Assessment of the Railroad Transport Impact on Physical and Chemical Soil Properties: The Case Study from Zduńska Wola Karsznice Railway Junction, Central Poland
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
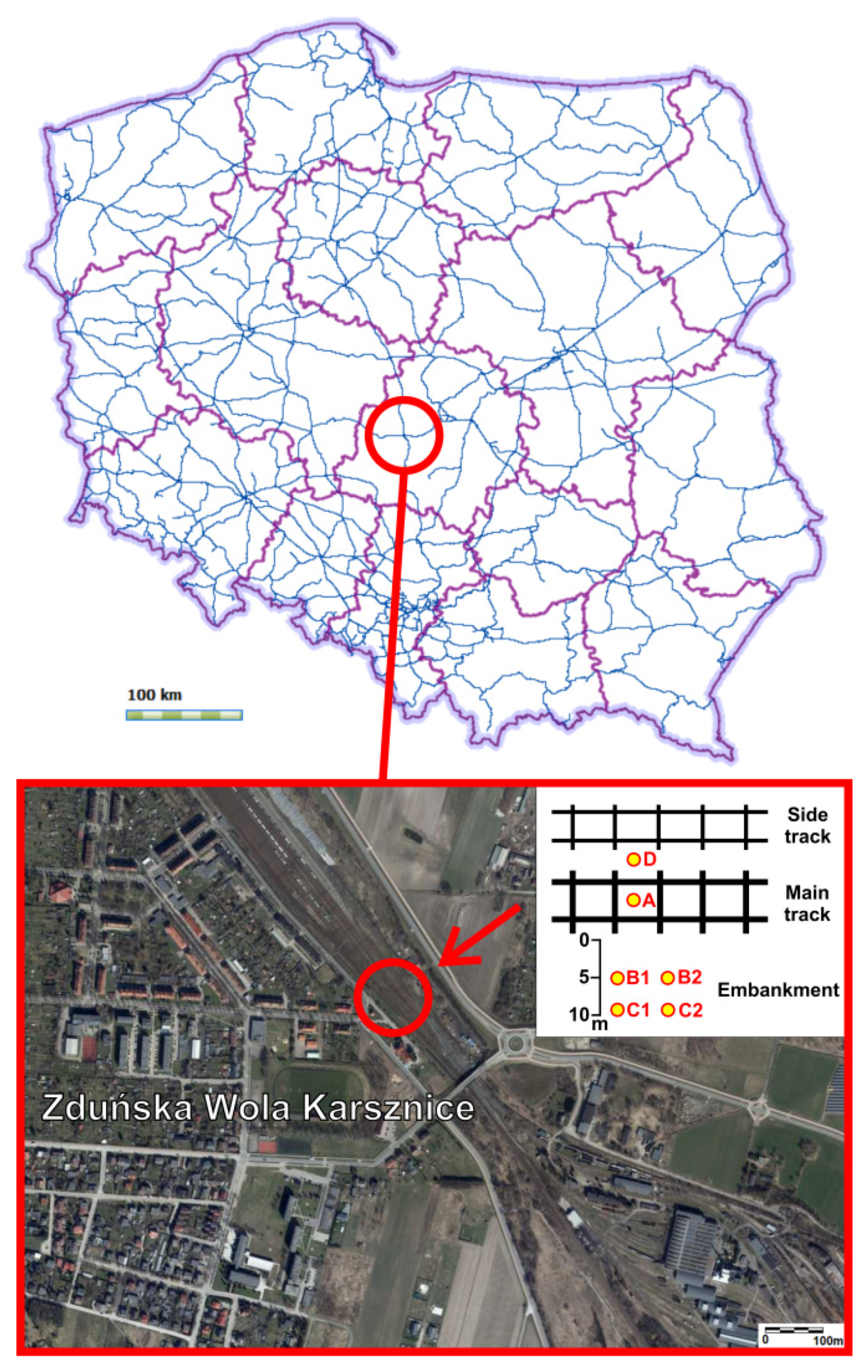
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Historical News of Zduńska Wola Karsznice Railway
2.3. Soil Sampling and Chemical Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
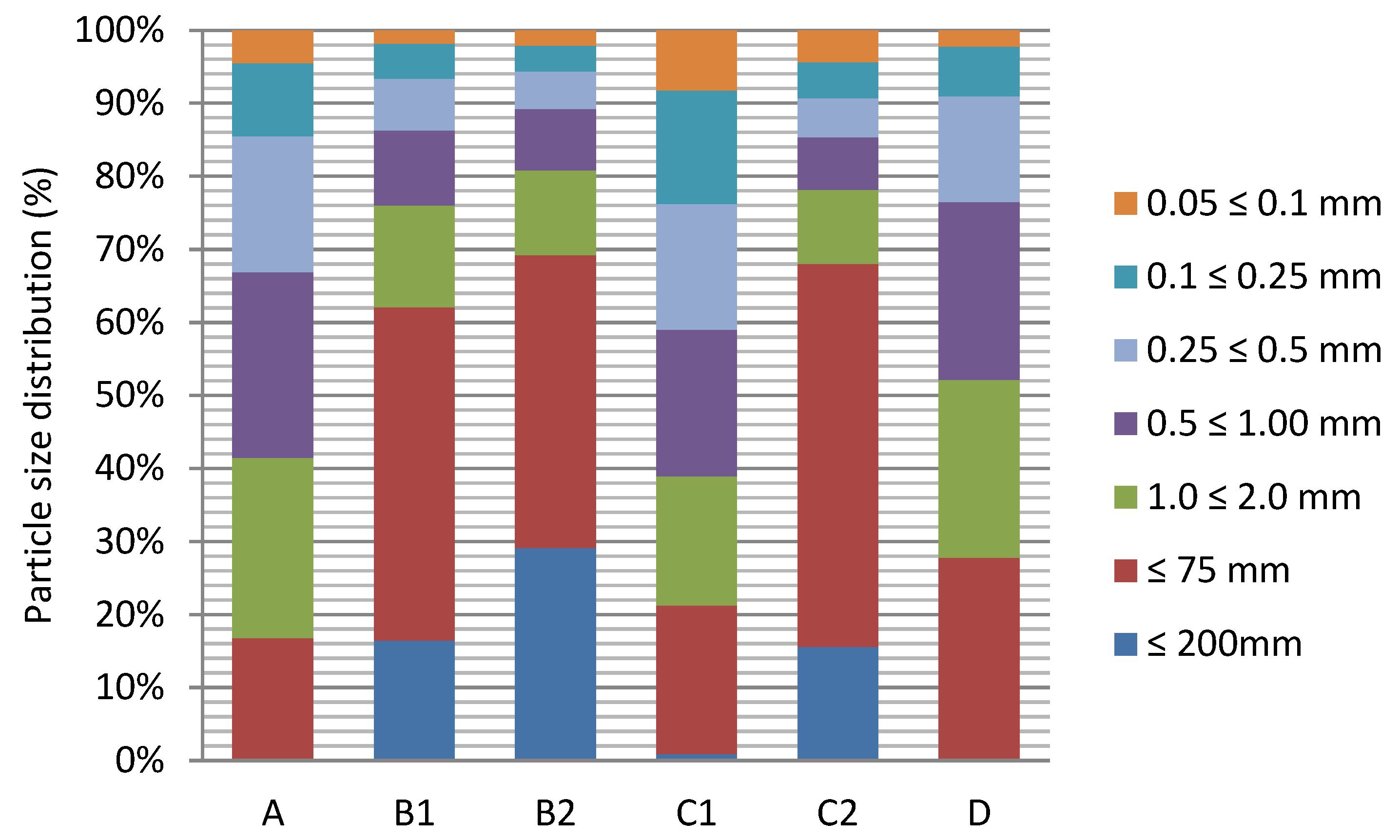
3.1. Physicochemical Properties of Soil Samples
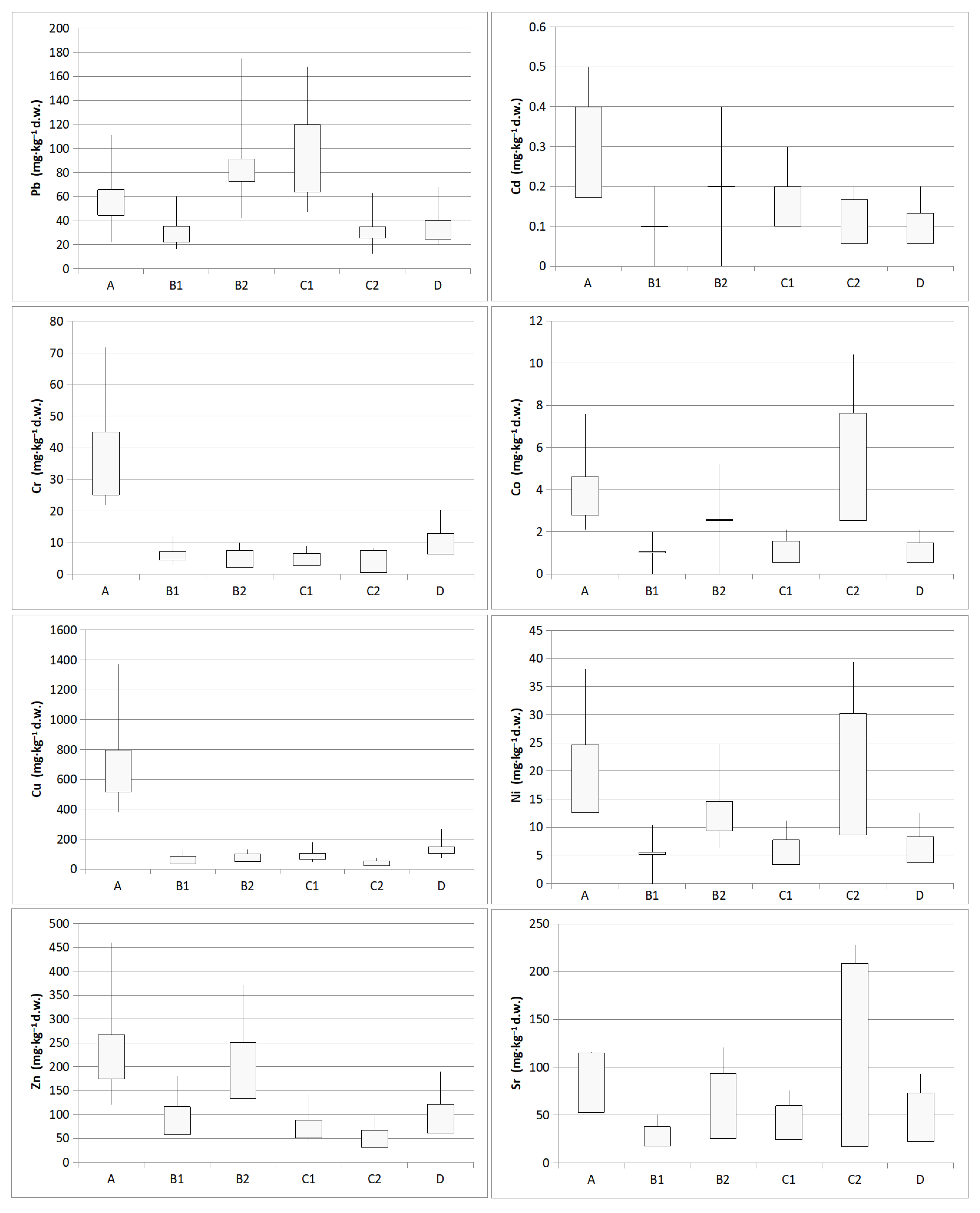
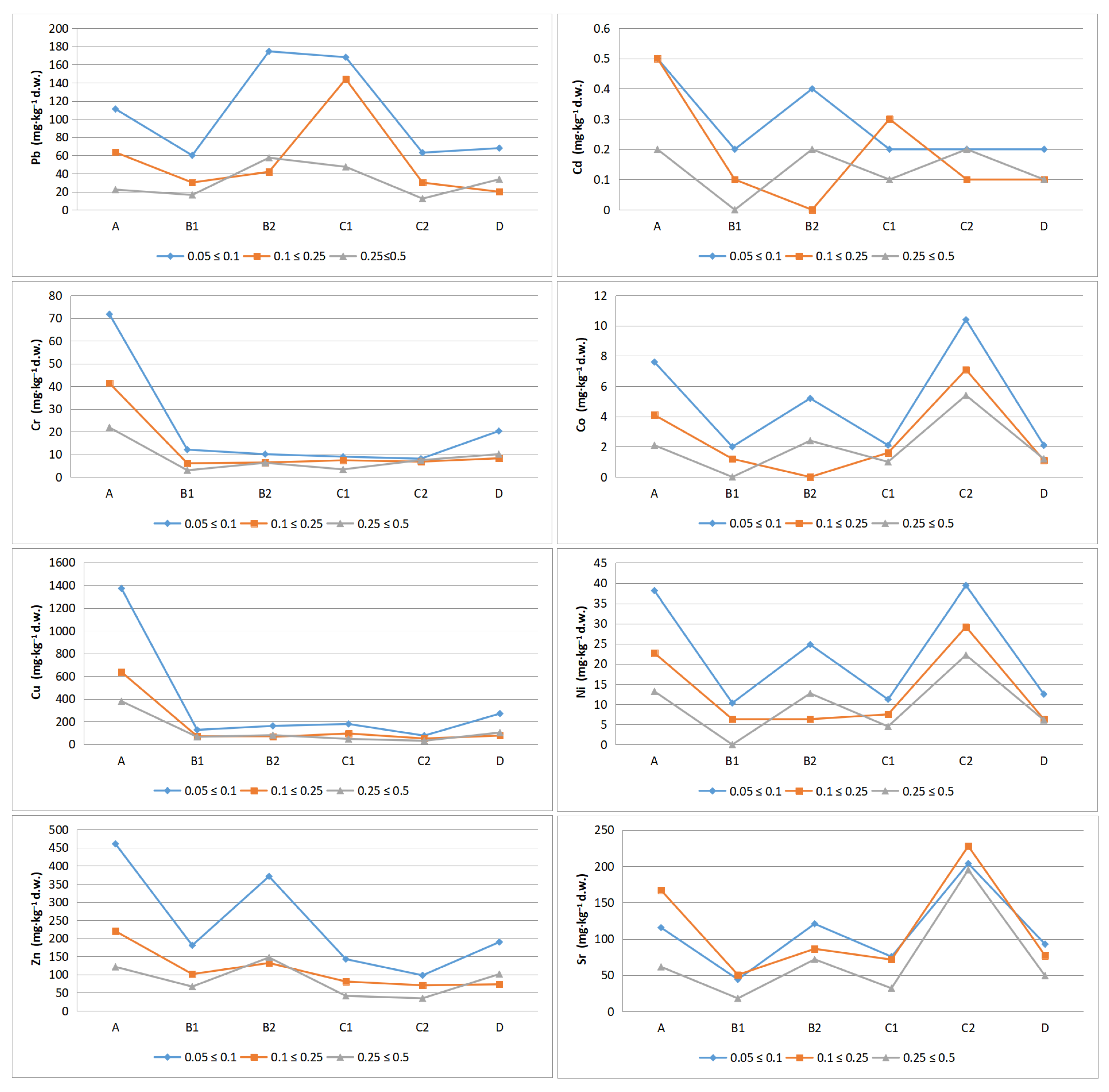
3.2. Levels of PHEs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duong, T.T.T.; Lee, B.K. Determining contamination level of heavy metals in road dust from busy traffic areas with different characteristics. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, H.; Choi, J.Y.; Ra, K. Potentially toxic elements pollution in road deposited sediments around the active smelting industry of Korea. Sci. Rep. 2021, 31, 7238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zhang, F.; Zeng, C.; Zhang, M.; Devkota, L.P.; Yao, T. Relationship between heavy metal concentrations in soils and grasses of roadside farmland in Nepal. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 3209–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, M.; Li, L. Identification of traffic-related metals and the effects of different environments on their enrichment in roadside soils along the Qinghai-Tibet highway. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 521–522, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golia, E.E.; Papadimou, S.G.; Cavalaris, C.; Tsiropoulos, N.G. Level of Contamination Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in the Urban Soils of Volos City (Central Greece). Sustainability 2021, 13, 2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamiec, E.; Jarosz-Krzemińska, E.; Wieszała, R. Heavy metals from non-exhaust vehicle emissions in urban and motorway road dusts. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 188, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krailertrattanachai, N.; Ketrot, D.; Wisawapipat, W. The Distribution of Trace Metals in Roadside Agricultural Soils, Thailand. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malawska, M.; Wiłkomirski, B. An analysis of soil and plant (Taraxacum officinale) contamination with heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the area of railway junction Iława Główna, Poland. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2001, 127, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.F.; Zhang, Y.L.; Hu, Z.J. The effects of the Qinghai–Tibet railway on heavy metals enrichment in soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 439, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, K.; Ai, Y.W.; Li, W.; Gao, H.; Fang, C. The effects of railway transportation on the enrichment of heavy metals in the artificial soil on railway cut slopes. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wierzbicka, M.; Bemowska-Kałabun, O.; Gworek, B. Multidimensional evaluation of soil pollution from railway tracks. Ecotoxicology 2015, 24, 805–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, P.S.; de Carvalho, R.G.; Grilo, C. Railway Disturbances on Wildlife: Types, Effects, and Mitigation Measures. Railw. Ecol. 2017, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šeda, M.; Ším, J.; Volavka, T.; Vondruška, J. Contamination of soils with Cu, Na and Hg due to the highway and railway transport. Eurasian J. Soil Sci. 2017, 6, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojic, N.; Pucarevic, M.; Stojic, G. Railway transportation as a source of soil pollution. Transp. Res. Part D Transport. Environ. 2017, 57, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiškūnaitė, R.; Jasiūnienė, V. The analysis of heavy metal pollutants emitted by railway transport. Transport 2020, 35, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarska, A.; Zelenko, Y.; Kovrov, O. Investigation of Heavy Metal Sources on Railways: Ballast Layer and Herbicides. J. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 21, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohrebennyk, V.; Ruda, M.; Paslavskyi, M.; Salamon, I. Consortiums of ecotones of protective type to ensure the environmental safety on railway lines, Acta Facultatis Studiorum Humanitatis Et Naturae Universitatis Prešoviensis. Nat. Sci. 2016, XLIII, 173–181. [Google Scholar]
- Radziemska, M.; Fronczyk, J.; Mazur, Z.; Vaverková, M. Impact of railway transport on soil and Pleurozium schreberi contamination with heavy metals. Infrastruct. Ecol. Rural Areas 2016, 1, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alok Gude, L. Heavy metal detection from sewage irrigated soil beside railway tracks in Mumbai. Kong. Res. J. 2017, 4, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Ai, Y.; Li, R.; Zhang, W. Effects of heavy metal pollution on enzyme activities in railway cut slope soils. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohsen, M.; Ahmed, M.B.; Zhou, J.L. Particulate matter concentrations and heavy metal contamination levels in the railway transport system of Sydney, Australia. Transp. Res. D Transp. Environ. 2018, 62, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarska, A.V.; Zelenko, Y.V. Assessment of the railway influence on the heavy metal accumulation in soil. Sci. Transp. Prog. Bull. Dnipropetr. Natl. Univ. Railw. Transp. 2018, 4, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, X.; Ai, Y.; Chen, J.; Luo, X.; Chen, J.; Zhong, S. Effects and mechanisms of revegetation modes on cadmium and lead pollution in artificial soil on railway rock-cut slopes. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 1602–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goth, A.; Michelsen, A.; Rousk, K. Railroad derived nitrogen and heavy metal pollution does not affectnitrogen fixation associated with mosses and lichens at a tundra site in Northern Sweden. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 247, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radziemska, M.; Gusiatin, Z.M.; Kowal, P.; Bęś, A.; Majewski, G.; Jeznach-Steinhagen, A.; Mazur, Z.; Liniauskienė, E.; Brtnický, M. Environmental impact assessment of risk elements from railway transport with the use of pollution indices, a biotest and bioindicators. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2021, 27, 517–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabata-Pendias, A.; Pendias, H. Biogeochemistry of Trace Elements; PWN: Warszawa, Poland, 1999. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Tomczyk, I. Ocena Zanieczyszczenia Metalami Ciężkimi Wierzchniego Poziomu Gruntu Terenów Kolejowych na Przykładzie Węzła Kolejowego Zduńska Wola Karsznice (Centralna Polska). Master’s Thesis, Jan Kochanowski University in Kielce, Kielce, Poland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kondracki, J. Geografia Regionalna Polski; Wydawnictwo Naukowe PWN: Warszawa, Poland, 2002. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Klatkowa, H. Szczegółówa Mapa Geologiczna Polski, 1:50,000, Arkusz Łask; Wydawnictwo Geologiczne: Warszawa, Poland, 1987.
- Maćków, A.; Gruszecki, J. Mapa Geośrodowiska Polski, 1:50,000, Arkusz Łask; PIG, MŚ: Warszawa, Poland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Geoportal Województwa Łódzkiego, the Agricultural Soil Suitability Complexes. Available online: http:/www.geoportal.lodzkie.pl (accessed on 22 September 2021).
- Wyżkowski, T.; Michalak, J. Raport Wojewódzkiego Inspektoratu Ochrony Środowiska w Łodzi; IV Ochrona Powierzchni Ziemi Okręgowa Stacja Chemiczno-Rolnicza w Łodzi: Łódź, Poland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Pecyna, I. Magistrala węglowa w regionie Szadkowskim. Biul. Szadkowski 2016, 16, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Railway Network on the Administrative Division of Poland. Available online: http:/www.mapa.plk-sa.pl (accessed on 22 September 2021).
- Orthophoto Map. Available online: http:/www.geoportal.gov.pl (accessed on 22 September 2021).
- Polskie Towarzystwo Gleboznawcze. Klasyfikacja uziarnienia gleb i utworów mineralnych—PTG 2008, Particle size distribution and textural classes of soils and mineral materials-classification of Polish Society of Soil Sciences 2008. Roczniki Gleboznawcze 2009, 60, 5–16. [Google Scholar]
- Czarnowska, K. Ogólna zawartość metali ciężkich w skałach macierzystych jako tło geochemiczne gleb. Gleboznawcze 1996, XLVII, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Zajęcka, E.; Świercz, A. Biomonitoring of the Urban Environment of Kielce and Olsztyn (Poland) Based on Studies of Total and Bioavailable Lead Content in Soils and Common Dandelion (Taraxacum officinale agg.). Minerals 2021, 11, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozłowski, R.; Szwed, M.; Żelezik, M. Environmental Aspect of the Cement Manufacturing in the Świętokrzyskie Mountains (Southeastern Poland). Minerals 2021, 11, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, L.P.; Ai, Y.W.; Yang, X.; Yu, Y.H.; Zuo, Y.B. Heavy metal contamination in soil alongside mountain railway in Sichuan, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 152, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malawska, M.; Wiłkomirski, B. Soil and plant contamination with heavy metals in the area of old railway junction Tarnowskie Góry and near two main railway routes. Rocz. Panstw. Zakl. Hig. 2000, 51, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ciazela, J.; Siepak, M. Environmental factors affecting soil metals near outlet roads in Poznań, Poland: Impact of grain size, soil depth, and wind dispersal. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wiłkomirski, B.; Sudnik-Wójcikowska, B.; Galera, H.; Wierzbicka, M.; Malawska, M. Railway transportation as a serious source of organic and inorganic pollution. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 218, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moczarski, M. Obsługiwanie pojazdów szynowych a zagrożenie środowiska. Rail vehicle maintenance—Environmental risk. Probl. Kolejnictwa 2006, 143, 59–86. [Google Scholar]
- Wiłkomirski, B.; Galera, H.; Sudnik-Wójcikowska, B.; Staszewski, T.; Malawska, M. Railway tracks—Habitat conditions, contamination, floristic settlement—A review. Environ. Nat. Resour. Res. 2012, 2, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antuniassi, U.R.; Velini, E.D.; Nogueira, H.C. Soil and weed survey for spatially variable herbicide application on railways. Precis. Agric. 2004, 5, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minister of the Environment. Regulation of the Minister of the Environment of 1 September 2016 on the Method of the Contamination Assessment of the Earth Surface. In Journal of Laws of 2016; Item 1395; Wydawnictwo Sejmowe: Warsaw, Poland, 2016. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Łukasiewicz, S. Struktura fizyczna gruntu, zawartość substancji organicznej oraz skład chemiczny gleb w podłożach 21 stanowisk zieleni miejskiej na terenie Poznania. Bad. Fizjogr. R. III Ser. Seria A Geogr. Geogr. 2011, A63, 49–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapalska, M. Analiza zawartości metali ciężkich w glebach Tatrzańskiego Parku Narodowego w części słowackiej (TANAP). In Proceedings of the V Krakowska Konferencja Młodych Uczonych, Kraków, Poland, 23–25 September 2010; pp. 327–335. [Google Scholar]

| Metal | Property | Sampling Location | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B1 | B2 | C1 | C2 | D | ||
| Pb | Range | 22.3–111.1 | 16.4–60.0 | 41.9–174.6 | 47.4–168.1 | 12.4–63.0 | 19.9–68.0 |
| Mean | 65.6 | 35.5 | 91.3 | 119.9 | 35.1 | 40.5 | |
| SD | 44.44 | 22.29 | 72.55 | 63.89 | 25.68 | 24.76 | |
| Cd | Range | 0.2–0.5 | 0.01–0.2 | 0.01–0.4 | 0.1–0.3 | 0.1–0.2 | 0.1–0.2 |
| Mean | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | |
| SD | 0.17 | 0.11 | 0.23 | 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.06 | |
| Cr | Range | 21.9–71.8 | 3.0–12.1 | 6.3–10.1 | 3.4–9.0 | 6.8–8.1 | 8.3–20.3 |
| Mean | 45.0 | 7.1 | 7.6 | 6.6 | 7.5 | 12.9 | |
| SD | 25.15 | 4.63 | 2.16 | 2.88 | 0.65 | 6.47 | |
| Co | Range | 2.1–7.6 | 0.01–2.0 | 0.01–5.2 | 1.0–2.1 | 5.4–10.4 | 1.1–2.1 |
| Mean | 4.6 | 1.1 | 2.5 | 1.6 | 7.6 | 1.5 | |
| SD | 2.78 | 1.01 | 2.60 | 0.55 | 2.54 | 0.55 | |
| Cu | Range | 379.4–1371.9 | 65.3–127.2 | 65.7–131.9 | 47.0–178.9 | 31.0–76.1 | 76.4–270.5 |
| Mean | 795.9 | 87.7 | 102.8 | 106.9 | 52.6 | 150.1 | |
| SD | 515.12 | 34.34 | 51.74 | 66.77 | 22.61 | 105.16 | |
| Ni | Range | 13.2–38.1 | 0.01–10.3 | 6.3–24.8 | 4.5–11.2 | 22.2–39.4 | 6.1–12.5 |
| Mean | 24.7 | 5.5 | 14.6 | 7.7 | 30.3 | 8.3 | |
| SD | 12.56 | 5.19 | 9.39 | 3.36 | 8.65 | 3.64 | |
| Zn | Range | 121.4–460.6 | 66.9–180.7 | 132.0–370.8 | 41.3–142.7 | 34.7–98.0 | 73.2–189.8 |
| Mean | 267.3 | 116.3 | 251.4 | 88.3 | 67.7 | 121.5 | |
| SD | 174.51 | 58.35 | 133.67 | 51.10 | 31.74 | 60.82 | |
| Sr | Range | 61.5–115.5 | 18.1–50.5 | 71.8–120.7 | 32.0–75.5 | 195.1–227.7 | 49.2–92.7 |
| Mean | 114.7 | 37.6 | 92.9 | 59.6 | 208.9 | 72.9 | |
| SD | 52.75 | 17.18 | 25.12 | 24.02 | 16.88 | 22.02 | |
| Sampling Location | Index of PHEs Accumulation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | Cd | Cr | Co | Cu | Ni | Zn | |
| Inter-railway | 5.5 | 1.89 | 1.49 | 1.00 | 97.46 | 2.21 | 7.69 |
| 5 m from the main track | 7.64 | 0.53 | 0.27 | 0.12 | 13.39 | 1.23 | 6.43 |
| 10 m from the main track | 2.92 | 0.88 | 0.28 | 1.84 | 6.95 | 2.89 | 2.07 |
| Side track | 3.65 | 0.66 | 0.44 | 0.35 | 18.37 | 0.77 | 3.74 |
| Study Area | Main Conclusion | References |
|---|---|---|
| Suining Railway Station, Suining, Sichuan Province, China | The concentrations of Cd, Pb showed increasing trend with increasing operation time of railways. | [10] |
| Railway that connects České Budějovice and Brno cities | The highest copper content was observed in soils taken close to the railroad. | [13] |
| Railway tracks on the territory of Srem, Serbia | The concentration values of Cu, Ni, Cd, Pb in samples collected from up to 1 km from the railroad line were higher than in samples collected from >1 km. | [14] |
| Suining, Sichuan, China | The railway transportation caused heavy metal pollution and the degree was Mn > Cd > Cu > Zn > Pb. | [20] |
| Railroad areas in Tarnowskie Góry | The level of PHEs contamination near railroad sites decreased with increasing distance from the rails. | [41] |
| Outlet roads in Poznań, Polska | The highest metal concentrations were observed in the smallest fraction (<0.063 mm), which were up to four times higher than those in sand fractions. | [42] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomczyk-Wydrych, I.; Świercz, A.; Przepióra, P. Assessment of the Railroad Transport Impact on Physical and Chemical Soil Properties: The Case Study from Zduńska Wola Karsznice Railway Junction, Central Poland. Toxics 2021, 9, 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9110296
Tomczyk-Wydrych I, Świercz A, Przepióra P. Assessment of the Railroad Transport Impact on Physical and Chemical Soil Properties: The Case Study from Zduńska Wola Karsznice Railway Junction, Central Poland. Toxics. 2021; 9(11):296. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9110296
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomczyk-Wydrych, Ilona, Anna Świercz, and Paweł Przepióra. 2021. "Assessment of the Railroad Transport Impact on Physical and Chemical Soil Properties: The Case Study from Zduńska Wola Karsznice Railway Junction, Central Poland" Toxics 9, no. 11: 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9110296
APA StyleTomczyk-Wydrych, I., Świercz, A., & Przepióra, P. (2021). Assessment of the Railroad Transport Impact on Physical and Chemical Soil Properties: The Case Study from Zduńska Wola Karsznice Railway Junction, Central Poland. Toxics, 9(11), 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9110296