A Simple and Accurate Approach for Determining the VFA Concentration in Anaerobic Digestion Liquors, Relying on Two Titration Points and an External Inorganic Carbon Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
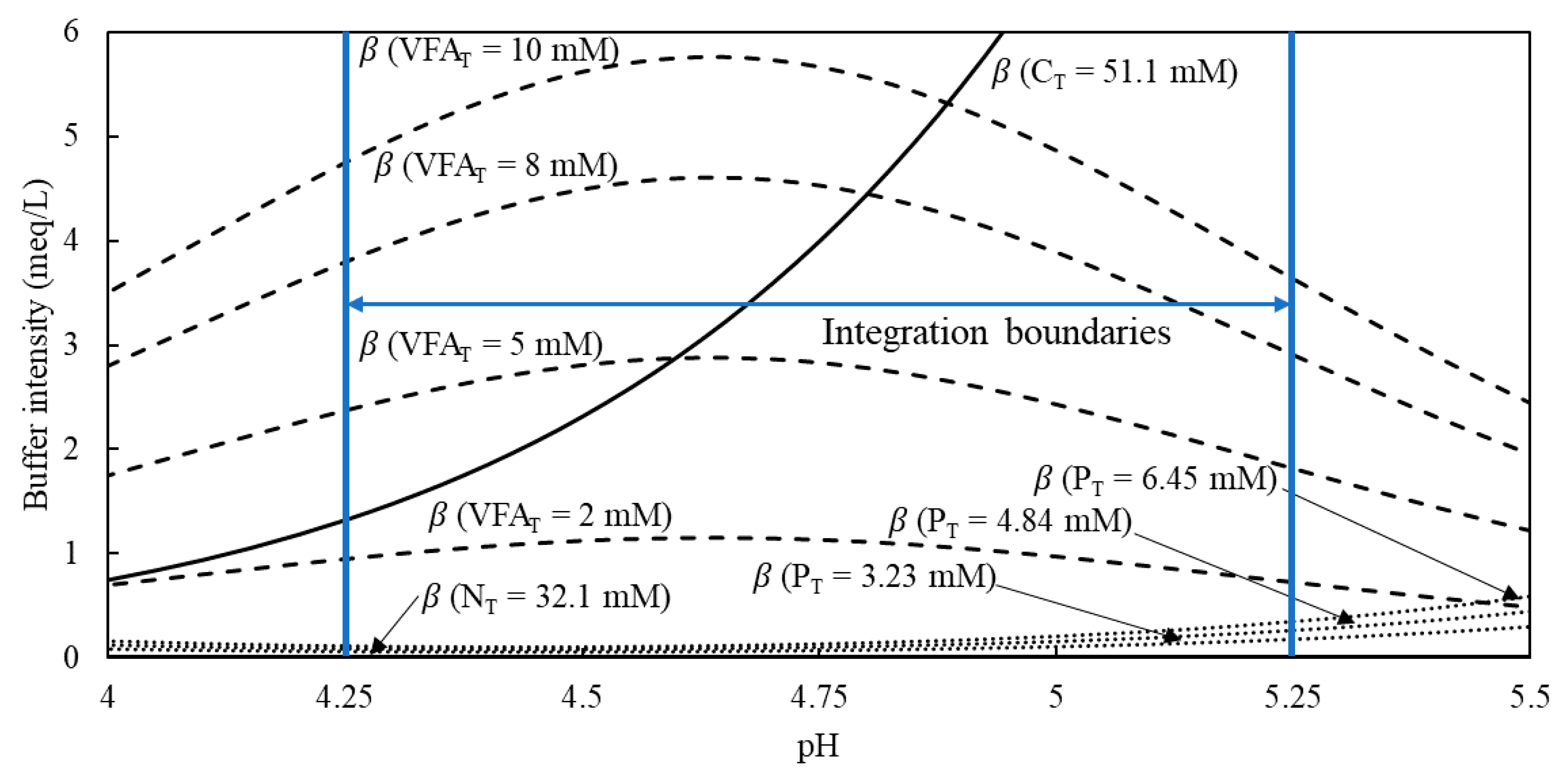
Development of the Titration-Data Interpretation Algorithm
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Titration Procedure
2.1.1. Titration of Synthetic Solutions
2.1.2. Titration of Anaerobic Liquor Solutions
2.2. Interpretation Program
2.2.1. Synthetic Solutions
2.2.2. Anaerobic Liquors
2.3. Calculating CT from the Knowledge of the CO2(g) Partial Pressure
2.4. Sample Preparation and Analyses
2.4.1. Sample Preparation
2.4.2. Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Comparison of the Newly Developed Algorithm to Previous Titration Methods Using Synthetic Solutions
3.2. Application of the New Method on Four (Raw and Spiked) Anaerobic Digester Liquors
3.3. Determining VFAT Using CT Values Estimated from CO2(g) Partial Pressure Values Measured in the Biogas
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Detailed Instructions for Performing the Analytic Procedure
Appendix A.1. pH and Temperature Measurement at the Sampling Point
Appendix A.2. Sampling and Sample Preparation
- Fill the test tube slowly, by letting the liquor outlet tube fill the test-tube from its bottom.
- Let the liquor to overflow for at least one volume of the test tube and then seal the tube tightly.
- After the centrifuge step, the test tubes kept closed until the titration.
- Only the supernatant part of the centrifuge step is used in the titration.
- If CT analysis is carried out using a TOC analyzer, the centrifuge supernatant should be sampled for this purpose.
Appendix A.3. Titration
- The titration must be performed in a sealed, gently magnetically stirred beaker (see Figure A1).
- The inlet holes for the pH and EC electrodes and for the acid tube or burette should be sealed as tightly as possible.
- Only analytical grade acid (HCl) ampules of a known concentration (diluted to a concentration of 0.05–0.2 eq/L) should be used.
- The pH and EC electrodes must be calibrated and be in a good working condition.
- From experience, to obtain accurate results, the alkalinity of the titrated solution (after dilution) should be around 300–400 mg/L as CaCO3. The sample should be diluted to meet this condition.
- A minimal head space should be left in the sealed beaker for allowing the addition of acid with a small safety margin.
- Place the required volume of deionized water for the required dilution in the beaker.
- Close the beaker cover. Insert the EC and pH electrodes in their designated inlet holes.
- Gently open the centrifuged test tube and take the required volume of the supernatant by using a pipette.
- Insert the volume of sample below the water level (to minimize CO2 losses) through the inlet hole of the acid tube or burette in the cap of the sealed beaker.
- Place the acid tube or burette in place.
- Wait for the pH reading to stabilize.
- After stabilization, register the EC and temperature values (the temperature can be measured via the EC or pH meters).
- Start titrating the strong acid to pH = 5.25. Register the exact pH that was reached and the volume of strong acid that was titrated. These measurements are marked pHX1 and VX1, respectively.
- Continue titrating the strong acid to pH = 4.25. Register the exact pH reached and the cumulative volume of strong acid up to that pH point. These measurements are marked pHX2 and VX2, respectively.

Appendix B. The Code Used for Calculating VFAT from the Acquired Data
Appendix C. Raw Data Showing the Analytical Results Obtained with the Four Anaerobic Digester Liquors + Computational Results
| VFAT | pHx1 | Vx1 | pHx2 | Vx2 | Temp | EC | Dilution | [HCl] | Spike Volume | TIC | PT | NT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg/L as HAc | mL | mL | °C | mS/cm | N | mL | ppm | mg/L as P | mg/L as N | |||
| 251.6 | 5.220 | 8.550 | 4.288 | 9.440 | 22.1 | 0.352 | 38.00 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 985 | 149 | 1038 |
| 260.2 | 5.278 | 8.606 | 4.272 | 9.608 | 22.6 | 0.352 | 38.00 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 985 | 149 | 1038 |
| 255.0 | 5.276 | 8.532 | 4.259 | 9.534 | 22.0 | 0.352 | 38.00 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 985 | 149 | 1038 |
| 352.7 | 5.260 | 8.410 | 4.260 | 9.470 | 21.9 | 0.352 | 38.01 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 985 | 149 | 1038 |
| 362.8 | 5.269 | 8.248 | 4.254 | 9.360 | 24.5 | 0.358 | 38.01 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 1000 | 149 | 1038 |
| 363.4 | 5.247 | 8.420 | 4.270 | 9.462 | 22.4 | 0.352 | 38.08 | 0.05 | 0.40 | 985 | 149 | 1038 |
| 455.8 | 5.307 | 8.122 | 4.231 | 9.388 | 23.0 | 0.352 | 38.02 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 985 | 149 | 1038 |
| 461.5 | 5.302 | 8.130 | 4.240 | 9.386 | 23.5 | 0.352 | 38.02 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 985 | 149 | 1038 |
| 474.1 | 5.269 | 8.354 | 4.290 | 9.510 | 22.9 | 0.352 | 38.16 | 0.05 | 0.80 | 985 | 149 | 1038 |
| 607.5 | 5.242 | 7.906 | 4.240 | 9.200 | 24.8 | 0.358 | 38.02 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 1000 | 149 | 1038 |
| 583.9 | 5.285 | 8.120 | 4.259 | 9.430 | 22.5 | 0.352 | 38.24 | 0.05 | 1.20 | 985 | 149 | 1038 |
| 603.5 | 5.270 | 8.160 | 4.247 | 9.480 | 23.7 | 0.352 | 38.24 | 0.05 | 1.20 | 985 | 149 | 1038 |
| 692.6 | 5.272 | 7.878 | 4.266 | 9.250 | 22.5 | 0.352 | 38.03 | 0.05 | 0.16 | 985 | 149 | 1038 |
| 690.9 | 5.271 | 8.000 | 4.264 | 9.372 | 22.4 | 0.352 | 38.32 | 0.05 | 1.60 | 985 | 149 | 1038 |
| 731.3 | 5.232 | 8.006 | 4.242 | 9.374 | 23.7 | 0.352 | 38.32 | 0.05 | 1.60 | 985 | 149 | 1038 |
| 814.9 | 5.267 | 7.800 | 4.274 | 9.260 | 22.5 | 0.352 | 38.40 | 0.05 | 2.00 | 985 | 149 | 1038 |
| 811.6 | 5.239 | 7.898 | 4.275 | 9.302 | 22.8 | 0.352 | 38.40 | 0.05 | 2.00 | 985 | 149 | 1038 |
| 809.0 | 5.230 | 7.800 | 4.263 | 9.200 | 22.8 | 0.352 | 38.40 | 0.05 | 2.00 | 985 | 149 | 1038 |
| VFAT | pHx1 | Vx1 | pHx2 | Vx2 | Temp | EC | Dilution | [HCl] | Spike Volume | TIC | PT | NT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg/L as HAc | mL | mL | °C | mS/cm | N | mL | ppm | mg/L as P | mg/L as N | |||
| 25.59 | 5.2 | 9.9 | 4.2 | 10.9 | 23.4 | 0.5 | 19.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 2.4 | 207.2 | 697.9 |
| 26.76 | 5.2 | 10.0 | 4.2 | 10.9 | 23.5 | 0.5 | 19.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 2.4 | 207.2 | 697.9 |
| 33.22 | 5.3 | 10.0 | 4.2 | 10.9 | 22.8 | 0.5 | 19.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 2.4 | 207.2 | 697.9 |
| 85.3 | 5.2 | 9.8 | 4.2 | 10.8 | 22.1 | 0.5 | 19.0 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 2.4 | 207.2 | 697.9 |
| 80.0 | 5.3 | 9.8 | 4.3 | 10.8 | 22.1 | 0.5 | 19.0 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 2.4 | 207.2 | 697.9 |
| 84.6 | 5.2 | 9.8 | 4.2 | 10.9 | 22.0 | 0.5 | 19.0 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 2.4 | 207.2 | 697.9 |
| 140.8 | 5.2 | 9.6 | 4.3 | 10.7 | 21.4 | 0.5 | 19.1 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 2.4 | 207.2 | 697.9 |
| 137.0 | 5.2 | 9.6 | 4.2 | 10.7 | 21.3 | 0.5 | 19.1 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 2.4 | 207.2 | 697.9 |
| 127.2 | 5.2 | 9.6 | 4.3 | 10.7 | 23.6 | 0.5 | 19.1 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 2.4 | 207.2 | 697.9 |
| 192.5 | 5.2 | 9.4 | 4.3 | 10.6 | 23.5 | 0.5 | 19.1 | 0.1 | 1.2 | 2.4 | 207.2 | 697.9 |
| 190.2 | 5.3 | 9.4 | 4.3 | 10.6 | 23.4 | 0.5 | 19.1 | 0.1 | 1.2 | 2.4 | 207.2 | 697.9 |
| 189.9 | 5.3 | 9.4 | 4.3 | 10.6 | 24.4 | 0.5 | 19.1 | 0.1 | 1.2 | 2.4 | 207.2 | 697.9 |
| 236.0 | 5.2 | 9.0 | 4.3 | 10.2 | 21.2 | 0.5 | 19.2 | 0.1 | 1.6 | 2.4 | 207.2 | 697.9 |
| 245.1 | 5.3 | 9.0 | 4.2 | 10.4 | 21.1 | 0.5 | 19.2 | 0.1 | 1.6 | 2.4 | 207.2 | 697.9 |
| 238.6 | 5.3 | 9.1 | 4.2 | 10.4 | 21.7 | 0.5 | 19.2 | 0.1 | 1.6 | 2.4 | 207.2 | 697.9 |
| 298.7 | 5.3 | 8.9 | 4.2 | 10.4 | 21.3 | 0.5 | 19.2 | 0.1 | 2.0 | 2.4 | 207.2 | 697.9 |
| 301.4 | 5.2 | 8.9 | 4.2 | 10.3 | 21.5 | 0.5 | 19.2 | 0.1 | 2.0 | 2.4 | 207.2 | 697.9 |
| 299.7 | 5.3 | 8.9 | 4.2 | 10.4 | 20.9 | 0.5 | 19.2 | 0.1 | 2.0 | 2.4 | 207.2 | 697.9 |
| VFAT | pHx1 | Vx1 | pHx2 | Vx2 | Temp | EC | Dilution | [HCl] | Spike Volume | TIC | PT | NT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg/L as HAc | mL | mL | °C | mS/cm | N | mL | ppm | mg/L as P | mg/L as N | |||
| 12.2 | 5.142 | 7.604 | 4.194 | 8.286 | 23.0 | 0.2744 | 19.0 | 0.05 | 0.0 | 511.05 | ||
| 17.4 | 5.161 | 7.692 | 4.181 | 8.412 | 22.3 | 0.2744 | 19.0 | 0.05 | 0.0 | 511.05 | ||
| 12.7 | 5.236 | 7.612 | 4.224 | 8.398 | 24.2 | 0.2744 | 19.0 | 0.05 | 0.0 | 511.05 | ||
| 113.3 | 5.252 | 7.278 | 4.237 | 8.254 | 24.2 | 0.2744 | 19.1 | 0.05 | 0.7 | 511.05 | ||
| 114.4 | 5.230 | 7.306 | 4.204 | 8.272 | 22.9 | 0.2744 | 19.1 | 0.05 | 0.7 | 511.05 | ||
| 121.9 | 5.238 | 7.290 | 4.244 | 8.258 | 25.1 | 0.2744 | 19.1 | 0.05 | 0.7 | 511.05 | ||
| 223.1 | 5.233 | 7.078 | 4.242 | 8.198 | 21.8 | 0.2744 | 19.1 | 0.05 | 1.4 | 511.05 | ||
| 225.9 | 5.189 | 7.082 | 4.219 | 8.160 | 21.9 | 0.2744 | 19.1 | 0.05 | 1.4 | 511.05 | ||
| 234.3 | 5.232 | 7.048 | 4.248 | 8.180 | 21.9 | 0.2744 | 19.1 | 0.05 | 1.4 | 511.05 | ||
| 344.4 | 5.240 | 6.720 | 4.228 | 8.088 | 23.7 | 0.2744 | 19.2 | 0.05 | 2.1 | 511.05 | ||
| 339.2 | 5.238 | 6.736 | 4.243 | 8.070 | 23.0 | 0.2744 | 19.2 | 0.05 | 2.1 | 511.05 | ||
| 329.1 | 5.236 | 6.730 | 4.228 | 8.070 | 24.9 | 0.2744 | 19.2 | 0.05 | 2.1 | 511.05 | ||
| 451.7 | 5.255 | 6.418 | 4.233 | 7.998 | 23.8 | 0.2744 | 19.3 | 0.05 | 2.8 | 511.05 | ||
| 435.3 | 5.242 | 6.474 | 4.247 | 7.978 | 23.2 | 0.2744 | 19.3 | 0.05 | 2.8 | 511.05 | ||
| 421.8 | 5.241 | 6.444 | 4.177 | 8.026 | 25.6 | 0.2744 | 19.3 | 0.05 | 2.8 | 511.05 | ||
| 536.3 | 5.257 | 6.120 | 4.244 | 7.842 | 24.6 | 0.2744 | 19.4 | 0.05 | 3.5 | 511.05 | ||
| 538.6 | 5.246 | 6.172 | 4.245 | 7.868 | 23.6 | 0.2744 | 19.4 | 0.05 | 3.5 | 511.05 | ||
| 527.5 | 5.242 | 6.140 | 4.223 | 7.850 | 25.5 | 0.2744 | 19.4 | 0.05 | 3.5 | 511.05 |
| VFAT | pHx1 | Vx1 | pHx2 | Vx2 | Temp | EC | Dilution | [HCl] | Spike Volume | TIC | PT | NT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg/L as HAc | mL | mL | °C | mS/cm | N | mL | ppm | mg/L as P | mg/L as N | |||
| 583.1 | 5.255 | 9.576 | 4.227 | 10.974 | 20.3 | 0.777 | 38.00 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 1170.75 | 61.9 | 2927.2 |
| 593.5 | 5.252 | 9.542 | 4.207 | 10.970 | 20.9 | 0.777 | 38.00 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 1170.75 | 61.9 | 2927.2 |
| 576.6 | 5.268 | 9.622 | 4.230 | 11.054 | 22.9 | 0.777 | 38.00 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 1170.75 | 61.9 | 2927.2 |
| 699.3 | 5.227 | 9.496 | 4.236 | 10.938 | 21.9 | 0.777 | 38.07 | 0.05 | 0.35 | 1170.75 | 61.9 | 2927.2 |
| 706.1 | 5.256 | 9.434 | 4.243 | 10.936 | 22.3 | 0.777 | 38.07 | 0.05 | 0.35 | 1170.75 | 61.9 | 2927.2 |
| 692.7 | 5.222 | 9.558 | 4.259 | 10.959 | 22.4 | 0.777 | 38.07 | 0.05 | 0.35 | 1170.75 | 61.9 | 2927.2 |
| 789.4 | 5.250 | 9.374 | 4.244 | 10.926 | 20.9 | 0.777 | 38.14 | 0.05 | 0.70 | 1170.75 | 61.9 | 2927.2 |
| 775.4 | 5.226 | 9.344 | 4.188 | 10.920 | 23.3 | 0.777 | 38.14 | 0.05 | 0.70 | 1170.75 | 61.9 | 2927.2 |
| 838.6 | 5.260 | 9.352 | 4.287 | 10.924 | 22.9 | 0.777 | 38.14 | 0.05 | 0.70 | 1170.75 | 61.9 | 2927.2 |
| 904.1 | 5.238 | 9.214 | 4.221 | 10.870 | 20.7 | 0.777 | 38.21 | 0.05 | 1.05 | 1170.75 | 61.9 | 2927.2 |
| 922.1 | 5.229 | 9.218 | 4.250 | 10.838 | 22.1 | 0.777 | 38.21 | 0.05 | 1.05 | 1170.75 | 61.9 | 2927.2 |
| 905.8 | 5.230 | 9.242 | 4.257 | 10.840 | 22.0 | 0.777 | 38.21 | 0.05 | 1.05 | 1170.75 | 61.9 | 2927.2 |
| 999.2 | 5.234 | 9.126 | 4.248 | 10.826 | 22.1 | 0.777 | 38.28 | 0.05 | 1.40 | 1170.75 | 61.9 | 2927.2 |
| 1028.2 | 5.227 | 9.118 | 4.246 | 10.834 | 22.8 | 0.777 | 38.28 | 0.05 | 1.40 | 1170.75 | 61.9 | 2927.2 |
| 1010.3 | 5.180 | 9.126 | 4.180 | 10.818 | 22.6 | 0.777 | 38.28 | 0.05 | 1.40 | 1170.75 | 61.9 | 2927.2 |
| 1119.0 | 5.212 | 8.960 | 4.259 | 10.698 | 22.7 | 0.777 | 38.35 | 0.05 | 1.75 | 1170.75 | 61.9 | 2927.2 |
| 1116.4 | 5.253 | 8.930 | 4.266 | 10.750 | 22.5 | 0.777 | 38.35 | 0.05 | 1.75 | 1170.75 | 61.9 | 2927.2 |
| 1124.4 | 5.224 | 8.944 | 4.244 | 10.730 | 21.4 | 0.777 | 38.35 | 0.05 | 1.75 | 1170.75 | 61.9 | 2927.2 |
References
- Dilallo, R.; Albertson, O.E. Volatile Acids by Direct Titration. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1961, 33, 356–365. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/25034391 (accessed on 28 February 2021).
- McGhee, T.J. A method for approximation of the volatile acid concentrations in anaerobic digesters. Water Sew. Work. 1968, 115, 162–166. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, B.; Radhakrishnan, L.; Mazumder, D. New approach for determination of volatile fatty acid in anaerobic digester sample. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2018, 35, 333–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Z.-X.; He, C.-S.; Jiang, J.-K.; Zhang, J.; Yang, H.-Y.; Mu, J. A modified two-point titration method for the determination of volatile fatty acids in anaerobic systems. Chemosphere 2018, 204, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wu, S.; Dong, R. Monitoring Volatile Fatty Acids and Carbonate Alkalinity in Anaerobic Digestion: Titration Methodologies. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2016, 39, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, F.; Zeng, Q.; Chi, K.; Hao, T.; Ekama, G.A. A novel approach for rapidly measuring volatile fatty acids in anaerobic process. Water Res. 2020, 182, 115960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, S.; Morgan, J.; Sawyer, C. Measuring Anaerobic Sludge Digestion and Growth by a Simple Alkalimetric Titration. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1983, 55, 448–453. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/25041903 (accessed on 28 February 2021).
- Moosbrugger, R.E.; Wentzel, M.C.; Ekama, G.A.; Marais, G.V.R. A 5 pH Point Titration Method for Determining the Carbonate and SCFA Weak Acid/Bases in Anaerobic Systems. Water Sci. Technol. 1993, 28, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchauer, K. A comparison of two simple titration procedures to determine volatile fatty acids in influents to waste-water and sludge treatment processes. Water SA 1998, 24, 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Münch, E.v.; Greenfield, P.F. Estimating VFA concentrations in prefermenters by measuring pH. Water Res. 1998, 32, 2431–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahav, O.; Morgan, B.E.; Loewenthal, R.E. Rapid Simple and Accurate Method for Measurement of VFA and Carbonate Alkalinity in Anaerobic Reactors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 2736–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, R.; Dinsdale, R.M.; Guwy, A.J.; Premier, G.C. Critical analysis of methods for the measurement of volatile fatty acids. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 46, 209–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charnier, C.; Latrille, E.; Lardon, L.; Miroux, J.; Steyer, J.P. Combining pH and electrical conductivity measurements to improve titrimetric methods to determine ammonia nitrogen, volatile fatty acids and inorganic carbon concentrations. Water Res. 2016, 95, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Guo, J.; Wu, S.; Liu, F.; Dong, R. Development and validation of a simplified titration method for monitoring volatile fatty acids in anaerobic digestion. Waste Manag. 2017, 67, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ripley, L.E.; Boyle, W.C.; Converse, J.C. Improved Alkalimetric Monitoring for Anaerobic Digestion of High-Strength Wastes. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1986, 58, 406–411. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/25042933 (accessed on 28 February 2021).
- Benjamin, M.M. Water Chemistry, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Lahav, O.; Morgan, B.E. Titration methodologies for monitoring of anaerobic digestion in developing countries—A review. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2004, 79, 1331–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahav, O.; Birnhack, L. Aquatic Chemistry, 1st ed.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moragaspitiya, C.; Rajapakse, J.; Millar, G.J.; Ali, I. Optimization of mesophilic anaerobic digestion of a conventional activated sludge plant for sustainability. Alex. Eng. J. 2019, 58, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, C.M.; Latif, M.A.; Bastrone, D.J. Improved phosphorus solubility during acidic anaerobic digestion. In Proceedings of the AWA Biosolids Conference, Melbourne, Australia, 25–27 June 2014; p. 60. [Google Scholar]
- Charlton, S.R.; Parkhurst, D.L. Modules based on the geochemical model PHREEQC for use in scripting and programming languages. Comput. Geosci. 2011, 37, 1653–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, R.B.; Montgomery, M.E.; Allen, P.R. Improved Method for Manual, Colorimetric Determination of Total Kjeldahl Nitrogen Using Salicylate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 1804–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGregor, A.J. A colorimetric modification of McLean’s method for the determination of phosphorus in soils. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1950, 1, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| NT = 450 mg/L PT = 100 mg/L | NT = 450 mg/L PT =150 mg/L | NT = 450 mg/L PT = 200 mg/L | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VFAT (mM) | VFAT (mM) Calculated by Neglecting NT and PT | Error | VFAT (mM) Calculated by Neglecting NT and PT | Error | VFAT (mM) Calculated by Neglecting NT and PT | Error |
| 2 | 2.13 | 6.8% | 2.2 | 10.2% | 2.27 | 13.5% |
| 5 | 5.13 | 2.7% | 5.2 | 4.0% | 5.27 | 5.4% |
| 8 | 8.13 | 1.7% | 8.2 | 2.5% | 8. 27 | 3.3% |
| 10 | 10.13 | 1.3% | 10.2 | 2.0% | 10. 27 | 2.7% |
| VFAT/Alkalinity | Dilution | VFAT * | 5-Point Method | 8-Point Method | 2-Point Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg/L as HAc | mg/L as HAc Relative Error | mg/L as HAc Relative Error | mg/L as HAc Relative Error | ||
| 0.49 | 3.4 | 59.3 ± 0.12 | 59.6 ± 0.7 | 61.2 ± 1.02 | 59.1 ± 0.32 |
| 0.5% | 3.1% | −0.4% | |||
| 0.33 | 3.4 | 59.3 ± 0.12 | 59.4 ± 0.8 | 60.1 ± 0.86 | 59.9 ± 0.77 |
| 0.2% | 1.3% | 1.0% | |||
| 0.26 | 3.6 | 55.3 ± 1.21 | 54.8 ± 0.57 | 55.7 ± 0.9 | 56.5 ± 1.78 |
| −0.8% | 0.9% | 2.3% | |||
| 0.20 | 3.4 | 59.3 ± 0.12 | 59.6 ± 1.23 | 60.5 ± 1.09 | 59.6 ± 0.96 |
| 0.5% | 1.9% | 0.4% | |||
| 0.12 | 3.8 | 52.5 ± 0.04 | 54.6 ± 0.31 | 55 ± 0.16 | 54.9 ± 0.51 |
| 4.1% | 4.8% | 4.5% | |||
| 0.10 | 3.4 | 59.3 ± 0.12 | 53.9 ± 4.07 | 53.9 ± 4.2 | 53.1 ± 3.18 |
| −9.1% | −9.1% | −10.5% | |||
| Butyric acid 0.31 | 3.4 | 59.3 ± 1.8 | 58.7 ± 0.17 −0.9% | 60.8 ± 0.7 2.7% | 58.8 ± 0.63 −0.8% |
| Sample # | Calculated with Measured NT, PT (mg/L as HAc) | Calculated with NT and PT = 0 (mg/L as HAc) | Relative Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shafdan raw | 255.6 ± 3.55 | 266.5 ± 3.84 | 4.3% |
| Shafdan spiked 1 | 359.6 ± 4.93 | 370.7 ± 5 | 3.1% |
| Shafdan spiked 2 | 463.8 ± 7.64 | 475.3 ± 7.4 | 2.5% |
| Shafdan spiked 3 | 598.3 ± 10.34 | 609.5 ± 10.26 | 1.9% |
| Shafdan spiked 4 | 705 ± 18.65 | 716 ± 18.51 | 1.6% |
| Shafdan spiked 5 | 811.8 ± 2.43 | 822.7 ± 2.59 | 1.3% |
| Haifa raw | 28.5 ± 3.35 | 43.6 ± 3.38 | 53% |
| Haifa spiked 1 | 83.3 ± 2.34 | 98.1 ± 2.17 | 18% |
| Haifa spiked 2 | 135 ± 5.74 | 149.7 ± 5.53 | 11% |
| Haifa spiked 3 | 190.9 ± 1.16 | 206 ± 1.06 | 8% |
| Haifa spiked 4 | 239.9 ± 3.83 | 254.7 ± 4.21 | 6% |
| Haifa spiked 5 | 300 ± 1.12 | 314.8 ± 0.81 | 5% |
| Acre raw | 584.4 ± 6.95 | 590.5 ± 6.8 | 1% |
| Acre spiked 1 | 699.4 ± 5.48 | 705.4 ± 5.57 | 1% |
| Acre spiked 2 | 801.1 ± 27.09 | 807.3 ± 27.23 | 1% |
| Acre spiked 3 | 910.7 ± 8.15 | 916.6 ± 8.19 | 1% |
| Acre spiked 4 | 1012.6 ± 11.96 | 1018.5 ± 12 | 1% |
| Acre spiked 5 | 1119.9 ± 3.34 | 1126 ± 3.2 | 1% |
| Reactor | CO2 in Dry Biogas | pH | EC | Temp | TOC-Measured CT | CO2 Pp-Calculated CT | Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | - | mS/cm | °C | mM | mM | % | |
| Shafdan 1 | 38.0 | 7.28 | 8.01 | 52.4 | 79.3 | 84.7 | +6.8% |
| Shafdan 2 | 38.1 | 7.27 | 7.99 | 53.2 | 82.1 | 81.6 | −0.7% |
| Shafdan 3 | 38.0 | 7.27 | 7.73 | 52.4 | 83.0 | 82.9 | −0.1% |
| Shafdan 5 | 38.2 | 7.26 | 7.89 | 53.1 | 77.6 | 79.6 | +2.5% |
| Shafdan 6 | 38.2 | 7.27 | 7.89 | 53.7 | 80.1 | 80.1 | 0.0% |
| Shafdan 7 | 17.6 | 7.70 | 9.32 | 53.7 | 96.7 | 97.3 | +0.6% |
| Shafdan 8 | 21.1 | 7.64 | 9.40 | 54.2 | 101.6 | 98.9 | −2.7% |
| Acre East | 29.3 | 7.46 | 9.09 | 52.1 | 97.5 | 101.7 | +4.4% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nativ, P.; Gräber, Y.; Aviezer, Y.; Lahav, O. A Simple and Accurate Approach for Determining the VFA Concentration in Anaerobic Digestion Liquors, Relying on Two Titration Points and an External Inorganic Carbon Analysis. ChemEngineering 2021, 5, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering5020015
Nativ P, Gräber Y, Aviezer Y, Lahav O. A Simple and Accurate Approach for Determining the VFA Concentration in Anaerobic Digestion Liquors, Relying on Two Titration Points and an External Inorganic Carbon Analysis. ChemEngineering. 2021; 5(2):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering5020015
Chicago/Turabian StyleNativ, Paz, Yonatan Gräber, Yaron Aviezer, and Ori Lahav. 2021. "A Simple and Accurate Approach for Determining the VFA Concentration in Anaerobic Digestion Liquors, Relying on Two Titration Points and an External Inorganic Carbon Analysis" ChemEngineering 5, no. 2: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering5020015
APA StyleNativ, P., Gräber, Y., Aviezer, Y., & Lahav, O. (2021). A Simple and Accurate Approach for Determining the VFA Concentration in Anaerobic Digestion Liquors, Relying on Two Titration Points and an External Inorganic Carbon Analysis. ChemEngineering, 5(2), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering5020015








