Pain Modulation after Oromucosal Cannabinoid Spray (SATIVEX®) in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis: A Study with Quantitative Sensory Testing and Laser-Evoked Potentials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Neurophysiological and Psychophysiological Testing
2.2.1. Laser-Evoked Potentials (LEPs)
2.2.2. Quantitative Sensory Testing (QST)
2.3. Statistical Analysis
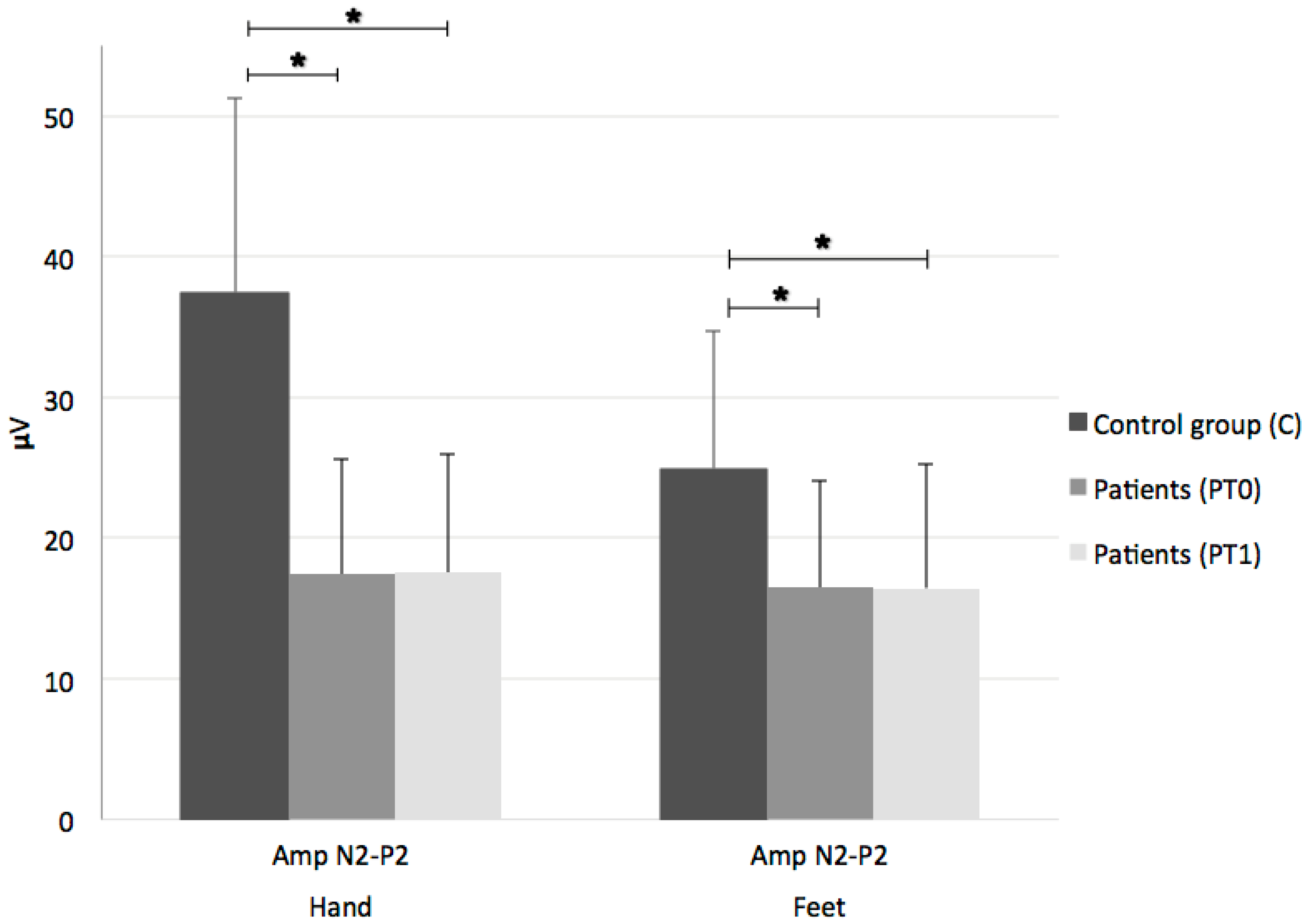
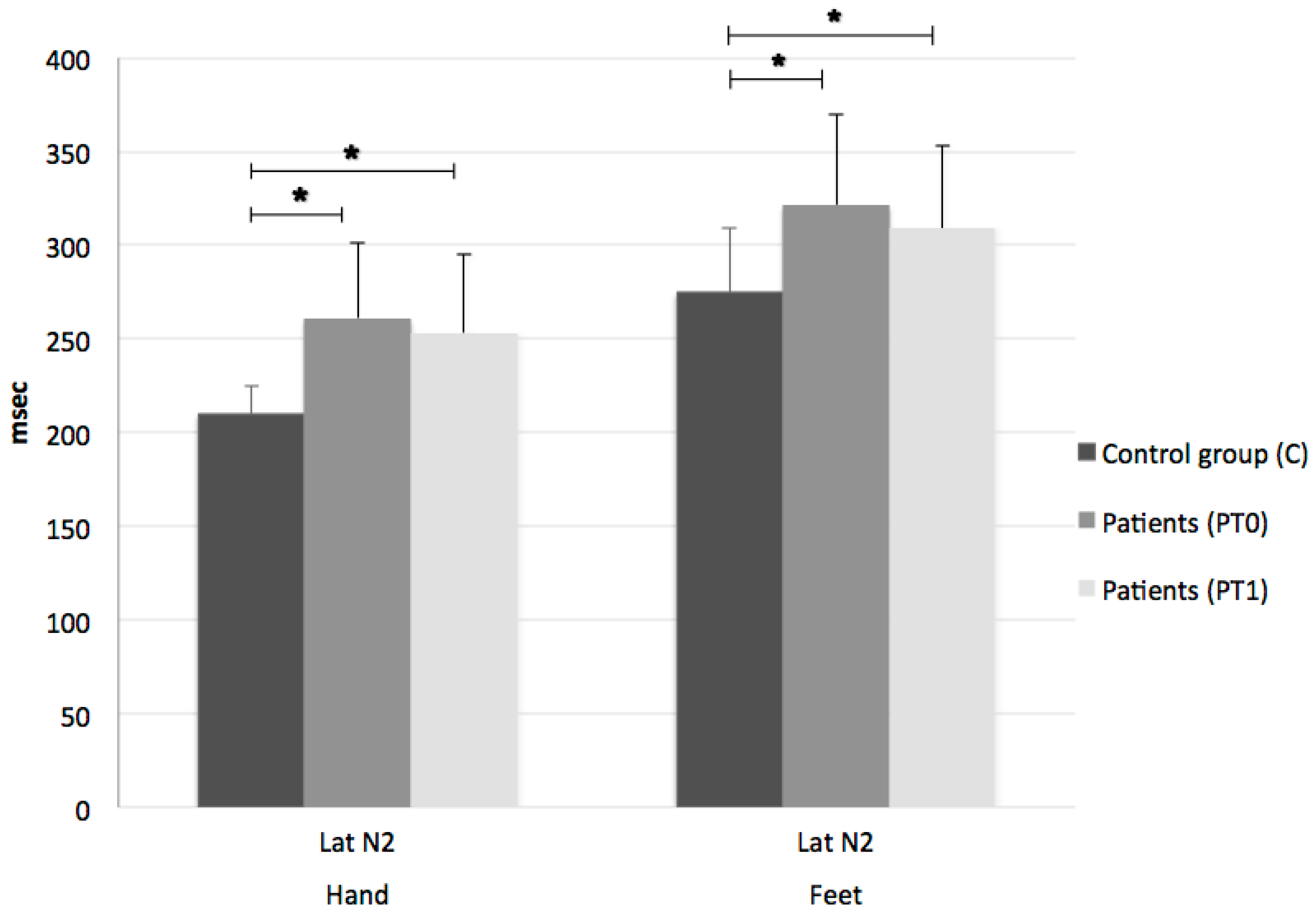
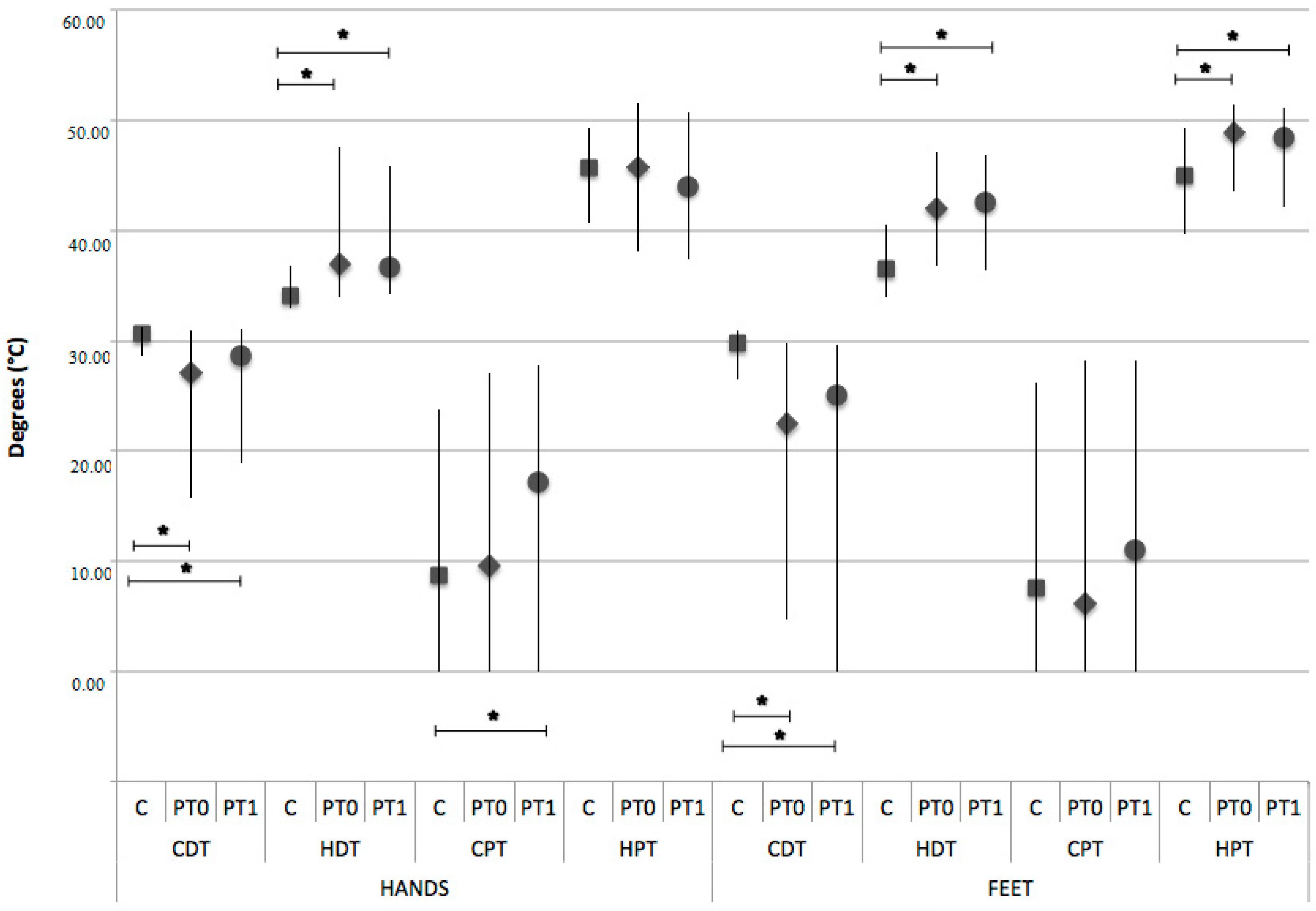
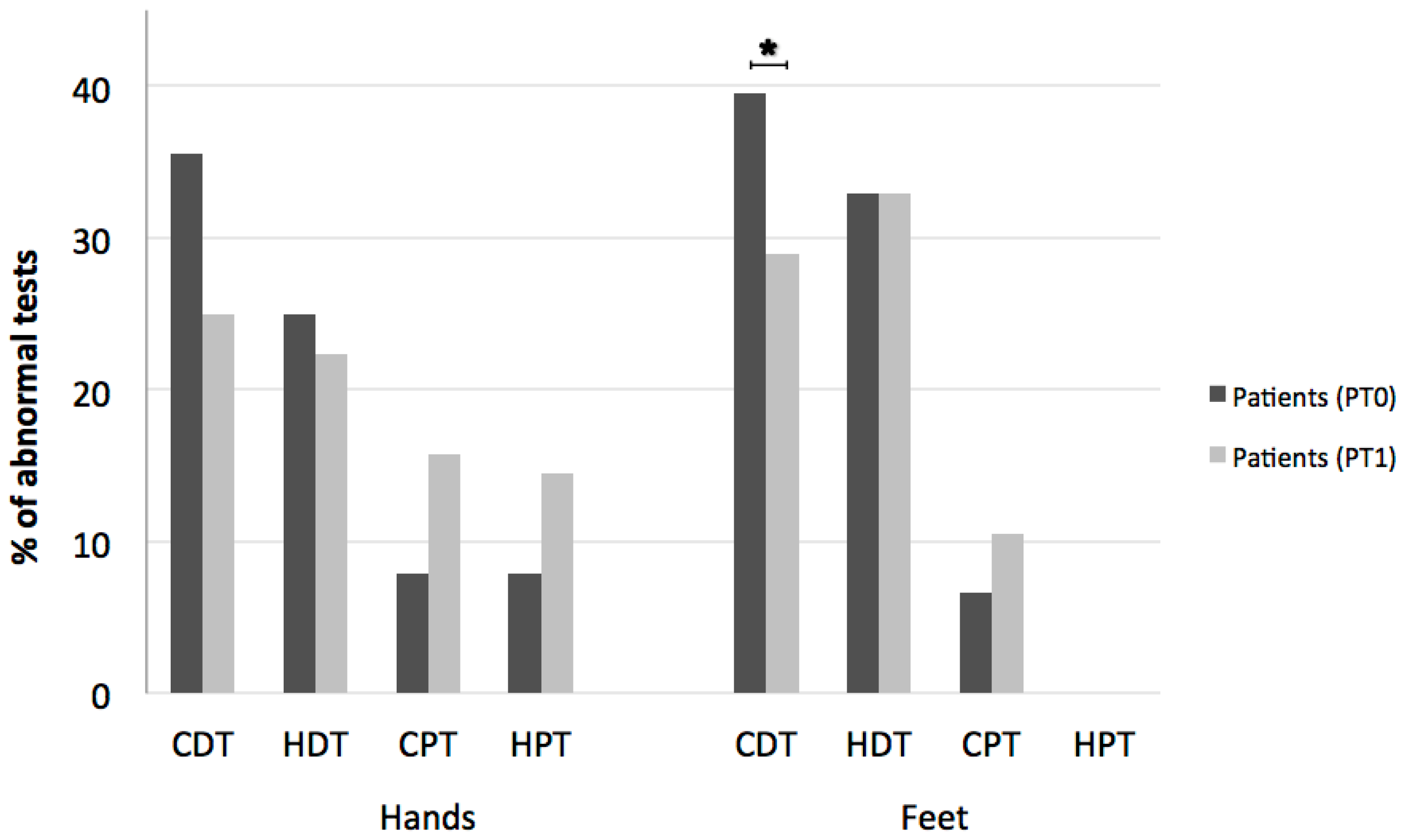
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Indaco, A.; Iachetta, C.; Nappi, C.; Socci, L.; Carrieri, P.B. Chronic and acute pain syndromes in patients with multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol. 1994, 16, 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Foley, P.L.; Vesterinen, H.M.; Laird, B.J.; Sena, E.S.; Colvin, L.A.; Chandran, S.; MacLeod, M.R.; Fallon, M.T. Prevalence and natural history of pain in adults with multiple sclerosis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain 2013, 154, 632–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svendsen, K.B.; Jensen, T.S.; Overvad, K.; Hansen, H.J.; Koch-Henriksen, N.; Bach, F.W. Pain in patients with multiple sclerosis: A population-based study. Arch. Neurol. 2003, 60, 1089–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archibald, C.J.; McGrath, P.J.; Ritvo, P.G.; Fisk, J.D.; Bhan, V.; Maxner, C.E.; Murray, T.J. Pain prevalence, severity and impact in a clinic sample of multiple sclerosis patients. Pain 1994, 58, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solaro, C.; Trabucco, E.; Messmer Uccelli, M. Pain and multiple sclerosis: Pathophysiology and treatment. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2013, 13, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, A.B.; Schwid, S.R.; Herrmann, D.N.; Markman, J.D.; Dworkin, R.H. Pain associated with multiple sclerosis: Systematic review and proposed classification. Pain 2008, 137, 96–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truini, A.; Barbanti, P.; Pozzilli, C.; Cruccu, G. A mechanism-based classification of pain in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. 2013, 260, 351–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treede, R.D.; Jensen, T.S.; Campbell, J.N.; Cruccu, G.; Dostrovsky, J.O.; Griffin, J.W.; Hansson, P.; Hughes, R.; Nurmikko, T.; Serra, J. Neuropathic pain: Redefinition and a grading system for clinical and research purposes. Neurology 2008, 70, 1630–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serpell, M.; Ratcliffe, S.; Hovorka, J.; Schofield, M.; Taylor, L.; Lauder, H.; Ehler, E. A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel group study of THC/CBD spray in peripheral neuropathic pain treatment. Eur. J. Pain 2014, 18, 999–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, J.; Schley, M.; Casutt, M.; Gerber, H.; Schuepfer, G.; Rukwied, R.; Schleinzer, W.; Ueberall, M.; Konrad, C. Tetrahydrocannabinol (Delta 9-THC) Treatment in Chronic Central Neuropathic Pain and Fibromyalgia Patients: Results of a Multicenter Survey. Anesthesiol. Res. Pract. 2009, 2009, 827290. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blake, A.; Wan, B.A.; Malek, L.; DeAngelis, C.; Diaz, P.; Lao, N.; Chow, E.; O’Hearn, S. A selective review of medical cannabis in cancer pain management. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2017, 6 (Suppl. 2), S215–S222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wade, D.T.; Makela, P.; Robson, P.; House, H.; Bateman, C. Do cannabis-based medicinal extracts have general or specific effects on symptoms in multiple sclerosis? A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study on 160 patients. Mult. Scler. 2004, 10, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novotna, A.; Mares, J.; Ratcliffe, S.; Novakova, I.; Vachova, M.; Zapletalova, O.; Gasperini, C.; Pozzilli, C.; Cefaro, L.; Comi, G.; et al. Sativex Spasticity Study Group. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, enriched-design study of nabiximols* (Sativex(®)), as add-on therapy, in subjects with refractory spasticity caused by multiple sclerosis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2011, 18, 1122–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langford, R.M.; Mares, J.; Novotna, A.; Vachova, M.; Novakova, I.; Notcutt, W.; Ratcliffe, S. A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study of THC/CBD oromucosal spray in combination with the existing treatment regimen, in the relief of central neuropathic pain in patients with multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. 2013, 260, 984–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syed, Y.Y.; McKeage, K.; Scott, L.J. Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol/cannabidiol (Sativex®): A review of its use in patients with moderate to severe spasticity due to multiple sclerosis. Drugs 2014, 74, 563–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, E.; Guy, G.W. A tale of two cannabinoids: The therapeutic rationale for combining tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol. Med. Hypotheses 2006, 66, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svízenská, I.; Dubový, P.; Sulcová, A. Cannabinoid receptors 1 and 2 (CB1 and CB2), their distribution, ligands and functional involvement in nervous system structures—A short review. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2008, 90, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, M.A.; Izydorczyk, I.; Mueller-Tribbensee, S.M.; Becker, C.; Neurath, M.F.; Reeh, P.W. Inhibitory CB1 and activating/desensitizing TRPV1-mediated cannabinoid actions on CGRP release in rodent skin. Neuropeptides 2011, 45, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wotherspoon, G.; Fox, A.; McIntyre, P.; Colley, S.; Bevan, S.; Winter, J. Peripheral nerve injury induces cannabinoid receptor 2 protein expression in rat sensory neurons. Neuroscience 2005, 135, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhaveri, M.D.; Sagar, D.R.; Elmes, S.J.; Kendall, D.A.; Chapman, V. Cannabinoid CB2 receptor-mediated anti-nociception in models of acute and chronic pain. Mol. Neurobiol. 2007, 36, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, D.; Pryce, G.; Giovannoni, G.; Thompson, A.J. The therapeutic potential of cannabis. Lancet Neurol. 2003, 2, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rog, D.J.; Nurmikko, T.J.; Friede, T.; Young, C.A. Randomized, controlled trial of cannabis-based medicine in central pain in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2005, 65, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zajicek, J.P.; Sanders, H.P.; Wright, D.E.; Vickery, P.J.; Ingram, W.M.; Reilly, S.M.; Nunn, A.J.; Teare, L.J.; Fox, P.J.; Thompson, A.J. Cannabinoids in multiple sclerosis (CAMS) study: Safety and efficacy data for 12 months follow up. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2005, 76, 1664–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patti, F.; Messina, S.; Solaro, C.; Amato, M.P.; Bergamaschi, R.; Bonavita, S.; Bruno Bossio, R.; Brescia Morra, V.; Costantino, G.F.; Cavalla, P.; et al. Efficacy and safety of cannabinoid oromucosal spray for multiple sclerosis spasticity. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2016, 87, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruccu, G.; Sommer, C.; Anand, P.; Attal, N.; Baron, R.; Garcia-Larrea, L.; Haanpaa, M.; Jensen, TS.; Serra, J.; Treede, RD. EFNS guidelines on neuropathic pain assessment: Revised 2009. Eur. J. Neurol. 2010, 17, 1010–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfau, D.B.; Geber, C.; Birklein, F.; Treede, R.D. Quantitative sensory testing of neuropathic pain patients: Potential mechanistic and therapeutic implications. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2012, 16, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, M.; Naro, A.; Leo, A.; Sessa, E.; D’Aleo, G.; Bramanti, P.; Calabrò, R.S. Evaluating Sativex® in Neuropathic Pain Management: A Clinical and Neurophysiological Assessment in Multiple Sclerosis. Pain Med. 2016, 17, 1145–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polman, C.H.; Reingold, S.C.; Banwell, B.; Clanet, M.; Choen, J.A.; Filippi, M.; Fujihara, K.; Havrdova, E.; Hutchinson, M.; Kappos, L.; et al. Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2010 revisions to the McDonald criteria. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 69, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finnerup, N.B.; Haroutounian, S.; Kamerman, P.; Baron, R.; Bennett, D.L.; Bouhassira, D.; Cruccu, G.; Freeman, R.; Hansson, P.; Nurmikko, T.; et al. Neuropathic pain: An updated grading system for research and clinical practice. Pain 2016, 157, 1599–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, Z.; MacDermid, J.C. Quantitative Sensory Testing in Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain. Pain Med. 2016, 17, 1694–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wade, D.T.; Makela, P.M.; House, H.; Bateman, C.; Robson, P. Long-term use of a cannabis-based medicine in the treatment of spasticity and other symptoms in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 2006, 12, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rog, D.J.; Nurmikko, T.J.; Young, C.A. Oromucosal delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol/cannabidiol for neuropathic pain associated with multiple sclerosis: An uncontrolled, open-label, 2-year extension trial. Clin. Ther. 2007, 29, 2068–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truini, A.; Galeotti, F.; La Cesa, S.; Di Rezze, S.; Biasiotta, A. Mechanisms of pain in multiple sclerosis: A combined clinical and neurophysiological study. Pain 2012, 153, 2048–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truini, A.; Panuccio, G.; Galeotti, F.; Maluccio, M.R.; Sartucci, F.; Avoli, M.; Cruccu, G. Laser-evoked potentials as a tool for assessing the efficacy of antinociceptive drugs. Eur. J. Pain 2014, 14, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruccu, G.; Leandri, M.; Iannetti, G.D.; Mascia, A.; Romaniello, A.; Truini, A.; Galeotti, F.; Manfredi, M. Small-fiber dysfunction in trigeminal neuralgia: Carbamazepine effect on laser-evoked potentials. Neurology 2001, 56, 1722–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svendsen, K.B.; Jensen, T.S.; Bach, F.W. Does the cannabinoid dronabinol reduce central pain in multiple sclerosis? Randomized double blind placebo controlled crossover trial. BMJ 2004, 329, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storozhuk, M.V.; Zholos, A.V. TRP channels as novel targets for endogenous ligands: Focus on endocannabinoids and nociceptive signalling. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2018, 16, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKemy, D.D. How cold is it? TRPM8 and TRPA1 in the molecular logic of cold sensation. Mol. Pain 2005, 1, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrus, M.; Peier, A.M.; Bandell, M.; Hwang, S.W.; Huynh, T.; Olney, N.; Jegla, T.; Patapoutian, A. A role of TRPA1 in mechanical hyperalgesia is revealed by pharmacological inhibition. Mol. Pain 2007, 3, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Camino, D.; Murphy, S.; Heiry, M.; Barrett, L.B.; Earley, T.J.; Cook, C.A.; Petrus, M.J.; Zhao, M.; D’Amours, M.; Deering, N.; et al. TRPA1 contributes to cold hypersensitivity. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 15165–15174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obata, K.; Katsura, H.; Mizushima, T.; Yamanaka, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Dai, Y.; Fukuoka, T.; Tokunaga, A.; Tominaga, M.; Noguchi, K. TRPA1 induced in sensory neurons contributes to cold hyperalgesia after inflammation and nerve injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 2393–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karashima, Y.; Talavera, K.; Everaerts, W.; Janssens, A.; Kwan, K.Y.; Vennekens, R.; Nilius, B.; Voets, T. TRPA1 acts as a cold sensor in vitro and in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1273–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flachenecker, P.; Henze, T.; Zettl, U.K. Long-term effectiveness and safety of nabiximols (tetrahydrocannabinol/cannabidiol oromucosal spray) in clinical practice. Eur. Neurol. 2014, 72, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavanaugh, E.J.; Simkin, D.; Kim, D. Activation of transient receptor potential A1 channels by mustard oil, tetrahydrocannabinol and Ca2+ reveals different functional channel states. Neuroscience 2008, 154, 1467–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Petrocellis, L.; Ligresti, A.; Moriello, A.S.; Allarà, M.; Bisogno, T.; Petrosino, S.; Stott, C.G.; Di Marzo, V. Effects of cannabinoids and cannabinoid-enriched Cannabis extracts on TRP channels and endocannabinoid metabolic enzymes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 163, 1479–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caterina, M.J. TRP channel cannabinoid receptors in skin sensation, homeostasis, and inflammation. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2014, 5, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Marzo, V.; Piscitelli, F. The Endocannabinoid System and its Modulation by Phytocannabinoids. Neurotherapeutics 2015, 12, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, P.; Hurst, D.P.; Reggio, P.H. Molecular Targets of the Phytocannabinoids: A Complex Picture. Prog. Chem. Org. Nat. Prod. 2017, 103, 103–131. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gentry, C.; Stoakley, N.; Andersson, D.A.; Bevan, S. The roles of iPLA2, TRPM8 and TRPA1 in chemically induced cold hypersensitivity. Mol. Pain 2010, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Petrocellis, L.; Vellani, V.; Schiano-Moriello, A.; Marini, P.; Magherini, P.C.; Orlando, P.; Di Marzo, V. Plant-derived cannabinoids modulate the activity of transient receptor potential channels of ankyrin type-1 and melastatin type-8. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 325, 1007–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karst, M.; Wippermann, S.; Ahrens, J. Role of cannabinoids in the treatment of pain and (painful) spasticity. Drugs 2010, 70, 2409–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrè, L.; Nuara, A.; Pavan, G.; Radaelli, M.; Moiola, L.; Rodegher, M.; Colombo, B.; Keller Sarmiento, I.J.; Martinelli, V.; Leocani, L.; et al. Efficacy and safety of nabiximols (Sativex(®)) on multiple sclerosis spasticity in a real-life Italian monocentric study. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 37, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruparel, N.B.; Patwardhan, A.M.; Akopian, A.N.; Hargreaves, K.M. Desensitization of transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 (TRPA1) by the TRP vanilloid 1-selective cannabinoid arachidonoyl-2 chloroethanolamine. Mol. Pharmacol. 2011, 80, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Case Number | Age | Gender | MS Subtype | Disease Duration (years) | EDSS | MAS | NRS | Type of Pain |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 56 | M | RR | 9 | 4.5 | 0.3 | 6 | neuropathic * |
| 2 | 54 | F | RR | 33 | 5.5 | 0.1 | 6 | nociceptive |
| 3 | 46 | M | PP | 15 | 7.5 | 0.8 | 4 | nociceptive |
| 4 | 37 | M | SP | 18 | 6 | 1.8 | 7 | mixed * |
| 5 | 63 | F | RR | 4 | 5.5 | 1.3 | 4 | nociceptive |
| 6 | 48 | F | SP | 21 | 7.5 | 2.0 | 6 | neuropathic |
| 7 | 58 | F | SP | 13 | 5.5 | 1.3 | 5.5 | nociceptive * |
| 8 | 48 | M | SP | 7 | 5.5 | 0.8 | 6 | nociceptive * |
| 9 | 61 | F | SP | 30 | 6.5 | 1.1 | 2 | nociceptive |
| 10 | 48 | F | RR | 16 | 6 | 1.8 | 7 | neuropathic |
| 11 | 59 | M | SP | 23 | 5.5 | 1.3 | 4 | neuropathic * |
| 12 | 61 | M | SP | 10 | 6 | 1.3 | 3.5 | mixed * |
| 13 | 65 | F | PP | 43 | 6.5 | 1.3 | 10 | neuropathic |
| 14 | 63 | F | SP | 17 | 7 | 1.6 | 6 | nociceptive |
| 15 | 49 | M | SP | 3 | 5.5 | 0.8 | 10 | mixed |
| 16 | 56 | F | SP | 23 | 7.5 | 2.0 | 9 | mixed |
| 17 | 57 | M | PP | 26 | 8 | 2.3 | 4.5 | nociceptive |
| 18 | 57 | M | RR | 17 | 5.5 | 0.7 | 6 | neuropathic * |
| 19 | 57 | F | SP | 33 | 6 | 0.5 | 2 | neuropathic |
| 20 | 58 | M | RR | 17 | 6 | 0.8 | 9 | neuropathic |
| 21 | 47 | F | RR | 16 | 3.5 | 0.3 | 8 | neuropathic |
| 22 | 59 | F | SP | 36 | 4.5 | 0.8 | 8.5 | neuropathic * |
| 23 | 51 | F | SP | 20 | 7 | 1.2 | 3 | nociceptive * |
| 24 | 65 | F | PP | 8 | 6 | 1.3 | 8 | mixed |
| 25 | 59 | F | SP | 18 | 7.5 | 1.3 | 7 | mixed |
| 26 | 61 | M | SP | 19 | 7.5 | 1.3 | 10 | neuropathic |
| 27 | 44 | F | RR | 1 | 2 | 0.1 | 6 | mixed |
| 28 | 44 | F | SP | 5 | 5.5 | 0.2 | 7 | neuropathic |
| Mean (SD) | 54.7 (7.3) | 11M/17F | 8 RR/4 PP/16 SP | 18 (10.5) | 6 (1.31) | 1.1 (0.6) | 6.3 (2.3) | 12 neuropathic 9 nociceptive 7 mixed |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Turri, M.; Teatini, F.; Donato, F.; Zanette, G.; Tugnoli, V.; Deotto, L.; Bonetti, B.; Squintani, G. Pain Modulation after Oromucosal Cannabinoid Spray (SATIVEX®) in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis: A Study with Quantitative Sensory Testing and Laser-Evoked Potentials. Medicines 2018, 5, 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines5030059
Turri M, Teatini F, Donato F, Zanette G, Tugnoli V, Deotto L, Bonetti B, Squintani G. Pain Modulation after Oromucosal Cannabinoid Spray (SATIVEX®) in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis: A Study with Quantitative Sensory Testing and Laser-Evoked Potentials. Medicines. 2018; 5(3):59. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines5030059
Chicago/Turabian StyleTurri, Mara, Francesco Teatini, Francesco Donato, Giampietro Zanette, Valeria Tugnoli, Luciano Deotto, Bruno Bonetti, and Giovanna Squintani. 2018. "Pain Modulation after Oromucosal Cannabinoid Spray (SATIVEX®) in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis: A Study with Quantitative Sensory Testing and Laser-Evoked Potentials" Medicines 5, no. 3: 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines5030059
APA StyleTurri, M., Teatini, F., Donato, F., Zanette, G., Tugnoli, V., Deotto, L., Bonetti, B., & Squintani, G. (2018). Pain Modulation after Oromucosal Cannabinoid Spray (SATIVEX®) in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis: A Study with Quantitative Sensory Testing and Laser-Evoked Potentials. Medicines, 5(3), 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines5030059







