Risk Assessment and Correlation Analysis of Potentially Toxic Element Pollution in Soil and Crops: A Case Study in a Typical Area
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
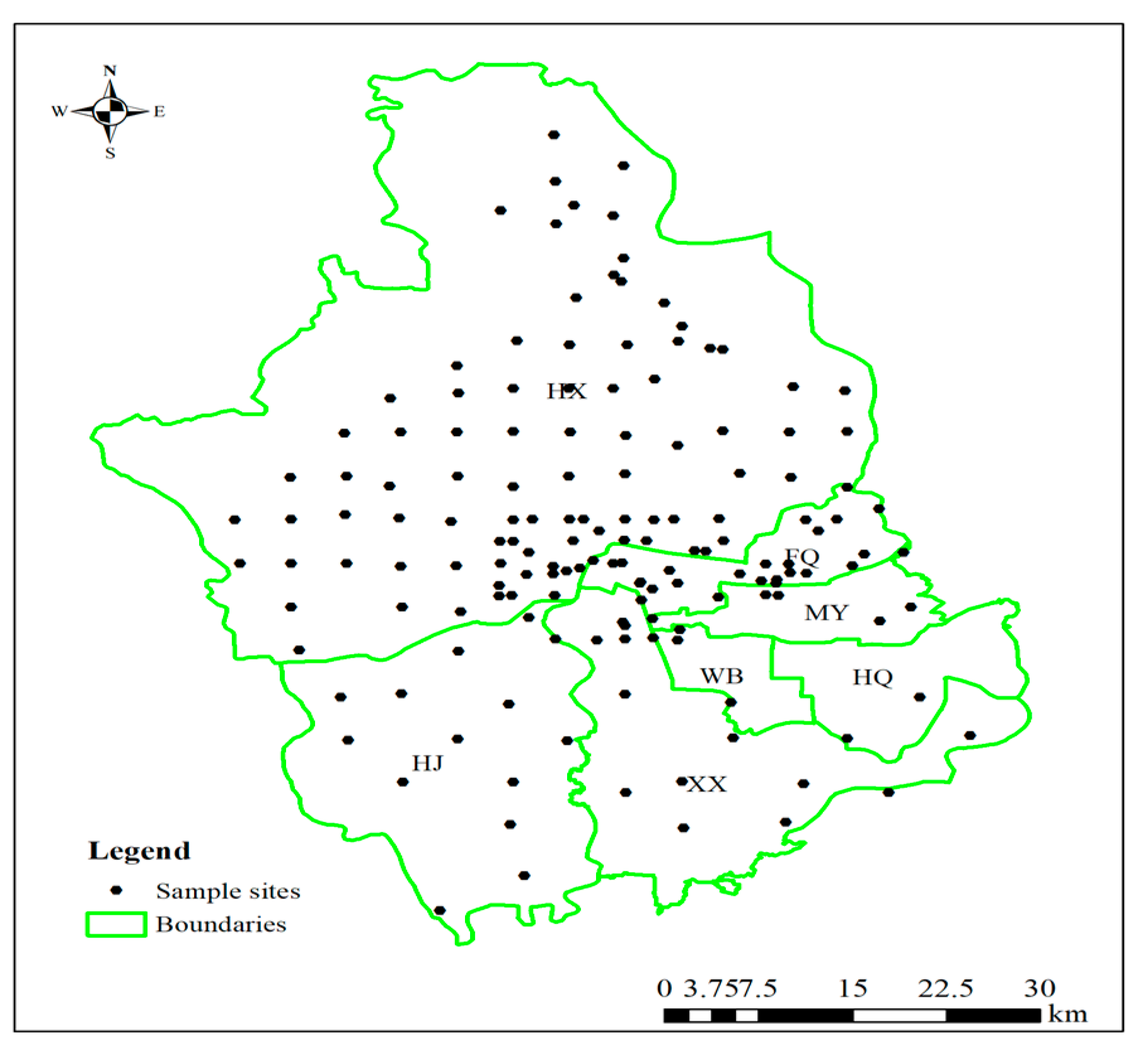
2.1. Study Area and Sample Collection
2.2. Research Methods
2.2.1. Potential Ecological Risk Assessment
2.2.2. Human Health Risk Assessment
2.2.3. Geographical Detector
2.2.4. Rank-Size Theory
2.2.5. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
Partial Correlation Analysis
Stepwise Linear Regression Analysis
2.3. Data Processing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Statistical Analysis of PTEs in Soil and Crops
3.1.1. Statistical Analysis of PTEs in Soil
3.1.2. Statistical Analysis of PTEs in Crops
3.2. Risk Assessment of Soil PTE Pollution
3.2.1. Potential Ecological Risks of Soil PTEs
3.2.2. Spatial Differentiation Characteristics of Potential Ecological Risks
3.2.3. Ecological Risk Level of Soil PTEs Based on Rank-Size
3.3. Risk Assessment of PTE Pollution in Crops
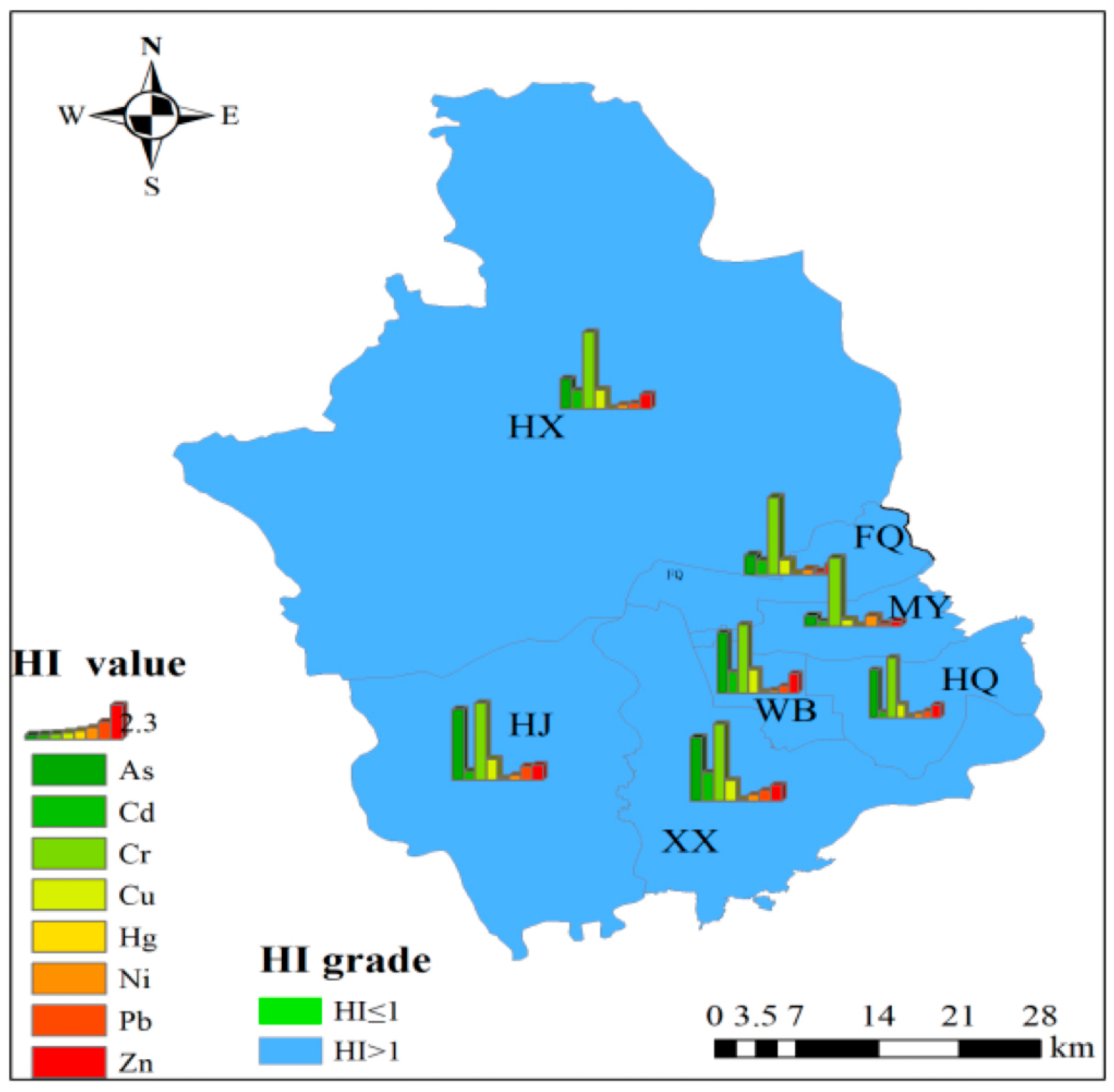
3.3.1. Human Health Risks of PTEs in Crops
3.3.2. Spatial Differentiation Characteristics of Human Health Risks
3.3.3. Human Health Risk Level Based on Rank-Size
3.4. Relationship Between PTE Content in Soil and Crops
3.4.1. Correlation Between PTE Content in Soil and Crops
3.4.2. Regression Analysis of PTE Content in Soil and Crops
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Q.Q.; Li, Z.Y.; Lu, X.N.; Duan, Q.N.; Huang, L.; Bi, J. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from industrial and agricultural regions in China: Pollution and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.D.; Zhao, D.; Ren, F.T.; Huang, L. Spatiotemporal variation of soil heavy metals in China: The pollution status and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 871, 161768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, S.F.; Hu, B.F.; Zhang, X.L.; Shao, S.; Jiang, Y.F.; Zhou, L.Q.; Shi, Z. Current Status and Temporal Trend of Potentially Toxic Elements Pollution in Agricultural Soil in the Yangtze River Delta Region: A Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.L.; O’Connor, D.; Ok, Y.S.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Liu, A.; Hou, D.Y. Assessment of sources of heavy metals in soil and dust at children’s playgrounds in Beijing using GIS and multivariate statistical analysis. Environ. Int. 2019, 124, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.F.; Zhao, R.Y.; Chen, S.C.; Zhou, Y.; Jin, B.; Li, Y.; Shi, Z. Heavy Metal Pollution Delineation Based on Uncertainty in a Coastal Industrial City in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, W.Q.; Wang, Z.W.; Hu, B.B.; Wang, Z.L.; Li, H.Y.; Goodman, R.C. Heavy metals in soil and plants after long-term sewage irrigation at Tianjin China: A case study assessment. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 171, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.L.; Song, S.; Wang, R.S.; Liu, Z.Y.; Meng, J.; Sweetman, A.J.; Jenkins, A.; Ferrier, R.C.; Li, H.; Luo, W.; et al. Impacts of soil and water pollution on food safety and health risks in China. Environ. Int. 2015, 77, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.H.; Zhu, K.Y.; Liu, L.; Sun, X.Y. Pollution-Induced Food Safety Problem in China: Trends and Policies. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 703832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Zhong, T.Y.; Liu, L.; Ouyang, X.Y. Impact of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution on Food Safety in China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.P.; Yan, S.; Duan, M.; Fu, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Z.F.; Song, F.M.; Tang, B.; Li, C.; Qin, G.W.; et al. Assessing heavy metal pollution and potential ecological risk of tea plantation soils. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2019, 12, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.Y.; Qin, C.Z.; Hong, X.; Kang, G.H.; Qin, M.Z.; Yang, D.; Pang, B.; Li, Y.Y.; He, J.J.; Dick, R.P. Risk assessment and source analysis of soil heavy metal pollution from lower reaches of Yellow River irrigation in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1136–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwolak, A.; Sarzynska, M.; Szpyrka, E.; Stawarczyk, K. Sources of Soil Pollution by Heavy Metals and Their Accumulation in Vegetables: A Review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Z.F.; Li, Y.H.; Liu, S.H.; Li, H.R.; Hao, Z.; Xu, Y.F. Assessment of the heavy metal pollution and health risks of rice cultivated in Hainan Island, China. Environ. Forensics 2021, 22, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.C.; Huang, Z.; Huang, J.X.; Wu, S.; Dao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Yang, B.C.; Xu, Y.Q.; Liu, N.Q.; Gong, Q.J. Environmental Pollution Assessment of Heavy Metals in Soils and Crops in Xinping Area of Yunnan Province, China. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sytar, O.; Taran, N. Effect of heavy metals on soil and crop pollution in Ukraine—A review. J. Cent. Eur. Agric. 2022, 23, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Patel, N.; Jindal, T.; Ranjan, M.R. Heavy Metal Contamination in Soils and Crops Irrigated by Kali River in Uttar Pradesh, India. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 107, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samma, S.; Khan, M.S.I.; Chowdhury, M.T.I.; Islam, M.A.; Fick, J.; Kaium, A. Evaluating Soil-Vegetable Contamination with Heavy Metals in Bogura, Bangladesh: A Risk Assessment Approach. Environ. Health Insights 2024, 18, 11786302241282601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.Y.; Li, F.X.; Zhang, J.Q.; Chen, Y.A.; Cao, T.H.; Tong, Z.J.; Liu, X.P.; Liang, X.H.; Zhao, X. Comprehensive assessment of heavy metals pollution of farmland soil and crops in Jilin Province. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 4369–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyika, J.; Dinka, M.O. Heavy Metal Pollution in Soils and Vegetables from Suburban Regions of Nairobi, Kenya and their Community Health Implications. Pollution 2022, 8, 1434–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoh, R.A.; Kocadal, K.; Alkas, F.B.; Kurt, M.A.; Battal, D.; Saygi, S. Heavy metal pollution of agricultural soils and vegetables of abandoned mining district in northern cyprus. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2021, 30, 1415–1423. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.P.; Xu, Y.N.; Zhang, J.H.; Wang, W.K.; Elwardany, R.M. Effects of heavy metal pollution on farmland soils and crops: A case study of the Xiaoqinling Gold Belt, China. China Geol. 2020, 3, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doabi, S.A.; Karami, M.; Afyuni, M.; Yeganeh, M. Pollution and health risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soil, atmospheric dust and major food crops in Kermanshah province, Iran. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2018, 163, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Hu, X.F.; Wu, X.H.; Shu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Yan, X.J. Affects of mining activities on Cd pollution to the paddy soils and rice grain in Hunan province, Central South China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 9843–9856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, K.K.; Singh, N.K.; Patel, M.P.; Tiwari, M.R.; Rai, U.N. Metal contamination of soil and translocation in vegetables growing under industrial wastewater irrigated agricultural field of Vadodara, Gujarat, India. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 1670–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.X.; Li, X.M.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.B.; Hedding, D.W.; Nel, W.; Ji, J.F.; Chen, J. Geochemical behavior and potential health risk of heavy metals in basalt-derived agricultural soil and crops: A case study from Xuyi County, eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 139058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, M.K.; Majumdar, A.; Barla, A.; Bose, S.; Srivastava, S. An assessment of arsenic hazard in groundwater-soil-rice system in two villages of Nadia district, West Bengal, India. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 2381–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, T.; Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Adrees, M.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M.; Qayyum, M.F.; Ok, Y.S.; Murtaza, G. Effect of biochar on alleviation of cadmium toxicity in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grown on Cd-contaminated saline soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 25668–25680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.N.; Sun, Y.; Yao, W.B.; Ba, Q.; Wang, H. Effects of Cadmium Exposure on the Immune System and Immunoregulation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 695484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimyan, K.; Alimohammadi, M.; Maleki, A.; Yunesian, M.; Nodehi, R.N.; Foroushani, A.R. The mobility of arsenic from highly polluted farmlands to wheat: Soil-Plant transfer model and health risk assessment. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 1560–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, M.T.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.Y.; Lei, K.G.; Li, Y.; Li, F.; Zheng, D.F.; Fang, X.Q.; Cao, Y. Heavy metal contamination risk assessment and correlation analysis of heavy metal contents in soil and crops. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 278, 116911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhao, H.F.; Wu, K.N.; Zhang, Z.; Hou, Y.X.; Chen, T.Y.; Jin, Q. Evaluation of heavy metal distribution characteristics of agricultural soil-rice system in a high geological background area according to the influence index of comprehensive quality (IICQ). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 20920–20933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jan, F.A.; Ishaq, M.; Khan, S.; Ihsanullah, I.; Ahmad, I.; Shakirullah, M. A comparative study of human health risks via consumption of food crops grown on wastewater irrigated soil (Peshawar) and relatively clean water irrigated soil (lower Dir). J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, R.D.; Li, Y.C.; Peng, Y.S.; Wen, X.F.; Ni, X.R. Distribution, accumulation, and potential risks of heavy metals in soil and tea leaves from geologically different plantations. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2020, 195, 110475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.L.; Guo, Z.H.; Xiao, X.; Peng, C.; Shi, L.; Ran, H.Z.; Xu, W.X. Atmospheric deposition as a source of cadmium and lead to soil-rice system and associated risk assessment. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2019, 180, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peijnenburg, W.; Zablotskaja, M.; Vijver, M.G. Monitoring metals in terrestrial environments within a bioavailability framework and a focus on soil extraction. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2007, 67, 163–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.F.; Shao, S.; Fu, T.T.; Fu, Z.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Qi, L.; Chen, S.C.; Shi, Z. Composite assessment of human health risk from potentially toxic elements through multiple exposure routes: A case study in farmland in an important industrial city in East China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2020, 210, 106443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.W.; Gui, H.R. Distribution features and internal relations of heavy metals in soil-maize system of mining area, Anhui Province, Eastern China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2019, 25, 863–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Jiao, Q.J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, H.T.; Yu, P.Y.; Liu, D.Y.; Hua, D.L.; Song, J. Evaluation of Heavy Metal Contamination and Associated Human Health Risk in Soils around a Battery Industrial Zone in Henan Province, Central China. Agriculture 2024, 14, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C. Geodetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.-F.; Li, X.-H.; Christakos, G.; Liao, Y.-L.; Zhang, T.; Gu, X.; Zheng, X.-Y. Geographical Detectors-Based Health Risk Assessment and its Application in the Neural Tube Defects Study of the Heshun Region, China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Wang, F.; Wang, K. Spatiotemporal evolution and optimization path of the coupling of administrative rank potential energy and administrative regional economy in Chengdu-Deyang-Mianyang region. Geogr. Res. 2022, 41, 441–455. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, C.; Hou, D.; Li, F.; Bao, G.; Deng, A.; Shen, H.; Sun, H. Assessment and spatial characteristics analysis of human health risk of heavy metals in cultivated soil. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 1440–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.X.; Zhang, Z.X.; Dong, H.; Liu, J.F.; Wang, D.W.; Yan, B.Q.; Chen, Y. Spatial differentiation and influencing factor analysis of soil heavy metal content at town level based on geographic detector. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 4566–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, J.X.; Hu, M.G.; Jia, L. Geographical detection of groundwater pollution vulnerability and hazard in karst areas of Guangxi Province, China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Deng, L.Y.; Zuo, S.D.; Luo, Y.J.; Shao, G.F.; Wei, X.H.; Hua, L.Z.; Yang, Y.S. Geographical modeling of spatial interaction between human activity and forest connectivity in an urban landscape of southeast China. Landsc. Ecol. 2014, 29, 1741–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.A.; Gao, Y.; He, X.W.; Liu, T.; Jiang, B.H.; Shao, H.Y.; Yao, Y.Z. Spatial-temporal pattern evolution and driving force analysis of ecological environment vulnerability in Panzhihua City. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 7151–7166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Wen, X.; Liu, Y. Evolutionary characteristics of China’s outbound tourism flow in rank-size distribution from 2001 to 2015. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2018, 73, 2468–2480. [Google Scholar]
- Yeganeh, M.; Afyuni, M.; Khoshgoftarmanesh, A.H.; Soffianian, A.R.; Schulin, R. Health Risks of Metals in Soil, Water, and Major Food Crops in Hamedan Province, Iran. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2012, 18, 547–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghaie, A.H.; Aghili, F. Health risk assessment of Pb and Cd in soil, wheat, and barley in Shazand County, central of Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2019, 17, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, M.K.; Shukla, A.; Yadav, P.; Srivastava, S. A review of arsenic in crops, vegetables, animals and food products. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.F.; Shen, R.F.; Shao, J.F. Transport of cadmium from soil to grain in cereal crops: A review. Pedosphere 2021, 31, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obayomi, O.; Seyoum, M.M.; Ghazaryan, L.; Tebbe, C.C.; Murase, J.; Bernstein, N.; Gillor, O. Soil texture and properties rather than irrigation water type shape the diversity and composition of soil microbial communities. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 161, 103834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edogbo, B.; Okolocha, E.; Maikai, B.; Aluwong, T.; Uchendu, C. Risk analysis of heavy metal contamination in soil, vegetables and fish around Challawa area in Kano State, Nigeria. Sci. Afr. 2020, 7, e00281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daulta, R.; Sridevi, T.; Garg, V.K. Spatial distribution of heavy metals in rice grains, rice husk, and arable soil, their bioaccumulation and associated health risks in Haryana, India. Toxin Rev. 2021, 40, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.B.; Wang, X.M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, K.; Xie, P.; Ji, H.B. The optimum pH and Eh for simultaneously minimizing bioavailable cadmium and arsenic contents in soils under the organic fertilizer application. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 135229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.F.; Xue, J.; Zhou, Y.; Shao, S.; Fu, Z.Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.C.; Qi, L.; Shi, Z. Modelling bioaccumulation of heavy metals in soil-crop ecosystems and identifying its controlling factors using machine learning. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 114308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, D.; Zhang, N.C.; Chen, W.L.; Cai, P.; Zheng, L.R.; Huang, Q.Y. Organic matter facilitates the binding of Pb to iron oxides in a subtropical contaminated soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 32130–32139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.G.; Li, Y.H. Spatial distribution and source identification of potentially toxic elements in Yellow River Delta soils, China: An interpretable machine-learning approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.R.; Li, H.Z.; Zhou, Y.Z.; Dou, L.; Cai, L.M.; Mo, L.P.; You, J. Bioavailability and soil-to-crop transfer of heavy metals in farmland soils: A case study in the Pearl River Delta, South China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.W.; Qiao, S.; Chen, H.; Zhao, S.L.; Li, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, D.H.; Li, L. Multiple pathway exposure risks and driving factors of heavy metals in soil-crop system in a Pb/Zn smelting city, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 459, 142523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.L.; Wang, H.J.; Sun, J.X.; Cai, B.Y.; Tang, R.; Song, X.Y.; Huang, X.M.; Liu, Y.F.; Fan, Z.Q. Human health risks of heavy metal(loid)s mediated through crop ingestion in a coal mining area in Eastern China. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2024, 276, 116305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.R.; Li, J.; He, C.; Hu, X.; Yin, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, H.Y.; Yang, S.G.; He, H.; et al. Distribution Characteristics and Relevance of Heavy Metals in Soils and Colloids Around a Mining Area in Nanjing, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 107, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum (mg/kg) | 5.50 | 0.26 | 43.4 | 15.3 | 0.0092 | 18.1 | 18.7 | 46.7 |
| Maximum (mg/kg) | 17.1 | 7.30 | 87.7 | 94.7 | 0.67 | 42.6 | 55.8 | 247 |
| Mean (mg/kg) | 10.6 | 1.11 | 65.1 | 30.1 | 0.066 | 29.9 | 28.2 | 88.5 |
| Standard deviation (mg/kg) | 2.58 | 1.19 | 8.27 | 11.6 | 0.073 | 5.16 | 5.09 | 29.9 |
| Median (mg/kg) | 10.5 | 0.70 | 65.1 | 28.1 | 0.047 | 29.8 | 28.0 | 81.4 |
| Coefficient of variation (%) | 24.4 | 107 | 12.7 | 38.6 | 110 | 17.2 | 18.1 | 33.8 |
| Risk screening values for China soil contamination (GB 15618-2018, 6.5 < pH ≤ 7.5) (mg/kg) | 30 | 0.30 | 200 | 100 | 2.40 | 100 | 120 | 250 |
| Background values of soil (mg/kg) | 11.4 | 0.074 | 63.8 | 19.7 | 0.034 | 26.7 | 19.6 | 60.1 |
| Hg | Cr | Ni | Cu | Zn | As | Cd | Pb | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum (mg/kg) | 0.00065 | 0.32 | 0.11 | 1.82 | 4.91 | 0.022 | 0.011 | 0.024 |
| Maximum (mg/kg) | 0.0038 | 11.7 | 14.3 | 6.82 | 39.5 | 0.19 | 1.04 | 0.55 |
| Mean (mg/kg) | 0.0017 | 1.30 | 0.58 | 4.00 | 22.5 | 0.056 | 0.092 | 0.11 |
| Standard deviation mg/kg) | 0.00085 | 1.38 | 1.25 | 0.73 | 5.50 | 0.032 | 0.14 | 0.090 |
| Median (mg/kg) | 0.0014 | 1.00 | 0.33 | 3.90 | 21.6 | 0.049 | 0.051 | 0.084 |
| Coefficient of variation (%) | 49.0 | 107 | 216 | 18.4 | 24.4 | 56.3 | 153 | 78.6 |
| Limit of each potentially toxic element in cereals (mg/kg) (NY 861-2004, GB 2762-2022) | 0.02 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 10.0 | 50.0 | 0.70 | 0.1 | 0.4 |
| As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FQ | 10.6 | 538 | 2.16 | 8.11 | 64.7 | 6.27 | 7.23 | 1.63 |
| HQ | 9.91 | 189 | 2.03 | 6.08 | 43.6 | 5.37 | 7.13 | 1.31 |
| HX | 8.73 | 456 | 1.98 | 7.78 | 85.4 | 5.54 | 7.29 | 1.48 |
| HJ | 9.44 | 244 | 2.07 | 7.33 | 55.2 | 5.33 | 6.68 | 1.45 |
| MY | 10.4 | 711 | 2.31 | 10.0 | 85.4 | 6.25 | 8.34 | 1.65 |
| WB | 8.22 | 416 | 1.82 | 7.07 | 75.6 | 4.90 | 7.68 | 1.50 |
| XX | 9.95 | 423 | 2.12 | 5.86 | 73.2 | 5.23 | 6.36 | 1.18 |
| q | 0.11 | 0.039 | 0.13 | 0.072 | 0.018 | 0.12 | 0.093 | 0.054 |
| As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FQ | 0.71 | 0.50 | 2.83 | 0.53 | 0.024 | 0.18 | 0.090 | 0.38 |
| HQ | 1.47 | 0.18 | 1.84 | 0.42 | 0.057 | 0.13 | 0.21 | 0.40 |
| HX | 0.81 | 0.49 | 2.08 | 0.53 | 0.026 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.40 |
| HJ | 1.61 | 0.20 | 1.75 | 0.48 | 0.045 | 0.11 | 0.32 | 0.34 |
| MY | 0.68 | 0.30 | 4.53 | 0.42 | 0.038 | 0.69 | 0.17 | 0.30 |
| WB | 1.41 | 0.48 | 1.60 | 0.54 | 0.028 | 0.062 | 0.15 | 0.45 |
| XX | 1.60 | 0.71 | 1.93 | 0.52 | 0.039 | 0.16 | 0.26 | 0.40 |
| q | 0.38 | 0.029 | 0.057 | 0.074 | 0.26 | 0.13 | 0.24 | 0.069 |
| Assoil | Cdsoil | Crsoil | Cusoil | Hgsoil | Nisoil | Pbsoil | Znsoil | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hgcorp | −0.058 | −0.096 | −0.146 | −0.238 | −0.062 | −0.327 | −0.167 | −0.148 |
| Crcorp | 0.143 | 0.177 * | 0.099 | 0.059 | 0.042 | 0.124 | 0.045 | −0.011 |
| Nicorp | 0.168 * | 0.217 ** | 0.115 | 0.032 | 0.02 | 0.117 | 0.001 | −0.012 |
| Cucorp | −0.119 | −0.004 | −0.087 | 0.097 | 0.064 | −0.042 | −0.028 | 0.079 |
| Zncorp | −0.007 | −0.031 | −0.076 | 0.018 | 0.086 | −0.068 | −0.028 | 0.206 * |
| Ascorp | 0.091 | −0.163 | −0.043 | −0.121 | 0.036 | −0.281 | −0.171 | −0.056 |
| Cdcorp | 0.058 | 0.777 ** | 0.242 ** | 0.126 | 0.15 | 0.344 ** | 0.151 | 0.063 |
| Pbcorp | −0.033 | −0.211 | −0.101 | −0.298 | −0.057 | −0.29 | −0.139 | −0.167 |
| PTEs | Regression Equations | F Values | Adjusted R2 | p Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hg | Hgcorp = −0.00009Nisoil + 0.00011Assoil + 0.003 | 13.9 | 0.15 | 0.00 |
| Cr | Crcorp = 0.21Cdsoil + 1.07 | 4.63 | 0.025 | 0.00 |
| Ni | Nicorp = 0.23Cdsoil + 0.32 | 7.06 | 0.040 | 0.00 |
| Zn | Zncorp = 0.075Znsoil − 0.13Cusoil + 19.85 | 6.08 | 0.066 | 0.00 |
| As | Ascorp = −0.004Nisoil + 0.007Assoil + 0.11 | 22.46 | 0.23 | 0.00 |
| Cd | Cdcorp = 0.092Cdsoil − 0.001Znsoil − 0.004Nisoil − 0.043 | 81.16 | 0.63 | 0.00 |
| Pb | Pbcorp = −0.002Cusoil + 0.18 | 13.94 | 0.082 | 0.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Gong, C.; Ba, Y.; Liu, S.; Wan, H.; Zhao, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Yang, Z. Risk Assessment and Correlation Analysis of Potentially Toxic Element Pollution in Soil and Crops: A Case Study in a Typical Area. Toxics 2025, 13, 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070554
Liu J, Gong C, Ba Y, Liu S, Wan H, Zhao X, Li Z, Liu X, Yang Z. Risk Assessment and Correlation Analysis of Potentially Toxic Element Pollution in Soil and Crops: A Case Study in a Typical Area. Toxics. 2025; 13(7):554. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070554
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jiufen, Cang Gong, Yinji Ba, Shuliang Liu, Huiyun Wan, Xiaofeng Zhao, Ziqi Li, Xiaohuang Liu, and Zhongfang Yang. 2025. "Risk Assessment and Correlation Analysis of Potentially Toxic Element Pollution in Soil and Crops: A Case Study in a Typical Area" Toxics 13, no. 7: 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070554
APA StyleLiu, J., Gong, C., Ba, Y., Liu, S., Wan, H., Zhao, X., Li, Z., Liu, X., & Yang, Z. (2025). Risk Assessment and Correlation Analysis of Potentially Toxic Element Pollution in Soil and Crops: A Case Study in a Typical Area. Toxics, 13(7), 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070554







