Chromatographic, Chemometric and Antioxidant Assessment of the Equivalence of Granules and Herbal Materials of Angelicae Sinensis Radix
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of the Extracts and Standards
2.3. Determination of Chemical Marker Content
2.4. Antioxidant Activity Assays
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Extraction Yields
3.2. UPLC-PDA Quantification of the Chemical Markers
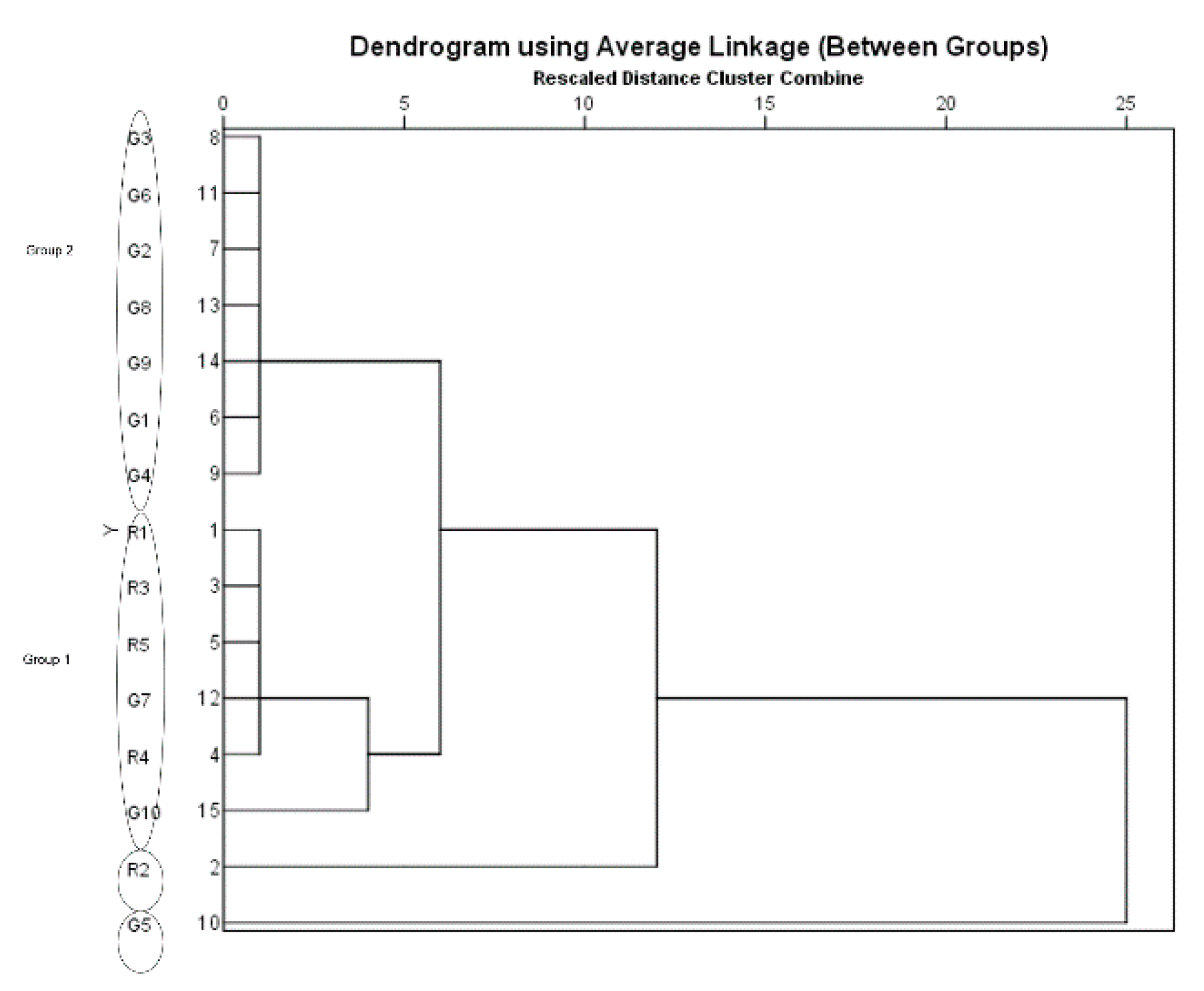
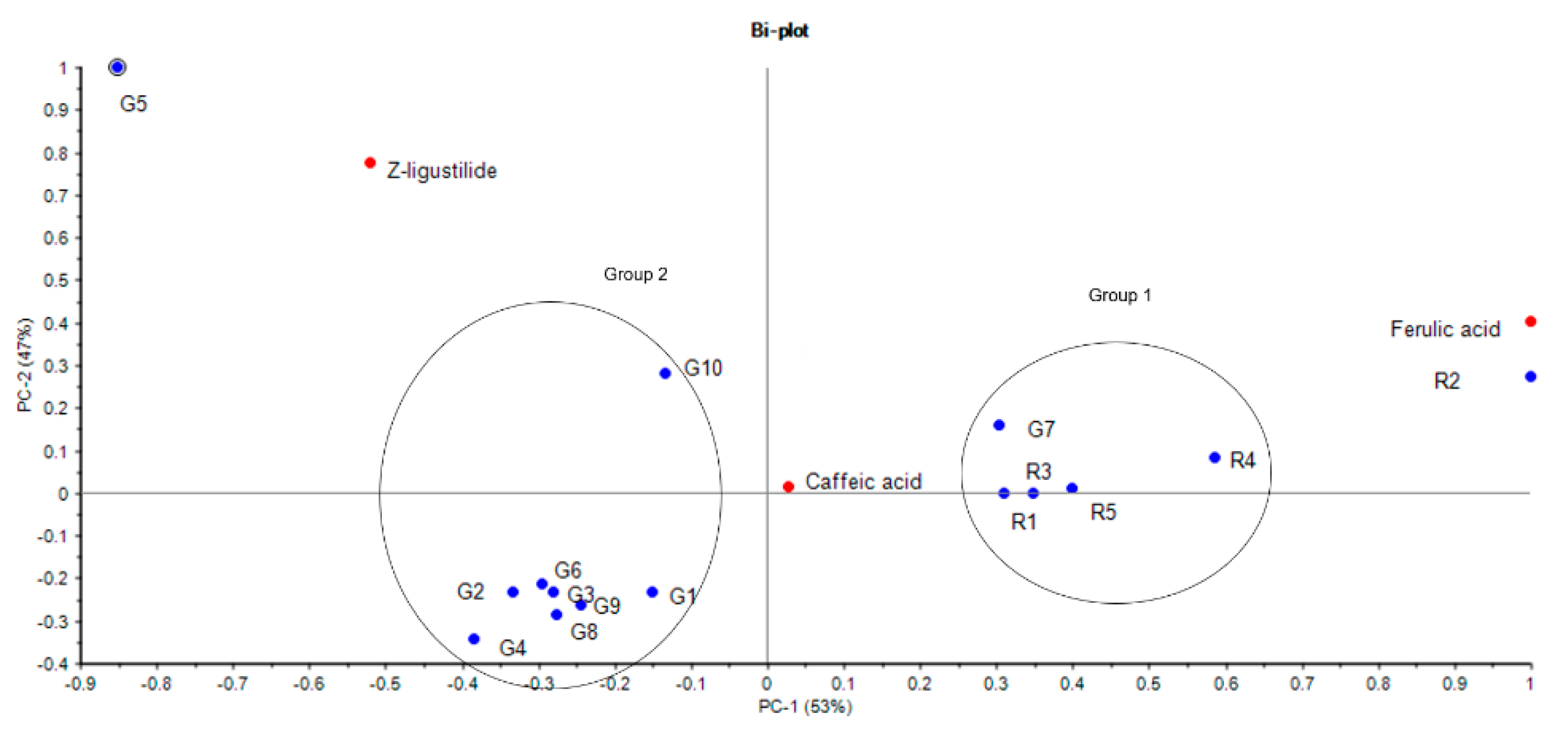
3.3. Multivariate Analysis Using HCA and PCA
3.4. Antioxidant Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klein, S.D.; van der Zypen, D.; Becker, S. Prescription patterns of Chinese medicinal herbs in Switzerland. Swiss J. Integr. Med. 2010, 22, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.L.; Song, J.Z.; Qiao, C.F.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, H.X. UPLC–PDA–TOFMS based chemical profiling approach to rapidly evaluate chemical consistency between traditional and dispensing granule decoctions of traditional medicine combinatorial formulae. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 52, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Li, Q.; Flower, A.; Lewith, G.; Liu, J. Comparison of effectiveness and safety between granules and decoction of Chinese herbal medicine: A systematic review of randomized clinical trials. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 140, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Tang, Y.; Chen, M.; Deng, H.; Yan, X.; Wu, D. Chemical correlation between Gegen Qinlian dispensing granule and its four raw herbs by LC fingerprint. Phytomedicine 2010, 17, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.Z.; Li, S.L.; Zhou, Y.; Qiao, C.F.; Chen, S.L.; Xu, H.X. A novel approach to rapidly explore analytical markers for quality control of Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae extract granules by robust principal component analysis with ultra-high performance liquid chromatography–ultraviolet–quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 53, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.L.; Yang, L.W.; Li, Y.X.; Cao, H.; Zhou, W.L.; Fang, Z.J.; Zhou, H.B.; Mo, J.L.; Xiao, S.X.; Lin, H.R. Applications of ultra-performance liquid chromatography to traditional Chinese medicines. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2010, 48, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhou, X.; Razmovski-Naumovski, V.; Chan, K. A multivariate analysis on the comparison of raw notoginseng (Sanqi) and its granule products by thin-layer chromatography and ultra-performance liquid chromatography. Chin. Med. 2015, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmovski-Naumovski, V.; Tongkao-on, W.; Kimble, B.; Qiao, V.L.; Beilun, L.; Li, K.M.; Roufogalis, B.; Depo, Y.; Meicun, Y.; Li, G.Q. Multiple chromatographic and chemometric methods for quality standardisation of Chinese herbal medicines. World Sci. Technol. 2010, 12, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State Pharmacopoeia Committee. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; People’s Medical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hook, I.L. Danggui to Angelica sinensis root: Are potential benefits to European women lost in translation? A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 152, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Circosta, C.; Pasquale, R.D.; Palumbo, D.R.; Samperi, S.; Occhiuto, F. Estrogenic activity of standardized extract of Angelica sinensis. Phytother. Res. 2006, 20, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.-L.; Zeng, R.; Gu, C.-M.; Qu, Y.; Huang, L.-F. Angelica sinensis in China-A review of botanical profile, ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and chemical analysis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 190, 116–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.-H.; Chan, K.; Leung, K.; Chan, C.-L.; Zhao, Z.-Z.; Jiang, Z.-H. Assay of free ferulic acid and total ferulic acid for quality assessment of Angelica sinensis. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1068, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO Monographs on Selected Medicinal Plants. Available online: http://apps.who.int/medicinedocs/en/d/Js4927e/5.html#Js4927e.5 (accessed on 24 May 2020).
- Wei, W.-L.; Huang, L.-F. Simultaneous determination of ferulic acid and phthalides of Angelica sinensis based on UPLC-Q-TOF/MS. Molecules 2015, 20, 4681–4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zschocke, S.; Liu, J.H.; Stuppner, H.; Bauer, R. Comparative study of roots of Angelica sinensis and related umbelliferous drugs by thin layer chromatography, high-performance liquid chromatography, and liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. Phytochem. Anal. 1998, 9, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.H.; Chan, K.; Chan, C.L.; Leung, K.; Jiang, Z.H.; Zhao, Z.Z. Quantification of ligustilides in the roots of Angelica sinensis and related umbelliferous medicinal plants by high-performance liquid chromatography and liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1046, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.J.; Dong, T.T.; Tu, P.F.; Song, Z.H.; Lo, C.K.; Tsim, K.W. Molecular genetic and chemical assessment of radix Angelica (Danggui) in China. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 2576–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Q.; Zheng, J. Simultaneous determination of eight components in Angelica sinensis based on UHPLC-ESI-MS/MS method for quality evaluation. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2019, 33, e4326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guideline, I.H.T. Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology, Q2 (R1), Current Step 4 Version, Parent Guidelines on Methodology Dated November 6 1996, Incorporated in November 2005. In International Conference on Harmonisation, Geneva, Switzerland. Available online: https://www.ich.org/page/quality-guidelines (accessed on 23 June 2020).
- Chan, C.C.; Lee, Y.; Lam, H.; Zhang, X.-M. Analytical Method Validation and Instrument Performance Verification; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Zhao, S.S.; Leung, K.S.Y. Improved quality assessment of proprietary Chinese medicines based on multi-chemical class fingerprinting. J. Sep. Sci. 2009, 32, 2892–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.A.; Jeon, S.K.; Lee, E.J.; Shim, C.H.; Lee, I.S. Comparative study of the chemical composition and antioxidant activity of six essential oils and their components. Nat. Prod. Res. 2010, 24, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaipong, K.; Boonprakob, U.; Crosby, K.; Cisneros-Zevallos, L.; Hawkins Byrne, D. Comparison of ABTS, DPPH, FRAP, and ORAC assays for estimating antioxidant activity from guava fruit extracts. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2006, 19, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Medicine Division. Hong Kong Chinese Materia Medica Standards; Department of Health, Government of Hong Kong Special Administrative Region: Hong Kong, China, 2005; Volume I, pp. 42–51.
- Loh, Z.H.; Er, D.Z.; Chan, L.W.; Liew, C.V.; Heng, P.W. Spray granulation for drug formulation. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2011, 8, 1645–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Cunningham, J.; Winstead, D. Understanding and predicting bed humidity in fluidized bed granulation. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 1564–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.-Z.; He, X.-G.; Lian, L.-Z.; King, W.; Elliott, J. Liquid chromatographic–electrospray mass spectrometric study of the phthalides of Angelica sinensis and chemical changes of Z-ligustilide. J. Chromatogr. A 1998, 810, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Liang, Y.; Wu, H.; Yuan, D. The analysis of Radix Angelicae Sinensis (Danggui). J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 1991–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission, C.P. TLC Atlas of Chinese Crude Drugs in Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; People’s Medical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sa, R.; Yan, H.; Pan, X.; Yang, Y.; Sun, Y. Metabolic fingerprinting of Angelica sinensis during growth using UPLC-TOFMS and chemometrics data analysis. Chem. Cent. J. 2013, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.Y.; Kim, H.M.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, K.Y.; Huang, D.S.; Kim, J.H.; Seong, R.S. Quantitative analysis of marker compounds in Angelica gigas, Angelica sinensis, and Angelica acutiloba by HPLC/DAD. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 63, c15-00081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Resource Sanjiu Medical & Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Manufacturing Technique. Available online: https://www.999.com.cn/index.html (accessed on 24 May 2020).
- Guangdong Yifang Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Producing Process of E-Fong. Available online: http://www.e-fong.com/en/ (accessed on 24 May 2020).
- Yeh, J.-C.; Garrard, I.J.; Cho, C.-W.C.; Bligh, S.A.; Lu, G.-H.; Fan, T.-P.; Fisher, D. Bioactivity-guided fractionation of the volatile oil of Angelica sinensis radix designed to preserve the synergistic effects of the mixture followed by identification of the active principles. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1236, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, S.; Li, S.; Kan, K.K.; Li, P.; Wan, J.; Wang, Y.; Dong, T.T.; Tsim, K.W. Identification and quantification of 13 components in Angelica sinensis (Danggui) by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry coupled with pressurized liquid extraction. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 526, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, X.; Huang, L. Correlation between antioxidant activities and phenolic contents of radix Angelicae sinensis (Danggui). Molecules 2009, 14, 5349–5361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-Y.; Tang, Y.-P.; Liu, X.; Zhu, M.; Tao, W.-W.; Li, W.-X.; Duan, J.-A. Effects of ferulic acid on antioxidant activity in Angelicae Sinensis Radix, Chuanxiong Rhizoma, and their combination. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2015, 13, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.H.; Chen, C.C.; Lin, C.M.; Chiang, B.H. Antioxidant and flavor properties of Angelica sinensis extracts as affected by processing. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2008, 21, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
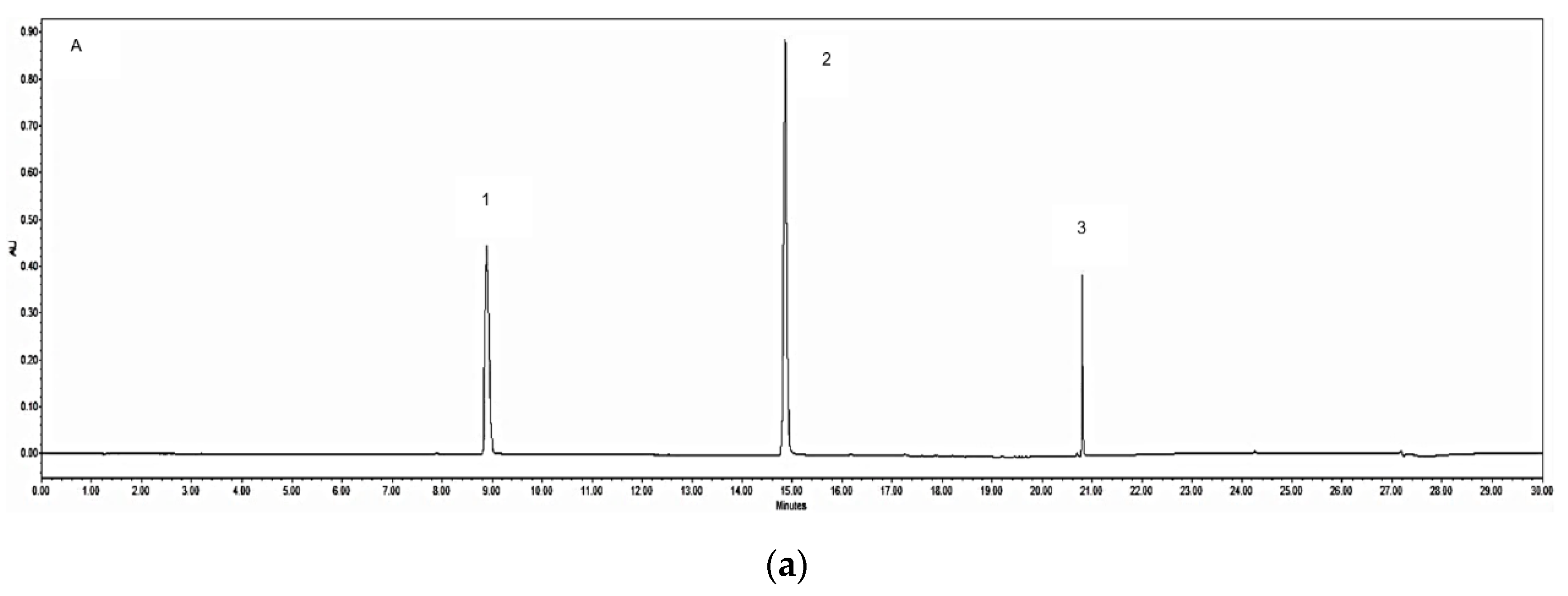
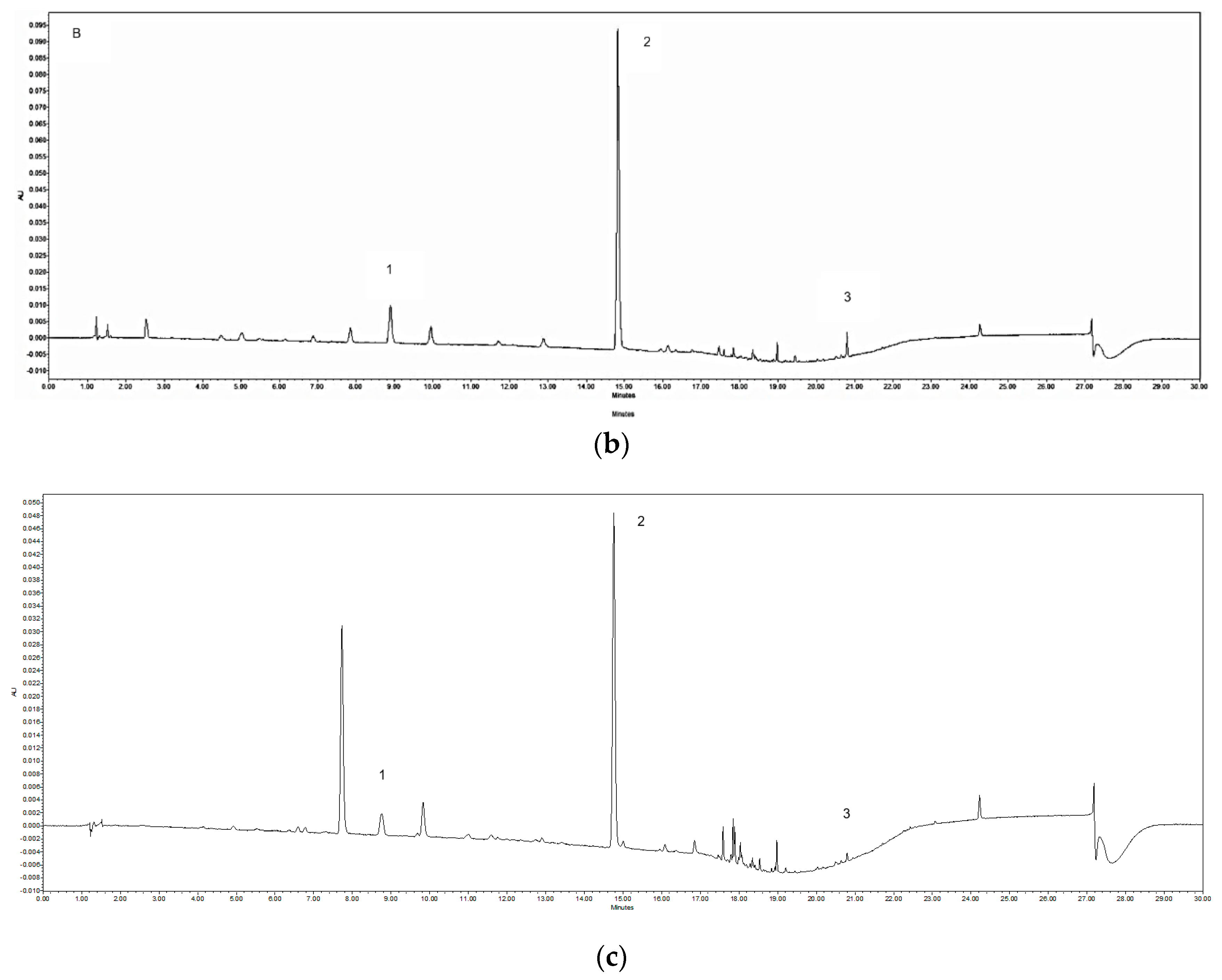
| Sample | Origin | Granule to Herb Ratio c | Yield d % (with Ratio) | Caffeic Acid (mg/g) | Ferulic Acid (mg/g) | Z-Ligustilide (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 a | Guangxi | 1:3 | 12.7 (4.2) | 0.0153 ± 0.001 | 0.111 ± 0.008 | 0.0105 ± 0.001 |
| G2 b | Guangdong | 1:5 | 31.7 (6.3) | 0.0155 ± 0.000 | 0.0631 ± 0.002 | 0.0359 ± 0.001 |
| G3 b | China | 1:5 | 28.5 (5.7) | 0.0142 ± 0.000 | 0.0772 ± 0.002 | 0.0284 ± 0.001 |
| G4 b | Sichuan | 1:10 | 27.3 (2.7) | 0.00491 ± 0.000 | 0.0300 ± 0.001 | 0.00460 ± 0.000 |
| G5 b | Taichung | 1:6 | 31.3 (5.2) | 0.00598 ± 0.000 | 0.145 ± 0.008 | 0.526 ± 0.032 *** |
| G6 a | Beijing | 1:5 | 27.1 (5.4) | 0.0179 ± 0.000 | 0.0764 ± 0.003 | 0.0367 ± 0.001 |
| G7 a | Jiangsu | 2:5 | 32.3 (12.9) | 0.0394 ± 0.002 ** | 0.299 ± 0.014 ** | 0.0810 ± 0.004 |
| G8 a | Guangdong | 3:10 | 28.2 (8.5) | 0.0122 ± 0.001 | 0.0688 ± 0.004 | 0.00923 ± 0.001 |
| G9 a | Sichuan | 1:5 | 35.4 (7.1) | 0.0113 ± 0.001 | 0.0808 ± 0.009 | 0.0129 ± 0.001 |
| G10 a | Guangdong | 1:3.3 | 29.5 (8.9) | 0.0312 ± 0.002 ** | 0.206 ± 0.015 ** | 0.183 ± 0.012 *** |
| R1 | 44.8 | ND | 0.274 ± 0.008 | 0.0262 ± 0.003 | ||
| R2 | 42.1 | 0.0407 ± 0.008 * | 0.503 ± 0.074 * | 0.0245 ± 0.003 | ||
| R3 | 42.3 | ND | 0.284 ± 0.013 | 0.0215 ± 0.003 | ||
| R4 | 41.8 | 0.00455 ± 0.000 | 0.361 ± 0.006 | 0.0168 ± 0.001 | ||
| R5 | 33.2 | 0.00396 ± 0.001 | 0.299 ± 0.013 | 0.0177 ± 0.002 |
| Compound | Regression Equation | R2 | LOD (µg/mL) | LOQ (µg/mL) | Intra-Day RSD (%) (n = 6) | Inter-Day RSD (%) (n = 3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caffeic acid | y = 1.9561x + 0.0108 | 0.998 | 1.496 | 4.492 | 2.770 | 2.598 |
| Ferulic acid | y = 1.9915x − 3.1394 | 0.999 | 0.701 | 2.106 | 1.496 | 2.790 |
| Z-Ligustilide | y = 0.6409x − 0.0103 | 0.997 | 3.268 | 9.813 | 2.725 | 4.108 |
| DPPH Assay a | FRAP Assay a | |
|---|---|---|
| Sample | mg TE/g of DW ± SD | mg TE/g of DW ± SD |
| G1 | 1.79 ± 0.27 | 9.96 ± 4.90 |
| G2 | 3.32 ± 0.29 | 13.60 ± 0.41 |
| G3 | 2.83 ± 0.20 | 9.29 ± 0.27 |
| G4 | 1.76 ± 0.04 | 6.21 ± 0.62 |
| G5 | 2.29 ± 0.45 | 10.75 ± 0.30 |
| G6 | 3.02 ± 0.44 | 10.28 ± 0.45 |
| G7 | 6.33 ± 0.54 | 26.30 ± 0.36 |
| G8 | 7.33 ± 0.32 | 30.82 ± 1.71 |
| G9 | 4.02 ± 0.92 | 16.03 ± 0.05 |
| G10 | 3.34 ± 0.66 | 13.09 ± 0.19 |
| R1 | 3.26 ± 0.81 | 50.34 ± 10.21 |
| R2 | 8.10 ± 0.59 | 69.38 ± 1.82 |
| R3 | 3.05 ± 0.36 | 23.04 ± 5.21 |
| R4 | 4.76 ± 0.42 | 25.73 ± 4.48 |
| R5 | 2.76 ± 0.09 | 32.06 ± 4.07 |
| Assay | DPPH | FRAP | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Markers | |||
| Caffeic acid | 0.582 * | 0.257 | |
| Ferulic acid | 0.507 | 0.791 ** | |
| Z-ligustilide | −0.202 | −0.229 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Razmovski-Naumovski, V.; Zhou, X.; Wong, H.Y.; Kam, A.; Pearson, J.; Chan, K. Chromatographic, Chemometric and Antioxidant Assessment of the Equivalence of Granules and Herbal Materials of Angelicae Sinensis Radix. Medicines 2020, 7, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines7060035
Razmovski-Naumovski V, Zhou X, Wong HY, Kam A, Pearson J, Chan K. Chromatographic, Chemometric and Antioxidant Assessment of the Equivalence of Granules and Herbal Materials of Angelicae Sinensis Radix. Medicines. 2020; 7(6):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines7060035
Chicago/Turabian StyleRazmovski-Naumovski, Valentina, Xian Zhou, Ho Yee Wong, Antony Kam, Jarryd Pearson, and Kelvin Chan. 2020. "Chromatographic, Chemometric and Antioxidant Assessment of the Equivalence of Granules and Herbal Materials of Angelicae Sinensis Radix" Medicines 7, no. 6: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines7060035
APA StyleRazmovski-Naumovski, V., Zhou, X., Wong, H. Y., Kam, A., Pearson, J., & Chan, K. (2020). Chromatographic, Chemometric and Antioxidant Assessment of the Equivalence of Granules and Herbal Materials of Angelicae Sinensis Radix. Medicines, 7(6), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines7060035








