Abstract
Sacha inchi oil (SIO) extraction has been extensively studied using various oil extraction techniques to achieve a high oil recovery. However, most studies relied on heat-based methods, which led to compromised oil quality and reduced nutritional values, particularly polyunsaturated fatty acids (omega-3 and omega-6), vitamin E, and phenolic compounds. To address these concerns, this study employed a hydraulic cold-pressed extraction (HCPE) technique for extracting SIO aiming to enhance oil yield while preserving its nutritional integrity. During the HCPE process of sacha inchi seeds (SIS), conducted at a constant temperature of 25 ± 1 °C, pressures and pressing times were varied within the range of 30–50 MPa and 10–30 min, respectively, to determine their impact on SIO yields. The results revealed that both pressure and pressing time significantly influenced the yields of SIO (p < 0.05), with the highest oil recovery of 86.31 wt.% on a wet basis achieved at 50 MPa for 30 min. Regarding physicochemical properties, the peroxide values (5.71–9.07 meq/kg), iodine values (176.22–197.76 g I2/100 g), acid values (1.82–2.16 mg KOH/g), and percentage of free fatty acids (0.91–1.08 wt.% as oleic acid) were found to be influenced by pressure and pressing time (p < 0.05). Additionally, the color variation by L* (34.22–35.17), −a* (0.39–0.81), and b* (3.48–5.62) changed with each oil yield. Notably, the high iodine value in SIO indicated a substantial content of polyunsaturated fatty acids, including omega-3 (40.86%), omega-6 (40.87%), and omega-9 (10.20%). Furthermore, a comparison with solvent extraction methods demonstrated that HCPE exhibited similar efficiency in extracting SIO, offering additional advantage in terms of its cold-pressed condition, eliminating of solvent use, simplicity, short extraction time, and higher oil recovery.
1. Introduction
Sacha inchi (Plukenetia volubilis L.) is a plant native to Peruvian people in the Amazon basin and belongs to the Euphorbiaceae family. Primarily cultivated in Latin America, Peru stands as the largest producer of the plant, generating an estimated 1200 tons yearly. Following suit, Latin America countries such as Colombia, Brazil, Ecuador, Bolivia, Nicaragua, Guatemala, Costa Rica, Mexico, and Cuba, as well as Asian countries including China, Cambodia, Lao, and Thailand, are also significant producers. The optimal growth conditions for Plukenetia volubilis encompass a temperature range of 10–37 °C, with preference for sandy, well-drained soil. Plukenetia volubilis thrives at altitudes ranging from approximately 200 to 1500 m [1,2]. Regarding seasonal variations, diverse irrigation systems, and fertilization techniques, sacha inchi seeds (SIS) typically yield around 150–750 kg/ha [3]. SIS are rich in oil content, ranging between 48 and 50%, and protein content, between 27 and 28% [4]. Notably, sacha inchi oil (SIO) is abundantly composed of essential fatty acids, including α-linolenic acid (ALA, ω-3, 46.8–50.8%), linoleic acid (ω-6, 33.4–36.2%), oleic acid (ω-9, 8.7–9.6%), alongside tocopherol and phenolic compounds. These essential fatty acids, particularly omega-3 and omega-6, found applications in various fields such as food supplements, cosmetics, and the prevention of diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, cancer, hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, and bacterial and viral infections, making them highly valued for food and pharmaceutical purposes [2,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15].
Due to the numerous valuable compounds and the significant benefits of SIO, many studies have been conducted to maximize oil yields using different extraction methods, including solvent extraction (e.g., petroleum ether and hexane) [8,14,16], supercritical fluid extraction with CO2 and n-propane [5,15], aqueous enzymatic extraction (proteases and cellulase) [17], and mechanical extraction [4,18]. Solvent extraction involved thermal processing, which may break down the double bond in polyunsaturated fatty acids, leading to oxidative rancidity. However, the use of toxic solvents and potential contamination of oil products raise environment and food safety concerns, respectively. Although supercritical fluid extraction was used as an alternative to solvent extraction, the requirement for high temperature (60 °C) can degrade oil quality [5]. In contrast, aqueous enzymatic extraction emerged as an eco-friendly method, replacing toxic solvents with enzymes within a specific temperature range (30–50 °C) [17]. However, despite its potential as a green extraction process for SIS oil, the extended extraction time (4.95 h) and a maximum oil yield of 28.45% indicate time-consuming and low-yield recovery when compared to reported oil content in SIS.
Among the various extraction methods, mechanical extraction gained attention for its simple setup, low investment, low operation costs, absence of toxic solvents, and ability to achieve high oil yields [4,19,20,21]. A previous study by Muangrat et al. [4] employed mechanical extraction using a single screw press machine with a feeding rate of 1.5 kg/h, a high drying temperature of 90 °C, and a press head temperature of 90 °C, resulting in a maximum oil yield of 40.63 wt.% on a wet basis. However, this approach involved the application of high temperature, in addition to screw press extraction, extraction duration, and heat to disrupt the oleosome structure, releasing oil from oilseeds. Hydraulic pressing achieved higher oil recovery, ranging from around 66–90% for SIO, Jatropha (Jatropha curcas L.) oil, palm (Elaeis guineensis) oil, and other oilseeds [22,23,24,25]. Moreover, valorization of oil press cakes and meals through mechanical extraction supports the concept of zero waste, as these residues also serve as sources of bioactive compounds, including proteins, dietary fibers, and antioxidants [26]. However, previous studies associated temperature with improved oil yield, but this comes at the cost of hydrogenation of polyunsaturated fatty acids and degradation of phenolic compounds and tocopherols due to the applied heat during extraction [27].
Therefore, this study aimed to extract SIO using HCPE at different pressures and pressing times to analyze the physicochemical qualities (peroxide value, iodine value, acid value, free fatty acids, and color) for each cold-pressed extraction condition. The results will aid in selecting suitable pressures and pressing times for the HCPE of SIO. While numerous studies previously explored different extraction techniques, this investigation is the first to assess HCPE, offering higher oil recovery without the use of toxic solvents and high temperatures, while obtaining higher unsaturated fatty acids from the maximum oil yield extracted.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Dried sacha inchi seeds (SIS) were procured from a wholesaler in Banlung, the capital of Ratanakiri, Cambodia. The seeds were stored at room temperature (25–27 °C) for further experiments. Before extraction, the SIS were dehulled and ground for approximately 5 min using a grinder (QD-200, Shanghai Quanda Food Machinery Co. Ltd., Shanghai, China) to obtain particle sizes ranging between 2 and 3 mm. The ground samples were packed in polyethylene bags, sealed, and stored in a refrigerator at 4 °C. Each extraction was carried out within 12 h of sample preparation. Analytical-grade chemical reagents were purchased from reputable suppliers: Dejung, Seoul, Republic of Korea (acetic acid, cyclohexane, and ethanol), Fisher, Schwerte, Germany (chloroform), Sigma-Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany (potassium iodide, sodium thiosulfate, starch solution, and potassium hydroxide), Acros, Geel, Belgium (Wjis solution), and Merck, Darmstadt, Germany (potassium hydroxide and phenolphthalein).
2.2. Hydraulic Oil Press Machine
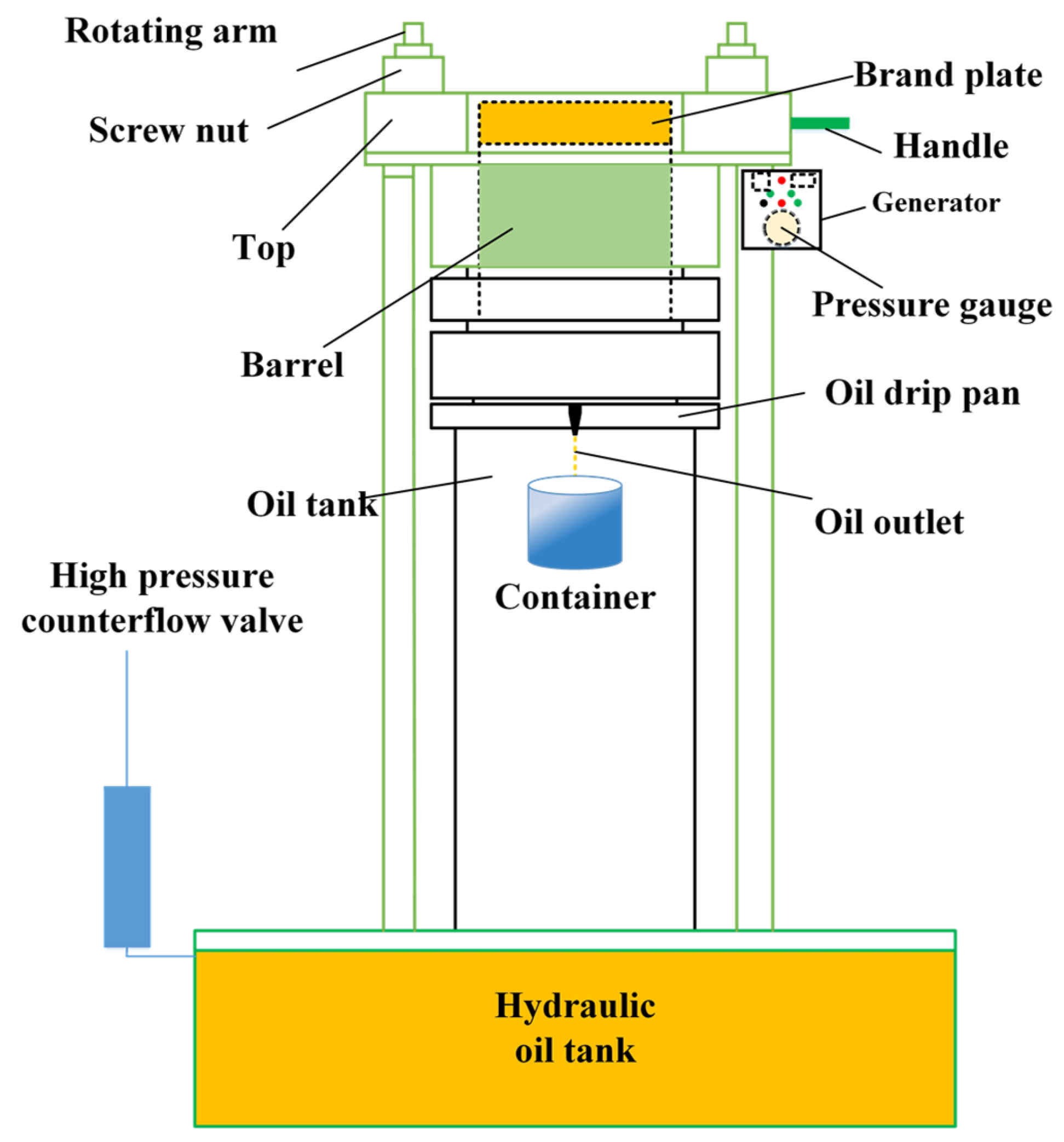
The hydraulic oil press machine (BY-180, Henan Beyrong Machinery Co.,Ltd., Shanghai, China) was used for extracting the sacha inchi oil (SIO). The machine, as depicted in Figure 1, consisted of a generator with adjustable pressure (0–55 MPa) and a pump controller. The maximum pressure used in this study was limited to ≤50 MPa. The temperature in the generator could be manually adjusted for cold or hot-pressed conditions. The machine’s barrel was a stainless steel cylinder with a maximum feeding capacity of 3–4 kg. Handle and screw nuts were movable to place a polypropylene fiber bag containing sacha inchi samples into the barrel. After pressing, a high-pressure counterflow value was used to relieve the pressure, and the pressed oil flowed into an oil drip pan, which was then collected in a container by gravity.
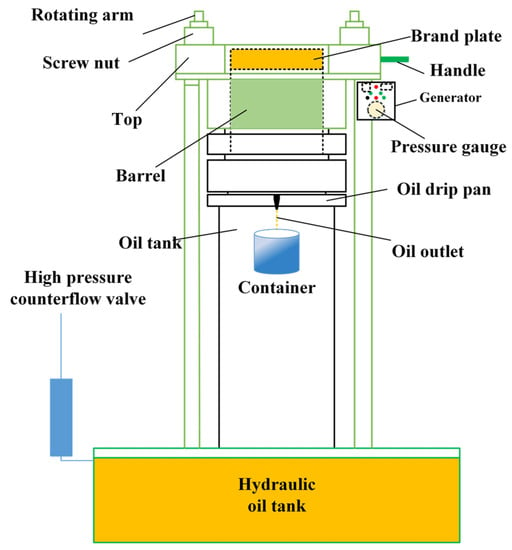
Figure 1.
A scheme of hydraulic oil press machine.
2.3. Analysis of Proximate Composition in the SIS
The proximate composition of the SIS, including moisture, total oil, total carbohydrates, protein, and ash content, was determined following the Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International [28]. The moisture content was determined using a drying oven (Memmert UNE400, Memmert, Munich, Germany) and the oil content was determined using a solvent extractor (SER 148/3, VELP Scientifica, Lombardy, Italy), according to AOAC 934.01 and AOAC 920.39, respectively. The total carbohydrates were calculated using the formula: %total carbohydrates = 100 − (%moisture + %total oil + %protein + %ash). Protein content was determined using Kjeldahl apparatuses (SpeedDigester K-439, Srubber K-415, and Steam distiller K-365, Buchi, Solothurn, Switzerland) following the Kjeldahl method of AOAC 960.52, and the ash content was determined by incineration using a muffle furnace (Nabertherm B180, Nabertherm, Pfullingen, Germany) according to AOAC 942.05. The composition of SIS was expressed as a percentage (% w/w, wet basis).
2.4. Extraction of Sacha Inchi Oil (SIO)
2.4.1. Hydraulic Cold-Pressed Extraction (HCPE)
HCPE was used to extract SIO at a constant temperature of 25 ± 1 °C, varying pressure and pressing time. Approximately 100 g of ground SIS packed in a polypropylene fiber bag was pre-pressed for 5–10 min to achieve a steady flow of oil before actual processing. Subsequently, 200 g of each sample was processed at different pressures (30, 40, and 50 MPa) and pressing times (10, 20, and 30 min). After pressing, the oil outlet was allowed to flow from the barrel for 5 min. The yields of crude oil, oil cake, and total mass balance were calculated and expressed as percentages using the following Equations (1)–(3). Crude oil obtained from each extraction condition was stored at 4 °C in amber glass and evaluated for physicochemical quality within 24 h.
where WOE: weight of oil extracted (g), WSIS: weight of sacha inchi samples (g), and WOC: weight of oil press-cake.
Crude oil (%) = (WOE/WSIS) × 100%
Oil cake (%) = (WOC/WSIS) × 100%
Total mass balance (%) = [(WOE + WOC)/WSIS] × 100%
2.4.2. Conventional Extraction (CE)
Ethanol and n-hexane were used for CE to extract SIO at a 1:20 ratio of solid to solvent (w/v). The extraction was performed using a magnetic stirrer (IKA® C-MAG HP 7, IKA Laboratory Technology Co., Ltd., Guangdong, China) at a constant temperature of 60 °C and a stirring speed of approximately 600 rpm for 60 min. Residues and supernatants were separated using filter paper (Watman No. 1) and then centrifuged at 4500 rpm for 15 min. The supernatants were evaporated using a rotatory evaporator (IKA® RV 10, IKA-Werke GmbH & Co. KG, Staufen, Germany) to obtain the oil yield.
2.4.3. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction (UAE)
UAE was performed using n-hexane with a sample-to-solvent ratio of 1:100 (w/v). The sacha inchi sample of 5 g was separately mixed with 100 mL and 150 mL of n-hexane in a 250 mL of conical flash, and the ratios were selected based on the highest oil yields obtained from preliminary data. The mixture was covered with aluminum foil and Parafilm to solvent evaporation. The sample was then placed in an ultrasonic bath (USC 600T, VWR International, Penang, Malaysia) at 60 °C for 75 min. After extraction, the extract was filtered, centrifuged, and evaporated as described for CE.
2.5. Physicochemical Analysis of SIO
The crude SIO obtained from each treatment of HCPE was analyzed for peroxide value (PV), iodine value (IV), and acid value (AV) using titration methods following the International AOAC [28].
2.5.1. Peroxide Value
A sample of 5 g of SIO was dissolved in 30 mL of acetic acid: chloroform (3:2, v/v) and 0.5 mL of saturated KI solution was added. The mixture was shaken for 1 min before mixing 30 mL of distilled water. The solution was continuously titrated with 0.01 M sodium thiosulphate (Na2SO3) and 0.5 mL of 1% starch solution. The peroxide value (PV) was calculated using Equation (4):
where VS is the volume of Na2SO3 titrated with the sample (mL), VB is the volume of Na2SO3 used as a blank, M is the molarity of Na2SO3 used, and W is the mass of the sample used (g).
PV (meq/kg oil) = 1000 × (VS − VB) × M/W
2.5.2. Iodine Value
A 0.1 g sample of SIO was dissolved in 15 mL of cyclohexane and 15 mL of Wijs solution. The mixture was left in the dark for 30 min, followed by the addition of 20 mL of potassium iodide (KI). After that, 100 mL of distilled water was added to the solution. The solution was titrated with 0.1 M Na2SO3 with a few drops of 1% starch solution until the color disappeared. The iodine value (IV) was calculated using Equation (5):
where VS is the volume of Na2SO3 titrated with the sample (mL), VB is the volume of Na2SO3 used as a blank, M is the molarity of Na2SO3 used, and W is the mass of the sample used (g).
IV (g I2/100 g oil) = 12.69 M × (VB − VS)/W
2.5.3. Acid Value and Free Fatty Acid
A 5 g sample of SIO was mixed with 80 mL of hot neutralized ethyl-alcohol and titrated with 0.1 M KOH solution, using 0.5 mL of phenolphthalein as an indicator. The acid value (AV) was calculated using Equation (6):
where V is the volume of the standard KOH solution used (mL), N is the normality of the standard KOH solution used, and W is the mass of the sample used (g). The free fatty acid (FFA) content was expressed as a percentage of oleic acid using Equation (7):
AV (mg KOH/g oil) = (56.1 × V × N)/W
FFA (% as oleic acid) = AV × 28.2/56.1
2.5.4. Color
The color of crude SIO was analyzed using a portable colorimeter (Chroma CR400, Konica-Minolta Ltd., Osaka, Japan) with coordinates of lightness (L*), greenness-redness (a*), and blueness-yellowness (b*).
2.6. Analysis of Fatty Acid Composition
The fatty acid composition of crude sacha inchi oil was determined using gas chromatography with flame ionization detection (GC-FID), following a modification of the method by Lee et al. [29]. The fatty acids were esterified to fatty acid methyl esters (FAMEs). A 100 mg oil sample was dissolved in 2 mL of hexane, and 0.1 mL of 2 M potassium hydroxide in methanol was added and mixed for 5 min. The supernatant was collected after centrifugation at 4000 rpm for 5 min and filtered using a 0.22 µm PTFE syringe filter. Fatty acid compositions were analyzed using an Agilent 6890 Series GC-FID (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) equipped with a split-splitless injector and SGE BPX70 column (25 m × 0.32 mm, film thickness 0.25 µm) (Trajan Scientific, Victoria, Australia). The GC conditions were as follows: the oven temperature was held at 100 °C for 5 min, followed by an increase of 4 °C/min to 240 °C. The injection volume was 1 µL with a split ratio of 20:1. The detector was set at 280 °C, and the gas flow rates were as follows: hydrogen gas at 40 mL/min, air at 450 mL/min, and nitrogen (auxiliary gas) at 25 mL/min. Nitrogen gas (carrier gas) was set at 10 psi. Pure standards of FAMEs at each retention time were used for comparison and identification of peaks on the chromatogram. The percentage of each major fatty acid composition was calculated by dividing the peak area of each fatty acid by the total peak area of all fatty acid majorities.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
All experimental data, conducted in duplicate, were expressed as mean ± standard deviation and analyzed using IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows (Version 26.0. Armonk, NY: IBM Corp). The effect of pressure and pressing times on oil yields and physicochemical parameters was analyzed using two-way ANOVA at 95% of confidence level. Comparison between different extraction methods was performed using one-way ANOVA with a significant level of p < 0.05.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Proximate Composition of Sacha Inchi Seeds (SIS)
The analysis of moisture, total oil, total carbohydrates, protein, and ash content in the SIS on a wet basis is presented in Table 1. The SIS exhibited a high total oil content of 48.80 ± 0.50 wt.%, which justified its selection for oil extraction in this study. This oil content was higher than that reported in other studies (39–44 wt.% by Muangrat et al. [4] and 42 wt.% by Gutiérrez et al. [8]) and fell withing the range reported by Kodahl et al. [1] and Wang et al. [7] (33–58% and 33–54%, respectively). The variation in oil content can be attributed to differences in cultivation technique, oil extraction methods, seed preparation techniques, and management practices [1,4,7,8].

Table 1.
Proximate composition of the sacha inchi seeds (SIS) per 100 g and expressed as % (w/w).
3.2. Effect of Pressure and Pressing Time on Yields of Sacha Inchi Oil (SIO) Using Hydraulic Cold-Pressed Extraction (HCPE)
The percentage of crude oil, oil cake, and total mass balance obtained from the HCPE of SIS are summarized in Table 2. The results showed that yields of the SIO obtained through HCPE ranged from 28.90 to 42.12 wt.% depending on the pressure and pressing time, ranging from 30 to 50 MPa and 10 to 30 min, respectively. The lowest oil yield was obtained at the lowest pressure (30 MPa) and pressing time (10 min), while the highest oil yield was achieved at the highest pressure (50 MPa) and pressing time (30 min). The results indicated that both pressure and pressing time significantly influenced the extraction efficiency of SIO. It should be noted that approximately 6 wt.% of oil remained in the oil press-cake, indicating that there is potential for increasing the pressing time to extract the remaining oil from the SIS. However, the economic feasibility of this approach should be considered. Additionally, the pressure should not exceed 50 MPa, as recommended by the equipment’s operation manual. Furthermore, the oil remaining in the press-cake can be utilized in various applications such as animal feeds, cookies, and biscuits, as these products require oil and contribute to their nutritive values [30].

Table 2.
Percentages (% w/w, wet basis) of crude oil, oil cake, and total mass balance obtained from sacha inchi samples using the HCPE.
The percentage of oil cake varied from 54.75% to 67.35%, depending on the oil yields obtained from each pressing condition. The quantity of SIO press-cake logically decreased as the extraction efficiency increased. The SIO press-cake generated during the extraction process can be utilized in various applications, including animal feeds, food products (beverages, biscuits, cookies, granola bars, extrudates, noodles, etc.), fermentation substrates, protein isolates, and hydrolysates, as it contains protein, carbohydrates, mineral, fiber, bioactive peptides, and other bioactive compounds [26].
The total mass balances for each treatment exhibited variations between 94.72% and 101.57%. These variations can be attributed to the loss of oil in the drop pan of the hydraulic oil press machine and the loss of mass during the removal of oil cakes before calculation. Oil losses occurred when the oil outflow time was shorter, as some oil remained in the oil drop pan. However, the total mass balances for the conditions of 10 and 20 min at 30 MPa were 101.57% and 100.20%, respectively, indicating that the oil yields obtained at lower pressure and pressing time were lower than those obtained at higher pressure and pressing time.
3.3. Physicochemical Properties of Sacha Inchi Oil (SIO) Obtained by Hydraulic Cold-Pressed Extraction (HCPE)
The physicochemical properties of the SIO extracts, including peroxide value (PV), iodine value (IV), acid value (AV), free fatty acid (FFA), and color value, are presented in Table 3. These parameters were significantly affected by the pressure and pressing times (p < 0.05) due to the absence of heat sources during the extraction process, which could alter the chemical composition of the oil. Some PV values ranged from 5.71 to 9.07 meq/kg, which can be attributed to the long storage of raw SIS (approximately 30–45 days) before extraction. However, all PV values were acceptable and complied with the CODEX-STAN 210-1999 standard set by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), which permits PV values up to 15 meq/kg oil [31].

Table 3.
Peroxide value, iodine value, acid value, free fatty acid, and color of the crude SIO extracted from the HCPE.
The IV of the SIO ranged from 176.22 to 197.76 g I2/100 g oil, indicating a higher quantity of unsaturated fatty acids. A study by Muangrat et al. [4], which used the screw press method at temperature between 60 and 90 °C, reported lower IV values (102.66–104.05 g I2/100 g oil) compared to this study. The current study demonstrated that the cold pressed condition employed in HCPE preserved the unsaturated fatty acids, resulting in higher IV values [27].
The AV ranged from 1.82 to 2.16 mg KOH/g oil, with no significant variation observed among different pressure and pressing time conditions. Similarly, the FFA content, calculated from the AV, showed relatively low levels ranging from 0.91% to 1.08%. The L* value represented the lightness of the samples and showed slight differences ranging from 34.22 to 35.17. The b* value represented pigment indicators present in the SIO samples, while the a* value could reflect impurities in the crude oil samples.
To compare the chemical properties of the SIO obtained under optimum conditions (50 MPa for 30 min) with previous studies, Table 4 presents PV, IV, AV, and % FFA values obtained from different extraction methods, including HCPE, solvent extraction (SE), subcritical extraction (SPE), and aqueous enzymatic extraction (AEE). The PV (8.11 ± 0.33 meq/kg) indicated the level of reactive oxygen in the crude SIO obtained in this study. This value was similar to the study conducted by Chasquibol et al. [25] using the same HCPE extraction method. However, the PV was higher than that reported in other studies by Muangrat et al. [4], Gutiérrez et al. [14], and Chinh et al. [18. This difference could be attributed to the absence of filtration or centrifugation of crude oil after the extraction, the long storage period of SIS, and the storage of crude oil for 24 h before testing. The IV indicated the amount of unsaturated fatty acids present in the SIO. Higher IV values indicated a great presence of unsaturated fatty acids and a higher number of double bonds (C=C) in the SIO. The AV represented the amount of carboxylic acid groups in the SIO and the obtained AV value was 2.15 ± 0.05 mg KOH/g. These results were similar to those reported by Nguyen et al. [17].

Table 4.
Physiochemical properties of the sacha inchi oil in this study compared to previous works.
3.4. Comparison of Different Extraction Methods on Yield of the Sacha Inchi Oil (SIO)
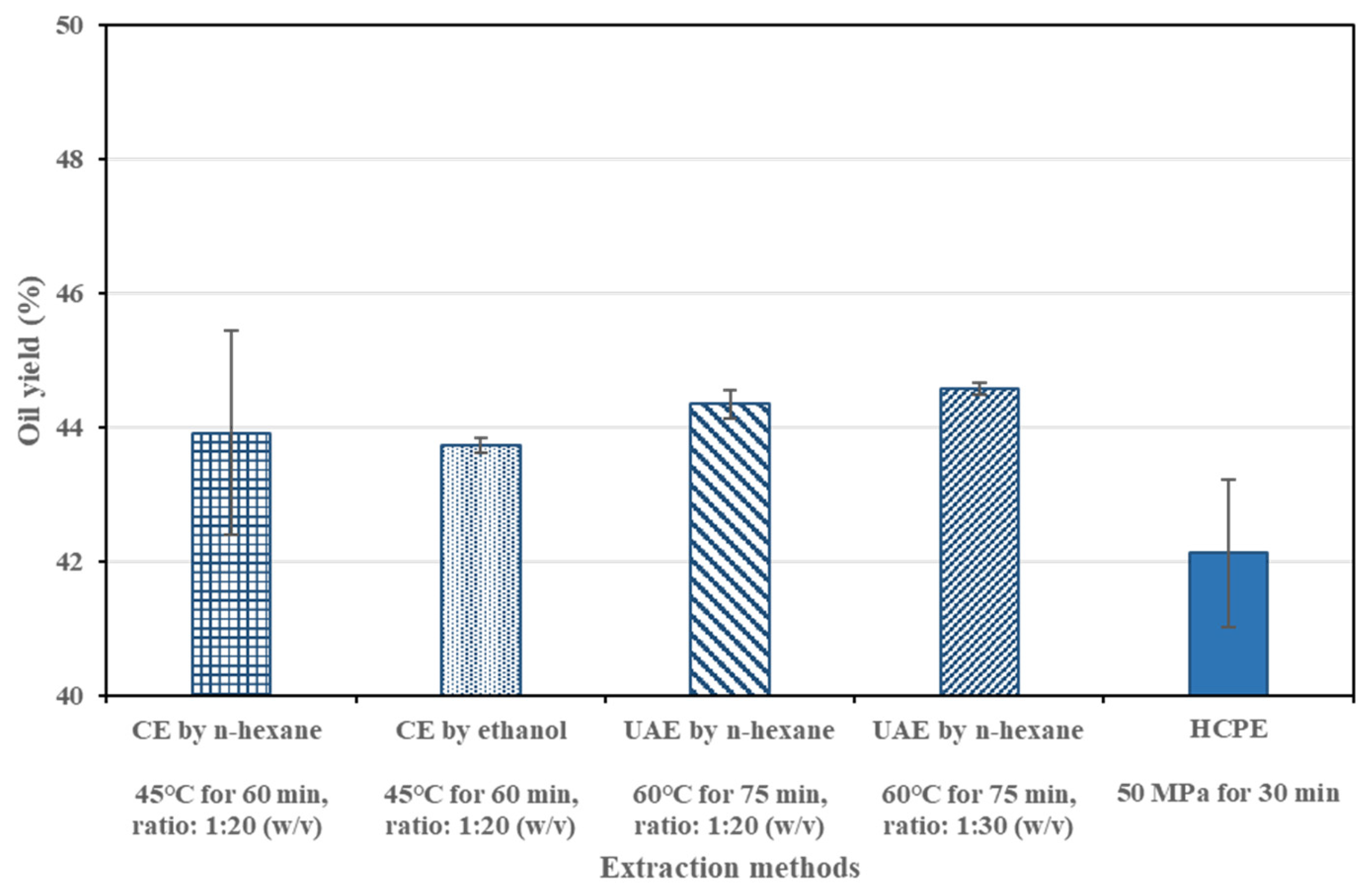
Figure 2 illustrates the yields of the SIO obtained from different extraction methods. The results indicated that there was no significant difference in the oil yield of the sacha inchi samples among the various extraction methods (p > 0.05). However, the extraction time required for ultrasonic-assisted extraction (UAE) and conventional extraction (CE) using n-hexane and ethanol was approximately double that of HCPE. CE and UAE involved more complex extraction steps and required solvent removal, making HCPE a more efficient method, providing a higher oil yield with shorter extraction time of only 30 min.
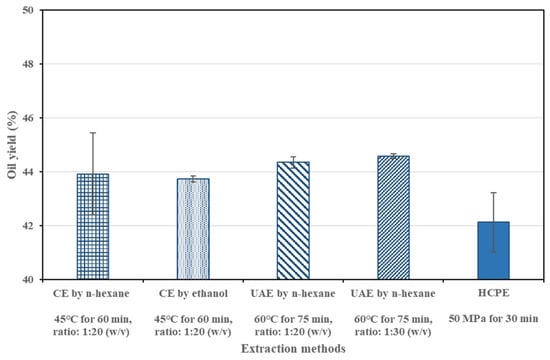
Figure 2.
Comparison of different oil extraction methods on yield of the SIO.
Table 5 shows the comparison of previous studies on yields of the SIO using different extraction methods. The oil yield obtained in this study was comparable to that reported for screw press extraction by Muangrat et al. [4] and hydraulic pressing by Chasquibol et al. [25]. The oil yield was also higher than that obtained using subcritical extraction with n-propane by Zanqui et al. [5] and aqueous enzymatic extraction by Nguyen et al. [17]. These results demonstrate the advantage of mechanical pressing methods, including hydraulic pressing and screw pressing, for extracting oil from oilseeds with high oil content compared to some solvent extraction methods.

Table 5.
Comparison of previous studies on oil yields of sacha inchi using different extraction methods.
3.5. Fatty Acid Profiles of Sacha Inchi Oil (SIO)
The fatty acid composition of SIO extracted by the HCPE was determined using GC-FID, and the results are presented in Table 6. The five-majority peaks on the chromatograph were identified as palmitic acid (4.48%), stearic acid (3.57%), oleic acid (10.20%), linoleic acid (40.87%), and linolenic (40.86%). These findings showed slight differences in the fatty acid composition compared to previous research, which could be attributed the variation in plant varieties, geographical and climate conditions, harvesting time of the seeds, oil extraction methods, and analytical methods [32]. Due to the high amount of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, which are essential for human health, SIO holds great potential for development as a supplement product.

Table 6.
Fatty acid composition (%) of crude sacha inchi oil (SIO) extracted.
4. Conclusions
This research work demonstrated that the yields of SIO were significantly influenced by the pressure and pressing time in the HCPE. The physicochemical properties of SIO, such as PV, IV, AV, % FFA, and color (L*, a*, and b*), were also significantly affected by the pressure and pressing time due to absence of heat sources during the extraction process. However, all these quality parameters were within acceptable limits according to the FAO standards. The HCPE method provided a higher oil recovery (86.31%) within a shorter extraction time of 30 min, and it did not significantly differ from the CE and UAE methods in terms of SIO yield. Future research should focus on the shelf-life of SIO extracted to determine if additional processing steps, such as sedimentation, centrifugation, and other physical refining processes, should be employed to extend its shelf life and prevent deterioration of oil quality during the storage. The press-cake generated from the extraction process can be utilized in various applications based on its physiochemical characteristics.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and methodology, S.K. and T.K.; validation, S.K., T.K. and M.S.; investigation, S.K., T.K. and M.B.; writing—original draft preparation, S.K. and M.S.; visualization, S.K. and M.S.; supervision, C.P.T. and R.T.; writing, review, and editing, S.K. and M.S.; project administration, Y.N. and M.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Cambodia Higher Education Improvement Project (Credit No. 6221-KH).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to thank to Cambodia Higher Education Improvement Project (Credit No. 6221-KH) for the fund fully supported.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kodahl, N.; Sørensen, M. Sacha inchi (Plukenetia volubilis L.) is an underutilized crop with a great potential. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, N.E.; Hatta-Sakoda, B.; Pascual-Chagman, G.; Rodriguez-Saona, L.E. Characterization and authentication of a novel vegetable source of omega-3 fatty acids, sacha inchi (Plukenetia volubilis L.) oil. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 1173–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, H.D.; Geng, Y.J.; Yang, C.; Jiao, D.Y.; Chen, L.; Cai, Z.Q. Yield and resource use efficiency of Plukenetia volubilis plants at two distinct growth stages as affected by irrigation and fertilization. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muangrat, R.; Veeraphong, P.; Chantee, N. Screw press extraction of Sacha inchi seeds: Oil yield and its chemical composition and antioxidant properties. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2018, 42, e13635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanqui, A.B.; Silva, C.M.; Morais, D.R.; Santos, J.M.; Oenning Ribeiro, S.A.; Eberlin, M.N.; Cardozo-Filho, L.; Visentainer, J.V.; Marques Gomes, S.T.; Matsushita, M. Sacha inchi (Plukenetia volubilis L.) oil composition varies with changes in temperature and pressure in subcritical extraction with n-propane. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 87, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Escudero, F.; Morales, M.T.; Ramos Escudero, M.; Muñoz, A.M.; Cancino Chavez, K.; Asuero, A.G. Assessment of phenolic and volatile compounds of commercial Sacha inchi oils and sensory evaluation. Food Res. Int. 2020, 140, 2–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhu, F.; Kakuda, Y. Sacha inchi (Plukenetia volubilis L.): Nutritional composition, biological activity, and uses. Food Chem. 2018, 265, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, L.F.; Rosada, L.M.; Jiméneza, Á. Chemical composition of sacha inchi (Plukenetia volubilis L.) seeds and characteristics of their lipid fraction. Grasas y Aceites 2011, 62, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, J.; Carvalho, M.G.; Garcia-Rojas, E.E. Fatty acids profile of Sacha Inchi oil and blends by 1H NMR and GC-FID. Food Chem. 2015, 181, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondioli, P.; Bella, L.D.; Rettke, P. Alpha linolenic acid rich oils. Composition of Plukenetia volubilis (Sacha Inchi) oil from Peru. Riv. Ital. Delle Sostanze Grasse 2006, 83, 120–123. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos-Escudero, F.; Muñoz, A.M.; Ramos Escudero, M.; Viñas-Ospino, A.; Morales, M.T.; Asuero, A.G. Characterization of commercial Sacha inchi oil according to its composition: Tocopherols, fatty acids, sterols, triterpene and aliphatic alcohols. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 4503–4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supriyanto, S.; Imran, Z.; Ardiansyah, R.; Auliyai, B.; Pratama, A.; Kadha, F. The Effect of Cultivation Conditions on Sacha Inchi (Plukenetia volubilis L.) Seed Production and Oil Quality (Omega 3, 6, 9). Agronomy 2012, 12, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanali, C.; Dugo, L.; Cacciola, F.; Beccaria, M.; Grasso, S.; Dacha, M.; Dugo, P.; Mondello, L. Chemical Characterization of Sacha Inchi (Plukenetia volubilis L.) Oil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 13043–13049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, L.F.; Quiñones-Segura, Y.; Sanchez-Reinoso, Z.; Díaz, D.L.; Abril, J.I. Physicochemical properties of oils extracted from γ-irradiated Sacha Inchi (Plukenetia volubilis L.) seeds. Food Chem. 2017, 237, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Follegatti-Romero, L.A.; Piantino, C.R.; Grimaldi, R.; Cabral, F.A. Supercritical CO2 extraction of omega-3 rich oil from Sacha inchi (Plukenetia volubilis L.) seeds. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2009, 49, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Li, J.; Chen, M.S.; Xu, Z.F. Determination of oil contents in Sacha inchi (Plukenetia volubilis) seeds at different developmental stages by two methods: Soxhlet extraction and time-domain nuclear magnetic resonance. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 56, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.C.; Vuong, D.P.; Tam Nguyen, N.T.; Nguyen, N.P.; Su, C.-H.; Wang, F.-M.; Juan, H.-Y. Aqueous enzymatic extraction of polyunsaturated fatty acid–rich sacha inchi (Plukenetia volubilis L.) seed oil: An eco-friendly approach. LWT 2020, 133, 109992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crimaldi, M.; Faugno, S.; Sannino, M.; Ardito, L. Optimization of hemp seeds (Canapa sativa L.) oil mechanical extraction. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2017, 58, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achten, W.M.J.; Mathijs, E.; Verchot, L.; Singh, V.P.; Aerts, R.; Muys, B. Jatropha biodiesel fueling sustainability? Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefining 2007, 1, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subroto, E.; Manurung, R.; Heeres, H.J.; Broekhuis, A.A. Mechanical extraction of oil from Jatropha curcas L. kernel: Effect of processing parameters. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 63, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, B.; Deshmukh, S.; Sharma, M. Optimization of Oil Extraction and Characterization from Tamarindus Indica Linn Seed Oil. Int. J. Oil Gas Coal Eng. 2014, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ileoye, O. Development of a Palm Oil Press Development of a Palm Oil Press. J. Fluid Mech. Mech. 2021, 3, 22–29. [Google Scholar]
- Yusuf, K.A.; Olawepo, B.B.; Braimah, M.; Imuran, A.S. Development of a Hydraulic Press for Jatropha Oil Extraction. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2021, 8, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, A.R.; Kumar, J.; Yuvaraj, J.M.; Vincent Joseph, P.V.; Shekar, K. Development of Domestic Purpose Hydraulic Press Oil Expeller. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2019, 8, 125–128. [Google Scholar]
- Chasquibol, N.A.; Aguila, C.; Yácono, J.C.; Guinda, Á.; Moreda, M.; Gómez-Coca, R.B.; Pérez-Camino, M.C. Characterization of glyceridic and unsaponifiable compounds of Sacha inchi (Plukenetia huayllabambana L.) oils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 10162–10169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancuta, P.; Sonia, A. Oil Press-Cakes and Meals Valorization through Circular Economy Approaches: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhibshi, E.A.; Ibraheim, J.A.; Hadad, A.S. Effect of Heat Processing and Storage on Characteristic and Stability of Some Edible Oils. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Agriculture, Environment and Biological Sciences, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 21–22 December 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC International. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International; AOAC International: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.-S.; Noh, B.-S.; Bae, S.-Y.; Kim, K. Characterization of fatty acids composition in vegetable oils by gas chromatography and chemometrics. Anal. Chim. Acta 1998, 358, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erwin, G.; Torres, S.; Blanca, H.-L.; Gutiérrez, L.-F. Sacha Inchi Oil Press-cake: Physicochemical Characteristics, Food-related Applications and Biological Activity. Food Rev. Int. 2021, 39, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization. Codex Standard for Named Vegetable Oils (CODEX-STAN 210—1999). Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/y2774e/y2774e04.htm (accessed on 7 June 2023).
- Yang, B.; Kallio, H. Effects of harvesting time on triacylglycerols and glycerophospholipids of sea buckthorn (Hippophaë rhamnoides L.) berries of different origins. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2002, 15, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liua, Q.; Xu, Y.K.; Zhang, P.; Na, Z.; Tang, T.; Shi, Y.X. Chemical composition and oxidative evolution of Sacha Inchi (Plukentia volubilis L.) oil from Xishuangbanna (China). Grasas y Aceites 2014, 65, e012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, W.; Quinteros, M.F.; Carpio, C.; Morales, D.; Vásquez, G.; Álvarez, M.; Silva, M. Identification of fatty acids in sacha inchi oil (Cursive plukenetia volubilis L.) from ecuador. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2018, 11, 279–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).