Modelling of Bubbly Flow Using CFD-PBM Solver in OpenFOAM: Study of Local Population Balance Models and Extended Quadrature Method of Moments Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Numerical Model
2.1. Population Balance Modeling
2.1.1. Class Methods
2.1.2. Quadrature-Based Moments Method
2.1.3. Quadrature Method of Moments
2.1.4. Direct Quadrature Method of Moments
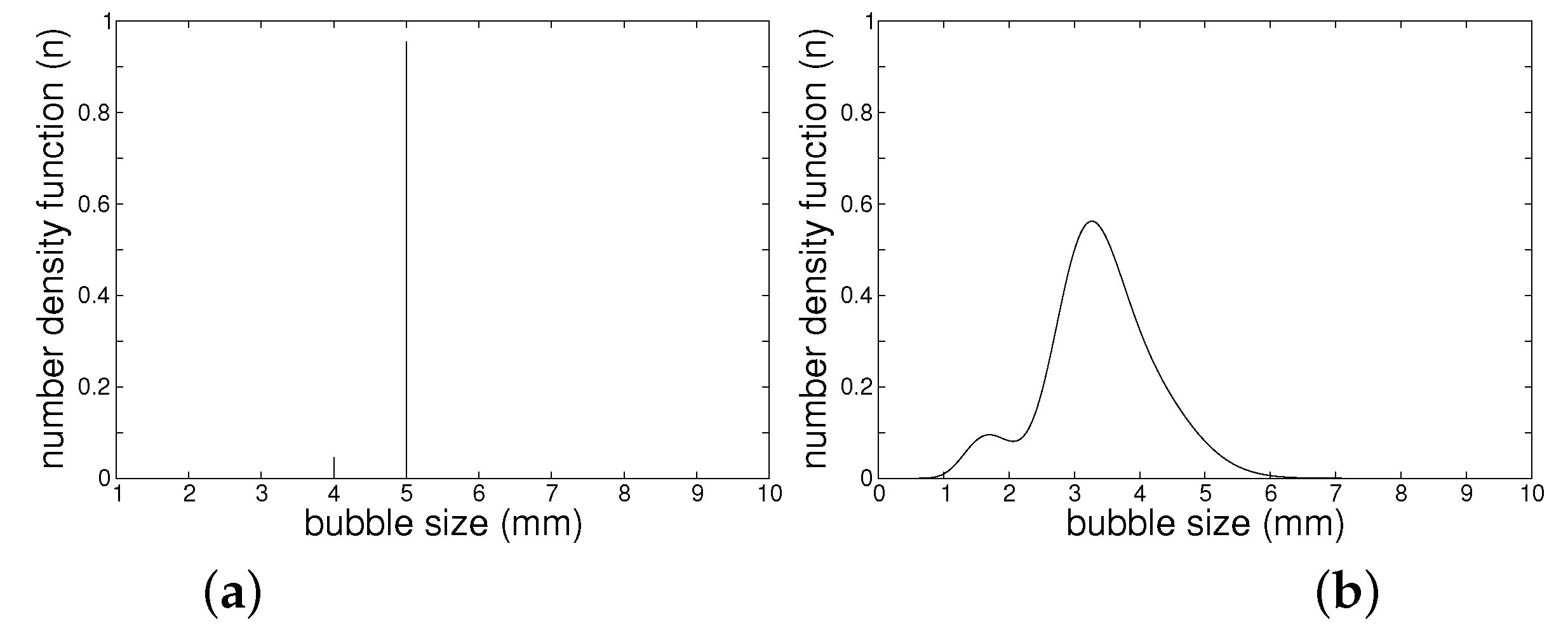
2.1.5. Extended Quadrature Method of Moments
2.1.6. Closure Models for Coalescence and Breakage
3. Numerical Solution
4. Results and Discussion
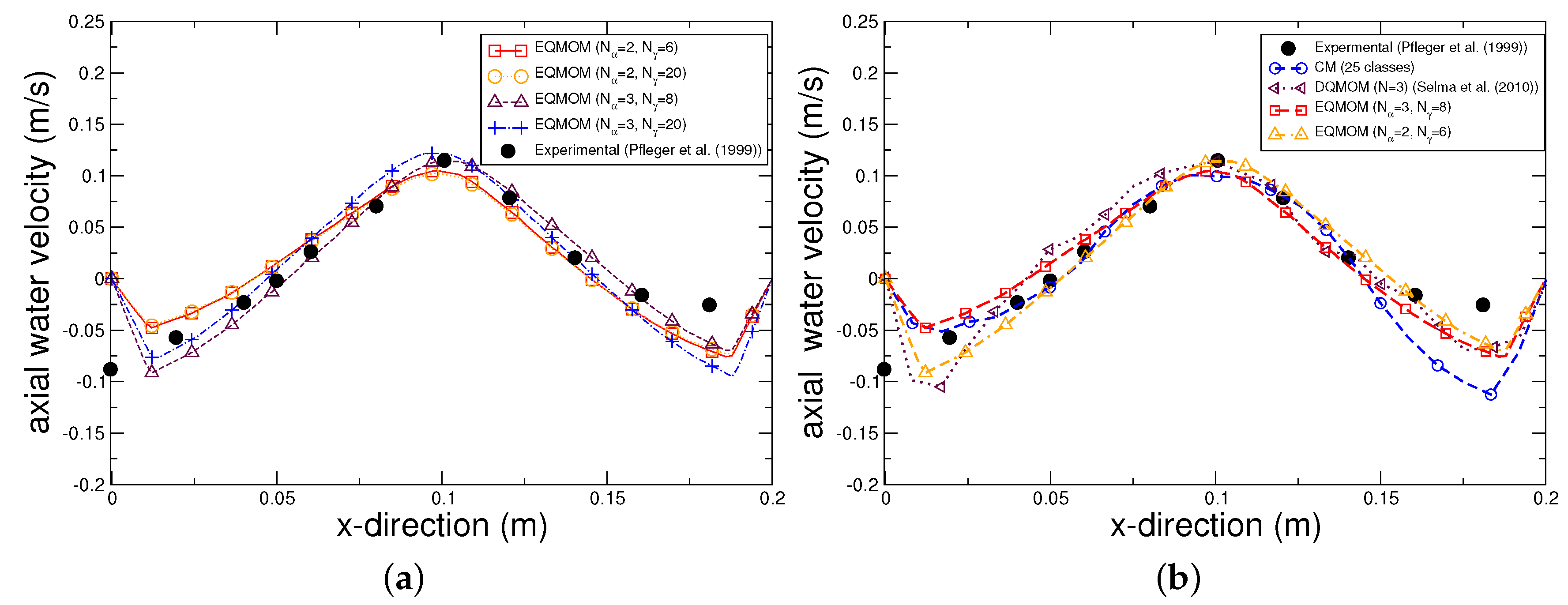
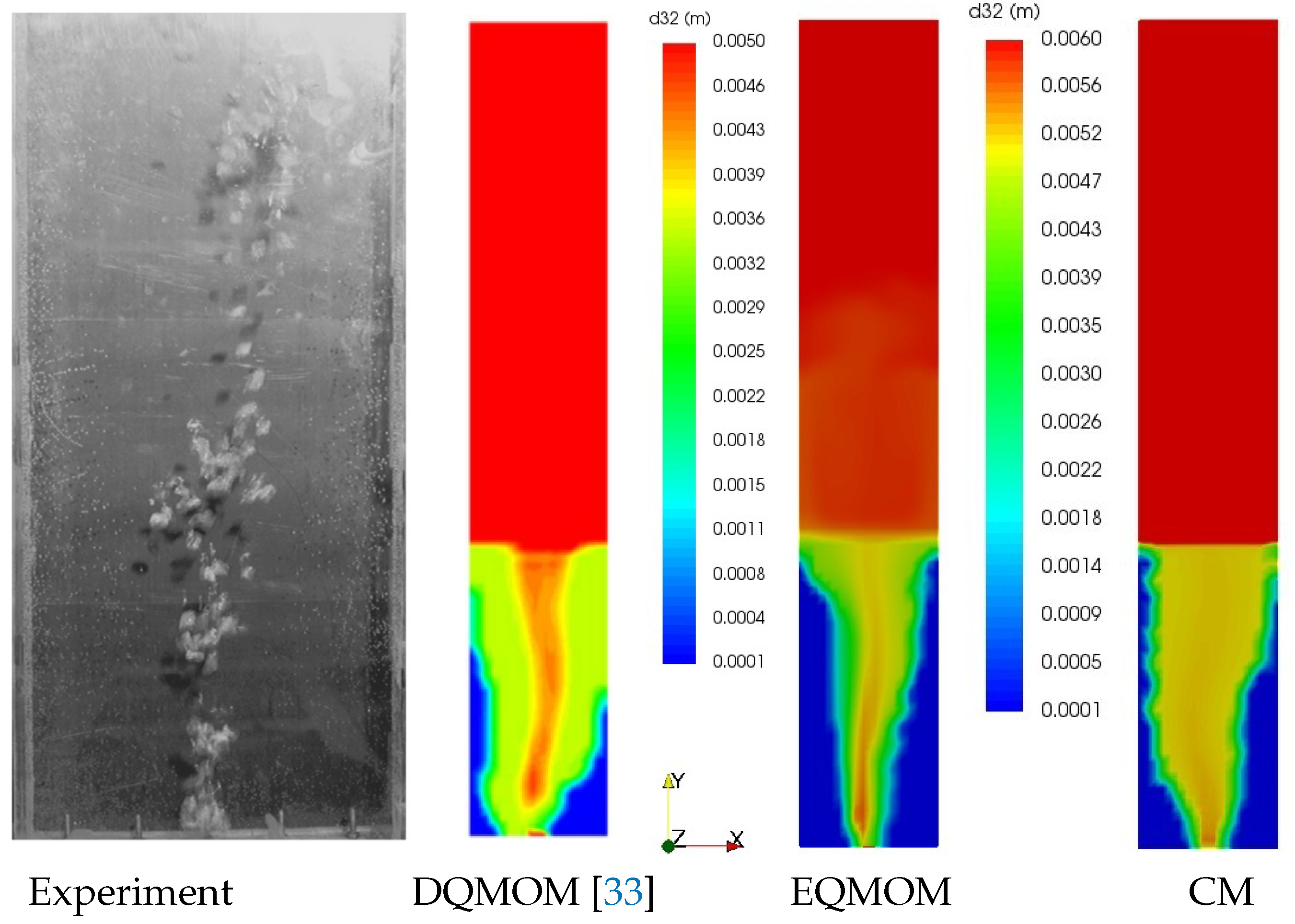
4.1. Test Case 1: Pseudo-2D Bubble Column
4.2. Test Case 2: 3D Bubble Column
4.3. Test Case 3: Water Electrolysis Reactor
- Reference electrode: Ag/AgCl saturated with KCl
- Counter electrode: platinum grid
- Working electrode (rotating electrode): made by embedding a platinum rod in an insulating Poly Vinylidene Fluoride (PVFD) cylinder.
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Symbols | ||
| breakage kernel | s | |
| B | birth | m s |
| break-up frequency function | s | |
| drag coefficient | − | |
| lift coefficient | − | |
| virtual mass coefficient | − | |
| increase coefficient of surface area | ||
| D | death | m s |
| d | bubble diameter | m |
| Sauter mean diameter | m | |
| Eotvos number | − | |
| f | friction coefficient for flow around bubbles | − |
| volume fraction of bubble class i | − | |
| volumetric force | N m | |
| acceleration vector due to gravity | m s | |
| unit tensor | ||
| k | turbulent kinetic energy | j kg |
| L | bubble size | m |
| mean number of daughter produced by breakage | − | |
| n | number density of bubbles | m |
| N | angular velocity | rad s |
| p | pressure | Pa |
| coalescence efficiency or collision probability | − | |
| pressure | N m | |
| position vector | m | |
| interphase force | N m | |
| Reynolds number | − | |
| Reynolds (turbulent) and viscous stress | m s | |
| t | Time | s |
| average velocity of phase | m s | |
| bubble approaching turbulent velocity | m s | |
| Weber number | − | |
| Greek Symbols | ||
| Volume fraction | − | |
| constant | or s | |
| coalescence rate | s | |
| Turbulent kinetic energy dissipation rate | m s | |
| collision frequency | m s | |
| dynamic viscosity of the continuous phase | N/m | |
| eddy size | m | |
| density | kg/m | |
| surface tension or variance | Nm or m | |
| internal variable | − | |
| breakage frequency | s | |
| bubble size or kinematic viscosity | m or m | |
| size ratio | ||
| incomplete Gamma function | − | |
| diameter ratio | ||
| stress tensor | kg m s | |
| Subscripts | ||
| aggregation | ||
| breakage | ||
| effective | ||
| G | gas phase | |
| L | liquid phase | |
| m | mixture | |
| i | phase number | |
| laminar | ||
| t | turbulent |
References
- Bannari, R.; Kerdouss, F.; Selma, B.; Bannari, A.; Proulx, P. Three dimensional mathematical modeling of dispersed two-phase flow using class method of population balance in bubble columns. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2008, 32, 3224–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusche, H. Computational Fluid Dynamics of Dispersed Two-Phase Flows at High Phase Fractions. Ph.D. Thesis, University of London, London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Nierhaus, T. Modeling and Simulation of Dispersed Two-Phase Flow Transport Phenomena in Electrochemical Processes. Ph.D. Thesis, Universiteit Brussel, Brussels, Belgium, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Karimi, M.; Droghetti, H.; Marchisio, D. PUFoam: A novel open-source CFD solver for the simulation of polyurethane foams. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2017, 217, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequira, C.A.C.; Santos, D.M.F.; Sljukie, B.; Amaral, L. Physics of electrolytic gas evolution. Braz. J. Phys. 2013, 43, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leahy, M.J.; Phillip Schwarz, M. Modeling Natural Convection in Copper Electrorefining: Describing Turbulence Behavior for Industrial-Sized Systems. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2011, 42, 875–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leahy, M.J.; Philip Schwarz, M. Experimental Validation of a Computational Fluid Dynamics Model of Copper Electrowinning. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2010, 41, 1247–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leahy, M.J.; Philip Schwarz, M. Computational Fluid Dynamics Modelling of Natural Convection in Copper Electrorefining. In Proceedings of the 16th Australasian Fluid Mechanics Conference, Gold Coast, Australia, 2–7 December 2007; pp. 112–116. [Google Scholar]
- Deen, N.G.; Solberg, T.; Hjertager, B.H. Flow generated by an aerated Rushton impeller: Two-phase PIV Experiments and numerical simulations. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2002, 80, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzinger, G. Eulerian Two-Phase Simulation of the Floating Process with OpenFOAM. Ph.D. Thesis, Johannes Kepler Universitat Linz, Linz, Austria, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Friberg, P.C. Three-Dimensional Modeling and Simulations of Gas-Liquid Flows Processes in Bioreactors. Ph.D. Thesis, Telemark Institute of Technology, Bø, Norway, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Morud, K.E.; Hjertager, B.H. LDA measurements and CFD modeling of gas-liquid flow in a stirred vessel. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1996, 51, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranade, V.V.; Deshpande, V.R. Gas-liquid flow in stirred vessels: Trailing vortices and gas accumulation behind impeller blades. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1999, 54, 2305–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranade, V.V. An efficient computational model for simulating flow in stirred vessels: A case of Rushton Turbine. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1997, 52, 4473–4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, M.P.; Turner, W.J. Applicability of the standard k-e turbulence model to gas-stirred baths. Appl. Math. Model. 1988, 12, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, M.P. Simulation of gas injection into liquid melts. Appl. Math. Model. 1996, 20, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresta, S.M.; Etchells, A.W., III; Dickey, D.S.; Atiemo-Obeng, V.A. Advances In Industrial Mixing; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kerdouss, F.; Bannari, A.; Proulx, P. CFD modeling of gas dispersion and bubble size in a double turbine stirred tank. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2006, 61, 3313–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, M.; Kim, S.; Uhle, J. Interfacial area transport equation: Model development and benchmark experiments. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2002, 45, 3111–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanasekharan, K.; Sanyal, J.; Jain, A.; Haidari, A. A generalize approach to model oxygen transfer in boreactors using population balances and computational fluid dynamics. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2005, 60, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venneker, B.C.H.; Derksen, J.J.; Van den Akker, H.E.A. Population balance modeling of aerated stirred vessels based on CFD. AIChE J. 2002, 48, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakin, B.V.; Hoffmann, A.C.; Kosinski, P. Coupling STAR-CD with a population balance technique based on the classes method. Powder Technol. 2014, 257, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, P.J.; Puel, F.; Henry, R.; Sheibat-Othman, N. Investigation of discrete population balance models and breakage kernels for dilute emulsification systems. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 11358–11374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Ramkrishna, D. On the solution of population balance equations by discretization-I. A fixed pivot technique. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1996, 51, 1311–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Ramkrishna, D. On the solution of population balance equations by discretization-II. A moving pivot technique. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1996, 51, 1333–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puel, F.; Fvotte, G.; Klein, J.P. Simulation and analysis of industrial crystal-lization processes through multidimensional population balance equations. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2003, 58, 3715–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGraw, R. Description ofaerosol dynamics by the quadrature method ofmoments. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 1997, 27, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchisio, D.L.; Vigil, R.D.; Fox, R.O. Quadrature method of moments for aggregation-breakage processes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 258, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchisio, D.L.; Pikturna, J.T.; Fox, R.O.; Vigil, R.D. Quadrature method of moments for population-balance equations. AIChE J. 2003, 49, 1266–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchisio, D.L.; Vigil, R.D.; Fox, R.O. Implementation of the quadrature method of moments in CFD codes for aggregation-breakage problems. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2003, 139, 3337–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, J.; Marchisio, D.L.; Fox, R.O.; Dhanasekharan, K. On the comparaison between population balance models for CFD simulation of bubble columns. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 5063–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.; Lage, P. Development and implementation of a polydispersed multiphase model in OpenFOAM. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2011, 35, 2653–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selma, B.; Bannari, R.; Proulx, P. Simulation of bubbly flows: Comparison between direct quadrature method of moments (DQMOM) and method of classes. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 1925–9141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchisio, D.L.; Fox, R.O. Solution of population balance equations using the direct quadrature method of moments. J. Aerosol Sci. 2005, 36, 43–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, R.; Laurant, F.; Massot, M. Numerical simulation of spray coalescence in an Eulerian framework: Direct quadrature method of moments and multi-fluid method. J. Comput. Phys. 2008, 227, 3058–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Laurant, F.; Fox, R.O. An extended quadrature method of moments for population balance equations. J. Aerosol Sci. 2012, 32, 1111–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Gao, Z.; Buffo, A.; Podgorska, W.; Marchisio, D.L. Droplet breakage and coalescence in liquid-liquid dispersions: Comparison of different kernels with EQMOM and QMOM. AIChE J. 2017, 63, 2293–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimbun, J.; Rielly, C.D.; Nagy, Z.K. Modelling of mass transfer in gas-liquid stirred tanks agitated by Rushton turbin and CD-6 impeller: A scale up study. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2017, 87, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Roy, S. Euler–Euler simulation of bubbly flow in a rectangular bubble column: Experimental validation with Radioactive Particle Tracking. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 225, 818–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askari, E.; Lemieux, G.S.P.; Vieira, C.B.; Litrico, G.; Proulx, P. Simulation of Bubbly Flow and Mass Transfer in a Turbulent Gas-Liquid Stirred Tank with CFD-PBM solver in OpenFOAM: EQMOM applicationg. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference of Numerical Analysis and Applied Mathematics, Thessaloniki, Greece, 25–30 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- OpenQBMM. An open-source implementation of Quadrature-Based Moment Methods. Zenodo 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiller, L.; Naumann, Z. A drag coefficient correlation. Z. Ver. Deutsch. Ing. 1935, 77, 318–320. [Google Scholar]
- Ishii, M.; Zuber, N. Drag coefficient and relative velocity in bubbly, droplet or particulate flows. AIChE J. 1979, 25, 843–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomiyama, A.; Celata, G.; Hosokawa, S.; Yoshida, S. Terminal velocity of single bubbles in surface tension force dominant regime. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2002, 28, 1497–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behzadi, B.; Issa, R.I.; Rusche, H. Modelling of dispersed bubble and droplet flow at high phase fractions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2004, 59, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Svendsen, H.F. Theoretical model for drop and bubble breakup in turbulent dispersions. AIChE J. 1996, 42, 1225–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagesather, L.; Jakobsen, H.A.; Hjarbo, K.; Svendsen, H.F. A coalescence and breakup module for implementation in CFD codes. Comput. Aided Chem. Eng. 2000, 8, 367–372. [Google Scholar]
- Saffman, P.G.; Turner, J.S. On the collision of drops in turbulent clouds. J. Fluid Mech. 1956, 1, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchisio, D.L.; Fox, R.O. Multiphase Reacting Flows: Modelling and Simulation; Springer: NewYork, NU, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ramkrishna, D. Population Balances; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, F. Homogeneous Nucleation Theory; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Tomasoni, F. Non-Intrusive Assessment of Transport Phenomena at Gas-Evolving Electrodes. Ph.D. Thesis, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Brussels, Belgium, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, S. Application of Population Balance to CFD Modeling of Bubbly Flow via the MUSIG Model; AEA Technology: Harwell, UK, 1996; p. 1096. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, C.; Kong, B.; Passalacqua, A.; Fox, R.O. An extended quadrature-based mass-velocity moment model for polydisperse bubbly flows. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2014, 92, 2053–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Marchisio, D.L.; Fox, R.O. Application of the direct quadrature method of moments to polydisperse gas–solid fluidized beds. Powder Technol. 2004, 139, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bove, S. Computational Fluid Dynamics of Gas–Liquid Flows Including Bubble Population Balances. Ph.D. Thesis, Aalborg University, Aalborg, Denmark, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Laurent, F.; Fox, R.O.; Massot, M. Solution of population balance equations in applications with fine particles: Mathematical modeling and numerical schemes. J. Comput. Phys. 2016, 325, 129–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madadi-Kandjani, E.; Passalacqua, A. An extended quadrature-based moment method with log-normal kernel density functions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 131, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerdouss, F.; Bannari, A.; Proulx, P. Two-phase mass transfer coefficient prediction in stirred vessel with a CFD model. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2007, 32, 1943–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerdouss, F.; Kiss, L.; Proulx, P.; Bilodeau, J.F.; Dupuis, C. Mixing Characteristics of an axial flow rotor: Experimental and numerical study. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. 2005, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OpenFOAM 4.0; The OpenFOAM Foundation: London, UK, 2017.
- Pfleger, D.; Gomes, S.; Gilbert, N.; Wagner, H.G. Hydrodynamic simulations of laboratory scale bubble columns. Fundamental studies of the Eulerian–Eulerian modeling approach. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1999, 54, 5091–5099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buwa, V.V.; Deo, D.S.; Ranade, V.V. Eulerian–Lagrangian simulations of unsteady gas–liquid flows in bubble columns. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2006, 32, 864–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deen, N.G. An Experimental and Computational Study of Fluid Dynamics in Gas-Liquid Chemical Reactors. Ph.D. Thesis, Aalborg University Esbjerg, Esbjerg, Denmark, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Van Parys, H.; Tourwe, E.; Breugelmans, T.; Depauw, M.; Deconinck, J.; Hubin, A. Modeling of mass and charge transfer in an inverted rotating disk electrode (IRDE) reactor. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2009, 622, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nierhaus, T.; Parys, H.V.; Dehaeck, S.; Beeck, J.V.; Deconinck, H.; Deconinck, J.; Hubinc, A. Simulation of the Two-Phase Flow Hydrodynamics in an IRDE Reactor. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2009, 156, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SuperMarine. Available online: https://github.com/Spationaute/SuperMarine (accessed on 8 January 2018).
- Cochran, W.G. The flow due to a rotating disc. Math. Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 1934, 30, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
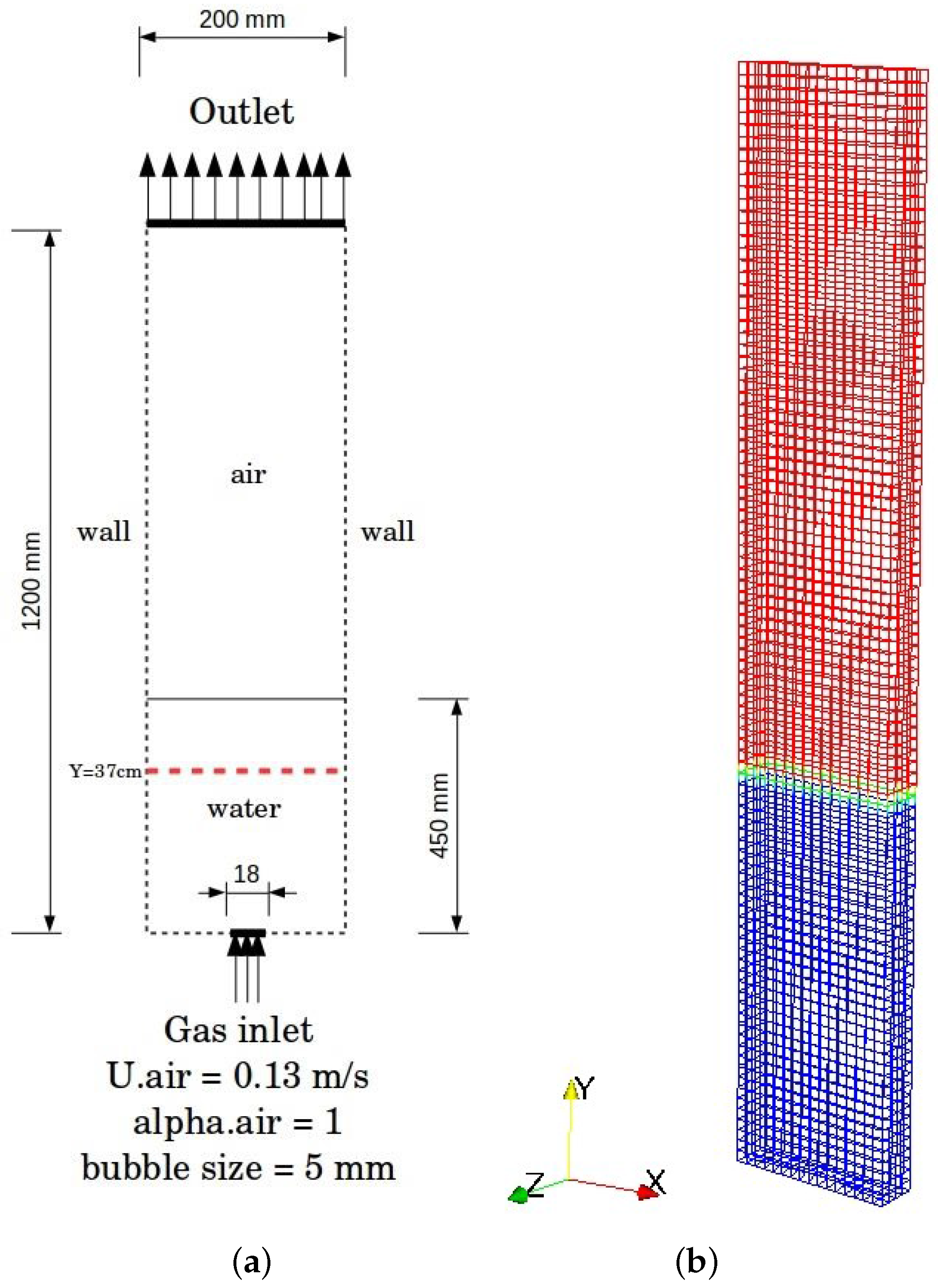
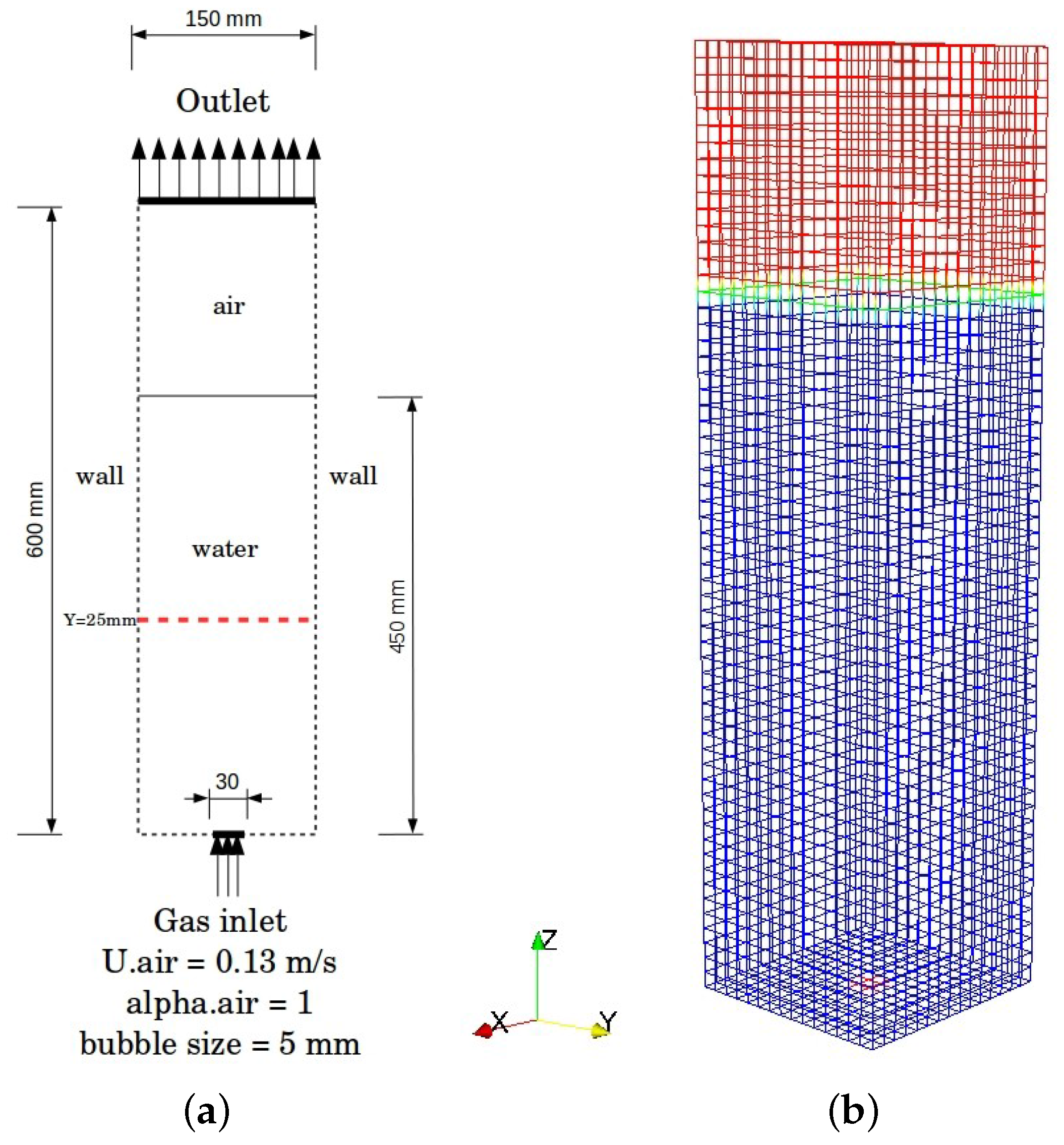
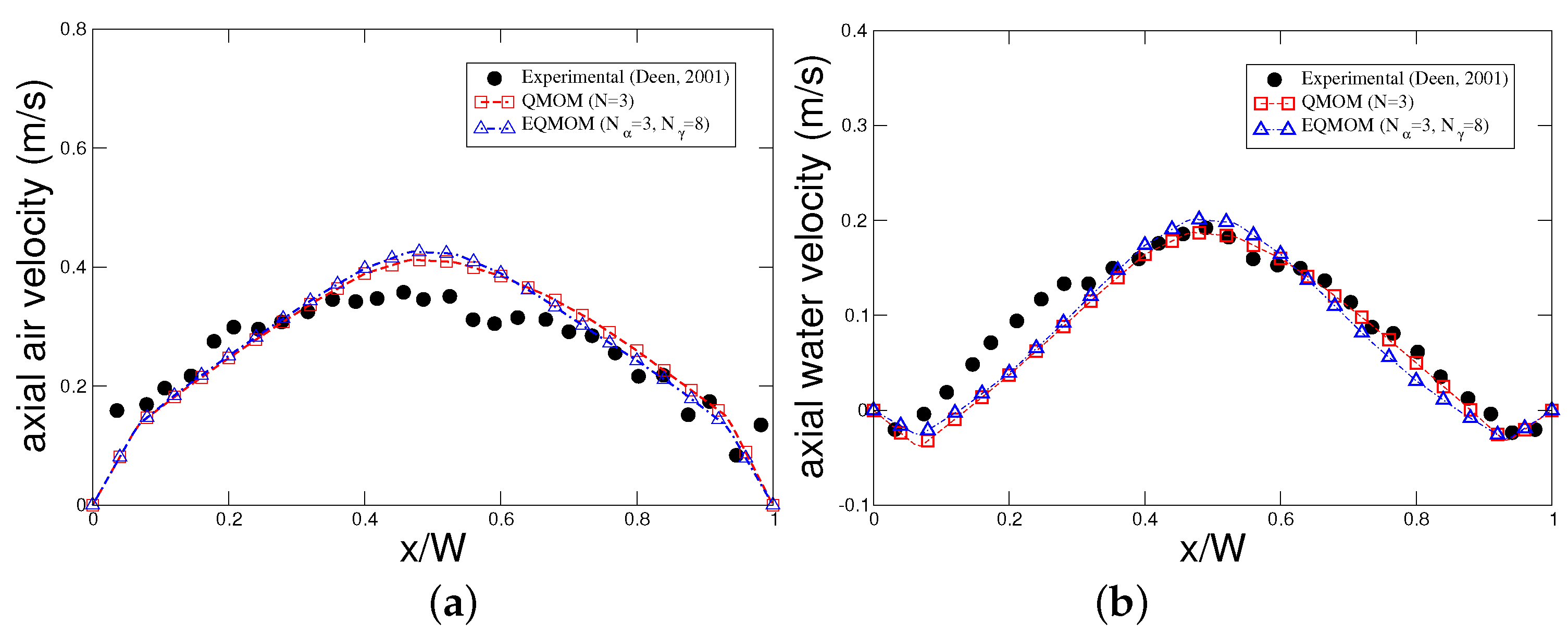
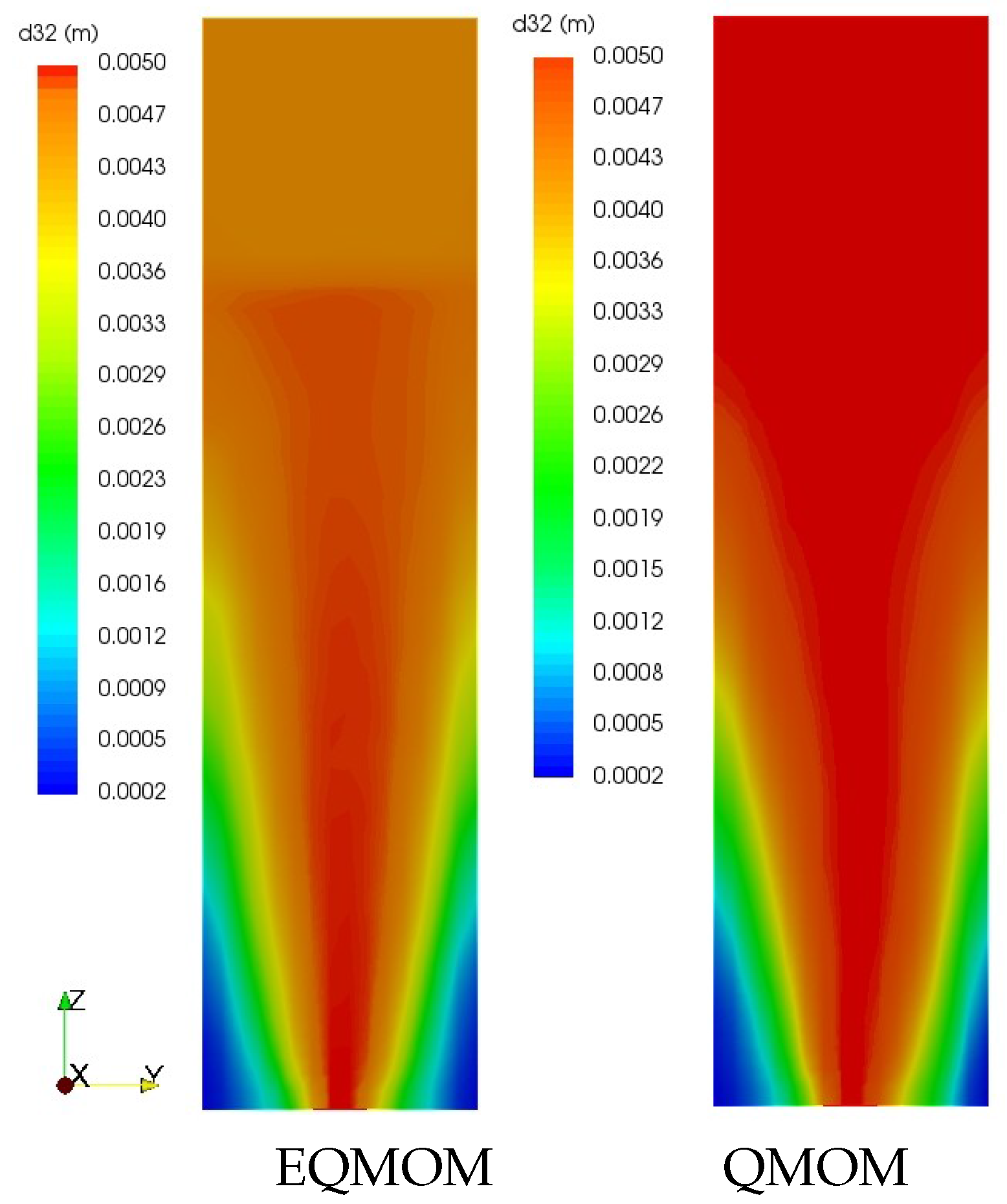
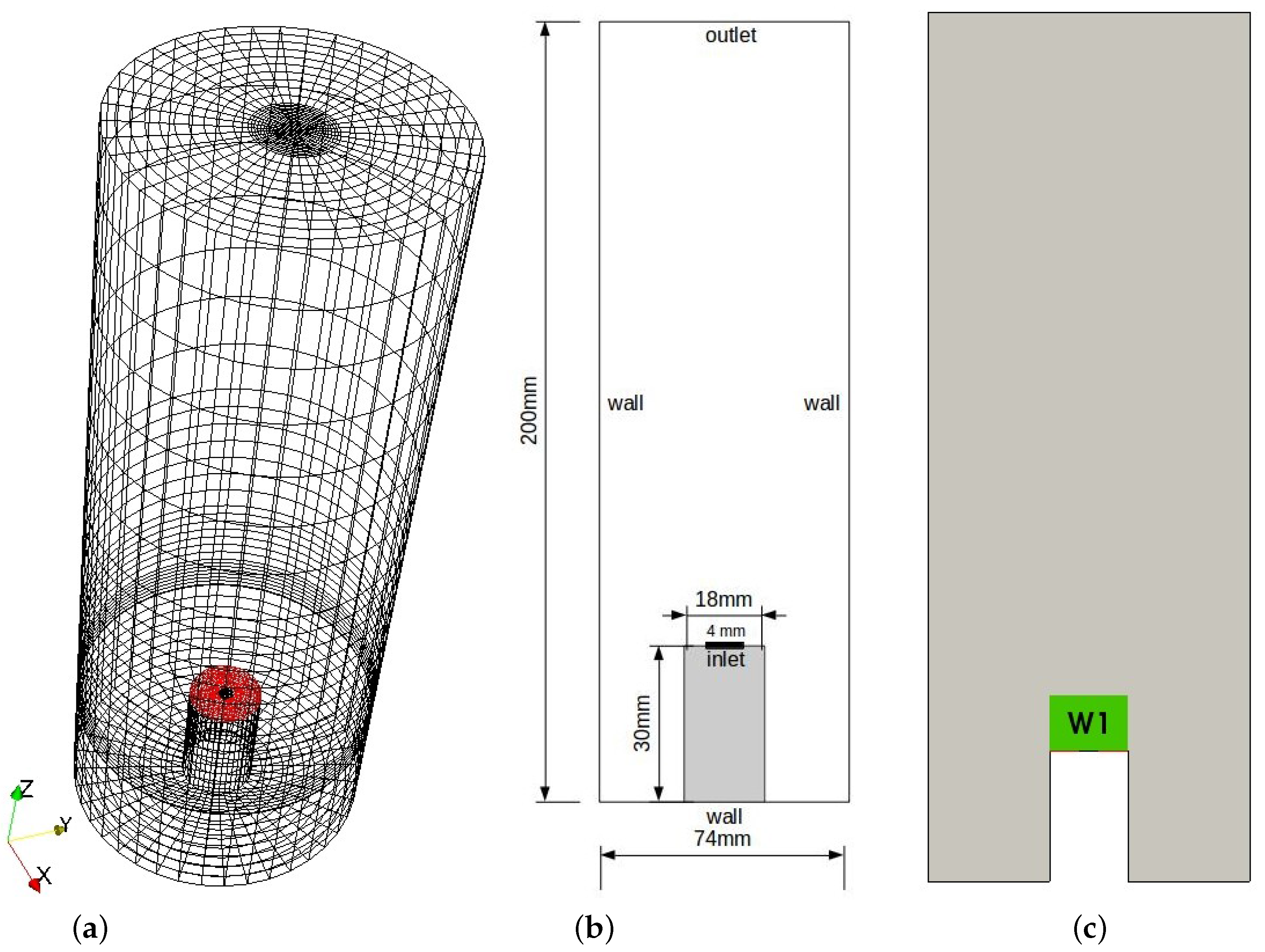
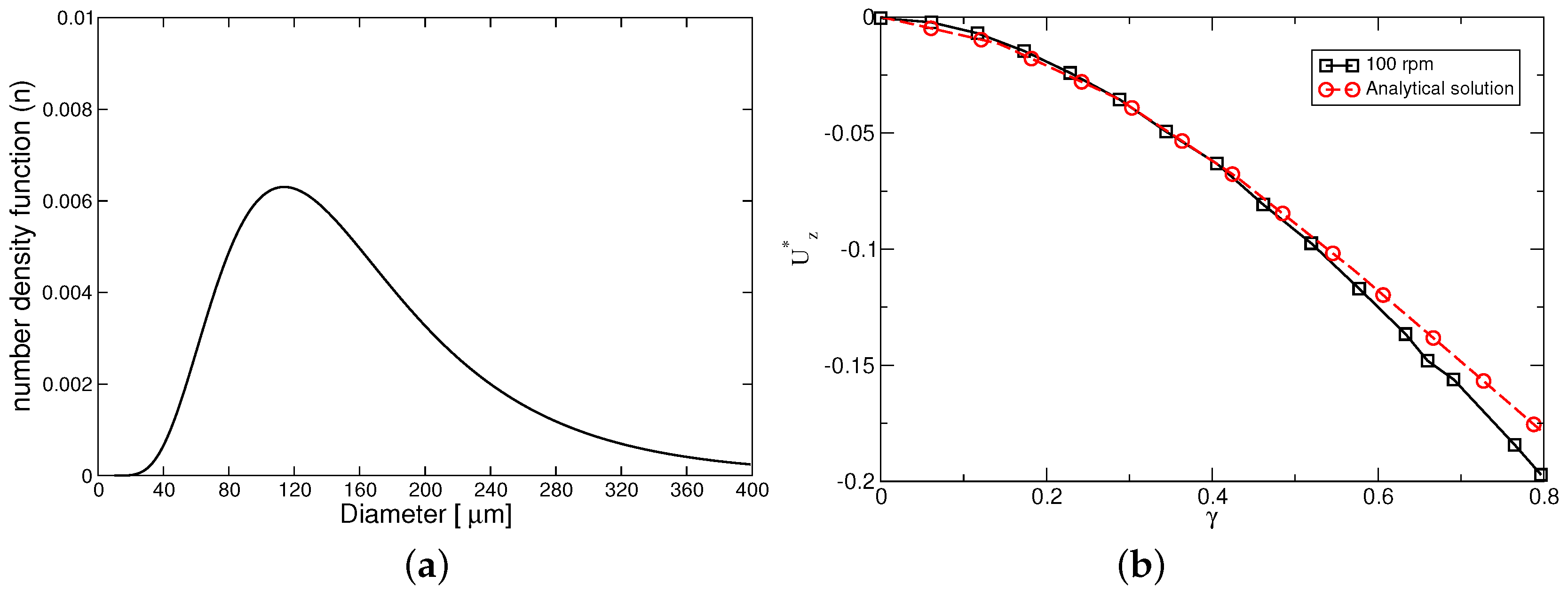
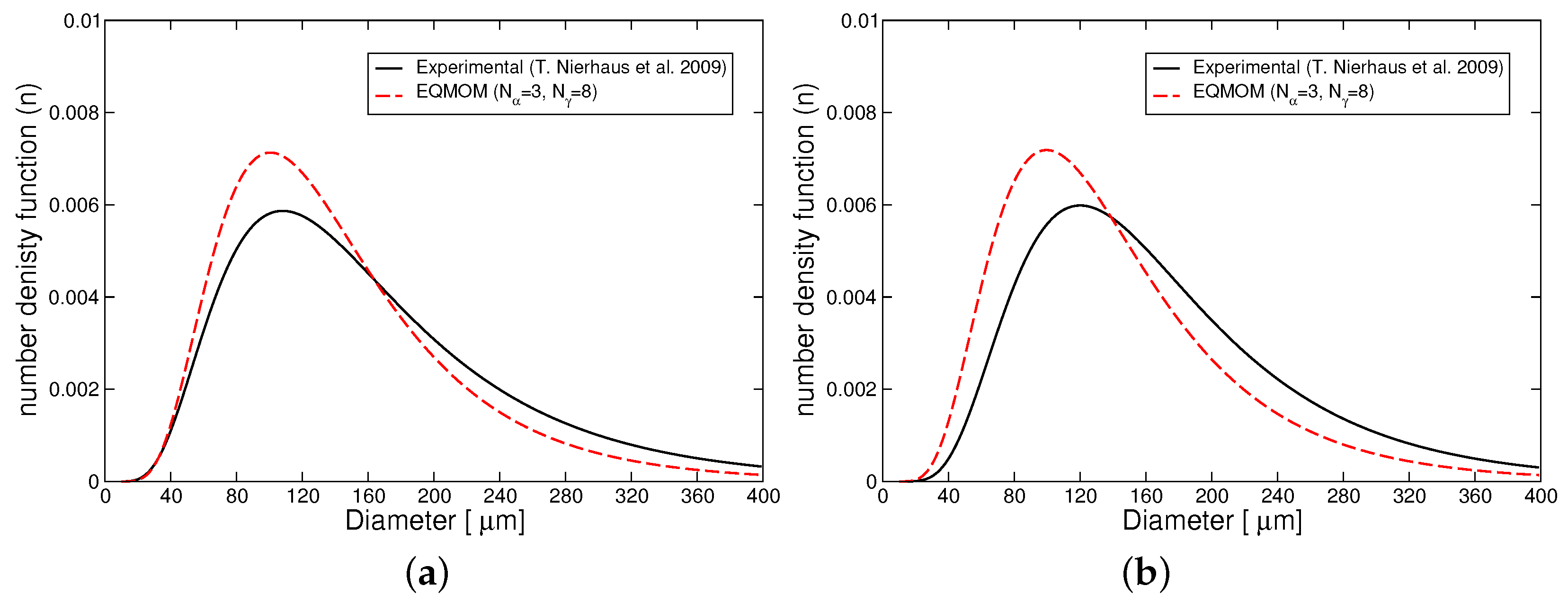
| Reference | Test Case | PBM | Hypotheses | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bannari et al. [1] | bubble column | CM | accumulation, advection, coalescence, breakage | Constant mean bubble size does not give satisfactory results compared to those based on PBM; 25 classes give better results |
| Gimbun et al. [38] | gas-liquid stirred tank | QMOM | accumulation, coalescence, breakage | Better agreement is achieved using PBM compared to a uniform bubble size |
| Li et al. [37] | liquid-liquid stirred tank | EQMOM and QMOM | accumulation, advection, coalescence, breakage | Similar predictions for EQMOM and QMOM; EQMOM provides a continuous BSD |
| Selma et al. [33] | gas-liquid stirred tank; bubble column | DQMOM and CM | accumulation, advection, coalescence, breakage | High number of classes is required; CM is computationally heavy; DQMOM is much more efficient (computationally) compared to CM |
| Gupta and Roy [39] | bubble column | DQMOM and QMOM | accumulation, coalescence, breakage | A summary of studies done on bubble columns flow modeling using PBM; no significant difference between DQMOM and QMOM |
| Askari et al. [40] | gas-liquid stirred tank | EQMOM | accumulation, coalescence, breakage | The agreement between experimental data and simulation results using EQMOM; reconstruction of bubble size distribution |
| PBM | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| CM | Intuitive and accurate | Computationally intensive |
| QMOM | Wide range of bubble sizes with a reduced computational cost | Disabled in case of null internal coordinates |
| DQMOM | Wide range of bubble sizes with a reduced computational cost | Shortcomings related to non-conservative quantities (weights and abscissas) |
| EQMOM | Wide range of bubble sizes with a reduced computational cost (ONLYcompared to CM) and reconstruction capability of continuous NDF | Heavy computation compared to QMOM and DQMOM |
| Equation | Formulation |
|---|---|
| Continuity (single-phase) | |
| Momentum (single-phase) | |
| Continuity (multi-phase) | |
| Reynolds stress tensor | |
| Momentum (multi-phase) | |
| Interfacial momentum exchange | |
| Liquid-gas exchange coefficient | |
| Schiller–Naumann drag coefficient [42] | |
| Ishii–Zuber drag coefficient [43] | |
| Tomiyama lift coefficient [44] | |
| Mixture k- model [45] | |
| Break-up rate function [46] | |
| Coalescence rate [47] | |
| Coalescence frequency [48] | |
| Coalescence efficiency [47] |
| Number of Classes | 7 | 11 | 15 | 25 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value of r | 3 | 5 | 7 | 12 |
| Value of s | 2 | 1.5157 | 1.3459 | 1.1892 |
| 0 |
| Boundary Conditions | Initial Condition | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Inlet | Wall | Outlet | Inlet value |
| Neumann | Neumann | ||
| Boundary Conditions | Initial Condition | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Inlet | Wall | Outlet | Inlet value |
| Equation (32) | Neumann | Neumann | |
| Boundary Conditions | Initial Condition | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Inlet | Wall | Outlet | Inlet value |
| and corresponding to | Neumann | Neumann | |
| Settings | Model |
|---|---|
| Two-phase flow | Two-fluid model (TFM) |
| Drag | Schiller and Naumann [42] |
| Lift | Tomiyama et al. [44] |
| Virtual mass | [33] |
| Turbulence | Standard k- model |
| Population balance | CM and EQMOM |
| Coalescence | Hagesather et al. [47] |
| Breakage | Luo and Svendsen [46] |
| Boundary Conditions | Initial Condition | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Inlet | Wall | Outlet | Inlet value |
| Neumann | Neumann | ||
| Boundary Conditions | Initial Condition | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Inlet | Wall | Outlet | Inlet value |
| Neumann | Neumann | ||
| Boundary Conditions | Initial Condition | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Inlet | Wall | Outlet | |
| Neumann | Neumann | ||
| Settings | Model |
|---|---|
| Two-phase flow | Two-fluid model |
| Drag | Ishii and Zuber [43] |
| Lift | |
| Virtual mass | |
| Turbulence | Behzadi et al. [45] |
| Population balance | EQMOM and QMOM |
| Coalescence | Hagesather et al. [47] |
| Breakage | Luo and Svendsen [46] |
| Settings | Model |
|---|---|
| single-phase flow | - |
| laminar | - |
| population balance | EQMOM |
| coalescence | no |
| breakage | no |
| Boundary Conditions | Initial Condition | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Inlet | Wall | Outlet | Inlet value |
| Neumann | Neumann | ||
| Case | DQMOM [33] | CM (25 Classes) | QMOM (n = 3) | EQMOM (n = 2) | EQMOM (n = 3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test Case 1 | 1 | 5 | - | 1.3 | 1.4 |
| Test Case 2 | - | - | 1 | - | 1.5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Askari, E.; Proulx, P.; Passalacqua, A. Modelling of Bubbly Flow Using CFD-PBM Solver in OpenFOAM: Study of Local Population Balance Models and Extended Quadrature Method of Moments Applications. ChemEngineering 2018, 2, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering2010008
Askari E, Proulx P, Passalacqua A. Modelling of Bubbly Flow Using CFD-PBM Solver in OpenFOAM: Study of Local Population Balance Models and Extended Quadrature Method of Moments Applications. ChemEngineering. 2018; 2(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering2010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleAskari, Ehsan, Pierre Proulx, and Alberto Passalacqua. 2018. "Modelling of Bubbly Flow Using CFD-PBM Solver in OpenFOAM: Study of Local Population Balance Models and Extended Quadrature Method of Moments Applications" ChemEngineering 2, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering2010008
APA StyleAskari, E., Proulx, P., & Passalacqua, A. (2018). Modelling of Bubbly Flow Using CFD-PBM Solver in OpenFOAM: Study of Local Population Balance Models and Extended Quadrature Method of Moments Applications. ChemEngineering, 2(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering2010008





