Necrostatin-1 Attenuates Inflammatory Response and Improves Cognitive Function in Chronic Ischemic Stroke Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
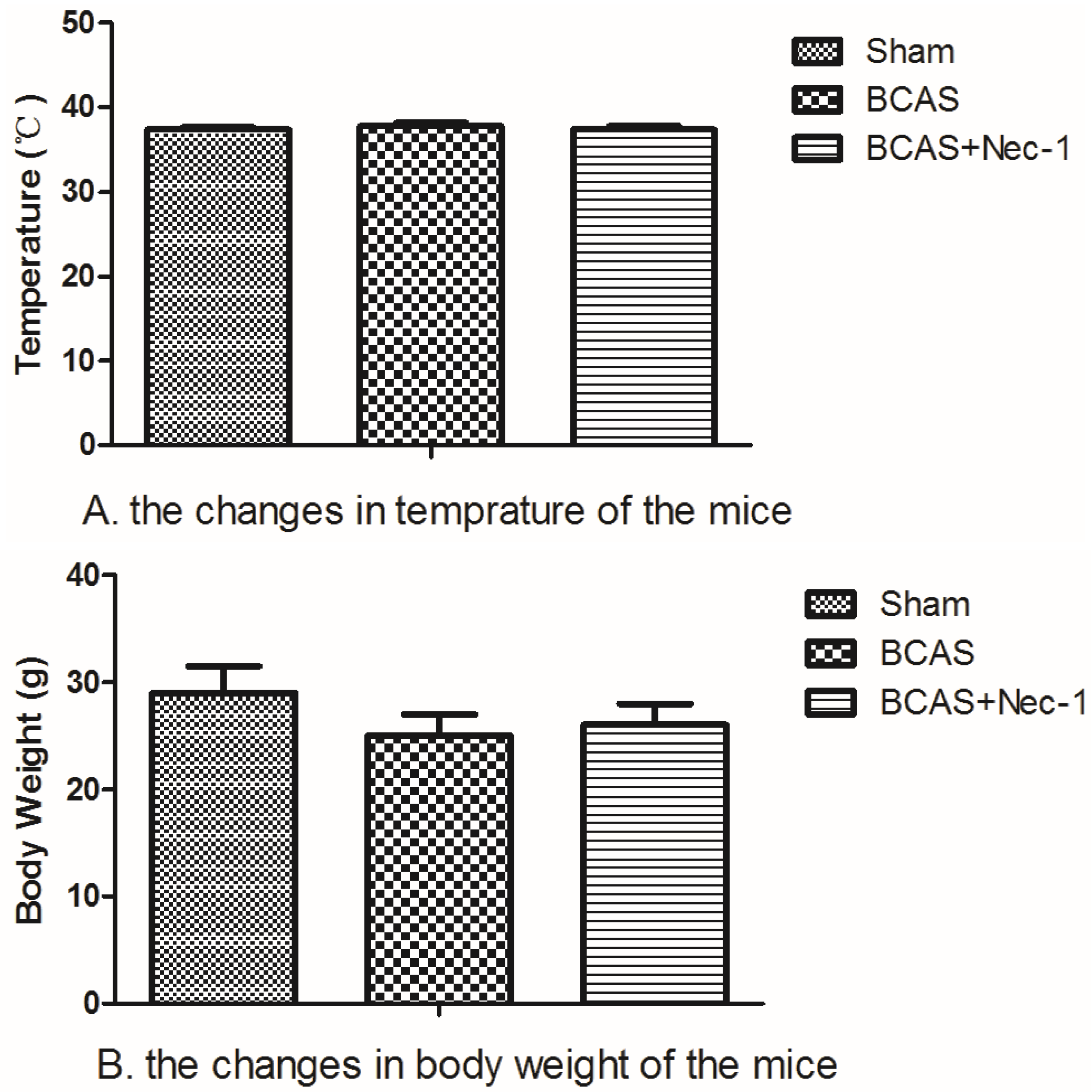
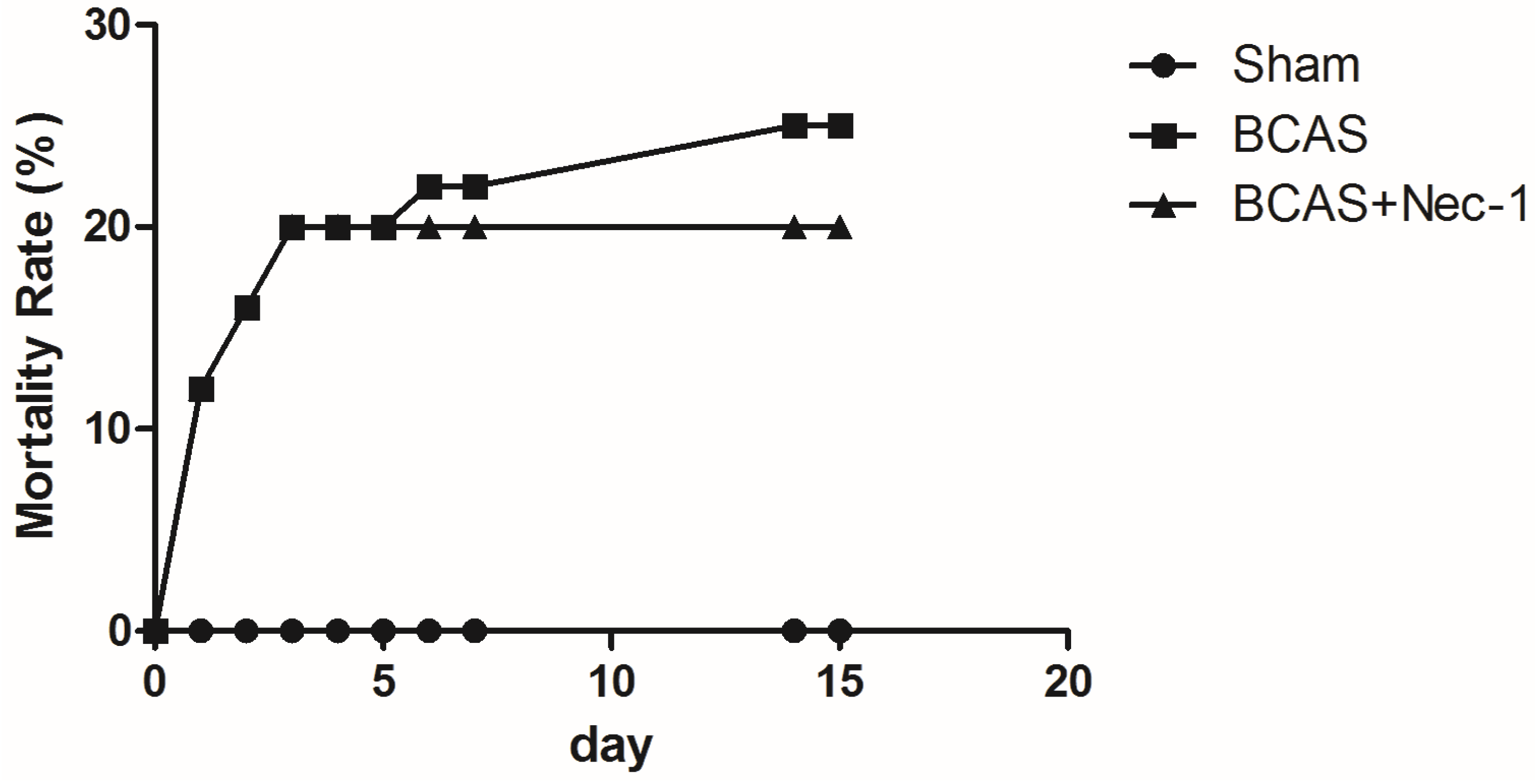
2.1. Physiological Index and Mortality Rates in the Experimental Animals
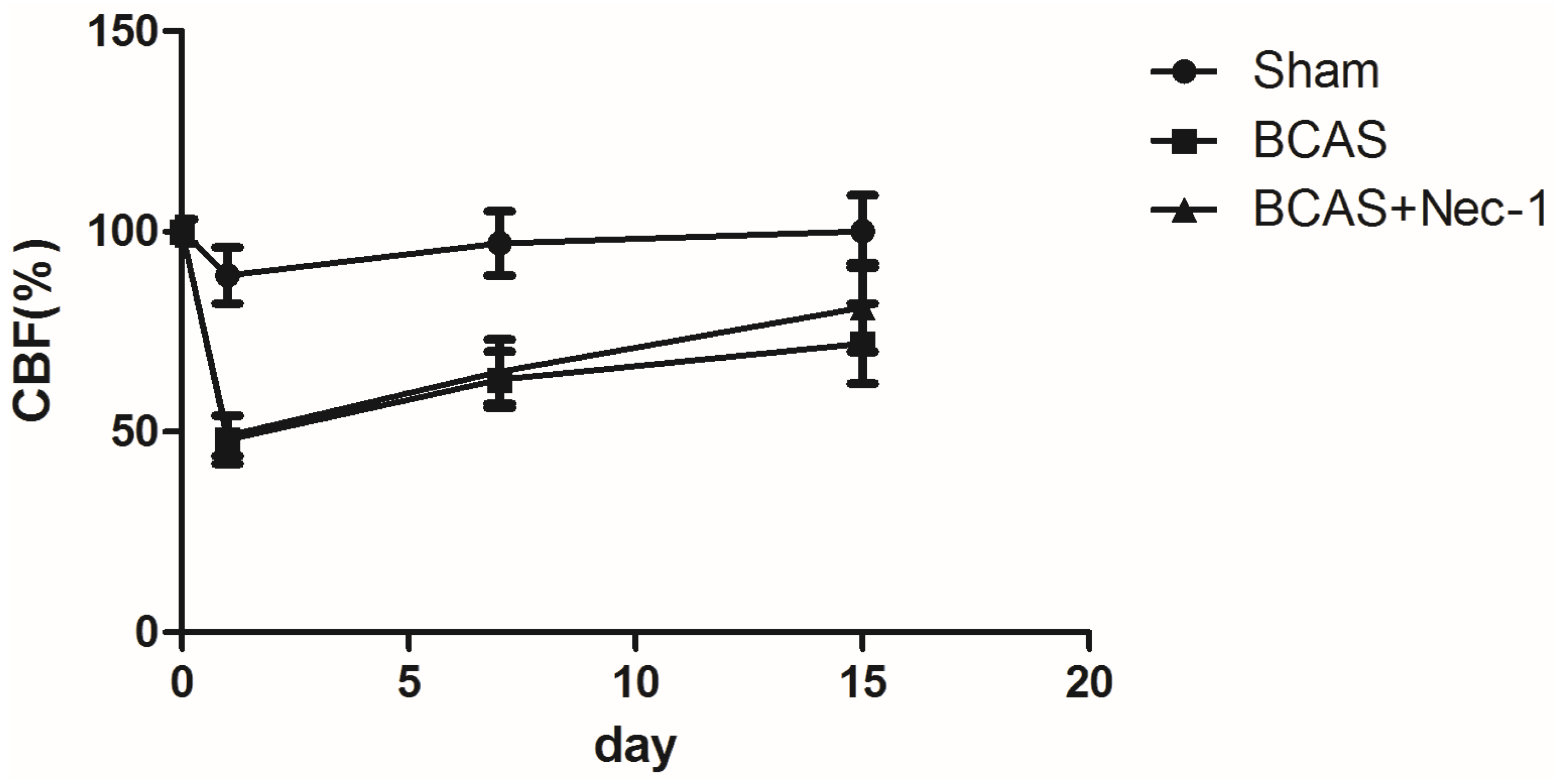
2.2. Changes of Cerebral Blood Flow (CBF) in the Experimental Mice
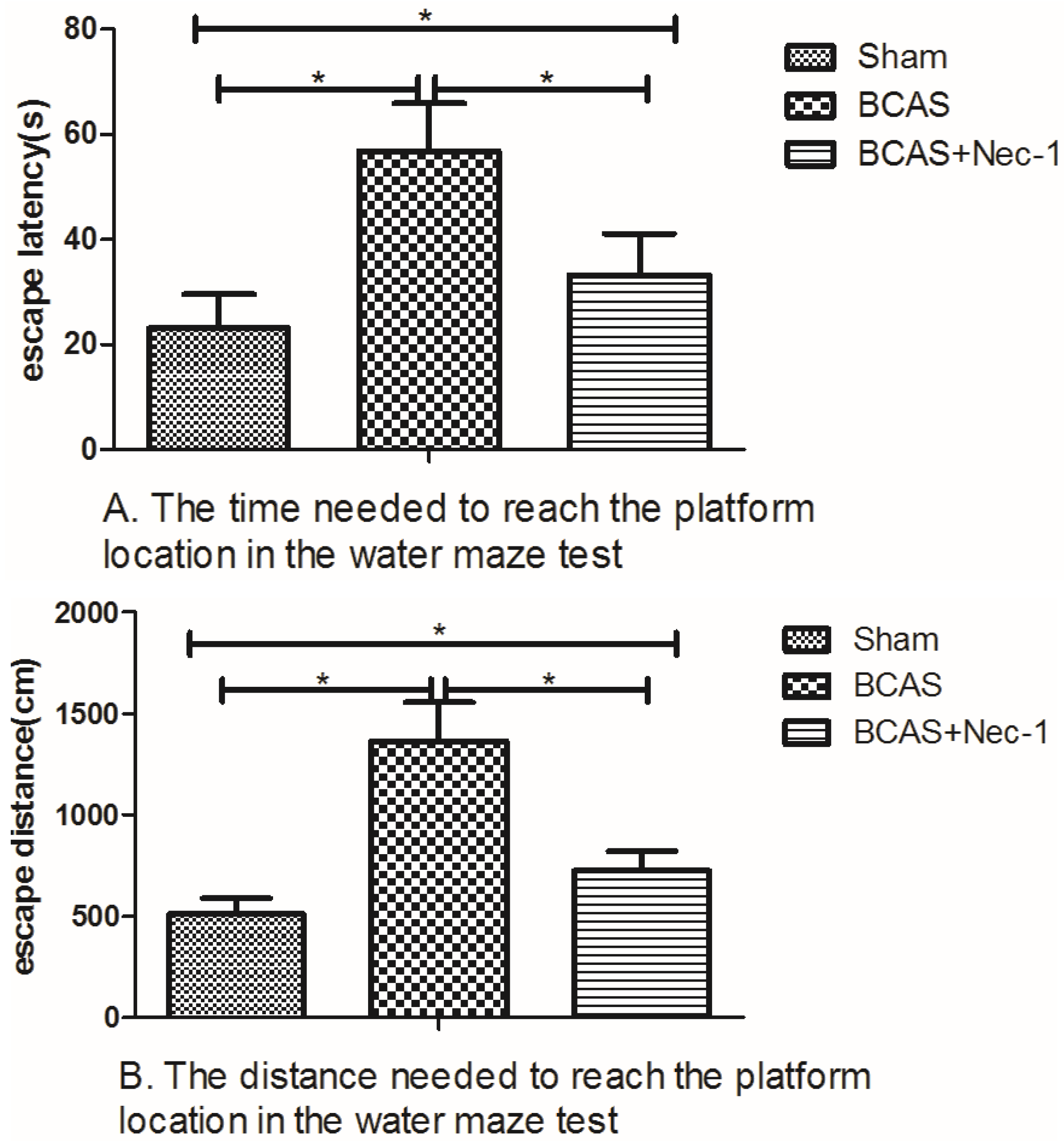
2.3. Nec-1 Improves Cognitive Decline in the BCAS Mice
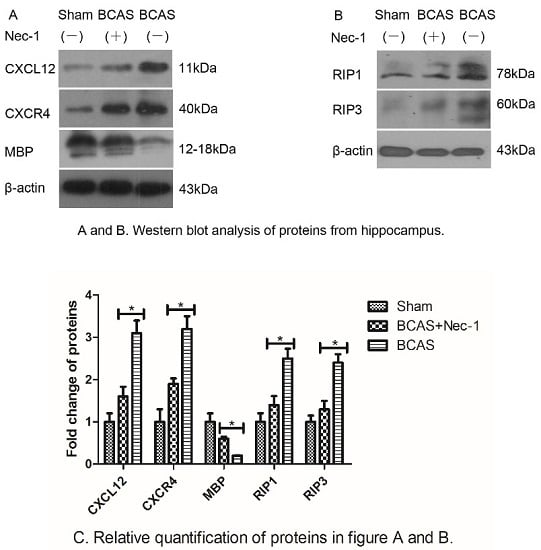
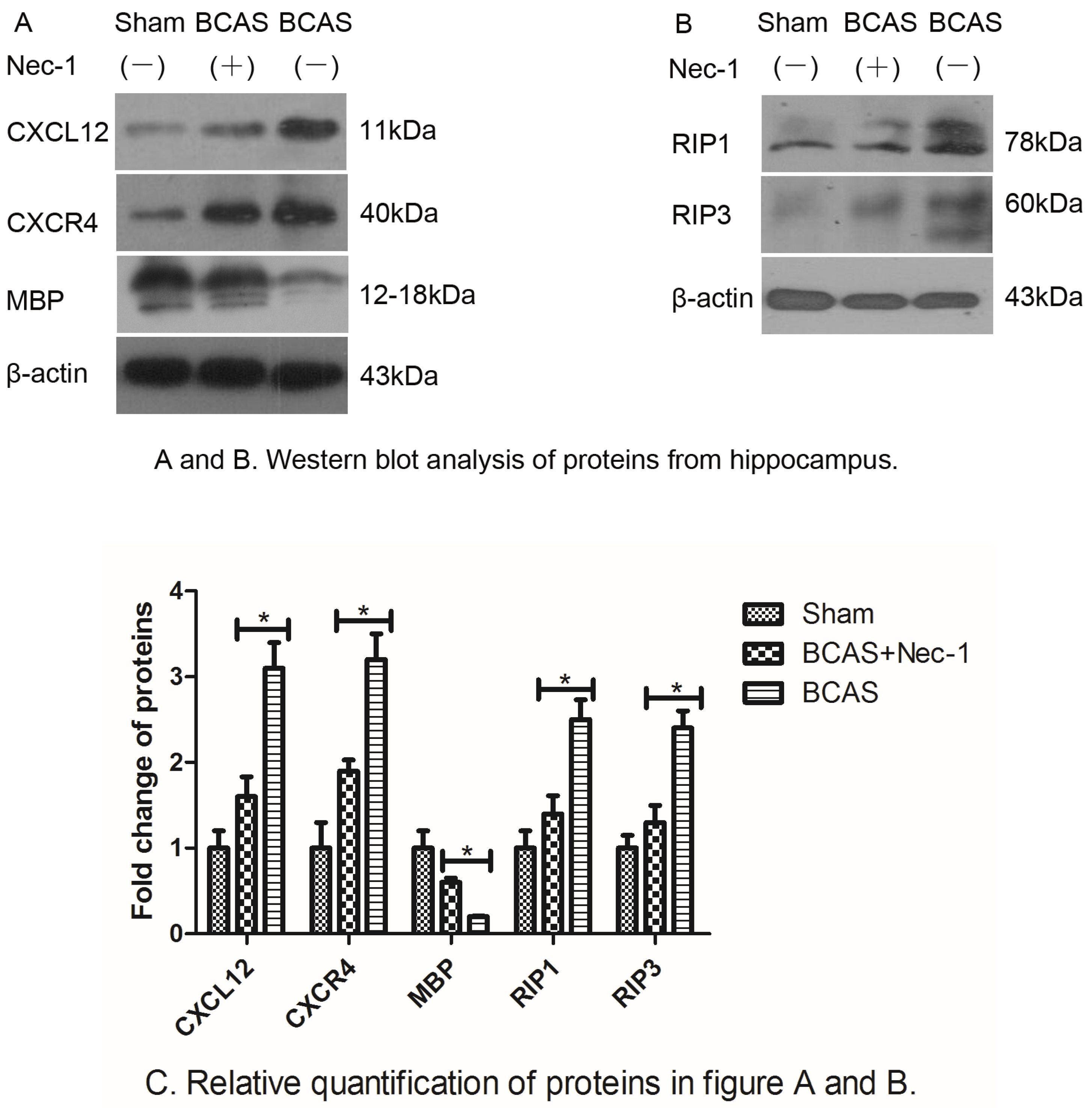
2.4. Nec-1 Decreased the Expression of Proteins from Hippocampus
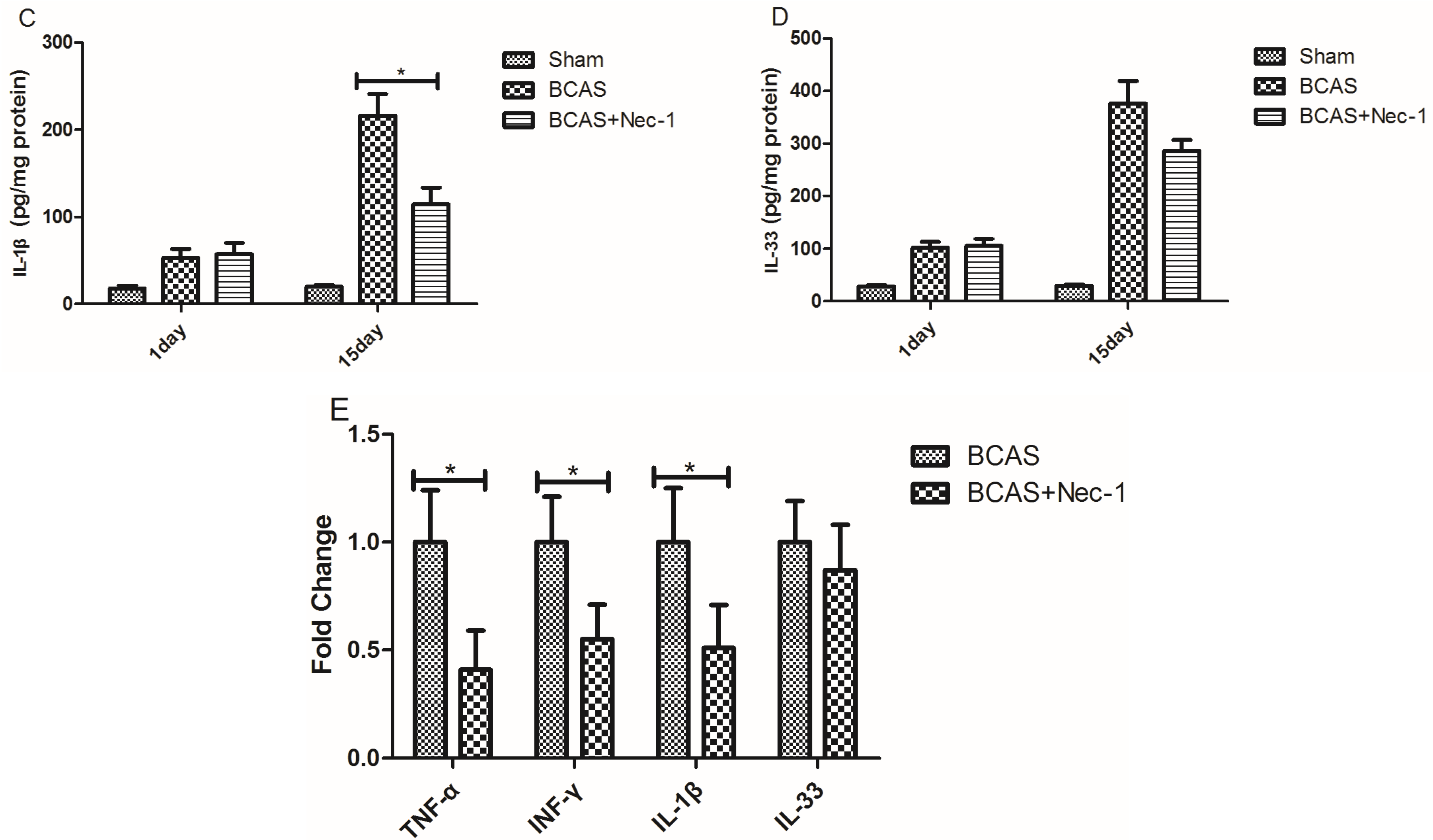
2.5. Inflammatory Cytokine Protein and mRNA Levels were Reduced by Nec-1
2.6. Discussion
3. Experimental Section
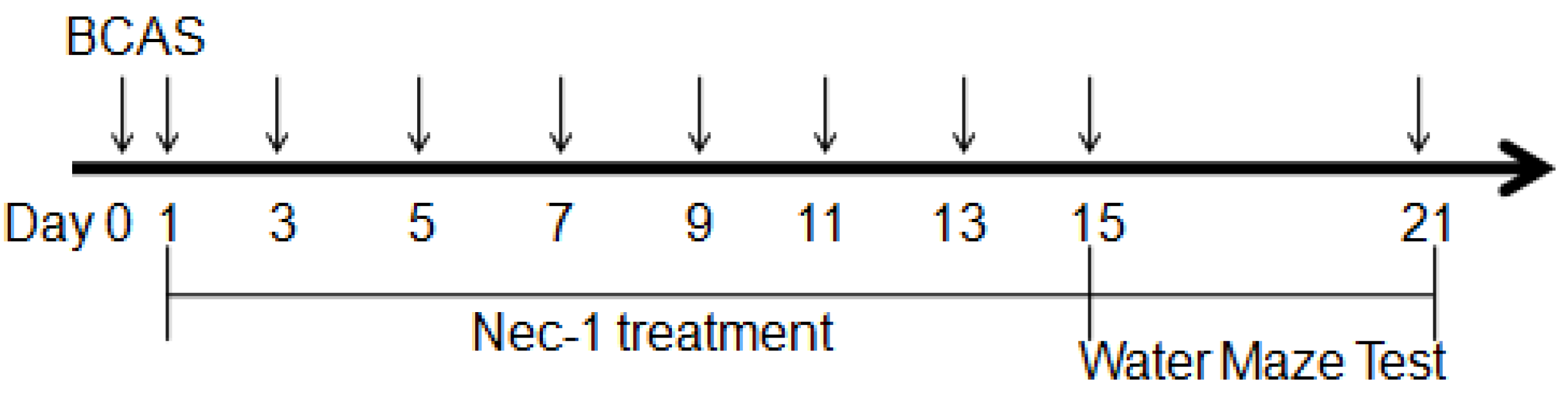
3.1. Animals and Experimental Design
3.2. Establishment of Mouse Model of Bilateral Carotid Artery Stenosis Procedure (BCAS)
3.3. Drug Treatment
3.4. Water Maze Testing
3.5. Sample Collection
3.6. Western Blot Analysis
3.7. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay Analysis (ELISA)
3.8. Real-Time PCR
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Durukan, A.; Tatlisumak, T. Acute ischemic stroke: Overview of major experimental rodent models, pathophysiology, and therapy of focal cerebral ischemia. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2007, 87, 179–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hachinski, V.; Iadecola, C.; Petersen, R.C.; Breteler, M.M.; Nyenhuis, D.L.; Black, S.E.; Powers, W.J.; DeCarli, C.; Merino, J.G.; Kalaria, R.N.; et al. National institute of neurological disorders and stroke-canadian stroke network vascular cognitive impairment harmonization standards. Stroke 2006, 37, 2220–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hachinski, V.C.; Bowler, J.V. Vascular dementia. Neurology 1993, 43, 2151–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vascular Cognitive Impairment; Bowler, J.V.; Hachinski, V.C. (Eds.) Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2003.
- Iadecola, C. The pathobiology of vascular dementia. Neuron 2013, 80, 844–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iadecola, C. The overlap between neurodegenerative and vascular factors in the pathogenesis of dementia. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 120, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, G.A. Inflammation and white matter damage in vascular cognitive impairment. Stroke 2009, 40 (Suppl. 3), 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantoni, L. Cerebral small vessel disease: From pathogenesis and clinical characteristics to therapeutic challenges. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Gui, L.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Y.; Tian, H.; Chen, J.F. Adenosine A2A receptor deficiency exacerbates white matter lesions and cognitive deficits induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in mice. J. Neurol. Sci. 2009, 285, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miki, K.; Ishibashi, S.; Sun, L.; Xu, H.; Ohashi, W.; Kuroiwa, T.; Mizusawa, H. Intensity of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion determines white/gray matter injury and cognitive/motor dysfunction in mice. J. Neurosci. Res. 2009, 87, 1270–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouns, R.; de Deyn, P.P. The complexity of neurobiological processes in acute ischemic stroke. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2009, 111, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degterev, A.; Huang, Z.; Boyce, M.; Li, Y.; Jagtap, P.; Mizushima, N.; Cuny, G.D.; Mitchison, T.J.; Moskowitz, M.A.; Yuan, J. Chemical inhibitor of nonapoptotic cell death with therapeutic potential for ischemic brain injury. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2005, 1, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishio, K.; Ihara, M.; Yamasaki, N.; Kalaria, R.N.; Maki, T.; Fujita, Y.; Ito, H.; Oishi, N.; Fukuyama, H.; Miyakawa, T.; et al. A mouse model characterizing features of vascular dementia with hippocampal atrophy. Stroke 2010, 41, 1278–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bamford, J.; Sandercock, P.; Dennis, M.; Burn, J.; Warlow, C. Classification and natural history of clinically identifiable subtypes of cerebral infarction. Lancet 1991, 337, 1521–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A.T.; Kissela, B.; Woo, D.; Kleindorfer, D.; Alwell, K.; Miller, R.; Szaflarski, J.; Gebel, J.; Khoury, J.; Shukla, R.; et al. Ischemic stroke subtypes: A population-based study of incidence rates among blacks and whites. Stroke 2004, 35, 1552–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, H.; Lazar, G. Early microglial reaction following mild forebrain ischemia induced by common carotid artery occlusion in rats. Brain Res. 2000, 862, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, H.; Nishikawa, H.; Kimura, H.; Anayama, H.; Miyamoto, M. Chronic Cerebral hypoperfusion by permanent internal carotid ligation produces learning impairment without brain damage in rats. Neuroscience 1997, 79, 1039–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, M.; Ohtani, R.; Ihara, M.; Tomimoto, H. White matter lesions and glial activation in a novel mouse model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Stroke 2004, 35, 2598–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantoni, L.; Garcia, J.H.; Gutierrez, J.A. Cerebral white matter is highly vulnerable to ischemia. Stroke 1996, 27, 1641–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchiya, M.; Sako, K.; Yura, S.; Yonemasu, Y. Cerebral blood flow and histopathological changes following permanent bilateral carotid artery ligation in Wistar rats. Exp. Brain Res. 1992, 89, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linkermann, A.; Heller, J.; Prókai, A.; Weinberg, J.M.; de Zen, F.; Himmerkus, N.; Szabó, A.J.; Bräsen, J.H.; Kunzendorf, U.; Krautwald, S. The RIP1-Kinase inhibitor necrostatin-1 prevents osmotic nephrosis and contrast-induced AKI in mice. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 1545–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linkermann, A.; Skouta, R.; Himmerkus, N.; Mulay, S.R.; Dewitz, C.; de Zen, F.; Prokai, A.; Zuchtriegel, G.; Krombach, F.; Welz, P.S.; et al. Synchronized renal tubular cell death involves ferroptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 16836–16841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jokinen, H.; Gouw, A.A.; Madureira, S.; Ylikoski, R.; van Straaten, E.C.; van der Flier, W.M.; Barkhof, F.; Scheltens, P.; Fazekas, F.; Schmidt, R.; et al. Incident lacunes influence cognitive decline: The LADIS study. Neurology 2011, 76, 1872–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieminen, A.L. Apoptosis and necrosis in health and disease: Role of mitochondria. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2003, 224, 29–55. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Ning, J.; Lemaire, A.; Koumpa, F.S.; Sun, J.J.; Fung, A.; Gu, J.; Yi, B.; Lu, K.; Ma, D. Necroptosis and parthanatos are involved in remote lung injury after receiving ischemic renal allografts in rats. Kidney Int. 2015, 87, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Jaffer, T.; Eguchi, S.; Wang, Z.; Linkermann, A.; Ma, D. Role of necroptosis in the pathogenesis of solid organ injury. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linkermann, A.; Green, D.R. Necroptosis. New Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, E.H.; Dalkara, T.; Moskowitz, M.A. Mechanisms, challenges and opportunities in stroke. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 399–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, F.K. Fueling the flames: Mammalian programmed necrosis in inflammatory diseases. Cold Spring Harb Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a008805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galluzzi, L.; Vitale, I.; Abrams, J.M.; Alnemri, E.S.; Baehrecke, E.H.; Blagosklonny, M.V.; Dawson, T.M.; Dawson, V.L.; El-Deiry, W.S.; Fulda, S.; et al. Molecular definitions of cell death subroutines: Recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2012. Cell Death Differ. 2012, 19, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.S.; Challa, S.; Moquin, D.; Genga, R.; Ray, T.D.; Guildford, M.; Chan, F.K. Phosphorylation-driven assembly of the RIP1-RIP3 complex regulates programmed necrosis and virus-induced inflammation. Cell 2009, 137, 1112–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Wang, L.; Miao, L.; Wang, T.; Du, F.; Zhao, L.; Wang, X. Receptor interacting protein kinase-3 determines cellular necrotic response to TNF-alpha. Cell 2009, 137, 1100–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, J.; Jalal, F.Y.; Yang, Y.; Thompson, J.; Rosenberg, G.A.; Liu, K.J. Tissue oxygen is reduced in white matter of spontaneously hypertensive-stroke prone rats: A longitudinal study with electron paramagnetic resonance. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2014, 34, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stys, P.K.; Waxman, S.G.; Ransom, B.R. Ionic mechanisms of anoxic injury in mammalian CNS white matter: Role of Na+ channels and Na (+)-Ca2+exchanger. J. Neurosci. 1992, 12, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rezaie, P.; Dean, A. Periventricular leukomalacia, inflammation and white matter lesions within the developing nervous system. Neuropathology 2002, 22, 106–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dammann, O.; Leviton, A. Maternal intrauterine infection, cytokines, and brain damage in the preterm newborn. Pediatr. Res. 1997, 42, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, M.; Yamasaki, N.; Miyakawa, T.; Kalaria, R.N.; Fujita, Y.; Ohtani, R.; Ihara, M.; Takahashi, R.; Tomimoto, H. Selective impairment of working memory in a mouse model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Stroke 2007, 38, 2826–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitaguchi, H.; Tomimoto, H.; Ihara, M.; Shibata, M.; Uemura, K.; Kalaria, R.N.; Kihara, T.; Asada-Utsugi, M.; Kinoshita, A.; Takahashi, R. Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion accelerates amyloid beta deposition in APPS-wind transgenic mice. Brain Res. 2009, 1294, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, M.; Ihara, M.; Okamoto, Y.; Maki, T.; Washida, K.; Kitamura, A.; Hase, Y.; Ito, H.; Takao, K.; Miyakawa, T.; et al. The influence of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion on cognitive function and amyloid Bmetabolism in APP over expressing mice. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Wu, Y.; Jia, J.; Liu, G.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, K.; Hu, Y.; Bai, Y.; Hu, R. Enriched environment preconditioning induced brain is chemic tolerance without reducing infarct volume and edema: The possible role of enrichment-related physical activity increase. Brain Res. 2013, 1508, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Yu, H.; Zhou, N.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Jia, J.; Zhang, Q.; Tian, S.; et al. Early exercise improves cerebral blood flow through increased angiogenesis in experimental stroke rat model. J. Neuro. Eng. Rehabil. 2012, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Li, Y.; Tang, Y.; Tang, G.; Yang, G.-Y.; Wang, Y. CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100protects blood-brain barrier integrity and reduces inflammatory response after focal ischemia in mice. Stroke 2013, 44, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Wu, J.; Si, W.; Wu, Y. Necrostatin-1 Attenuates Inflammatory Response and Improves Cognitive Function in Chronic Ischemic Stroke Mice. Medicines 2016, 3, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines3030016
Zhang S, Wang Y, Li D, Wu J, Si W, Wu Y. Necrostatin-1 Attenuates Inflammatory Response and Improves Cognitive Function in Chronic Ischemic Stroke Mice. Medicines. 2016; 3(3):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines3030016
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shehong, Yuyang Wang, Dake Li, Junfa Wu, Wen Si, and Yi Wu. 2016. "Necrostatin-1 Attenuates Inflammatory Response and Improves Cognitive Function in Chronic Ischemic Stroke Mice" Medicines 3, no. 3: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines3030016
APA StyleZhang, S., Wang, Y., Li, D., Wu, J., Si, W., & Wu, Y. (2016). Necrostatin-1 Attenuates Inflammatory Response and Improves Cognitive Function in Chronic Ischemic Stroke Mice. Medicines, 3(3), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines3030016