Total and Metabolically Active Microbial Community of Aerobic Granular Sludge Systems Operated in Sequential Batch Reactors: Effect of Pharmaceutical Compounds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design of Bioreactors, Configuration, and Operation
2.2. Physico-Chemical Determinations
2.3. Pharmaceutical Concentration Determination
2.4. Biomass Collection and Nucleic Acid Extraction
2.5. Massive Parallel Sequencing Procedure
2.6. Bioinformatics Pipeline
2.7. Absolute Quantification of Total and Metabolically Active Microorganisms
2.8. Statistical Analysis
2.9. Multivariate Redundancy Analysis and PERMANOVA
3. Results and Discussion
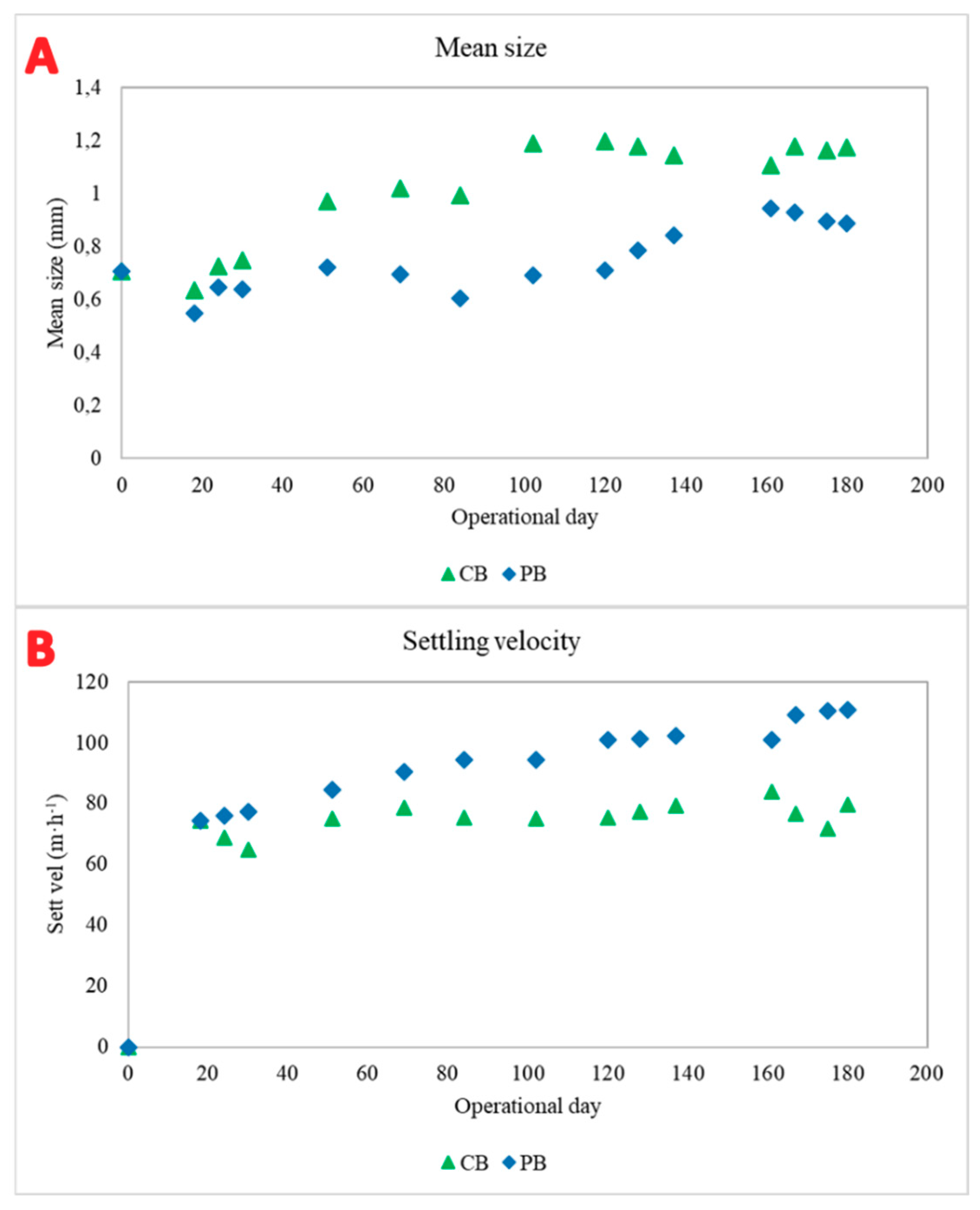
3.1. Granular Development and Biomass Characteristics
3.2. Physico-Chemical Removal Efficiencies
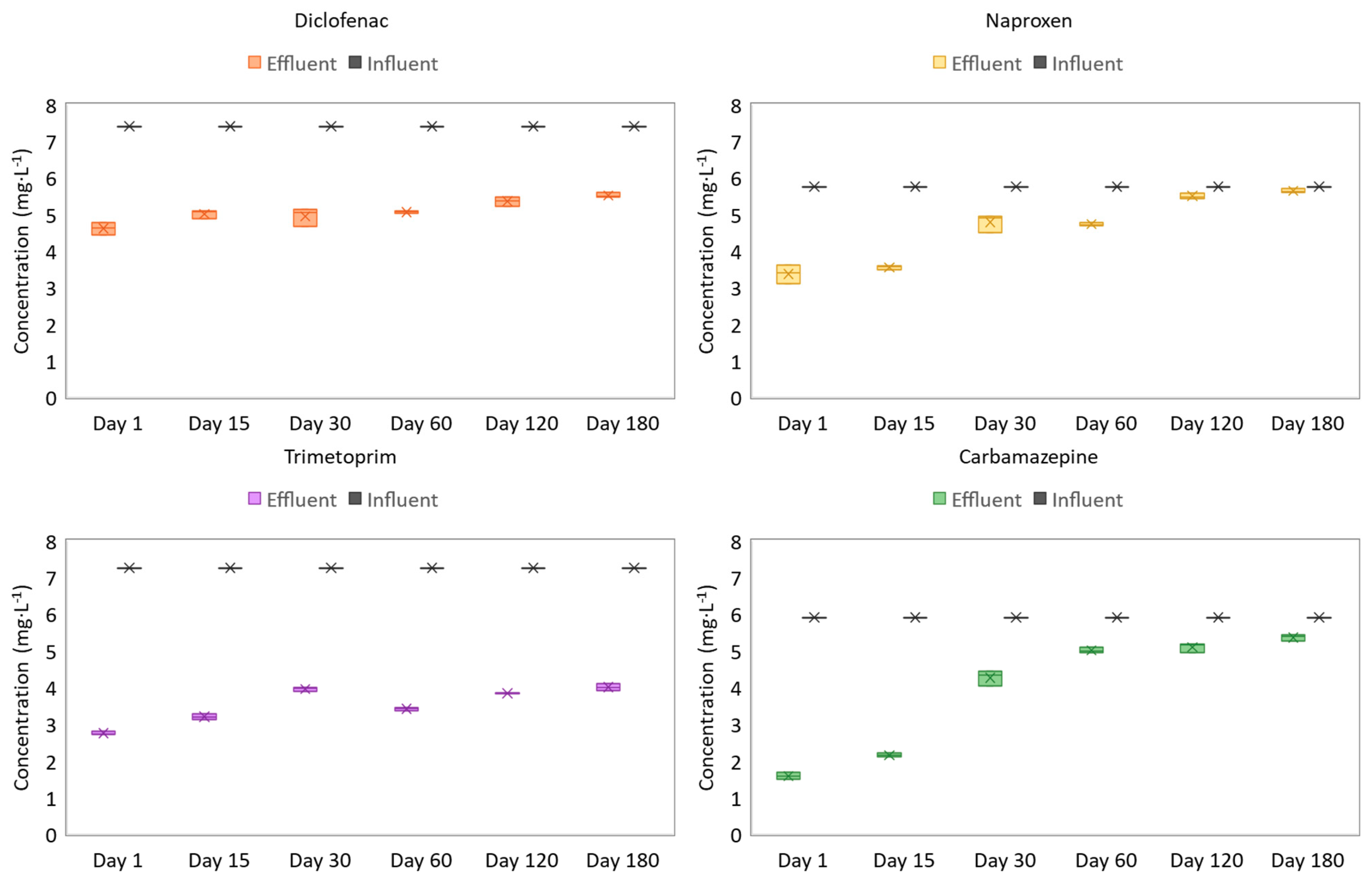
3.3. Pharmaceutical Compound Analysis
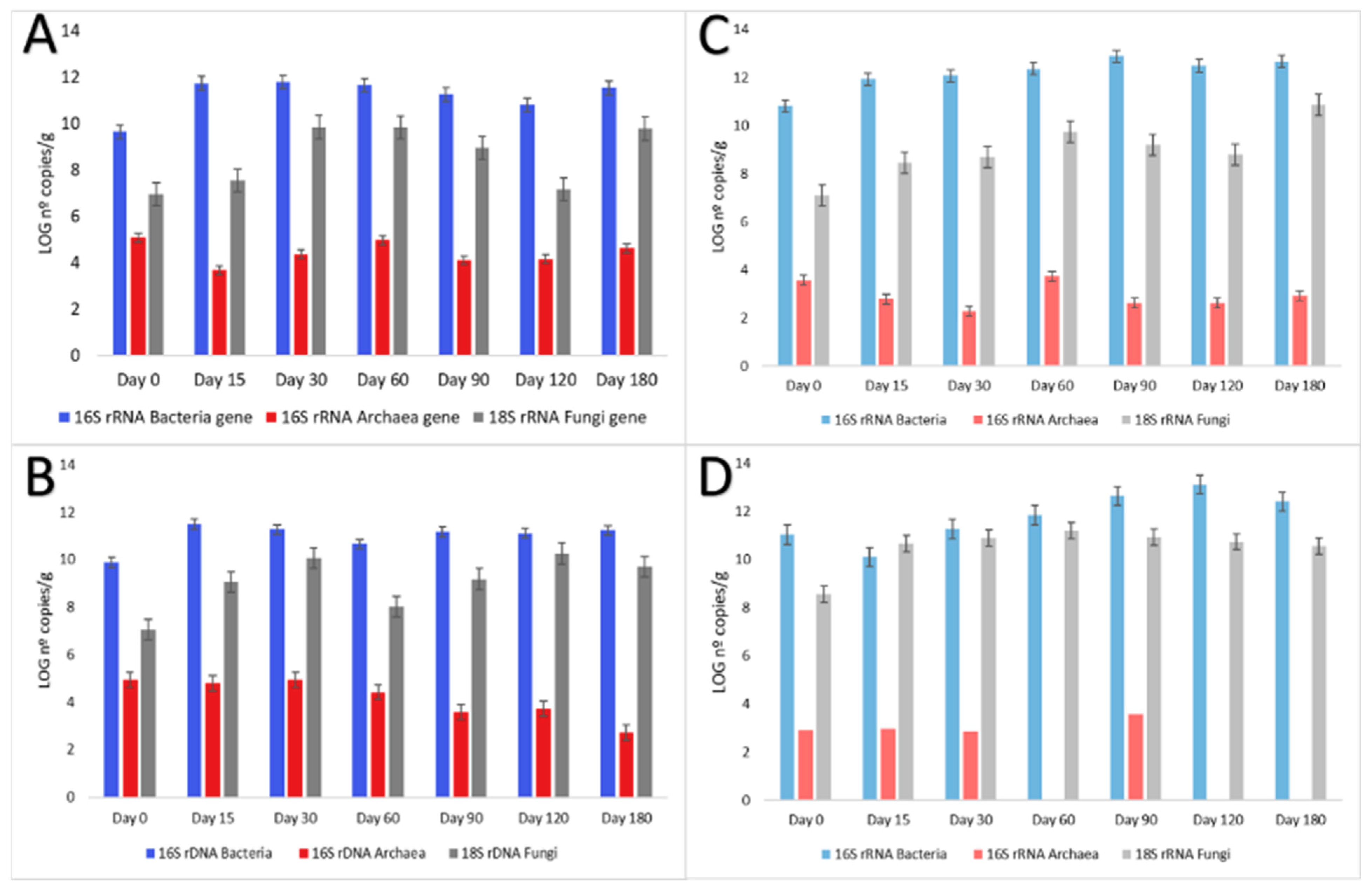
3.4. Abundance of Total and Metabolically Active Populations of Bacteria, Archaea, and Fungi in Aerobic Granular Sludge Reactor
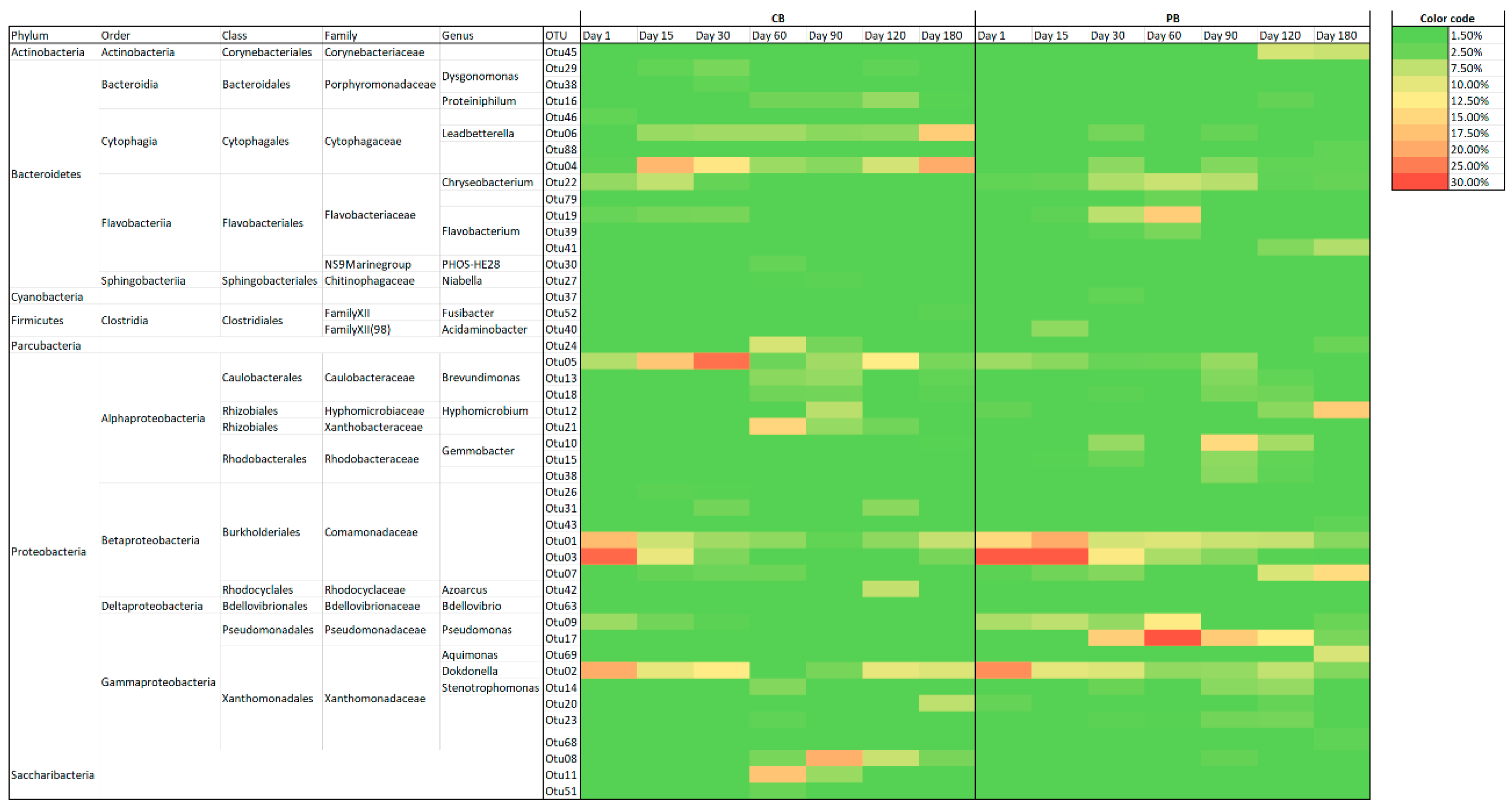
3.5. Aerobic Granular Sludge Prokaryotic Composition of Total and Active Population Analysed by Massive Parallel Sequencing
3.5.1. Dynamics of Total and Active Metabolically Bacterial Communities
3.5.2. Archaeal Population
3.6. Alpha and Beta Diversity Analyses
3.7. Similarity Analysis of Bacterial Samples
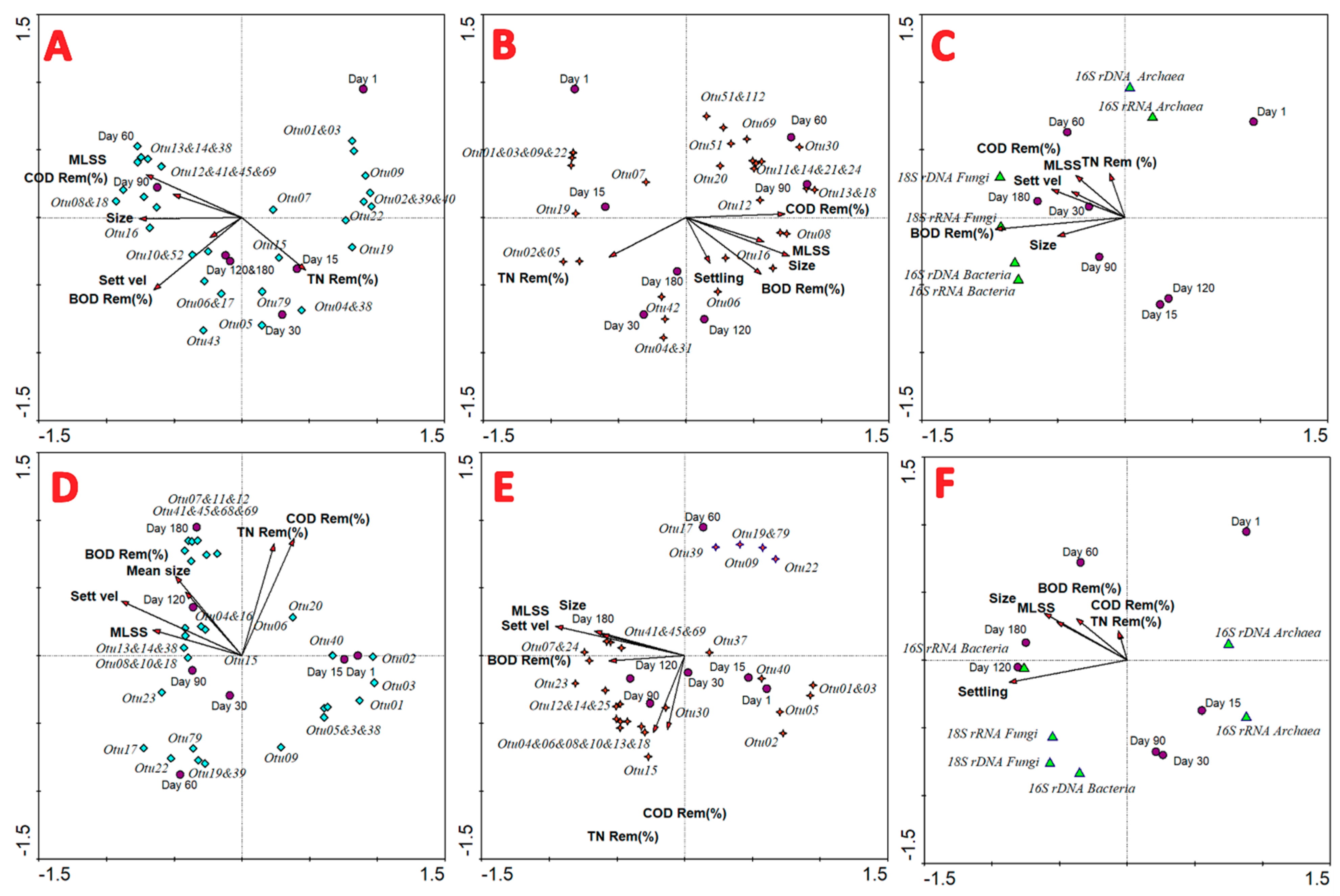
3.8. Multivariate Redundancy and PERMANOVA Analyses
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cardoso, O.; Porcher, J.-M.; Sanchez, W. Factory-discharged pharmaceuticals could be a relevant source of aquatic environment contamination: Review of evidence and need for knowledge. Chemosphere 2014, 115, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caracciolo, A.B.; Topp, E.; Grenni, P. Pharmaceuticals in the environment: Biodegradation and effects on natural microbial communities. A review. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 106, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olicón-Hernández, D.R.; González-López, J.; Aranda, E. Overview on the Biochemical Potential of Filamentous Fungi to Degrade Pharmaceutical Compounds. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, J.; Tay, J.H. Treatment of 17α-ethinylestradiol, 4-nonylphenol, and carbamazepine in wastewater using an aerobic granular sludge sequencing batch reactor. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 1270–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolar, B.; Arnuš, L.; Jeretin, B.; Gutmaher, A.; Drobne, D.; Durjava, M.K. The toxic effect of oxytetracycline and trimethoprim in the aquatic environment. Chemosphere 2014, 115, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEneff, G.; Barron, L.; Kelleher, B.; Paull, B.; Quinn, B. A year-long study of the spatial occurrence and relative distribution of pharmaceutical residues in sewage effluent, receiving marine waters and marine bivalves. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 476, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.; Chamorro, S.; Marti, E.; Huerta, B.; Gros, M.; Sànchez-Melsió, A.; Balcázar, J.L. (Occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in hospital and urban wastewaters and their impact on the receiving river. Water Res. 2015, 69, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, N.H.; Khan, S.J. Enantioselective analysis of ibuprofen, ketoprofen and naproxen in wastewater and environmental water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 4746–4754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnefille, B.; Gomez, E.; Courant, F.; Escande, A.; Fenet, H. Diclofenac in the marine environment: A review of its occurrence and effects. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 131, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madikizela, L.M.; Chimuka, L. Occurrence of naproxen, ibuprofen, and diclofenac residues in wastewater and river water of KwaZulu-Natal Province in South Africa. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nancharaiah, Y.V.; Reddy, G.K.K. Aerobic granular sludge technology: Mechanisms of granulation and bio-technological applications. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 1128–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Palazon, B.; Rodriguez-Sanchez, A.; Hurtado-Martinez, M.; de Castro, I.M.; Juarez-Jimenez, B.; Gonzalez-Martinez, A.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J. Performance and microbial community structure of an aerobic granular sludge system at different phenolic acid concentrations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 376, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Martinez, A.; Muñoz-Palazon, B.; Rodriguez-Sanchez, A.; Maza-Márquez, P.; Mikola, A.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J.; Vahala, R. Start-up and operation of an aerobic granular sludge system under low working temperature inoculated with cold-adapted activated sludge from Finland. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 239, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adav, S.S.; Lee, D.-J.; Show, K.-Y.; Tay, J.-H. Aerobic granular sludge: Recent advances. Biotechnol. Adv. 2008, 26, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maza-Márquez, P.; Castellano-Hinojosa, A.; González-Martínez, A.; Juárez-Jiménez, B.; González-López, J.; Rodelas, B. Abundance of total and metabolically active Candidatus Microthrix and fungal populations in three full-scale wastewater treatment plants. Chemosphere 2019, 232, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maza-Márquez, P.; Vargas, R.V.; Boon, N.; González-López, J.; Martínez-Toledo, M.; Rodelas, B. The ratio of metabolically active versus total Mycolata populations triggers foaming in a membrane bioreactor. Water Res. 2016, 92, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Martinez, A.; Muñoz-Palazon, B.; Maza-Márquez, P.; Rodriguez-Sanchez, A.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J.; Vahala, R. Performance and microbial community structure of a polar Arctic Circle aerobic granular sludge system operating at low temperature. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 256, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kreuk, M.; Pronk, M.; van Loosdrecht, M. Formation of aerobic granules and conversion processes in an aerobic granular sludge reactor at moderate and low temperatures. Water Res. 2005, 39, 4476–4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patneedi, C.B.; Prasadu, K.D. Impact of pharmaceutical wastes on human life and environment. Rasayan J. Chem. 2015, 8, 67–70. [Google Scholar]
- WEF. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. 2012. Available online: http://www.standardmethods.org/ (accessed on 23 April 2021).
- Laguna, A.; Ouattara, A.; Gonzalez, R.O.; Baron, O.; Fama, G.; El Mamouni, R.; Macarie, H. A simple and low cost technique for determining the granulometry of upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor sludge. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 40, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Palazon, B.; Rodriguez-Sanchez, A.; Hurtado-Martinez, M.; Santana, F.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J.; Mack, L.; Gonzalez-Martinez, A. Polar Arctic Circle biomass enhances performance and stability of aerobic granular sludge systems operated under different temperatures. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 300, 122650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohorquez, L.C.; Delgado-Serrano, L.; López, G.; Osorio-Forero, C.; Klepac-Ceraj, V.; Kolter, R.; Junca, H.; Baena, S.; Zambrano, M.M. In-depth Characterization via Complementing Culture-Independent Approaches of the Microbial Community in an Acidic Hot Spring of the Colombian Andes. Microb. Ecol. 2012, 63, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Liang, Q.; Niu, M.; Wang, F. High occurrence of Bathyarchaeota (MCG) in the deep-sea sediments of South China Sea quantified using newly designed PCR primers. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2017, 9, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing Mothur: Open-Source, Platform-Independent, Community-Supported Software for Describing and Comparing Microbial Communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Sanchez, A.; Margareto, A.; Robledo-Mahon, T.; Aranda, E.; Diaz-Cruz, S.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J.; Gonzalez-Martinez, A. Performance and bacterial community structure of a granular autotrophic nitrogen removal bio-reactor amended with high antibiotic concentrations. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 325, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for meta-genomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIlroy, S.J.; Kirkegaard, R.H.; McIlroy, B.; Nierychlo, M.; Kristensen, J.M.; Karst, S.M.; Nielsen, P.H. MiDAS 2.0: An ecosystem-specific taxonomy and online database for the organisms of wastewater treatment systems expanded for anaerobic digester groups. Database 2017, 2017, bax016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awang, N.A.; Shaaban, M.G. Effect of reactor height/diameter ratio and organic loading rate on formation of aerobic granular sludge in sewage treatment. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 112, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Gao, M.; Ye, M.; Wang, Y.K.; Xu, H.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.H. Formation, characteristics and microbial com-munity of aerobic granular sludge in the presence of sulfadiazine at environmentally relevant concentrations. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 250, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Palazon, B.; Pesciaroli, C.; Rodriguez-Sanchez, A.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J.; Gonzalez-Martinez, A. Pollutants degradation performance and microbial community structure of aerobic granular sludge systems using inoculums adapted at mild and low temperature. Chemosphere 2018, 204, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Othman, I.; Anuar, A.N.; Ujang, Z.; Rosman, N.H.; Harun, H.; Chelliapan, S. Livestock wastewater treatment using aerobic granular sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 133, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.Q.; Yang, W.Y.; Wang, Z.; Hao, X.D. Role of extracellular polymeric substance in adsorption of quinolone antibiotics by microbial cells in excess sludge. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 370, 684–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, C.L.; Moreira, I.S.; Ribeiro, A.R.; Santos, L.H.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Tiritan, M.E.; Castro, P.M. Treatment of a simulated wastewater amended with a chiral pharmaceuticals mixture by an aerobic granular sludge sequencing batch reactor. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 115, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, C.L.; Alves, M.; Castro, P.M.; Henriques, I. Bacterial community dynamics within an aerobic granular sludge reactor treating wastewater loaded with pharmaceuticals. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, J.; Fu, J.; Xu, X.; Zhu, L. Enhancement of PPCPs removal by shaped microbial com-munity of aerobic granular sludge under condition of low C/N ratio influent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 394, 122583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihciokur, H.; Oguz, M. Removal of oxytetracycline and determining its biosorption properties on aerobic granular sludge. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 46, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carballa, M.; Omil, F.; Alder, A.; Lema, J. Comparison between the conventional anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge and its combination with a chemical or thermal pre-treatment concerning the removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products. Water Sci. Technol. 2006, 53, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunt, S.M.; Sackett, J.D.; Rosen, M.R.; Benotti, M.J.; Trenholm, R.A.; Vanderford, B.J.; Moser, D.P. Association between degradation of pharmaceuticals and endocrine-disrupting compounds and microbial communities along a treated wastewater effluent gradient in Lake Mead. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622, 1640–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, A.R.M.; Argenta, T.S.; Carvalho, C.D.A.D.; Oliveira, F.D.S.; Firmino, P.I.M.; dos Santos, A.B. Effects of the antibiotics trimethoprim (TMP) and sulfamethoxazole (SMX) on granulation, microbiology, and performance of aerobic granular sludge systems. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 127840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, Z.-L.; Wang, X.-C.; Shen, J.-M.; Xu, H. PPCPs removal by aerobic granular sludge membrane bioreactor. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 9843–9848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; He, J.; Wang, M.; Li, L. Cultivation and stable operation of aerobic granular sludge at low temperature by sieving out the batt-like sludge. Chemosphere 2018, 211, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-C.; Kim, S.; Shin, T.; Kim, H.; Sang, B.-I. Comparison of the Bacterial Communities in Anaerobic, Anoxic, and Oxic Chambers of a Pilot A2O Process Using Pyrosequencing Analysis. Curr. Microbiol. 2013, 66, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, B.; Sellamuthu, B.; Piché-Choquette, S.; Drogui, P.; Tyagi, R.D.; Vaudreuil, M.A.; Dubé, R. The bacterial community structure of submerged membrane bioreactor treating synthetic hospital wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 286, 121362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pujalte, M.J.; Lucena, T.; Ruvira, M.A.; Arahal, D.R.; Macián, M.C. The Family Rhodobacteraceae; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 439–512. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, D.; He, Y.; Yue, H.; Gao, J.; Wang, Q.; Yang, S. Enhanced long-term nitrogen removal by organotrophic anammox bacteria under different C/N ratio constraints: Quantitative molecular mechanism and microbial community dynamics. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 87593–87606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Wen, P.; Yuan, Y.; Tang, J.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, S. Identification of nitrogen-incorporating bacteria in a sequencing batch reactor: A combining cultivation-dependent and cultivation-independent method. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 316, 123964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martineau, C.; Mauffrey, F.; Villemur, R. Comparative Analysis of Denitrifying Activities of Hyphomicrobium nitrativorans, Hyphomicrobium denitrificans, and Hyphomicrobium zavarzinii. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 5003–5014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chen, Z.; Kang, J.; Zhao, X.; Shen, J. Removal of tetracycline by aerobic granular sludge and its bacterial community dynamics in SBR. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 18284–18293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Zhan, G.; Li, D.; He, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Liu, H.; Wang, C. Performance and microbial community of a novel non-aeration-based up-flow bioelectrochemical filter (UBEF) treating real domestic wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 348, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Cui, C.-W.; Qiu, S.; Shi, S.-N.; Li, A.; Ma, F. Nitrogen removal and microbial community shift in an aerobic denitrification reactor bioaugmented with a Pseudomonas strain for coal-based ethylene glycol industry wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 11435–11445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.-H.; Kang, S.-J.; Oh, T.-K. Dokdonella koreensis gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meunier, C.; Henriet, O.; Schoonbroodt, B.; Boeur, J.-M.; Mahillon, J.; Henry, P. Influence of feeding pattern and hydraulic selection pressure to control filamentous bulking in biological treatment of dairy wastewaters. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 221, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muñoz-Palazon, B.; Rosa-Masegosa, A.; Hurtado-Martinez, M.; Rodriguez-Sanchez, A.; Link, A.; Vilchez-Vargas, R.; Gonzalez-Martinez, A.; Lopez, J.G. Total and Metabolically Active Microbial Community of Aerobic Granular Sludge Systems Operated in Sequential Batch Reactors: Effect of Pharmaceutical Compounds. Toxics 2021, 9, 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9050093
Muñoz-Palazon B, Rosa-Masegosa A, Hurtado-Martinez M, Rodriguez-Sanchez A, Link A, Vilchez-Vargas R, Gonzalez-Martinez A, Lopez JG. Total and Metabolically Active Microbial Community of Aerobic Granular Sludge Systems Operated in Sequential Batch Reactors: Effect of Pharmaceutical Compounds. Toxics. 2021; 9(5):93. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9050093
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuñoz-Palazon, Barbara, Aurora Rosa-Masegosa, Miguel Hurtado-Martinez, Alejandro Rodriguez-Sanchez, Alexander Link, Ramiro Vilchez-Vargas, Alejandro Gonzalez-Martinez, and Jesus Gonzalez Lopez. 2021. "Total and Metabolically Active Microbial Community of Aerobic Granular Sludge Systems Operated in Sequential Batch Reactors: Effect of Pharmaceutical Compounds" Toxics 9, no. 5: 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9050093
APA StyleMuñoz-Palazon, B., Rosa-Masegosa, A., Hurtado-Martinez, M., Rodriguez-Sanchez, A., Link, A., Vilchez-Vargas, R., Gonzalez-Martinez, A., & Lopez, J. G. (2021). Total and Metabolically Active Microbial Community of Aerobic Granular Sludge Systems Operated in Sequential Batch Reactors: Effect of Pharmaceutical Compounds. Toxics, 9(5), 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9050093










