Ozone Kinetic Studies Assessment for the PPCPs Abatement: Mixtures Relevance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
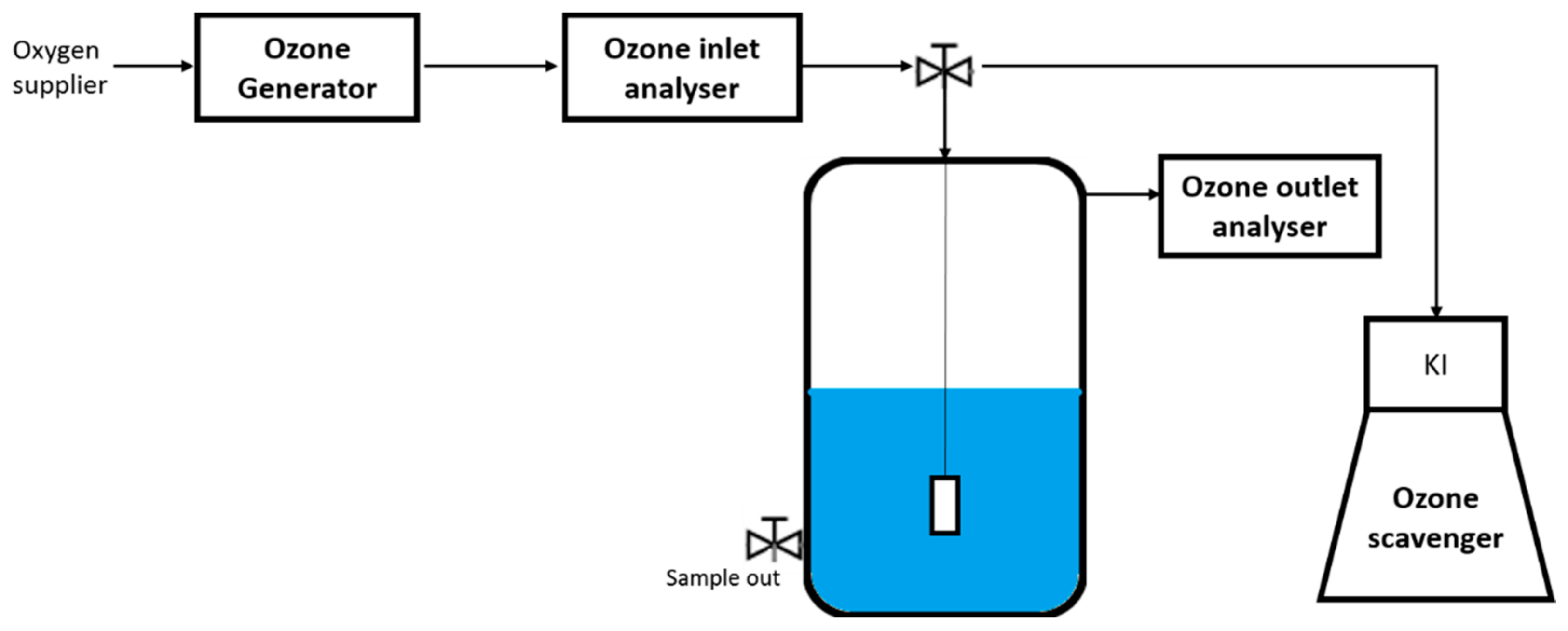
2.2. Experimental Set-Up
2.3. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
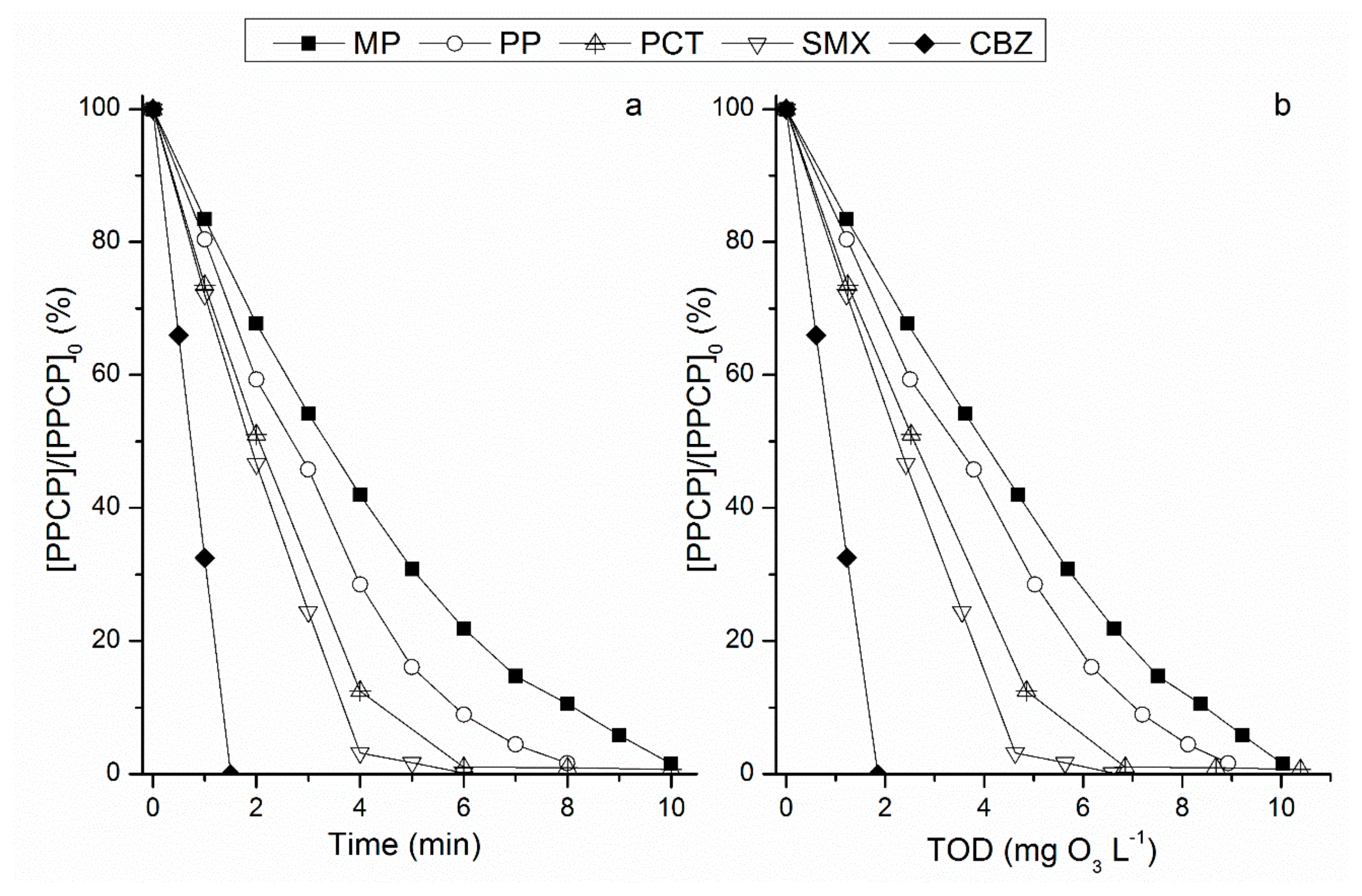
3.1. Degradation of Individual PPCPs
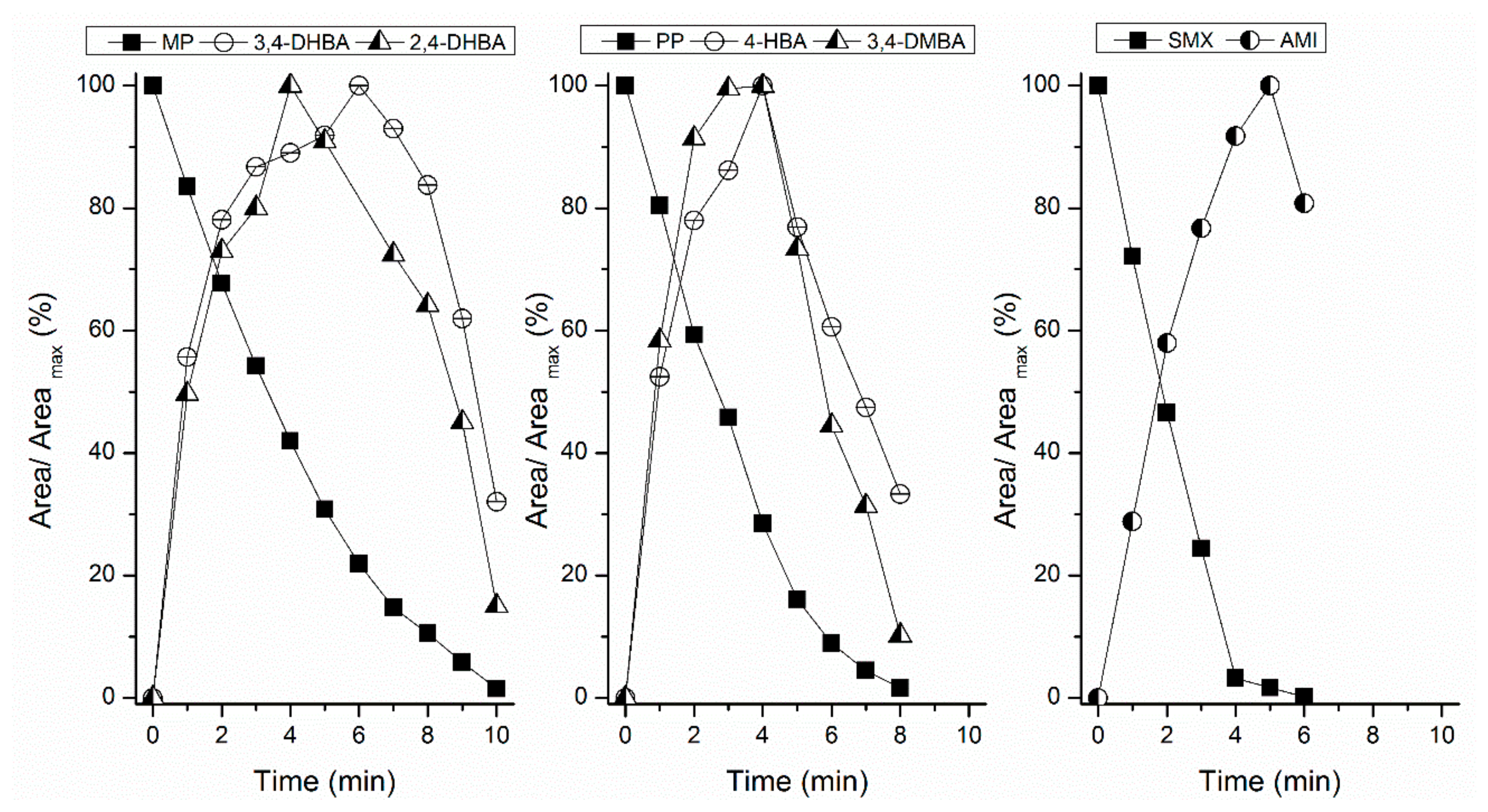
By-Products Assessment
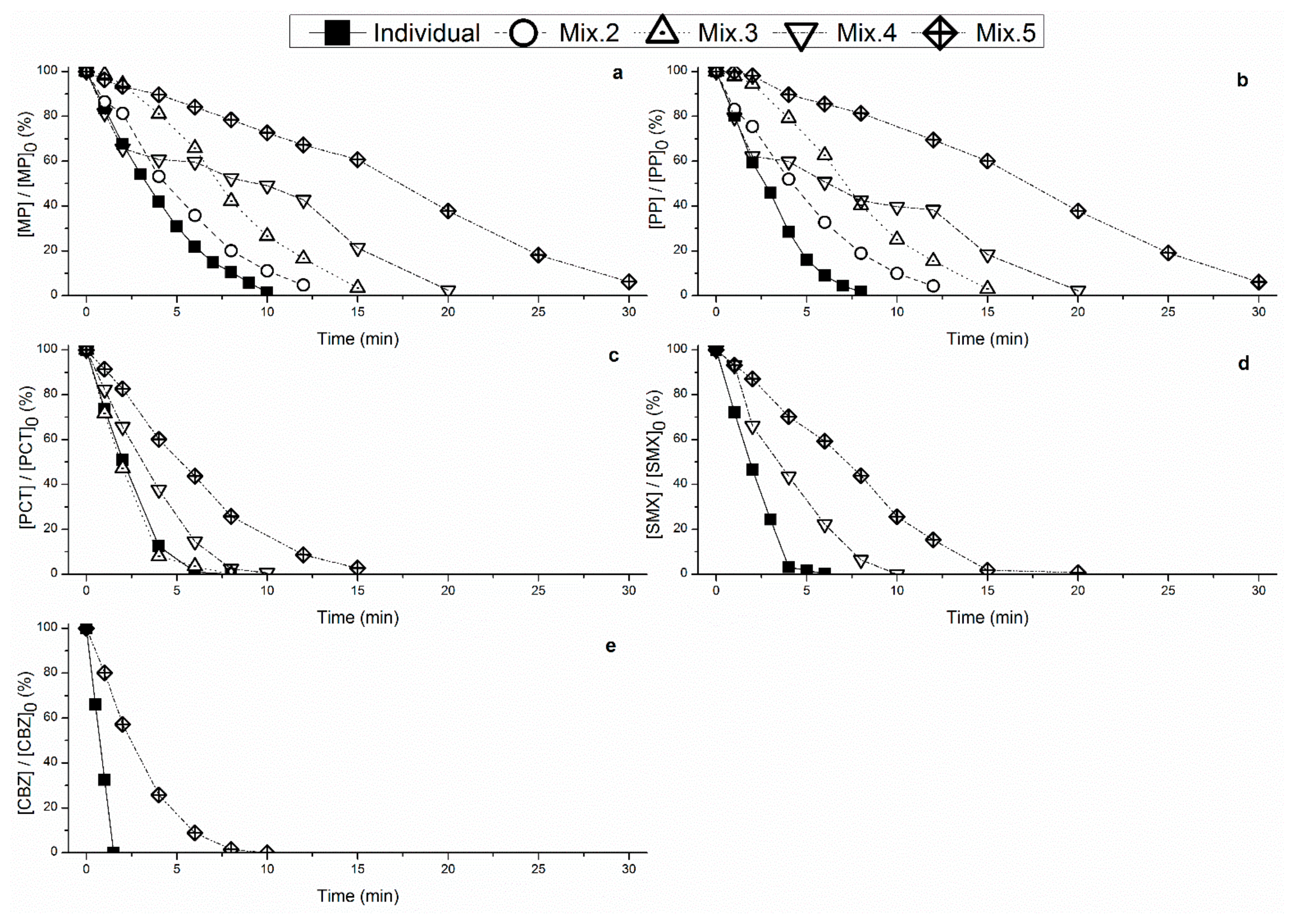
3.2. Degradation of PPCPs in Mixture
3.3. General Economic Considerations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kılıç, Z. The importance of water and conscious use of water. Int. J. Hydrol. 2020, 4, 239–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gittins, J.R.; Hemingway, J.R.; Dajka, J.C. How a water-resources crisis highlights social-ecological disconnects. Water Res. 2021, 194, 116937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beddington, J. Food security: Contributions from science to a new and greener revolution. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boretti, A.; Rosa, L. Reassessing the projections of the World Water Development Report. NPJ Clean Water 2019, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molins-Delgado, D.; Díaz-Cruz, M.S.; Barceló, D. Ecological risk assessment associated to the removal of endocrine-disrupting parabens and benzophenone-4 in wastewater treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 310, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.B.; Zhou, J.L.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Thomaidis, N.S.; Xu, J. Progress in the biological and chemical treatment technologies for emerging contaminant removal from wastewater: A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 323, 274–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, E.; Fernandes, E.; Gomes, J.; Martins, R.C. Advanced oxidation processes perspective regarding swine wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 776, 145958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimi, M.; Esrafili, A.; Gholami, M.; Jafari, A.J.; Kalantary, R.R.; Farzadkia, M.; Kermani, M.; Sobhi, H.R. Contaminants of emerging concern: A review of new approach in AOP technologies. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lincho, J.; Martins, R.; Gomes, J. Paraben Compounds—Part I: An Overview of Their Characteristics, Detection, and Impacts. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, J.; Costa, R.; Quinta-Ferreira, R.M.; Martins, R. Application of ozonation for pharmaceuticals and personal care products removal from water. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 265–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeid, S.; Kråkström, M.; Tolvanen, P.; Kumar, N.; Eränen, K.; Mikkola, J.-P.; Kronberg, L.; Eklund, P.; Peurla, M.; Aho, A.; et al. Advanced Oxidation Process for Degradation of Carbamazepine from Aqueous Solution: Influence of Metal Modified Microporous, Mesoporous Catalysts on the Ozonation Process. Catalysts 2020, 10, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neamţu, M.; Bobu, M.; Kettrup, A.; Siminiceanu, I. Ozone photolysis of paracetamol in aqueous solution. J Environ. Sci. Heal Part A Toxic/Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2013, 48, 1264–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, M.; Bueno, M.J.M.; Lacorte, S.; Fernández-Alba, A.; Agüera, A. Pilot survey monitoring pharmaceuticals and related compounds in a sewage treatment plant located on the Mediterranean coast. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, Y.; Tian, J.; Qi, H.; Lin, W.; Cui, F. Oxidation of sulfamethoxazole (SMX) by chlorine, ozone and permanganate—A comparative study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 274, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Yi, H.; Lai, C.; Liu, X.; Huo, X.; An, Z.; Li, L.; Fu, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, M.; et al. Critical review of advanced oxidation processes in organic wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 130104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakaraju, D.; Glass, B.D.; Oelgemoeller, M. Advanced oxidation process-mediated removal of pharmaceuticals from water: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 219, 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miklos, D.B.; Remy, C.; Jekel, M.; Linden, K.G.; Drewes, J.E.; Hübner, U. Evaluation of advanced oxidation processes for water and wastewater treatment—A critical review. Water Res. 2018, 139, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Ziółek, M.; Nawrocki, J. Catalytic ozonation and methods of enhancing molecular ozone reactions in water treatment. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2003, 46, 639–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Gunten, U. Ozonation of drinking water: Part I. Oxidation kinetics and product formation. Water Res. 2003, 37, 1443–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecha, A.C.; Onyango, M.S.; Ochieng, A.; Fourie, C.J.; Momba, M.N. Synergistic effect of UV–vis and solar photocatalytic ozonation on the degradation of phenol in municipal wastewater: A comparative study. J. Catal. 2016, 341, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itzel, F.; Gehrmann, L.; Bielak, H.; Ebersbach, P.; Boergers, A.; Herbst, H.; Maus, C.; Simon, A.; Dopp, E.; Hammers-Wirtz, M.; et al. Investigation of full-scale ozonation at a municipal wastewater treatment plant using a toxicity-based evaluation concept. J. Toxicol. Environ. Heal. Part A 2017, 80, 1242–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, K.S.; Rahman, N.A.; Bin Abas, M.R. Kinetic studies of the degradation of parabens in aqueous solution by ozone oxidation. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2009, 8, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kråkström, M.; Saeid, S.; Tolvanen, P.; Kumar, N.; Salmi, T.; Kronberg, L.; Eklund, P. Ozonation of carbamazepine and its main transformation products: Product determination and reaction mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 23258–23269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doná, G.; Carpiné, D.; Leifeld, V.; Dantas, T.L.P.; Castilhos, F.; Igarashi-Mafra, L. Efficient remove methylparaben by ozonation process. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 16, 2441–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, R.C.; Dantas, R.F.; Sans, C.; Esplugas, S.; Quinta-Ferreira, R.M. Ozone/H2O2Performance on the Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole. Ozone: Sci. Eng. 2015, 37, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, J. Degradation of sulfamethoxazole by ozonation combined with ionizing radiation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 407, 124377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levenspiel, O. Chemical Reaction Engineering: An Introduction to the Design of Chemical Reactor; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Saunders, F.; Gould, J.P.; Southerland, C.R. The effect of solute competition on ozonolysis of industrial dyes. Water Res. 1983, 17, 1407–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, J.F.; Leal, I.; Bednarczyk, K.; Gmurek, M.; Stelmachowski, M.; Diak, M.; Quinta-Ferreira, M.E.; Costa, R.; Quinta-Ferreira, R.M.; Martins, R. Photocatalytic ozonation using doped TiO2 catalysts for the removal of parabens in water. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, J.F.; Leal, I.; Bednarczyk, K.; Gmurek, M.; Stelmachowski, M.; Zaleska-Medynska, A.; Quinta-Ferreira, M.E.; Costa, R.; Quinta-Ferreira, R.M.; Martins, R.C. Detoxification of parabens using UV-A enhanced by noble metals—TiO2 supported catalysts. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 3065–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, H.; Barışçı, S.; Turkay, O. Paracetamol degradation and kinetics by advanced oxidation processes (Aops): Electro-peroxone, ozonation, goethite catalyzed electro-fenton and electro-oxidation. Environ. Eng. Res. 2021, 26, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Garoma, T.; Chen, Z.; Wang, L.; Wu, Y. SMX degradation by ozonation and UV radiation: A kinetic study. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 1134–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, R.R.; Ozaki, H.; Ota, S.; Takanami, R.; Taniguchi, S. Degradation of common pharmaceuticals and personal care products in mixed solutions by advanced oxidation techniques. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 7, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nawrocki, J.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. The efficiency and mechanisms of catalytic ozonation. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2010, 99, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.G.; Órfão, J.J.M.; Pereira, M.F.R. Catalytic ozonation of sulphamethoxazole in the presence of carbon materials: Catalytic performance and reaction pathways. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 239–240, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naddeo, V.; Uyguner-Demirel, C.S.; Prado, M.; Cesaro, A.; Belgiorno, F. Enhanced ozonation of selected pharmaceutical compounds by sonolysis. Environ. Technol. 2015, 36, 1876–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naddeo, V.; Meric, S.; Kassinos, D.; Belgiorno, V.; Guida, M. Fate of pharmaceuticals in contaminated urban wastewater effluent under ultrasonic irradiation. Water Res. 2009, 43, 4019–4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, K.S.; Rahman, N.A.; Bin Abas, M.R. Ozonation of parabens in aqueous solution: Kinetics and mechanism of degradation. Chemosphere 2010, 81, 1446–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, F.J.; Sagasti, J.; Encinas, A.; Gimeno, O. Contaminants abatement by ozone in secondary effluents. Evaluation of second-order rate constants. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2011, 86, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villota, N.; Lombraña, J.; Cruz-Alcalde, A.; Marcé, M.; Esplugas, S. Kinetic study of colored species formation during paracetamol removal from water in a semicontinuous ozonation contactor. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 1434–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollender, J.; Zimmermann, S.G.; Koepke, S.; Krauss, M.; McArdell, C.S.; Ort, C.; Singer, H.; von Gunten, U.; Siegrist, H. Elimination of Organic Micropollutants in a Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plant Upgraded with a Full-Scale Post-Ozonation Followed by Sand Filtration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 7862–7869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margot, J.; Kienle, C.; Magnet, A.; Weil, M.; Rossi, L.; De Alencastro, L.F.; Abegglen, C.; Thonney, D.; Chèvre, N.; Schärer, M.; et al. Treatment of micropollutants in municipal wastewater: Ozone or powdered activated carbon? Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 461–462, 480–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Chemical Structure | 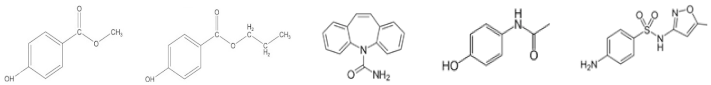 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Methylparaben | Propylparaben | Carbamazepine | Paracetamol | Sulfamethoxazole |
| Molecular Formula | C8H8O3 | C10H12O3 | C15H12N2O | C8H9NO2 | C10H11N3O3S |
| Molecular Weight | 152.15 g mol−1 | 180.20 g mol−1 | 236.27 g mol−1 | 151.16 g mol−1 | 253.28 g mol−1 |
| Water Solubility (at 25 °C) | 25 mg mL−1 | 0.50 mg mL−1 | 0.018 mg mL−1 | 14 mg mL−1 | 0.50 mg mL−1 |
| pKa | 8.50 | 8.50 | 13.9 | 9.38 | 1.6 and 5.7 |
| Log Kow | 1.96 | 3.04 | 2.45 | 0.46 | 0.89 |
| Mix.2 | Mix.3 | Mix.4 | Mix.5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composition | MP + PP | MP + PP + PCT | MP + PP + PCT + SMX | MP + PP + PCT + SMX + CBZ |
| MP | PP | PCT | SMX | CBZ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k’1 (min−1) (adj R2) | 0.25 | 0.33 | 0.42 | 0.50 | 1.25 |
| (0.98) | (0.97) | (0.97) | (0.95) | (0.90) | |
| k’1,TOD (mgO3−1) (adj R2) | 0.23 | 0.27 | 0.35 | 0.42 | 1.02 |
| (0.96) | (0.96) | (0.96) | (0.94) | (0.90) |
| MP | PP | PCT | SMX | CBZ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k’1 (min−1) (adj R2) | 0.252 (0.98) | 0.331 (0.97) | 0.425 (0.98) | 0.496 (0.95) | 1.255 (0.90) |
| k’2 (min−1) (adj R2) | 0.188 (0.98) | 0.196 (0.98) | |||
| k’3 (min−1) (adj R2) | 0.123 (0.92) | 0.127 (0.93) | 0.453 (0.96) | ||
| k’4 (min−1) (adj R2) | 0.083 (0.90) | 0.098 (0.92) | 0.288 (0.98) | 0.255 (0.96) | |
| k’5 (min−1) (adj R2) | 0.049 (0.90) | 0.051 (0.92) | 0.178 (0.96) | 0.131 (0.96) | 0.342 (0.98) |
| MP | PP | PCT | SMX | CBZ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k’1 TOD (mgO3−1) (adj R2) | 0.228 (0.96) | 0.271 (0.96) | 0.352 (0.96) | 0.422 (0.94) | 1.022 (0.90) |
| k’2 TOD (mgO3−1) (adj R2) | 0.171 (0.98) | 0.178 (0.96) | |||
| k’3 TOD (mgO3−1) (adj R2) | 0.119 (0.92) | 0.123 (0.90) | 0.393 (0.97) | ||
| k’4 TOD (mgO3−1) (adj R2) | 0.083 (0.90) | 0.097 (0.92) | 0.248 (0.98) | 0.211 (0.95) | |
| k’5 TOD (mgO3−1) (adj R2) | 0.057 (0.88) | 0.059 (0.86) | 0.167 (0.93) | 0.129 (0.91) | 0.294 (0.97) |
| Energy Consumption (kWh m−3) | Individual | Mix.2 | Mix.3 | Mix.4 | Mix.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MP | 0.120 | 0.137 | 0.174 | 0.221 | 0.264 |
| PP | 0.107 | 0.137 | 0.174 | 0.221 | 0.264 |
| PCT | 0.104 | 0.100 | 0.146 | 0.166 | |
| SMX | 0.080 | 0.126 | 0.201 | ||
| CBZ | 0.022 | 0.123 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gomes, J.; Bernardo, C.; Jesus, F.; Pereira, J.L.; Martins, R.C. Ozone Kinetic Studies Assessment for the PPCPs Abatement: Mixtures Relevance. ChemEngineering 2022, 6, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering6020020
Gomes J, Bernardo C, Jesus F, Pereira JL, Martins RC. Ozone Kinetic Studies Assessment for the PPCPs Abatement: Mixtures Relevance. ChemEngineering. 2022; 6(2):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering6020020
Chicago/Turabian StyleGomes, João, Carla Bernardo, Fátima Jesus, Joana Luísa Pereira, and Rui C. Martins. 2022. "Ozone Kinetic Studies Assessment for the PPCPs Abatement: Mixtures Relevance" ChemEngineering 6, no. 2: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering6020020
APA StyleGomes, J., Bernardo, C., Jesus, F., Pereira, J. L., & Martins, R. C. (2022). Ozone Kinetic Studies Assessment for the PPCPs Abatement: Mixtures Relevance. ChemEngineering, 6(2), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering6020020










