Modelling Short-Term Maximum Individual Exposure from Airborne Hazardous Releases in Urban Environments. Part ΙI: Validation of a Deterministic Model with Wind Tunnel Experimental Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Wind Tunnel Measurements
2.1. Description of the Concentration Measurements
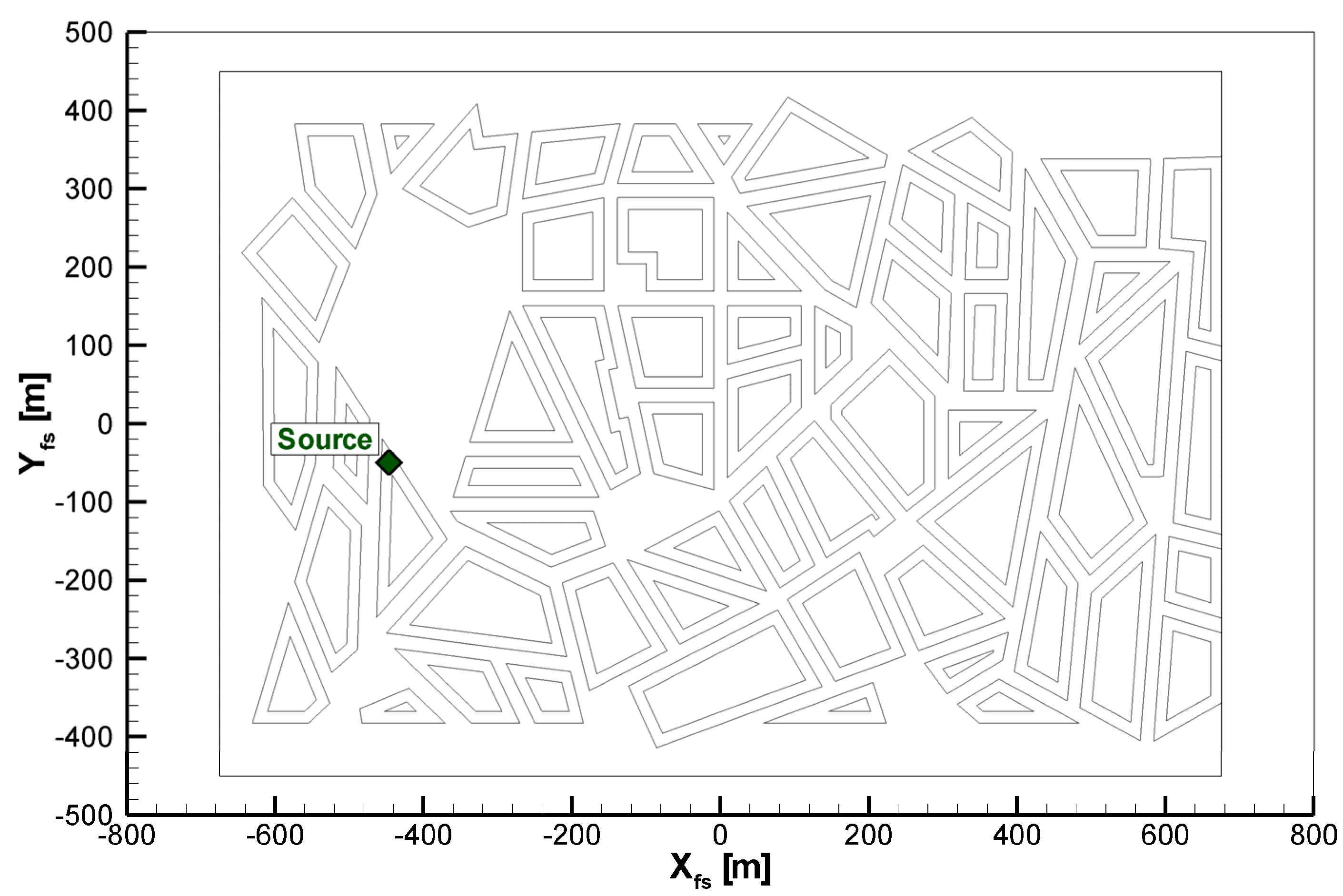
2.2. Evaluation of the Concentration Data
3. Model Refinement and Uncertainties
Estimation of the Uncertainty of the β Parameter


4. Performance of the Model for Δτ = Δτ0
| Parameter β | FAC2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Original model | 1.72 | 81.63% |
| Present model | 2.88 | 95.41% |
5. The Model’s Overall Performance (Δτ ≥ Δτ0)
- For small time integrals the results of the model should be the same as before.
- For large time integrals the results of the model should be decreased.
| Parameter β | FAC2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Original model | 1.72 | 97.4% |
| Present model | 2.88 | 95% |

6. Μodel Improvements

7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lung, T.; Muller, H.J.; Glaser, M.; Moller, B. Measurements and modelling of full-scale concentration fluctuations. Agratechnische Forsch. 2002, 8, 5–15. [Google Scholar]
- Yee, Ε. The shape of the probability density function of short-term concentration fluctuations of plumes in the atmospheric boundary layer. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1990, 51, 269–298. [Google Scholar]
- Yee, E.; Kosteniuk, P.R.; Chandler, G.M.; Biltoft, C.A.; Bowers, J.F. Statistical characteristics of concentration fluctuations in dispersing plumes in the atmospheric surface layer. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1993, 65, 69–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gailis, R.M.; Hill, A.; Yee, E.; Hilderman, T. Extension of a fluctuating plume model of tracer dispersion to a sheared boundary layer and to a large array of obstacles. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2007, 122, 3–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gailis, R.M.; Hill, A. A Wind-Tunnel Simulation of Plume Dispersion within a Large Array of Obstacles. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2006, 119, 289–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykes, R.I.; Parker, S.F.; Henn, D.S.; Cerasoli, C.P.; Santos, L.P. PC-SCIPUFF Version 1.2PD Technical Documentation; Titan Research & Technology Division: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Efthimiou, G.C.; Berbekar, E.; Harms, F.; Bartzis, J.G.; Leitl, B. Prediction of high concentrations and concentration distribution of a continuous point source release in a semi-idealized urban canopy using CFD-RANS modeling. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 100, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartzis, J.G.; Sfetsos, A.; Andronopoulos, S. On the individual exposure from airborne hazardous releases: the effect of atmospheric turbulence. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 150, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, E.; Biltoft, C.A. Concentration fluctuation measurements in a plume dispersing through a regular array of obstacles. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2004, 111, 363–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Efthimiou, G.C.; Bartzis, J.G.; Berbekar, E.; Hertwig, D.; Harms, F.; Leitl, B. Modelling Short-Term Maximum Individual Exposure from Airborne Hazardous Releases in Urban Environments. Part ΙI: Validation of a Deterministic Model with Wind Tunnel Experimental Data. Toxics 2015, 3, 259-267. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics3030259
Efthimiou GC, Bartzis JG, Berbekar E, Hertwig D, Harms F, Leitl B. Modelling Short-Term Maximum Individual Exposure from Airborne Hazardous Releases in Urban Environments. Part ΙI: Validation of a Deterministic Model with Wind Tunnel Experimental Data. Toxics. 2015; 3(3):259-267. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics3030259
Chicago/Turabian StyleEfthimiou, George C., John G. Bartzis, Eva Berbekar, Denise Hertwig, Frank Harms, and Bernd Leitl. 2015. "Modelling Short-Term Maximum Individual Exposure from Airborne Hazardous Releases in Urban Environments. Part ΙI: Validation of a Deterministic Model with Wind Tunnel Experimental Data" Toxics 3, no. 3: 259-267. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics3030259





