Effect of Surfactant HLB Value on Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Chitosan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. The Hydrolysis of Chitosan
2.3. The Characterization of Chitosan Hydrolysis Product
3. Results and Discussion
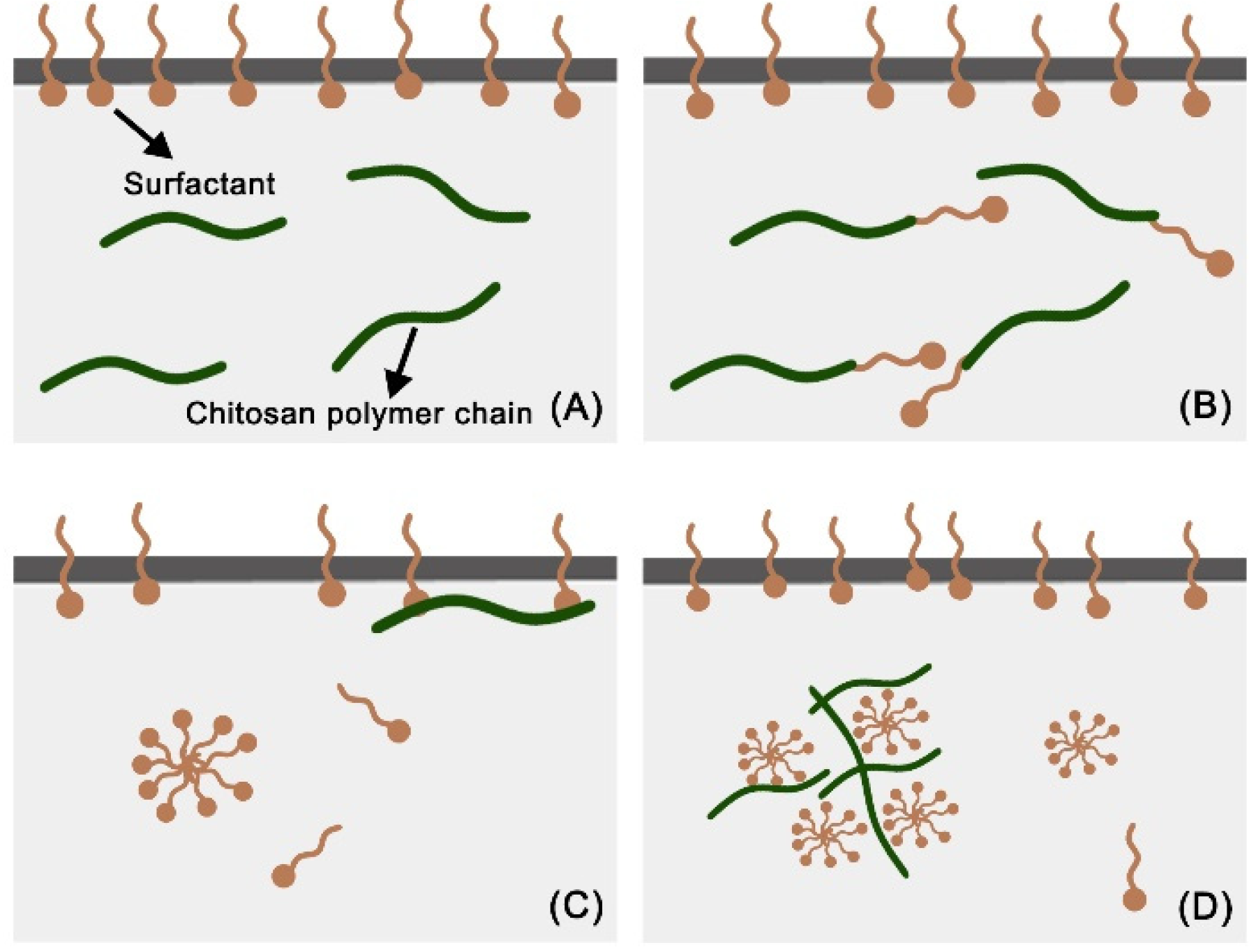
3.1. The Effect of Surfactant HLB Value
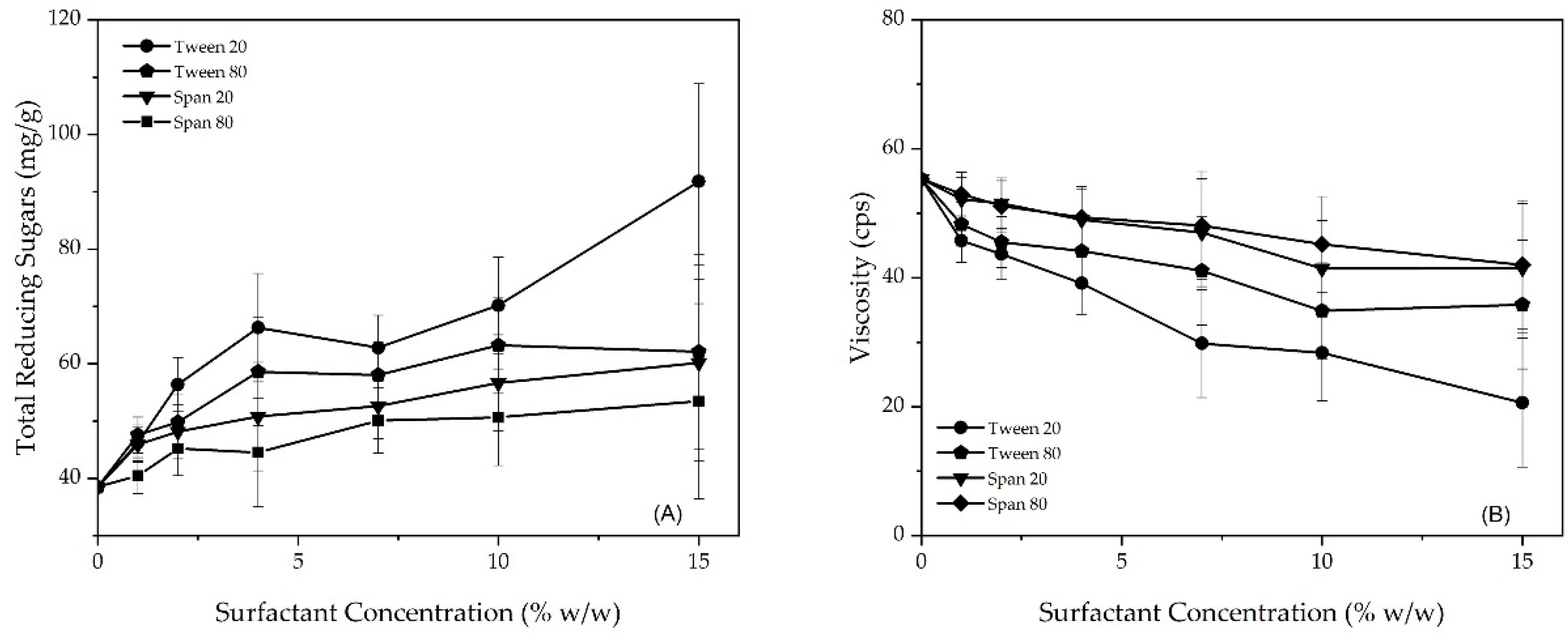
3.2. The Effect of Surfactant Concentration
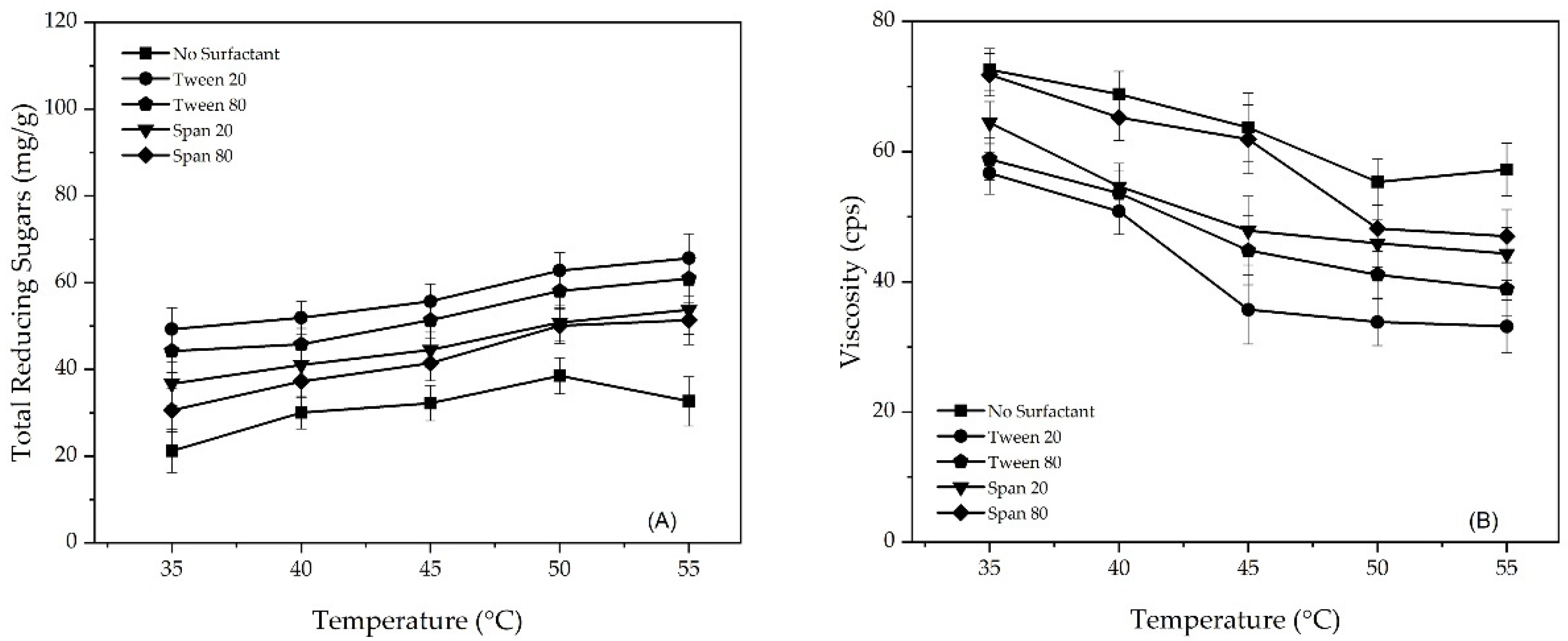
3.3. The Effect of Operating Temperature
3.4. The Effect of Stirring Speed
3.5. Characterization of Hydrolyzed Chitosan
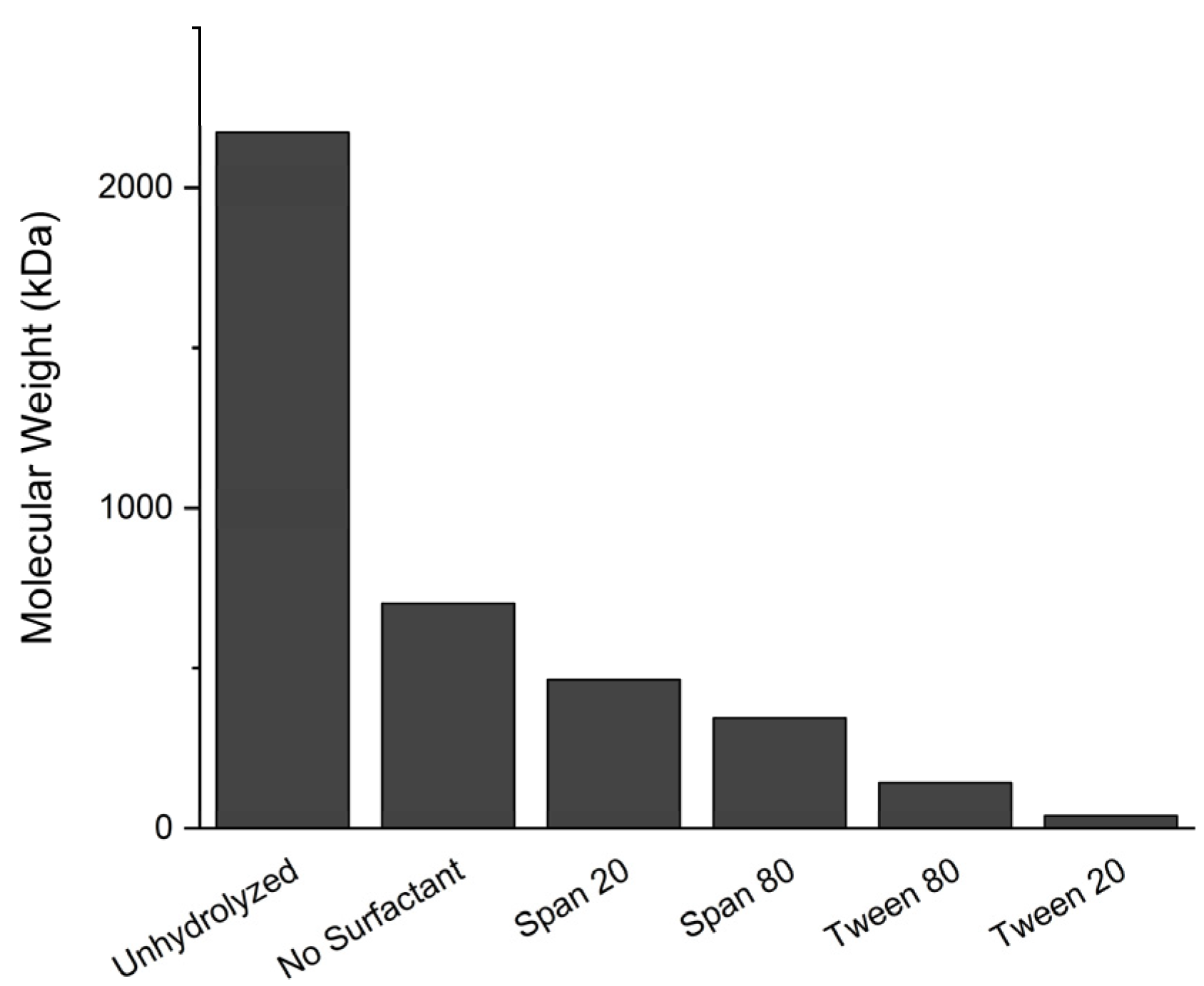
3.5.1. Molecular Weight
3.5.2. UV–Vis Spectrophotometry
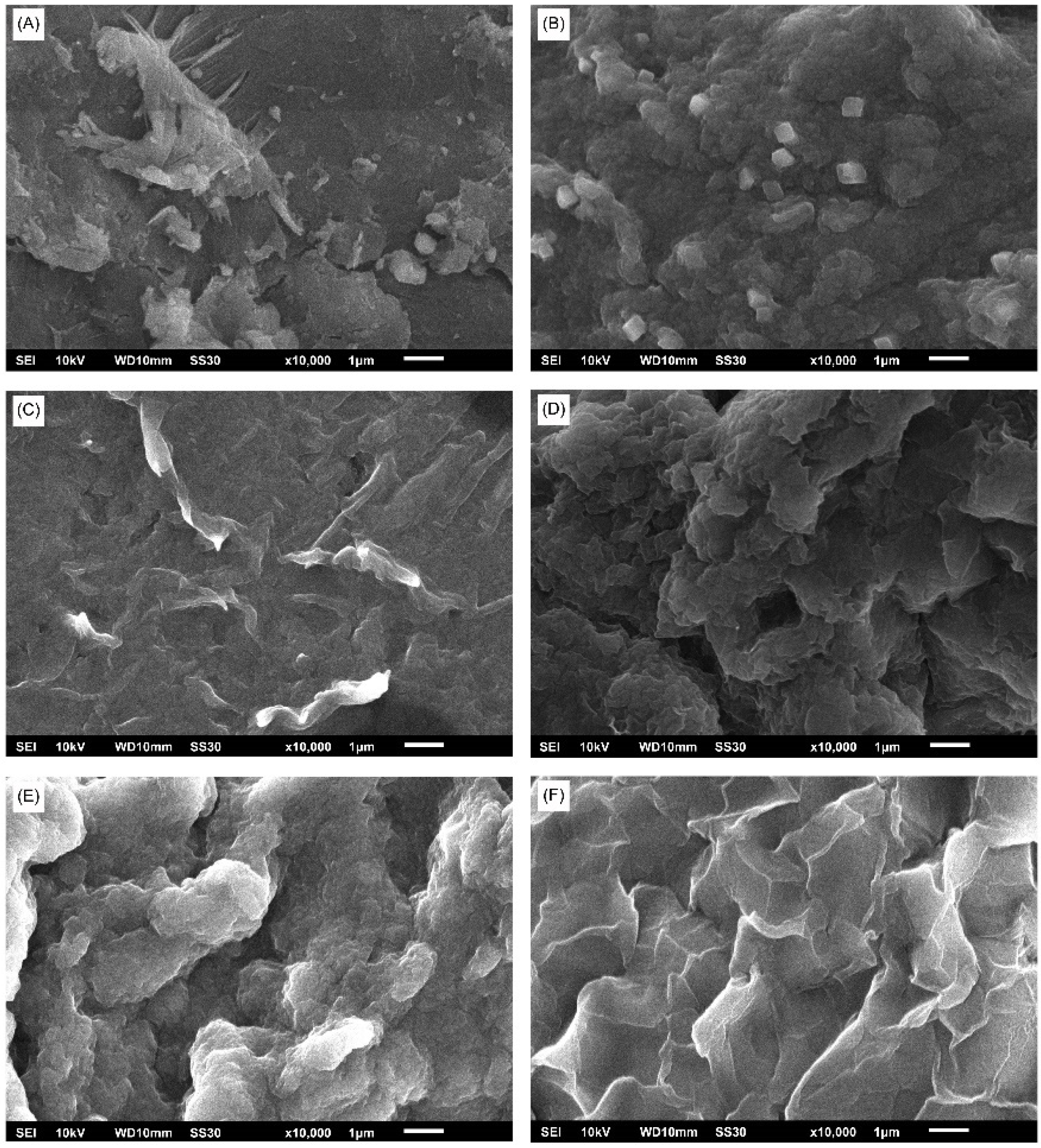
3.5.3. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
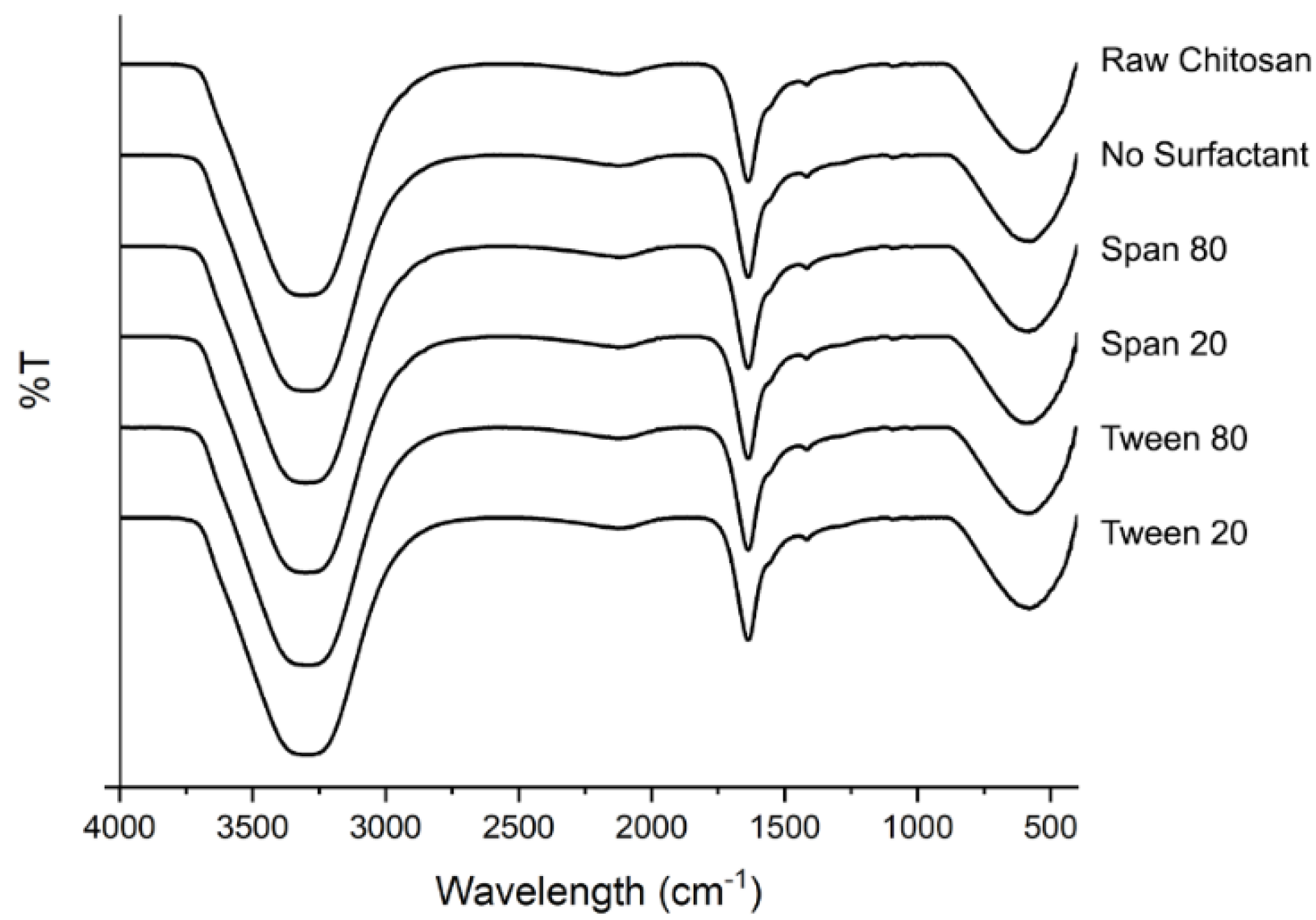
3.5.4. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
3.5.5. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmad, M.; Ahmed, S.; Ikram, S. Adsorption of heavy metal ions: Role of chitosan and cellulose for water treatment. Int. J. Pharmacogn. 2015, 2, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, K.A.; El-Eswed, B.I.; Abu-Sbeih, K.A.; Arafat, T.A.; Al Omari, M.M.H.; Darras, F.H.; Badwan, A.A. Preparation of chito-oligomers by hydrolysis of chitosan in the presence of zeolite as adsorbent. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakshi, P.S.; Selvakumar, D.; Kadirvelu, K.; Kumar, N.S. Chitosan as an environment friendly biomaterial—A review on recent modifications and applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 150, 1072–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljbour, N.D.; Beg, M.D.H.; Gimbun, J. Acid Hydrolysis of Chitosan to Oligomers Using Hydrochloric Acid. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2019, 42, 1741–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poshina, D.N.; Raik, S.V.; Poshin, A.N.; Skorik, Y.A. Accessibility of chitin and chitosan in enzymatic hydrolysis: A review. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 156, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Saldaña, M.D.A. Hydrolysis of cassava starch, chitosan and their mixtures in pressurized hot water media. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2019, 147, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Wu, S.; Chen, J. Preparation of water soluble chitosan by hydrolysis using hydrogen peroxide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 59, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Moriano, P.; Fernandez-Arrojo, L.; Mengibar, M.; Belmonte-Reche, E.; Peñalver, P.; Acosta, F.N.; Ballesteros, A.O.; Morales, J.C.; Kidibule, P.; Fernandez-Lobato, M.; et al. Enzymatic production of fully deacetylated chitooligosaccharides and their neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory properties. Biocatal. Biotransformation 2018, 36, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncal, T.; Oviedo, A.; de Armentia, I.L.; Fernández, L.; Villarán, M.C. High yield production of monomer-free chitosan oligosaccharides by pepsin catalyzed hydrolysis of a high deacetylation degree chitosan. Carbohydr. Res. 2007, 342, 2750–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria de Medeiros Dantas, J.; Sousa da Silva, N.; Eduardo de Araújo Padilha, C.; Kelly de Araújo, N.; Silvino dos Santos, E. Enhancing chitosan hydrolysis aiming chitooligosaccharides production by using immobilized chitosanolytic enzymes. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 28, 101759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, H.; Qi, F.; Zhao, X.; Liu, D. Non-ionic surfactants do not consistently improve the enzymatic hydrolysis of pure cellulose. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 182, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, H.; Zeng, M.; Hu, Q.; Cai, C.; Lin, X.; Qiu, X.; Yang, D.; Pang, Y. Nonionic surfactants enhanced enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose by reducing cellulase deactivation caused by shear force and air-liquid interface. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 249, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parnthong, J.; Kungsanant, S.; Chavadej, S. The Influence of Nonionic Surfactant Adsorption on Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Oil Palm Fruit Bunch. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2018, 186, 895–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Fan, H.; Zhou, M.; Zhou, Z.; Yan, L.; Ju, X.; Li, L. Synergistic effect of ionic liquid and surfactant for enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulose by Paenibacillus sp. LLZ1 cellulase. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 142, 105760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, T.; Börjesson, J.; Tjerneld, F. Mechanism of surfactant effect in enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulose. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2002, 31, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmatinejad, N.; Vahabzadeh, F.; Kordestani, S.S. Effect of surfactants on enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulosic fabric. Iran. Polym. J. 2002, 11, 333–338. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Sun, Z.; Ge, X.; Zhang, J. Effects of lignin and surfactant on adsorption and hydrolysis of cellulases on cellulose. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2016, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.A.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhao, X.; Qin, Y. Evaluation of the action of Tween 20 non-ionic surfactant during enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulose: Pretreatment, hydrolysis conditions and lignin structure. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 269, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menegol, D.; Scholl, A.L.; Fontana, R.C.; Dillon, A.J.P.; Camassola, M. Increased release of fermentable sugars from elephant grass by enzymatic hydrolysis in the presence of surfactants. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 88, 1252–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, R.; Satlewal, A.; Kapoor, M.; Mondal, S.; Basu, B. Investigating the enzyme-lignin binding with surfactants for improved saccharification of pilot scale pretreated wheat straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 224, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caenn, R.; Darley†, H.C.H.; Gray†, G.R. The Surface Chemistry of Drilling Fluids. Compos. Prop. Drill. Complet. Fluids 2017, 285–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokhati, N.; Susanto, H.; Haryani, K.; Pramudono, B. Enhanced enzymatic hydrolysis of chitosan by surfactant addition. Period. Polytech. Chem. Eng. 2018, 62, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.R.; Gaber, Y.; Fraaije, M.W. A fast, sensitive and easy colorimetric assay for chitinase and cellulase activity detection. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2014, 7, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd-Elmohdy, F.A.; El Sayed, Z.; Essam, S.; Hebeish, A. Controlling chitosan molecular weight via bio-chitosanolysis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 82, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R. Emulsifiers: Types and Uses, 1st ed.; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; ISBN 9780123849533. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, I.K.; Kim, S.I.; Lee, S.B. Effects of HLB value on oil-in-water emulsions: Droplet size, rheological behavior, zeta-potential, and creaming index. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 67, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speranza, A.; Corradini, M.G.; Hartman, T.G.; Ribnicky, D.; Oren, A.; Rogers, M.A. Influence of emulsifier structure on lipid bioaccessibility in oil-water nanoemulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 6505–6515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegl, G.; Öhlknecht, C.; Vielnascher, R.; Kosma, P.; Hofinger-Horvath, A.; Guebitz, G.M. Commercial cellulases from Trichoderma longibrachiatum enable a large-scale production of chito-oligosaccharides. Pure Appl. Chem. 2016, 88, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Qin, W.; Guo, C.; Guo, X.; Xiao, D. Enhanced enzymatic xylose/cellulose fractionation from alkaline liquor-pretreated corn cob by surfactant addition and separate fermentation to bioethanol. Turkish J. Biol. 2014, 38, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wagner, N.J. Universal binding behavior for ionic alkyl surfactants with oppositely charged polyelectrolytes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 17547–17555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappisi, L.; Gradzielski, M. Co-assembly in chitosan-surfactant mixtures: Thermodynamics, structures, interfacial properties and applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 220, 92–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerwin, B.A. Polysorbates 20 and 80 Used in the Formulation of Protein Biotherapeutics: Structure and Degradation Pathways. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 2924–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, R.; Wang, D.; Jenkins, B. Non-ionic surfactants and non-catalytic protein treatment on enzymatic hydrolysis of pretreated creeping wild ryegrass. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2008, 146, 231–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okino, S.; Ikeo, M.; Ueno, Y.; Taneda, D. Effects of Tween 80 on cellulase stability under agitated conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 142, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Zhang, A.; Liu, B.; Li, W.; Xing, J. Improvement of cellulose conversion caused by the protection of Tween-80 on the adsorbed cellulase. Biochem. Eng. J. 2011, 56, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussatto, S.I.; Dragone, G.; Fernandes, M.; Milagres, A.M.F.; Roberto, I.C. The effect of agitation speed, enzyme loading and substrate concentration on enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose from brewer’s spent grain. Cellulose 2008, 15, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujeeb Rahman, P.; Muraleedaran, K.; Mujeeb, V.M.A. Applications of chitosan powder with in situ synthesized nano ZnO particles as an antimicrobial agent. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 77, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marei, N.H.; El-Samie, E.A.; Salah, T.; Saad, G.R.; Elwahy, A.H.M. Isolation and characterization of chitosan from different local insects in Egypt. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 82, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasikiewicz, J.M.; Yeates, S.G. “Green” molecular weight degradation of chitosan using microwave irradiation. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 863–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corazzari, I.; Nisticò, R.; Turci, F.; Faga, M.G.; Franzoso, F.; Tabasso, S.; Magnacca, G. Advanced physico-chemical characterization of chitosan by means of TGA coupled on-line with FTIR and GCMS: Thermal degradation and water adsorption capacity. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 112, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasertsung, I.; Damrongsakkul, S.; Saito, N. Degradation of β-chitosan by solution plasma process (SPP). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 2089–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rokhati, N.; Kusworo, T.D.; Prasetyaningrum, A.; Hamada, N.‘A.; Utomo, D.P.; Riyanto, T. Effect of Surfactant HLB Value on Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Chitosan. ChemEngineering 2022, 6, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering6010017
Rokhati N, Kusworo TD, Prasetyaningrum A, Hamada N‘A, Utomo DP, Riyanto T. Effect of Surfactant HLB Value on Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Chitosan. ChemEngineering. 2022; 6(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering6010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleRokhati, Nur, Tutuk Djoko Kusworo, Aji Prasetyaningrum, Nur ‘Aini Hamada, Dani Puji Utomo, and Teguh Riyanto. 2022. "Effect of Surfactant HLB Value on Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Chitosan" ChemEngineering 6, no. 1: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering6010017
APA StyleRokhati, N., Kusworo, T. D., Prasetyaningrum, A., Hamada, N. ‘A., Utomo, D. P., & Riyanto, T. (2022). Effect of Surfactant HLB Value on Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Chitosan. ChemEngineering, 6(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering6010017







