Toxicity Response and Swimming Speed Regularity in Daphnia magna After Short-Term Exposure to Diuron
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Domestication of Organisms
2.3. Exposure Experiment
2.4. Swimming Behavior Collection
2.5. Data Processing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Changes in the Average Speed V Index Exposed to DCMU
3.2. Significance Analysis of V Exposed to DCMU
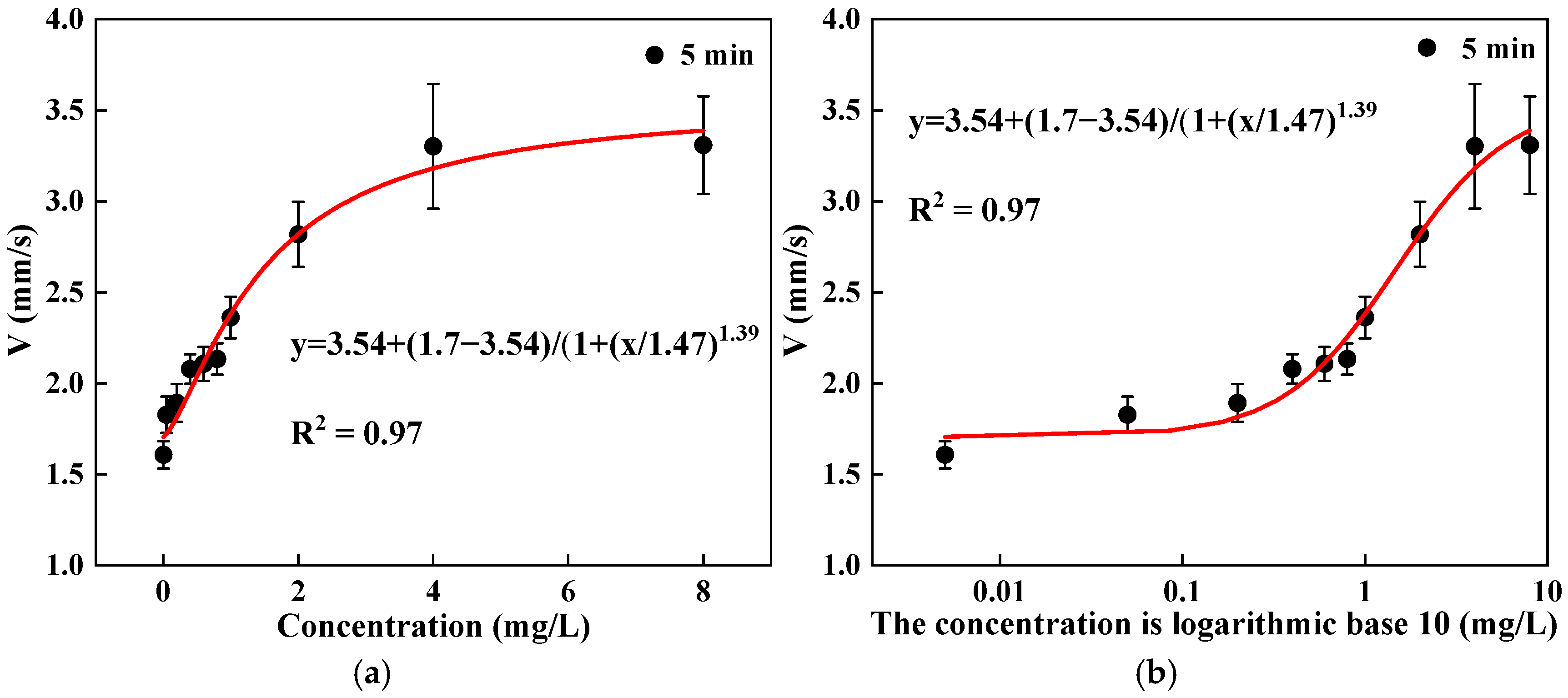
3.3. Relationship Between Swimming Behavior and Dose–Response
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Calvo, S.; Romo, S.; Soria, J.; Picó, Y. Pesticide contamination in water and sediment of the aquatic systems of the Natural Park of the Albufera of Valencia (Spain) during the rice cultivation period. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Zhang, H.; Wu, C.; Wang, C.; Li, Q. Pesticides in surface waters of tropical river basins draining areas with rice–vegetable rotations in Hainan, China: Occurrence, relation to environmental factors, and risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 283, 117100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Mahmood, A.; Shao, Y.; Jarosiewicz, P.; Gonsior, G.; Cuellar-Bermudez, S.P.; Chen, Z.; Stibany, F.; Schäffer, A. Combined simulation on pesticides fate, toxicities and ecological risk in rice paddies for Sustainable Development Goals achievements. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.K.; Sanghvi, G.; Yadav, M.; Padhiyar, H.; Christian, J.; Singh, V. Fate of pesticides in agricultural runoff treatment systems: Occurrence, impacts and technological progress. Environ. Res. 2023, 237, 117100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, A.; Shin, W.S.; Masud, M.A.A.; Nandi, R.; Islam, T. A critical review of sustainable pesticide remediation in contaminated sites: Research challenges and mechanistic insights. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 341, 122940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.H.M.; Malik, A.; Li, M.; Lenzen, M.; Maggi, F. International demand for food and services drives environmental footprints of pesticide use. Commun. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zheng, M.; Xu, H.; Hua, Y.; Liu, A.; Li, Y.; Fang, L.; Chen, X. Fate and ecological risks of current-use pesticides in seawater and sediment of the Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Environ. Res. 2022, 207, 112673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Ruiz, E.B.; Agha, R.; Spahr, S.; Wolinska, J. Widely used herbicide metolachlor can promote harmful bloom formation by stimulating cyanobacterial growth and driving detrimental effects on their chytrid parasites. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 344, 123437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.S.; Singh, P.; Nistala, S.; Mohanty, K. Understanding the environmental fate and removal strategies of phenylurea herbicides: A comprehensive review. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2024, 16, 100496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, I.A.; Zouari, N.; Al-Ghouti, M.A. Removal of pesticides from water and wastewater: Chemical, physical and biological treatment approaches. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 101026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lofrano, G.; Libralato, G.; Meric, S.; Vaiano, V.; Sacco, O.; Venditto, V.; Guida, M.; Carotenuto, M. 1—Occurrence and potential risks of emerging contaminants in water. In Visible Light Active Structured Photocatalysts for the Removal of Emerging Contaminants; Sacco, O., Vaiano, V., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, Q. Performance of electro-Fenton process coupling with microbial fuel cell for simultaneous removal of herbicide mesotrione. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 319, 124244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giardina, A.; Tampieri, F.; Biondo, O.; Marotta, E.; Paradisi, C. Air non-thermal plasma treatment of the herbicides mesotrione and metolachlor in water. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 372, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syafrudin, M.; Kristanti, R.A.; Yuniarto, A.; Hadibarata, T.; Rhee, J.; Al-onazi, W.A.; Algarni, T.S.; Almarri, A.H.; Al-Mohaimeed, A.M. Pesticides in Drinking Water—A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-H.; Kabir, E.; Jahan, S.A. Exposure to pesticides and the associated human health effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Harwood, J.D.; Zhang, Q. Oxidative stress and DNA damage in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) exposed to the herbicide mesotrione. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 1080–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damalas, C.A.; Eleftherohorinos, I.G. Pesticide Exposure, Safety Issues, and Risk Assessment Indicators. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2011, 8, 1402–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matamoros, V.; Caiola, N.; Rosales, V.; Hernández, O.; Ibáñez, C. The role of rice fields and constructed wetlands as a source and a sink of pesticides and contaminants of emerging concern: Full-scale evaluation. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 156, 105971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Mukome, F.N.D.; Yan, D.; Wang, H.; Scow, K.M.; Parikh, S.J. Phenylurea herbicide sorption to biochars and agricultural soil. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2015, 50, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Spilsbury, F.D.; Warne, M.S.J.; Backhaus, T. Risk Assessment of Pesticide Mixtures in Australian Rivers Discharging to the Great Barrier Reef. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 14361–14371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanan, C.; Ali, J.; Sellaoui, L.; Dhaoudi, F.; Franco, D.S.P.; Georgin, J.; Erto, A.; Vieillard, J.; Badawi, M. Elucidating the adsorption mechanism of herbicide Diuron onto activated carbons via steric, energetic and thermodynamic investigations. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 53, 103910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silburn, D.M.; Fillols, E.; Rojas-Ponce, S.; Lewis, S.; McHugh, A.D. Direct comparison of runoff of residual and knockdown herbicides in sugarcane using a rainfall simulator finds large difference in runoff losses and toxicity relative to diuron. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 863, 160976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melero-Jiménez, I.J.; Bañares-España, E.; Reul, A.; Flores-Moya, A.; García-Sánchez, M.J. Detection of the maximum resistance to the herbicides diuron and glyphosate, and evaluation of its phenotypic cost, in freshwater phytoplankton. Aquat. Toxicol. 2021, 240, 105973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, O.C.; van de Merwe, J.P.; Brown, C.J.; Warne, M.S.J.; Smith, R.A. Individual and combined effects of diuron and light reduction on marine microalgae. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 241, 113729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.-y.; Zhong, X.-f.; Dupuy, C.; Che, S.; Lavaud, J. Diuron effects on photosynthesis and vertical migration of microphytobenthos: Potential rapid bioassessment of herbicide toxicity in coastal sediments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 170, 112619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.-E.; Haque, M.N.; Do, S.D.; Rhee, J.-S. Chronic effects of environmental concentrations of antifoulant diuron on two marine fish: Assessment of hormone levels, immunity, and antioxidant defense system. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 263, 109510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadonléké, R.D.; LeBerre, B.; Perreau, F.; Humbert, J.-F. Responses of lake bacterioplankton activities and composition to the herbicide diuron. Aquat. Toxicol. 2009, 94, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.S.; Midya, S. Growth regulatory pattern of zooplankton in herbicide and antibiotic contaminated aquatic ecosystem: An overview. Watershed Ecol. Environ. 2023, 5, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camuel, A.; Guieysse, B.; Alcántara, C.; Béchet, Q. Fast algal eco-toxicity assessment: Influence of light intensity and exposure time on Chlorella vulgaris inhibition by atrazine and DCMU. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 140, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulieu, M.; Cabana, H.; Huot, Y. Adverse effects of atrazine, DCMU and metolachlor on phytoplankton cultures and communities at environmentally relevant concentrations using Fast Repetition Rate Fluorescence. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 136239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.W.; Chu, C.Y.; Hsu, J.D.; Wang, C.J. Haemotoxic effect of phenylurea herbicides in rats: Role of haemoglobin-adduct formation in splenic toxicity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1993, 31, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, A.; Barbisan, L.F.; Martins, P.R.; Spinardi-Barbisan, A.L.T. Diuron exposure induces systemic and organ-specific toxicity following acute and sub-chronic exposure in male Wistar rats. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2011, 31, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, A.; Bassey, A.; Ebari, S.; Eni, G. Hormonal and haematological biomarkers as indicators of stress induced by Diuron herbicide toxicity on Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822) sub-adults. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2024, 276, 109802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, L.B.; Diamante, G.; Giroux, M.; Coffin, S.; Xu, E.G.; Moledo de Souza Abessa, D.; Schlenk, D. Impacts of Salinity and Temperature on the Thyroidogenic Effects of the Biocide Diuron in Menidia beryllina. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3146–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nebeker, A.V.; Schuytema, G.S. Chronic Effects of the Herbicide Diuron on Freshwater Cladocerans, Amphipods, Midges, Minnows, Worms, and Snails. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1998, 35, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nederstigt, T.A.P.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Blom, R.; Vijver, M.G. Correlation analysis of single- and multigenerational endpoints in D. magna toxicity tests: A case-study using TiO2 nanoparticles. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 241, 113792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melvin, S.D.; Wilson, S.P. The utility of behavioral studies for aquatic toxicology testing: A meta-analysis. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 2217–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, D. Daphnia as a versatile model system in ecology and evolution. EvoDevo 2022, 13, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltanighias, T.; Umar, A.; Abdullahi, M.; Abdallah, M.A.-E.; Orsini, L. Combined Toxicity of Perfluoroalkyl substances and Microplastics on the sentinel species Daphnia magna: Implications for Freshwater Ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 363, 125133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Li, X.; Du, M.; Ren, Z.; Li, Q.; Li, Y. Identification and regulation of ecotoxicity of polychlorinated naphthalenes to aquatic food Chain (green algae-D. magna-fish). Aquat. Toxicol. 2021, 233, 105774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, L.; Van de Maele, M.; Delnat, V.; Theys, C.; Mukherjee, S.; De Meester, L.; Stoks, R. Evolution of pesticide tolerance and associated changes in the microbiome in the water flea Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 240, 113697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, R.; Kwak, J.I.; An, Y.-J. Comparative study of the sensitivity of Daphnia galeata and Daphnia magna to heavy metals. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 162, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Hu, L.; Hou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Nie, X. Toxic effects of environmentally relevant concentrations of naproxen exposure on Daphnia magna including antioxidant system, development, and reproduction. Aquat. Toxicol. 2024, 266, 106794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Long, Y.; Xiao, W.; Liu, D.; Tian, Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, L.; Pan, Y. Ecotoxicology of microplastics in Daphnia: A review focusing on microplastic properties and multiscale attributes of Daphnia. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 249, 114433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reif, D.M.; Truong, L.; Mandrell, D.; Marvel, S.; Zhang, G.; Tanguay, R.L. High-throughput char-acterization of chemical-associated embryonic behavioral changes predicts teratogenic outcomes. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 1459–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soose, L.J.; Hügl, K.S.; Oehlmann, J.; Schiwy, A.; Hollert, H.; Jourdan, J. A novel approach for the assessment of invertebrate behavior and its use in behavioral ecotoxicology. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 897, 165418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bownik, A. Daphnia swimming behaviour as a biomarker in toxicity assessment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bownik, A.; Wlodkowic, D. Advances in real-time monitoring of water quality using automated analysis of animal behaviour. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 147796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.H.; Zhao, N.J.; Yin, G.F.; Wang, T.; Jv, X.; Han, S.L.; An, L.S. Rapid Response of Daphnia magna Motor Behavior to Mercury Chloride Toxicity Based on Target Tracking. Toxics 2024, 12, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomazzi, S.; Cochet, N. Environmental impact of diuron transformation: A review. Chemosphere 2004, 56, 1021–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Sun, J. YOLOX: Exceeding YOLO Series in 2021. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.08430. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, P.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, D.; Weng, F.; Yuan, Z.; Luo, P.; Liu, W.; Wang, X. ByteTrack: Multi-object Tracking by Associating Every Detection Box. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision 2022, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Behrens, D.; Rouxel, J.; Burgeot, T.; Akcha, F. Comparative embryotoxicity and genotoxicity of the herbicide diuron and its metabolites in early life stages of Crassostrea gigas: Implication of reactive oxygen species production. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 175, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerhardt, A.; Janssens de Bisthoven, L.; Soares, A.M.V. Evidence for the Stepwise Stress Model: Gambusia holbrooki and Daphnia magna under Acid Mine Drainage and Acidified Reference Water Stress. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 4150–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerhardt, A.; Janssens de Bisthoven, L.; Mo, Z.; Wang, C.; Yang, M.; Wang, Z. Short-term responses of Oryzias latipes (Pisces: Adrianichthyidae) and Macrobrachium nipponense (Crustacea: Palaemonidae) to municipal and pharmaceutical waste water in Beijing, China: Survival, behaviour, biochemical biomarkers. Chemosphere 2002, 47, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Qi, P.; Zhang, B.; Zeng, Y.; Fu, R.; Miao, M. AChE inhibition: One dominant factor for swimming behavior changes of D. magna under DDVP exposure. Chemosphere 2015, 120, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozman, K.K. Quantitative definition of toxicity: A mathematical description of life and death with dose and time as variables. Med. Hypotheses 1998, 51, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, F.; Zhao, N.; Yin, G.; Luo, Y.; Gan, T. Toxicity Response and Swimming Speed Regularity in Daphnia magna After Short-Term Exposure to Diuron. Toxics 2025, 13, 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050395
Qin F, Zhao N, Yin G, Luo Y, Gan T. Toxicity Response and Swimming Speed Regularity in Daphnia magna After Short-Term Exposure to Diuron. Toxics. 2025; 13(5):395. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050395
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Feihu, Nanjing Zhao, Gaofang Yin, Yunfei Luo, and Tingting Gan. 2025. "Toxicity Response and Swimming Speed Regularity in Daphnia magna After Short-Term Exposure to Diuron" Toxics 13, no. 5: 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050395
APA StyleQin, F., Zhao, N., Yin, G., Luo, Y., & Gan, T. (2025). Toxicity Response and Swimming Speed Regularity in Daphnia magna After Short-Term Exposure to Diuron. Toxics, 13(5), 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050395






