Waste and Solar Energy: An Eco-Friendly Way for Glass Melting
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Characterization Techniques
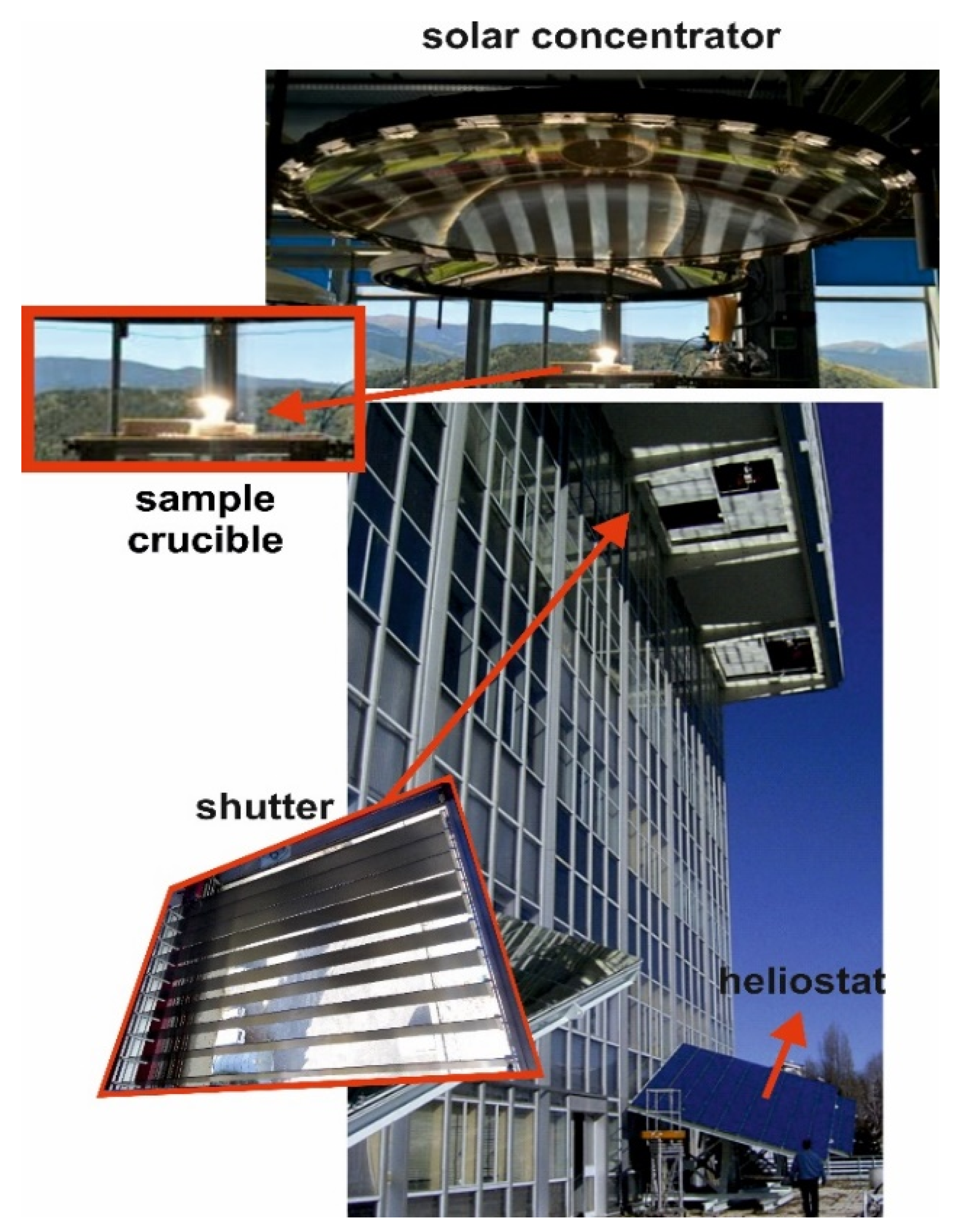
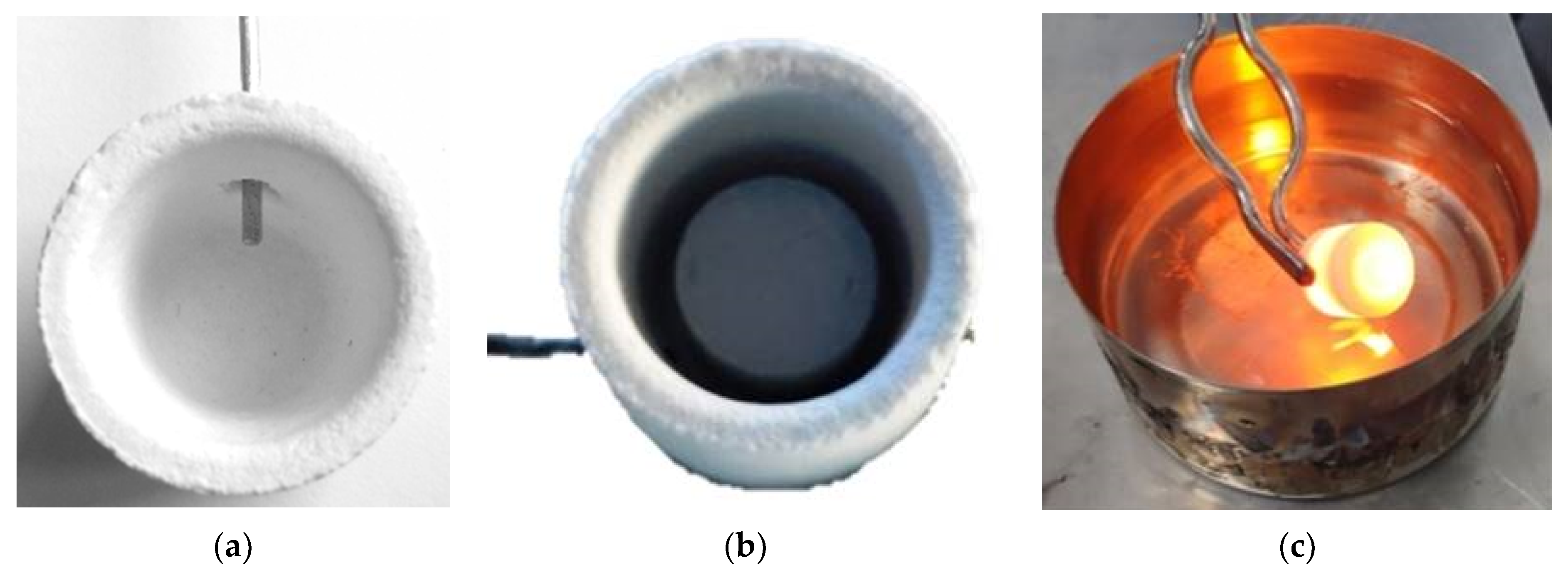
2.3. Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Raw Materials
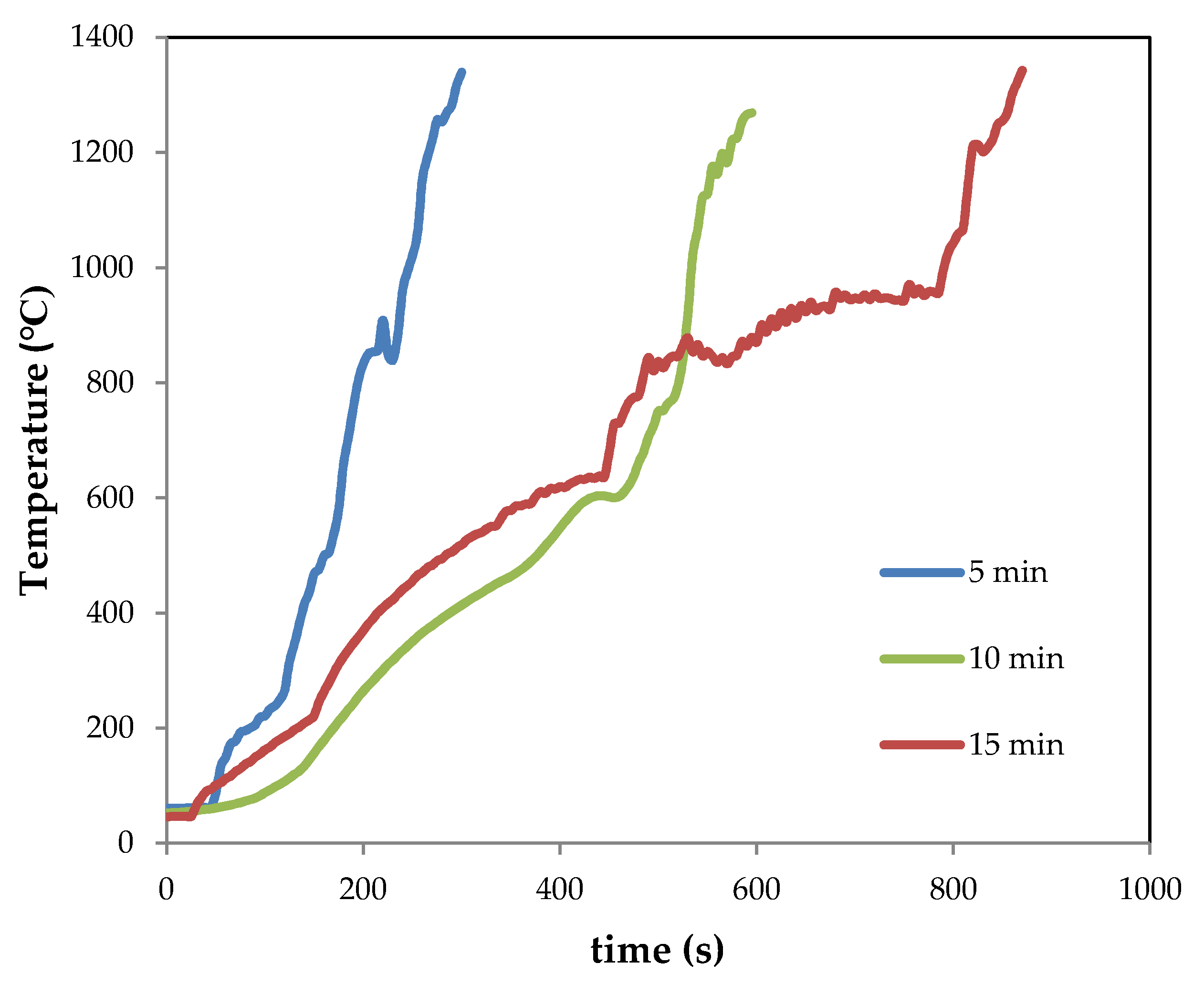
3.2. Thermal Behavior of Initial Mixtures
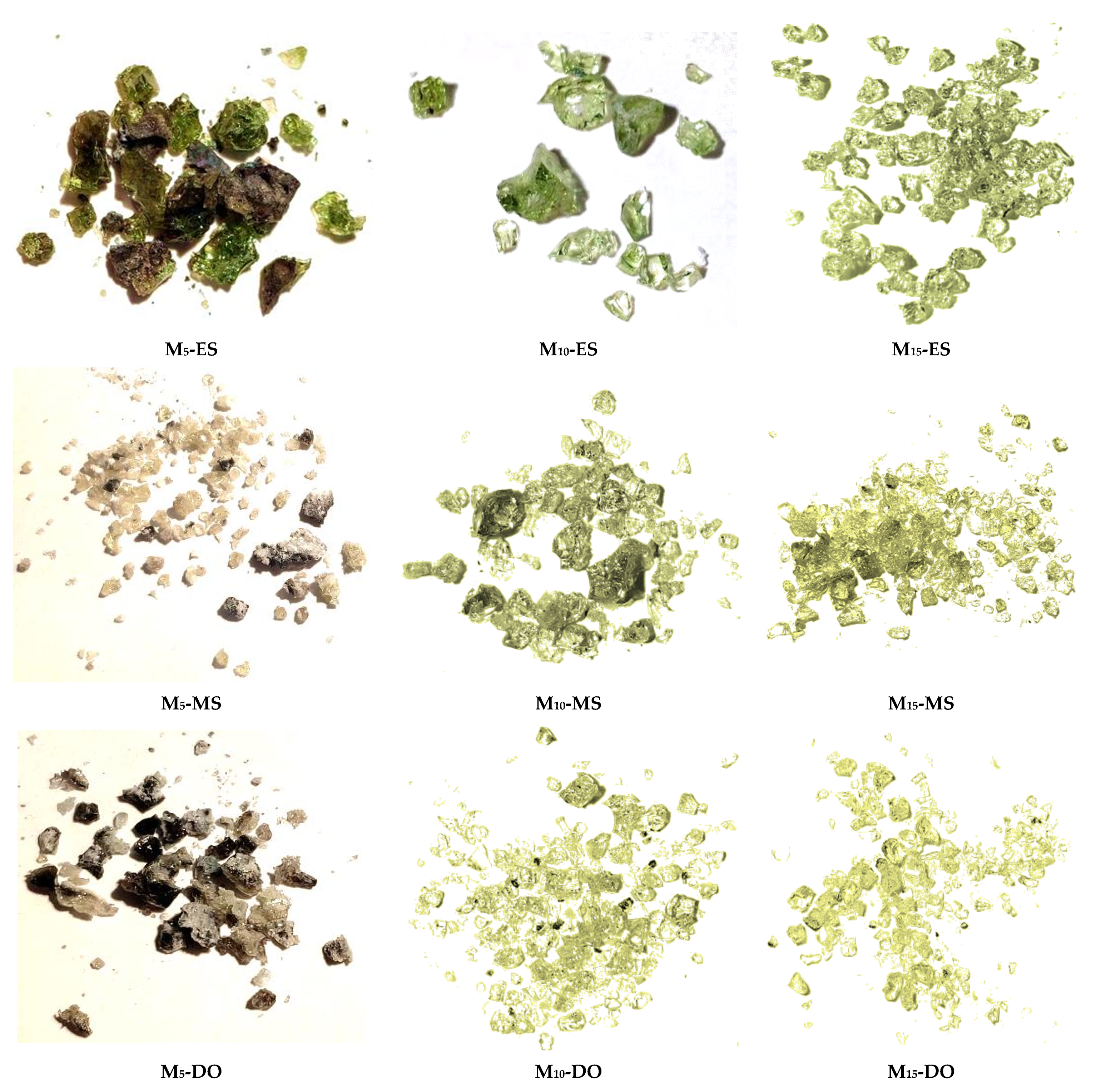
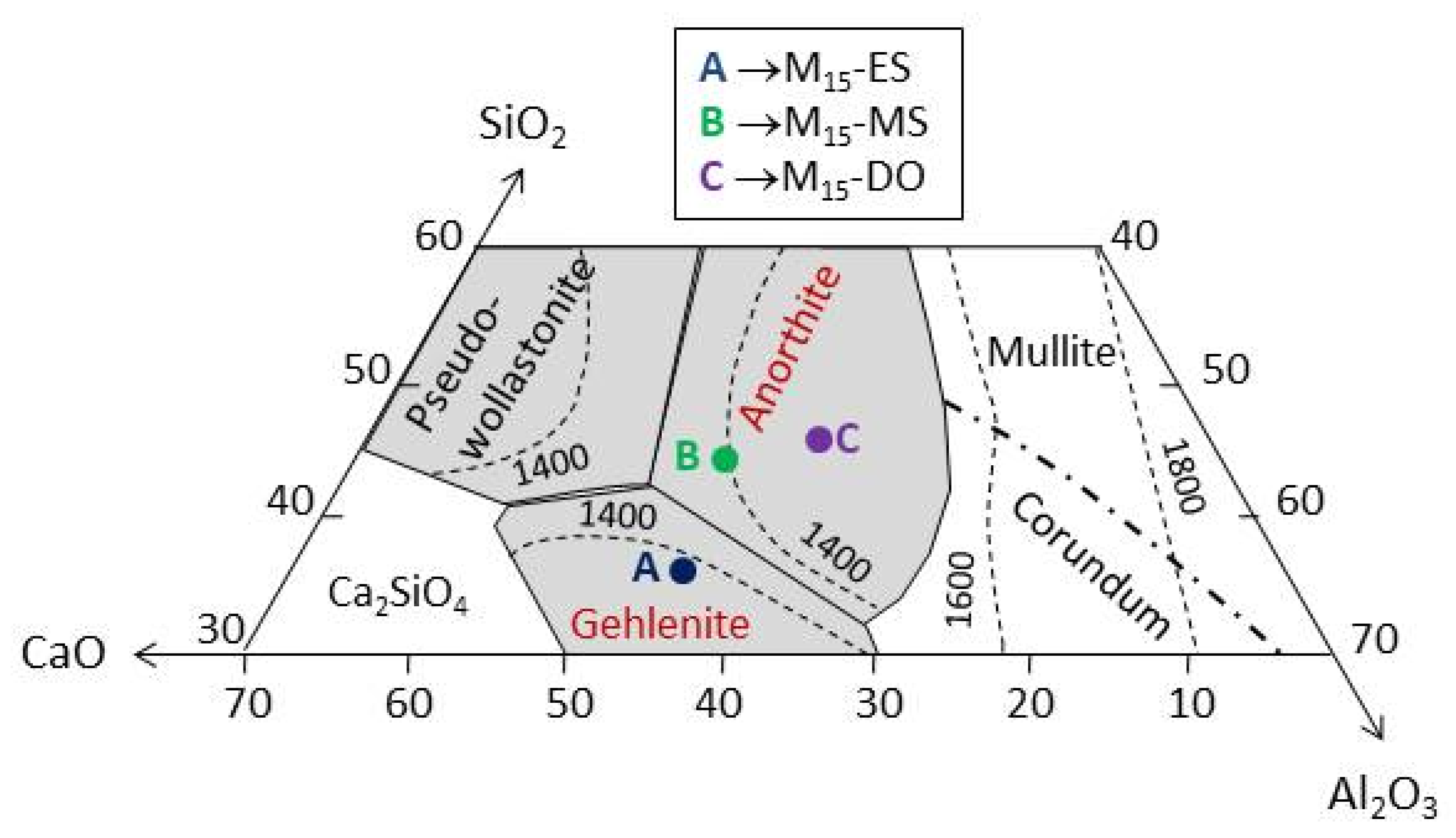
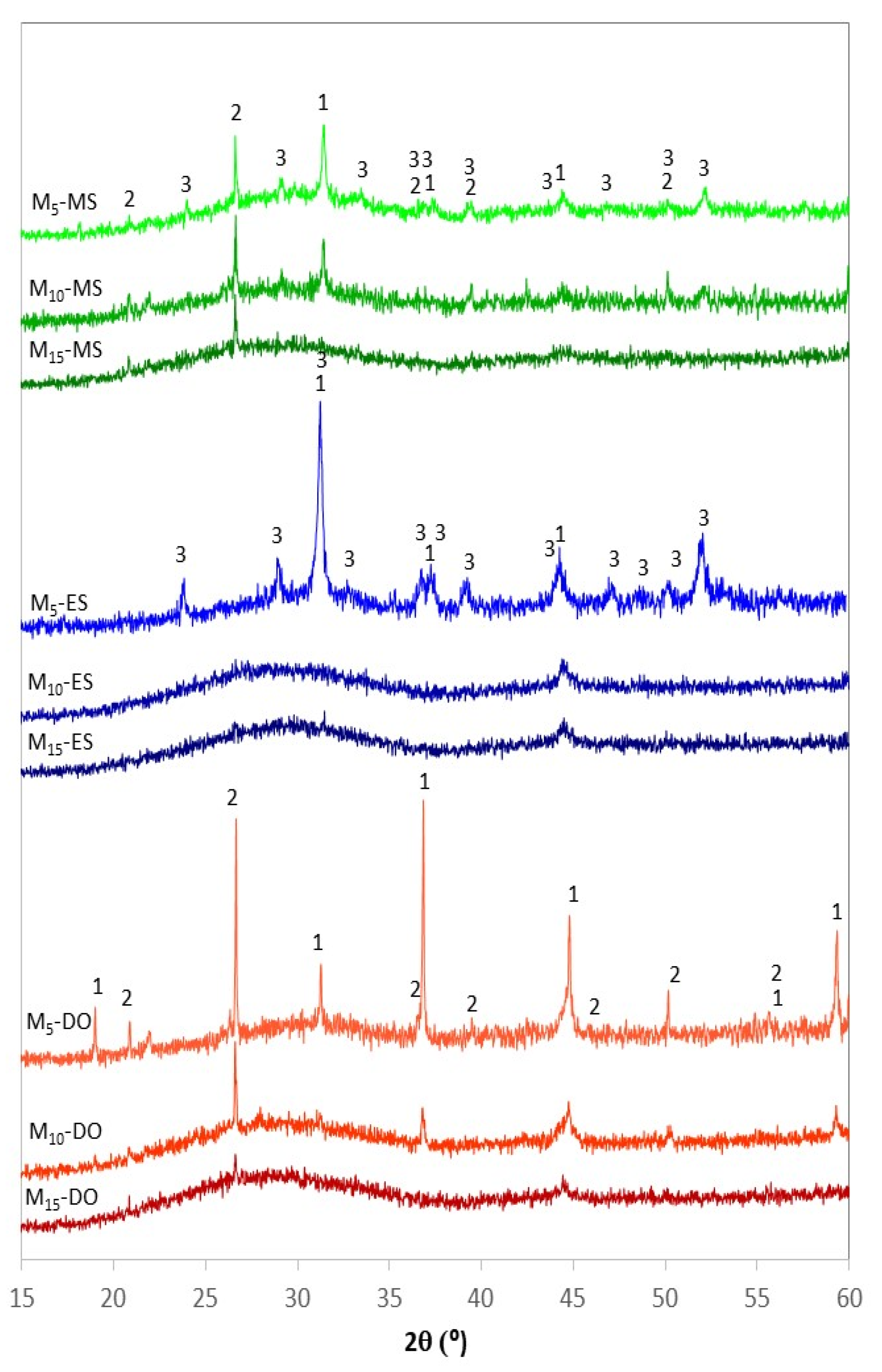
3.3. Characterization of Samples Obtained by CSE
3.3.1. Chemical Composition
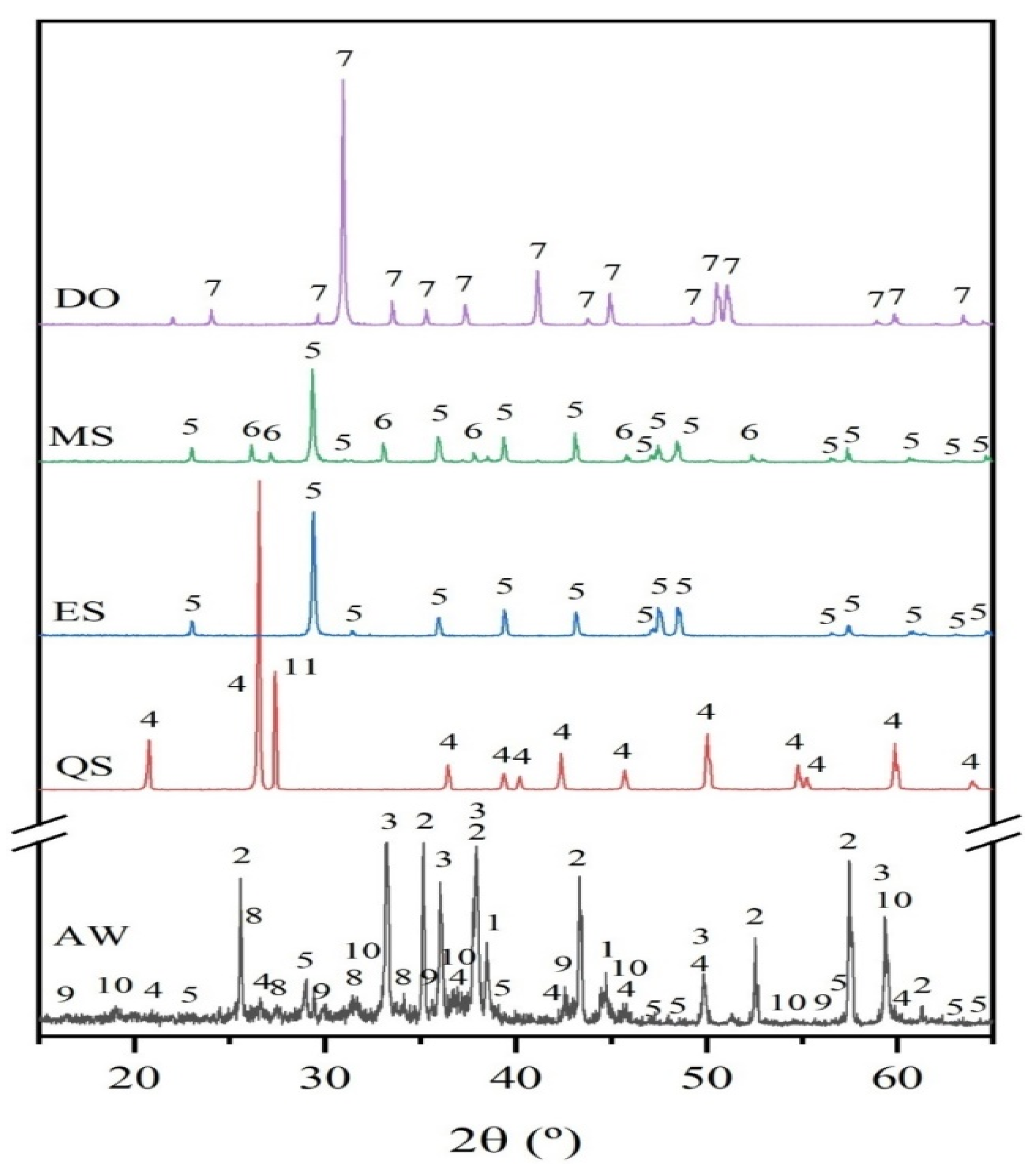
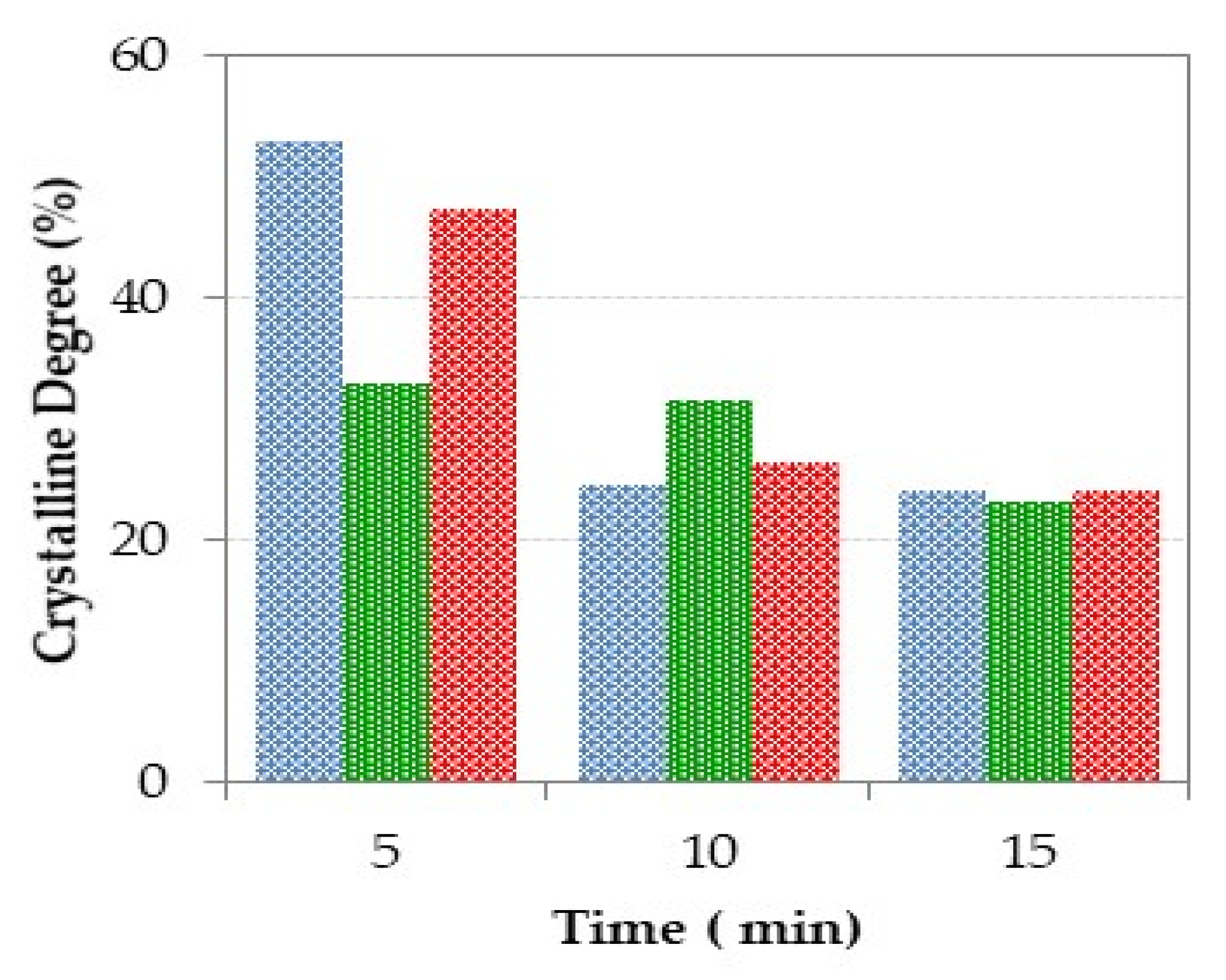
3.3.2. Powder X-Ray Diffraction Analysis
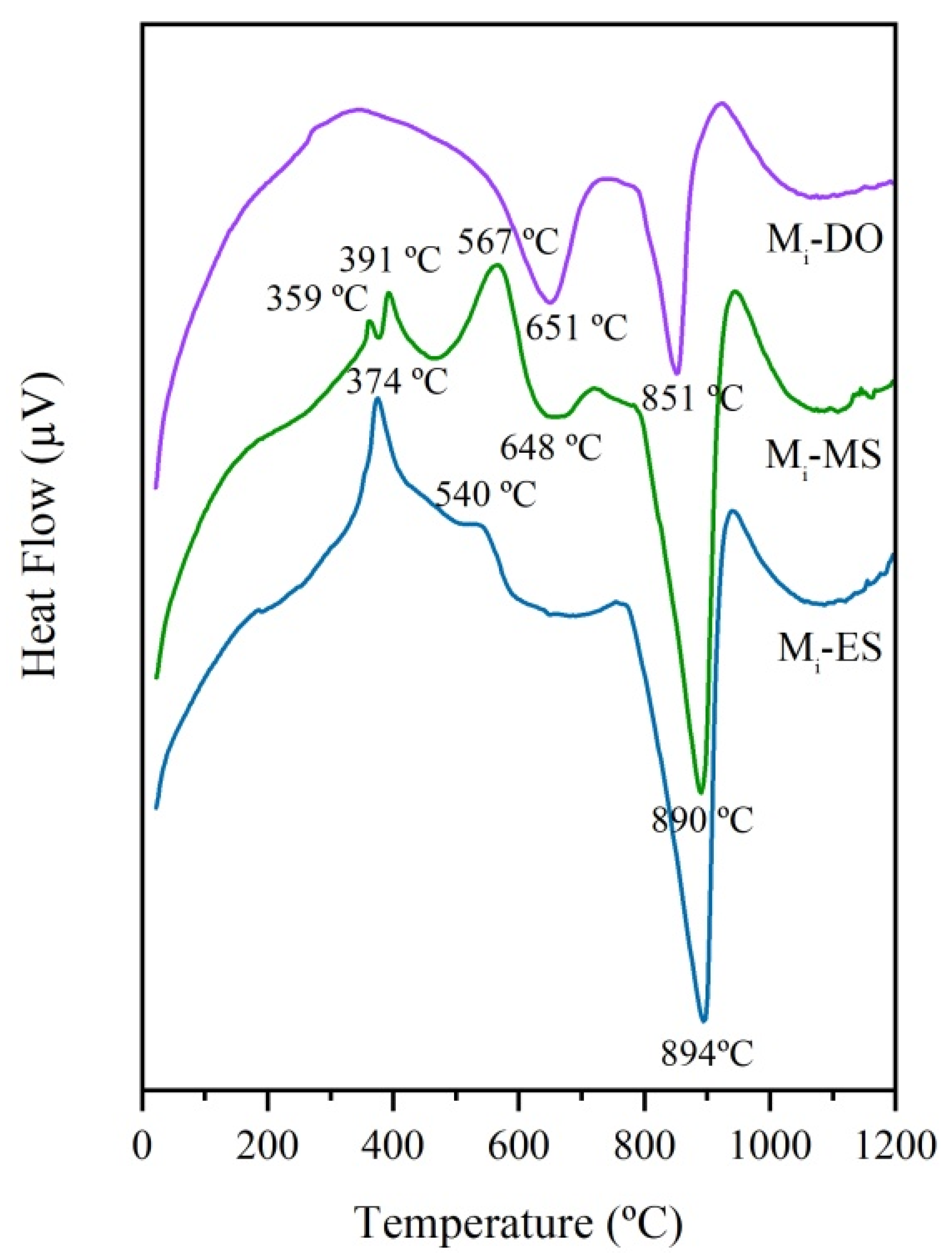
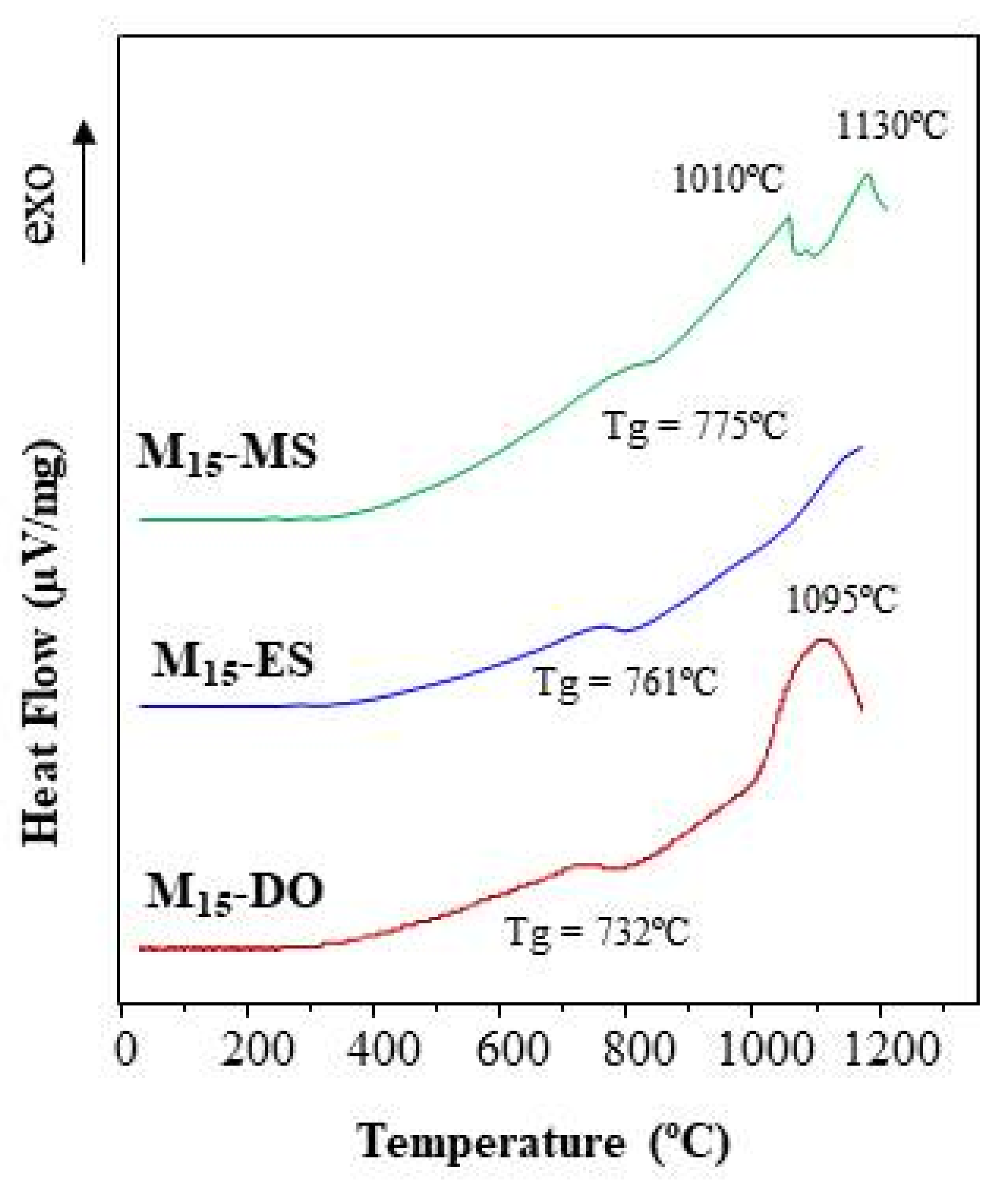
3.3.3. Differential Thermal Analysis of Glasses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Plaza, D.M.; Martinez, I.C.; Gasch, G.M.; Sufrategui, F.T.; García, J.R. A case study of the feasibility of using solar concentrating technologies for manufacturing ceramics. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 87, 977–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalet, B.M.; Garcia Muñoz, M.; Sissa Aivi, Q.; Roudier, S.; Luis, D.S. Best Available Techniques (BAT) Reference Document for the Manufacture of Glass; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2013; ISBN 9789279282843. [Google Scholar]
- Trends in Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide. Available online: https://www.esrl.noaa.gov/gmd/ccgg/trends/gl_trend.html (accessed on 23 February 2021).
- United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. Available online: https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/sustainable-development-goals/ (accessed on 24 February 2021).
- McMillan, P.; Piriou, B.; Navrotsky, A. A Raman spectroscopic study of glasses along the joins silica-calcium aluminate, silica-sodium aluminate, and silica-potassium aluminate. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 1982, 46, 2021–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navrotsky, A.; Peraudeau, G.; McMillan, P.; Coutures, J.P. A thermochemical study of glasses and crystals along the joins silica-calcium aluminate and silica-sodium aluminate. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 1982, 46, 2039–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, P.; Piriou, B. The structures and vibrational spectra of crystals and glasses in the silica-alumina system. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 1982, 53, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, M.; Robla, J.I.; Padilla, I.; García-Hierro, J.; López-Delgado, A. Eco-efficient melting of glass frits by concentrated solar energy. Sol. Energy 2018, 174, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Delgado, A.; Tayibi, H.; Pérez, C.; Alguacil, F.J.; López, F.A. A hazardous waste from secondary aluminium metallurgy as a new raw material for calcium aluminate glasses. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarinci, G.; Brusatin, G.; Barbieri, L.; Corradi, A.; Lancellotti, I.; Colombo, P.; Hreglich, S.; Dall’Igna, R. Vitrification of industrial and natural wastes with production of glass fibres. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2000, 20, 2485–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán-Carrillo, H.R.; Pérez, J.M.; Aguilar Reyes, E.A.; Romero, M. Coal fly ash and steel slag valorisation throughout a vitrification process. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 15, 1757–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, E.; Varrasso, M.; Cadamuro, F.; Hreglich, S. Vitrification of wastes and preparation of chemically stable sintered glass-ceramic products. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 2006, 352, 4017–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higby, P.L.; Ginther, R.J.; Aggarwal, I.D.; Friebele, E.J. Glass formation and thermal properties of low-silica calcium aluminosilicate glasses. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 1990, 126, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormier, L.; Neuville, D.R.; Calas, G. Structure and properties of low-silica calcium aluminosilicate glasses. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 2000, 274, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.K.R.; Tangeman, J.A.; Key, T.S.; Hiera, K.J.; Paradis, P.F.; Ishikawa, T.; Yu, J.; Yoda, S. Novel synthesis of calcium oxide-aluminum oxide glasses. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 41, 3029–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, R.; Padilla, I.; Sánchez-Hernández, R.; Robla, J.I.; Monrós, G.; López-Delgado, A. Production of added-value materials from a hazardous waste in the aluminium tertiary industry: Synergistic effect between hydrotalcites and glasses. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2552–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, S.R.; Magalhães, R.S.; Arenales, A.; Souza, A.E.; Romero, M.; Rincón, J.M. Valorization of sugarcane bagasse ash: Producing glass-ceramic materials. J. Environ. Manage. 2014, 134, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, R.; Padilla, I.; Rodríguez, O.; Sánchez-Hernández, R.; López-Andrés, S.; López-Delgado, A. Characterization of Solid Wastes from Aluminum Tertiary Sector: The Current State of Spanish Industry. J. Miner. Mater. Charact. Eng. 2015, 3, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, M.; Martín, M.I.; Barbieri, L.; Andreola, F.; Lancellotti, I.; López-Delgado, A. Valorization of Al slag in the production of green ceramic tiles: Effect of experimental conditions on microstructure and crystalline phase composition. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 104, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procédés, Matériaux et Énergie Solaire. Available online: https://www.promes.cnrs.fr/index.php?page=home-en (accessed on 30 September 2020).
- Yoshioka, S.; Kitano, Y. Transformation of aragonite to calcite through heating. Geochem. J. 1985, 19, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamester, M.R.R.; Balzer, P.S.; Becker, D. Characterization of calcium carbonate obtained from oyster and mussel shells and incorporation in polypropylene. Mater. Res. 2012, 15, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.L.S. Analysis on the properties of calcined waste mussel shell. Anal. Chem. Indian J. 2013, 13, 167–171. [Google Scholar]
- Rat’Ko, A.I.; Ivanets, A.I.; Kulak, A.I.; Morozov, E.A.; Sakhar, I.O. Thermal decomposition of natural dolomite. Inorg. Mater. 2011, 47, 1372–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde, J.M.; Perejon, A.; Medina, S.; Perez-Maqueda, L.A. Thermal decomposition of dolomite under CO2: Insights from TGA and in situ XRD analysis. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 30162–30176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durham, J.; Risbud, G. Low silica calcium aluminate oxynitride glasses. Mater. Lett. 1988, 7, 208–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelby, J.E. Formation and properties of aluminosilicate glasses. J. Am. Ceram. Soc 1985, 68, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höland, W.; Beal, G.H. Glass-Ceramic Technology, 2nd ed.; The American Ceramic Society: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; ISBN 9781118265987. [Google Scholar]

| Shutter Opening (%) | Power (W) | Exposure Time (min) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M5-ES M5-MS M5-DO | M10-ES M10-MS M10-DO | M15-ES M15-MS M15-DO | ||
| 20 | 90 | - | 1 | 1 |
| 30 | 150 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 50 | 350 | 1 | 3 | 5 |
| 70 | 600 | 1 | 2 | 6 |
| 100 | 970 | 2 | 3 | 2 |
| ttotal (min) | 5 | 10 | 15 | |
| Oxide | AW | ES | MS | DO | QS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 | 79.05 | -- | -- | 1.08 | |
| SiO2 | 3.26 | 0.13 | 0.19 | 0.09 | 98.00 |
| MgO | 3.90 | 0.40 | 0.10 | 20.09 | 0.01 |
| TiO2 | 5.10 | -- | -- | -- | 0.57 |
| K2O | 4.05 | 0.67 | 0.70 | 0.42 | 0.01 |
| CaO | 1.64 | 97.24 | 97.68 | 77.23 | 0.08 |
| Cl | 0.15 | 0.27 | 0.29 | 0.35 | -- |
| Na2O | 1.00 | --- | 0.30 | 0.80 | 0.07 |
| ZrO2 | 0.74 | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Fe2O3 | 0.51 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.31 |
| SO3 | 0.24 | 0.98 | 0.45 | 0.09 | -- |
| ZnO | 0.09 | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| V2O5 | 0.12 | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| CuO | 0.05 | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| SrO | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.20 | 0.03 | -- |
| MnO | 0.02 | -- | -- | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| Compounds | M15-ES | M15-MS | M15-DO |
|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 34.09 | 41.85 | 39.22 |
| Al2O3 | 23.03 | 22.49 | 24.34 |
| CaO | 36.27 | 30.41 | 21.91 |
| MgO | 1.30 | 1.00 | 9.20 |
| TiO2 | 1.83 | 1.50 | 1.82 |
| K2O | 0.95 | 0.73 | 0.89 |
| Na2O | 0.70 | 0 40 | 0.70 |
| Cl | 0.50 | 0.47 | 0.61 |
| SO3 | 0.47 | 0.38 | 0.48 |
| Fe2O3 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.41 |
| ZrO2 | 0.29 | 0.24 | 0.27 |
| CuO | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| SrO | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.02 |
| ZnO | 0.01 | <<0.01 | 0 02 |
| SnO2 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Cr2O3 | 0.02 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| MnO | 0.02 | <<0.01 | <<0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Padilla, I.; Romero, M.; Robla, J.I.; López-Delgado, A. Waste and Solar Energy: An Eco-Friendly Way for Glass Melting. ChemEngineering 2021, 5, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering5020016
Padilla I, Romero M, Robla JI, López-Delgado A. Waste and Solar Energy: An Eco-Friendly Way for Glass Melting. ChemEngineering. 2021; 5(2):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering5020016
Chicago/Turabian StylePadilla, Isabel, Maximina Romero, José I. Robla, and Aurora López-Delgado. 2021. "Waste and Solar Energy: An Eco-Friendly Way for Glass Melting" ChemEngineering 5, no. 2: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering5020016
APA StylePadilla, I., Romero, M., Robla, J. I., & López-Delgado, A. (2021). Waste and Solar Energy: An Eco-Friendly Way for Glass Melting. ChemEngineering, 5(2), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering5020016









