Use of Calcined Dolomite as Chemical Precipitant in the Simultaneous Removal of Ammonium and Phosphate from Synthetic Wastewater and from Agricultural Sludge
Abstract
1. Introduction
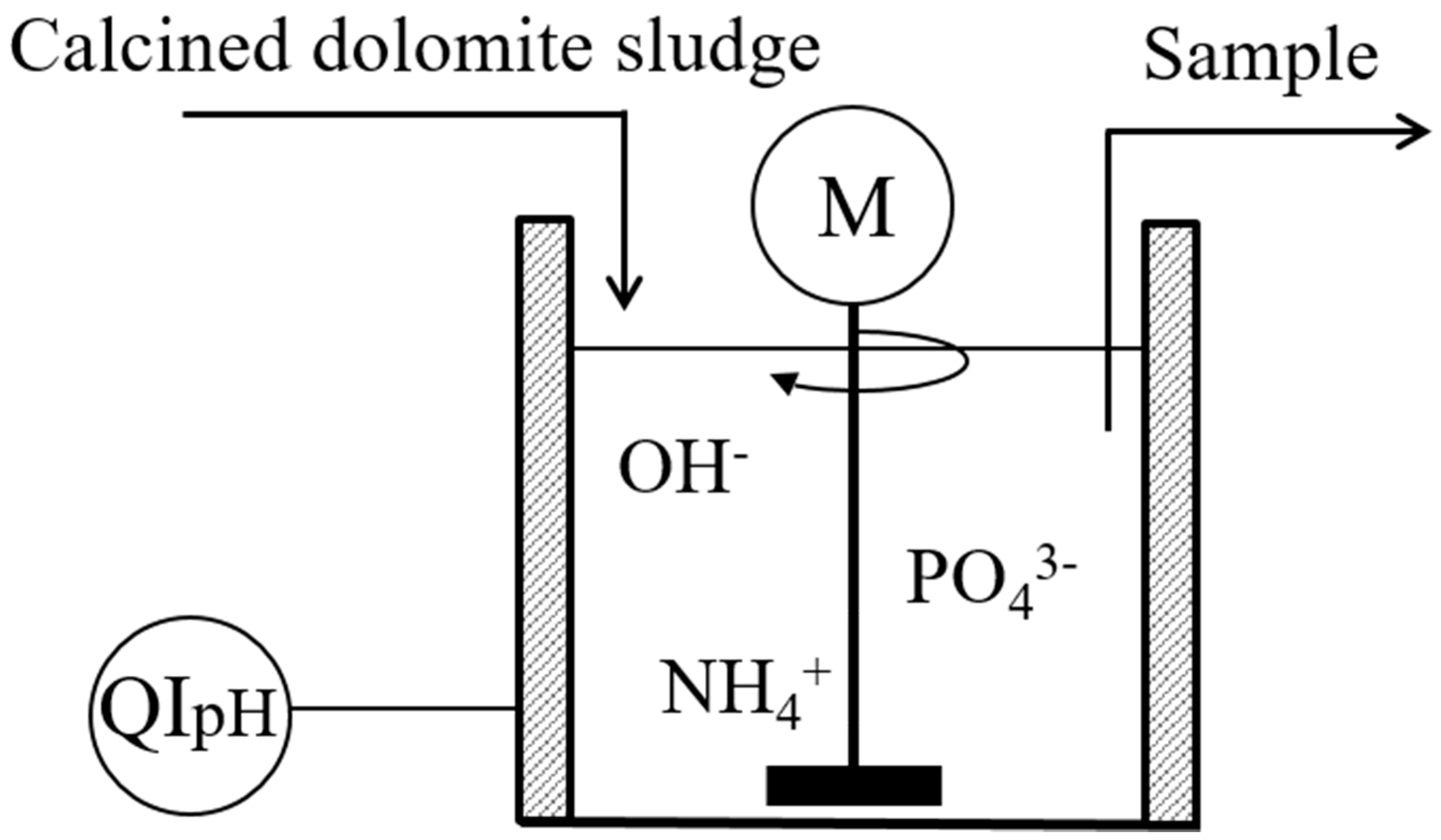
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
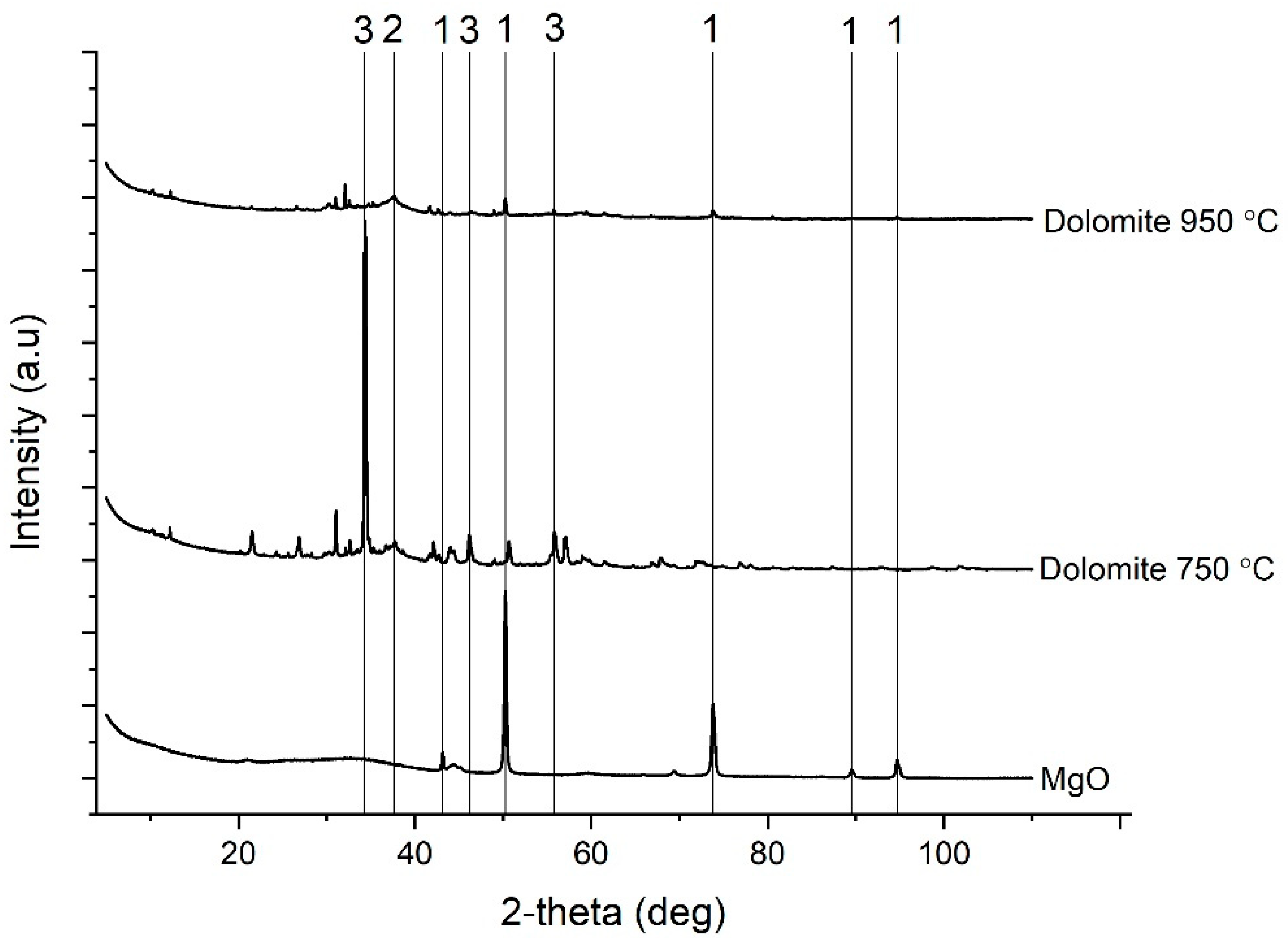
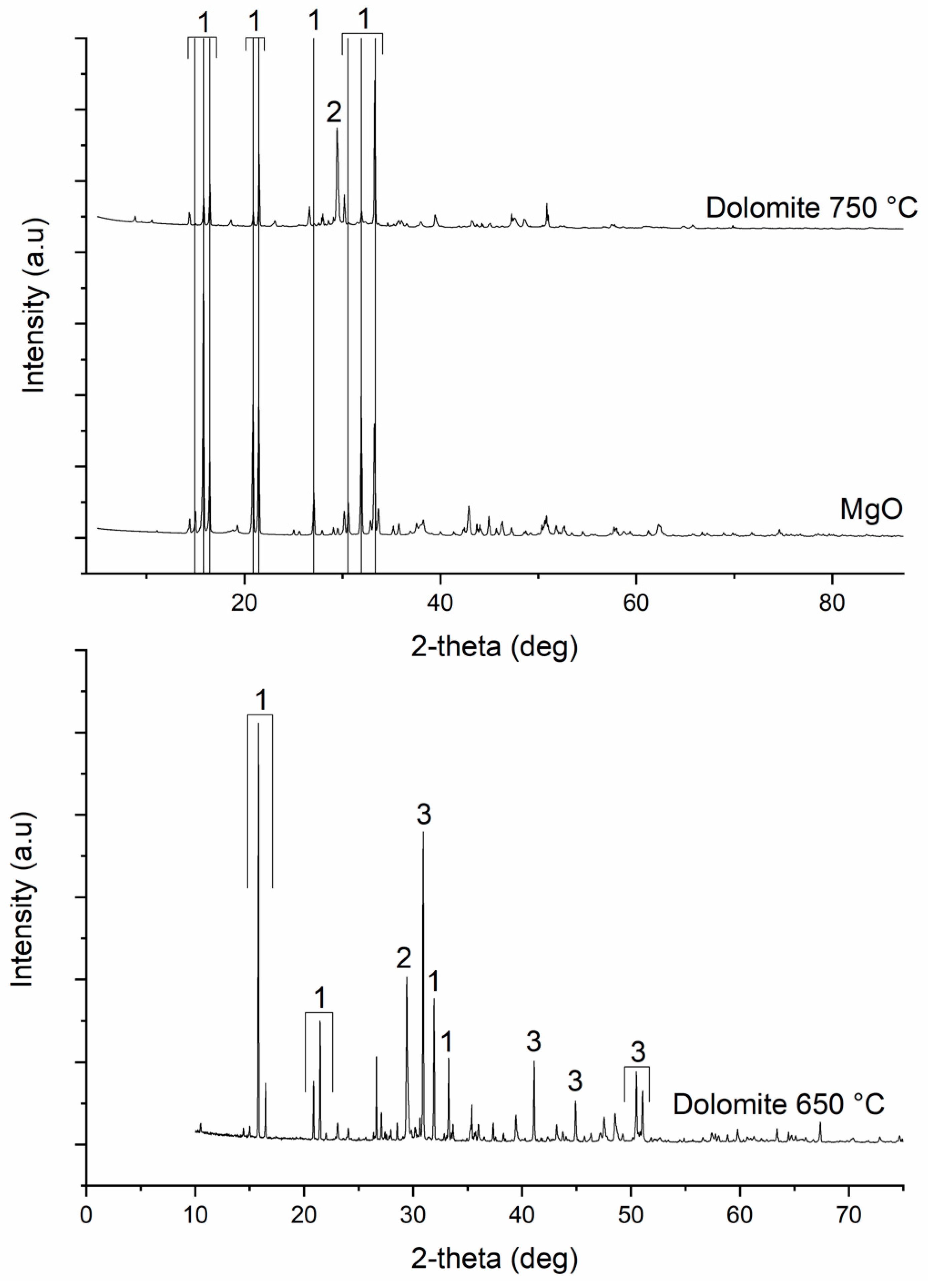
3.1. Characterization of the Dolomite
3.2. Ammonium Removal
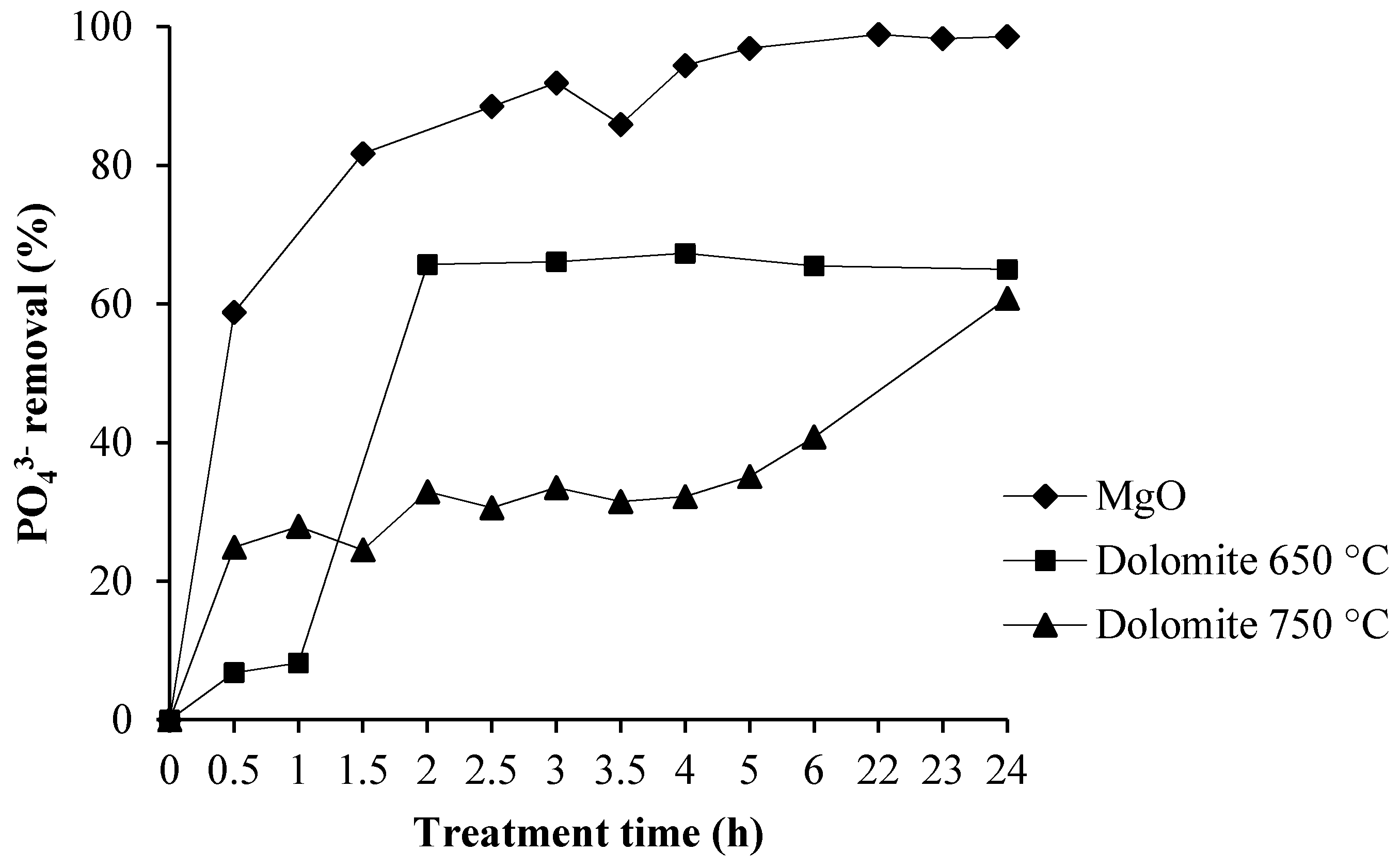
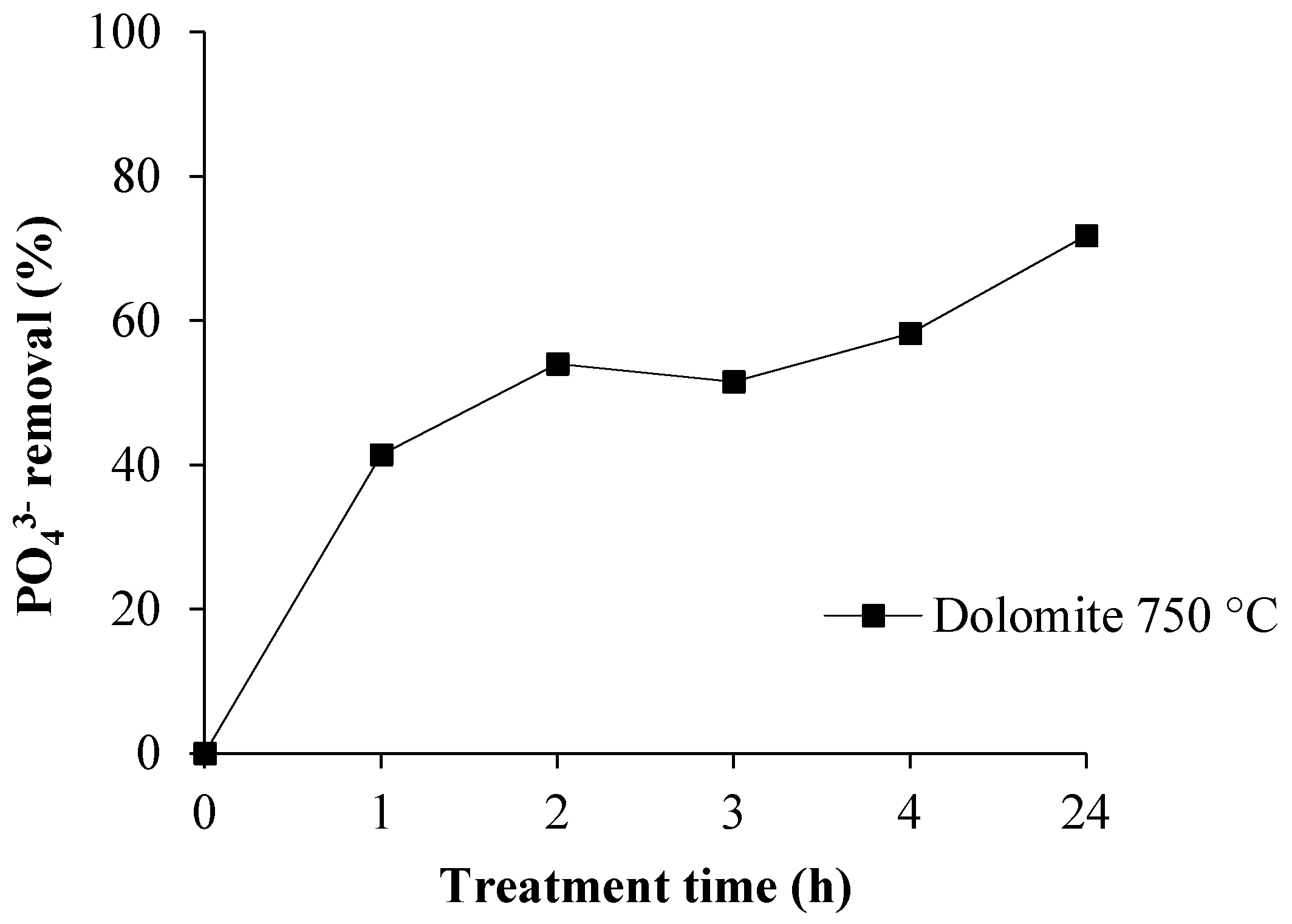
3.3. Phosphate Removal
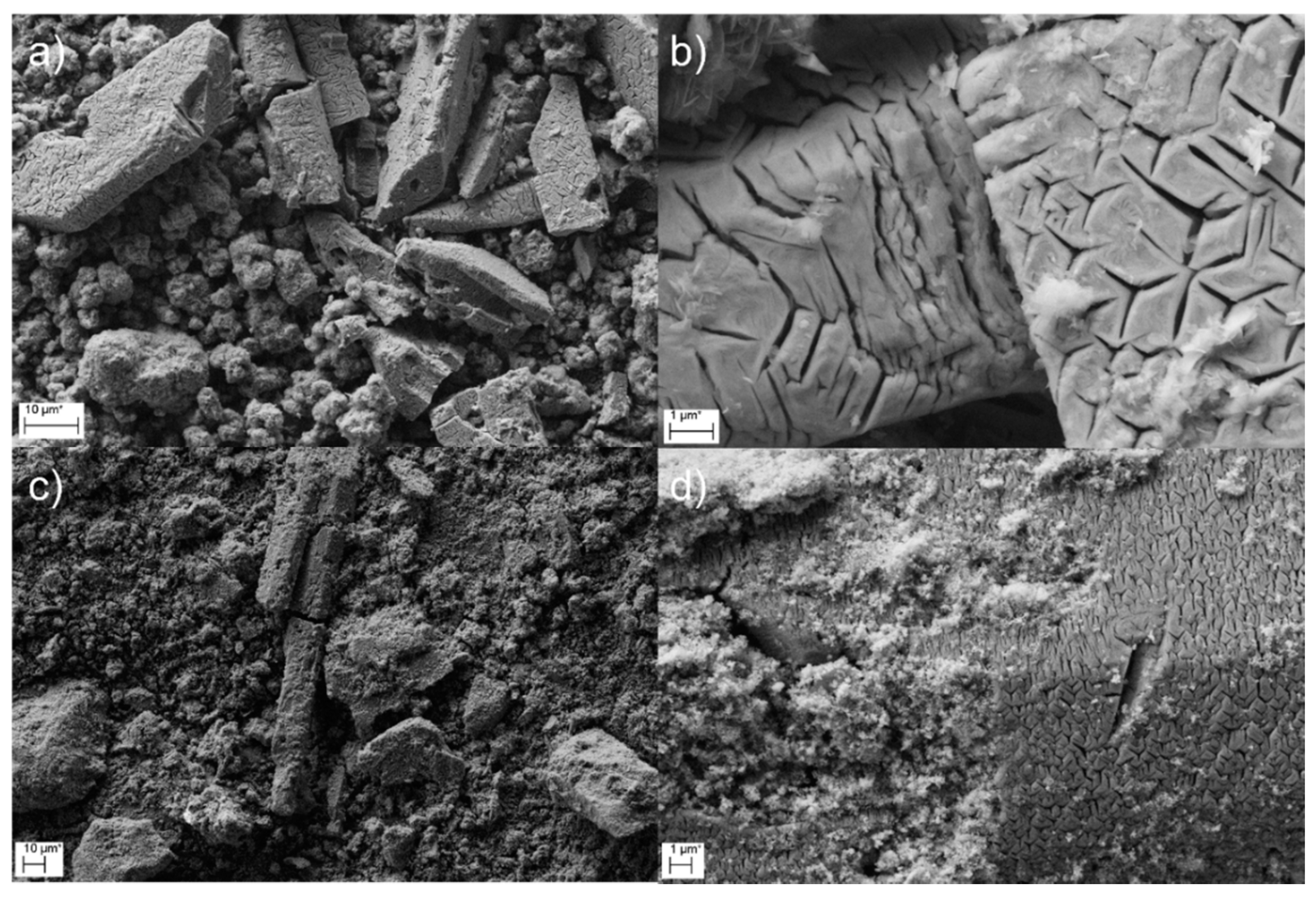
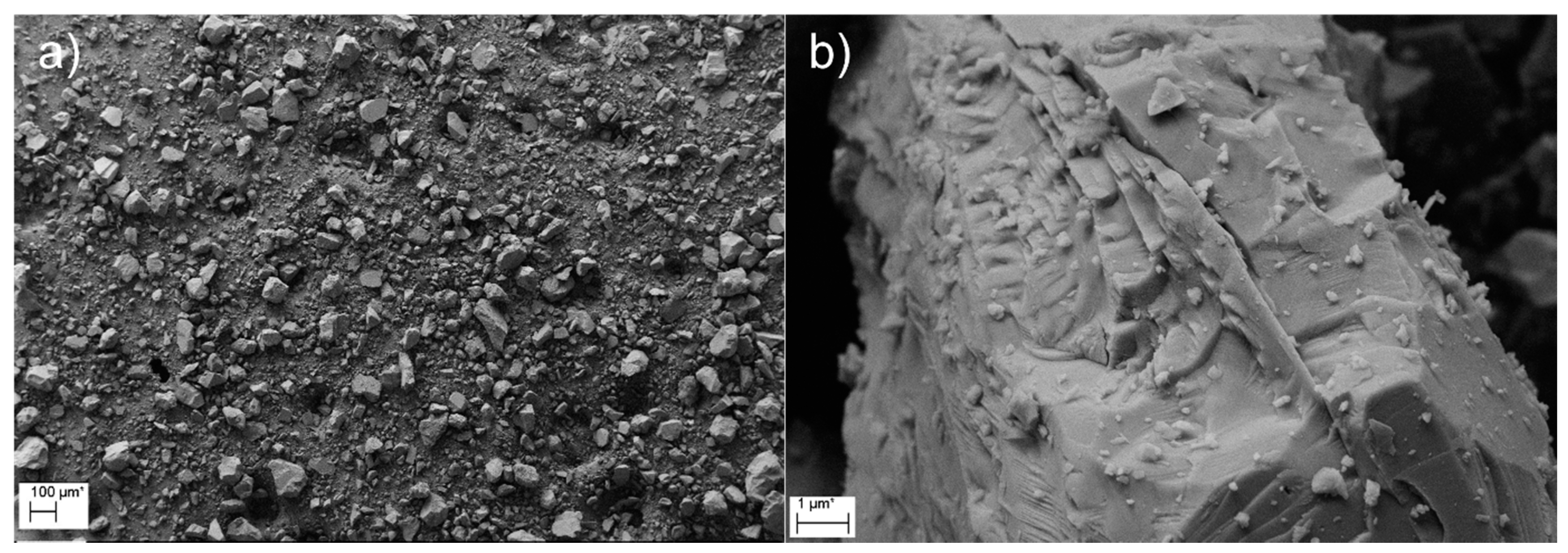
3.4. Characterization of the Precipitates
3.5. Agricultural Sludge
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rumble, J. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 99th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Proposal for a Regulation of the European Parliament and of the Council Laying down Rules on the Making Available on the Market of CE Marked Fertilising Products and Amending Regulations (EC) No 1069/2009 and (EC) No 1107/2009; European Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Aho, M.; Pursula, T.; Saario, M.; Miller, T.; Kumpulainen, A.; Päällysaho, M.; Autio, M.; Hillgren, A.; Descombes, L. Ravinteiden Kierron Taloudellinen Arvo ja Mahdollisuudet Suomelle; Sitran selvityksiä; Sitra: Helsinki, Finland, 2015; p. 50. [Google Scholar]
- Elvers, B. Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-3-527-30673-2. [Google Scholar]
- Herring, J.R.; Fantel, R.J. Phosphate rock demand into the next century: Impact on wolld food supply. Nat. Resour. Res. 1993, 2, 226–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.; Lombardi, R.; Boardman, D.; Carliell-Marquet, C. The future distribution and production of global phosphate rock reserves. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2011, 57, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benredjem, Z.; Delimi, R. Use of extracting agent for decadmiation of phosphate rock. Phys. Procedia 2009, 2, 1455–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Kumar, S.; Kwag, J.-H.; Ra, C. Magnesium ammonium phosphate formation, recovery and its application as valuable resources: A review. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 88, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunay, A.; Karadag, D.; Tosun, I.; Ozturk, M. Use of magnesit as a magnesium source for ammonium removal from leachate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 156, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.M.; Xiao, X.M.; Yang, L.P.; Yan, B. Removal of ammonium from rare-earth wastewater using natural brucite as a magnesium source of struvite precipitation. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 63, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siciliano, A.; Rosa, S.D. Recovery of ammonia in digestates of calf manure through a struvite precipitation process using unconventional reagents. Environ. Technol. 2014, 35, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Ding, L. Treatment of swine wastewater combined with MgO-saponification wastewater by struvite precipitation technology. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 254, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crutchik, D.; Sánchez, A.; Garrido, J.M. Simulation and experimental validation of multiple phosphate precipitates in a saline industrial wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 118, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Giannis, A.; Zhang, J.; Chang, V.W.-C.; Wang, J.-Y. Characterization of induced struvite formation from source-separated urine using seawater and brine as magnesium sources. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 2738–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakthivel, S.R.; Tilley, E.; Udert, K.M. Wood ash as a magnesium source for phosphorus recovery from source-separated urine. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 419, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Røsberg, I.; Frank, J.; Stuanes, A.O. Effects of liming and fertilization on tree growth and nutrient cycling in a Scots pine ecosystem in Norway. For. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 237, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Huang, H.; Zhang, P.; Gao, Z.; Zhao, N. Utilizing the supernatant of waste sulfuric acid after dolomite neutralization to recover nutrients from swine wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 337, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paszek, A.; Jarszek, H. Spent electrolyte from lead-acid battery utilization. Chemik 2012, 66, 1196–1202. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, C.H.; Zhang, H.; Tong, D.S.; Yu, W.H.; Yang, H.M.; Chu, M.Q. Capture and recycling of ammonium by dolomite-aided struvite precipitation and thermolysis. Chemosphere 2017, 187, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, R.K.; Fahmi, M.N.; Mat, A.H.; Zainal, A.A. The synthesis of hydroxyapatite through the precipitation method. Med. J. Malays. 2004, 59 (Suppl. B), 75–76. [Google Scholar]
- Olszak-Humienik, M.; Jablonski, M. Thermal behavior of natural dolomite. J. Anal. Calorim. 2015, 119, 2239–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry. Maa- ja Metsätalousministeriön Asetus Lannoitevalmisteista 24/11; Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry: Helsinki, Finland, 2011.
- Kuokkanen, T.; Pesonen, J.; Kaakinen, J.; Välimäki, I.; Illikainen, M. Comparison of standard methods for evaluating the metal concentrations in bio ash. Int. J. Environ. Waste Manag. 2017, 20, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, M.J. (Ed.) The Merck Index—An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs and Biologicals; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Sheng, X.; Dong, Y.; Ma, Y. Removal of high-concentration phosphate by calcite: Effect of sulfate and pH. Desalination 2012, 289, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.K. Hydration/dehydration characteristics of struvite and dittmarite pertaining to magnesium ammonium phosphate cement systems. J. Mater. Sci. 1991, 26, 2514–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Yang, J.; Ma, H.; Liu, C. Crystal structural transformation and kinetics of /Na+ ion-exchange in analcime. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 222, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukkonen, T.; Sarkkinen, M.; Kemppainen, K.; Rämö, J.; Lassi, U. Metakaolin geopolymer characterization and application for ammonium removal from model solutions and landfill leachate. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 119, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sample | CaO (%) | MgO (%) | SiO2 (%) | Al2O3 (%) | FeO (%) | P2O5 (%) | K2O (%) | Na2O (%) | S (%) | TiO2 (%) | Others (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dolomite | 50.6 | 27.4 | 15.3 | 1.3 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 3.5 |
| Sample | As (mg·kg−1) | Cd (mg·kg−1) | Cr (mg·kg−1) | Cu (mg·kg−1) | Ni (mg·kg−1) | Pb (mg·kg−1) | Zn (mg·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dolomite | 21 | <5 | 68 | 30 | 36 | 10 | 41 |
| Limit value field/forest fertilizers | 25/40 | 1.5/25 | 300 | 600/700 | 100/150 | 100/150 | 1500/4500 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pesonen, J.; Myllymäki, P.; Tuomikoski, S.; Vervecken, G.; Hu, T.; Prokkola, H.; Tynjälä, P.; Lassi, U. Use of Calcined Dolomite as Chemical Precipitant in the Simultaneous Removal of Ammonium and Phosphate from Synthetic Wastewater and from Agricultural Sludge. ChemEngineering 2019, 3, 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering3020040
Pesonen J, Myllymäki P, Tuomikoski S, Vervecken G, Hu T, Prokkola H, Tynjälä P, Lassi U. Use of Calcined Dolomite as Chemical Precipitant in the Simultaneous Removal of Ammonium and Phosphate from Synthetic Wastewater and from Agricultural Sludge. ChemEngineering. 2019; 3(2):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering3020040
Chicago/Turabian StylePesonen, Janne, Pekka Myllymäki, Sari Tuomikoski, Gwen Vervecken, Tao Hu, Hanna Prokkola, Pekka Tynjälä, and Ulla Lassi. 2019. "Use of Calcined Dolomite as Chemical Precipitant in the Simultaneous Removal of Ammonium and Phosphate from Synthetic Wastewater and from Agricultural Sludge" ChemEngineering 3, no. 2: 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering3020040
APA StylePesonen, J., Myllymäki, P., Tuomikoski, S., Vervecken, G., Hu, T., Prokkola, H., Tynjälä, P., & Lassi, U. (2019). Use of Calcined Dolomite as Chemical Precipitant in the Simultaneous Removal of Ammonium and Phosphate from Synthetic Wastewater and from Agricultural Sludge. ChemEngineering, 3(2), 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering3020040






