Characterization of the Chemical Composition, Cytotoxicity, and Metabolomic Effects of PM2.5 in a Plateau City, China
Highlights
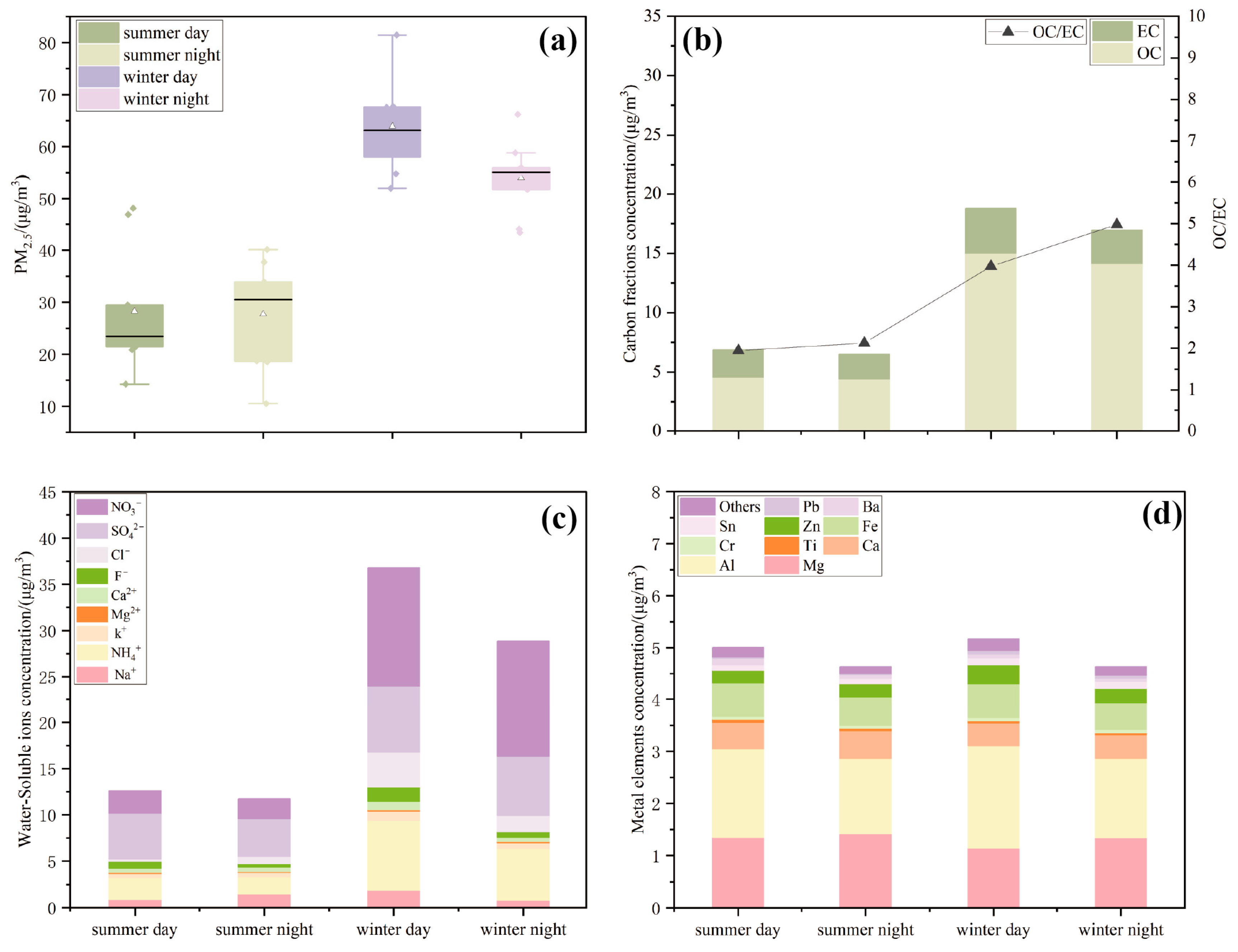
- The average PM2.5 mass concentration in Xining was 2.10 times higher in winter than in summer, with increases in OC, NO3− and NH4+ proving significant.
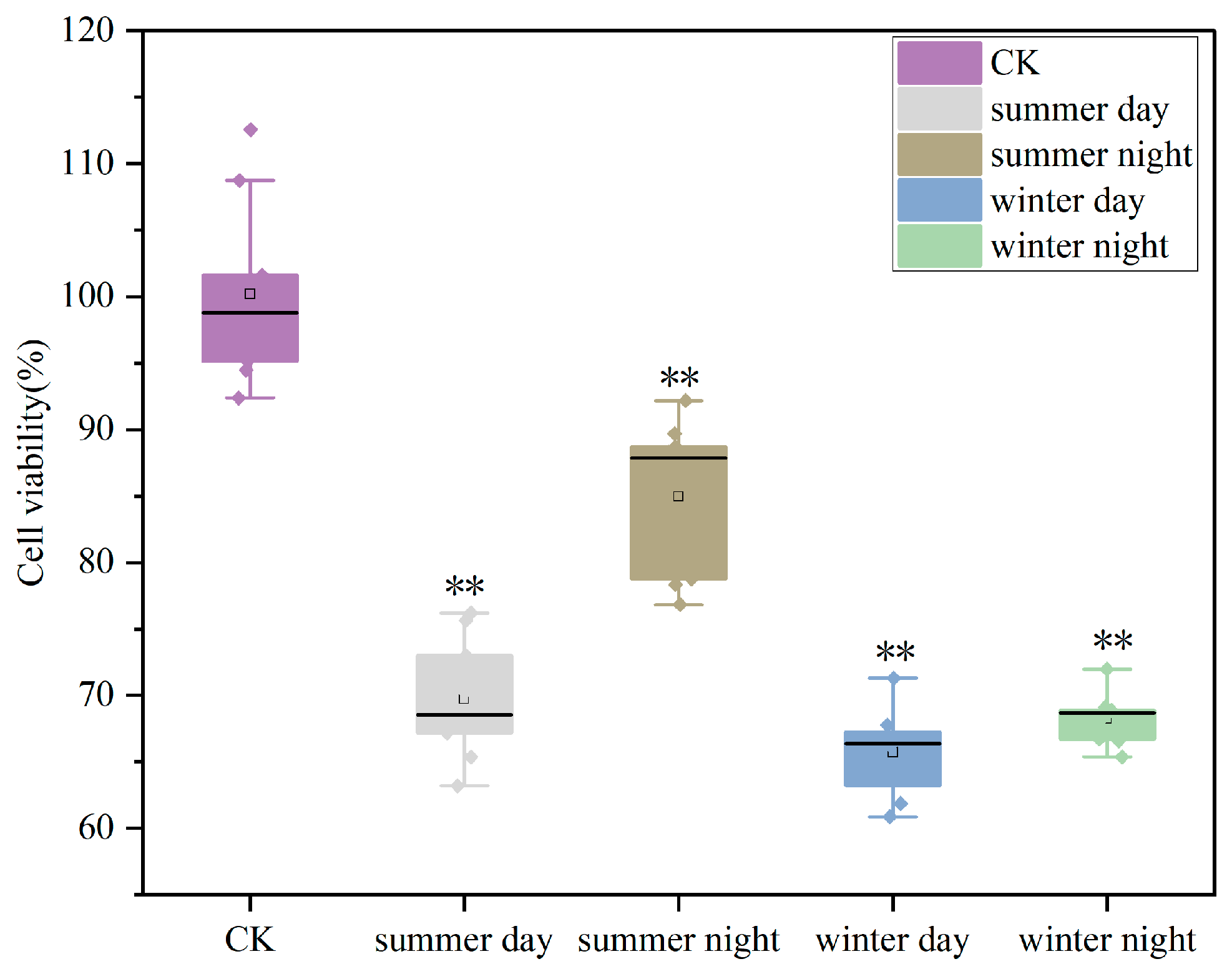
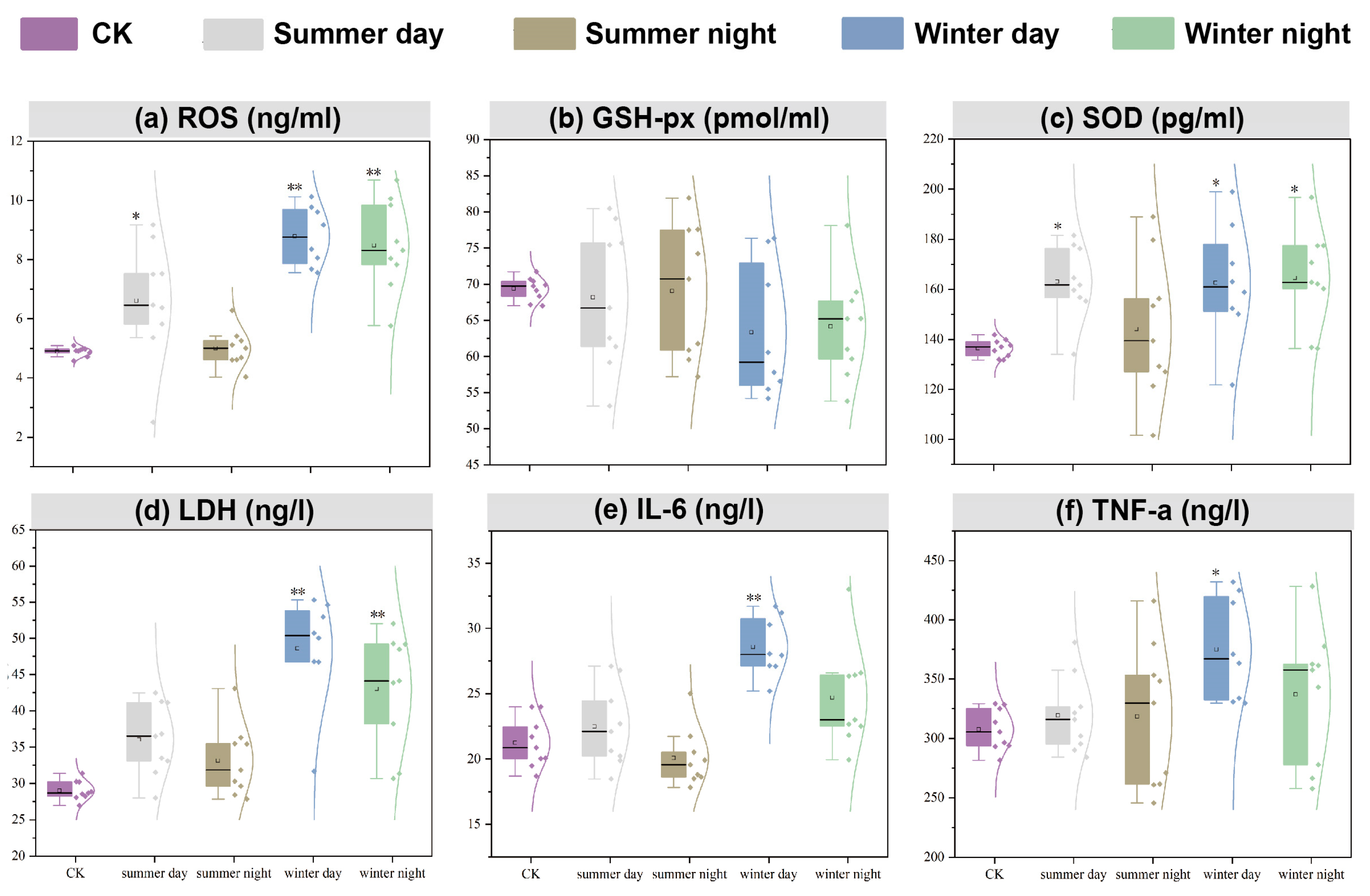
- PM2.5 exhibited seasonal variations in cytotoxicity effects, with ROS (winter) and LDH (summer) as the most impacted indicators.
- Multiple chemical components may synergistically exacerbate oxidative stress and inflammation in A549 cells.
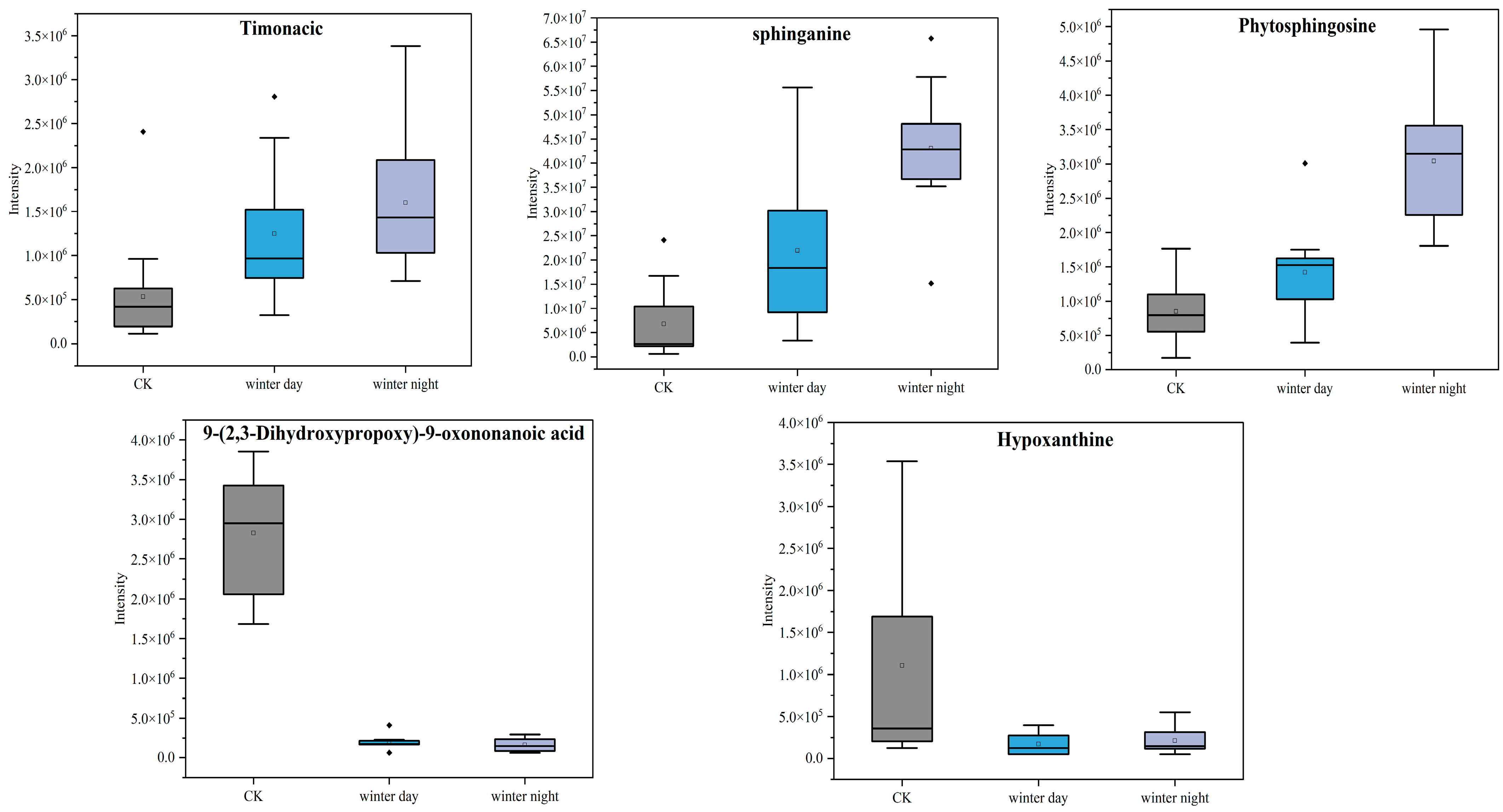
- Glutathione, amino acid and sphingolipid metabolism were key pathways to the cytotoxicity mechanism in Xining.
- The results highlight the extent to which PM2.5 in plateau cities affects cytotoxicity in different seasons and what the key metabolic pathways are.
- They emphasize the urgent need for the accurate implementation of local population health risk assessments and the formulation of health protection measures.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
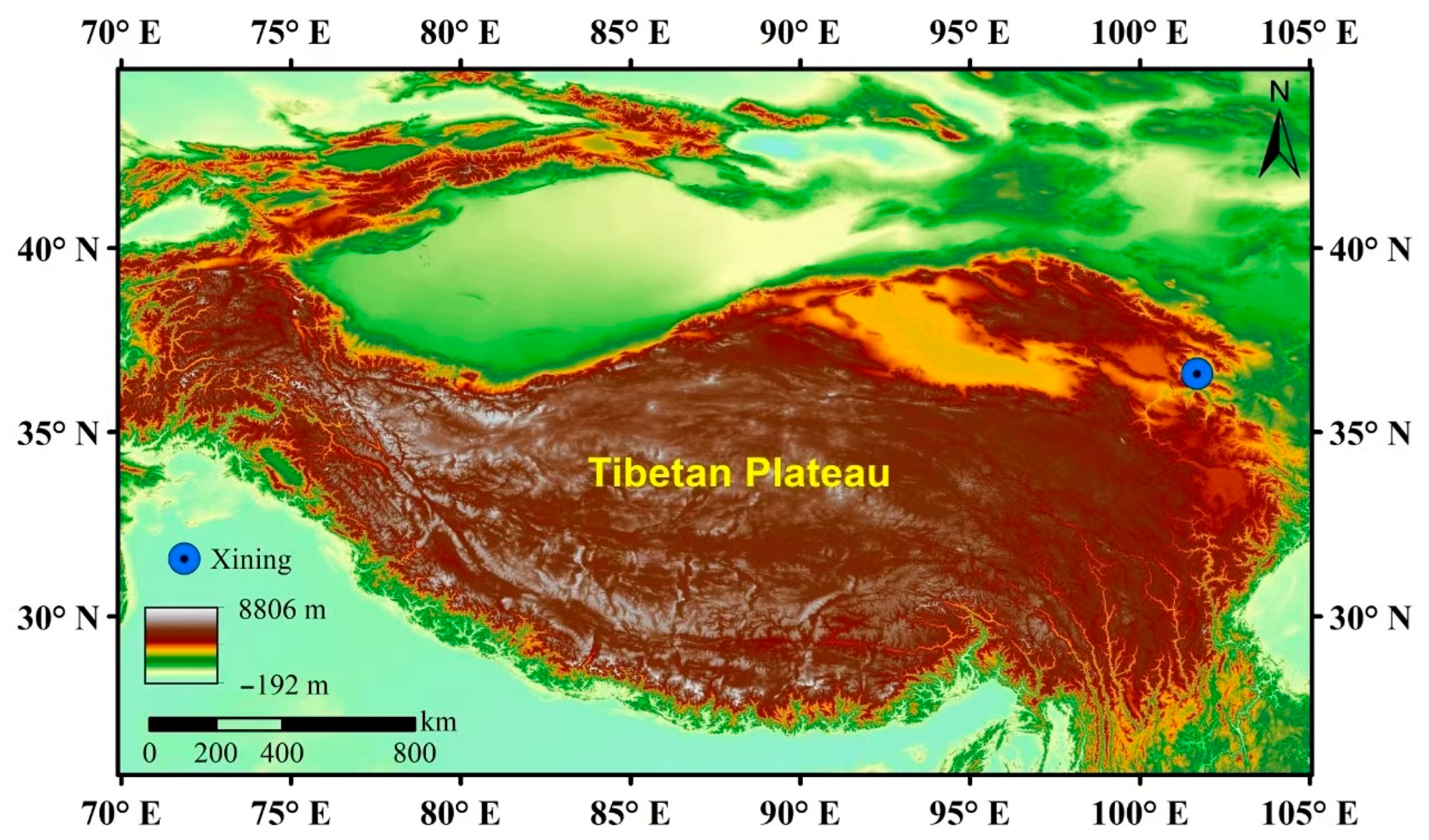
2.1. Study Area and PM2.5 Sampling
2.2. PM2.5 Chemical Composition Analysis
2.3. Preparation of PM2.5 Suspension for Cell Exposure
2.4. Cell Culture
2.5. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.6. UPLC-MS-Based Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of PM2.5 Chemical Components in the Plateau City
3.1.1. PM2.5 Mass Concentration
3.1.2. Concentration of Carbonaceous Components in PM2.5 Samples
3.1.3. Concentration of Water-Soluble Ions in PM2.5 Samples
3.1.4. Concentration of Metallic Elements in PM2.5 Samples
3.2. In Vitro Cytotoxicity of PM2.5 in the Plateau City
3.2.1. Effects of PM2.5 on A549 Cell Viability
3.2.2. Oxidative Stress of A549 Cells Induced by PM2.5 Exposure
3.2.3. Cell Membrane Injury of A549 Cells Induced by PM2.5 Exposure
3.2.4. Inflammatory Injury of A549 Cells Induced by PM2.5 Exposure
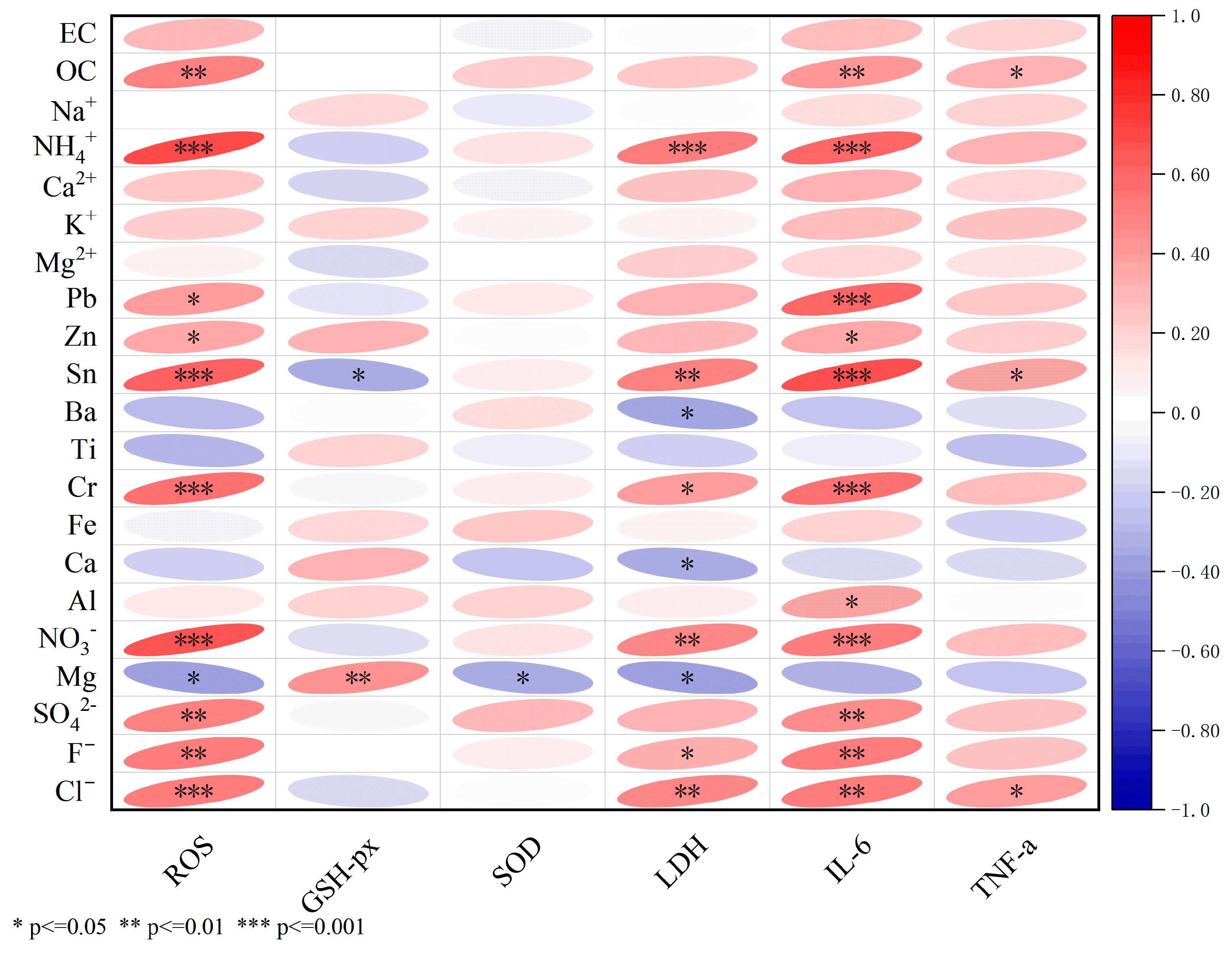
3.2.5. Correlation Between the Cytotoxicity and Chemical Components of PM2.5
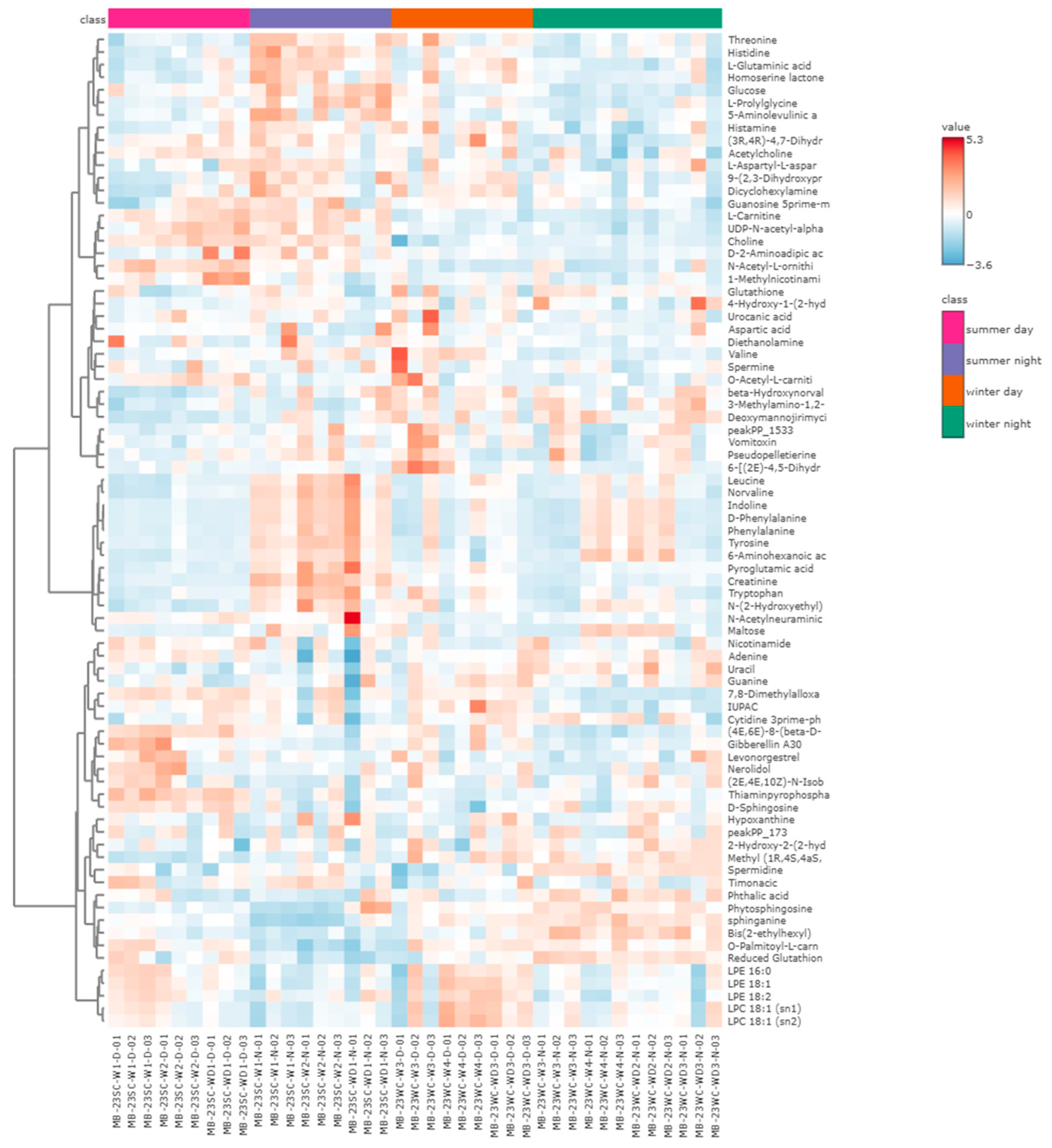
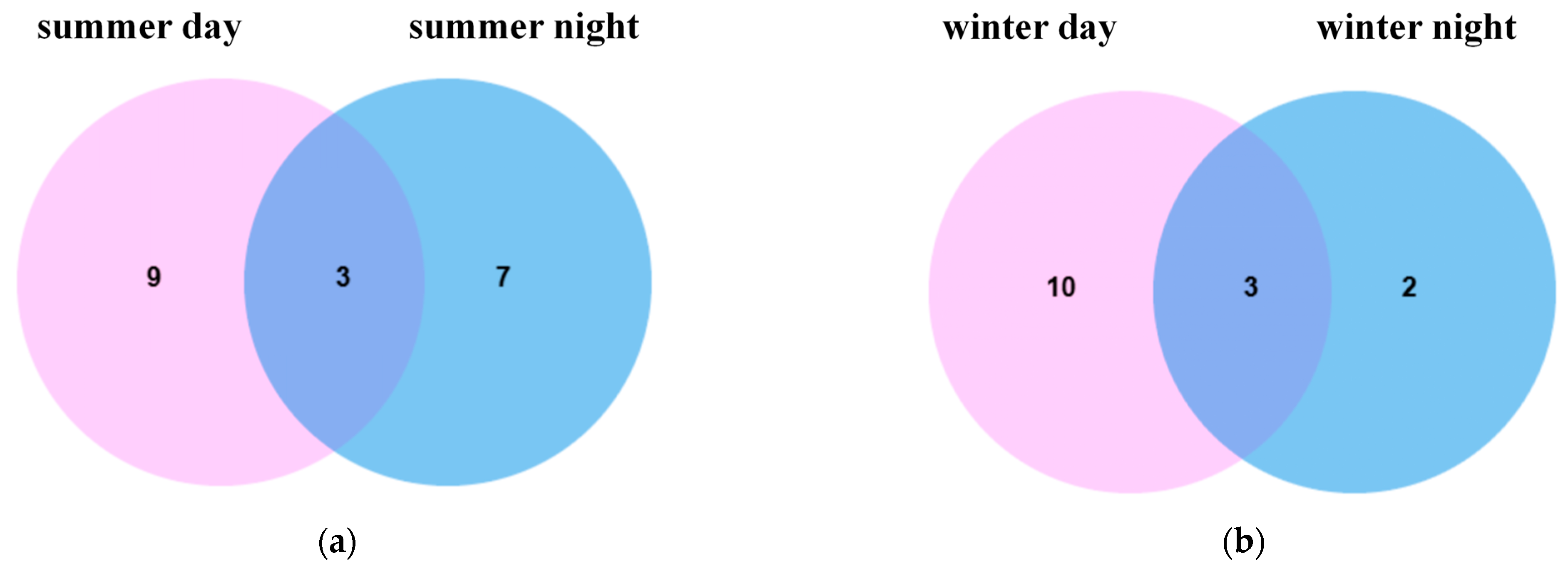
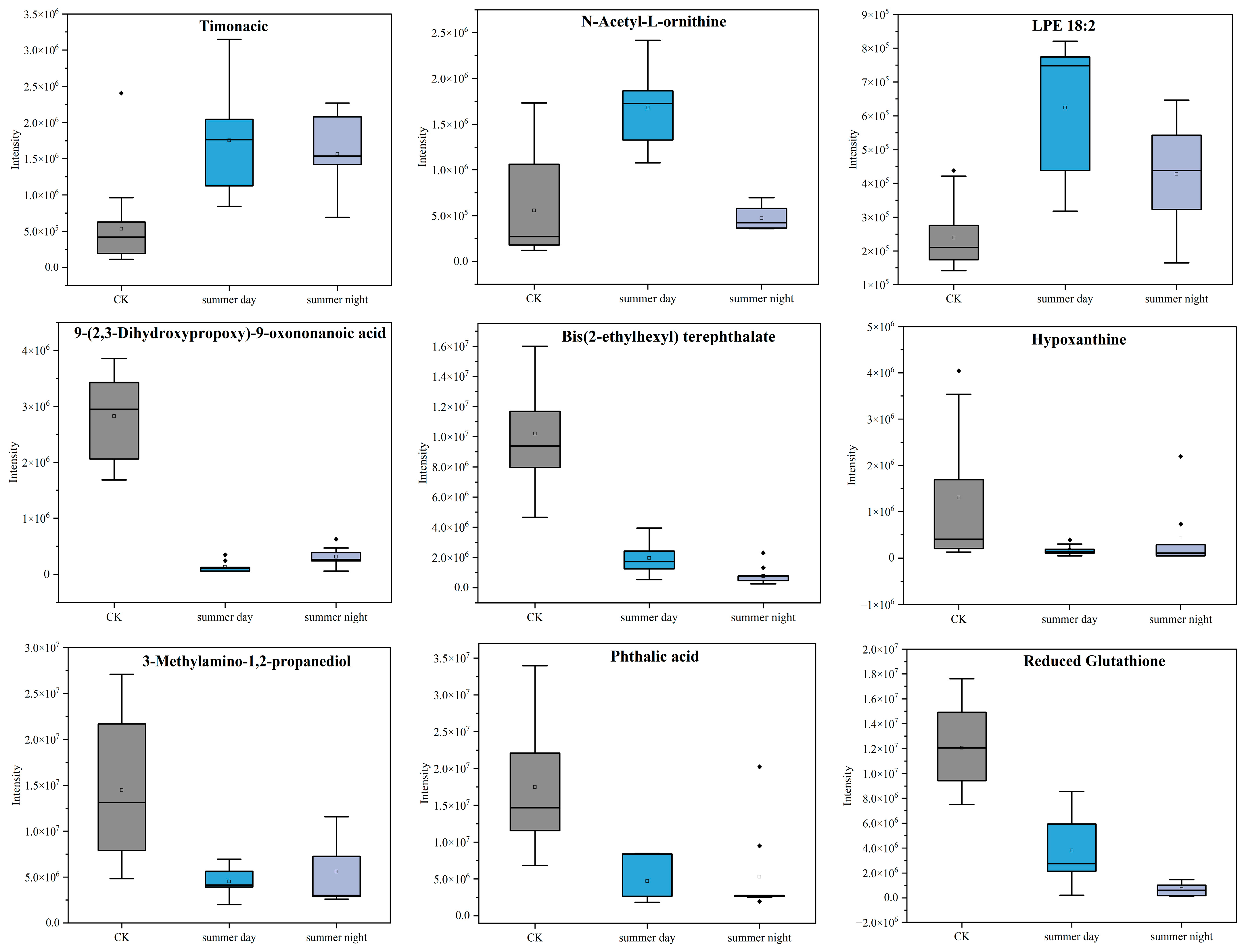
3.3. Metabolite Effects of PM2.5 Exposure on A549 Cells in the Plateau City
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, L.; Chen, X.; Tian, X. The Impact of Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) on China’s Agricultural Production from 2001 to 2010. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 178, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-S.; Lin, Y.-C.; Chiueh, P.-T. Nexus of Ecosystem Service-Human Health-Natural Resources: The Nature-Based Solutions for Urban PM2.5 Pollution. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 91, 104441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.J.; Brauer, M.; Burnett, R.; Anderson, H.R.; Frostad, J.; Estep, K.; Balakrishnan, K.; Brunekreef, B.; Dandona, L.; Dandona, R.; et al. Estimates and 25-Year Trends of the Global Burden of Disease Attributable to Ambient Air Pollution: An Analysis of Data from the Global Burden of Diseases Study 2015. Lancet 2017, 389, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Chen, X.; Hays, M.D.; Holder, A.L. Composition and Light Absorption of N-Containing Aromatic Compounds in Organic Aerosols from Laboratory Biomass Burning. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 2899–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, T.-T.; Leveque, T.; Austruy, A.; Goix, S.; Schreck, E.; Dappe, V.; Sobanska, S.; Foucault, Y.; Dumat, C. Foliar Uptake and Metal(Loid) Bioaccessibility in Vegetables Exposed to Particulate Matter. Environ. Geochem. Health 2014, 36, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahanzaib, M.; Iqbal, S.; Shoukat, S.; Park, D. Personal Exposure Assessment of Respirable Particulate Matter Among University Students Across Microenvironments During the Winter Season Using Portable Monitoring Devices. Toxics 2025, 13, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, C.A.; Dockery, D.W. Health Effects of Fine Particulate Air Pollution: Lines That Connect. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2006, 56, 709–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaapen, A.M.; Borm, P.J.A.; Albrecht, C.; Schins, R.P.F. Inhaled Particles and Lung Cancer. Part A: Mechanisms. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 109, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Luo, X.-S.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Hong, Y.; Pang, Y.; Huang, W.; Wang, Y.; Jin, L. Seasonally Varied Cytotoxicity of Organic Components in PM2.5 from Urban and Industrial Areas of a Chinese Megacity. Chemosphere 2019, 230, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippmann, M. Toxicological and Epidemiological Studies of Cardiovascular Effects of Ambient Air Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) and Its Chemical Components: Coherence and Public Health Implications. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2014, 44, 299–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieme, D.; Cabral-Ndior, M.; Garçon, G.; Verdin, A.; Billet, S.; Cazier, F.; Courcot, D.; Diouf, A.; Shirali, P. Relationship between Physicochemical Characterization and Toxicity of Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) Collected in Dakar City (Senegal). Environ. Res. 2012, 113, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrone, M.G.; Gualtieri, M.; Ferrero, L.; Porto, C.L.; Udisti, R.; Bolzacchini, E.; Camatini, M. Seasonal Variations in Chemical Composition and in Vitro Biological Effects of Fine PM from Milan. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 1368–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Huang, W.; Luo, X.-S.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Tang, M.; Hong, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, H. In-Vitro Human Lung Cell Injuries Induced by Urban PM2.5 during a Severe Air Pollution Episode: Variations Associated with Particle Components. Ecotoxic. Environ. Safety 2020, 206, 111406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, F.; Zhao, J.; Wei, X.; Zheng, K.; Wu, J.; Li, B.; Pan, B. Toxicity and Endocrine-Disrupting Potential of PM2.5: Association with Particulate Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons, Phthalate Esters, and Heavy Metals. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292 Pt A, 118349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Pakbin, P.; Shafer, M.M.; Antkiewicz, D.; Schauer, J.J.; Sioutas, C. Macrophage Reactive Oxygen Species Activity of Water-Soluble and Water-Insoluble Fractions of Ambient Coarse, PM2.5 and Ultrafine Particulate Matter (PM) in Los Angeles. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobels, I.; Vanparys, C.; Van den Heuvel, R.; Vercauteren, J.; Blust, R. Added Value of Stress Related Gene Inductions in HepG2 Cells as Effect Measurement in Monitoring of Air Pollution. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 55, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Happo, M.; Markkanen, A.; Markkanen, P.; Jalava, P.; Kuuspalo, K.; Leskinen, A.; Sippula, O.; Lehtinen, K.; Jokiniemi, J.; Hirvonen, M.-R. Seasonal Variation in the Toxicological Properties of Size-Segregated Indoor and Outdoor Air Particulate Matter. Toxicol. Vitr. 2013, 27, 1550–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, S.; Dailey, L.A.; Soukup, J.M.; Grambow, S.C.; Devlin, R.B.; Huang, Y.-C.T. Seasonal Variations in Air Pollution Particle-Induced Inflammatory Mediator Release and Oxidative Stress. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 1032–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Luo, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Alamdar, A.; Peng, S.; Liu, L.; Tian, M.; Shen, H. Metabolomics Reveals Disturbed Metabolic Pathways in Human Lung Epithelial Cells Exposed to Airborne Fine Particulate Matter. Toxicol. Res. 2015, 4, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Shi, Z.; Wu, J.; Yang, X.; Feng, L.; Ren, L.; Duan, J.; Sun, Z. Metabolic Impact Induced by Total, Water Soluble and Insoluble Components of PM2.5 Acute Exposure in Mice. Chemosphere 2018, 207, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Kang, S.; Li, C.; Yan, F.; Chen, P.; Gao, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Sillanpää, M. Light Absorption of Biomass Burning and Vehicle Emission-Sourced Carbonaceous Aerosols of the Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 15369–15378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Wu, D.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Jin, L.N.; Zhao, B.; Li, S.; Sun, Y.; Dong, Z.; Wu, Q.; et al. Control of Toxicity of Fine Particulate Matter Emissions in China. Nature 2025, 643, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Yang, T.; Shi, S.; Meng, X.; Chen, R.; Long, H.; Hu, Y.; Chai, D.; Liu, W.; Tong, Y.; et al. Ambient Particulate Matter Associates with Asthma in High Altitude Region: A Population-Based Study. World Allergy Organ. J. 2023, 16, 100774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ding, Z.; Jin, H.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, B. The Interactive Effects of Extreme Temperatures and PM2.5 Pollution on Mortalities in Jiangsu Province, China. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, Q.; Geng, C.; Wang, X.; Han, B.; Bai, Z. Comparative Source Apportionment of PM2.5 for 2014/2019 at a Plateau City: Implications for Air Quality Improvement in High-Altitude Areas. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2024, 15, 101964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 3095-2012; Ambient Air Quality Standards. China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Li, H.; Zhao, Z.; Luo, X.-S.; Fang, G.; Zhang, D.; Pang, Y.; Huang, W.; Mehmood, T.; Tang, M. Insight into Urban PM2.5 Chemical Composition and Environmentally Persistent Free Radicals Attributed Human Lung Epithelial Cytotoxicity. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 234, 113356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Z.; Yang, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, W. Trace Elements in PM2.5 in Shandong Province: Source Identification and Health Risk Assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 558–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batterman, S.; Xu, L.; Chen, F.; Chen, F.; Zhong, X. Characteristics of PM2.5 Concentrations across Beijing during 2013–2015. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 145, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, H.; Lv, X.; Gong, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, G. Seasonal Variations and Chemical Characteristics of PM2.5 in Wuhan, Central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 518–519, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Gao, C.; Deng, S.; Yuan, M.; Song, W.; Lu, Z.; Qiu, Z. Chemical Characterisation of PM2.5 Emitted from Motor Vehicles Powered by Diesel, Gasoline, Natural Gas and Methanol Fuel. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 674, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozlaker, A.; Peccia, J.; Chellam, S. Indoor/Outdoor Relationships and Anthropogenic Elemental Signatures in Airborne PM2.5 at a High School: Impacts of Petroleum Refining Emissions on Lanthanoid Enrichment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4851–4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainur, D.; Chen, Q.; Sha, T.; Zarak, M.; Dong, Z.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Z.; Dina, K.; An, T. Outdoor Health Risk of Atmospheric Particulate Matter at Night in Xi’an, Northwestern China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 9252–9265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Cao, J.; Shen, Z.; Huang, R.-J.; Hu, T.; Wang, P.; Zhang, T.; Liu, S. Chemical Composition of PM2.5 at a High–Altitude Regional Background Site over Northeast of Tibet Plateau. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2015, 6, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Z.; Kang, S.; Kawamura, K.; Liu, B.; Wan, X.; Wang, Z.; Gao, S.; Fu, P. Carbonaceous Aerosols on the South Edge of the Tibetan Plateau: Concentrations, Seasonality and Sources. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 1573–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Kang, S.; Wang, Y.; Xin, J.; Liu, B.; Guo, Y.; Wen, T.; Zhang, G.; Cong, Z. Size Distribution of Carbonaceous Aerosols at a High-Altitude Site on the Central Tibetan Plateau (Nam Co Station, 4730 m a.s.l.). Atmos. Res. 2015, 153, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Kang, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, R.; Lu, X.; Qian, Y.; Paudyal, R.; Wang, S.; Shi, X.; Yan, X. Seasonal Variation and Light Absorption Property of Carbonaceous Aerosol in a Typical Glacier Region of the Southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 6441–6460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.-S.; Xu, M.-X.; Snape, C.; He, J.; Behera, S.N.; Xu, H.-H.; Ji, D.-S.; Wang, C.-J.; Yu, H.; Xiao, H.; et al. Temporal and Spatial Variation in Major Ion Chemistry and Source Identification of Secondary Inorganic Aerosols in Northern Zhejiang Province, China. Chemosphere 2017, 179, 316–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Liu, Z.; Hu, B.; Yan, G.; Zou, J.; Zhao, S.; Zhou, J.; Liu, X.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, X.; et al. Chemical Characterization and Source Identification of PM2.5 in Luoyang after the Clean Air Actions. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 115, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostro, B.; Roth, L.; Malig, B.; Marty, M. The Effects of Fine Particle Components on Respiratory Hospital Admissions in Children. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Chen, J.; Zhao, W.; Cheng, J.; Cheng, S. Seasonal Variations and Correlation Analysis of Water-Soluble Inorganic Ions in PM2.5 in Wuhan, 2013. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Yang, L.; Dong, C.; Yan, C.; Meng, C.; Sui, X.; Wang, W. Temporal Variations, Acidity, and Transport Patterns of PM2.5 Ionic Components at a Background Site in the Yellow River Delta, China. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2014, 7, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Luo, X.S.; Jing, Y.; Li, H.; Pang, Y.; Wu, L.; Chen, Q.; Jin, L. In Vitro Assessments of Bioaccessibility and Bioavailability of PM2.5 Trace Metals in Respiratory and Digestive Systems and Their Oxidative Potential. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 409, 124638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmatinia, T.; Kermani, M.; Farzadkia, M.; Nicknam, M.H.; Soleimanifar, N.; Mohebbi, B.; Jafari, A.J.; Shahsavani, A.; Fanaei, F. Potential Cytotoxicity of PM2.5-Bound PAHs and Toxic Metals Collected from Areas with Different Traffic Densities on Human Lung Epithelial Cells (A549). J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2021, 19, 1701–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Y. Study on the Composition and Toxic Effects of Inhalable Particulates from Typical Motor Vehicle Exhaust Emissions. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing, China, 2021. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.-M.; Yang, X.-Z.; Yang, Q.-Q.; Clermont, A.C.; Yin, Y.-G.; Liu, G.-L.; Hu, L.-G.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, Q.-F.; Liu, Q.S.; et al. PM2.5 Induces Vascular Permeability Increase through Activating MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathway and ROS Generation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 386, 121659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Luo, X.-S.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, Q.; Wu, D.; Sun, X.; Wu, L.; Jin, L. Summer–Winter Differences of PM2.5 Toxicity to Human Alveolar Epithelial Cells (A549) and the Roles of Transition Metals. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 165, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cachon, B.F.; Firmin, S.; Verdin, A.; Ayi-Fanou, L.; Billet, S.; Cazier, F.; Martin, P.J.; Aissi, F.; Courcot, D.; Sanni, A.; et al. Proinflammatory Effects and Oxidative Stress within Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells Exposed to Atmospheric Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM>2.5) Collected from Cotonou, Benin. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 185, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amouei Torkmahalleh, M.; Hopke, P.K.; Broomandi, P.; Naseri, M.; Abdrakhmanov, T.; Ishanov, A.; Kim, J.; Shah, D.; Kumar, P. Exposure to Particulate Matter and Gaseous Pollutants during Cab Commuting in Nur-Sultan City of Kazakhstan. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 880–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Tang, M.; Luo, X.; Li, W.; Pang, Y.; Huang, W.; Zhao, Z.; Wei, Y.; Long, T.; Mehmood, T. Compositional Characteristics and Toxicological Responses of Human Lung Epithelial Cells to Inhalable Particles (PM10) from Ten Typical Biomass Fuel Combustions. Particuology 2023, 78, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, U.S.; Rastogi, N.; McWhinney, R.D.; Urch, B.; Chow, C.-W.; Evans, G.J.; Scott, J.A. The Combined Effects of Physicochemical Properties of Size-Fractionated Ambient Particulate Matter on in Vitro Toxicity in Human A549 Lung Epithelial Cells. Toxicol. Rep. 2014, 1, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhou, J.; Chen, M.; Huang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Xie, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Kan, H.; et al. Metabolomics Analysis of a Mouse Model for Chronic Exposure to Ambient PM2.5. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 247, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pniewska, E.; Sokolowska, M.; Kupryś-Lipińska, I.; Przybek, M.; Kuna, P.; Pawliczak, R. The Step Further to Understand the Role of Cytosolic Phospholipase A2 Alpha and Group X Secretory Phospholipase A2 in Allergic Inflammation: Pilot Study. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 670814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maceyka, M.; Spiegel, S. Sphingolipid Metabolites in Inflammatory Disease. Nature 2014, 510, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Vivancos, P.; de Simone, A.; Kiddle, G.; Foyer, C.H. Glutathione—Linking Cell Proliferation to Oxidative Stress. Free. Radic. Bio. Med. 2015, 89, 1154–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radi, R. Oxygen Radicals, Nitric Oxide, and Peroxynitrite: Redox Pathways in Molecular Medicine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 5839–5848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Zou, Y.; Abbas, A.; Dai, B. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance-Based Metabolomic Investigation Reveals Metabolic Perturbations in PM2.5-Treated A549 Cells. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 31656–31665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moro, J.; Tomé, D.; Schmidely, P.; Demersay, T.-C.; Azzout-Marniche, D. Histidine: A Systematic Review on Metabolism and Physiological Effects in Human and Different Animal Species. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Zeng, X.; Pan, K.; Zhang, J.; Song, L.; Zhou, J.; Chen, R.; Xie, Y.; Sun, Q.; Zhao, J.; et al. Metabolomics Analysis of Urine from Healthy Wild Type Mice Exposed to Ambient PM2.5. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Y.; Du, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Shen, H. Comprehensive Pulmonary Metabolome Responses to Intratracheal Instillation of Airborne Fine Particulate Matter in Rats. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 592, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhu, L.; Li, R.; Wang, H.; Cai, Z. Omics Approach Reveals Metabolic Disorders Associated with the Cytotoxicity of Airborne Particulate Matter in Human Lung Carcinoma Cells. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losito, I.; Patruno, R.; Conte, E.; Cataldi, T.R.I.; Megli, F.M.; Palmisano, F. Phospholipidomics of Human Blood Microparticles. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 6405–6413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarowski, E.R.; Boucher, R.C. Purinergic Receptors in Airway Epithelia. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2009, 9, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.; Qi, L.; Xu, X.; Zhao, R.; Wang, X.; Ha, Y.; Lin, Z.; Lu, S.; Chen, R.; Zhao, J. Characterization of the Chemical Composition, Cytotoxicity, and Metabolomic Effects of PM2.5 in a Plateau City, China. Toxics 2025, 13, 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090729
Li M, Qi L, Xu X, Zhao R, Wang X, Ha Y, Lin Z, Lu S, Chen R, Zhao J. Characterization of the Chemical Composition, Cytotoxicity, and Metabolomic Effects of PM2.5 in a Plateau City, China. Toxics. 2025; 13(9):729. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090729
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Mengying, Lijuan Qi, Xinyi Xu, Rong Zhao, Xiaotong Wang, Yanhui Ha, Zhe Lin, Sujin Lu, Rong Chen, and Junchao Zhao. 2025. "Characterization of the Chemical Composition, Cytotoxicity, and Metabolomic Effects of PM2.5 in a Plateau City, China" Toxics 13, no. 9: 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090729
APA StyleLi, M., Qi, L., Xu, X., Zhao, R., Wang, X., Ha, Y., Lin, Z., Lu, S., Chen, R., & Zhao, J. (2025). Characterization of the Chemical Composition, Cytotoxicity, and Metabolomic Effects of PM2.5 in a Plateau City, China. Toxics, 13(9), 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090729







