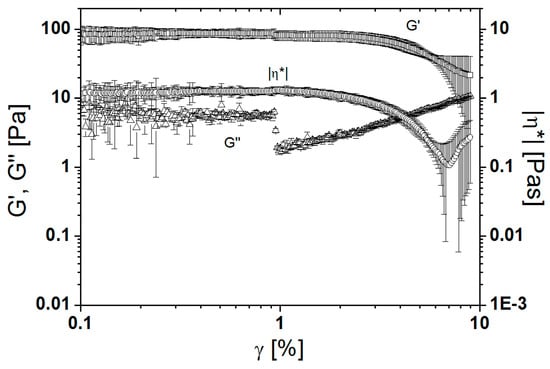
Figure 4.
Storage modulus, loss modulus, and complex viscosity versus strain for ferrofluid at 90 mT.
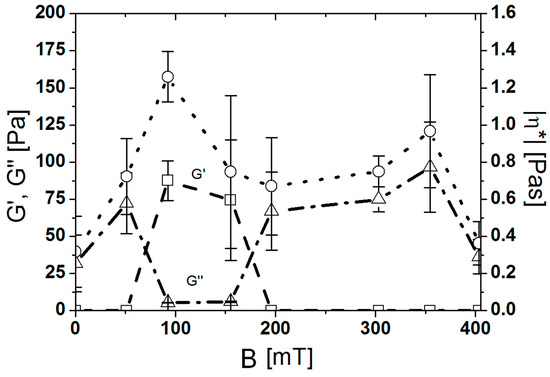
Figure 5.
Storage modulus (dashed line), loss modulus (dashed–dotted line), and complex viscosity (dotted line) versus magnetic field at 0.7% strain.
4. Discussion
The rheological behaviour of the ferrofluid can be explained by the formation of an internal structure and the sedimentation of the particles under the influence of the magnetic field. The observed shear thinning behaviour of the ferrofluid at zero magnetic fields indicates the partial agglomeration of the dispersed particles. Outside and at low magnetic fields, the dipole–dipole interactions are weak compared with kT, and the nanoparticles do not magnetically agglomerate. As the magnetic field increases, the dipole–dipole interactions prevail over kT, and the particles start to form chain-like agglomerates. The magnetic torque tends to align the chains parallel to the magnetic field, but the mechanical torque tends to align them parallel to the shearing, which is perpendicular to the magnetic field. The chains position themselves in the equilibrium state determined by the torques. When the magnetic torque is higher than the mechanical torque, then the equilibrium position is more parallel to the magnetic field, and the viscosity is higher. As the mechanical load is removed, the chains reposition themselves parallel to the magnetic field, thus acting in a similar way to a spring. As a result, G′ becomes higher than G″ as the ferrofluid exhibits a gel-like character. This behaviour can be observed up to B = 145 mT (Figure 3) and shear rates below 10 s−1.
At low shear rates, the hydrodynamic forces are relatively weak when compared with the magnetic dipole–dipole interactions. Thus, the chains remain long, and the viscosity of the ferrofluid is high. The longer chains affect the flow to a much greater extent than the short ones, and as the shear rate increases, so do the hydrodynamic forces. When the length of the chains decreases, so does the viscosity. Due to weak hydrodynamic forces, the differences in the viscosity at different magnetic fields are more pronounced at low shear rates. Above = 10 s−1, the length of the remaining chains becomes too small to have any significant influence on the rheology of the ferrofluid.
The decrease of the viscosity and the change of the rheological character from a gel-like substance to a liquid at higher magnetic fields can be explained by the transformation of the chain-like agglomerates into globular agglomerates. Figure 6 shows the total free energy of the agglomerates as a function of the number of nanoparticles in the agglomerate for different magnetic fields calculated using Equations (10) and (11). When the total free energy has a negative value, the chain-like agglomerates are energetically more favourable than the globular agglomerates. As can be seen from Figure 6, the theoretical magnetic field at which the transition from chain-like agglomerates into globular agglomerates occurred is at approximately B = 210 mT. Because the globules affect the flow to a lesser degree, the viscosity of the ferrofluid decreases.
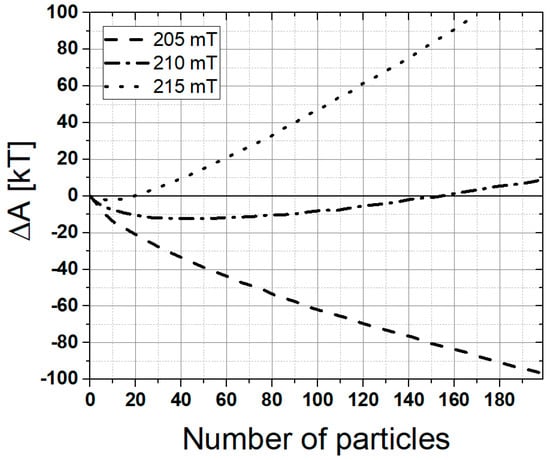
Figure 6.
Total free energy of the agglomerates.
Above the magnetic field of B = 200 mT, the character of the ferrofluid reverts from a gel-like liquid (Figure 5), which is in good agreement with the predicted value. The difference between the calculated field of the transition and the observed one can be attributed to the simplifications made in the calculations. The particles were considered to have a uniform size of 14 nm, and the magnetization of the particles was 68 emu/g. As can be seen from Figure 1, the dispersed particles did not have a uniform size. The magnetization of the particles depends on their size. Due to a “nonmagnetic” surface layer, the larger particles have higher magnetizations than the smaller ones. Also, the distance between the particles in the suspension decreases with the magnetic field. The proximity of the particles results in the coupling of their magnetic moments and the possible creation of superspins [48], thereby increasing the magnetization of the interacting nanoparticles. The higher magnetization of the nanoparticles increases the free energy of the globules to a greater extent than the free energy of the chains. Thus, the globules become energetically favourable at a lower magnetic field.
With a further increase in the magnetic field above the transition from chain agglomerates to globular ones, the viscosity of the ferrofluid reduces to below the initial value. The reason for the reduction of the final viscosity below the initial viscosity is the irreversibility of the agglomeration and sedimentation of agglomerates. The citric acid only provides an additional surface charge but does not provide stearic repulsion. Outside the magnetic field, the charge is high enough to prevent agglomeration and sedimentation of particles, making ferrofluid stable for long periods of time [31]. Once the magnetic attraction due to the external magnetic field is strong enough, particles irreversible agglomerate and ferrofluid becomes unstable. In contrast, oleic acid provides stearic repulsion, and the particles do not come in direct contact even at higher magnetic fields, making the ferrofluid more stable [26]. Once the particles are irreversibly agglomerated, the gravitational force prevails over the translational Brownian motion, and the agglomerates settle. Since the particles are no longer suspended in the liquid, they do not affect the viscosity of the liquid in the presence of an external magnetic field.
5. Conclusions
The iron oxide nanoparticles were prepared via co-precipitation of Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions. Citric acid was used to prepare stable aqueous ferrofluid. The average hydrodynamical size of the particles determined with DLS was 17 nm. The stability of an aqueous ferrofluid stabilized with citric acid was related to its rheological properties, i.e., viscosity η, storage modulus G′ and loss modulus G″, measured as a function of the applied magnetic field. From the rheological measurements, the following can be concluded:
- -
- At low magnetic fields below 200 mT, the ferrofluid behaves similarly to the observation made by other authors. The viscosity increases with the magnetic field, and the ferrofluid exhibits gel-like behaviour with G′ higher than G″;
- -
- At magnetic fields above 200 mT, the viscosity starts to decrease, and the character of ferrofluid is reverted to liquid;
- -
- The increase of the viscosity and a gel-like character can be associated with the formation of a chain-like agglomerate, as predicted in the model by Zubarev;
- -
- The change from gel-like to liquid character can be associated with the transition of chain-like into globular agglomerates and eventual sedimentation of particles;
- -
- Citric acid will not provide a high enough electrostatic charge to prevent agglomeration of nanoparticles at high magnetic fields.
Future investigations will focus on:
- -
- Rheological behaviour of non-polar ferrofluid with similar nanoparticles coated with fatty acids;
- -
- The influence of ferromagnetic nanoplatelets on rheological properties;
- -
- Another interesting study will be the development of composite material of elastomer and ferromagnetic nanoplatelets.
Funding
This research was funded by the Ministry of Higher Education, Science and Technology of the Republic of Slovenia, grant number P2-0089.
Data Availability Statement
The data that supports the findings of this study are available within the article.
Acknowledgments
The author also acknowledges the use of equipment in the Centre of Excellence on Nanoscience and Nanotechnology–Nanocenter.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of this study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Calarasu, D.; Cotae, C.; Olaru, R. Magnetic fluid brake. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 201, 401–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Nakatsuka, K.; Fujita, T.; Atarashi, T. Application of hydrophilic magnetic fluid to oil seal. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 201, 361–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaranarayanan, V.K.; Prakash, O.; Pant, R.P.; Islam, M. Lithium ferrite nanoparticles for ferrofluid applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2002, 252, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangthieng, C.; Finlayson, B.A.; Maulbetsch, J.; Cader, T. Heat transfer enhancement in ferrofluids subjected to steady magnetic fields. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 201, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kole, M.; Khandekar, S. Engineering apllications of ferrofluids: A review. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2021, 537, 168222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattanaik, M.S.; Varma, V.B.; Cheekati, S.K.; Chaudhary, V.; Ramanujan, R.V. Optimal ferrofluids for magnetic cooling devices. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinod, S.; Philip, J. Thermal and rheological properties of magnetic nanofluids: Recent advances and future directions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 307, 102729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekzadeh, A.; Pouranfard, A.R.; Hatami, N.; Kazemnejad Banari, A.; Rahimi, M.R. Experimantal Investigations on the Viscosity of Magnetic Nanofluids under the Infuence of Temperature, Volume Fractions of Nanoparticles and External Magnetic Field. J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 2016, 9, 693–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phor, L.; Kumar, V. Self-cooling by ferrofluid in magnetic field. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, A. Effect of the diameter of magnetic core and surfactant thickness on the viscosity of ferrofluid. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2022, 548, 168975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Tang, X.; Hong, R.Y.; Feng, W.G.; Xie, H.D.; Chen, D.X.; Badami, D. Ubbelohde viscometer measurement of water-based Fe3O4 magnetic fluid prepared by coprecipitation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 348, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewlin, R.L., Jr.; Edwards, M.; Schultz, C. Design and Development of a Traveling Wave Ferro-Microfluidic Device and System Rig for Potential Magnetophoretic Cell Separation and Sorting in a Water-Based Ferrofluid. Micromachines 2023, 14, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baraton, M.-I. Synthesis, Functionalization and Surface Treatment of Nanoparticles; American Scientific Publishers: Stevenson Ranch, CA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, C.C.; Curtis, A.S.G. Functionalization of magnetic nanoparticles for applications in biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, R198–R206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, F. Nanoengineering of particles surfaces. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin, J.-P.; Wilhelm, C.; Servais, J.; Ménager, C.; Bacri, J.-C.; Gazeau, F. Size-sorted anionic iron oxide nanomagnets as colloidal mediators for magnetic hyperthermia. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 2628–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Gupta, M. Synthesis and surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 3995–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, A.; Shinaki, M.; Honda, H.; Kobayashi, T. Medical application of functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2005, 100, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankhurst, Q.A.; Connoly, J.; Jones, S.K.; Dobson, J. Application of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, R167–R181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartaj, P.; del Puerto Morales, M.; Veintemillas-Verdaguer, S.; González-Carreno, T.; Serna, C.J. The preparation of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, R182–R197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, N.T.K. Magnetic Nanoparticles: From Fabrication to Clinical Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Veish, O.; Gunn, J.W.; Zhang, M. Design and fabrication of magnetic nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery and imaging. Adv. Drug Del. Rev. 2010, 62, 284–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wängler, B.; Morgenstern, B.; Zentgraf, H.; Eisenhut, M.; Untenecker, H.; Krüger, R.; Huss, R.; Seliger, C.; Semmler, W.; et al. Silica- and alkoxysilane-coated ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide particles: A promising tool to label cells for magnetic resonance imaging. Langmuir 2007, 23, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosensweig, R.E. Ferrohydrodynamics; Dover Publications: Mineloa, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Tadros, T.F. Correlation of viscoelastic properties of stable and flocculated suspensions with their interparticle interactions. Adv. Colloid Interf. Sci. 1996, 68, 97–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinod, S.; Camp, P.J.; Philip, J. Observation of soft glassy behavior in a magnetic colloid exposed to an external magnetic field. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 7126–7136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryapolov, P.A.; Shel’deshova, E.V.; Postnikov, E.B. Temperature and field dependences of magnetic fluid’s shear viscosity: Decoupling inputs from a carrier fluid and magnetic nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 382, 121887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craciunescu, I.; Chitanu, E.; Codescu, M.M.; Iacob, N.; Kuncser, V.; Socoliuc, V.; Susan-Resiga, D.; Balanean, F.; Ispas, G.; Borbath, I.; et al. High performance magnetorheological fluids: Very high magnetization FeCO-Fe3O4 nanoclusters in a ferrofluid carrier. Soft Matter 2022, 18, 626–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nor, N.M.; Razak, K.A.; Tan, S.C.; Noordin, R. Properties of surface functionalized iron oxide nanoparticles (ferrofluid) conjugted antibody for lateral flow immunoassay application. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 538, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čampelj, S.; Makovec, D.; Drofenik, M. Preparation of water-based ferrofluids with citric acid as a surfactant. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2008, 20, 204101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikelashvili, V.; Kekutia, S.; Markhulia, J.; Saneblidze, L.; Maisuradze, N.; Kriechbaum, M.; Almasy, L. Synthesis and Characterization of Citric Acis-Modified Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Prepared with Electrohydraulic Discharge Treatment. Materials 2023, 16, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, R.Y.; Ren, Z.Q.; Han, Y.P.; Li, H.Z.; Zheng, Y.; Ding, J. Rheological properties of water-based Fe3O4 ferrofluids. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2007, 62, 5912–5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susan-Resiga, D.; Malaescu, I.; Marinica, O.; Marin, C.N. Magnetorheological properties of a kerosene-based ferrofluid with magnetite particles hydrophobized in the absence of the dispersion medium. Phys. B Condens. 2020, 587, 412150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odenbach, S. Magnetoviscous Effects in Ferrofluids; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Zubarev, A.Y.; Iskakova, L.Y. To the theory of rheological properties of ferrofluids: Influence of drop-like agglomerates. Phys. A 2004, 343, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantrell, R.W.; Bradbury, A.; Poppewell, J.; Charles, S.W. Agglomerate formation in a magnetic fluid. J. Appl. Phys. 1982, 53, 2742–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilg, P.; Kröger, M.; Hess, S. Magnetoviscosity and orientational order parameters of dilute ferrofluids. J. Chem. Phys. 2002, 116, 9078–9088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, A.O.; Zubarey, A.Y. Non-linear evolution of system of elongated droplike aggregates in a metastable magnetic fluid. Phys. A 1998, 251, 348–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelev, V.; Ivanov, A. Magnetic properties of ferrofluids: An influence of chain agglomerates. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 289, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pshenichnikov, A.F.; Mekhonoshin, V.V. Equilibrium magnetization and microstructure of the system of superparamagnetic interacting particles: Numerical simulation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2000, 213, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, A.; Chantrell, R.W.; Kamiyama, S.-I.; Coverdale, G.N. Three dimensional Monte Carlo simulation of thick chainlike clusters composed of ferromagnetic fine particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1996, 181, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubarev, A.Y.; Fleischer, J.; Odenbach, S. Towards a theory of dynamical properties of polydispersed magnetic fluid: Effect of chain-like agglomerates. Phys. A 2005, 358, 475–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubarev, A.Y.; Iskakova, L.Y. Condensation phase transition in ferrofluids. Phys. A 2004, 335, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullity, B.D.; Graham, C.D. Introduction to Magnetic Materials; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jiles, D. Introduction to Magnetism and Magnetic Materials; Champman & Hall: London, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Odenbach, S.; Störk, H. Shear dependence of field-induced contributions to the viscosity of magnetic fluids at low shear rates. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1998, 183, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odenbach, S. Ferrofluids: Magnetically Controllable Fluids and Their Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Jagodič, M.; Gyergyek, S.; Jagličić, Z.; Makovec, D.; Trontelj, Z. Detection of magnetic nanoparticles fusion by magnetic measurements. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 104, 074319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).