MTF1 Is Essential for the Expression of MT1B, MT1F, MT1G, and MT1H Induced by PHMG, but Not CMIT, in the Human Pulmonary Alveolar Epithelial Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
2.4. Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
2.5. Western Blotting
2.6. Library Preparation and Sequencing
2.7. Data Analyses
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
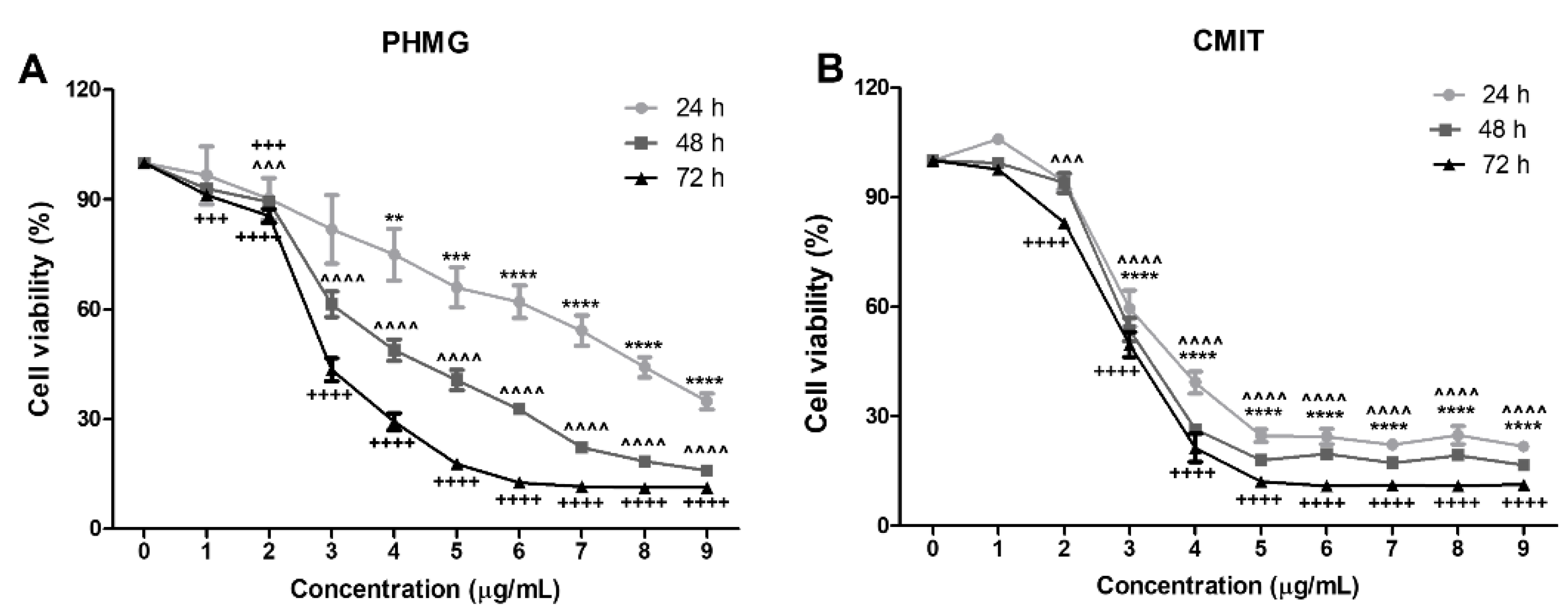
3.1. Measurement of Cell Viability
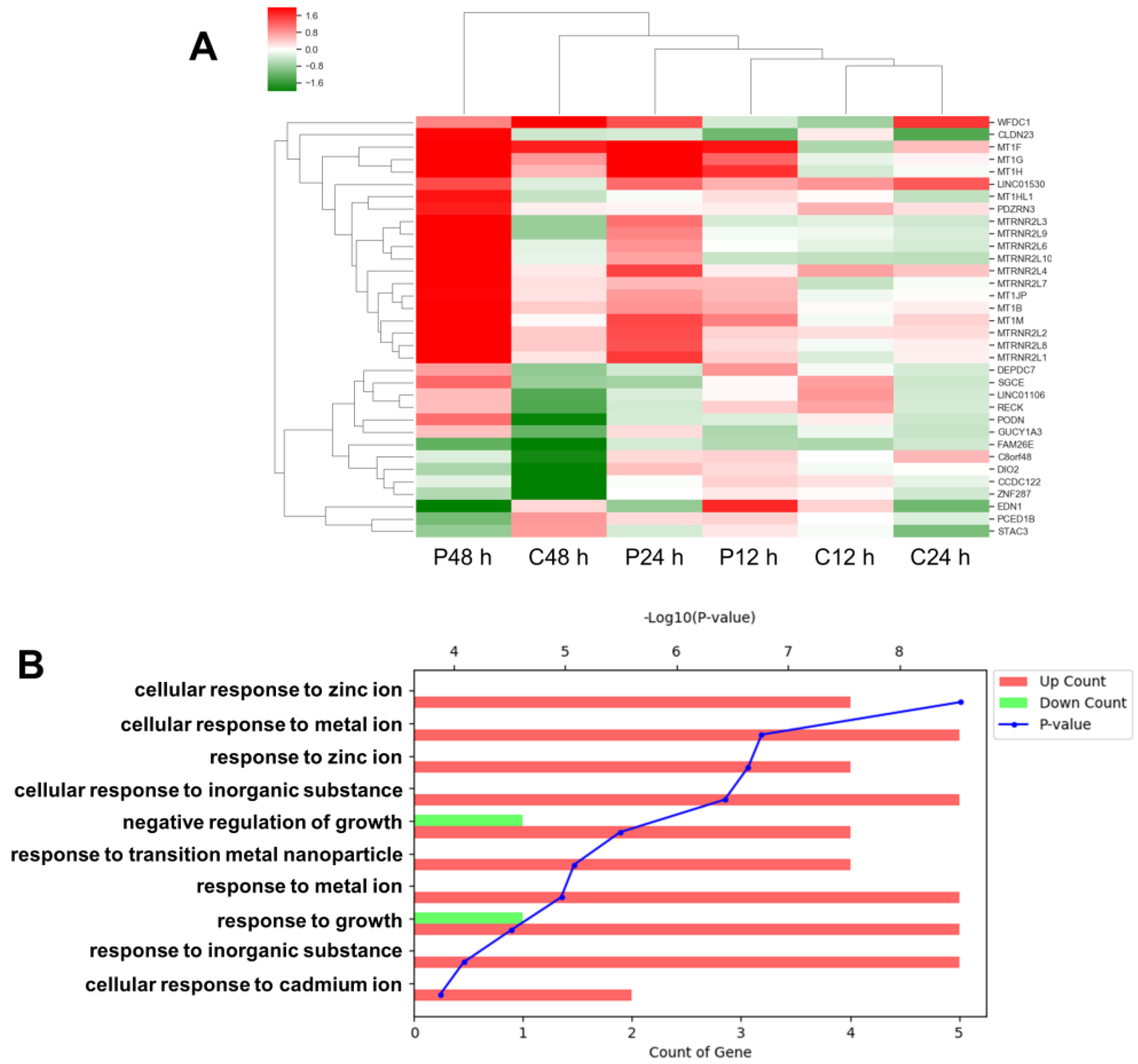
3.2. Comparative Analysis of Gene Expression after PHMG and CMIT Exposure
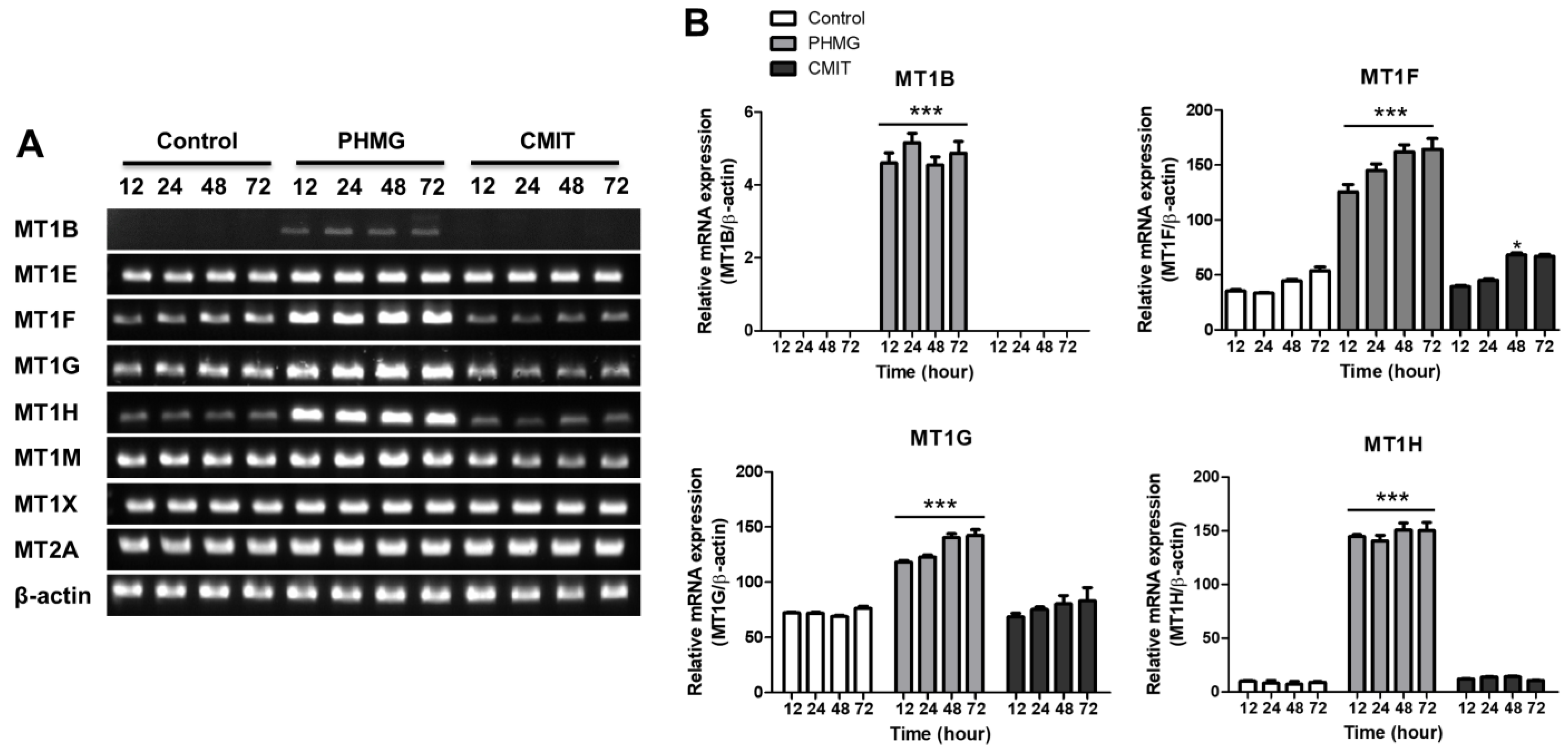
3.3. Upregulation of MT1B, MT1F, MT1G and MT1H in Cells Treated with PHMG but Not in Cells Treated with CMIT
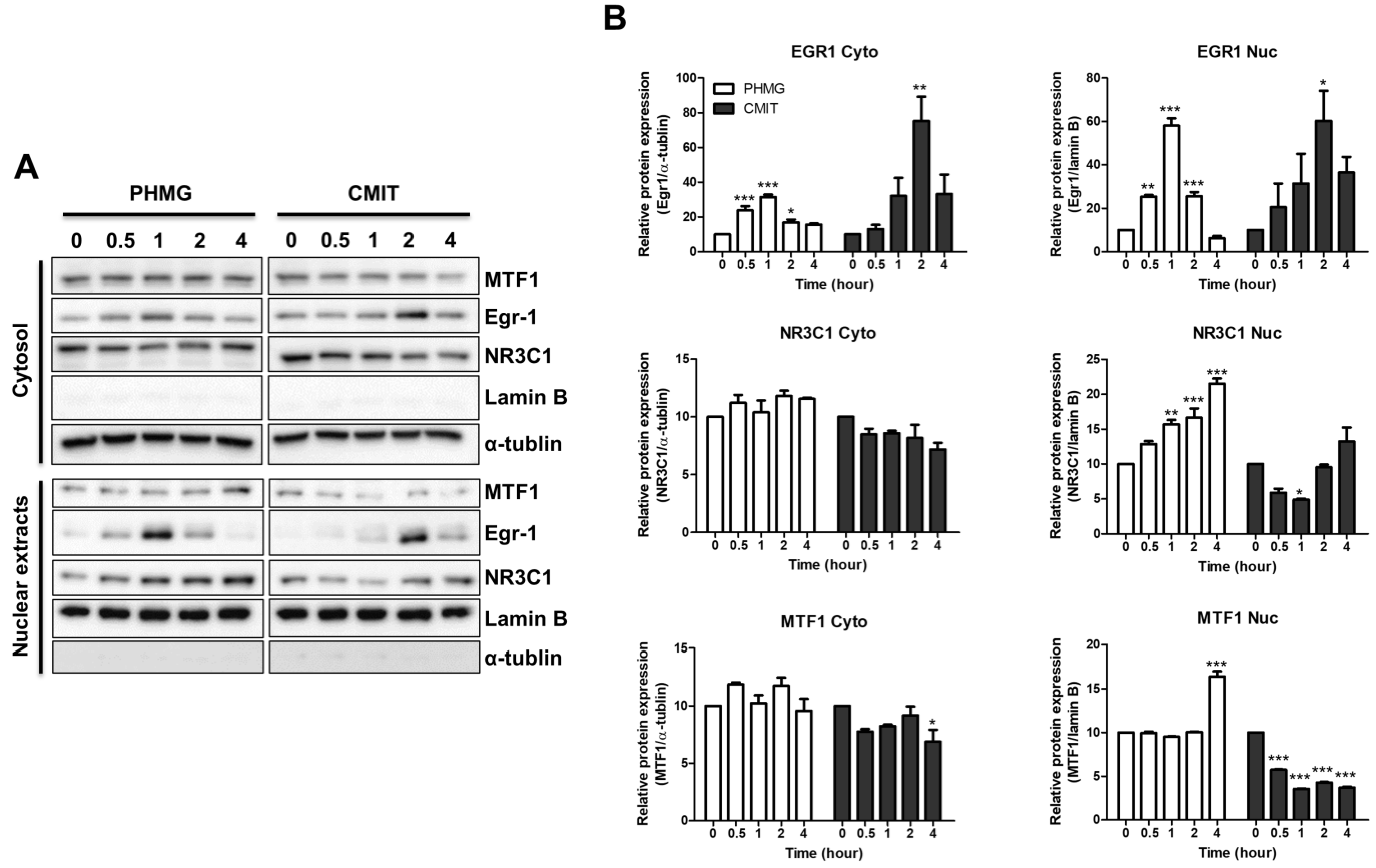
3.4. Role of MTF1 in the Induction of MT1B, MT1F, MT1G, and MT1H
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, D.U.; Ryu, S.H.; Lim, H.K.; Kim, S.K.; Choi, Y.Y.; Ahn, J.J.; Lee, E.; Hong, S.B.; Do, K.H.; Cho, J.I.; et al. Types of household humidifier disinfectant and associated risk of lung injury (HDLI) in South Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 596, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.H.; Park, D.U.; Lee, E.; Park, S.; Lee, S.Y.; Jung, S.; Hong, S.B.; Park, J.; Hong, S.J. Humidifier disinfectant and use characteristics associated with lung injury in Korea. Indoor Air 2019, 29, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.J.; Park, D.U.; Yoon, J.; Lee, E.; Yang, S.I.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Hong, S.J. Effects of a mixture of chloromethylisothiazolinone and methylisothiazolinone on peripheral airway dysfunction in children. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, E.; Son, S.K.; Yoon, J.; Cho, H.J.; Yang, S.I.; Jung, S.; Do, K.H.; Cho, Y.A.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, D.U.; et al. Two cases of chloromethylisothiazolinone and methylisothiazolinone-associated toxic lung injury. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2018, 33, e119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.R.; Shin, D.Y.; Chung, K.H. The role of NF-κB signaling pathway in polyhexamethylene guanidine phosphate induced inflammatory response in mouse macrophage RAW264. 7 cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 233, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.J.; Park, S.J.; Kim, S.; Lee, K.; Chang, J. Lung fibroblasts may play an important role in clearing apoptotic bodies of bronchial epithelial cells generated by exposure to PHMG-P-containing solution. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 286, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.S.; Park, Y.J.; Kim, H.R.; Chung, K.H. Polyhexamethylene guanidine phosphate-induced ROS-mediated DNA damage caused cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in lung epithelial cells. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2019, 44, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, J.; Jung, K.J.; Yoon, S.J.; Lee, K.; Kim, B. Polyhexamethyleneguanidine phosphate induces cytotoxicity through disruption of membrane integrity. Toxicology 2019, 414, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Kwon, D.; Lee, S.; Ki, S.H.; Jeong, H.G.; Hong, J.T.; Lee, Y.H.; Jung, Y.S. Polyhexamethyleneguanidine phosphate-induced cytotoxicity in liver cells is alleviated by Tauroursodeoxycholic Acid (TUDCA) via a reduction in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cells 2019, 8, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, H.-N.; Zerin, T.; Podder, B.; Song, H.-Y.; Kim, Y.S. Cytotoxicity and gene expression profiling of polyhexamethylene guanidine hydrochloride in human alveolar A549 cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2014, 28, 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.Y.; Jeong, M.H.; Bang, I.J.; Kim, H.R.; Chung, K.H. MicroRNA regulatory networks reflective of polyhexamethylene guanidine phosphate-induced fibrosis in A549 human alveolar adenocarcinoma cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 287, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, H.; Jang, S.; Hong, S.H.; Kim, W.J.; Ryu, S.M.; Park, S.M.; Lee, K.H.; Cho, S.J.; Yang, S.R. CMIT/MIT induce apoptosis and inflammation in alveolar epithelial cells through p38/JNK/ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 2019, 15, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Chen, H.; Qi, M.; Dou, Y.; Wang, Q. Balance between metallothionein and metal response element binding transcription factor 1 is mediated by zinc ions. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 1582–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Helal, G.K.; Helal, O.K. Metallothionein attenuates carmustine-induced oxidative stress and protects against pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Arch. Toxicol. 2009, 83, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, K.I.; Takano, H.; Kaewamatawong, T.; Shimada, A.; Suzuki, J.; Yanagisawa, R.; Tasaka, S.; Ishizaka, A.; Satoh, M. Role of metallothionein in lung inflammation induced by ozone exposure in mice. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 45, 1714–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, M.; Wang, Y.M.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, Z.M.; Zhang, T.F.; He, J.; Ren, S.P.; Peng, S.Q. Metallothioneins attenuate paraquat-induced acute lung injury in mice through the mechanisms of anti-oxidation and anti-apoptosis. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 73, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, H.; Inoue, K.; Yanagisawa, R.; Sato, M.; Shimada, A.; Morita, T.; Sawada, M.; Nakamura, K.; Sanbongi, C.; Yoshikawa, T. Protective role of metallothionein in acute lung injury induced by bacterial endotoxin. Thorax 2004, 59, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, X.; Jagadapillai, R.; Cai, J.; Cai, L.; Shao, G.; Gozal, E. Metallothionein induction attenuates the progression of lung injury in mice exposed to long-term intermittent hypoxia. Inframm. Res. 2020, 69, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, M.; Lang, J. The roles of metallothioneins in carcinogenesis. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theocharis, S.; Karkantaris, C.; Philipides, T.; Agapitos, E.; Gika, A.; Margeli, A.; Kittas, C.; Koutselinis, A. Expression of metallothionein in lung carcinoma: Correlation with histological type and grade. Histopathology 2002, 40, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Yu, H.; Wang, C.; Sun, L.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, P.; Xiao, Q.; Han, D.; Saiyin, H.; Zhu, J.; et al. Metallothionein MT1M is a tumor suppressor of human hepatocellular carcinomas. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 2568–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quinlan, A.R.; Hall, I.M. BEDTools: A flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 841–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gentleman, R.C.; Carey, V.J.; Bates, D.M.; Bolstad, B.; Dettling, M.; Dudoit, S.; Ellis, B.; Gautier, L.; Ge, Y.; Gentry, J.; et al. Bioconductor: Open software development for computational biology and bioinformatics. Genome Biol. 2004, 5, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dennis, G.; Sherman, B.T.; Hosack, D.A.; Yang, J.; Gao, W.; Lane, H.C.; Lempicki, R.A. DAVID: Database for annotation, visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol. 2003, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kimura, T.; Kambe, T. The functions of metallothionein and ZIP and ZnT transporters: An overview and perspective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krężel, A.; Maret, W. The functions of metamorphic metallothioneins in zinc and copper metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.S.; Kim, S.H.; Jeon, D.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, K. Changes in expression of cytokines in polyhexamethylene guanidine-induced lung fibrosis in mice: Comparison of bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis. Toxicology 2018, 393, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamichhane, D.K.; Leem, J.H.; Lee, S.M.; Yang, H.J.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.H.; Ko, J.K.; Kim, H.C.; Park, D.U.; Cheong, H.K. Family-based case-control study of exposure to household humidifier disinfectants and risk of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Park, J.-H.; Lee, J.-Y.; Jeong, Y.-J.; Song, J.A.; Lee, K.; Kim, D.-J. Establishment of a mouse model for pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis by intratracheal instillation of polyhexamethyleneguanidine phosphate. J. Toxicol. Pathol. 2016, 29, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaudhuri, A.R.; Nussenzweig, A. The multifaceted roles of PARP1 in DNA repair and chromatin remodelling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesselkamper, S.C.; McDowell, S.A.; Medvedovic, M.; Dalton, T.P.; Deshmukh, H.S.; Sartor, M.A.; Case, L.M.; Henning, L.N.; Borchers, M.T.; Tomlinson, C.R.; et al. The role of metallothionein in the pathogenesis of acute lung injury. Am. J. Respir. Cell Moll. Biol. 2006, 34, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fu, Z.; Guo, J.; Jing, L.; Li, R.; Zhang, T.; Peng, S. Enhanced toxicity and ROS generation by doxorubicin in primary cultures of cardiomyocytes from neonatal metallothionein-I/II null mice. Toxicol. In Vitro 2010, 24, 1584–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruttkay-Nedecky, B.; Nejdl, L.; Gumulec, J.; Zitka, O.; Masarik, M.; Eckschlager, T.; Stiborova, M.; Adam, V.; Kizek, R. The role of metallothionein in oxidative stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 6044–6066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, C.; Jeong, S.H.; Kim, J.; Lee, K.Y.; Cha, J.; Lee, C.H.; Park, E.-K.; Lee, J.H. Evaluation of polyhexamethylene guanidine-induced lung injuries by chest CT, pathologic examination, and RNA sequencing in a rat model. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, B.; Zhai, D.; Cabezas, E.; Welsh, K.; Nouraini, S.; Satterthwait, A.C.; Reed, J.C. Humanin peptide suppresses apoptosis by interfering with Bax activation. Nature 2003, 423, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, D.; Luciano, F.; Zhu, X.; Guo, B.; Satterthwait, A.C.; Reed, J.C. Humanin binds and nullifies Bid activity by blocking its activation of Bax and Bak. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 15815–15824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ayala, M.A.M.; Gottardo, M.F.; Zuccato, C.F.; Pidre, M.L.; Candia, A.J.N.; Asad, A.S.; Imsen, M.; Romanowski, V.; Creton, A.; Larrain, M.I.; et al. Humanin promotes tumor progression in experimental triple negative breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, S.-H.; Kim, C.; Kim, J.; Nam, Y.-J.; Lee, H.; Togloom, A.; Kang, J.-Y.; Choi, J.-Y.; Lee, H.; Song, M.-O.; et al. MTF1 Is Essential for the Expression of MT1B, MT1F, MT1G, and MT1H Induced by PHMG, but Not CMIT, in the Human Pulmonary Alveolar Epithelial Cells. Toxics 2021, 9, 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9090203
Jeong S-H, Kim C, Kim J, Nam Y-J, Lee H, Togloom A, Kang J-Y, Choi J-Y, Lee H, Song M-O, et al. MTF1 Is Essential for the Expression of MT1B, MT1F, MT1G, and MT1H Induced by PHMG, but Not CMIT, in the Human Pulmonary Alveolar Epithelial Cells. Toxics. 2021; 9(9):203. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9090203
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Sang-Hoon, Cherry Kim, Jaeyoung Kim, Yoon-Jeong Nam, Hong Lee, Ariunaa Togloom, Ja-Young Kang, Jin-Young Choi, Hyejin Lee, Myeong-Ok Song, and et al. 2021. "MTF1 Is Essential for the Expression of MT1B, MT1F, MT1G, and MT1H Induced by PHMG, but Not CMIT, in the Human Pulmonary Alveolar Epithelial Cells" Toxics 9, no. 9: 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9090203
APA StyleJeong, S.-H., Kim, C., Kim, J., Nam, Y.-J., Lee, H., Togloom, A., Kang, J.-Y., Choi, J.-Y., Lee, H., Song, M.-O., Park, E.-K., Baek, Y.-W., Lee, J.-H., & Lee, K.-Y. (2021). MTF1 Is Essential for the Expression of MT1B, MT1F, MT1G, and MT1H Induced by PHMG, but Not CMIT, in the Human Pulmonary Alveolar Epithelial Cells. Toxics, 9(9), 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9090203





