Mitochondrial Morphology and Function of the Pancreatic β-Cells INS-1 Model upon Chronic Exposure to Sub-Lethal Cadmium Doses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Treatments
2.2. Viability Measurements
2.3. Immunofluorescence Measurements
2.4. ATP Measurements
2.5. Respiration Rates
2.6. Other Measurements
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Cadmium on INS-1 Cells
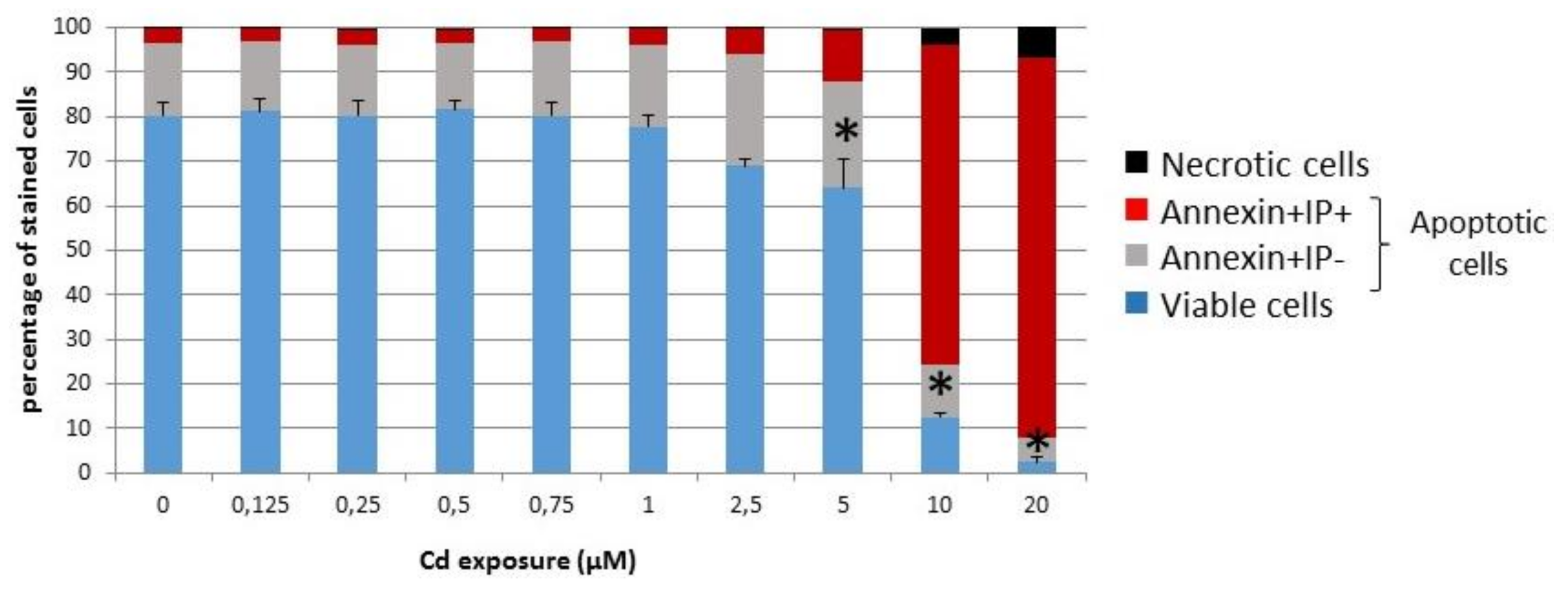
3.1.1. Viability of INS-1 Cells upon Long-Term Exposure to Cadmium
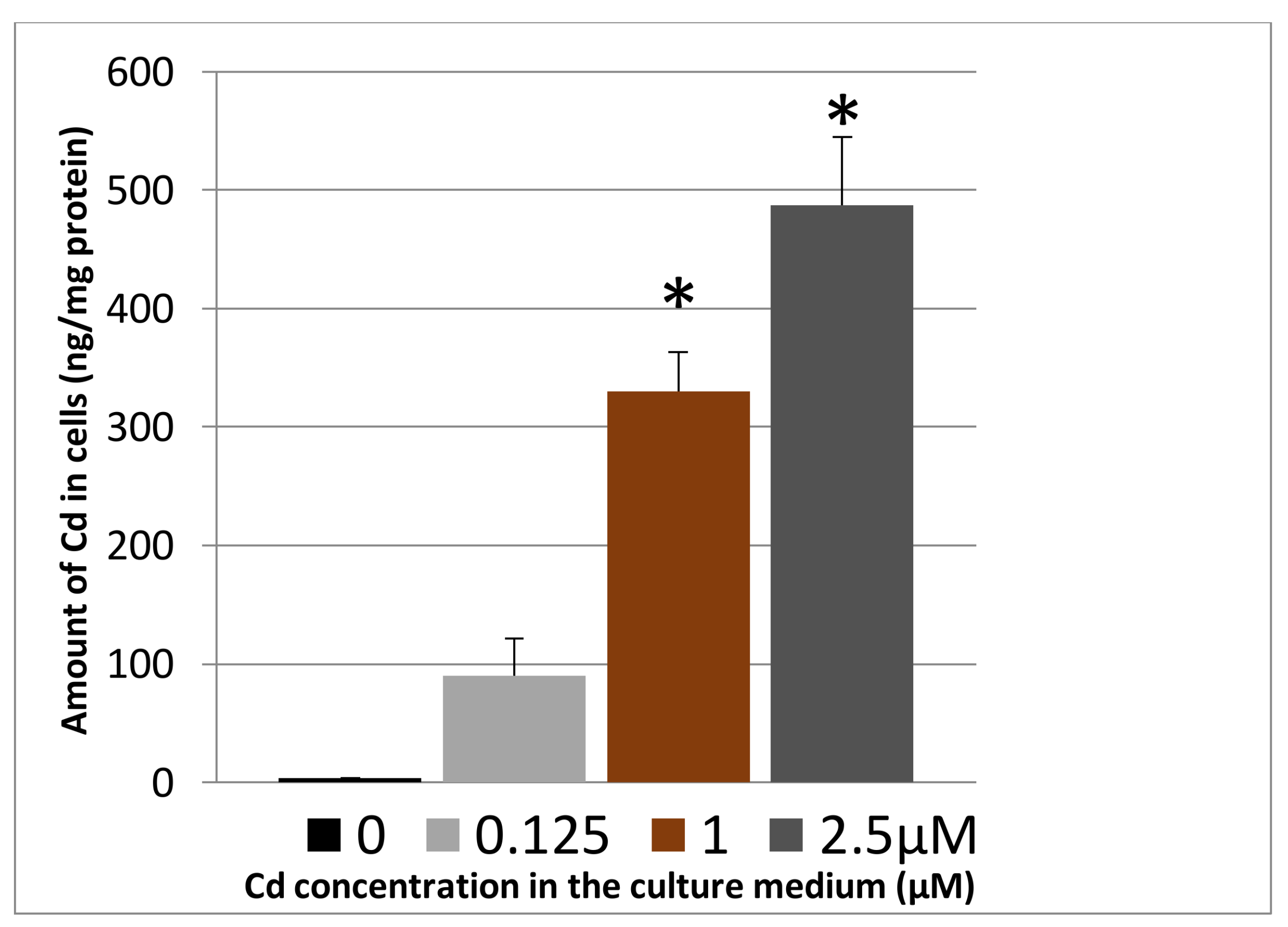
3.1.2. Cadmium Uptake
3.2. Organization of the Mitochondrial Network and Impact of Long-Term Cadmium Exposure
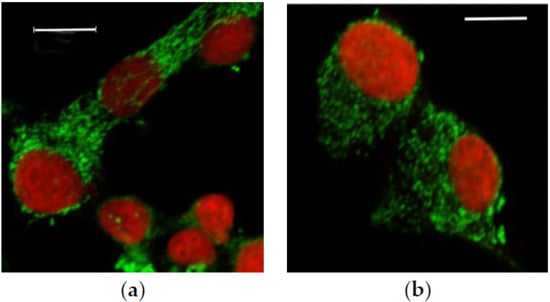
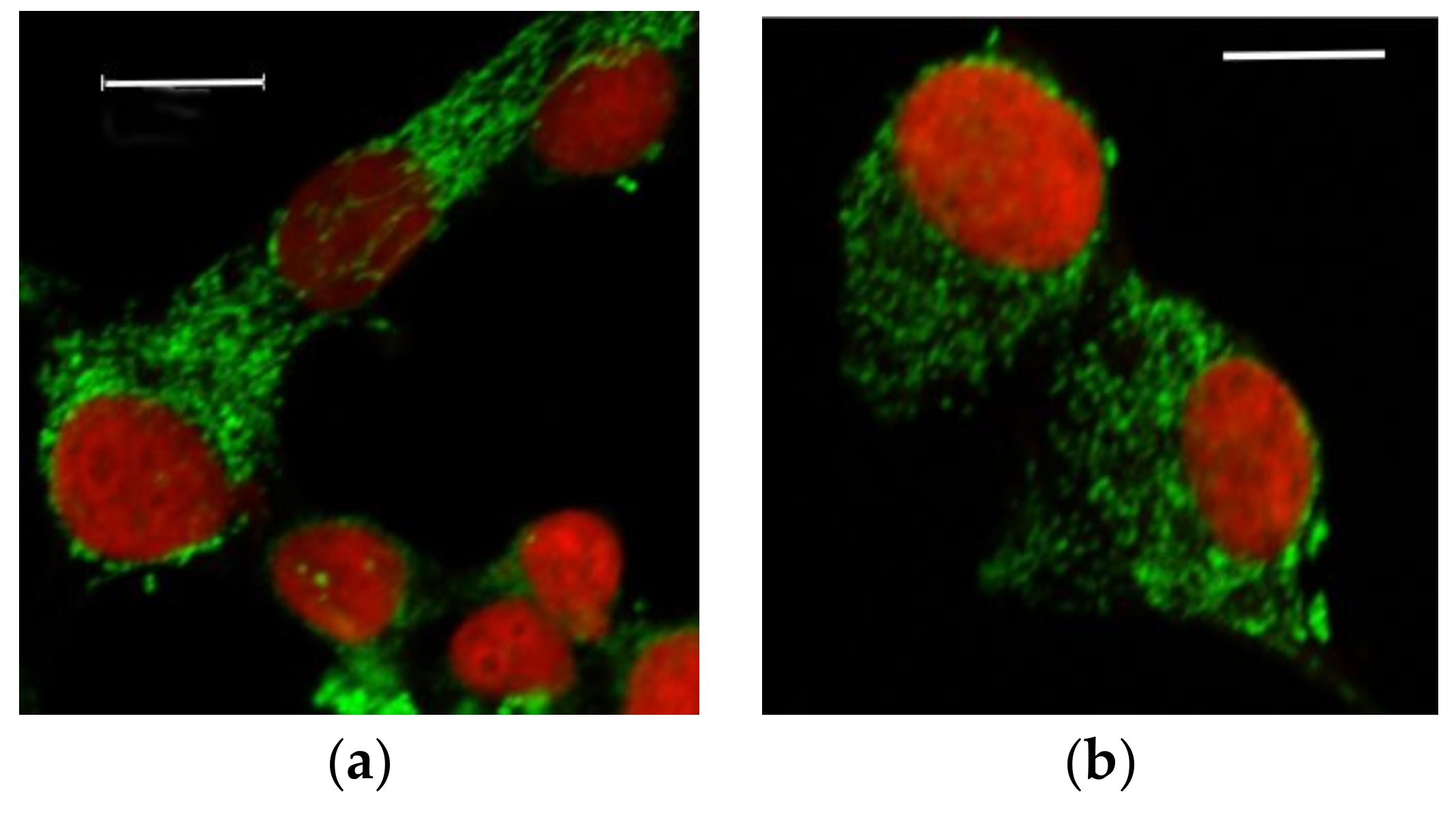
3.2.1. Microscopic Examination of Mitochondria
3.2.2. Quantitative Analysis of the Mitochondrial Network
3.3. Functional Analysis of Mitochondria
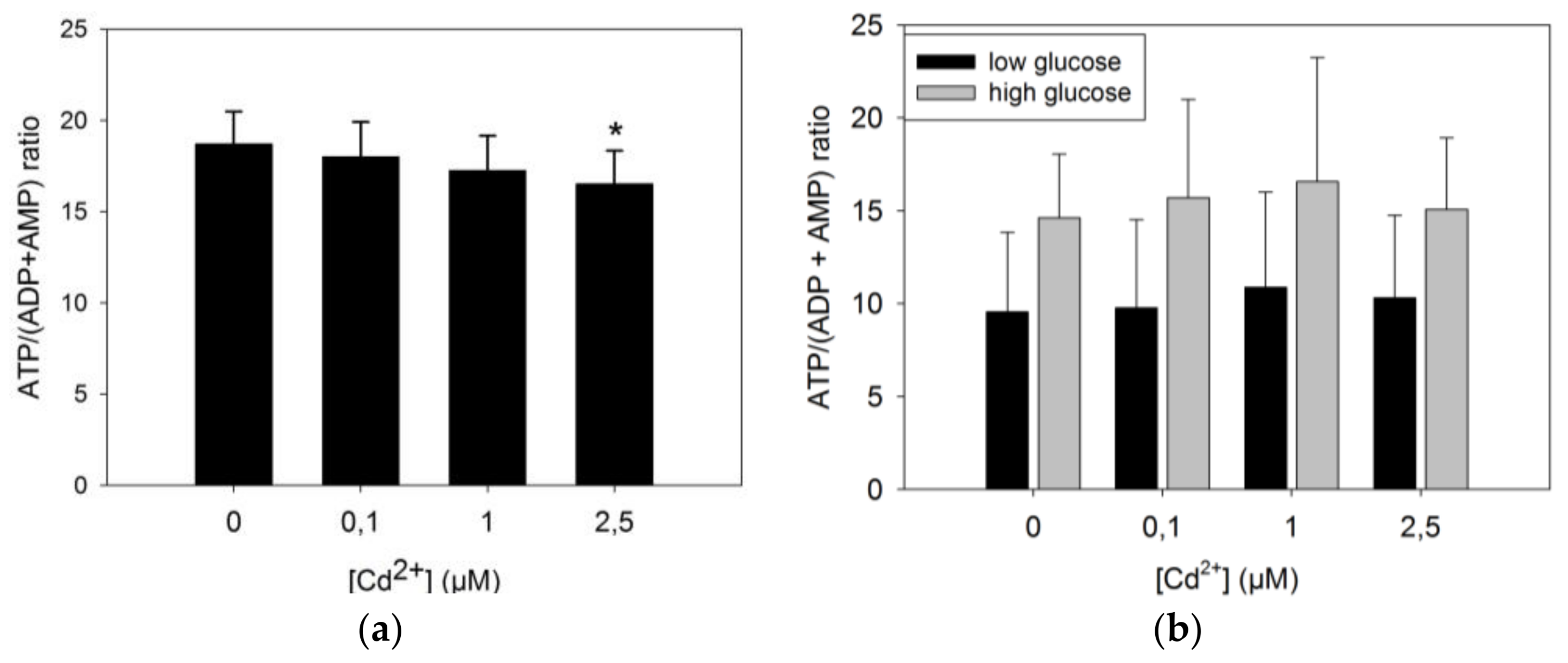
3.3.1. ATP Production by INS-1 Cells after Long Term Exposure to Moderate Levels of Cadmium
3.3.2. Oxygen Consumption of INS-1 Cells after Long Term Exposure to Moderate Levels of Cadmium
4. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nawrot, T.S.; Staessen, J.A.; Roels, H.A.; Munters, E.; Cuypers, A.; Richart, T.; Ruttens, A.; Smeets, K.; Clijsters, H.; Vangronsveld, J. Cadmium exposure in the population: From health risks to strategies of prevention. Biometals 2010, 23, 769–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR). Toxicological Profile for Cadmium; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2012; pp. 1–487.
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Cadmium dietary exposure in the european population. EFSA J. 2012, 10, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satarug, S.; Garrett, S.H.; Sens, M.A.; Sens, D.A. Cadmium, environmental exposure, and health outcomes. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulis, J.M. Cellular mechanisms of cadmium toxicity related to the homeostasis of essential metals. Biometals 2010, 23, 877–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulis, J.M.; Bourguignon, J.; Catty, P. Cadmium. In Binding, Transport and Storage of Metal Ions in Biological Cells; Maret, W., Wedd, A., Eds.; Royal Chemical Society: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 695–746. [Google Scholar]
- Maret, W.; Moulis, J.M. The bioinorganic chemistry of cadmium in the context of its toxicity. In Metal Ions in Life Sciences; Sigel, A., Sigel, H., Sigel, R.K.O., Eds.; Springer Science + Business Media B.V.: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 11, pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Thevenod, F.; Lee, W.K. Toxicology of cadmium and its damage to mammalian organs. Met. Ions Life Sci. 2013, 11, 415–490. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Viau, M.; Collin-Faure, V.; Richaud, P.; Ravanat, J.L.; Candeias, S.M. Cadmium and T cell differentiation: Limited impact in vivo but significant toxicity in fetal thymus organ culture. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2007, 223, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uetani, M.; Kobayashi, E.; Suwazono, Y.; Honda, R.; Nishijo, M.; Nakagawa, H.; Kido, T.; Nogawa, K. Tissue cadmium (Cd) concentrations of people living in a Cd polluted area, Japan. Biometals 2006, 19, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Muayed, M.; Raja, M.R.; Zhang, X.; MacRenaris, K.W.; Bhatt, S.; Chen, X.; Urbanek, M.; O’Halloran, T.V.; Lowe, W.L., Jr. Accumulation of cadmium in insulin-producing beta cells. Islets 2012, 4, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.C.; Moon, K.; Thayer, K.A.; Navas-Acien, A. Environmental chemicals and type 2 diabetes: An updated systematic review of the epidemiologic evidence. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2013, 13, 831–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinkov, A.A.; Filippini, T.; Ajsuvakova, O.P.; Aaseth, J.; Gluhcheva, Y.G.; Ivanova, J.M.; Bjorklund, G.; Skalnaya, M.G.; Gatiatulina, E.R.; Popova, E.V.; et al. The role of cadmium in obesity and diabetes. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 741–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Song, J.; Zhu, C.; Wang, Y.; Yin, X.; Huang, G.; Zhao, K.; Zhu, J.; Duan, Z.; Su, L. Association between cadmium exposure and diabetes mellitus risk: A prisma-compliant systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 113129–113141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacquet, A.; Ounnas, F.; Lenon, M.; Arnaud, J.; Demeilliers, C.; Moulis, J.M. Chronic exposure to low-level cadmium in diabetes: Role of oxidative stress and comparison with polychlorinated biphenyls. Curr. Drug Targets 2016, 17, 1385–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rorsman, P.; Braun, M. Regulation of insulin secretion in human pancreatic islets. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2013, 75, 155–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martelli, A.; Rousselet, E.; Dycke, C.; Bouron, A.; Moulis, J.M. Cadmium toxicity in animal cells by interference with essential metals. Biochimie 2006, 88, 1807–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, K.C.; Hsu, C.C.; Liu, S.H.; Su, C.C.; Yen, C.C.; Lee, M.J.; Chen, K.L.; Ho, T.J.; Hung, D.Z.; Wu, C.C.; et al. Cadmium induces apoptosis in pancreatic beta-cells through a mitochondria-dependent pathway: The role of oxidative stress-mediated c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54374. [Google Scholar]
- Cannino, G.; Ferruggia, E.; Luparello, C.; Rinaldi, A.M. Cadmium and mitochondria. Mitochondrion 2009, 9, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maechler, P.; de Andrade, P.B. Mitochondrial damages and the regulation of insulin secretion. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2006, 34, 824–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Asfari, M.; Janjic, D.; Meda, P.; Li, G.; Halban, P.A.; Wollheim, C.B. Establishment of 2-mercaptoethanol-dependent differentiated insulin-secreting cell lines. Endocrinology 1992, 130, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacquet, A.; Arnaud, J.; Hininger-Favier, I.; Hazane-Puch, F.; Couturier, K.; Lénon, M.; Lamarche, F.; Ounnas, F.; Fontaine, E.; Moulis, J.-M.; et al. Impact of chronic and low cadmium exposure of rats: Sex specific disruption of glucose metabolism. Chemosphere 2018. in revision. [Google Scholar]
- Dhingra, R.; Kirshenbaum, L.A. Regulation of mitochondrial dynamics and cell fate. Circ. J. 2014, 78, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wakabayashi, N.; Wakabayashi, J.; Tamura, Y.; Song, W.J.; Sereda, S.; Clerc, P.; Polster, B.M.; Aja, S.M.; Pletnikov, M.V.; et al. The dynamin-related GTPase Opa1 is required for glucose-stimulated ATP production in pancreatic beta cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2011, 22, 2235–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anello, M.; Lupi, R.; Spampinato, D.; Piro, S.; Masini, M.; Boggi, U.; Del Prato, S.; Rabuazzo, A.M.; Purrello, F.; Marchetti, P. Functional and morphological alterations of mitochondria in pancreatic beta cells from type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetologia 2005, 48, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twig, G.; Elorza, A.; Molina, A.J.; Mohamed, H.; Wikstrom, J.D.; Walzer, G.; Stiles, L.; Haigh, S.E.; Katz, S.; Las, G.; et al. Fission and selective fusion govern mitochondrial segregation and elimination by autophagy. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Affourtit, C.; Brand, M.D. Uncoupling protein-2 contributes significantly to high mitochondrial proton leak in INS-1E insulinoma cells and attenuates glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Biochem. J. 2008, 409, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Men, X.; Wang, H.; Li, M.; Cai, H.; Xu, S.; Zhang, W.; Xu, Y.; Ye, L.; Yang, W.; Wollheim, C.B.; et al. Dynamin-related protein 1 mediates high glucose induced pancreatic beta cell apoptosis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 41, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Men, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H.; Xu, S.; Xu, M.; Xu, Y.; Yang, W.; Lou, J. Dynamin-related protein 1 is implicated in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced pancreatic beta-cell apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2011, 28, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Molina, A.J.; Wikstrom, J.D.; Stiles, L.; Las, G.; Mohamed, H.; Elorza, A.; Walzer, G.; Twig, G.; Katz, S.; Corkey, B.E.; et al. Mitochondrial networking protects beta-cells from nutrient-induced apoptosis. Diabetes 2009, 58, 2303–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerf, M.E. Beta cell dynamics: Beta cell replenishment, beta cell compensation and diabetes. Endocrine 2013, 44, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulis, J.-M. Cadmium exposure, cellular and molecular adaptations. In Encyclopedia of Metalloproteins; Kretsinger, R.H., Uversky, V.N., Permyakov, E.A., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 364–371. [Google Scholar]
- Thévenod, F. Cadmium and cellular signaling cascades: To be or not to be? Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 238, 221–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Dong, X.; Sun, J.; Zhong, C.; Li, B.; You, X.; Liu, B.; Liu, Z. Two-photon fluorescent probe for cadmium imaging in cells. Analyst 2012, 137, 1837–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luz, A.L.; Godebo, T.R.; Smith, L.L.; Leuthner, T.C.; Maurer, L.L.; Meyer, J.N. Deficiencies in mitochondrial dynamics sensitize Caenorhabditis elegans to arsenite and other mitochondrial toxicants by reducing mitochondrial adaptability. Toxicology 2017, 387, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Pi, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, N.; Guo, P.; Lu, Y.; He, M.; Xie, J.; Zhong, M.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Cadmium induced drp1-dependent mitochondrial fragmentation by disturbing calcium homeostasis in its hepatotoxicity. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Pi, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, N.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Tang, J.; Li, H.; Feng, M.; Deng, P.; et al. Melatonin prevents abnormal mitochondrial dynamics resulting from the neurotoxicity of cadmium by blocking calcium-dependent translocation of drp1 to the mitochondria. J. Pineal Res. 2016, 60, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacquet, A.; Barbeau, D.; Arnaud, J.; Hijazi, S.; Hazane-Puch, F.; Lamarche, F.; Quiclet, C.; Couturier, K.; Fontaine, E.; Moulis, J.-M.; et al. Impact of maternal low-level cadmium exposure before and during gestation, and during lactation on metabolism of offspring at different ages. 2018; in preparation. [Google Scholar]


© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jacquet, A.; Cottet-Rousselle, C.; Arnaud, J.; Julien Saint Amand, K.; Ben Messaoud, R.; Lénon, M.; Demeilliers, C.; Moulis, J.-M. Mitochondrial Morphology and Function of the Pancreatic β-Cells INS-1 Model upon Chronic Exposure to Sub-Lethal Cadmium Doses. Toxics 2018, 6, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics6020020
Jacquet A, Cottet-Rousselle C, Arnaud J, Julien Saint Amand K, Ben Messaoud R, Lénon M, Demeilliers C, Moulis J-M. Mitochondrial Morphology and Function of the Pancreatic β-Cells INS-1 Model upon Chronic Exposure to Sub-Lethal Cadmium Doses. Toxics. 2018; 6(2):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics6020020
Chicago/Turabian StyleJacquet, Adeline, Cécile Cottet-Rousselle, Josiane Arnaud, Kevin Julien Saint Amand, Raoua Ben Messaoud, Marine Lénon, Christine Demeilliers, and Jean-Marc Moulis. 2018. "Mitochondrial Morphology and Function of the Pancreatic β-Cells INS-1 Model upon Chronic Exposure to Sub-Lethal Cadmium Doses" Toxics 6, no. 2: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics6020020
APA StyleJacquet, A., Cottet-Rousselle, C., Arnaud, J., Julien Saint Amand, K., Ben Messaoud, R., Lénon, M., Demeilliers, C., & Moulis, J.-M. (2018). Mitochondrial Morphology and Function of the Pancreatic β-Cells INS-1 Model upon Chronic Exposure to Sub-Lethal Cadmium Doses. Toxics, 6(2), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics6020020