Biodegradation of Benzo(a)pyrene in Contaminated Soil: Plant and Microorganism Contributions from Isotope Tracing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Preparation
2.2. Experimental Setups
2.3. Plant Selection
2.4. BaP and 13C Isotope Analytical Methods
2.4.1. Determination of the BaP Concentration
2.4.2. Calculation of the Relative Isotope Abundance
2.5. High-Throughput Sequencing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Temporal Evolution of the BaP Concentration
3.2. Temporal Evolution in the 13C Isotope Abundance
3.2.1. 13C Isotope Abundance in Air
3.2.2. 13C Isotope Abundance in Plants
3.2.3. 13C Isotope Abundance of the Adsorption Resins
3.2.4. 13C Isotope Abundance in Soil
3.3. Contributions of 13C-BaP Removal in Soil
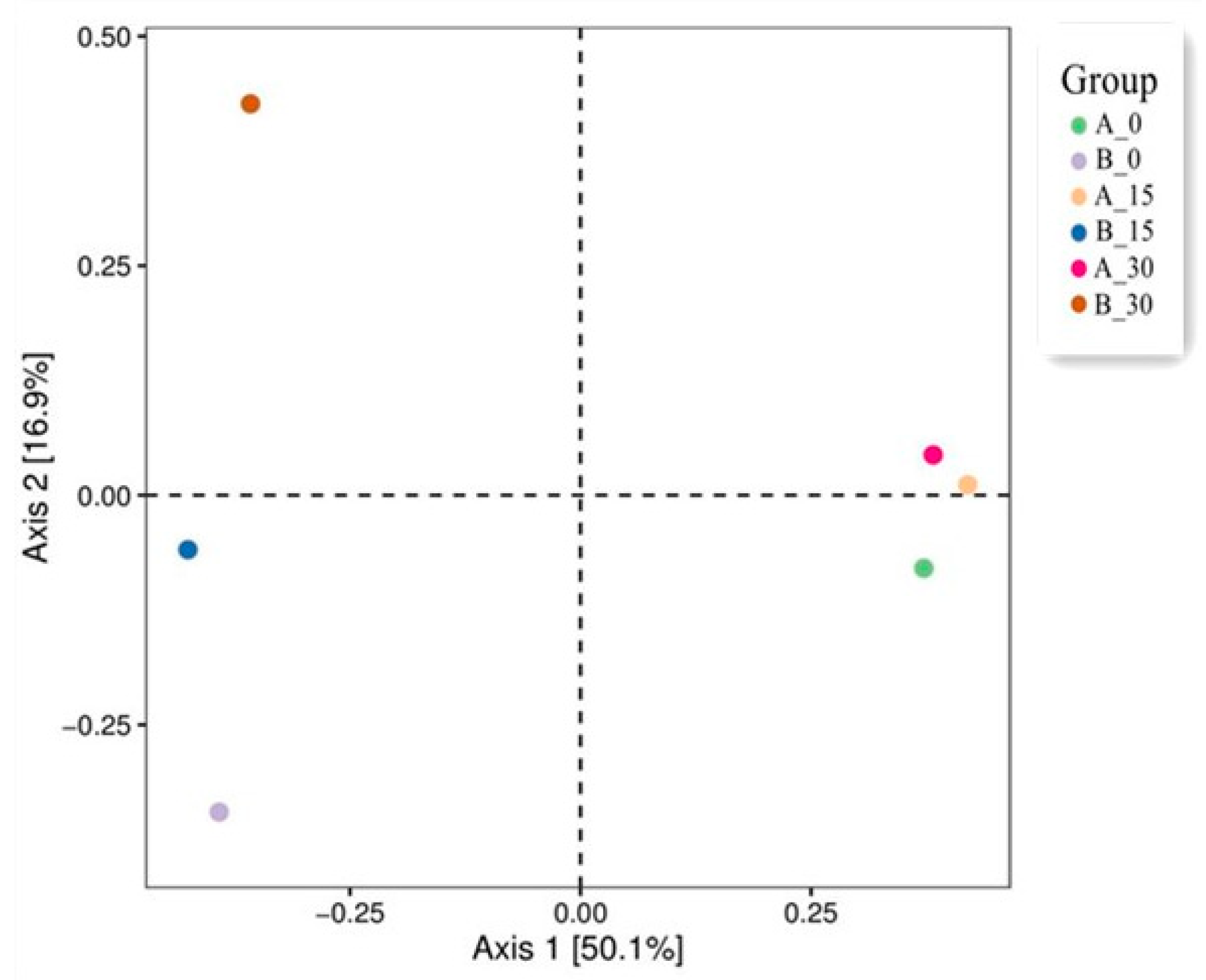
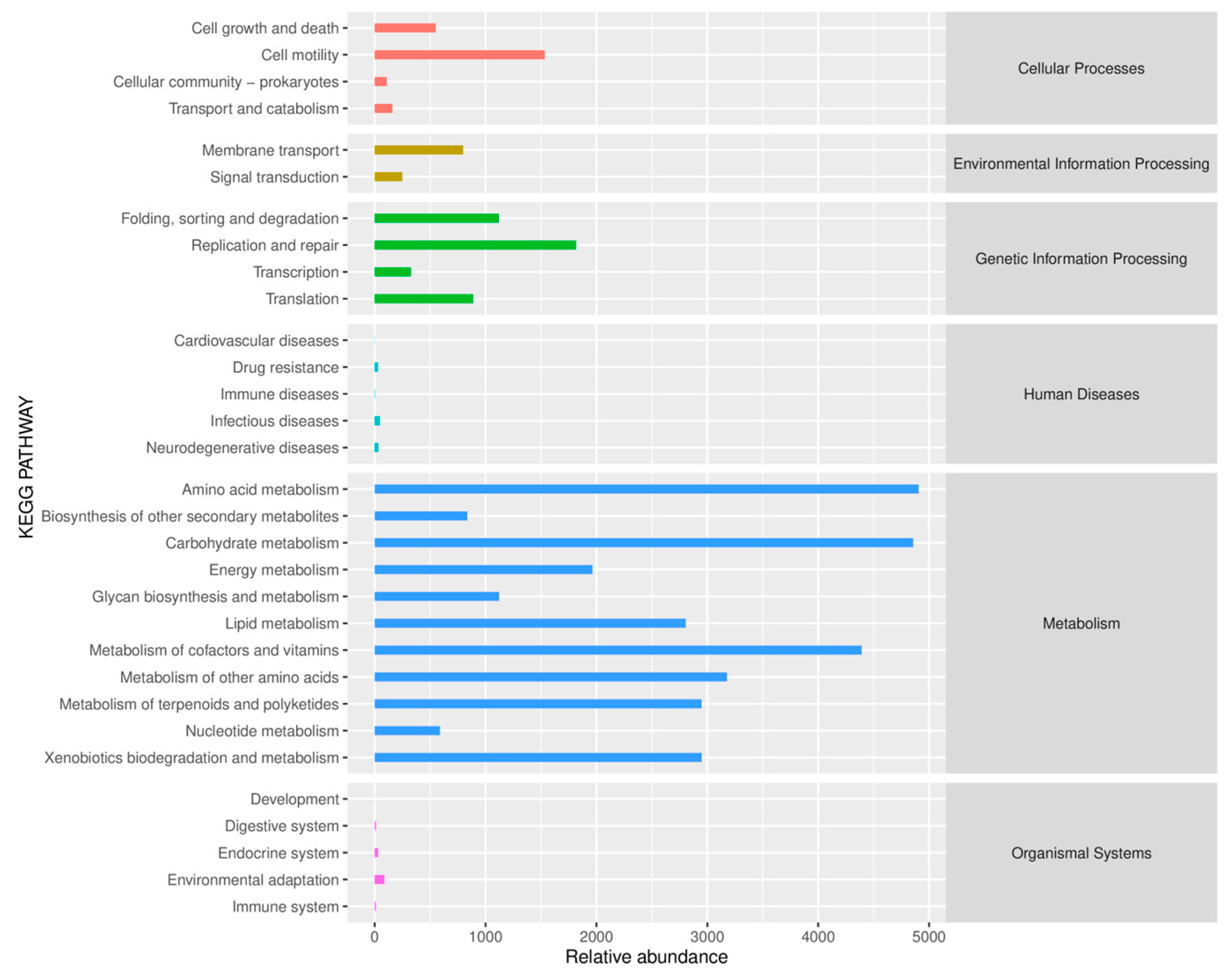
3.4. Evolution Characteristics of the Microbial Community Structure
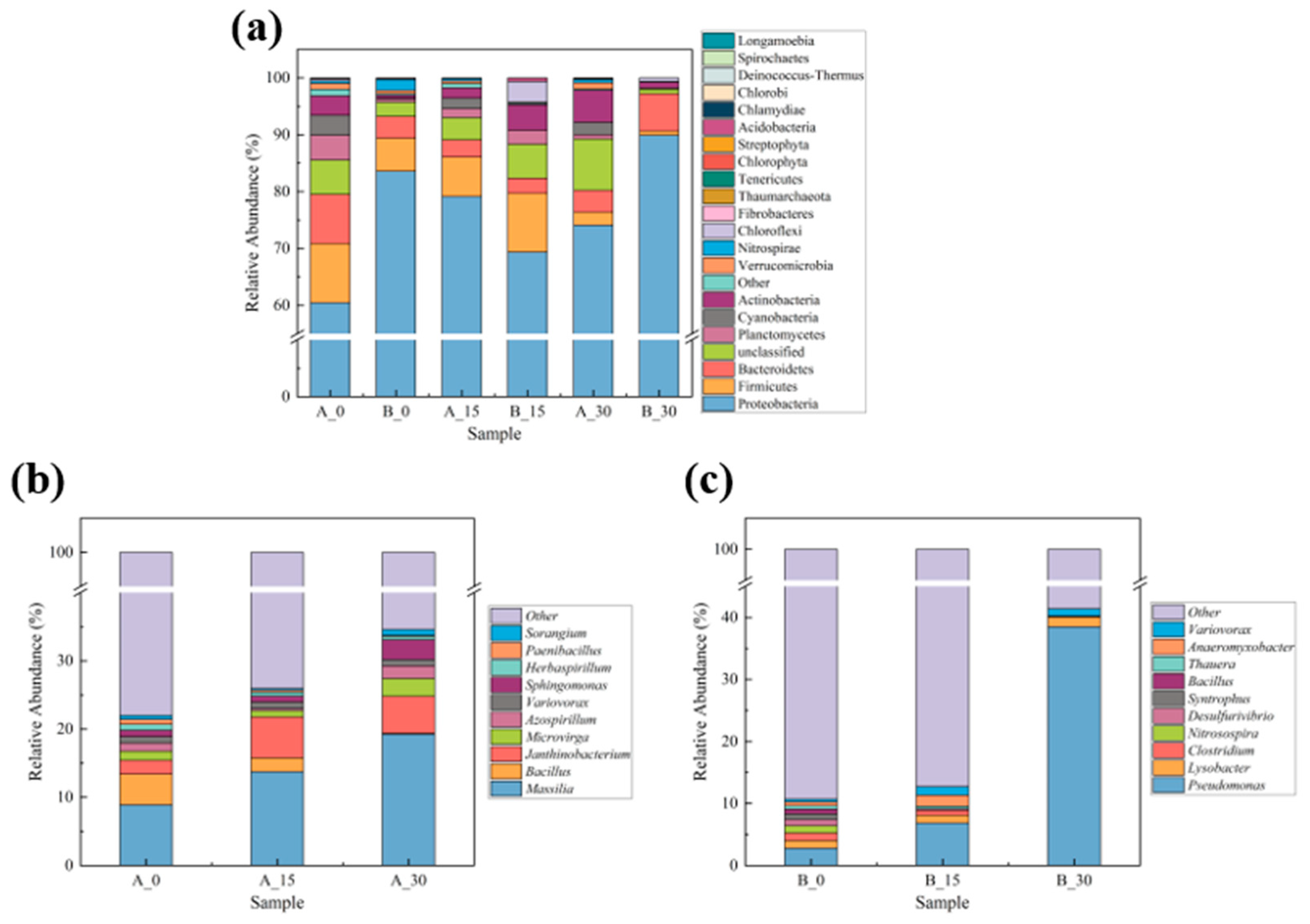
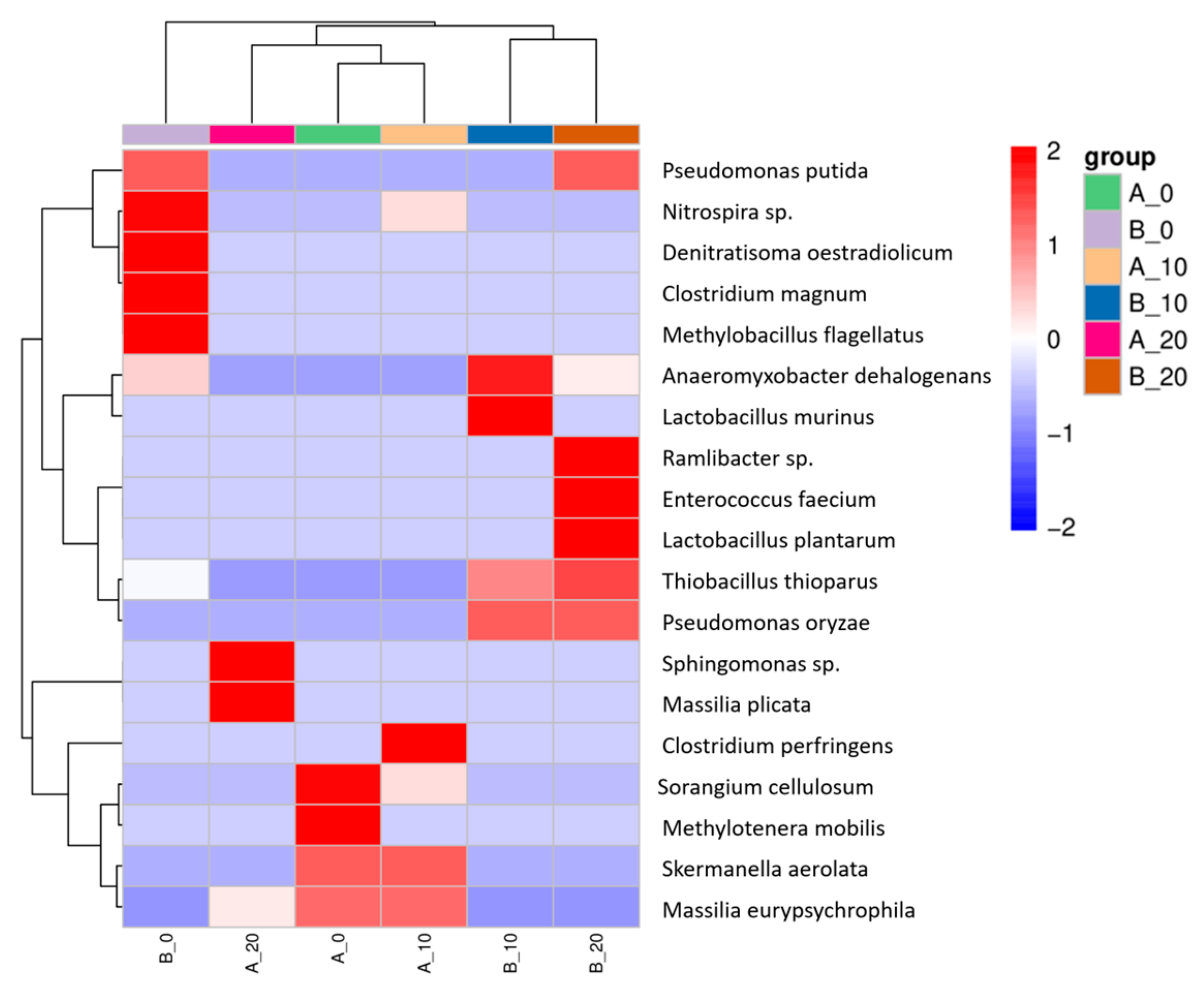
3.4.1. Taxonomic Annotation of Species
3.4.2. Diversity of the Soil Bacterial Community
3.4.3. Structural Composition of the Soil Bacterial Community
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, H.C.; Qian, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yu, F.; Huang, T.; Zhang, B.; Peng, T.; Hu, Z. Comparative genomics reveals evidence of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degradation in the moderately halophilic genus Pontibacillus. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 462, 132724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Dutta, R.; Das, P. A critical review on plant biomonitors for determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in air through solvent extraction techniques. Chemosphere 2020, 251, 126441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burks, G.C.; Harmon, T. Volatilization of solid-phase polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from model mixtures and lampblack-contaminated soils. J. Chem. Eng. Data ACS J. Data 2001, 46, 944–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eker, G.; Hatipoglu, M. Effect of UV Wavelength, Temperature and Photocatalyst on Removal of PAHs From Industrial Soil with Photodegradation Applications. Environ. Technol. 2018, 40, 3793–3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haein, K.; Guyoung, K.; Eun Hea, J. Optimization of hydrogen peroxide-to-hemoglobin ratio for biocatalytic mineralization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs)-contaminated soils. Chemosphere 2017, 187, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Owino, G.F.; Wu, C.; Wanting, L.; Hassan, E.; Ahmed, M.; Wang, J. Contributions of partition and adsorption to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons sorption by fractionated soil at different particle sizes. Chemosphere 2022, 301, 134715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Wang, L.; Yang, S.; Xun, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wei, W. Thermally enhanced anoxic biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in a highly contaminated aged soil. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, H.; Nava, A.R.; Prasad, M.N.V. Mechanistic understanding and future prospect of microbe-enhanced phytoremediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2019, 13, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, W.; Ji, L.; Song, F.; Li, T.; Fu, X.; Li, Q.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J. Effects of Salinity on the Biodegradation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Oilfield Soils Emphasizing Degradation Genes and Soil Enzymes. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 824319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Bi, C.; Jin, X.; Zeng, Y.; Deng, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z. Uptake, translocation, and risk assessment of PAHs in contaminated soil-air-vegetable systems based on a field simulation experiment. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 271, 116361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristaldi, A.; Conti, G.O.; Jho, E.H.; Zuccarello, P.; Grasso, A.; Copat, C.; Ferrante, M. Phytoremediation of contaminated soils by heavy metals and PAHs. A brief review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2017, 8, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Gong, Y.; Ni, H.G. Contribution of soil erosion to PAHs in surface water in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, L. Assessment on the cumulative effect of pollutants and the evolution of micro-ecosystems in bioretention systems with different media. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 228, 112957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Sun, J.; Liu, R.; Zheng, T.; Tang, Y. Plant contribution to the remediation of PAH-contaminated soil of Dagang Oilfield by Fire Phoenix. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 43126–43137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davin, M.; Starren, A.; Marit, E.; Lefébure, K.; Fauconnier, M.L.; Colinet, G. Investigating the Effect of Medicago sativa L. and Trifolium pratense L. Root Exudates on PAHs Bioremediation in an Aged-Contaminated Soil. Water Air Soil Pollut. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 230, 597–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premnath, N.; Mohanrasu, K.; Guru Raj Rao, R.; Dinesh, G.H.; Prakash, G.S.; Ananthi, V.; Ponnuchamy, K.; Muthusamy, G.; Arun, A. A crucial review on polycyclic aromatic Hydrocarbons-Environmental occurrence and strategies for microbial degradation. Chemosphere 2021, 280, 130608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosal, D.; Ghosh, S.; Dutta, T.; Ahn, Y.H. Current State of Knowledge in Microbial Degradation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs): A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urana, R.; Yadav, J.; Panchal, S.; Sharma, P.; Singh, N. Phytoremediation of PAH compounds by microbial communities in sodic soil. Int. J. Phytoremed. 2023, 25, 1501–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandary, S.; Tahmourespour, A.; Hoodaji, M.; Abdollahi, A. The synergistic use of plant and isolated bacteria to clean up polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from contaminated soil. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2017, 15, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarahmadi, Z.; Shokoohi, R.; Baharloie, J.; Alikhani, M.; Abdollahi, A.; Goodini, K. Biological removal of PAHs by bacteria from contaminated soils. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2016, 34, 1406–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.D.; Lee, C.G. Microbial degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil by bacterium-fungus co-cultures. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2007, 12, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Han, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wang, M.; Li, H.; Gao, D. Effects of soil colloids on adsorption and migration of benzo(a)pyrene on contaminated sites under runoff infiltration processes. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 353, 124150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharathi, D.; Lee, J.; Vinayagam, Y.; Banerjee, M.; Ramanathan, G.; Al-Ansari, M.M.; Venkatraman, G. Benzopyrene elimination from the environment using graphitic carbon nitride-SnS nanocomposites. Chemosphere 2024, 352, 141352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Yao, L.; Li, Y. Bioremediation of a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon–contaminated urban soil: Degradation dynamics and phytotransformation pathways. J. Soils Sediments 2022, 22, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Miao, R.; Guo, M.; Shang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, J. Biochar enhanced polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons degradation in soil planted with ryegrass: Bacterial community and degradation gene expression mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, S.; Hou, X.; Zhao, G.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Jiang, G. Migration of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the rhizosphere micro-interface of soil-ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) system. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 903, 166299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Luo, C.; Zhang, D.; Cai, X.; Jiang, L.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, G. Diversity of the active phenanthrene degraders in PAH-polluted soil is shaped by ryegrass rhizosphere and root exudates. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 128, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wen, X. Performance and kinetics of benzo(a)pyrene biodegradation in contaminated water and soil and improvement of soil properties by biosurfactant amendment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 207, 111292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, D.W.; Rasmussen, C. Absolute Carbon Stable Isotope Ratio in the Vienna Peedee Belemnite Isotope Reference Determined by 1H NMR Spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 5240–5247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woese, C.R.; Fox, G.E. Phylogenetic structure of the prokaryotic domain: The primary kingdoms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 5088–5090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berbee, M.L.; Taylor, J.W.H. Detecting morphological convergence in true fungi, using 18S rRNA gene sequence data. BioSystems 1992, 28, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Jiao, Y.; Che, R.; Holden, N.M.; Zhang, X.; Biswas, A.; Feng, Q. The effects of grazer exclosure duration on soil microbial communities on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 839, 156238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorenko, A.G.; Chernikova, N.; Minkina, T.; Sushkova, S.; Dudnikova, T.; Antonenko, E.; Fedorenko, G.; Bauer, T.; Mandzhieva, S.; Barbashev, A. Effects of benzo[a]pyrene toxicity on morphology and ultrastructure of Hordeum sativum. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 1551–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, S.; Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, W.; Wei, G. Bacterial communities in oil contaminated soils: Biogeography and co-occurrence patterns. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 98, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sizhong, Y.; Xi, W.; Yulan, S.; Susanne, L.; Huijun, J.; Amedea, P. Hydrocarbon degraders establish at the costs of microbial richness, abundance and keystone taxa after crude oil contamination in permafrost environments. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Ding, A.; Zhao, X.; Chang, W.; Ren, L.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jin, N.; Zhang, D. Response of soil microbial communities to petroleum hydrocarbons at a multi-contaminated industrial site in Lanzhou, China. Chemosphere 2022, 306, 135559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, L.; Qi, Q.; Liu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Lv, X.; Mao, Z.; et al. Shifts in soil microbial community functional gene structure across a 61-year desert revegetation chronosequence. Geoderma 2019, 347, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Borjigin, Q.; Gao, J.L.; Yu, X.F.; Hu, S.P.; Zhang, B.Z.; Han, S.C. Community succession and functional prediction of microbial consortium with straw degradation during subculture at low temperature. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhang, M. Effect of rhamnolipids on the uptake of PAHs by ryegrass. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 156, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, R.; David Gara, P.M.; Rosso, J.A.; Del Panno, M.T. Effects of organic matter addition on chronically hydrocarbon-contaminated soil. Biodegradation 2021, 32, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriele, I.; Race, M.; Papirio, S.; Esposito, G. Phytoremediation of pyrene-contaminated soils: A critical review of the key factors affecting the fate of pyrene. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 293, 112805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sushkova, S.; Minkina, T.; Deryabkina, I.; Antonenko, E.; Mandzhieva, S.; Zamulina, I.; Bauer, T.; Gromakova, N.; Vasilyeva, G. Phytoaccumulation of Benzo[a]pyrene by the Barley in Artificially Contaminated Soil. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 2017, 39, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Teng, Y.; Shen, Y.; Sun, M.; Tu, C.; Luo, Y.; Li, Z.; Christie, P. Dissipation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and microbial activity in a field soil planted with perennial ryegrass. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2012, 6, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Qin, J.; Xie, B.; Sun, H.; Li, X.; Chen, W. Volatilization behavior of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from the oil-based residues of shale drill cuttings. Chemosphere 2021, 288, 132455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, L.A.; Reynolds, C.M. Phytodegradation of organic compounds. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2024, 15, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strotmann, U.; Durand, M.J.; Thouand, G.; Eberlein, C.; Heipieper, H.J.; Gartiser, S.; Pagga, U. Microbiological toxicity tests using standardized ISO/OECD methods—Current state and outlook. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 108, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Rene, E.R.; Chen, Z.; Ma, W. Fate of PAHs in treated wastewater reused as irrigation water: Environmental risks in water-soil-ryegrass multimedia system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gan, Z.; Gu, J.; Su, H.; Yu, H. Volatilization Loss of 6 PAHs with 2–4 Rings Related to Coal Extracts. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 2016, 38, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafra, G.; Absalón, Á.E.; Anducho-Reyes, M.Á.; Fernandez, F.J.; Cortés-Espinosa, D.V. Construction of PAH-degrading mixed microbial consortia by induced selection in soil. Chemosphere 2017, 172, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, N.A.; Kasmuri, N.; Hamzah, N. Microbial Bioremediation Techniques for Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon (PAHs)—A Review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2022, 233, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Kaehler, B.D.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.; Bolyen, E.; Knight, R.; Huttley, G.A.; Gregory Caporaso, J. Optimizing taxonomic classification of marker-gene amplicon sequences with QIIME 2’s q2-feature-classifier plugin. Microbiome 2018, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Q.; Fu, W.; Chen, B.; Zhang, X.; Xing, S.; Ji, C.; Zhang, X. Community response of soil microorganisms to combined contamination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and potentially toxic elements in a typical coking plant. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1143742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Fan, F.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, G. Microbial diversity and activity of an aged soil contaminated by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 41, 871–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Hong, Y.K.; Kim, H.S.; Oh, E.J.; Park, Y.H.; Kim, S.C. Metagenomic Analysis for Evaluating Change in Bacterial Diversity in TPH-Contaminated Soil after Soil Remediation. Toxics 2021, 9, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerniglia, C.E. Biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 1993, 4, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Tang, J.; Liu, X.; Song, B.; Zhen, M.; Ashbolt, N.J. Vertical response of microbial community and degrading genes to petroleum hydrocarbon contamination in saline alkaline soil. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 81, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zheng, X.; Fu, W.; Liu, A.; Wang, W.; Wang, G.; Ji, J.; Guan, C. Microplastics reduced bioavailability and altered toxicity of phenanthrene to maize (Zea mays L.) through modulating rhizosphere microbial community and maize growth. Chemosphere 2023, 345, 140444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaac, P.; Martínez, F.; Bourguignon, N.; Sánchez, L.; Ferrero, M. Improved PAHs removal performance by a defined bacterial consortium of indigenous Pseudomonas and actinobacteria from Patagonia, Argentina. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 101, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, M.; Chen, X.; Yang, Y.; Hou, L.; Wu, S.; Zhu, P. Indigenous PAH degraders along the gradient of the Yangtze Estuary of China: Relationships with pollutants and their bioremediation implications. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 142, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, X.; Yang, Z.; Tang, T.T. Effects of cellulose on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons removal and microbial community structure variation during anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge. J. Environ. Sci. Health 2020, 55 Pt A, 1104–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lou, J.; Gu, H.; Luo, X.; Yang, L.; Wu, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Xu, J. Efficient biodegradation of phenanthrene by a novel strain Massilia sp. WF1 isolated from a PAH-contaminated soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 13378–13388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Qian, Y. Structural, metabolic, and functional characteristics of soil microbial communities in response to benzo[a]pyrene stress. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 431, 128632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, B. Sphingomonas Relies on Chemotaxis to Degrade Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Maintain Dominance in Coking Sites. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatawadekar, V.; Damare, S.; Garg, A. Biodegradation of mixed polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by Pseudomonas sp. isolated from estuarine sediment. Bioremed. J. 2021, 27, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, F.; Hehemann, J.H.; Rebuffet, E.; Czjzek, M.; Michel, G. Environmental and gut bacteroidetes: The food connection. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satola, B.; Wübbeler, J.H.; Steinbüchel, A. Metabolic characteristics of the species Variovorax paradoxus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 541–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, A.R.; Wick, L.Y.; Harms, H. Principles of microbial PAH-degradation in soil. Environ. Pollut. 2005, 133, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Wang, W.; Li, F.; Zhu, L. Mixed-surfactant-enhanced phytoremediation of PAHs in soil: Bioavailability of PAHs and responses of microbial community structure. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haritash, A.K.; Kaushik, C.P. Biodegradation aspects of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs): A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, X.; Lu, C.; Wang, J.; Qin, C.; Ling, W. Responses of soil bacterial communities and PAH-degrading genes to PAHs during soil self-purification: Evidence from a microcosm experiment. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2025, 211, 106147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

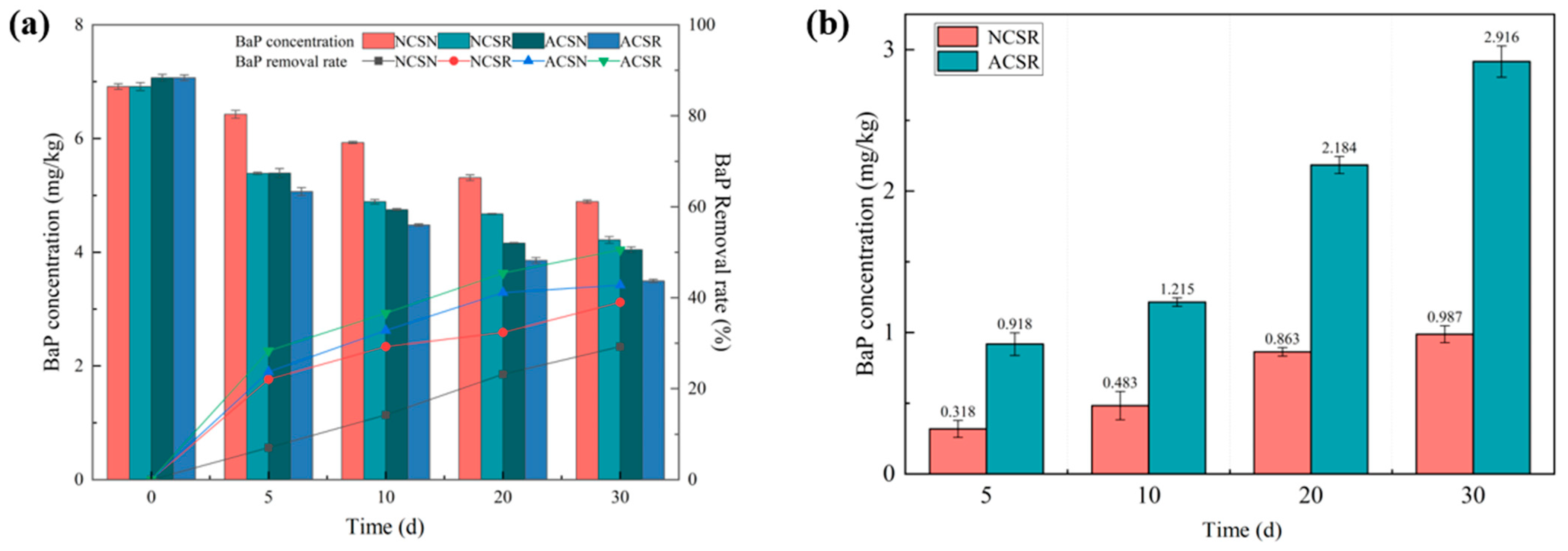

| Time (d) | Soil Residue (%) | Uptake by Plants (%) | Microbiological Degradation (%) | Volatilization (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 87.793 | 2.331 | 9.836 | 0.044 |
| 10 | 76.352 | 4.441 | 17.081 | 0.126 |
| 20 | 63.022 | 11.604 | 25.327 | 0.047 |
| 30 | 54.072 | 16.453 | 29.471 | 0.004 |
| Time (d) | Soil Residue (%) | Uptake by Plants (%) | Microbiological Degradation (%) | Volatilization (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 92.262 | 2.344 | 5.348 | 0.046 |
| 10 | 81.278 | 4.269 | 14.333 | 0.120 |
| 20 | 67.098 | 8.073 | 18.735 | 0.094 |
| 30 | 63.269 | 12.771 | 20.955 | 0.005 |
| Sample | Phylum | Class | Order | Family | Genus | Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A_0 | 17 | 28 | 41 | 181 | 154 | 7 |
| B_0 | 4 | 48 | 18 | 70 | 59 | 8 |
| A_15 | 19 | 10 | 23 | 139 | 130 | 7 |
| B_15 | 14 | 34 | 16 | 56 | 48 | 6 |
| A_30 | 10 | 15 | 29 | 134 | 103 | 3 |
| B_30 | 18 | 16 | 2 | 27 | 134 | 12 |
| Sample ID | Chao1 Index | Simpson | Shannon | Pielou’s Evenness | Observed Species | Faith’s PD | Good’s Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A_0 | 2888.52 | 0.99 | 11.23 | 0.97 | 3043.91 | 306.98 | 0.94 |
| A_15 | 2269.22 | 0.99 | 10.52 | 0.98 | 2499.62 | 281.13 | 0.88 |
| A_30 | 1836.98 | 0.98 | 9.07 | 0.85 | 1575.70 | 198.67 | 0.97 |
| B_0 | 1539.23 | 0.96 | 6.86 | 0.73 | 694.36 | 57.46 | 0. 89 |
| B_15 | 1318.93 | 0.97 | 6.06 | 0.78 | 542.55 | 49.70 | 0.92 |
| B_30 | 1502.24 | 0.96 | 7.02 | 0.74 | 675.47 | 63.46 | 0.96 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Su, X.; Zhang, C.; Han, Z.; Wang, M. Biodegradation of Benzo(a)pyrene in Contaminated Soil: Plant and Microorganism Contributions from Isotope Tracing. Toxics 2025, 13, 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050405
Wang J, Su X, Zhang C, Han Z, Wang M. Biodegradation of Benzo(a)pyrene in Contaminated Soil: Plant and Microorganism Contributions from Isotope Tracing. Toxics. 2025; 13(5):405. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050405
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jianlong, Xiaobing Su, Changhe Zhang, Zhimeng Han, and Meiqi Wang. 2025. "Biodegradation of Benzo(a)pyrene in Contaminated Soil: Plant and Microorganism Contributions from Isotope Tracing" Toxics 13, no. 5: 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050405
APA StyleWang, J., Su, X., Zhang, C., Han, Z., & Wang, M. (2025). Biodegradation of Benzo(a)pyrene in Contaminated Soil: Plant and Microorganism Contributions from Isotope Tracing. Toxics, 13(5), 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050405






