Alkali-Activated Adsorbents from Slags: Column Adsorption and Regeneration Study for Nickel(II) Removal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Geopolymer (GP)
2.3. Methods of Characterization
2.4. Nickel(II) Removal with Powdered Slag-Based Geopolymer: Column Experiments
2.5. Kinetic Models
2.5.1. Adams–Bohart Model
2.5.2. Thomas Model
2.5.3. Yoon and Nelson Model
3. Results and Discussion
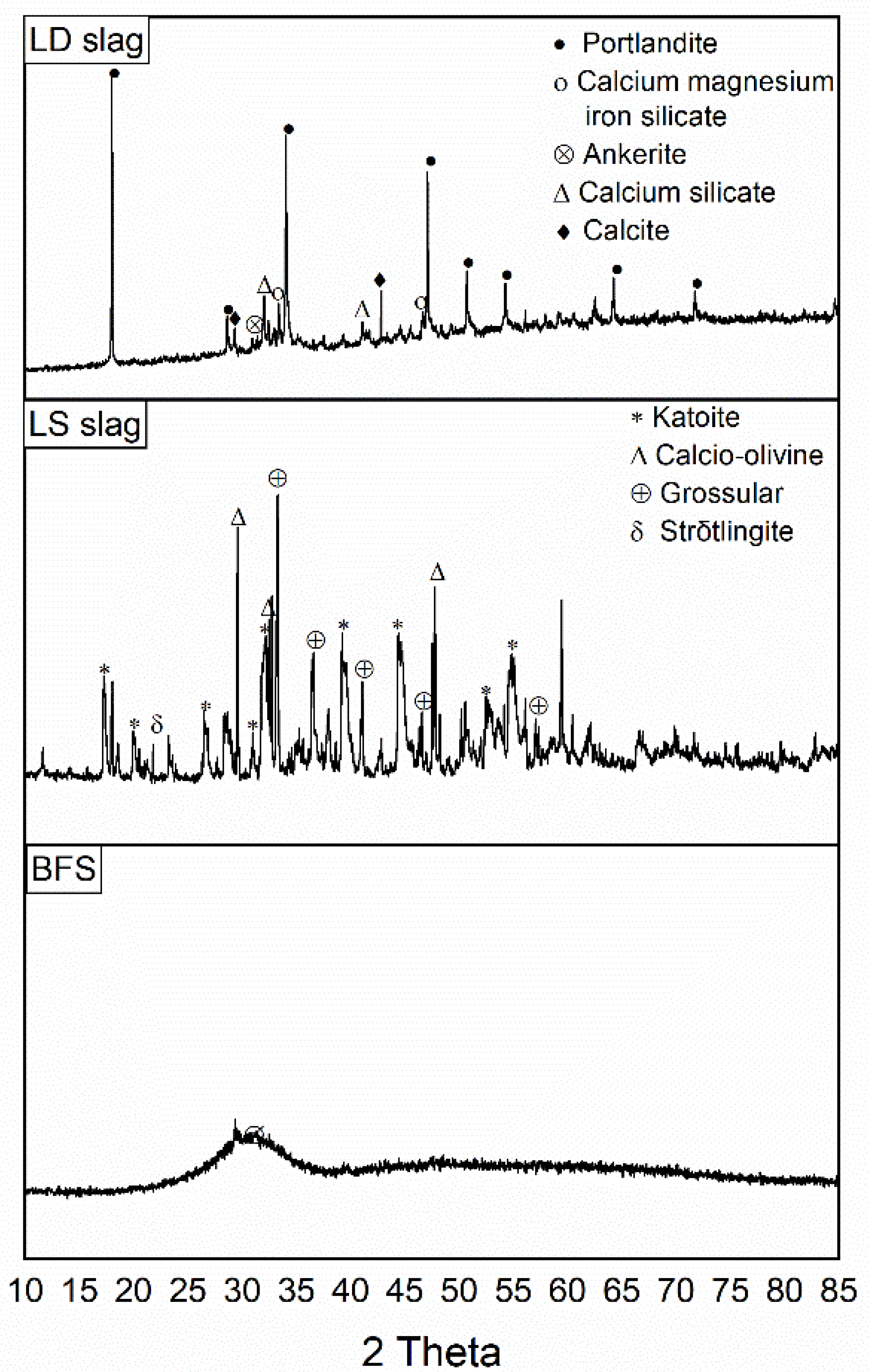
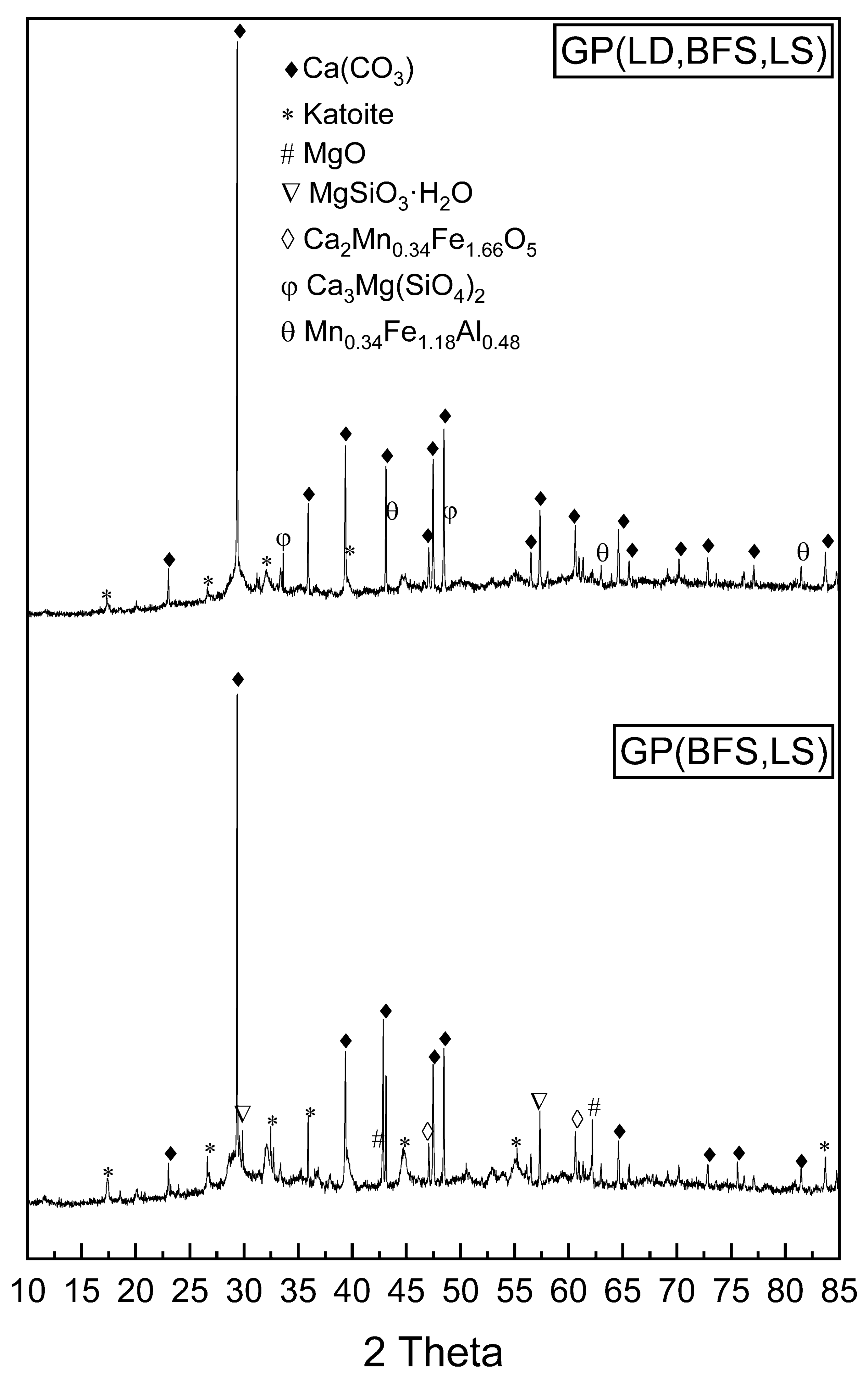
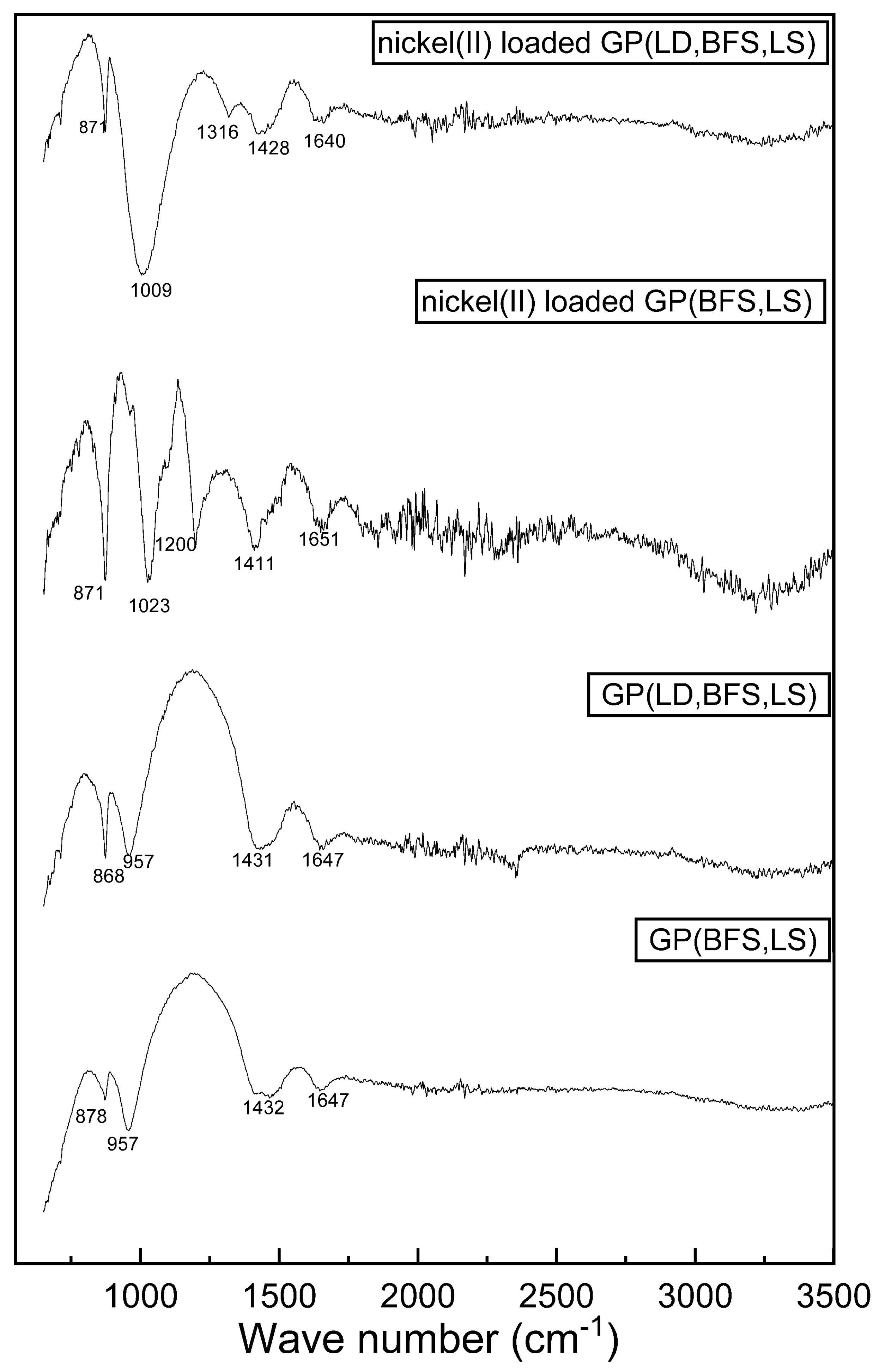
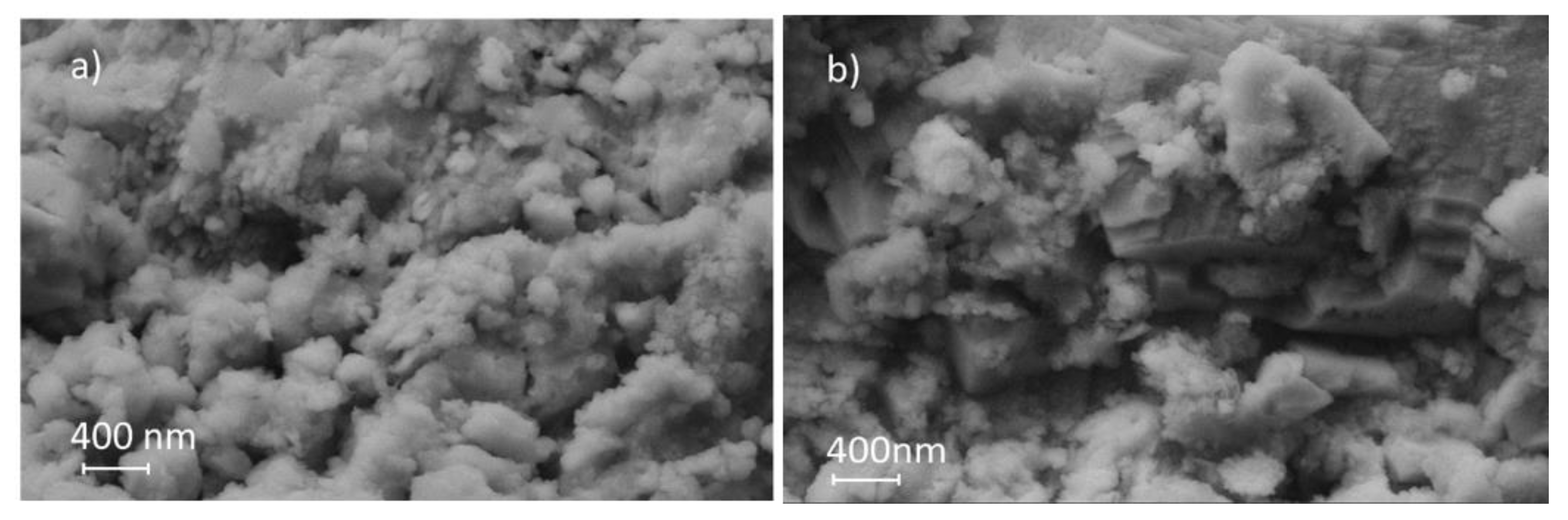
3.1. Characteristics of Slag-Based Geopolymers
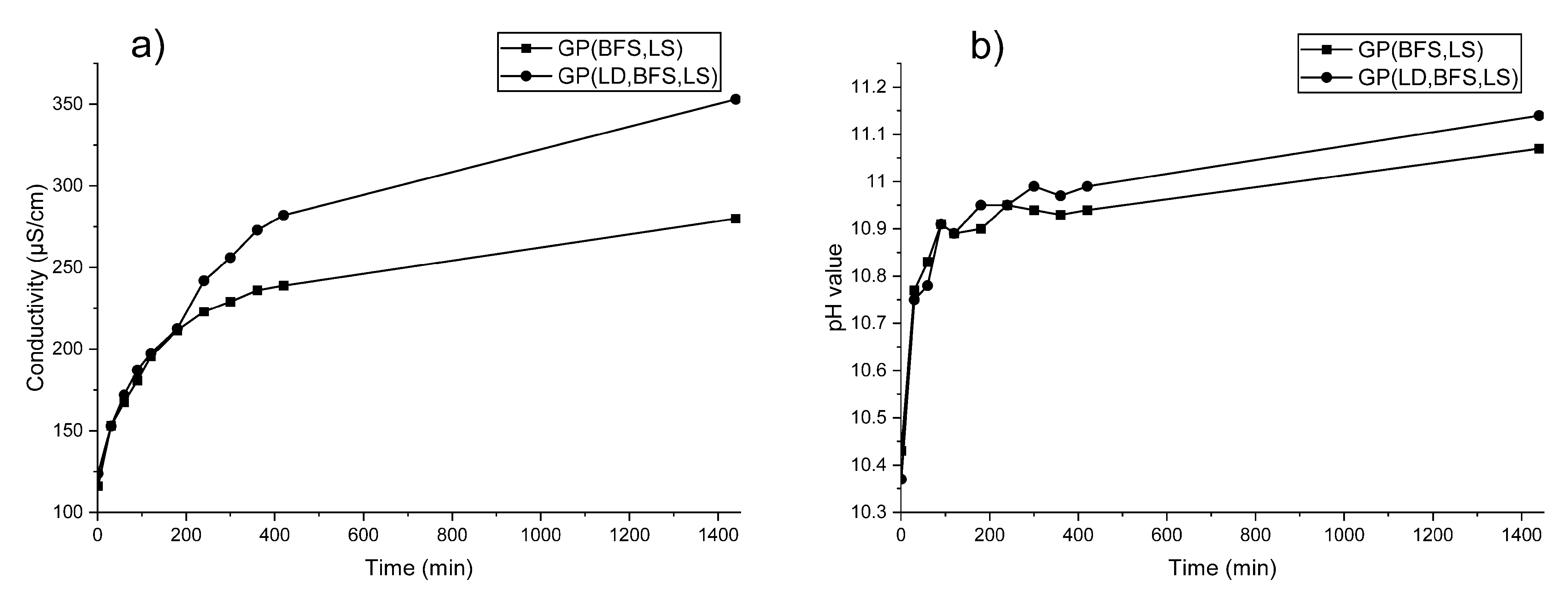
3.2. Leaching Test for Stability
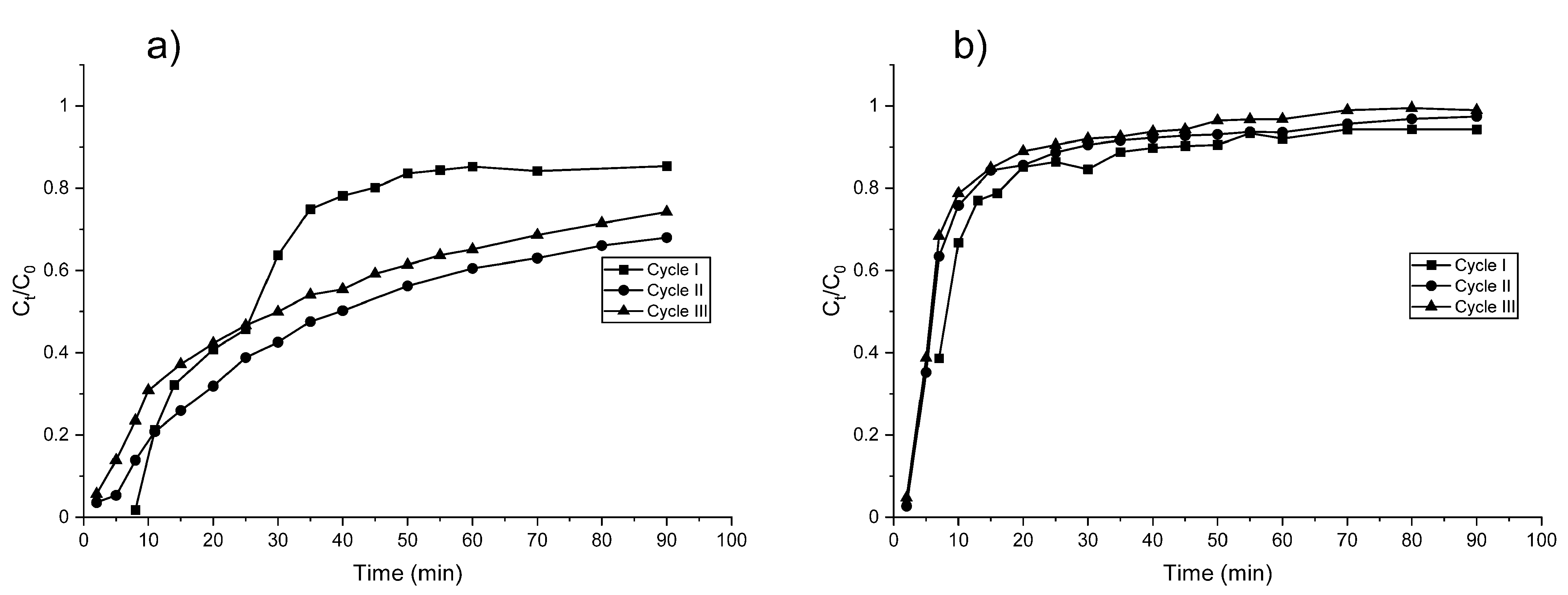
3.3. Adsorption–Regeneration Experiments
3.4. Adsorption Kinetics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, T.; Lee, M.; Ko, M.; Ueng, T.; Yang, S. The heavy metal adsorption characteristics on metakaolin-based geopolymer. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 56, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siyal, A.A.; Shamsuddin, M.R.; Khan, M.I.; Rabat, N.E.; Zulfiqar, M.; Man, Z.; Siame, J.; Azizli, K.A. A review on geopolymers as emerging materials for the adsorption of heavy metals and dyes. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 224, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J.K.; Ahmaruzzaman, M. A review on potential usage of industrial waste materials for binding heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions. J. Water Process. Eng. 2016, 10, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zboon, K.; Al-Harahsheh, M.S.; Hani, F.B. Fly ash-based geopolymer for Pb removal from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 188, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javadian, H.; Ghorbani, F.; Tayebi, H.-A.; Asl, S.H. Study of the adsorption of Cd (II) from aqueous solution using zeolite-based geopolymer, synthesized from coal fly ash; kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic studies. Arab. J. Chem. 2015, 8, 837–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medpelli, D.; Sandoval, R.; Sherrill, L.; Hristovski, K.D.; Seo, D.-K. Iron oxide-modified nanoporous geopolymers for arsenic removal from ground water. Resour. Technol. 2015, 1, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, C.; Basu, J.K.; Samanta, A.N. Synthesis of mesoporous geopolymeric powder from LD slag as superior adsorbent for Zinc (II) removal. Adv. Powder Technol. 2018, 29, 1142–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harahsheh, M.S.; Al Zboon, K.; Al-Makhadmeh, L.; Hararah, M.; Mahasneh, M. Fly ash based geopolymer for heavy metal removal: A case study on copper removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 1669–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Yan, C.; Zhou, W.; Ren, D. Development of fly ash and iron ore tailing based porous geopolymer for removal of Cu(II) from wastewater. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 13507–13518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, K.; He, Y.; Cui, X. Preparation of geopolymer-based inorganic membrane for removing Ni2+ from wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 299, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukkonen, T.; Věžníková, K.; Tolonen, E.-T.; Runtti, H.; Yliniemi, J.; Hu, T.; Kemppainen, K.; Lassi, U. Removal of ammonium from municipal wastewater with powdered and granulated metakaolin geopolymer. Environ. Technol. 2018, 39, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sočo, E.; Kalembkiewicz, J. Adsorption of nickel(II) and copper(II) ions from aqueous solution by coal fly ash. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukkonen, T.; Runtti, H.; Niskanen, M.; Tolonen, E.-T.; Sarkkinen, M.; Kemppainen, K.; Rämö, J.; Lassi, U. Simultaneous removal of Ni(II), As(III), and Sb(III) from spiked mine effluent with metakaolin and blast-furnace-slag geopolymers. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 166, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, I.; Yilmazer, D.; Akar, S.T. Metakaolin based geopolymer as an effective adsorbent for adsorption of zinc(II) and nickel(II) ions from aqueous solutions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 139, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, C.; Basu, J.K.; Samanta, A.N. Removal of Ni2+ ion from waste water by Geopolymeric Adsorbent derived from LD Slag. J. Water Process. Eng. 2017, 17, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goretta, K.; Chen, N.; Mora, F.G.; Routbort, J.; Lukey, G.; Van Deventer, J. Solid-particle erosion of a geopolymer containing fly ash and blast-furnace slag. Wear 2004, 256, 714–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provis, J.L.; Van Deventer, J.S.J. Geopolymers. In Geopolymers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 1–464. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmaruzzaman, M. A review on the utilization of fly ash. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2010, 36, 327–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Khalid, H.R.; Lee, H. Adsorption characteristics of cesium onto mesoporous geopolymers containing nano-crystalline zeolites. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 242, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.K.; Das, S.N.; Dhundasi, S. Nickel, its adverse health effects & oxidative stress. Indian J. Med. Res. 2008, 128, 412–425. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kapur, M.; Mondal, M.K. Design and model parameters estimation for fixed–bed column adsorption of Cu(II) and Ni(II) ions using magnetized saw dust. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 57, 12192–12203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runtti, H.; Luukkonen, T.; Niskanen, M.; Tuomikoski, S.; Kangas, T.; Tynjälä, P.; Tolonen, E.-T.; Sarkkinen, M.; Kemppainen, K.; Rämö, J.; et al. Sulphate removal over barium-modified blast-furnace-slag geopolymer. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 317, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raval, N.P.; Shah, P.U.; Shah, N.K. Adsorptive removal of nickel(II) ions from aqueous environment: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 179, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Yang, Y.; Huang, C.; Huang, M.; Chen, J.; Rao, T.; Ran, X. Removal of the heavy metal ion nickel (II) via an adsorption method using flower globular magnesium hydroxide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 373, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohart, G.S.; Adams, E.Q. Some aspects of the behavior of charcoal with respect to chlorine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1920, 42, 523–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.H.; Vu, T.M.; Le, T.T.; Trinh, V.T.; Tran, T.P.; Van Tuyen, T. Ammonium removal from aqueous solutions by fixed-bed column using corncob-based modified biochar. Environ. Technol. 2019, 40, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, H.C. Heterogeneous Ion Exchange in a Flowing System. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1944, 66, 1664–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.H.; Nelson, J.H. Application of Gas Adsorption Kinetics—II. A Theoretical Model for Respirator Cartridge Service Life and Its Practical Applications. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 1984, 45, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djobo, J.N.; Tchadjié, L.; Tchakoute, H.; Kenne, B.; Elimbi, A.; Njopwouo, D. Synthesis of geopolymer composites from a mixture of volcanic scoria and metakaolin. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2014, 2, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Han, M.; Yi, R. Microstructure and properties of fly ash-based geopolymeric material with 5A zeolite as a filler. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 33, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoo-Ngernkham, T.; Chindaprasirt, P.; Sata, V.; Hanjitsuwan, S.; Hatanaka, S. The effect of adding nano-SiO2 and nano-Al2O3 on properties of high calcium fly ash geopolymer cured at ambient temperature. Mater. Des. 2014, 55, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mácová, P.; Sotiriadis, K.; Slížková, Z.; Šašek, P.; Řehoř, M.; Závada, J. Evaluation of Physical Properties of a Metakaolin-Based Alkali-Activated Binder Containing Waste Foam Glass. Materials 2020, 13, 5458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasaki, S.A.; Bingxue, Z.; Guarecuco, R.; Thomas, T.; Minghui, Y. Geopolymer for use in heavy metals adsorption, and advanced oxidative processes: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 213, 42–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannopoulou, I.; Panias, D. Hydrolytic stability of sodium silicate gels in the presence of aluminum. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 5370–5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Provis, J.L. Quantitative study of the reactivity of fly ash in geopolymerization by FTIR. J. Sustain. Cem. Mater. 2012, 1, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, Z.; Vance, E.R.; Perera, D.S.; Hanna, J.V.; Griffith, C.S.; Davis, J.; Durce, D. Aqueous leachability of metakaolin-based geopolymers with molar ratios of Si/Al=1.5–4. J. Nucl. Mater. 2008, 378, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancellotti, I.; Kamseu, E.; Michelazzi, M.; Barbieri, L.; Corradi, A.; Leonelli, C. Chemical stability of geopolymers containing municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H. Fixed-bed column adsorption study: A comprehensive review. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Champagne, P. Fixed-bed column study for the removal of cadmium (II) and nickel (II) ions from aqueous solutions using peat and mollusk shells. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Długosz, O.; Banach, M. Sorption of Ag+ and Cu2+ by Vermiculite in a Fixed-Bed Column: Design, Process Optimization and Dynamics Investigations. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahya, M.; Abubakar, H.; Obayomi, K.; Iyaka, Y.; Suleiman, B. Simultaneous and continuous biosorption of Cr and Cu (II) ions from industrial tannery effluent using almond shell in a fixed bed column. Results Eng. 2020, 6, 100113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borba, C.; Guirardello, R.; Silva, E.; Veit, M.; Tavares, C. Removal of nickel(II) ions from aqueous solution by biosorption in a fixed bed column: Experimental and theoretical breakthrough curves. Biochem. Eng. J. 2006, 30, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, A.L.P.; Adarme, O.F.H.; Furtado, L.M.; Ferreira, G.M.D.; Da Silva, L.H.M.; Gil, L.F.; Gurgel, L.V.A. Modeling adsorption of copper(II), cobalt(II) and nickel(II) metal ions from aqueous solution onto a new carboxylated sugarcane bagasse. Part II: Optimization of monocomponent fixed-bed column adsorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 516, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, A.C.D.C.; Scaratti, G.; Moura-Nickel, C.D.; Da Silva, T.L.; Vieira, M.G.A.; Peralta, R.M.; Peralta, R.A.; De Noni, A.; Moreira, R.D.F.P.M. Economical and Technological Aspects of Copper Removal from Water Using a Geopolymer and Natural Zeolite. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Composition (%) | BFS | LS Slag | LD Slag |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 | 8.42 | 27.9 | 1.5 |
| SiO2 | 27.20 | 11.2 | 14.6 |
| K2O | 0.55 | 0.13 | 0.08 |
| CaO | 38.47 | 43.2 | 46.4 |
| Fe | - | 1.38 | 13.9 |
| FeO3 | 0.78 | - | - |
| TiO2 | 1.28 | - | - |
| Ti | - | 0.46 | 0.47 |
| MgO | 9.39 | 6.1 | 1.5 |
| SO3 | 3.76 | - | - |
| S | - | 0.25 | 0.08 |
| Mn | 0.26 | 0.69 | 1.8 |
| Na2O | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.09 |
| Adsorbent | C0 (mg/L) | Q (mL/min) | Z (cm) | qtotal (mg) | qe (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GP (BFS, LS) | |||||
| Cycle I | 50 | 5 | 0.5 | 8.79 | 2.92 |
| Cycle II | 50 | 5 | 0.5 | 11.40 | 3.78 |
| Cycle III | 50 | 5 | 0.5 | 10.25 | 3.40 |
| GP (LD, BFS, LS) | |||||
| Cycle I | 50 | 5 | 0.5 | 4.01 | 1.34 |
| Cycle II | 50 | 5 | 0.5 | 3.28 | 1.10 |
| Cycle III | 50 | 5 | 0.5 | 2.94 | 0.98 |
| Adsorbent | Removed Ion | Flow Rate (mL/min) | Bed Height (cm) | qexp | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vermiculite | Ag+, Cu2+ | 4 | 3 | Ag+: 23.96 mg/g; Cu2+: 28.39 mg/g | [40] |
| Almond shell | Cr, Cu2+ (simultaneous removal) | 6.0 | 7.0 | Cr: 28.47 mg/g; Cu2+: 3.446 mg/g | [41] |
| Marine algae, Sargassum filipendula | Ni2+ | 4 | 30.5 | 1.350 meq/g | [42] |
| Carboxylated sugarcase bagasse | Cu2+ | 1.4 | 1.66 | 1.00 mmol/g | [43] |
| Carboxylated sugarcase bagasse | Co2+ | 1.4 | 1.83 | 0.73 mmol/g | [43] |
| Carboxylated sugarcase bagasse | Ni2+ | 1.4 | 0.98 | 0.89 mmol/g | [43] |
| Mollusk shells | Cd2+, Ni2+ | 3.4 | 10 | Cd2+: 1.6 mg/g, Ni2+: 0.55 mg/g | [39] |
| Natural zeolite | Cu2+ | 3 | 15 | 0.15 mmol/g | [44] |
| Geopolymer from fly ash and metakaolin | Cu2+ | 3 | 15 | 0.90 mmol/g | [44] |
| GP (BFS, LS) | Ni2+ | 5 | 0.5 | 2.92 mg/g | This study |
| GP (LD, BFS, LS) | Ni2+ | 5 | 0.5 | 1.34 mg/g | This study |
| Adsorbents | Adams–Bohart Model | Thomas Model | Yoon–Nelson Model | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q (mL/min) | kAB × 10–3 (L/mg min) | F (cm/min) | N0 (mg/L) | R2 | kTH × 10–3 (L/min mg) | q0 (mg/g) | R2 | kYN (L/min) | τ (min) | R2 | |
| GP (BFS, LS) | |||||||||||
| Cycle I | 5 | 8.61 | 0.0271 | 47.198 | 0.855 | 9.714 | 1.322 | 0.875 | 0.541 | 14.729 | 0.875 |
| Cycle II | 5 | 4.89 | 0.0179 | 28.368 | 0.947 | 5.293 | 1.264 | 0.941 | 0.244 | 15.920 | 0.941 |
| Cycle III | 5 | 5.10 | 0.0223 | 29.152 | 0.978 | 5.853 | 0.987 | 0.985 | 0.274 | 12.099 | 0.985 |
| GP (LD, BFS, LS) | |||||||||||
| Cycle I | 5 | 2.25 | 0.0311 | 46.684 | 0.898 | 5.460 | 0.713 | 0.953 | 0.279 | 8.275 | 0.953 |
| Cycle II | 5 | 12.95 | 0.0647 | 46.553 | 0.947 | 16.767 | 0.526 | 0.983 | 0.839 | 6.114 | 0.983 |
| Cycle III | 5 | 10.28 | 0.0652 | 50.916 | 0.958 | 14.311 | 0.545 | 0.993 | 0.762 | 5.842 | 0.993 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sundhararasu, E.; Tuomikoski, S.; Runtti, H.; Hu, T.; Varila, T.; Kangas, T.; Lassi, U. Alkali-Activated Adsorbents from Slags: Column Adsorption and Regeneration Study for Nickel(II) Removal. ChemEngineering 2021, 5, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering5010013
Sundhararasu E, Tuomikoski S, Runtti H, Hu T, Varila T, Kangas T, Lassi U. Alkali-Activated Adsorbents from Slags: Column Adsorption and Regeneration Study for Nickel(II) Removal. ChemEngineering. 2021; 5(1):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering5010013
Chicago/Turabian StyleSundhararasu, Elavarasi, Sari Tuomikoski, Hanna Runtti, Tao Hu, Toni Varila, Teija Kangas, and Ulla Lassi. 2021. "Alkali-Activated Adsorbents from Slags: Column Adsorption and Regeneration Study for Nickel(II) Removal" ChemEngineering 5, no. 1: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering5010013
APA StyleSundhararasu, E., Tuomikoski, S., Runtti, H., Hu, T., Varila, T., Kangas, T., & Lassi, U. (2021). Alkali-Activated Adsorbents from Slags: Column Adsorption and Regeneration Study for Nickel(II) Removal. ChemEngineering, 5(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering5010013







