Flood–Ebb and Discharge Variations in Observed Salinity and Suspended Sediment in a Mesotidal Estuary
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
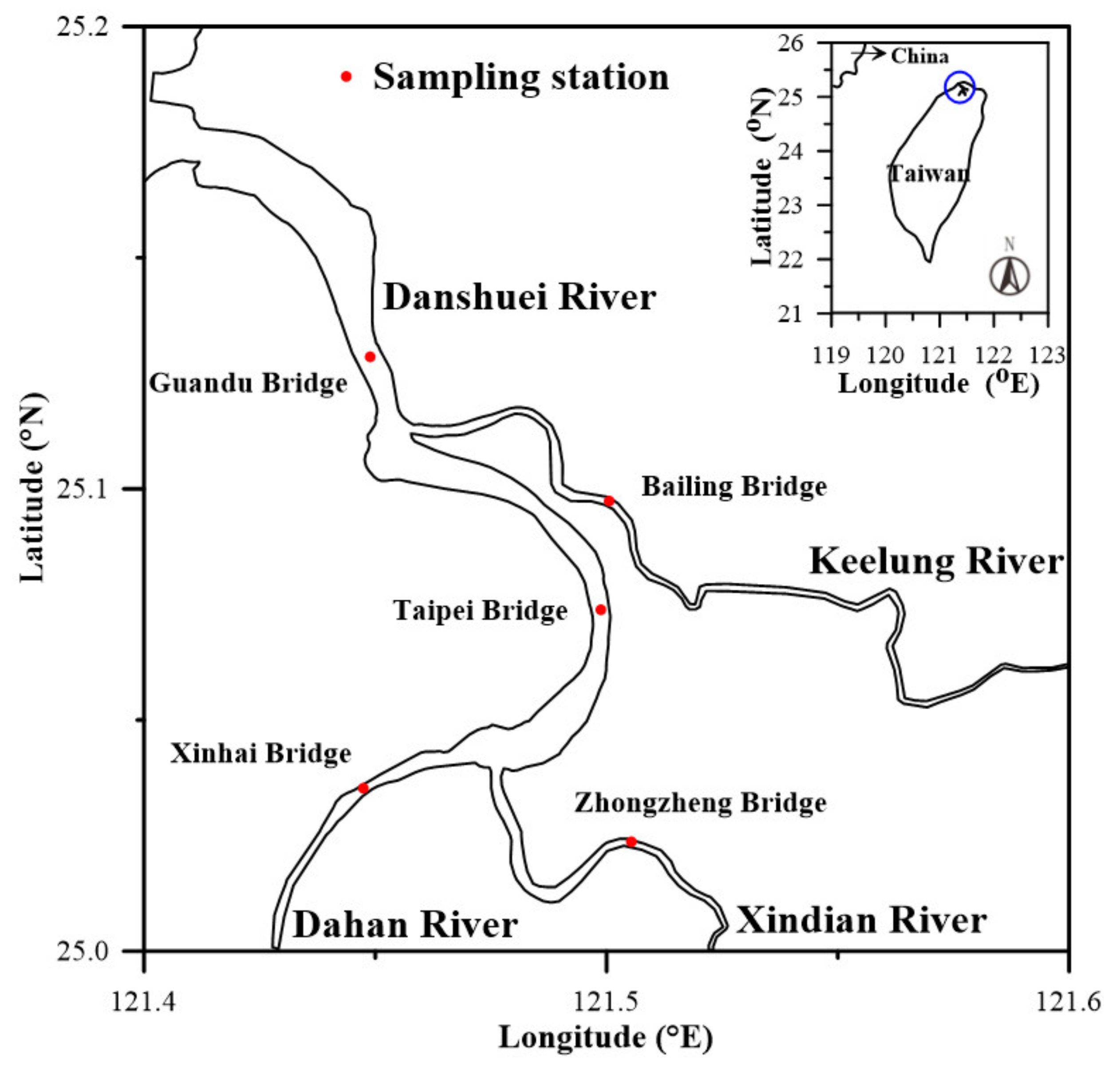
2.1. Description of Study Area
2.2. Field Survey and Data Collection
2.3. Stratification Indices
- Salinity stratification parameter (N)
- 2.
- Bulk/layer Richardson number (RiL)
- 3.
- Gradient Richardson number (Rig)
2.4. Barotropic and Baroclinic Modes
3. Results
3.1. Tidal Characteristics
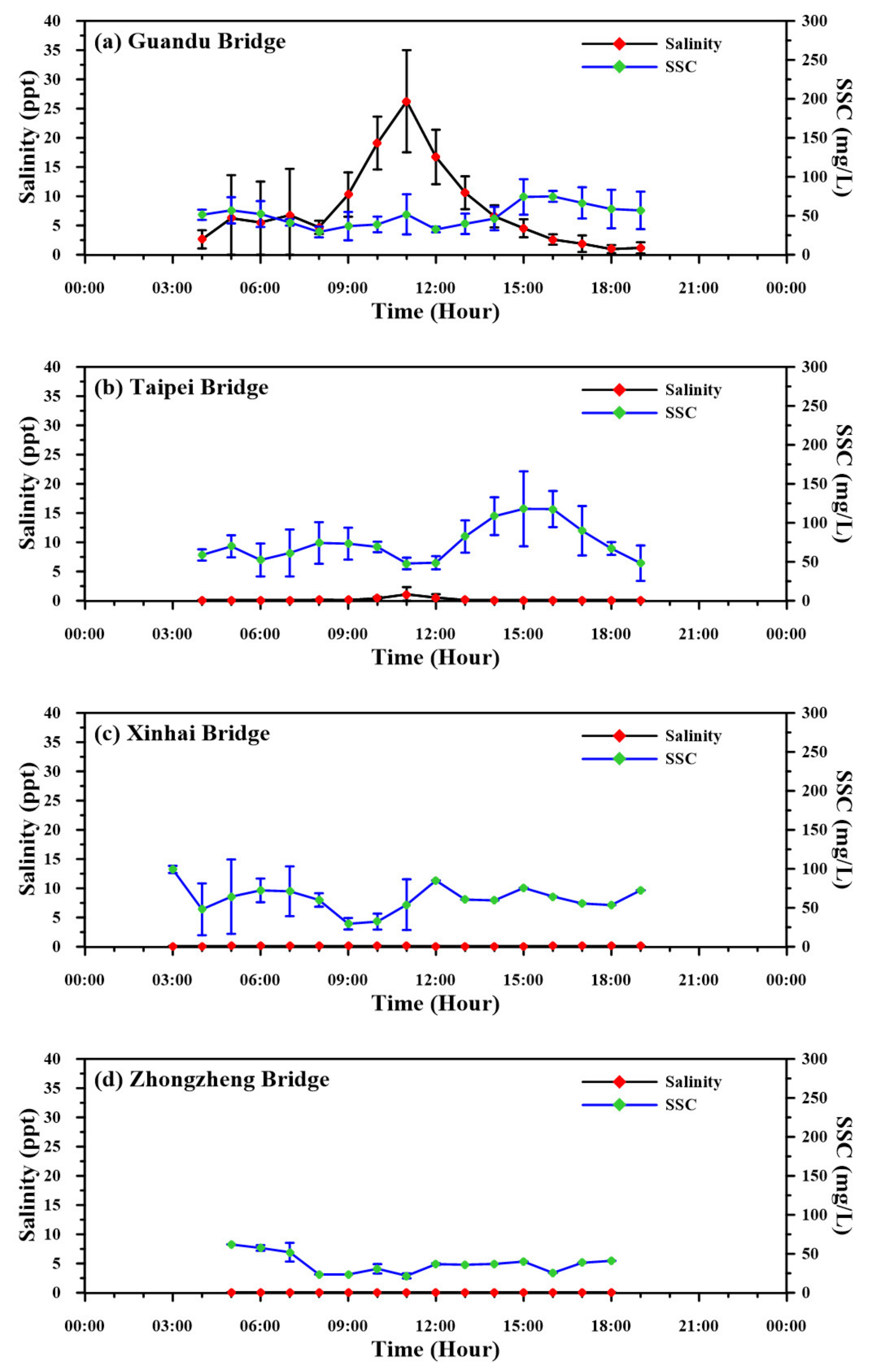
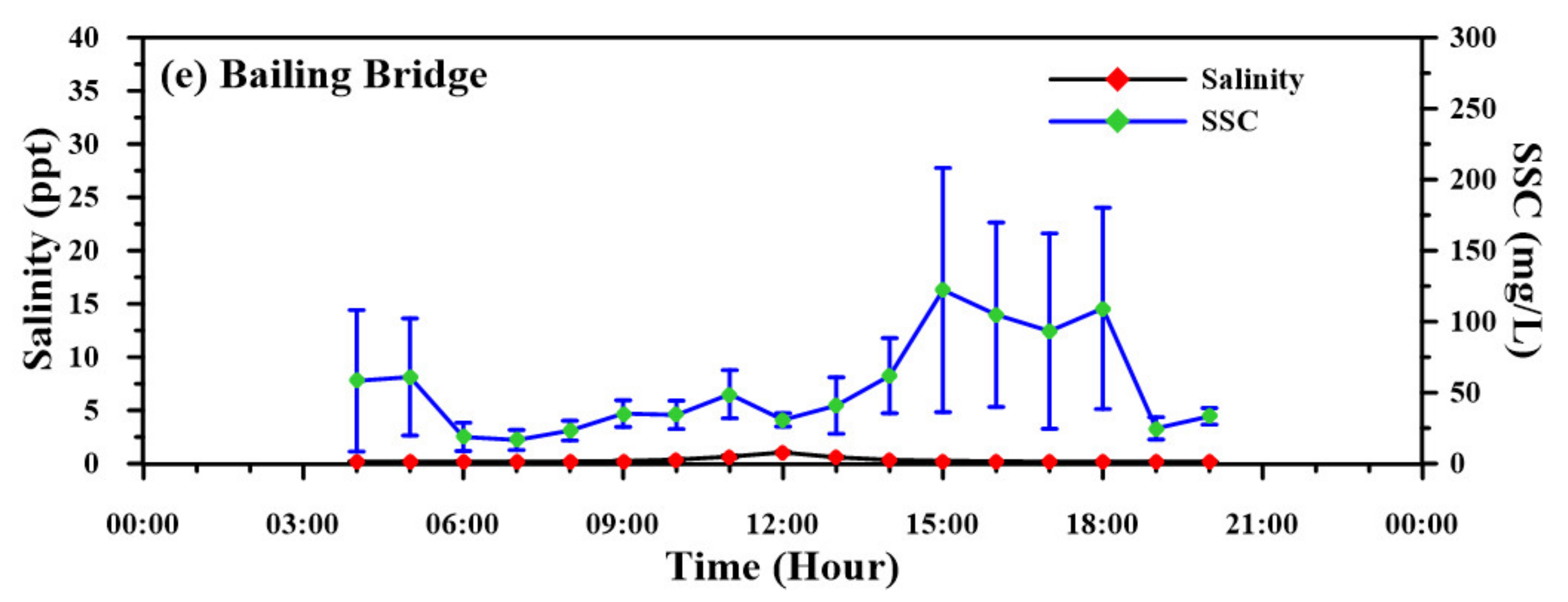
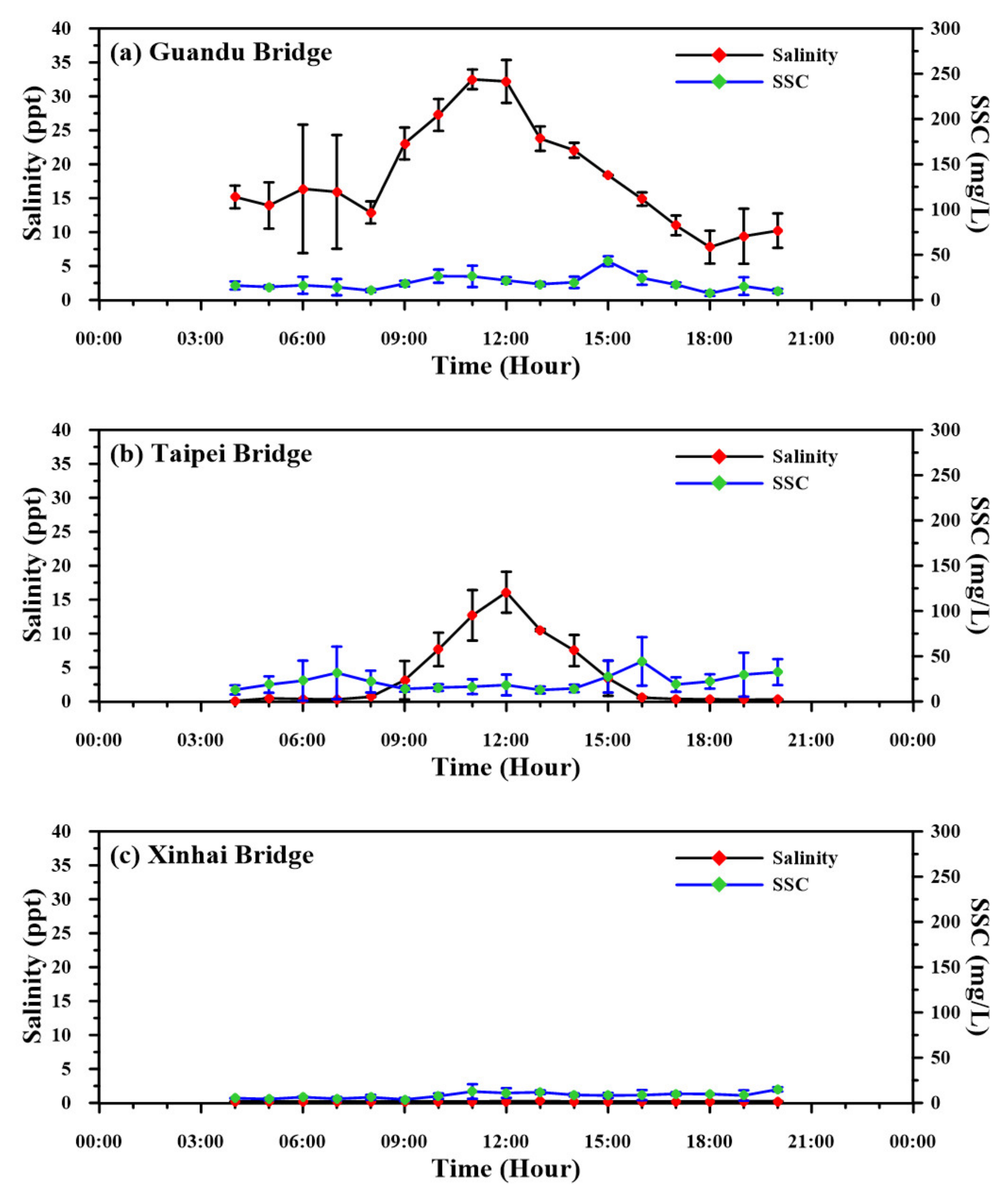
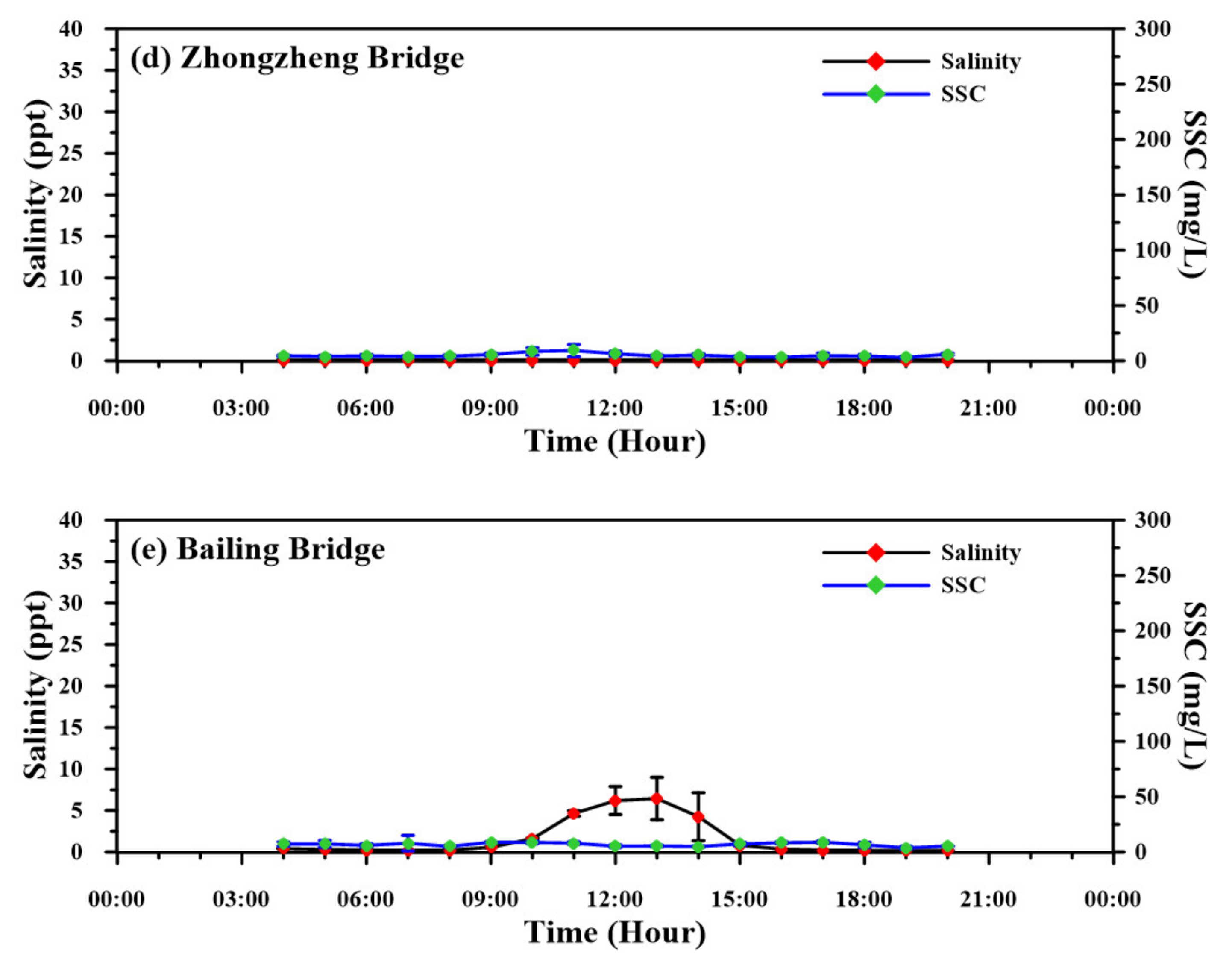
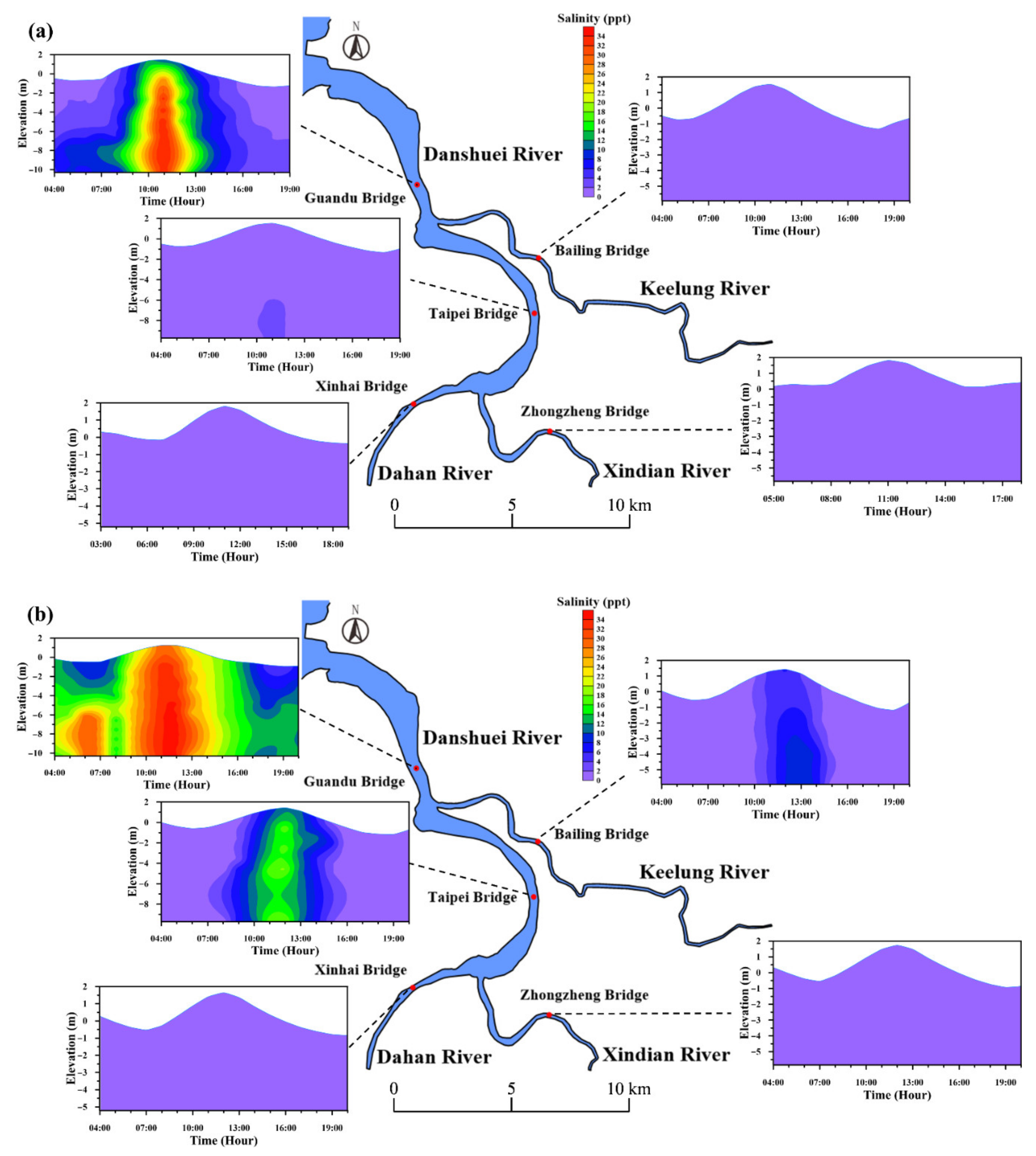
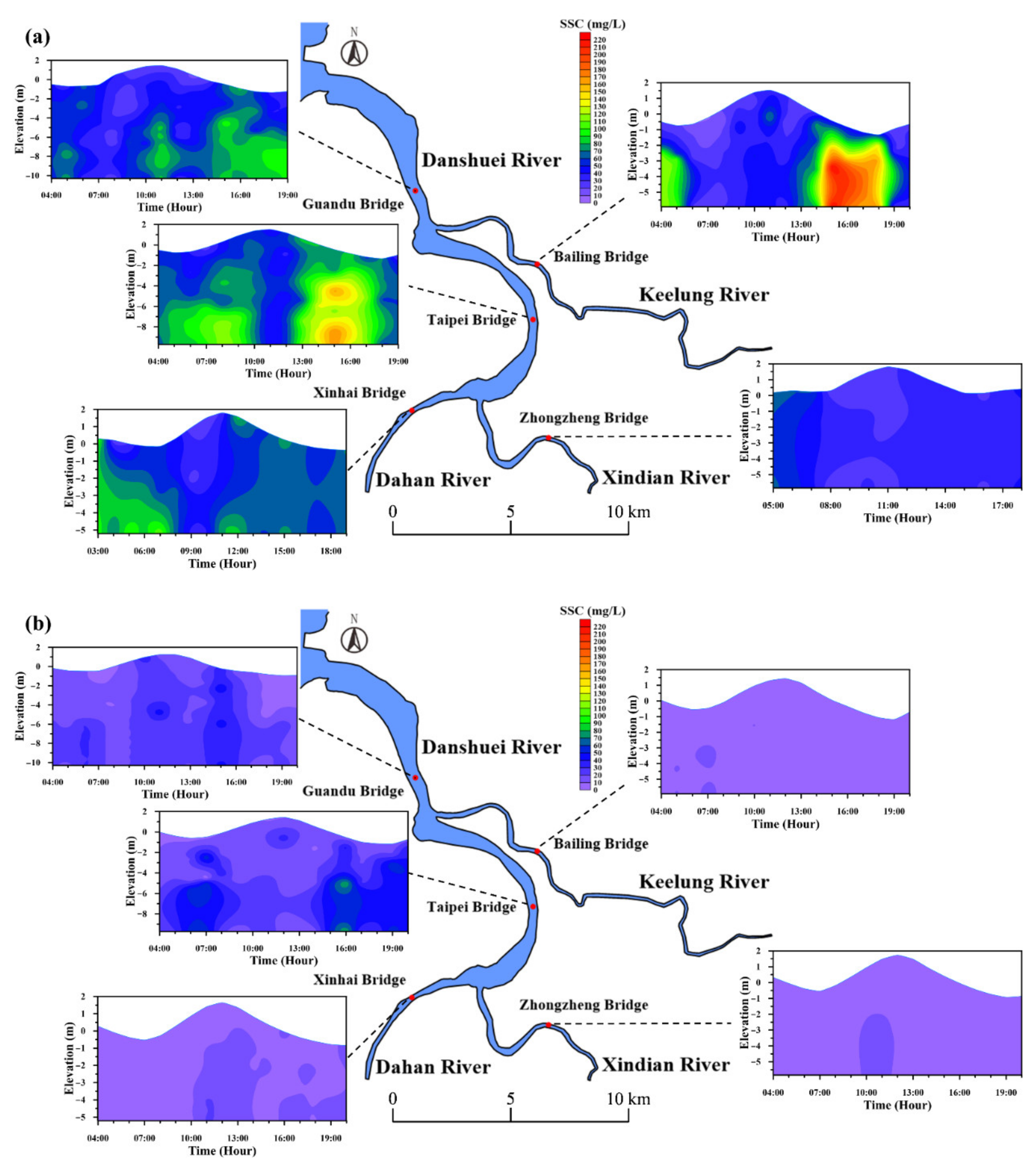
3.2. Salinity and Suspended-Sediment Concentration
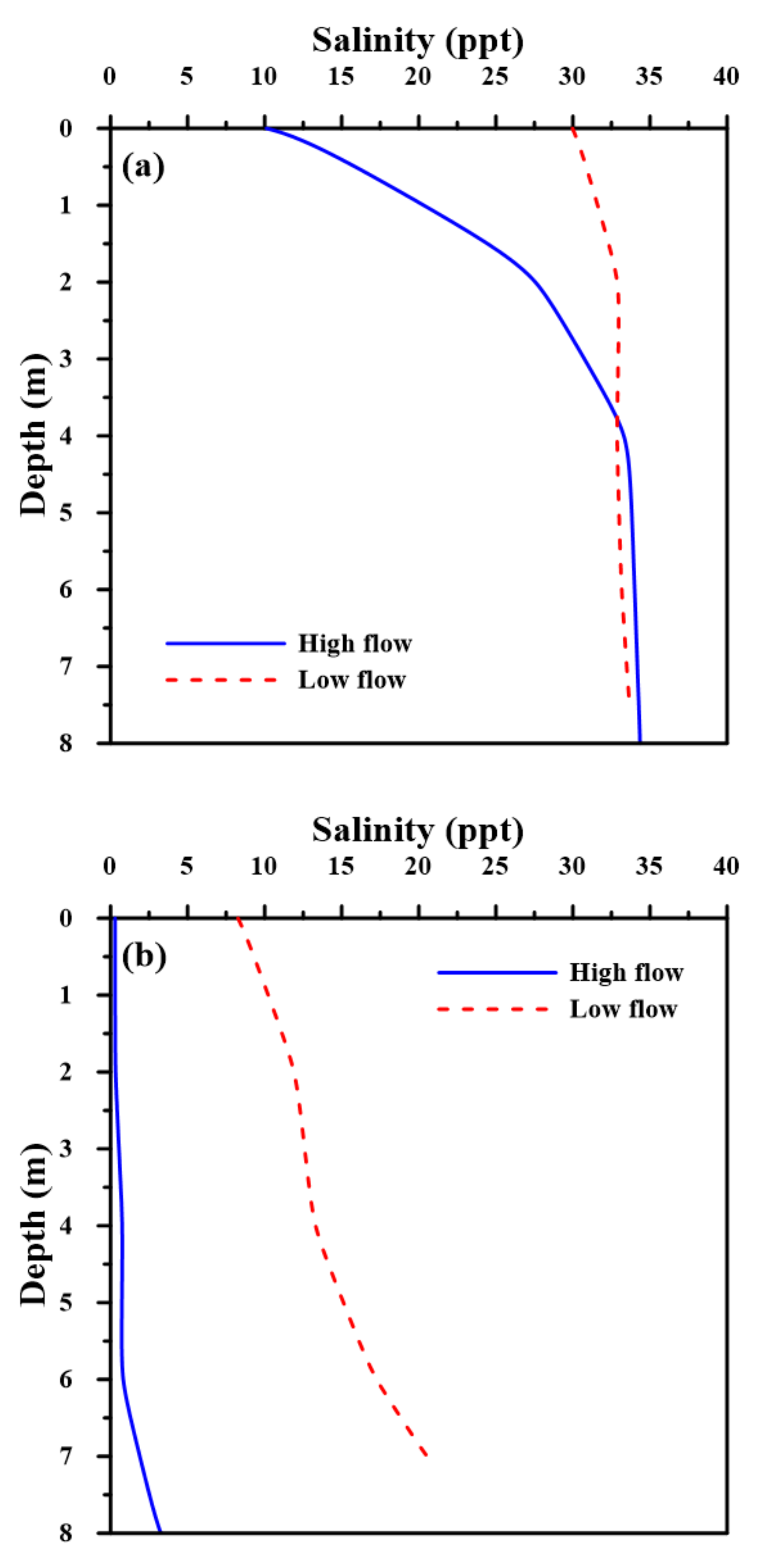
3.3. Stratification Variability
4. Discussion
4.1. Estuarine Circulation and Mixing Conditions
4.2. Longitudinal Changes in Salinity and SSC
4.3. Possibility of Modeling and Future Work
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, W.C.; Huang, W.C. Modeling the transport and distribution of fecal coliform in tidal estuary. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 431, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skerratt, J.; Wild-Allen, K.; Rizwi, F.; Whitehead, J.; Coughanowr, C. Use of a high resolution 3D fully coupled hydrodynamic, sediment and biogeochemical model to understand estuarine nutrient dynamics under various water quality scenarios. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2013, 83, 52–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Chua, V.P. A numerical study on land-based pollutant transport in Singapore coastal waters with a coupled hydrologic-hydrodynamic model. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2017, 14, 119–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Chai, F.; Dugdale, R.; Chao, Y.; Xue, H.; Rao, S.; Wilkerson, F.; Farrara, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; et al. San Francisco Bay nutrients and plankton dynamics as simulated by a coupled hydrodynamic-ecosystem model. Cont. Shelf Res. 2018, 161, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.B.; Liu, W.C.; Hsu, M.H. Water quality modeling in tidal estuarine system using a three-dimensional model. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2011, 28, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Justic, D.; Inoue, M.; Hoda, A.; Huang, H.; Park, D. Impact of Mississippi River diversions on salinity gradients in a deltaic Louisiana estuary: Ecological and management implications. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 111, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, I.C.; Bordalo, A.A.; Duarte, P. Influence of freshwater inflow variability on the Douro estuary primary productivity: A modelling study. Ecol. Model. 2014, 272, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.C.; Chan, W.T. Assessment of climate change impacts on water quality in a tidal estuarine system using a three-dimensional model. Water 2016, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naithani, J.; de Brye, B.; Buyze, E.; Vyverman, W.; Legat, V.; Deleersnijder, E. An ecological model for the Scheldt estuary and tidal rivers ecosystem: Spatial and temporal variability of plankton. Hydrobiologia 2016, 775, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Shen, J.; Jia, L. Salt intrusion during the dry season in the Huangmaohai Estuary, Pearl River Delta, China. J. Mar. Syst. 2013, 111–112, 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarzuelo, C.; Lopez-Ruiz, A.; Diez-Minguito, M.; Ortega-Sanchez, M. Tidal and subtidal hydrodynamics and energetics in a constricted estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 185, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Park, K.; Shen, J.; Dzwonkowski, B.; Yu, X.; Yoon, B., II. Role of baroclinic processes on flushing characteristics in a highly stratified estuarine system, Mobile Bay, Alabama. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean 2018, 123, 4518–4537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garel, E.; Cai, H. Effect of tidal-forcing variations on tidal properties along a narrow convergent estuary. Estuar. Coast. 2018, 41, 1924–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ijaz, M.W.; Mahar, R.B.; Ansari, K.; Siyal, A.A. Optimization pf salinity intrusion control through freshwater and tidal inlet modification for the Indus River Estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 224, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherin, V.R.; Durand, P.; Papa, F.; Islam, A.S. Recent salinity intrusion in the Bengal delta: Observations and possible causes. Cont. Shelf Res. 2020, 202, 104–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, L.; He, Z.; Kalhoro, N.A.; Xu, D. Numerical modelling study of seawater intrusion in Indus River Estuary, Pakistan. Ocean Eng. 2019, 184, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Jiang, A.; Zhang, J.; Xu, H.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, S.; Yu, X. Comprehensive hydrodynamic fitness of an estuary channel and the effect of a water diversion inflow. Estuar. Coast. 2022, 45, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, L.; Alahmd, S.; Smith, S.M.C.; Roberts, G. Tidal and subtidal transport in short, tidally-driven estuaries with low rates of freshwater input. Cont. Shelf Res. 2021, 224, 104453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.Z. Tidal resuspension and transport processes of fine sediment within the river plume in the partially-mixed Changjiang River estuary, China: A personal perspective. Geomorphology 2010, 121, 133–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meselhe, E.A.; Georgiou, I.; Allison, M.A.; McCorquodale, J.A. Numerical modeling of hydrodynamics and sediment transport in lower Mississippi at a proposal delta building diversion. J. Hydrol. 2012, 472–473, 340–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uncles, R.J.; Stephens, J.A.; Harris, C. Towards predicting the influence of freshwater abstractions on the hydrodynamics and sediment transport of a small, strongly tidal estuary: The Devonshire Avon. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2013, 79, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, C.P.; Gourgue, O.; Sassi, M.; HoitinkTon, A.J.F.; Deleersnijder, E.; Soares-Frazao, S. Modeling fine-grained sediment transport in the Mahakam land-sea continuum, Indonesia. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2016, 13, 103–120. [Google Scholar]
- Miguel, L.L.A.J.; Castrol, J.W.A.; Nehama, F.P.J. Tidal impact on suspended sediments in the Macuse estuary in Mozambique. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2017, 16, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesse, R.F.; Zorndt, A.; Frohle, P. Modelling dynamics of the estuarine turbidity maximum and local net deposition. Ocean Dyn. 2019, 69, 489–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Song, D.; Bao, X.; Wang, N. The response of turbidity maximum to peak river discharge in a macrotidal estuary. Water 2021, 13, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, L.; Fortunato, A.B.; Zhang, Y.; Oliveria, A.; Sancho, F.E.P. Development and validation of a three-dimensional morphodynamic modelling system for non-cohesive sediments. Ocean Model. 2012, 57–58, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourgue, O.; Baeyens, W.; Chen, M.S.; de Brauwere, A.; de Brye, B.; Deleersnijder, E.; Elskens, M.; Legat, V. A depth-averaged two-dimensional sediment transport model for environmental studies in the Scheldt Estuary and tidal river network. J. Mar. Syst. 2013, 128, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Cao, A.; Zhang, J.; Fan, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. A three-dimensional cohesive sediment transport model with data assimilation; Model development, sensitivity analysis and parameter estimation. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 206, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, F.; Le Hir, P. Influence of morphological changes on suspended sediment dynamics in a macrotidal estuary: Diachronic analysis in the Seine Estuary (France) from 1960 to 2010. Ocean Dyn. 2019, 69, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krvavica, N.; Ruzic, I. Assessment of sea-level rise impact on salt-wedge intrusion in idealized and Neretva River Estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2020, 234, 106638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, C.; van Maren, D.S.; Guo, L.; Lin, J.; He, Q.; Wang, Z.B. Effects of sediment-induced density gradients on the estuarine turbidity maximum in the Yangtze Estuary. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean 2021, 126, e2020JC016927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.P.; Voulgaries, G.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Gao, J.; Chen, J.; Gao, S. Sediment resuspension flocculation, and settling in a macrotidal estuary. J. Geophys. Res. 2013, 118, 5591–5608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Jia, L.; Shen, J.; Liu, J.T. Sediment transport in response to changes in river discharge and tidal mixing in a funnel-shaped micro-tidal estuary. Cont. Shelf Res. 2014, 76, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chen, Z.; Finlayson, B.; Wei, T.; Chen, J.; Wu, X.; Xu, H.; Webber, M.; Barnett, J.; Wang, M. Water diversion and sea-level rise: Potential threats to freshwater supplies in the Changjiang River estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 156, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, M.H.; Wu, C.R.; Liu, W.C.; Kuo, A.Y. Investigation of turbidity maximum in a mesotidal estuary, Taiwan. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2006, 42, 901–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.C.; Ke, M.H.; Liu, H.M. Response of salt transport and residence time to geomorphologic changes in an estuarine system. Water 2020, 12, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, M.H.; Kuo, A.Y.; Kuo, J.T.; Liu, W.C. Procedure to calibrate and verify numerical models of estuarine hydrodynamics. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1999, 125, 166–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.C.; Hsu, M.H.; Wu, C.R.; Wang, C.F.; Kuo, A.Y. Modeling salt water intrusion in Tanshui River estuarine system-Case-study contrasting now and then. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2004, 130, 849–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Methods for Chemical Analysis of Water and Waste; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1983.
- Hansen, D.V.; Rattray, M. New dimension in estuary classification. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1966, 11, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prandle, D. Estuaries: Dynamic, Mixing, Sedimentation and Morphology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009; 236p. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, W.; Kot, S.; Wolanski, E. 3-D fluid-mud dynamics in the Jiaojiang Estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2005, 65, 747–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, K.R.; New, A.L. Intermittency in estuarine mixing. In Estuarine Variability; Wolfe, D.A., Ed.; Academic Press, Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1986; pp. 321–329. [Google Scholar]
- Miles, J.W. On the stability of heterogeneous shear flows. J. Fluid Mech. 1961, 10, 496–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geyer, W.R.; Smith, J.D. Shear stability in a highly stratified estuary. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1987, 17, 1668–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.B.; Liu, W.C. Modeling investigation of asymmetric tidal mixing and residual current in a partially stratified estuary. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2016, 16, 167–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.C. Modelling circulation and vertical mixing in estuaries. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Marit. Eng. 2006, 159, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskalski, S.; Torres, R. Influences of tides, weather, and discharge on suspended sediment concentration. Cont. Shelf Res. 2012, 37, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, S.B.; Green, M.O.; MacDonald, I.T.; Pritchard, M. Field studies of estuarine turbidity under different freshwater flow conditions, Kaipara River, New Zealand. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 198, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.F.; Yang, S.L.; Xu, K.H. River-sea transitions of sediment dynamics: A case study of the tide-impacted Yangtze River estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 196, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restrepo, J.C.; Schrottke, K.; Traini, C.; Bartholomae, A.; Ospino, S.; Ortiz, J.C.; Otero, L.; Orejarena, A. Estuarine and sediment dynamics in a microtidal tropical estuary of high fluvial discharge: Magdalena River (Colombia, South America). Mar. Geol. 2018, 398, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Jia, J.; Wang, Y.P.; Zhang, G. Net suspended sediment transport modulated by multiple flood-ebb asymmetries in the progressive tidal wave dominated partially stratified Changjiang Estuary. Mar. Geol. 2022, 443, 106702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Hir, P.; Cayocca, F. 3D application of the continuous modelling concept to mud slides in open seas. In Proceedings in Marine Science; Winterwerp, J.C., Kranenburg, C., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 545–562. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, P.; Wilson, R.E.; Chant, R.J.; Fugate, D.C.; Flood, R.D. Modeling influence of stratification on lateral circulation in a stratified estuary. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2009, 39, 2324–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zheng, J.; Ji, X.; Hoitink, A.J.F.; van der Vegt, M.; Zhu, Y. Surficial sediment distribution and the associated net sediment transport pattern in the Pearl River Estuary, South China. Cont. Shelf Res. 2013, 61–62, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, R.L.; Schramkowski, G.P.; Dijkstra, Y.M.; Schuttelaars, H.M. Time evolution of estuarine turbidity maxima in well-mixed, tidally dominated estuaries: The role of availability- and erosion-limited conditions. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2018, 48, 1629–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Maren, D.; Vroom, J.; Fettweis, M.; Vanlede, J. Formation of the Zeebrugge coastal turbidity maximum: The role if uncertainty in near-bed exchange processes. Mar. Geol. 2020, 425, 106186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, W.-C.; Liu, H.-M.; Huang, W.-C. Flood–Ebb and Discharge Variations in Observed Salinity and Suspended Sediment in a Mesotidal Estuary. Standards 2022, 2, 209-225. https://doi.org/10.3390/standards2020016
Liu W-C, Liu H-M, Huang W-C. Flood–Ebb and Discharge Variations in Observed Salinity and Suspended Sediment in a Mesotidal Estuary. Standards. 2022; 2(2):209-225. https://doi.org/10.3390/standards2020016
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Wen-Cheng, Hong-Ming Liu, and Wei-Che Huang. 2022. "Flood–Ebb and Discharge Variations in Observed Salinity and Suspended Sediment in a Mesotidal Estuary" Standards 2, no. 2: 209-225. https://doi.org/10.3390/standards2020016
APA StyleLiu, W.-C., Liu, H.-M., & Huang, W.-C. (2022). Flood–Ebb and Discharge Variations in Observed Salinity and Suspended Sediment in a Mesotidal Estuary. Standards, 2(2), 209-225. https://doi.org/10.3390/standards2020016






