A Combination of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Techniques to Localize the Dural Defect in a Case of Superficial Siderosis—A Case Report
Abstract
1. Introduction
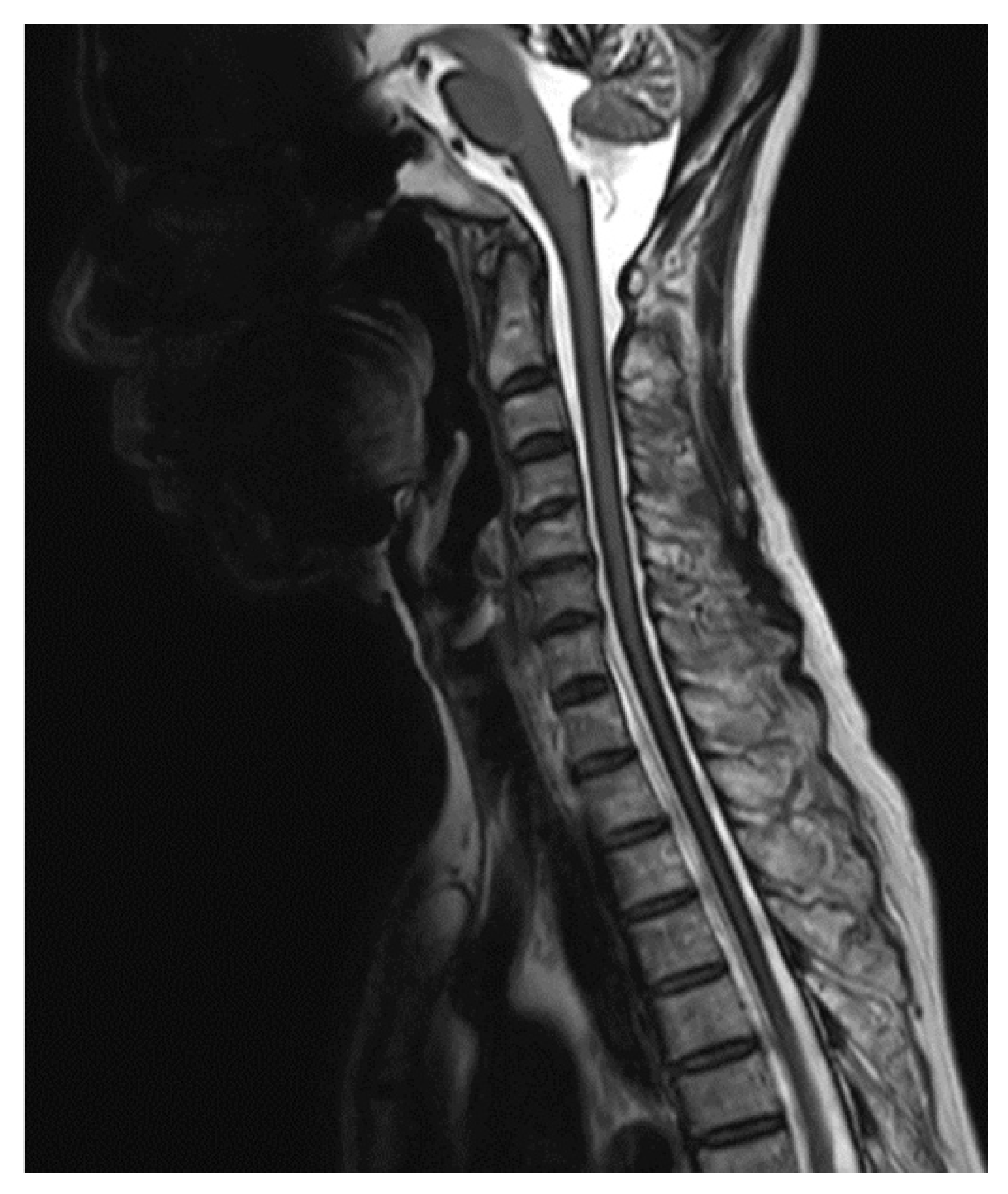
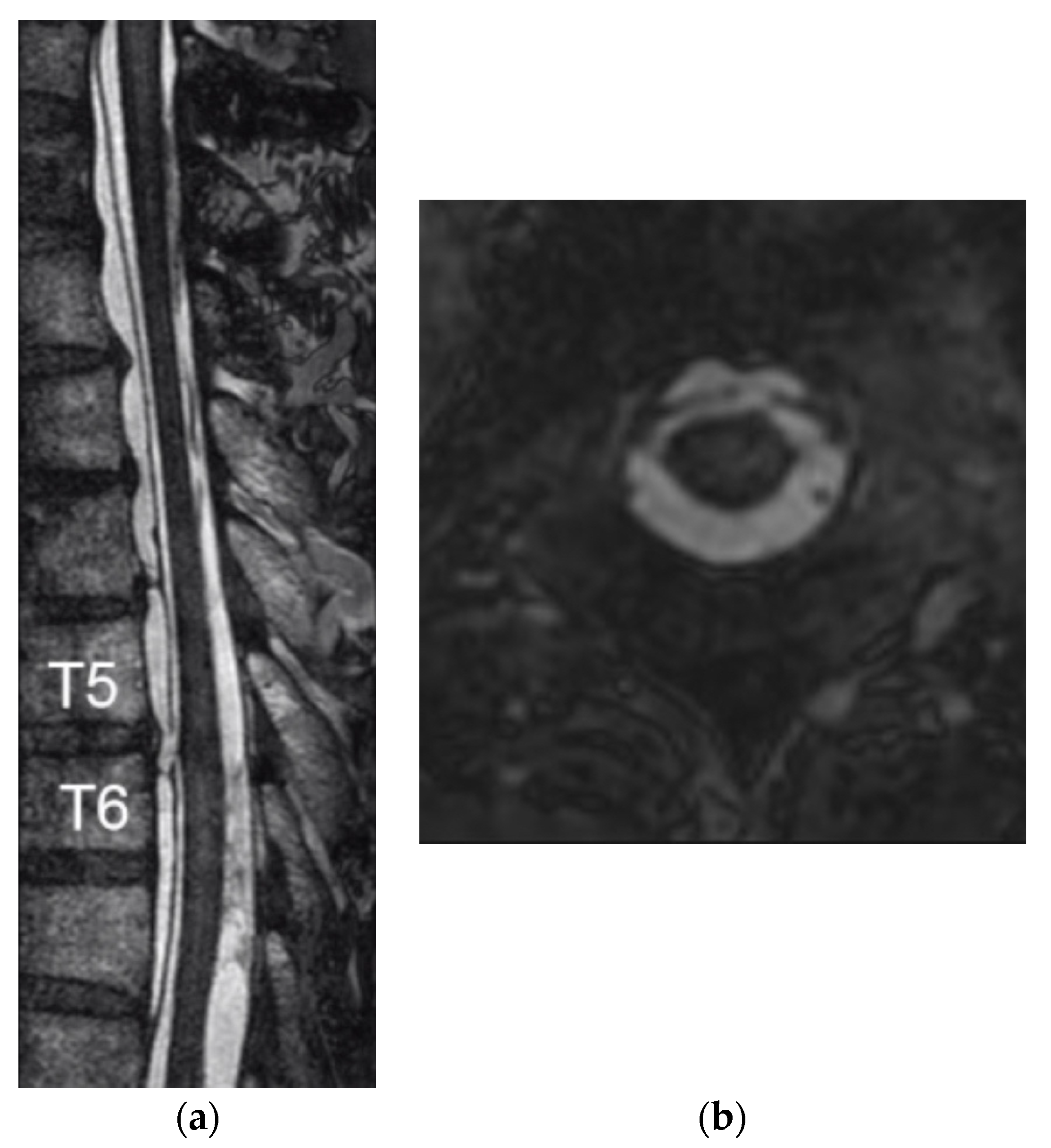
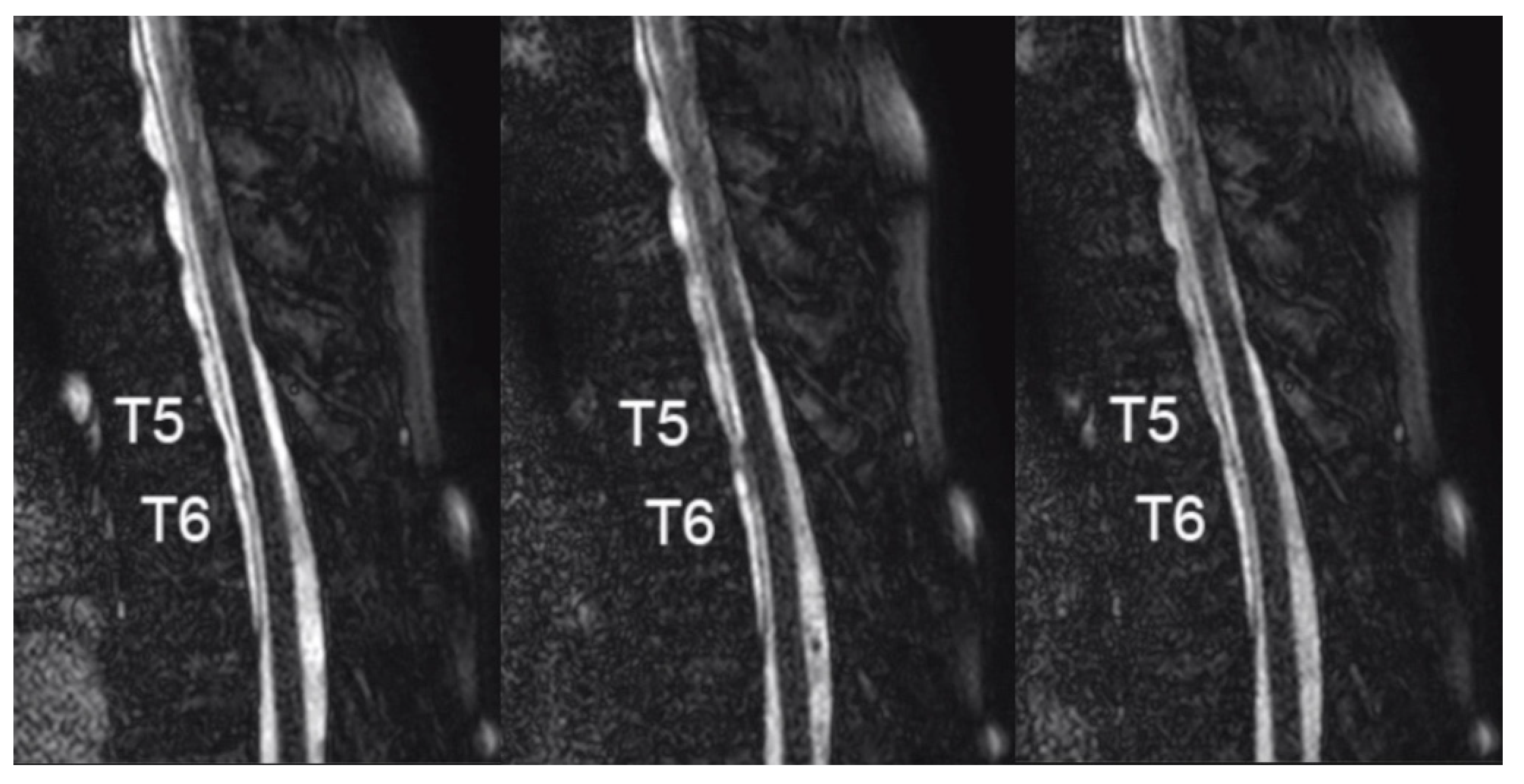
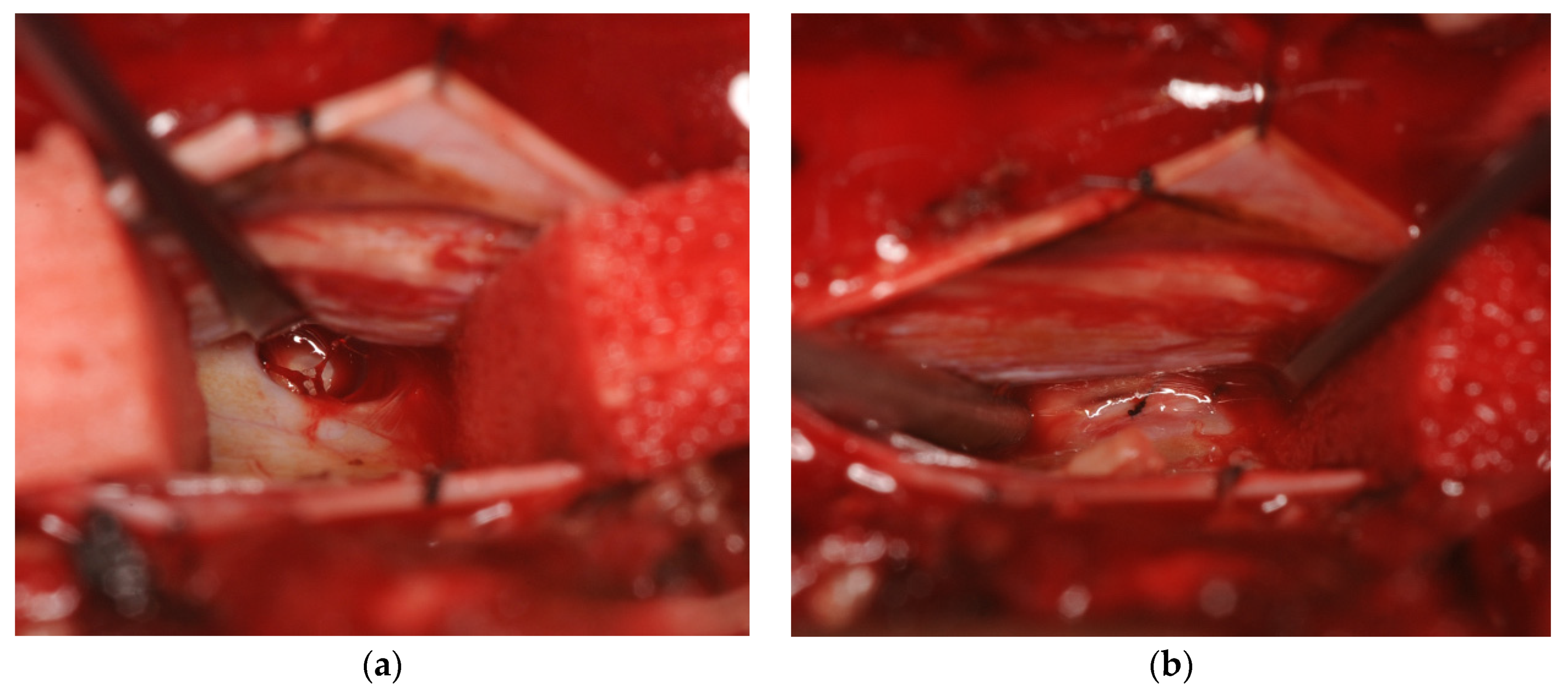
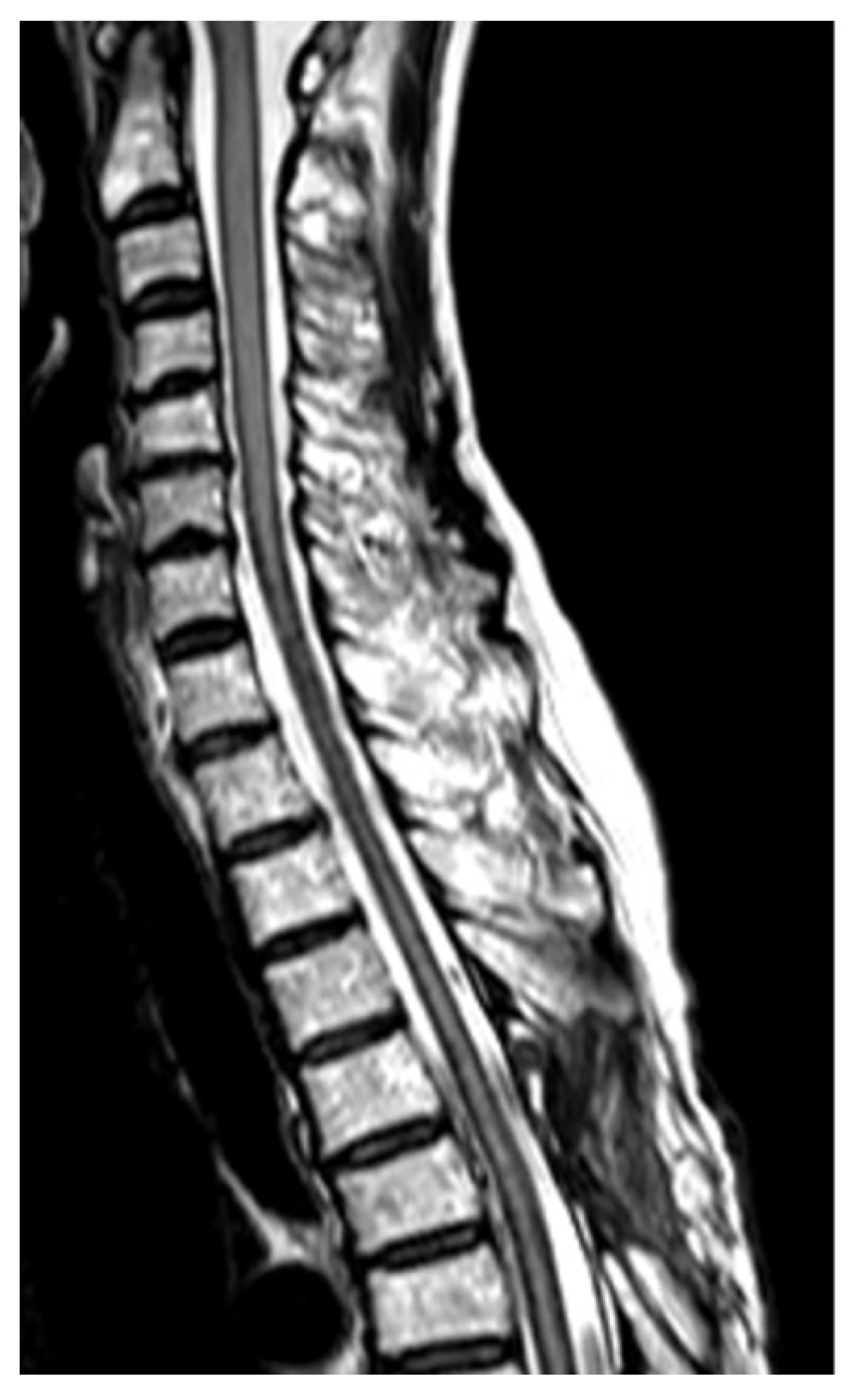
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fearnley, J.M.; Stevens, J.M.; Rudge, P. Superficial siderosis of the central nervous system. Brain 1995, 118 Pt 4, 1051–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N. Neuroimaging in superficial siderosis: An in-depth look. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2010, 31, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohira, M.; Takao, M. Nationwide epidemiological survey of superficial hemosiderosis in Japan. J. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 404, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schievink, W.I.; Chu, R.M.; Maya, M.M.; Johnson, J.P.; Cohen, H.C. Spinal manifestations of spontaneous intracranial hypotension. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2013, 18, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N. Beyond superficial siderosis: Introducing “duropathies”. Neurology 2012, 78, 1992–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egawa, S.; Yoshii, T.; Sakaki, K.; Inose, H.; Kato, T.; Kawabata, S.; Tomizawa, S.; Okawa, A. Dural closure for the treatment of superficial siderosis. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2013, 18, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horie, T.; Kajihara, N.; Matsumae, M.; Obara, M.; Hayashi, N.; Hirayama, A.; Takizawa, K.; Takahara, T.; Yatsushiro, S.; Kuroda, K. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Technique for Visualization of Irregular Cerebrospinal Fluid Motion in the Ventricular System and Subarachnoid Space. World Neurosurg. 2017, 97, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angstwurm, K.; Schielke, E.; Zimmer, C.; Kivelitz, D.; Weber, J.R. Superficial siderosis of the central nervous system: Response to steroid therapy. J. Neurol. 2002, 249, 1223–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, M.; Llinas, R.H. Deferiprone reduces hemosiderin deposits in the brain of a patient with superficial siderosis. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2011, 32, E1–E2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Lindell, E.P.; Wilden, J.A.; Davis, D.H. Role of dynamic CT myelography in identifying the etiology of superficial siderosis. Neurology 2005, 65, 486–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.M.; Kim, E.S.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, S.H.; Eoh, W. Superficial Siderosis of the Central Nervous System Originating from the Thoracic Spine: A Case Report. Korean J. Spine 2016, 13, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoxworth, J.M.; Trentman, T.L.; Kotsenas, A.L.; Thielen, K.R.; Nelson, K.D.; Dodick, D.W. The role of digital subtraction myelography in the diagnosis and localization of spontaneous spinal CSF leaks. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2012, 199, 649–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schievink, W.I.; Maya, M.M.; Moser, F.G.; Prasad, R.S.; Cruz, R.B.; Nuno, M.; Farb, R.I. Lateral decubitus digital subtraction myelography to identify spinal CSF-venous fistulas in spontaneous intracranial hypotension. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2019, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arishima, H.; Higashino, Y.; Yamada, S.; Akazawa, A.; Arai, H.; Tsunetoshi, K.; Matsuda, K.; Kodera, T.; Kitai, R.; Awara, K.; et al. Spinal endoscopy combined with selective CT myelography for dural closure of the spinal dural defect with superficial siderosis: Technical note. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2018, 28, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraka, T.; Kanoto, M.; Toyoguchi, Y.; Igari, R.; Kato, T.; Hosoya, T. Superficial Siderosis Associated with a Spinal Dural Defect. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2018, 17, 189–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takai, K.; Komori, T.; Niimura, M.; Taniguchi, M. Superficial siderosis of the central nervous system associated with intraspinal hemorrhage from ventral thoracic epidural veins and a ventral spinal CSF leak: Case report. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2017, 26, 751–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, K.; Aoki, C.; Hachiya, J. Evaluation of MR cisternography of the cerebellopontine angle using a balanced fast-field-echo sequence: Preliminary findings. Eur. Radiol. 2004, 14, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumi, T.; Sumi, M.; Van Cauteren, M.; Kimura, Y.; Nakamura, T. Parallel imaging technique for the external carotid artery and its branches: Comparison of balanced turbo field echo, phase contrast, and time-of-flight sequences. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2007, 25, 1028–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doita, M.; Nishida, K.; Miura, J.; Takada, T.; Kurosaka, M.; Fujii, M. Kinematic magnetic resonance imaging of a thoracic spinal extradural arachnoid cyst: An alternative suggestion for exacerbation of symptoms during straining. Spine (Phila PA 1976) 2003, 28, E229–E233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neo, M.; Koyama, T.; Sakamoto, T.; Fujibayashi, S.; Nakamura, T. Detection of a dural defect by cinematic magnetic resonance imaging and its selective closure as a treatment for a spinal extradural arachnoid cyst. Spine (Phila PA 1976) 2004, 29, E426–E430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibe, T.; Senzoku, F.; Ikeda, N.; Kamba, Y.; Mikawa, Y. Detection of the communicating hole(s) of spinal extradural arachnoid cysts using time-spatial labeling inversion pulse magnetic resonance imaging. Spine (Phila PA 1976) 2014, 39, E1394–E1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atsumi, H.; Horie, T.; Kajihara, N.; Sunaga, A.; Sakakibara, Y.; Matsumae, M. Simple Identification of Cerebrospinal Fluid Turbulent Motion Using a Dynamic Improved Motion-sensitized Driven-equilibrium Steady-state Free Precession Method Applied to Various Types of Cerebrospinal Fluid Motion Disturbance. Neurol. Med. Chir. (Tokyo) 2020, 60, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horie, T.; Kajihara, N.; Saito, H.; Shibukawa, S.; Obara, M.; Ogino, T.; Niwa, T.; Kuroda, K.; Matsumae, M. Visualization of Cerebrospinal Fluid Motion in the Whole Brain Using Three-dimensional Dynamic Improved Motion-sensitized Driven-equilibrium Steady-state Free Precession. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Katoh, H.; Shibukawa, S.; Yamaguchi, K.; Hiyama, A.; Horie, T.; Sato, M.; Watanabe, M. A Combination of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Techniques to Localize the Dural Defect in a Case of Superficial Siderosis—A Case Report. Medicines 2020, 7, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines7060036
Katoh H, Shibukawa S, Yamaguchi K, Hiyama A, Horie T, Sato M, Watanabe M. A Combination of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Techniques to Localize the Dural Defect in a Case of Superficial Siderosis—A Case Report. Medicines. 2020; 7(6):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines7060036
Chicago/Turabian StyleKatoh, Hiroyuki, Shuhei Shibukawa, Keiko Yamaguchi, Akihiko Hiyama, Tomohiko Horie, Masato Sato, and Masahiko Watanabe. 2020. "A Combination of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Techniques to Localize the Dural Defect in a Case of Superficial Siderosis—A Case Report" Medicines 7, no. 6: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines7060036
APA StyleKatoh, H., Shibukawa, S., Yamaguchi, K., Hiyama, A., Horie, T., Sato, M., & Watanabe, M. (2020). A Combination of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Techniques to Localize the Dural Defect in a Case of Superficial Siderosis—A Case Report. Medicines, 7(6), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines7060036





