Characteristics of Ship-Emitted VOCs and Their Contributions to Urban Atmospheric VOCs in Guangzhou, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Sampling and Data Analysis
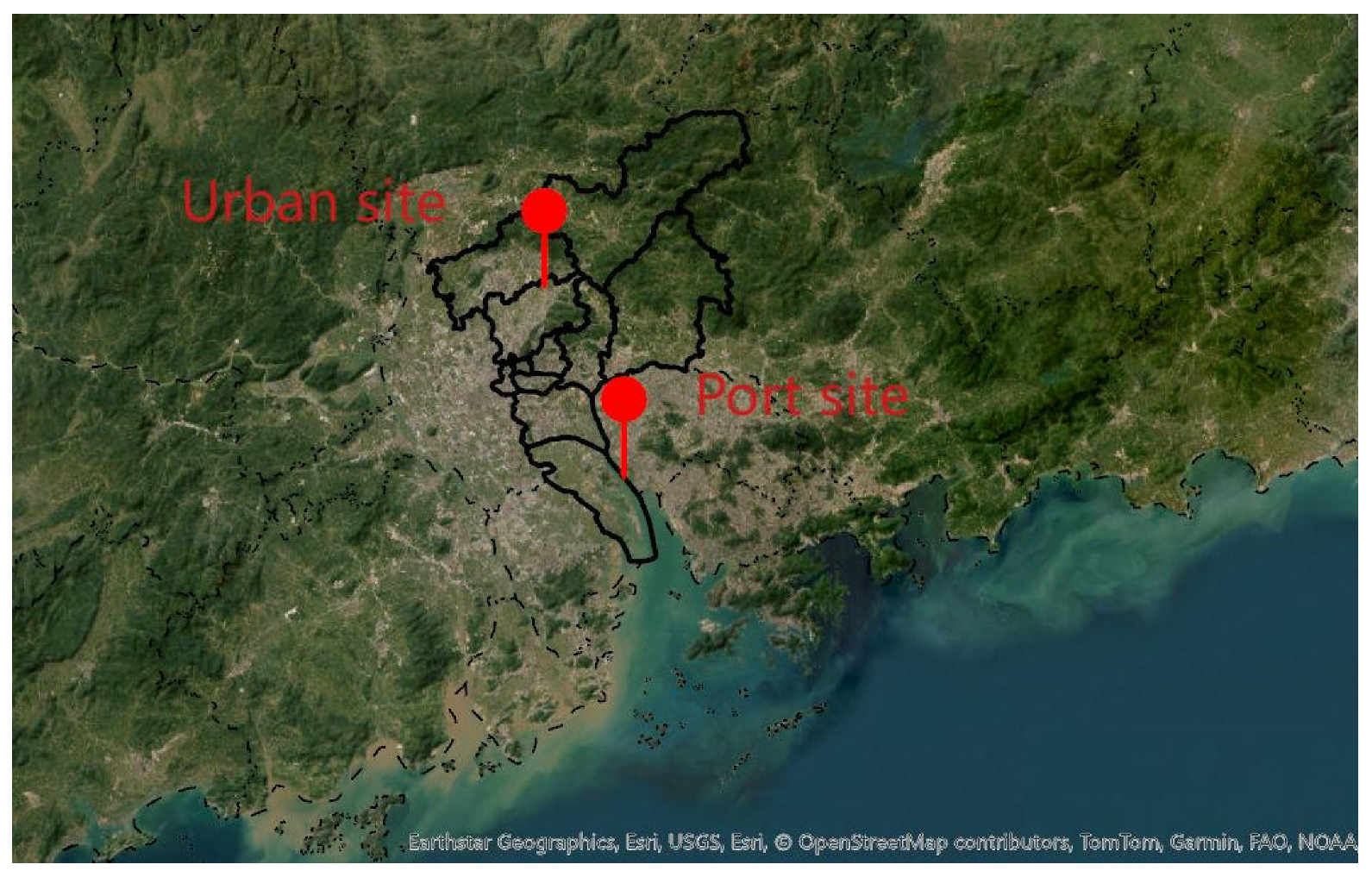
2.1. Samples Collection
2.2. Analysis of VOCs and OVOCs
2.3. QA/QC
2.4. Data Analysis
2.4.1. VOC Source Profile Construction
2.4.2. Calculation of Ozone Formation Potential
2.4.3. Potential Source Contribution Function Analysis
2.4.4. PMF Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
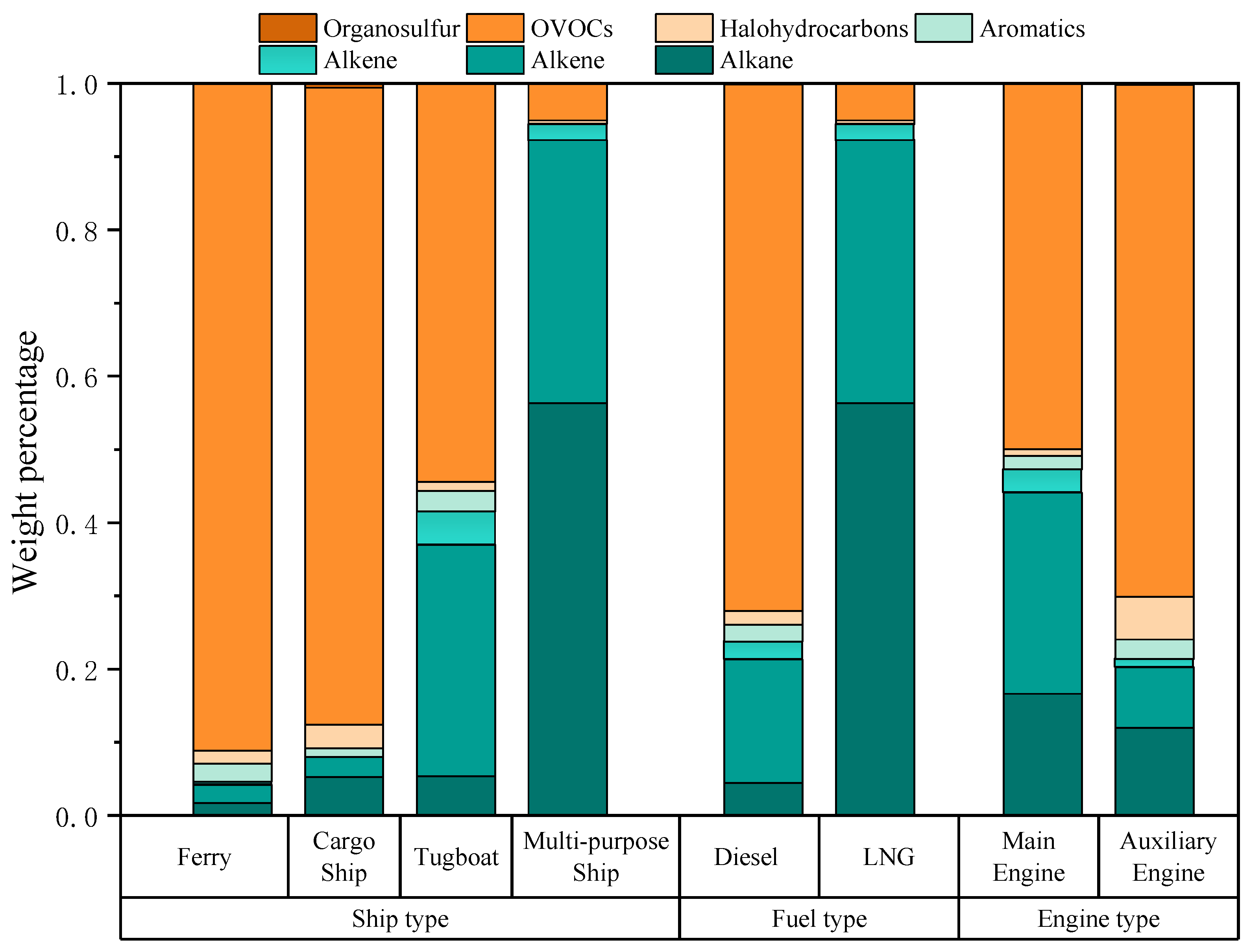
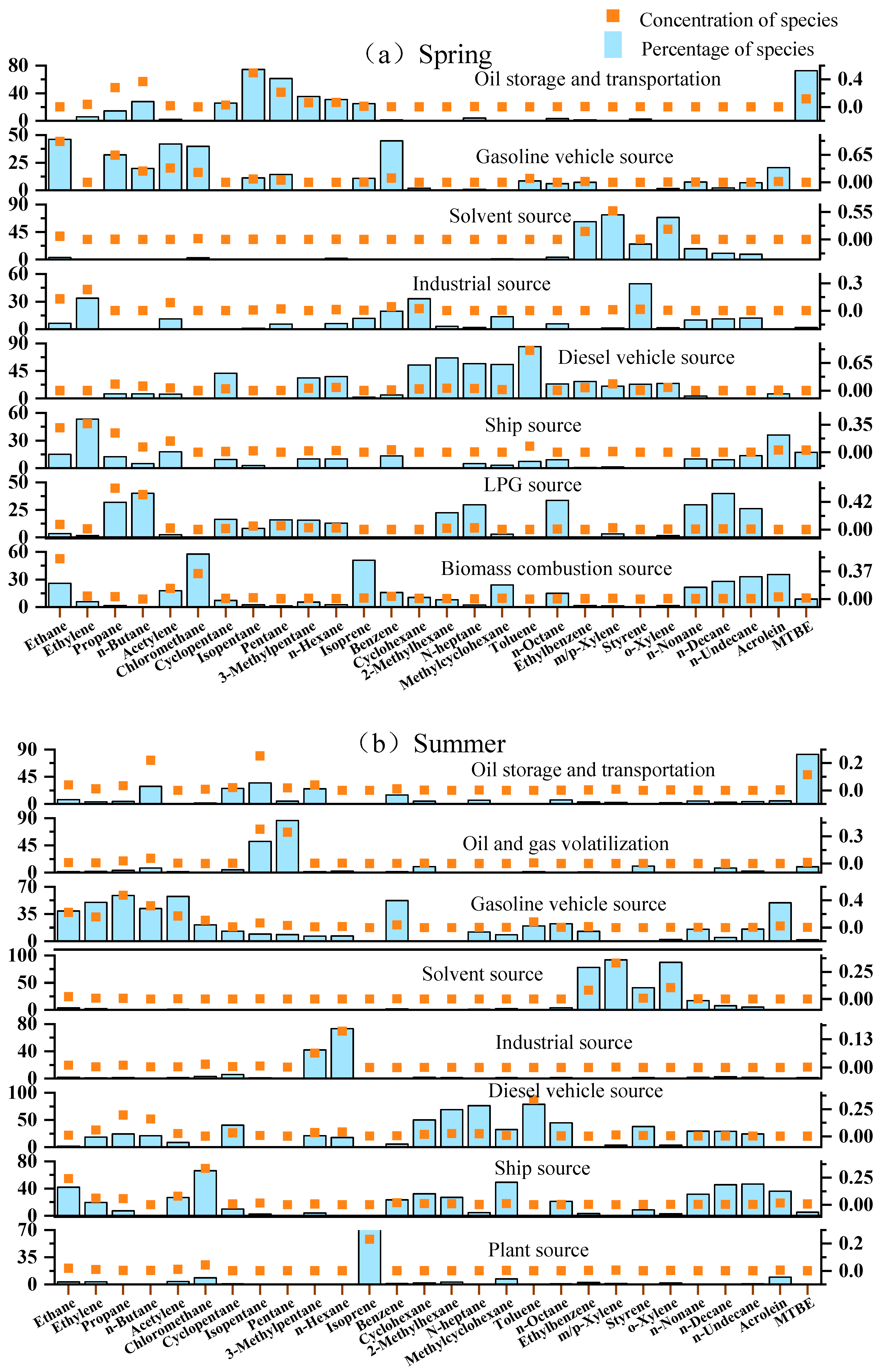
3.1. The Source Profile of Ship-Emitted VOCs
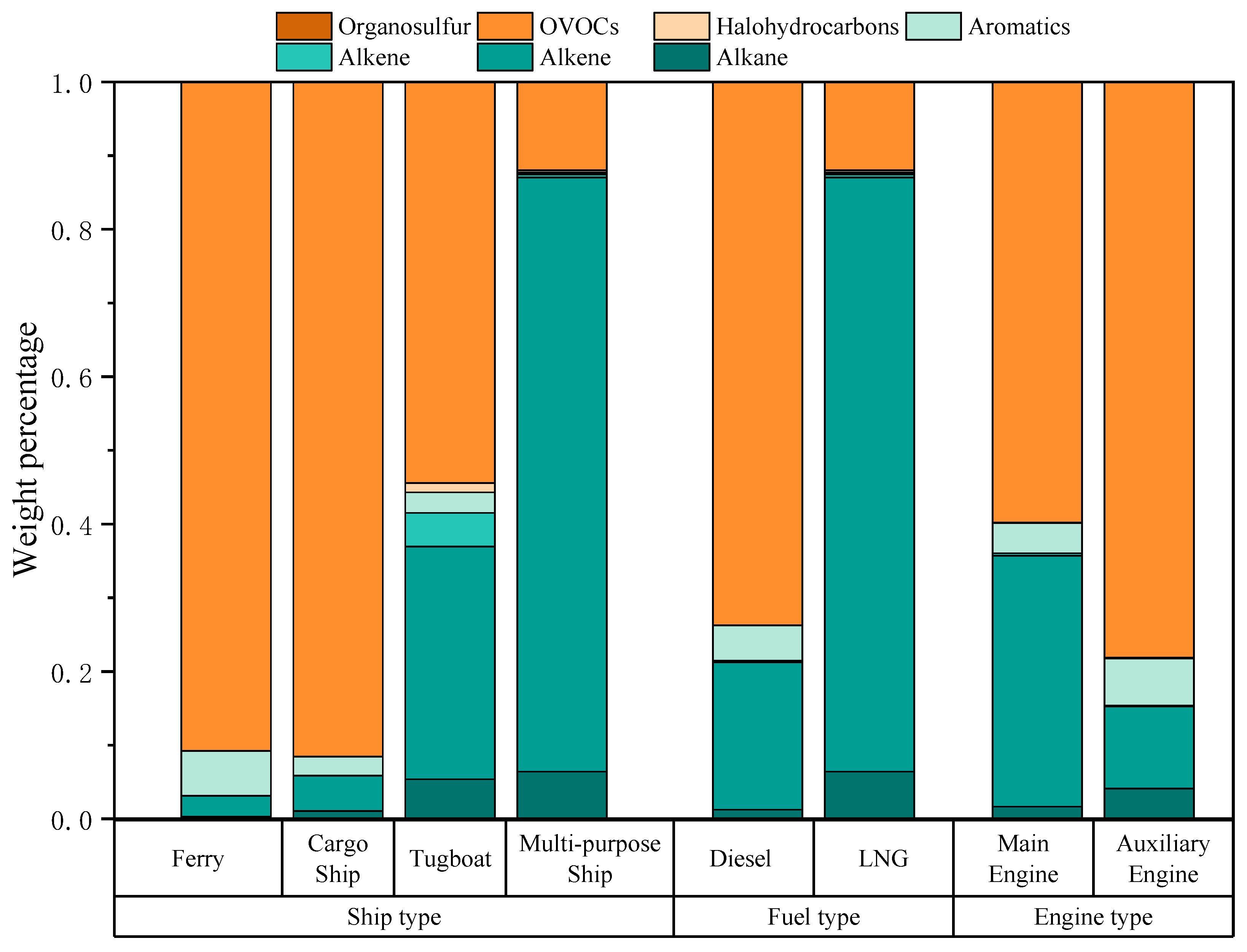
3.2. Analysis of Ozone Formation Potential of Ship-Emitted VOCs
3.3. Contribution of Ship-Emitted VOCs to Ambient Atmospheric VOCs in Guangzhou
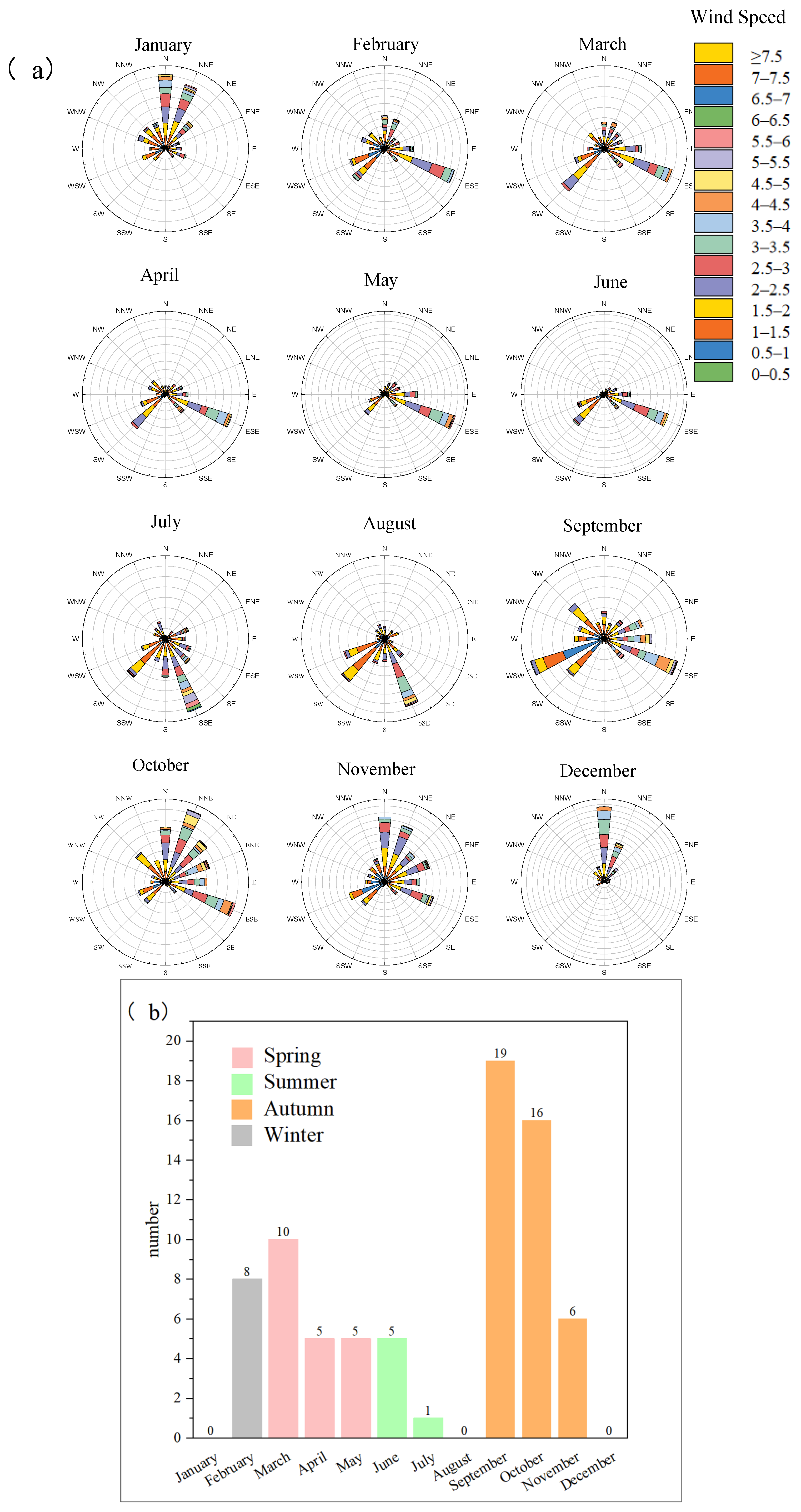
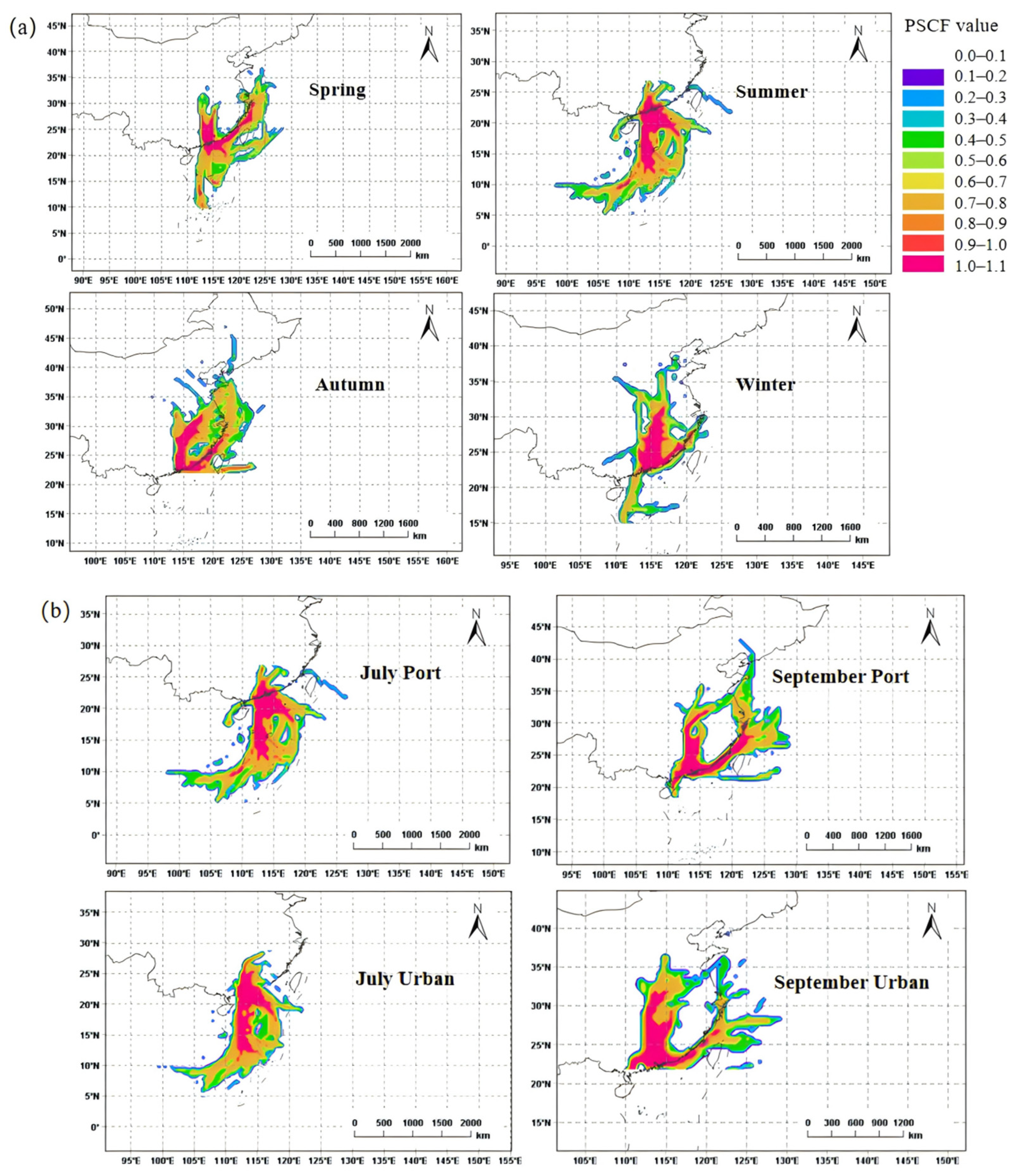
3.3.1. Analysis of Air Mass Transport Trajectories at the Port Site
3.3.2. Source Apportionment of Ambient Atmospheric VOCs and the Contribution of Ship-Emitted VOCs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yi, W.; He, T.; Wang, X.; Soo, Y.H.; Luo, Z.; Xie, Y.; Peng, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Lv, Z.; et al. Ship Emission Variations during the COVID-19 from Global and Continental Perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, Y.; Tian, C.; Lou, D.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Matthias, V. Emission Factors for Gaseous and Particulate Pollutants from Offshore Diesel Engine Vessels in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 6319–6334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yuan, Z.; Ou, J.; Fan, X.; Ye, S.; Xiao, T.; Shi, Y.; Huang, Z.; Ng, S.K.W.; Zhong, Z.; et al. An AIS-Based High-Resolution Ship Emission Inventory and Its Uncertainty in Pearl River Delta Region, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivarolo, M.; Piccardo, S.; Montagna, G.N.; Bellotti, D. A Multi-Criteria Approach for Comparing Alternative Fuels and Energy Systems Onboard Ships. Energy Convers. Manag. X 2023, 20, 100460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, P.; Fancello, G. Towards the IMO’s GHG Goals: A Critical Overview of the Perspectives and Challenges of the Main Options for Decarbonizing International Shipping. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDuffie, E.E.; Smith, S.J.; O’Rourke, P.; Tibrewal, K.; Venkataraman, C.; Marais, E.A.; Zheng, B.; Crippa, M.; Brauer, M.; Martin, R.V. A Global Anthropogenic Emission Inventory of Atmospheric Pollutants from Sector- and Fuel-Specific Sources (1970–2017): An Application of the Community Emissions Data System (CEDS). Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020, 12, 3413–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Aardenne, J.; Colette, A.; Degraeuwe, B.; de Vlieger, I.; Hammingh, P.; Viana, M. The Impact of International Shipping on European Air Quality and Climate Forcing; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence, M.G.; Crutzen, P.J. Influence of NOx Emissions from Ships on Tropospheric Photochemistry and Climate. Nature 1999, 402, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshiul, A.M.; Mohd Zaki, N.I.; Abu Husain, M.K. Review of Sulphur Emission from International Shipping-Effects and Regulatory Global Abatement Steps. Int. J. Mech. Eng. Technol. 2019, 10, 924–933. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Z.; Liu, H.; Ying, Q.; Fu, M.; Meng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wei, W.; Gong, H.; He, K. Impacts of Shipping Emissions on PM2.5 Pollution in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 15811–15824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; He, J.; Chen, H.; Huang, X.; Wang, Y.; Yu, X.; Yang, W.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, M.; et al. Dramatic Increase in Reactive Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) Emissions from Ships at Berth after Implementing the Fuel Switch Policy in the Pearl River Delta Emission Control Area. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 1887–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yi, W.; Lv, Z.; Deng, F.; Zheng, S.; Xu, H.; Zhao, J.; Liu, H.; He, K. Ship Emissions around China under Gradually Promoted Control Policies from 2016 to 2019. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 13835–13853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Li, M.; Liu, H.; Fu, M.; Deng, F.; Lv, Z.; Man, H.; Jin, X.; Liu, S.; He, K. Characteristics of Marine Shipping Emissions at Berth: Profiles for Particulate Matter and Volatile Organic Compounds. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 9527–9545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Xiao, B.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, C.; Li, R.; Wu, C.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wan, X.; et al. Real-World Emission Characteristics of VOCs from Typical Cargo Ships and Their Potential Contributions to Secondary Organic Aerosol and O3 under Low-Sulfur Fuel Policies. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2024, 24, 8999–9017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, D.; Pei, C.; Guo, H.; Song, W.; Yang, X.; Wang, X. Contribution of Ship Emission to Volatile Organic Compounds Based on One-Year Monitoring at a Coastal Site in the Pearl River Delta Region. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2024, 129, e2023JD039999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Feng, Y.; Zheng, M.; Li, Q.; Chen, J. Emission Characteristics and Formation Pathways of Intermediate Volatile Organic Compounds from Ocean-Going Vessels: Comparison of Engine Conditions and Fuel Types. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 12917–12925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Zhou, C.; Huang, L.; Xiao, C.; Wen, Y.; Li, J.; Lu, Z. Inland Ship Emission Inventory and Its Impact on Air Quality over the Middle Yangtze River, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 843, 156770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Weng, J. Impacts of the COVID-19 Epidemic on Merchant Ship Activity and Pollution Emissions in Shanghai Port Waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 790, 148198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wu, L.; Feng, X.; Mao, H. An AIS-Based Emission Inventory and the Impact on Air Quality in Tianjin Port Based on Localized Emission Factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 783, 146869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Kong, L.; Shi, Y.; Cao, X.; Li, X.; Wu, B.; Zhang, H.; Yao, Z. Multi-Type Air Pollutant Emission Inventory of Non-Road Mobile Sources in China for the Period 1990–2017. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2021, 21, 210003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu-Van, T.; Ristovski, Z.; Pourkhesalian, A.M.; Rainey, T.; Garaniya, V.; Abbassi, R.; Jahangiri, S.; Enshaei, H.; Kam, U.-S.; Kimball, R.; et al. On-Board Measurements of Particle and Gaseous Emissions from a Large Cargo Vessel at Different Operating Conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 832–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Ji, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J.; Wang, Q. Shipping Emission Inventories in China’s Bohai Bay, Yangtze River Delta, and Pearl River Delta in 2018. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 151, 110882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Hu, Q.; Wang, H.; Qiao, L.; Jing, S.; Wang, H.; Zhou, M.; Zhu, S.; Ma, Y.; Lou, S.; et al. Emission Factors of Particulate and Gaseous Compounds from a Large Cargo Vessel Operated under Real-World Conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Yuan, Z.; Zheng, J.; Li, C.; Huang, Z.; Li, W.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, K.; Duan, L. Characterization of VOC Emissions from Construction Machinery and River Ships in the Pearl River Delta of China. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 96, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, H.; Jing, S.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, T.; Tao, S.; Lou, S.; Qiao, L.; Li, L.; Chen, J. Characteristics and Sources of Atmospheric Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) along the Mid-Lower Yangtze River in China. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 190, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, S.; Dong, M.; Li, W.; Gao, X.; Ye, R.; Zhang, D. VOCs Emission Characteristics and Priority Control Analysis Based on VOCs Emission Inventories and Ozone Formation Potentials in Zhoushan. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 182, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Cheng, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Liu, M.; Li, M. Exploration of O3-Precursor Relationship and Observation-Oriented O3 Control Strategies in a Non-Provincial Capital City, Southwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 800, 149422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Pei, C.; Cheng, C.; Shen, H.; Zhang, Q.; Lian, X.; Xiong, X.; Gao, W.; Liu, M.; Wang, Z.; et al. Emission Factors and Source Profiles of Volatile Organic Compounds from Typical Industrial Sources in Guangzhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 869, 161758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, W.P.L. Development of Ozone Reactivity Scales for Volatile Organic Compounds. Air Waste 1994, 44, 881–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Charlesworth, E.; Wang, N.; Flores, R.M.; Liu, Q.Q.; Li, F.; Deng, T.; Deng, X.J. Characterization and Ozone Formation Potential (OFP) of Non-Methane Hydrocarbons under the Condition of Chemical Loss in Guangzhou, China. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 262, 118630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Xie, P.; Xu, J.; Li, A.; Tian, X.; Hu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Ren, H.; et al. Use of the PSCF Method to Analyze the Variations of Potential Sources and Transports of NO2, SO2, and HCHO Observed by MAX-DOAS in Nanjing, China during 2019. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 782, 146865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paatero, P.; Tapper, U. Positive Matrix Factorization: A Non-Negative Factor Model with Optimal Utilization of Error Estimates of Data Values. Environmetrics 1994, 5, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, B.; Song, C.; Lv, G.; Li, B.; Liu, X.; Wang, K.; Liu, Y. Evaluation of the Reduction in Carbonyl Emissions from a Diesel Engine Using Fischer–Tropsch Fuel Synthesized from Coal. Fuel 2014, 133, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.H.; Zhao, J.; Fan, S.J.; Wang, X.M. Sources of Formaldehyde and Their Contributions to Photochemical O3 Formation at an Urban Site in the Pearl River Delta, Southern China. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, A.L.; Cohen, R.C.; Harley, R.A.; Tonse, S.; Millet, D.B.; Schade, G.W.; Goldstein, A.H. VOC Reactivity in Central California: Comparing an Air Quality Model to Ground-Based Measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 351–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Lü, S.; Huang, Z.; Li, L. Sources of C2–C4 Alkenes, the Most Important Ozone Nonmethane Hydrocarbon Precursors in the Pearl River Delta Region. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 502, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Liu, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhang, Q.; Mao, H. Emissions of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) from Gasoline- and Liquified Natural Gas (LNG)-Fueled Vehicles in Tunnel Studies. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 234, 117626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S. Ship Emissions Inventory, Social Cost and Eco-Efficiency in Shanghai Yangshan Port. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 82, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. Ambient Air Quality Standards. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/dqhjbh/dqhjzlbz/201203/t20120302_224165.shtml (accessed on 30 May 2025).
- Yuan, X.; Huang, Z.; Lu, M.; Jia, G.; Duan, J.; Shen, J.; Zhong, M.; Chen, D.; Zheng, J. Seasonal Characteristics and Causes of Ozone Pollution in the Pearl River Delta Based on Observation and Machine Learning. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 43, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Li, T.; Hu, S.; Xie, X.; Liu, S. Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of Algal Blooms in Coastal Waters of Guangdong Province. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2020, 39, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, S.; Zhu, R.; Zhang, R.; Zu, L.; Wang, Y.; Bao, X. On-Road Tailpipe Emission Characteristics and Ozone Formation Potentials of VOCs from Gasoline, Diesel and Liquefied Petroleum Gas Fueled Vehicles. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 223, 117294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Mu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J.; Liu, P.; He, X.; Li, X. A Comparison Investigation of Atmospheric NMHCs at Two Sampling Sites of Beijing City and a Rural Area during Summertime. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 783, 146867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Cheng, H.R.; Ling, Z.H.; Louie, P.K.K.; Ayoko, G.A. Which Emission Sources Are Responsible for the Volatile Organic Compounds in the Atmosphere of Pearl River Delta? J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 188, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Fu, S.; Gao, S.; Zhang, S.; Che, X.; Wang, Q.; Jiao, Z. Update on Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) Source Profiles and Ozone Formation Potential in Synthetic Resins Industry in China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 291, 118253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shao, M.; Fu, L.; Lu, S.; Zeng, L.; Tang, D. Source Profiles of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) Measured in China: Part I. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 6247–6260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Ling, Z.H.; Lee, S.C.; Ho, S.S.H.; Cao, J.J.; Blake, D.R.; Cheng, Y.; Lai, S.C.; Ho, K.F.; Gao, Y.; et al. Characterization of Volatile Organic Compounds at a Roadside Environment in Hong Kong: An Investigation of Influences after Air Pollution Control Strategies. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 122, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.F.; Lee, S.C.; Ho, W.K.; Blake, D.R.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Y.S.; Ho, S.S.H.; Fung, K.; Louie, P.K.K.; Park, D. Vehicular Emission of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) from a Tunnel Study in Hong Kong. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 7491–7504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, M.C.; Aklilu, Y.-A.; Brown, S.G.; Lyder, D.A. Source Apportionment of Volatile Organic Compounds Measured in Edmonton, Alberta. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 81, 504–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Xiang, P.; Liang, S.; Chen, W.; Wang, M.; Lu, S.; Wang, Z. Sources Profiles of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) Measured in a Typical Industrial Process in Wuhan, Central China. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-C.; Wang, J.-L.; Liu, S.-C.; Candice Lung, S.-C. Assessment of Vehicular and Non-Vehicular Contributions to Hydrocarbons Using Exclusive Vehicular Indicators. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 6349–6361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Ship Type | Fuel Type | Tonnage, t |
|---|---|---|
| Ferry | Diesel | 750 |
| Cargo ship | Diesel | 2156 |
| Tugboat 1 | Diesel | 351 |
| Tugboat 2 | Diesel | 323 |
| Multi-purpose ship | LNG | 2388 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, X.; Wang, L.; Wu, H.; Pei, C.; Ju, H.; He, J.; Liu, M.; Li, M.; Chen, D.; Xu, Y.; et al. Characteristics of Ship-Emitted VOCs and Their Contributions to Urban Atmospheric VOCs in Guangzhou, China. Toxics 2025, 13, 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060479
Zeng X, Wang L, Wu H, Pei C, Ju H, He J, Liu M, Li M, Chen D, Xu Y, et al. Characteristics of Ship-Emitted VOCs and Their Contributions to Urban Atmospheric VOCs in Guangzhou, China. Toxics. 2025; 13(6):479. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060479
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Xueying, Liwei Wang, Haining Wu, Chenglei Pei, Hong Ju, Junjie He, Ming Liu, Mei Li, Daiwei Chen, Yongjiang Xu, and et al. 2025. "Characteristics of Ship-Emitted VOCs and Their Contributions to Urban Atmospheric VOCs in Guangzhou, China" Toxics 13, no. 6: 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060479
APA StyleZeng, X., Wang, L., Wu, H., Pei, C., Ju, H., He, J., Liu, M., Li, M., Chen, D., Xu, Y., Tang, W., Li, J., & Cheng, C. (2025). Characteristics of Ship-Emitted VOCs and Their Contributions to Urban Atmospheric VOCs in Guangzhou, China. Toxics, 13(6), 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060479








