Evaluating Management Practices in Precision Agriculture for Maize Yield with Spatial Econometrics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. Maize Production in Portugal and the World
2.2. Determinants of Maize Crop
2.3. Time and Space in Agricultural Econometrics
3. Data, Methods and Results
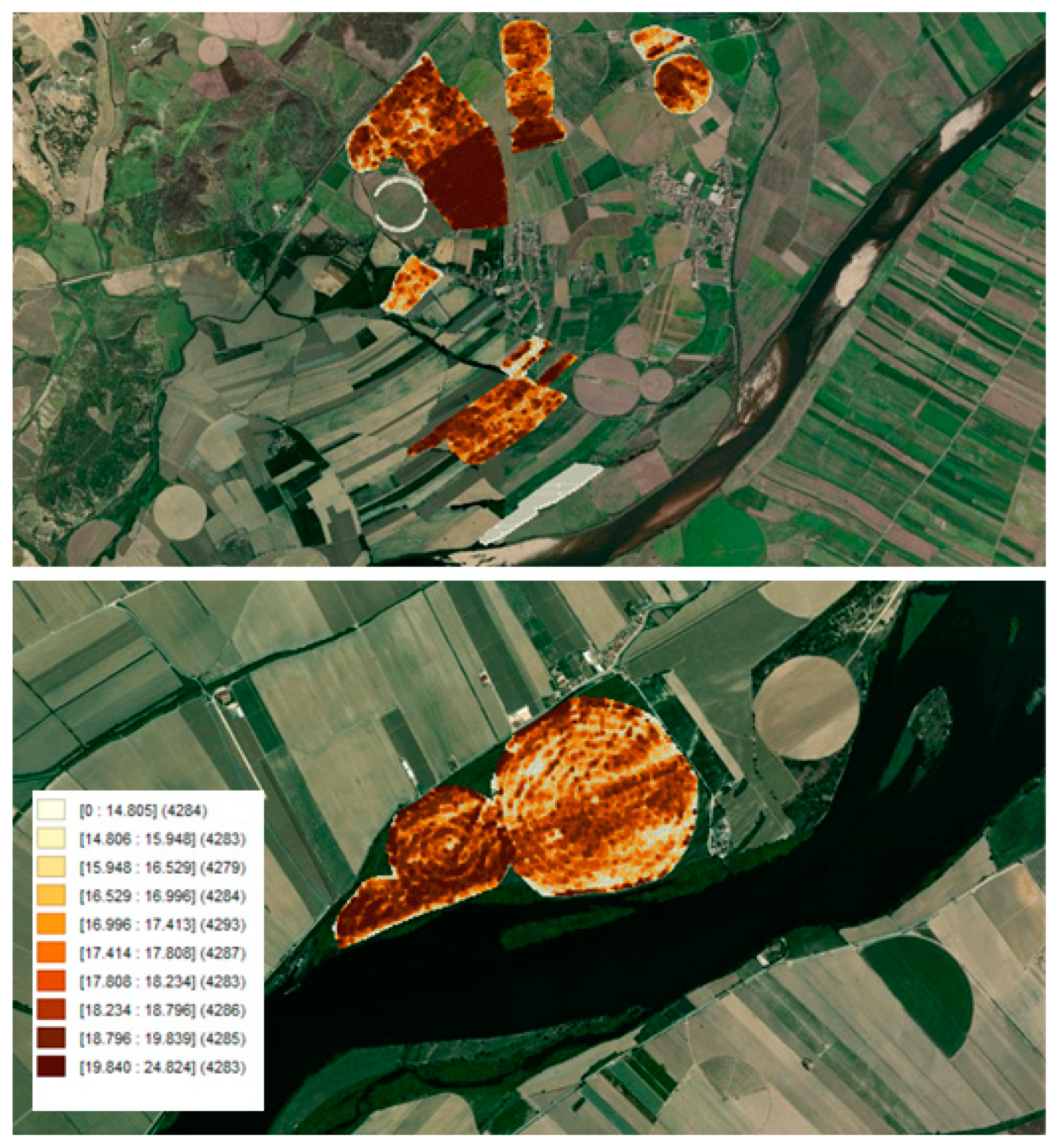
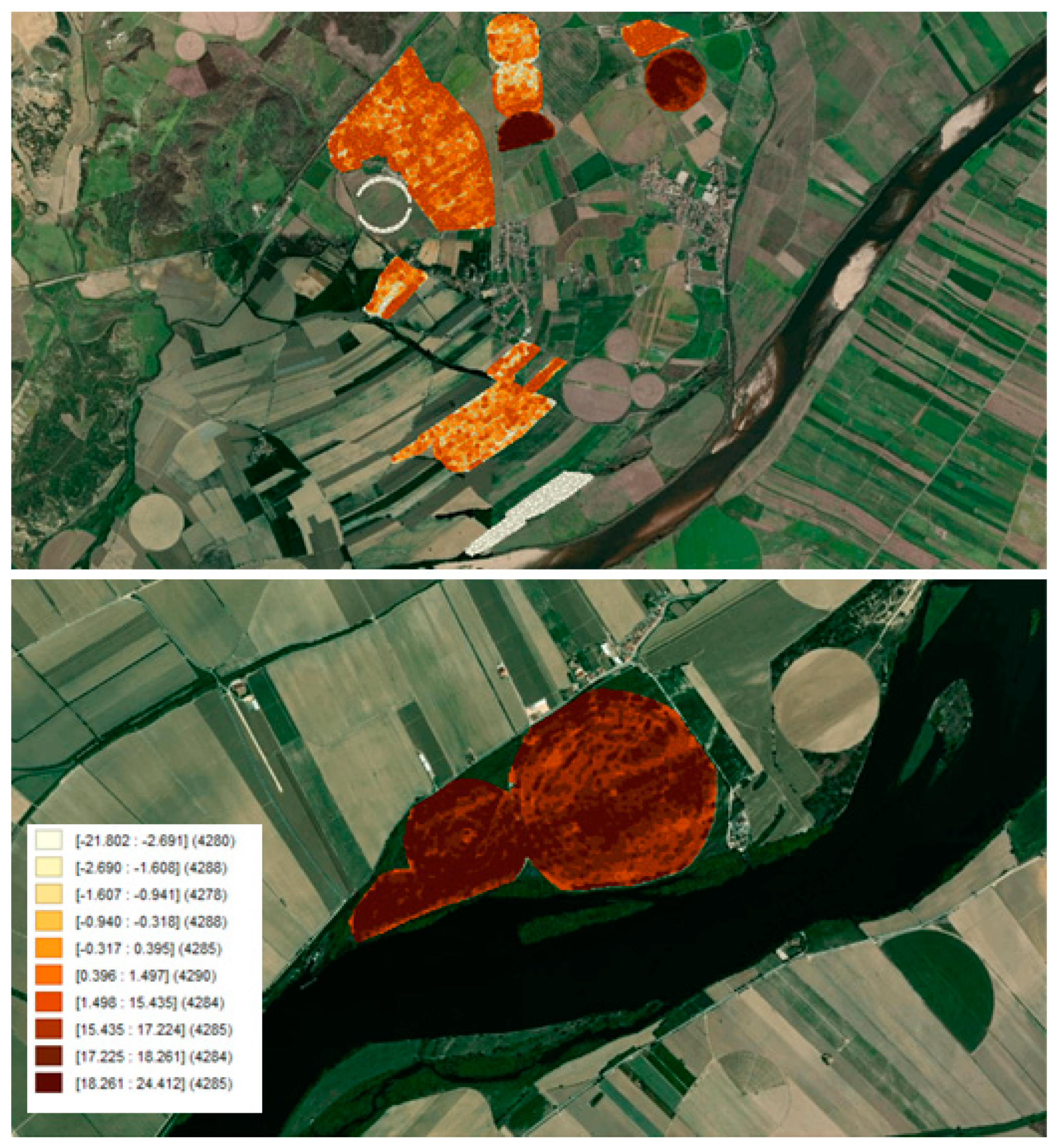
3.1. Data
3.2. Methods and Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


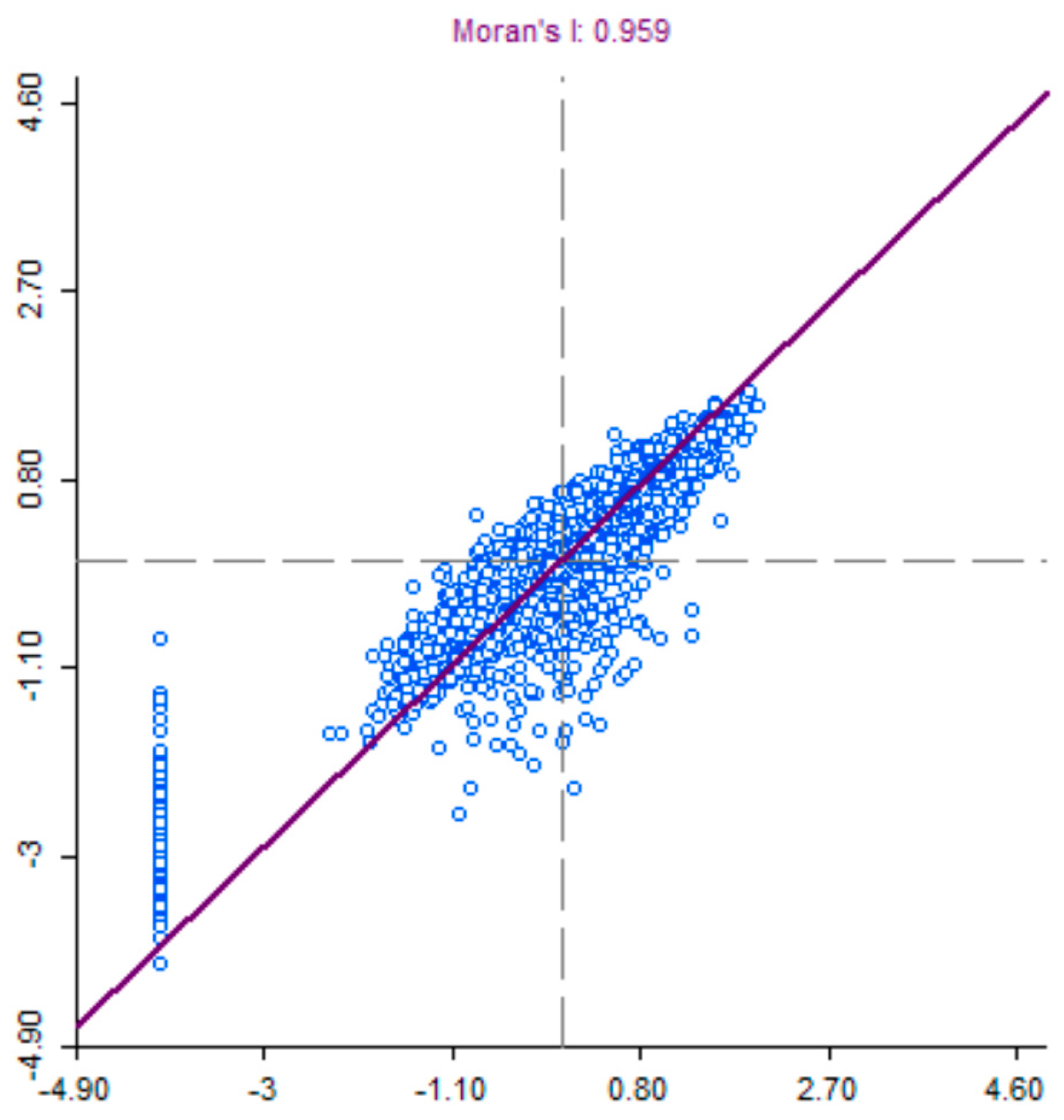

References
- Oliver, M.A.; Bishop, T.F.; Marchant, B.P. (Eds.) Precision Agriculture for Sustainability and Environmental Protection; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Liaghat, S.; Balasundram, S.K. A review: The role of remote sensing in precision agriculture. Am. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 2010, 5, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsouros, D.C.; Bibi, S.; Sarigiannidis, P.G. A review on UAV-based applications for precision agriculture. Information 2019, 10, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bullock, D.S.; Bullock, D.G. From agronomic research to farm management guidelines: A primer on the economics of information and precision technology. Precis. Agric. 2000, 2, 71–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, M.; Carberry, P.; Brennan, L. Economic benefits of variable rate technology: Case studies from Australian grain farms farms. Crop. Pasture Sci. 2009, 60, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wang, M.; Wang, N. Precision agriculture—A worldwide overview. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2002, 36, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOSTAT. Crops and Livestock Products [Data Base]. 2021. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL/visualize (accessed on 18 November 2021).
- Chhetri, S.; Poudel, A.; Kandel, B.P.; Lamjung, N. Effect of Sowing Dates on Grain Yield and Other Agronomic Traits of Different Maize Inbred Lines. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2018, 9, 428–434. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.; Su, Y. Effects of Soils and Irrigation Volume on Maize Yield, Irrigation Water Productivity, and Nitrogen Uptake. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobell, D.; Hammer, G.; McLean, G.; Messina, C.; Roberts, M.J.; Schlenker, W. The critical role of extreme heat for maize production in the United States. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlenker, W.; Roberts, M.J. Nonlinear temperature effects indicate severe damages to U.S. crop yields under climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 15594–15598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chavas, J.-P.; Di Falco, S.; Adinolfi, F.; Capitanio, F. Weather effects and their long-term impact on the distribution of agricultural yields: Evidence from Italy. Eur. Rev. Agric. Econ. 2018, 46, 29–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, W.; Tang, A.; Shen, J.; Cui, Z.; Vitousek, P.; Erisman, J.W.; Goulding, K.; Christie, P.; et al. Enhanced nitrogen deposition over China. Nature 2013, 494, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampitti, I.A.; Vyn, T.J. Understanding Global and Historical Nutrient Use Efficiencies for Closing Maize Yield Gaps. Agron. J. 2014, 106, 2107–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anselin, L.; Bongiovanni, R.; Lowenberg-DeBoer, J. A Spatial Econometric Approach to the Economics of Site-Specific Nitrogen Management in Corn Production. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2004, 86, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongiovanni, R.; Lowenberg-DeBoer, J. Economics of nitrogen response variability over space and time: Results from the 1999–2001 field trials in Argentina. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Precision Agriculture and Other Precision Resources Management, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 14–17 July 2002; pp. 1826–1841. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, D.M.; Lowenberg-DeBoer, J.; Malzer, G.L. Economic Analysis of Spatial-Temporal Patterns in Corn and Soybean Response to Nitrogen and Phosphorus. Agron. J. 2006, 98, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Swinton, S.M.; Miller, N.R. Is Site-Specific Yield Response Consistent over Time? Does It Pay? Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2006, 88, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisan, R.G.; Bullock, D.S.; Martin, N.F. Spatial variability of crop responses to agronomic inputs in on-farm precision experimentation. Precis. Agric. 2021, 22, 342–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockstael, N.E. Modeling Economics and Ecology: The Importance of a Spatial Perspective. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 1996, 78, 1168–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lark, R.; Stafford, J.; Bolam, H. Limitations on the Spatial Resolution of Yield Mapping for Combinable Crops. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 1997, 66, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravchenko, A.N.; Bullock, D.G. Correlation of corn and soybean grain yield with topography and soil properties. Agron. J. 2000, 92, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, J.R.; Gilliam, J.W.; Cassel, D.K.; Daniels, R.B.; Nelson, L.A.; Kleiss, H.J. Effect of Erosion and Landscape Position on the Productivity of Piedmont Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1985, 49, 987–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, R.; Rossiter, D.; van Es, H. Spatio-temporal analysis of yield and weather data for defining site-specific crop management zones. Precis. Agric. 2021, 22, 1952–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afyuni, M.M.; Cassel, D.K.; Robarge, W.P. Effect of Landscape Position on Soil Water and Corn Silage Yield. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1993, 57, 1573–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spomer, R.G.; Piest, R.F. Soil Productivity and Erosion of Iowa Loess Soils. Trans. ASAE 1982, 25, 1295–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspar, T.C.; Colvin, T.S.; Jaynes, D.B.; Karlen, D.L.; James, D.E.; Meek, D.W.; Pulido, D.; Butler, H. Relationship Between Six Years of Corn Yields and Terrain Attributes. Precis. Agric. 2003, 4, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, B.L.; Hollinger, S.E.; Garcia, P.; Tirupattur, V. Estimating Corn Yield Response Models to Predict Impacts of Climate Change. J. Agric. Resour. Econ. 1994, 19, 58–68. [Google Scholar]
- Huff, F.A.; Neill, J.C. Assessment of Effects and Predictability of Climate Fluctuations as Related to Agricultural Production; Illinois State Water Survey: Champaign, IL, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Offutt, S.E.; Garcia, P.; Pinar, M. Technological Advance, Weather, and Crop Yield Behavior. North Central J. Agric. Econ. 1987, 9, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daughtry, C.S.T.; Gallo, K.P.; Bauer, M.E. Spectral Estimates of Solar Radiation Intercepted by Corn Canopies 1. Agron. J. 1983, 75, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stafford, J.V.; Bolam, H.C. Near-Ground and Aerial Radiometry Imaging for Assessing Spatial Variability in Crop Condition. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Precision Agriculture; Robert, P., Rust, R., Larson, W., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy, Crop Science Society of America, Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1999; pp. 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Tang, L.; Hupy, J.P.; Wang, Y.; Shao, G. A commentary review on the use of normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) in the era of popular remote sensing. J. For. Res. 2021, 32, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelejian, H.H.; Prucha, I.R. On the asymptotic distribution of the Moran I test statistic with applications. J. Econ. 2001, 104, 219–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anselin, L. Spatial Econometrics: Methods and Models; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Boston, MA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Anselin, L.; Bera, A.K.; Florax, R.; Yoon, M.J. Simple diagnostic tests for spatial dependence. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 1996, 26, 77–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelejian, H.H.; Prucha, I.R. A Generalized Spatial Two-Stage Least Squares Procedure for Estimating a Spatial Autoregressive Model with Autoregressive Disturbances. J. Real Estate Financ. Econ. 1998, 17, 99–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelejian, H.H.; Prucha, I.R. Specification and estimation of spatial autoregressive models with autoregressive and heteroskedastic disturbances. J. Econ. 2010, 157, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Stage | Plant Activity | Starting Date | Ending Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Emergence of the seedling from below the soil | Planting date (March/April/May) | Emergence date (April/May/June) |
| 2 | Early vegetative growth | Emergence date (April/May/June) | Flowering start date (June/July) |
| 3 | Flowering | Flowering start date (June/July) | Flowering end date (June/July/August) |
| 4 | Grain fill until maturity (harvest) | Flowering end date (June/July/August) | Harvest date (September) |
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Maize yield (tons/ha) | |
| Annual change in Maize yield in 2018 (tons/ha) | |
| Total Nitrogen (Kg/ha) | |
| Total Phosphorus (Kg/ha) | |
| Total Potassium (Kg/ha) | |
| Total Irrigation (mm/ha) | |
| Average daily Temperature on Stage i (i = 1 to 4) | |
| Dummy variable equal to 1 if there was a change of Seeds used in previous year on the spatial unit, and 0 otherwise | |
| Dummy variable equal to 1 if there was a change in Treatment (herbicides, insecticides) from the previous year on the spatial unit, and 0 otherwise | |
| Dummy variable equal to 1 if the soil is clayey and equal to 0 otherwise | |
| First observed NDVI (early stage). |
| Variables | N | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Std. Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50,547 | 0 | 24.82 | 16.50 | 3.87 | |
| 50,547 | −21.80 | 24.41 | 3.88 | 9.34 | |
| 50,547 | 0 | 407.54 | 358.26 | 62.71 | |
| 50,547 | 0 | 171.10 | 147.30 | 38.92 | |
| 50,547 | 0 | 180.88 | 87.15 | 58.64 | |
| 50,547 | 507.29 | 645.78 | 564.67 | 40.82 | |
| T_S1 | 50,547 | 13.40 | 18.79 | 16.77 | 1.12 |
| T_S2 | 50,547 | 17.99 | 19.99 | 19.32 | 0.41 |
| T_S3 | 50,547 | 20.12 | 24.70 | 20.55 | 0.64 |
| T_S4 | 50,547 | 21.05 | 22.27 | 21.76 | 0.35 |
| 50,547 | 0.14 | 0.36 | 0.20 | 0.05 | |
| 50,547 | 0 | 1 | 0.50 | 0.50 | |
| 50,547 | 0 | 1 | 0.30 | 0.46 | |
| 50,547 | 0 | 1 | 0.50 | 0.50 |
| Statistical Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Lagrange Multiplier (lag) | 111,070.210 | 0.0000 |
| Robust LM (lag) | 108.396 | 0.0000 |
| Lagrange Multiplier (error) | 123,629.758 | 0.0000 |
| Robust LM (error) | 12,667.944 | 0.0000 |
| Variables | Coefficient | Std.Error | z-Statistic | Probability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| constant | −3.26400 | 0.74712 | −4.37 | 0.000 |
| 0.19722 | 0.01783 | 11.06 | 0.000 | |
| 1.16329 | 0.08493 | 13.70 | 0.000 | |
| −0.00130 | 0.00012 | −11.30 | 0.000 | |
| 0.25149 | 0.04668 | 5.39 | 0.000 | |
| −0.00125 | 0.00020 | −6.24 | 0.000 | |
| 0.22823 | 0.00852 | 26.79 | 0.000 | |
| −0.00166 | 0.00006 | −29.39 | 0.000 | |
| 0.26508 | 0.01983 | 13.37 | 0.000 | |
| −0.00021 | 0.00001 | −13.96 | 0.000 | |
| 12.80467 | 2.19045 | 5.85 | 0.000 | |
| −2.44472 | 0.14507 | −16.85 | 0.000 | |
| −7.42977 | 0.55548 | −13.38 | 0.000 | |
| −2.58341 | 0.13634 | −18.95 | 0.000 | |
| −13.33222 | 0.59488 | −22.41 | 0.000 | |
| 0.29953 | 0.22001 | 1.36 | 0.173 | |
| 10.50346 | 0.85817 | 12.24 | 0.000 | |
| −9.51526 | 0.74883 | −12.71 | 0.000 | |
| lambda | 0.92361 | 0.00333 | 277.11 | 0.000 |
| Pseudo R-squared = 0.9350. | ||||
| n = 50,547 | ||||
| Variable | Maximizer (M) | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | % Above M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 447.04 | 0 | 407.54 | 358.26 | 0.% | |
| 100.84 | 0 | 171.10 | 147.30 | 84.8% | |
| 68.76 | 0 | 180.88 | 87.15 | 27.6% | |
| 645.90 | 507.29 | 645.78 | 564.67 | 0% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santos, N.; Proença, I.; Canavarro, M. Evaluating Management Practices in Precision Agriculture for Maize Yield with Spatial Econometrics. Standards 2022, 2, 121-135. https://doi.org/10.3390/standards2020010
Santos N, Proença I, Canavarro M. Evaluating Management Practices in Precision Agriculture for Maize Yield with Spatial Econometrics. Standards. 2022; 2(2):121-135. https://doi.org/10.3390/standards2020010
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantos, Nuno, Isabel Proença, and Mariana Canavarro. 2022. "Evaluating Management Practices in Precision Agriculture for Maize Yield with Spatial Econometrics" Standards 2, no. 2: 121-135. https://doi.org/10.3390/standards2020010
APA StyleSantos, N., Proença, I., & Canavarro, M. (2022). Evaluating Management Practices in Precision Agriculture for Maize Yield with Spatial Econometrics. Standards, 2(2), 121-135. https://doi.org/10.3390/standards2020010







