Pharmaceutical Contaminants Occurrence and Ecological Risk Assessment Along the Romanian Black Sea Coast
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
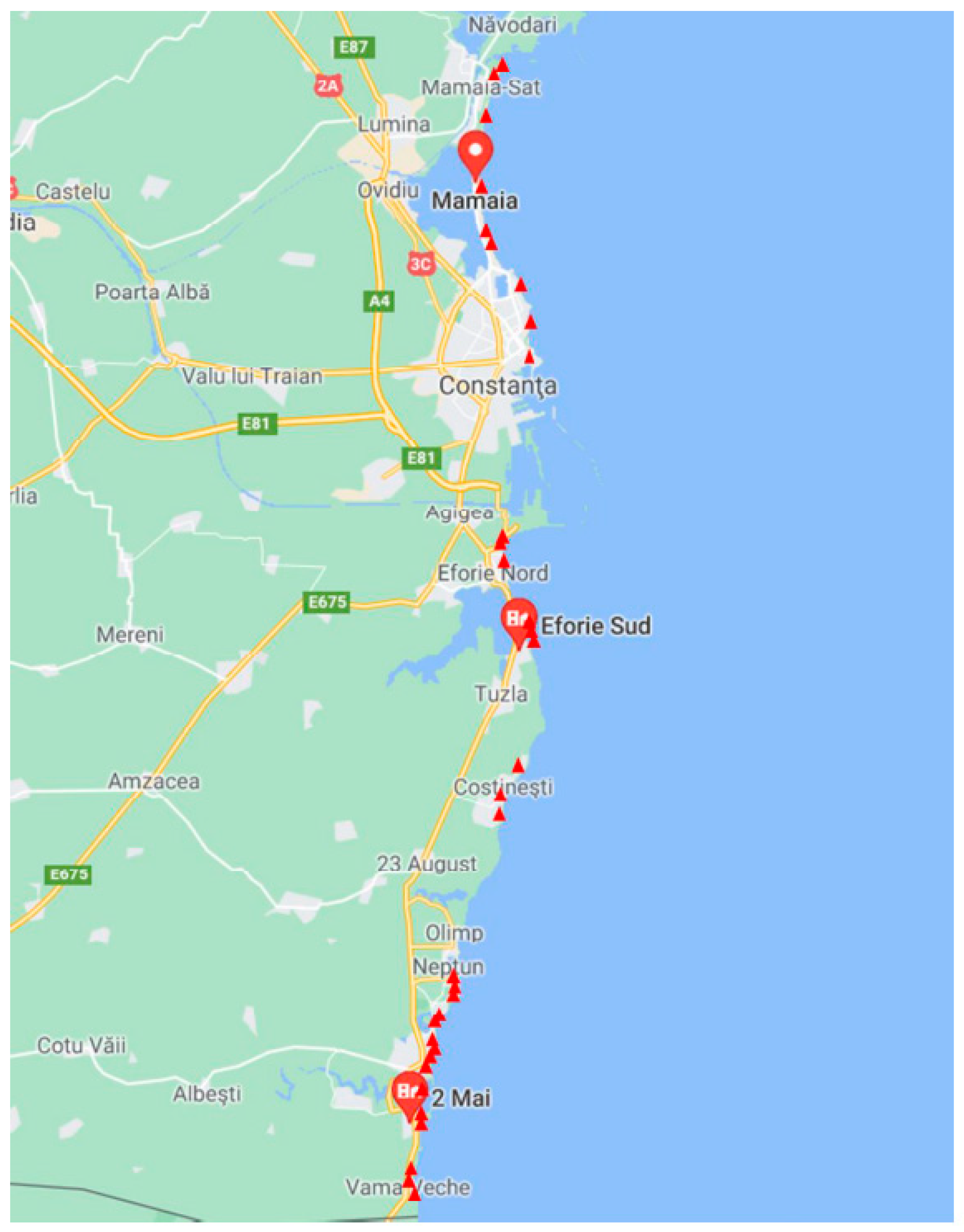
2.2. Water Sampling Sites
2.3. Extraction of Pharmaceuticals from Seawater
2.4. LC–MS/MS Sample Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. SPE-LC-MS/MS Method Development
3.2. Performance Parameters of the Method
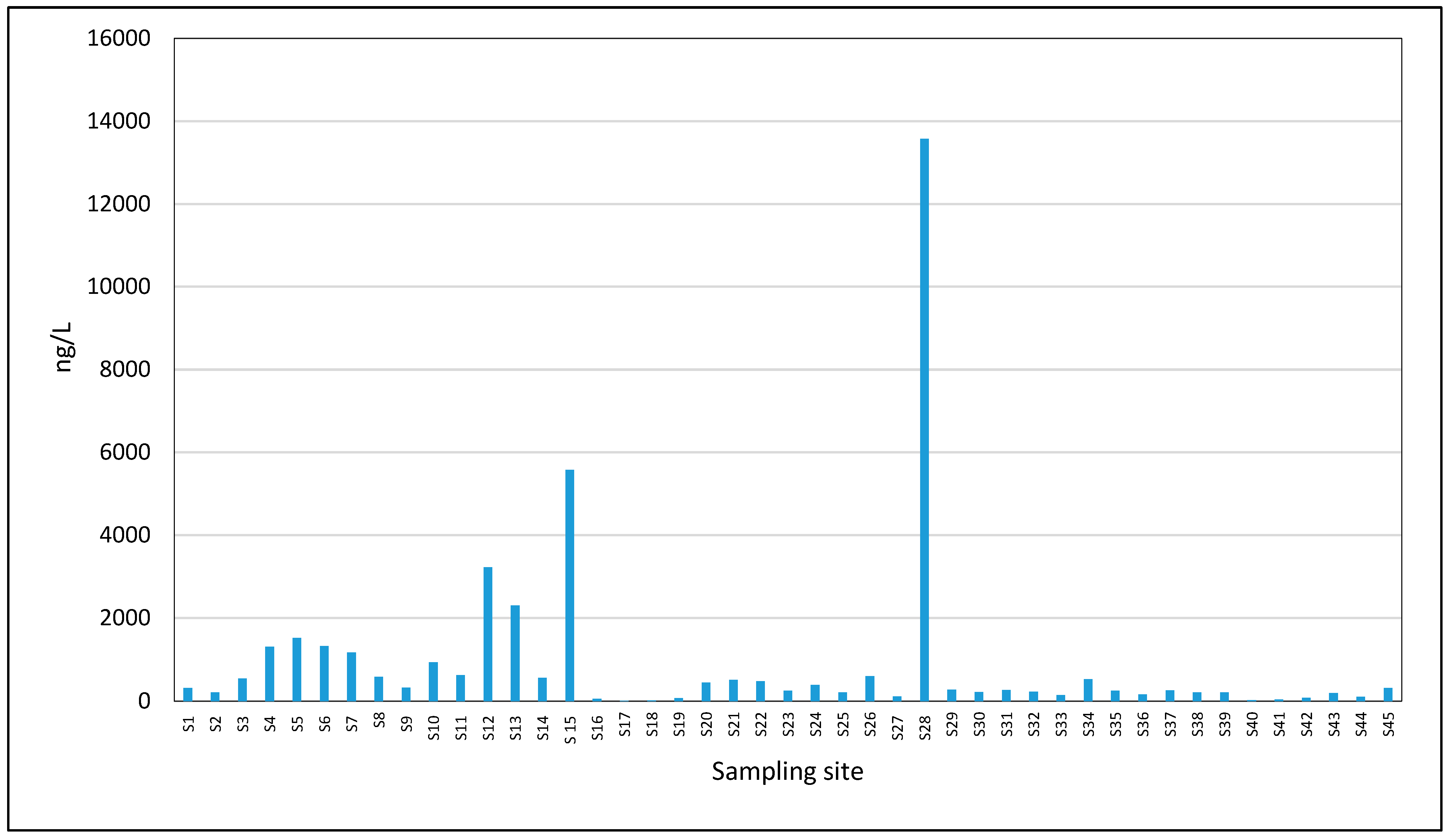
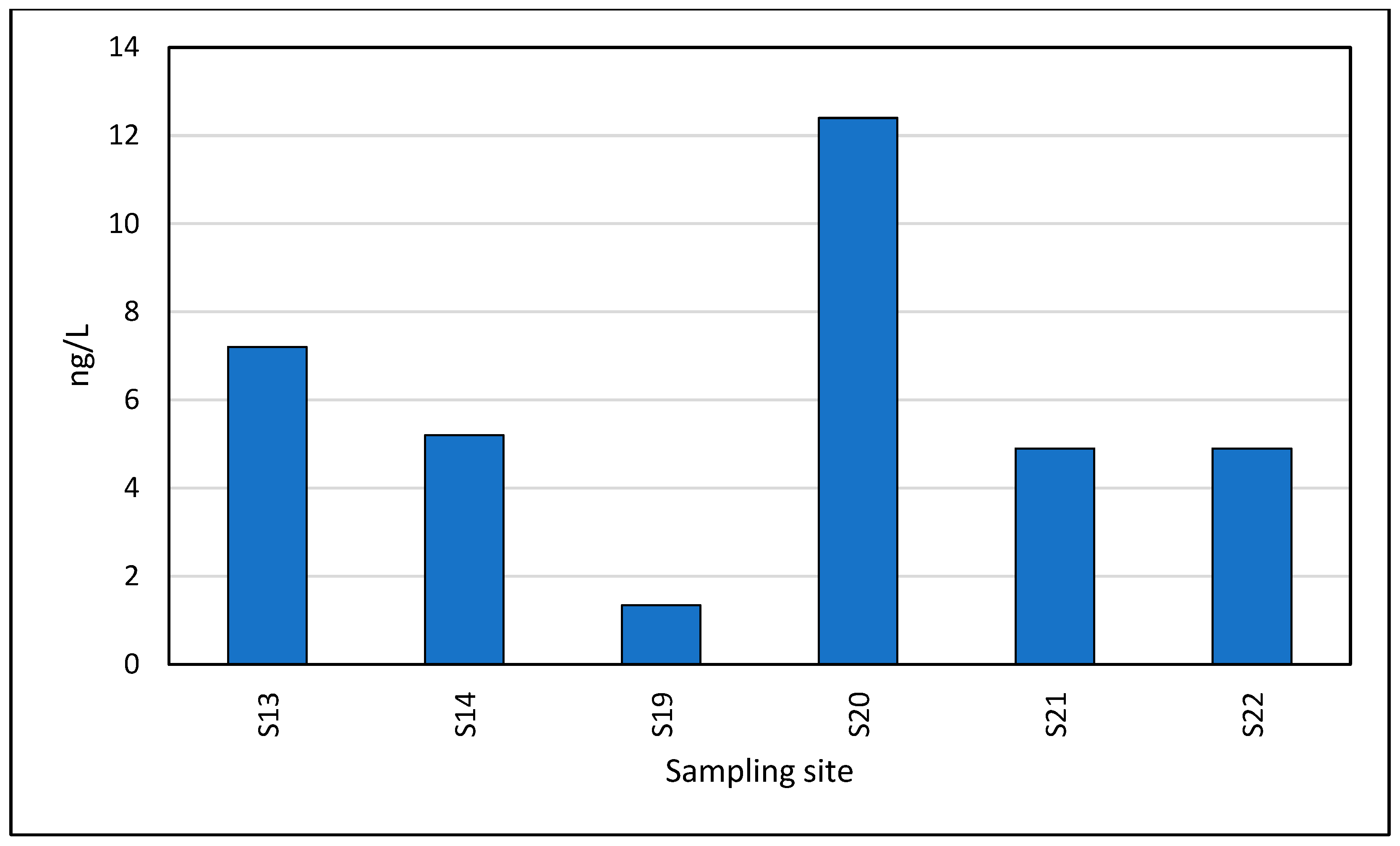
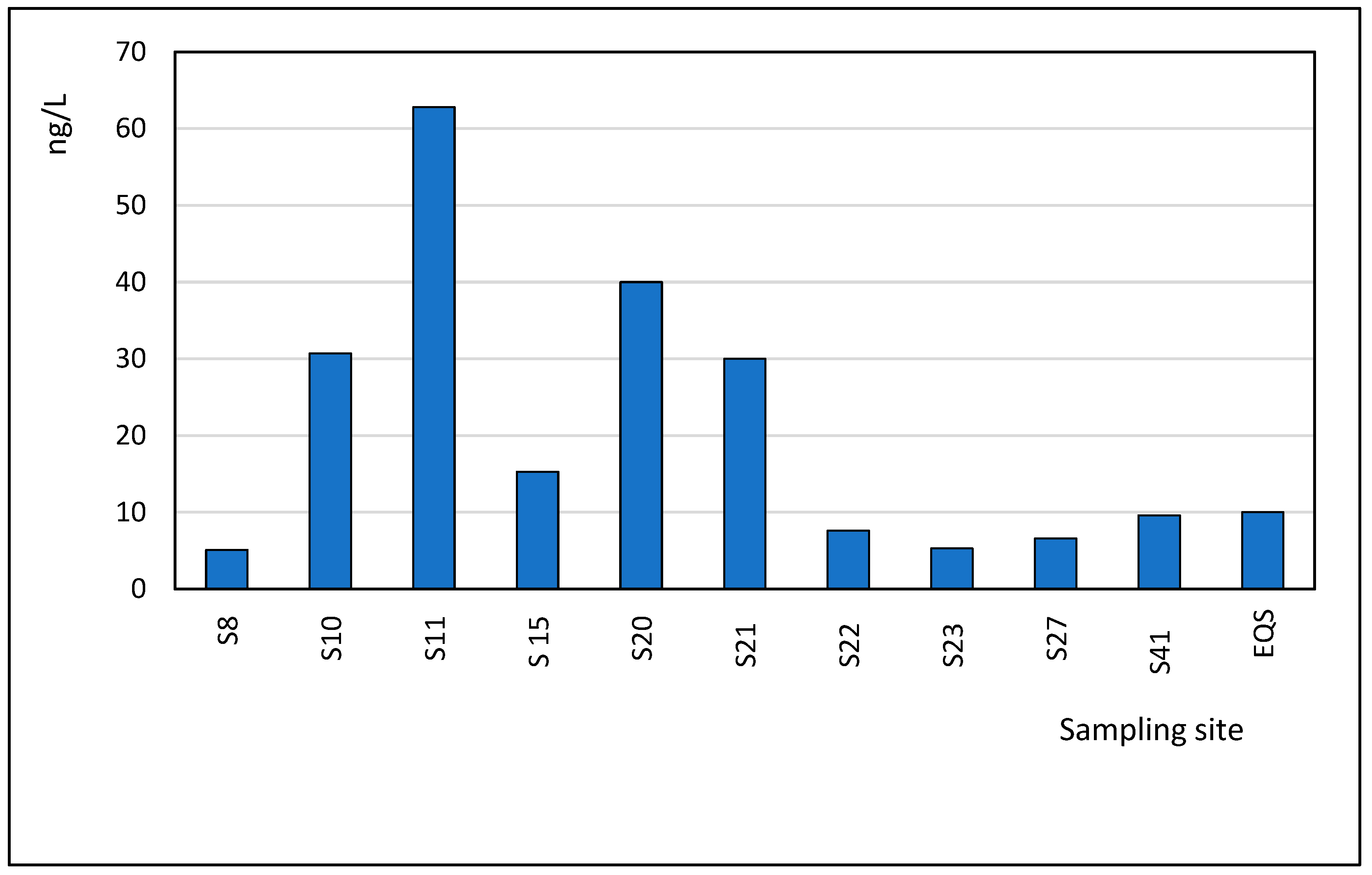
3.3. Occurrence of Pharmaceuticals in Seawater Samples
3.4. Ecological Risk Assessment
3.5. Correlation Between Target Pharmaceuticals in the Romanian Seawater
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Branchet, P.; Arpin-Pont, L.; Piram, A.; Boissery, P.; Wong-Wah- Chung, P.; Doumenq, P. Pharmaceuticals in the marine environment: What are the present challenges in their monitoring? Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 766, 142644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.D.; Ternes, T.A. Water Analysis: Emerging Contaminants and Current Issues. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 2813–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tijani, J.O.; Fatoba, O.O.; Babajide, O.O.; Petrik, L.F. Pharmaceuticals, endocrine disruptors, personal care products, nanomaterials and perfluorinated pollutants: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2016, 14, 27–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heberer, T. Occurrence, fate, and removal of pharmaceutical residues in the aquatic environment: A review of recent research data. Toxicol. Lett. 2002, 131, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieno, N.M.; Tuhkanen, T.; Kronberg, L. Seasonal variation in the occurrence of pharmaceuticals in effluents from a sewage treatment plant and in the recipient water seasonal variation in the occurrence of pharmaceuticals in effluents from a sewage treatment plant and in the recipient water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 9, 8220–8226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, D.R.; Webb, S.F.; Petry, T. Hot spot pollutants: Pharmaceuticals in the environment. Toxicol. Lett. 2002, 131, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, J.B. Pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) in urban receiving waters. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 44, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desbiolles, F.; Malleret, L.; Tiliacos, C.; Wong-Wah-Chung, P.; Laffont-Schwob, I. Occurrence and ecotoxicological assessment of pharmaceuticals: Is there a risk for the Mediterranean aquatic environment? Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 1334–13480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezzelani, M.; Gorbi, S.; Regoli, F. Pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environments: Evidence of emerged threat and future challenges for marine organisms. Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 140, 41–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drzymala, J.; Kalka, J. Ecotoxic interactions between pharmaceuticals in mixtures:diclofenac and sulfamethoxazole. Chemosphere 2020, 259, 127407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandaric, L.; Kalogianni, E.; Skoulikidis, N.; Petrovic, M.; Sabater, S. Contamination patterns and attenuation of pharmaceuticals in a temporary Mediterranean river. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratola, N.; Cincinelli, A.; Alves, A.; Katsoyiannis, A. Occurrence of organic microcontaminants in the wastewater treatment process. A mini review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 239–240, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, F.A.; Bergmann, A.; Hickmann, S.; Ebert, I.; Hein, A.; Küster, A. Pharmaceuticals in the environment–global occurrences and perspectives. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 35, 823–835. [Google Scholar]
- European Medicines Agency. Guideline on the Environmental Risk Assessment of Medicinal Products for Human Use; Ref EMEA/CHMP/SWP/4447/00 Corr 2; European Medicines Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006.
- Gunnarsson, L.; Snape, B.; Verbruggen, J.R.; Owen, S.F.; Kristiansson, E.; Margiotta-Casaluci, L.; Österlund, T.; Hutchinson, K.; Leverett, D.; Marks, B.; et al. Pharmacology beyond the patient—The environmental risks of human drugs. Environ. Int. 2019, 129, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigel, S.; Kuhlmann, J.; Hühnerfuss, H. Drugs and personal care products as ubiquitous pollutants: Occurrence and distribution of clofibric acid, caffeine and DEET in the North Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 295, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gros, M.; Rodríguez-Mozaz, S.; Barceló, D. Fast and comprehensive multi-residue analysis of a broad range of human and veterinary pharmaceuticals and some of their metabo-lites in surface and treated waters by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to quadrupole-linear ion trap tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1248, 104–121. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Navas, C.; Bjoerklund, E.; Bak, S.A.; Hansen, M.; Krogh, K.A.; Maya, F.; Forteza, R.; Cerda, V. Pollution pathways of pharmaceutical residues in the aquatic environment on the Island of Mallorca, Spain. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2013, 65, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togola, A.; Budzinski, H. Multi-residue analysis of pharmaceutical compounds in aqueous samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1177, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loos, R.; Tavazzi, S.; Paracchini, B.; Canuti, E.; Weissteiner, C. Analysis of polar organic contaminants in surface water of the northern Adriatic Sea by solid-phase extraction followed by ultrahigh-pressure liquid chromatography-QTRAP(A (R)) MS using a hybrid triple-quadrupole linear ion trap instrument. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 5875–5885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal-Dorsch, D.E.; Bay, S.M.; Maruya, K.; Snyder, S.A.; Trenholm, R.A.; Vanderford, B.J. Contaminants of emerging concern in municipal wastewater effluents and marine receiving water. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 2674–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.-H.; Nan, F.-H.; Chin, T.-S.; Feng, H.-M. The occurrence and distribution of pharmaceutical compounds in the effluents of a major sewage treatment plant in Northern Taiwan and the receiving coastal waters. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 1435–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Qian, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, L. Study on the matrix effect in the determination of selected pharmaceutical residues in seawater by solid-phase extraction and ultra-highperformance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization low-energy collisioninduced dissociation tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 1471–1475. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wille, K.; Noppe, H.; Verheyden, K.; Vanden Bussche, J.; DeWulf, E.; Van Caeter, P.; Janssen, C.R.; De Brabander, H.F.; Vanhaecke, L. Validation and application of an LC–MS/MS method for the simultaneous quantification of 13 pharmaceuticals in seawater. Anal. Bioanal.Chem. 2010, 397, 1797–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nödler, K.; Licha, T.; Bester, K.; Sauter, M. Development of a multi-residue analytical method, based on liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry, for the simultaneous determination of 46 micro-contaminants in aqueous samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 6511–6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebot, C.; Gibb, S.W.; Boyd, K.G. Quantification of human pharmaceuticals in water samples by high performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 598, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://chemicalize.com/app/calculation (accessed on 28 April 2025).
- Parolini, M. Toxicity of the Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) acetylsalicylic acid, paracetamol, diclofenac, ibuprofen and naproxen towards freshwater invertebrates: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Bratty, M.; Al-Rajab, A.J.; Rehman, J.; Sharma, M.; Alhazmi, H.A.; Najmi, A.; Muzafar, M.A.H.; Javed, S.A. Fast and efficient removal of caffeine from water using dielectric barrier discharge. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Rønning, H.T.; Alarif, W.; Kallenborn, R.; Al-Lihaibi, S.S. Occurrence of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in effluent-dominated Saudi Arabian coastal waters of the Red Sea. Chemosphere 2017, 175, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolić, A.; Paíga, P.; Santos, L.H.M.L.M.; Ramos, S.; Correia, M.; Delerue-Matos, C. Assessment of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and analgesic pharmaceuticals in seawaters of North of Portugal: Occurrence and environmental risk. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 508, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biel-Maeso, M.; Baena-Nogueras, R.M.; Corada-Fernández, C.; Lara-Martín, P.A. Occurrence, distribution and environmental risk of pharmaceutically active compounds (PhACs) in coastal and ocean waters from the Gulf of Cadiz (SWSpain). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshvar, A.; Aboulfadl, K.; Viglino, L.; Broseus, R.; Sauve, S.; Madoux-Humery, A.S. Evaluating pharmaceuticals and caffeine as indicator of fecal contamination in drinking water sources of the Greater Montreal region. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigel, S.; Berger, U.; Jensen, E.; Kallenborn, R.; Thoresen, H.; Hühnerfuss, H. Determination of selected pharmaceuticals and caffeine in sewage and seawater from Tromsø/Norway with emphasis on ibuprofen and its metabolites. Chemosphere 2004, 56, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantwell, M.G.; Katz, D.R.; Sullivan, J.C.; Borci, T.; Chen, R.F. Caffeine in Boston Harbor past and present, assessing its utility as a tracer of wastewater contamination in an urban estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 108, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojcieszyńska, D.; Guzik, U. Naproxen in the environment: Its occurrence, toxicity to nontarget organisms and biodegradation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 1849–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2015/495 of 20 March 2015 establishing a watch list of substances for Union-wide monitoring in the field of water policy pursuant to Directive 2008/105/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council (notified under document C (2015) 1756). Off. J. Eur. Union L 2015, 78, 40–42. [Google Scholar]
- Vieno, N.; Sillanpää, M. Fate of diclofenac in municipal wastewater treatment plant-a review. Environ. Int. 2014, 69, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, H.R. Sources, behaviour and fate of organic contaminants during sewage treatment and in sewage sludges. Sci. Total Environ. 1996, 185, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feo, M.L.; Bagnati, R.; Passoni, A.; Riva, F.; Salvagio Manta, D.; Sprovieri, M.; Traina, A.; Zuccato, E.; Castiglioni, S. Pharmaceuticals and other contaminants in waters and sediments from Augusta Bay (southern Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gravel, A.; Vijayan, M.M. Salicylate disrupts interrenal steroidogenesis and brain glucocorticoid receptor expression in rainbow trout. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 93, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, J.; Winter, M.J.; Tyler, C.R. Pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment: A critical review of the evidence for health effects in fish. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2010, 40, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernando, M.D.; Mezcua, M.; Fernández-Alba, A.R.; Barceló, D. Environmental risk assessment of pharmaceutical residues in wastewater effluents, surface waters and sediments. Talanta 2006, 66, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Mei, C.F.; Ying, G.G.; Xu, M.Y. Toxicity thresholds for diclofenac, acetaminophen and ibuprofen in the water flea Daphnia magna. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 97, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleavers, M. Mixture toxicity of the anti-inflammatory drugs diclofenac, ibuprofen, naproxen, and acetylsalicylic acid. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2004, 39, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triebskorn, R. Toxic effects of the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug diclofenac, Part II. Cytological effects in liver, kidney, gills and intestine of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquat. Toxicol. 2004, 68, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre-Martínez, G.V.; Owuor, M.A.; Garrido-Pérez, C.; Salamanca, M.J.; Del Valls, T.A.; Martín-Díaz, M.L. Are standard tests sensitive enough to evaluate effects of human pharmaceuticals in aquatic biota? Facing changes in research approaches when performing risk assessment of drugs. Chemosphere 2015, 120, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre-Martínez, G.V.; Buratti, S.; Fabbri, E.; Del Valls, T.A.; Martín-Díaz, M.L. Stability of lysosomal membrane in Carcinus maenas acts as a biomarker of exposure to pharmaceuticals. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 3783–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isidori, M.; Lavorgna, M.; Nardelli, A.; Parrella, A.; Previtera, L.; Rubino, M. Ecotoxicity of naproxen and its phototransformation products. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 348, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.T.; Greenway, S.L.; Farris, J.L.; Guerra, B. Assessing caffeine as an emerging environmental concern using conventional approaches. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 54, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komori, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Minamiyama, M.; Harada, A. Occurrence of selected pharmaceuticals in river water in Japan and assessment of their environmental risk. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 4529–4536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabchoubi, I.B.; Bouchhima, R.A.; Louhichi, N.; Baanannou, A.; Masmoudi, S.; Hentati, O. Short-term effects of various non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) on Danio rerio embryos. MethodsX 2023, 11, 102215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldas, L.L.; Moreira, R.A.; Espíndola, E.L.G.; Novelli, A. Environmental Risk Assessment of Drugs in Tropical Freshwaters Using Ceriodaphnia silvestrii as Test Organism. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2023, 110, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyumina, E.; Subbotina, M.; Polygalov, M.; Tyan, S.; Ivshina, I. Ketoprofen as an emerging contaminant: Occurrence, ecotoxicity and (bio)removal. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1200108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Ying, G.G.; Zhao, J.L.; Yang, X.B.; Chen, F.; Tao, R.; Liu, S.; Zhou, L.J. Occurrence and risk assessment of acidic pharmaceuticals in the Yellow River, Hai River and Liao River of north China. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 3139–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuer-Lauridsen, F.; Birkved, M.; Hansen, L.P.; Lützhøft, H.C.; Halling-Sørensen, B. Environmental risk assessment of human pharmaceuticals in Denmark after normal therapeutic use. Chemosphere 2000, 40, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grung, M.; Källqvist, T.; Sakshaug, S.; Skurtveit, S.; Thomas, K.V. Environmental assessment of Norwegian priority pharmaceuticals based on the EMEA guideline. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2008, 71, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.C.; Dumont, E.; Williams, R.J.; Oldenkamp, R.; Cisowska, I.; Sumpter, J.P. Do concentrations of ethinylestradiol, estradiol, and diclofenac in European Rivers exceed proposed EU Environmental Quality Standards? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 12297–12304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adenaya, A.; Quintero, R.R.; Brinkhoff, T.; Lara-Martín, P.A.; Wurl, O.; Ribas-Ribas, M. Vertical distribution and risk assessment of pharmaceuticals and other micropollutants in southern North Sea coastal waters. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 200, 116099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbato, J.; Becchi, A.; Bises, C.; Siena, F.; Lasagni, M.; Saliu, F.; Galli, P.; Montano, S. Occurrence of phthalic acid esters (PAEs) and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) in key species of anthozoans in Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 200, 116078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, N.E.; Caglar, N.B.; Aksu, A.; Unsal, T.; Balcıoglu, E.B.; Cavus Arslan, H.; Demirel, N. Occurrence, bioconcentration, and human health risks of pharmaceuticals in biota in the Sea of Marmara, Türkiye. Chemosphere 2023, 325, 138296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

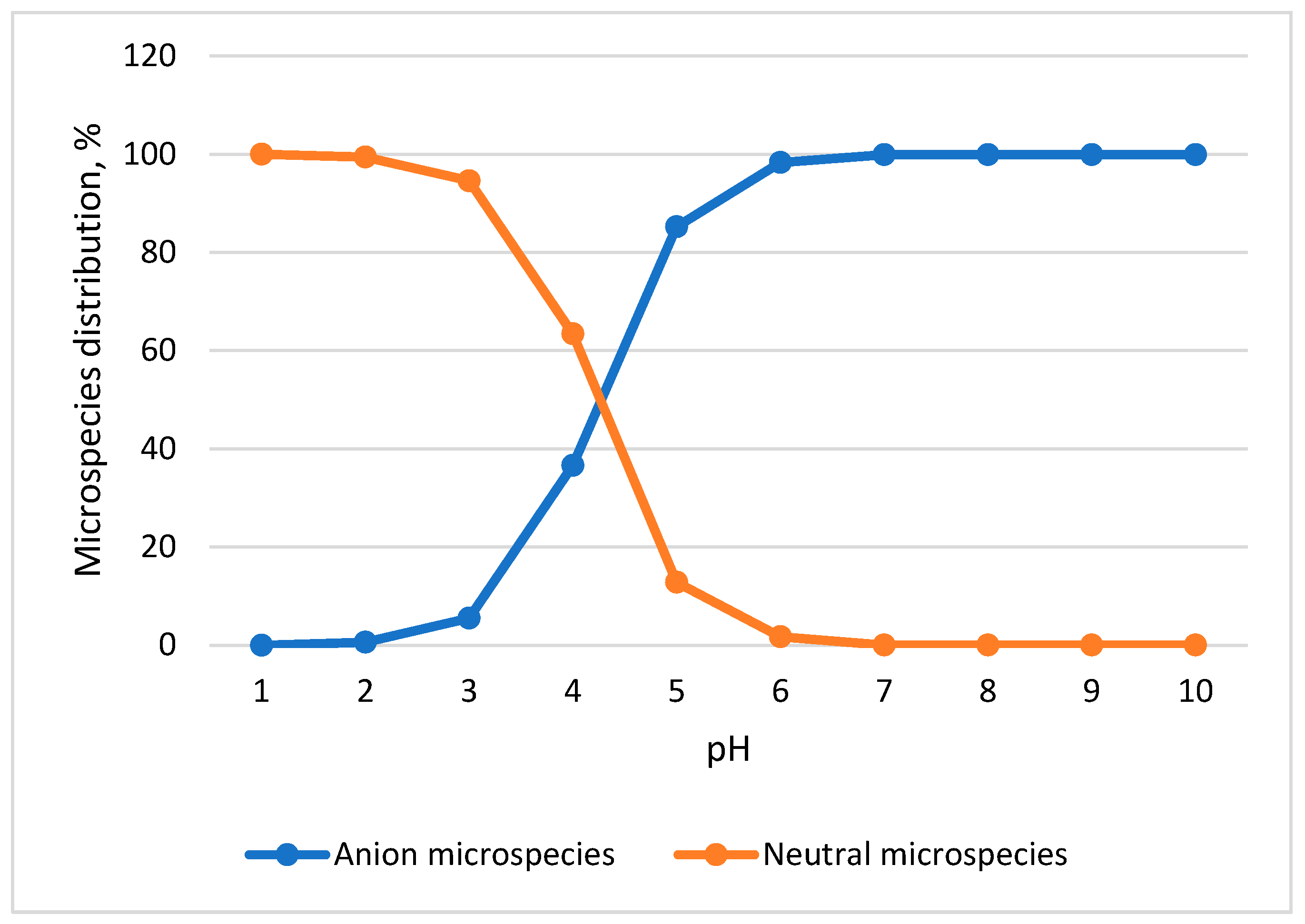


| Compound | Structural Formula | Molecular Mass, g/mol | Log Kow | Log Dow (pH 2) | Log Dow (pH 7.2) | pKa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetaminophen |  | 151.06 | 0.46 | 0.90 | 9.38 | |
| Piroxicam (PIR) | 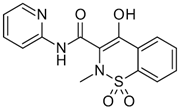 | 331.06 | 3.06 | −0.38 | −1.11 | 6.3 |
| Ketoprofen (KET) |  | 254.09 | 3.12 | 3.6 | 0.58 | 4.45 |
| Naproxen (NAP) | 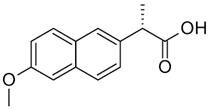 | 230.09 | 3.18 | 2.98 | 0.12 | 4.15 |
| Indometacin (IND) |  | 379.05 | 4.50 | 3.53 | 0.78 | 0.91 |
| Diclofenac (DIC) | 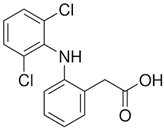 | 295.01 | 4.51 | 4.25 | 1.23 | 4.15 |
| Ibuprofen (IBU) |  | 206.13 | 3.97 | 3.84 | 1.52 | 5.20 |
| Caffeine (CAF) | 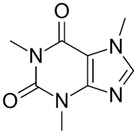 | 194.19 | −0.55 | −0.54 | −0.54 | 14.0; 10.4 |
| Location | Sample Code | Latitude (N) | Longitude (E) | Location | Sample Code | Latitude (N) | Longitude (E) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vama Veche | S1 | 43,748 | 28,578 | Eforie North | S24 | 44,047 | 28,649 |
| Vama Veche | S2 | 43,750 | 28,577 | Eforie North | S25 | 44,049 | 28,644 |
| Vama Veche | S3 | 43,755 | 28,575 | Eforie North | S26 | 44,048 | 28,644 |
| 2 Mai | S4 | 43,784 | 28,580 | Eforie North | S27 | 44,047 | 28,645 |
| 2 Mai | S5 | 43,786 | 28,580 | Costinesti | S28 | 44,070 | 28,641 |
| 2 Mai | S6 | 43,789 | 28,581 | Costinesti | S29 | 44,068 | 28,641 |
| Mangalia | S7 | 43,818 | 28,589 | Costinesti | S30 | 44,066 | 28,642 |
| Mangalia | S8 | 43,811 | 28,587 | Navodari | S31 | 44,299 | 28,627 |
| Mangalia | S9 | 43,813 | 28,587 | Navodari | S32 | 44,303 | 28,628 |
| Mangalia | S10 | 43,814 | 28,588 | Navodari | S33 | 44,305 | 28,629 |
| Mangalia | S11 | 43,815 | 28,588 | Navodari | S34 | 44,307 | 28,631 |
| Saturn | S12 | 43,835 | 28,591 | Navodari | S35 | 44,309 | 28,631 |
| Saturn | S13 | 43,833 | 28,591 | Navodari | S36 | 44,311 | 28,632 |
| Saturn | S14 | 43,831 | 28,591 | Navodari | S37 | 44,314 | 28,633 |
| Venus | S15 | 43,879 | 28,607 | Navodari | S38 | 44,315 | 28,634 |
| Jupiter | S16 | 43,878 | 28,607 | Navodari | S39 | 44,317 | 28,635 |
| Jupiter | S17 | 43,877 | 28,607 | Constanta | S40 | 44,179 | 28,658 |
| Neptun | S18 | 43,888 | 28,611 | Constanta | S41 | 44,181 | 28,657 |
| Neptun | S19 | 43,887 | 28,611 | Constanta | S42 | 44,192 | 28,657 |
| Neptun | S20 | 43,951 | 28,639 | Mamaia | S43 | 44,236 | 28,627 |
| Eforie South | S21 | 43,951 | 28,639 | Mamaia | S44 | 44,260 | 28,622 |
| Eforie South | S22 | 43,950 | 28,638 | Mamaia | S45 | 44,280 | 28,622 |
| Eforie South | S23 | 44,024 | 28,657 |
| Time (Minute) | Solvent B, Acetonitrile, (%) | HCOOH (A), 0.10% | Flow Rate (mL/min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10.0 | 90.0 | 0.30 |
| 2.00 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 0.30 |
| 6.00 | 100 | 0 | 0.30 |
| 9.00 | 100 | 0 | 0.30 |
| 9.01 | 100 | 0 | 0.50 |
| 14.01 | 10.0 | 90.0 | 0.50 |
| 14.50 | 10.0 | 90.0 | 0.30 |
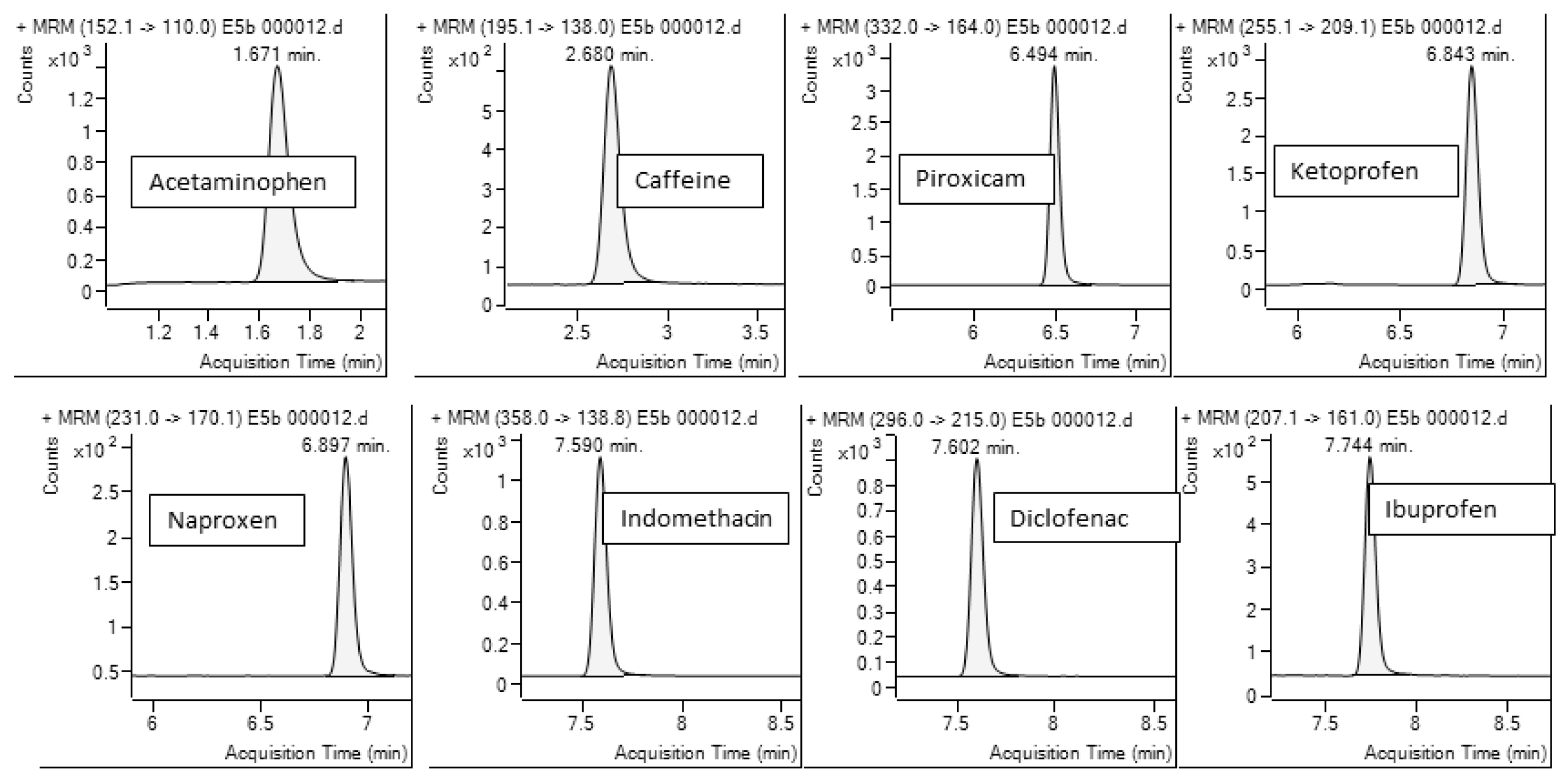
| Compound | Retention Time (min) | MRM Transition | Fragmentor Voltage (V) | Collision Energy (V) | Dwell Time (msec) | Cell Accelerator Voltage (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetaminophen | 1.69 | 152.1→110 | 90 | 15.0 | 200 | 7.00 |
| Caffeine | 2.70 | 195.1→138 | 80 | 20.0 | 200 | 7.00 |
| Piroxicam | 6.49 | 332→164 | 135 | 15.0 | 100 | 5.00 |
| Ketoprofen | 6.84 | 255.1→209.1 | 140 | 10.0 | 100 | 6.00 |
| Naproxen | 6.89 | 231→170.1 | 110 | 30.0 | 100 | 7.00 |
| Indomethacin | 7.59 | 358→138.8 | 135 | 10.0 | 100 | 7.00 |
| Diclofenac | 7.61 | 296→215 | 75 | 20.0 | 100 | 8.00 |
| Ibuprofen | 7.74 | 207.1→161 | 110 | 5.00 | 100 | 5.00 |
| Compound | R2 | LOQ (ng/L) | RSDr (%) | RSDR (%) | Recovery (%) | Matrix Effect, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetaminophen | 0.996 | 1.30 | 7.09 | 13.7 | 80.4 | 77.3 |
| Caffeine | 0.994 | 1.20 | 8.01 | 12.2 | 82.0 | 87.2 |
| Piroxicam | 0.999 | 0.10 | 7.48 | 10.4 | 76.5 | 79.4 |
| Ketoprofen | 0.999 | 1.10 | 8.50 | 16.5 | 86.5 | 88.4 |
| Naproxen | 0.999 | 1.40 | 6.90 | 15.6 | 86.9 | 90.2 |
| Indometacin | 0.997 | 0.20 | 5.90 | 13.6 | 95.1 | 80.1 |
| Diclofenac | 0.999 | 0.80 | 4.90 | 13.8 | 84.2 | 78.7 |
| Ibuprofen | 0.999 | 1.50 | 5.20 | 14.6 | 88.3 | 82.5 |
| Compound | Strata X, pH 2 | Strata X, pH 7.2 | Strata C18, PH 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACE | 80.4 | 60.7 | 37.3 |
| CAF | 82.0 | 48.3 | 27.7 |
| PIR | 76.5 | 37.7 | 29.5 |
| KET | 86.5 | 55.9 | 35.2 |
| NAP | 86.9 | 41.7 | 47.3 |
| IND | 95.1 | 37.2 | 44.2 |
| DIC | 84.2 | 44.1 | 61.4 |
| IBU | 88.3 | 51.2 | 37.3 |
| Compound | Frequency Detection, % | Minimum | Maximum | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caffeine | 100 | 7.90 | 13, 575 | 936 |
| Ketoprofen | 30.9 | 1.34 | 13.7 | 6.25 |
| Naproxen | 21.4 | 5.50 | 69.6 | 19.2 |
| Diclofenac | 23.8 | 5.10 | 62.8 | 21.3 |
| Ibuprofen | 42.9 | 7.40 | 134 | 38.0 |
| Compound | Seawater | Country | Concentration, ng/L | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetaminophen | Mediterranean Sea | Spain | 23.0 | [17] |
| France | 200,000 | [19] | ||
| Red Sea | Saudi Arabi | 2363 | [29,30] | |
| Atlantic Ocean | Portugal | 51.2–584 | [31] | |
| Black Sea | Romania | nd | This study | |
| Diclofenac | Mediterranean Sea | Spain | 4.0 | [17] |
| France | 1500 | [19] | ||
| Spain | 31.9 | [32] | ||
| Atlantic Ocean | Portugal | <0.02–241 | [31] | |
| Black Sea | Romania | 5.10–62.8 | This study | |
| Ibuprofen | Mediterranean Sea | Spain | 16.0 | [17] |
| France | 1500 | [19] | ||
| Adriatic Sea | Italy | <0.05–1143 | [20] | |
| Atlantic Ocean | Portugal | <0.08–222 | [31] | |
| Black Sea | Romania | 7.40–134 | This study | |
| Ketoprofen | Mediterranean Sea | France | 6000 | [19] |
| Spain | 2.60 | [32] | ||
| Indian Ocean | Taiwan | <1.70–6.60 | [22] | |
| Atlantic Ocean | Portugal | <0.30–89.7 | [31] | |
| Black Sea | Romania | 1.34–13.7 | This study | |
| Naproxen | Mediterranean Sea | Spain | 6.0 | [17] |
| 95.8 | [32] | |||
| France | 2000 | [19] | ||
| Atlantic Ocean | Portugal | <0.02–178 | [31] | |
| Black Sea | Romania | 5.50–69.6 | This study | |
| Caffeine | Mediterranean Sea | Spain | 327 | [32] |
| Red Sea | Saudi Arabi | 7708 | [30] | |
| Black Sea | Romania | 7.90–13,575 | This study |
| Compound | Toxicity | Species | End Point | µg/L | Reference | MEC µg/L | AF | PNEC | RQ | Level Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIC | Chronic | Daphnia magna | LC50 | 2000 | [44] | 0.063 | 100 | 20 | 0.003 | Very low |
| Acute | Lemna minor | EC50 | 7500 | [45] | 0.063 | 1000 | 7.5 | 0.008 | Very low | |
| Chronic | Oncorhynchus mykiss | LOEC | 1 | [46] | 0.063 | 100 | 0.01 | 6.3 | ||
| IBU | Chronic | Daphnia magna | LC50 | 3970 | [44] | 0.134 | 100 | 39.7 | 0.003 | Very low |
| Chronic | Parocentrotus lividus | EC50 | 0.01 | [47] | 0.134 | 100 | 0.0001 | 1340 | High | |
| Chronic | Carcinus maenas | LOEC | 5 | [48] | 0.134 | 100 | 0.05 | 2.68 | High | |
| NAP | Chronic | Thamnocephalus platyurus | EC50 | 560 | [49] | 0.07 | 100 | 5.6 | 0.012 | Low |
| Chronic | Ceriodaphnia dubia | EC50 | 330 | [49] | 0.07 | 100 | 3.3 | 0.021 | Low | |
| CAF | Acute | Ceriodaphnia dubia | LC50 | 60,000 | [50] | 13,575 | 1000 | 60 | 0.226 | Medium |
| Acute | Fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas) | LC50 | 10,000 | [50] | 13,575 | 1000 | 10 | 1.35 | High | |
| Acute | Daphnia magna | NOEC | 5.2 | [51] | 13,575 | 1000 | 0.005 | 2611 | High | |
| KET | Acute | Danio rerio | LC50 | 1520 | [52] | 0.014 | 1000 | 1.52 | 0.009 | Very low |
| Acute | Ceriodaphnia silvestrii | EC50 | 24,840 | [53] | 0.014 | 1000 | 24.84 | 0.0006 | Very low | |
| Acute | Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata | EC50 | 240 | [54] | 0.014 | 1000 | 0.24 | 0.058 | Low |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iancu, V.-I.; Chiriac, L.-F.; Paun, I.; Dinu, C.; Pirvu, F.; Cojocaru, V.; Tenea, A.G.; Cimpean, I.A. Pharmaceutical Contaminants Occurrence and Ecological Risk Assessment Along the Romanian Black Sea Coast. Toxics 2025, 13, 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060498
Iancu V-I, Chiriac L-F, Paun I, Dinu C, Pirvu F, Cojocaru V, Tenea AG, Cimpean IA. Pharmaceutical Contaminants Occurrence and Ecological Risk Assessment Along the Romanian Black Sea Coast. Toxics. 2025; 13(6):498. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060498
Chicago/Turabian StyleIancu, Vasile-Ion, Laura-Florentina Chiriac, Iuliana Paun, Cristina Dinu, Florinela Pirvu, Victor Cojocaru, Anda Gabriela Tenea, and Ioana Antonia Cimpean. 2025. "Pharmaceutical Contaminants Occurrence and Ecological Risk Assessment Along the Romanian Black Sea Coast" Toxics 13, no. 6: 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060498
APA StyleIancu, V.-I., Chiriac, L.-F., Paun, I., Dinu, C., Pirvu, F., Cojocaru, V., Tenea, A. G., & Cimpean, I. A. (2025). Pharmaceutical Contaminants Occurrence and Ecological Risk Assessment Along the Romanian Black Sea Coast. Toxics, 13(6), 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060498








