Glacial Waters Under Threat: Risk Assessment and Source Identification of Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Meili Snow Mountains, Southeastern Tibetan Plateau
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Analytical Methods
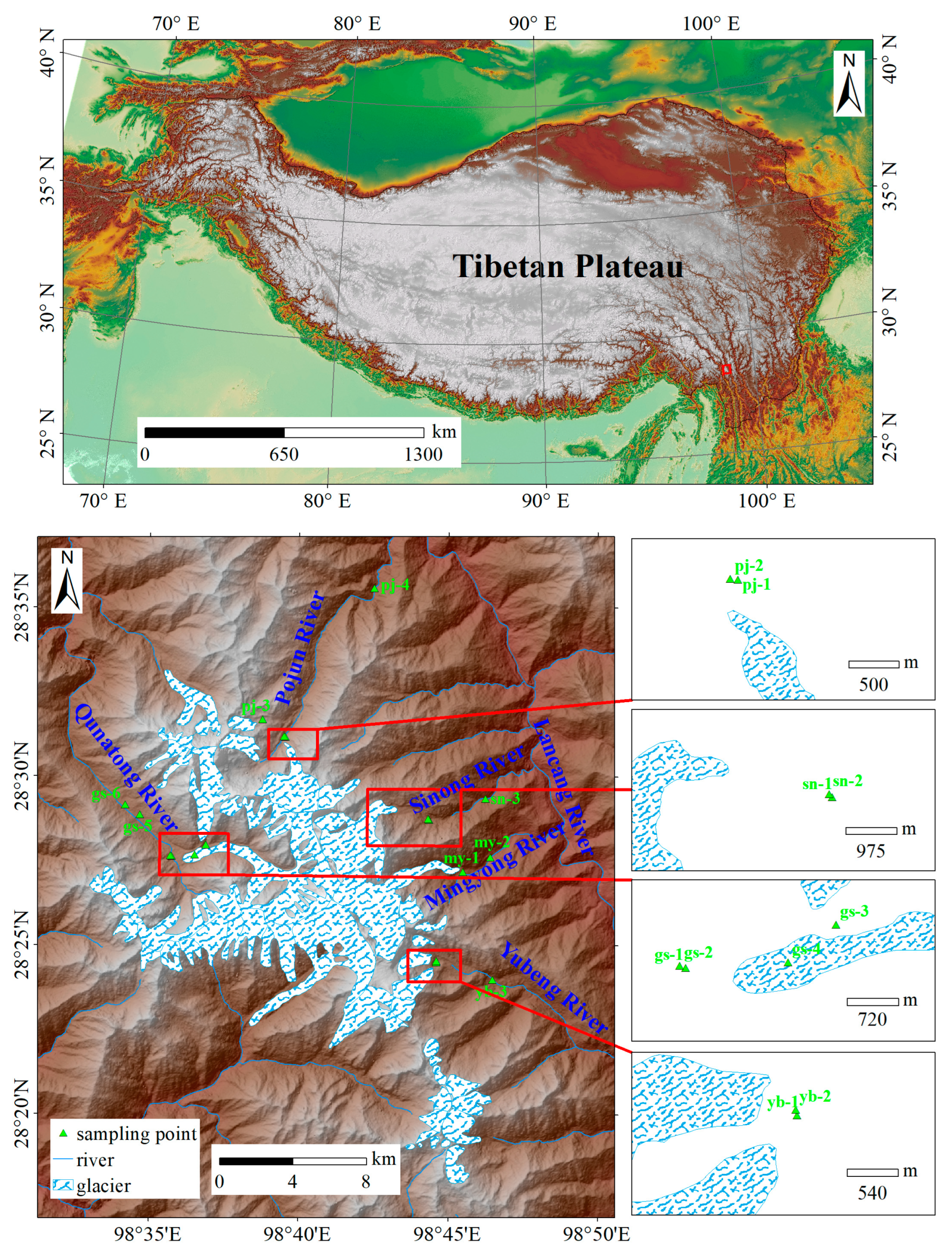
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Chemicals and Reagents
2.3. Sample Pretreatment
2.4. Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Analysis
2.5. Quality Assurance and Quality Control
2.6. Risk Assessment Methods
2.7. Air Masses Backward Trajectories
3. Results
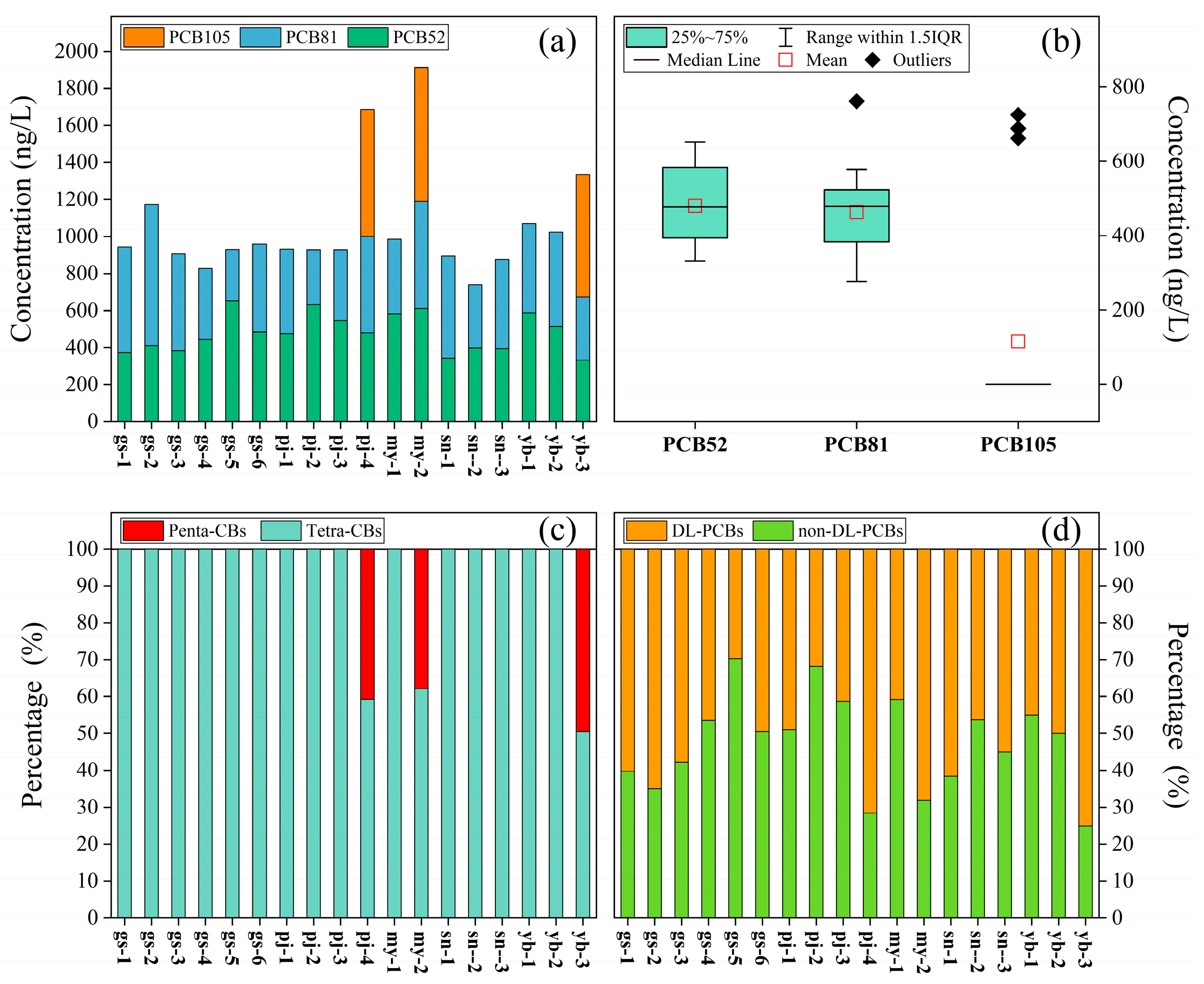
3.1. Occurrence and Composition of PCBs
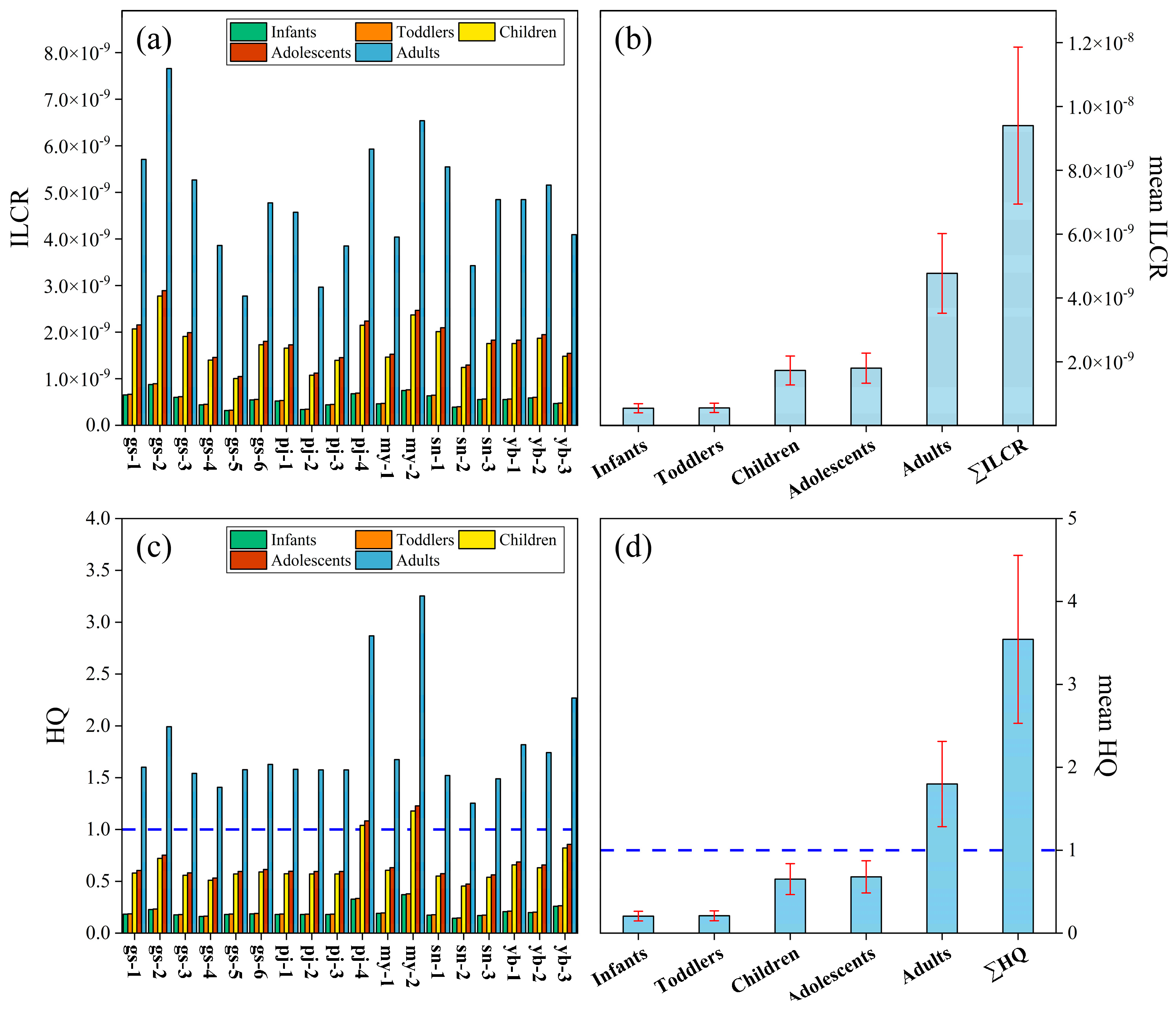
3.2. Health Risk Values
3.3. Ecotoxicological Risk Values
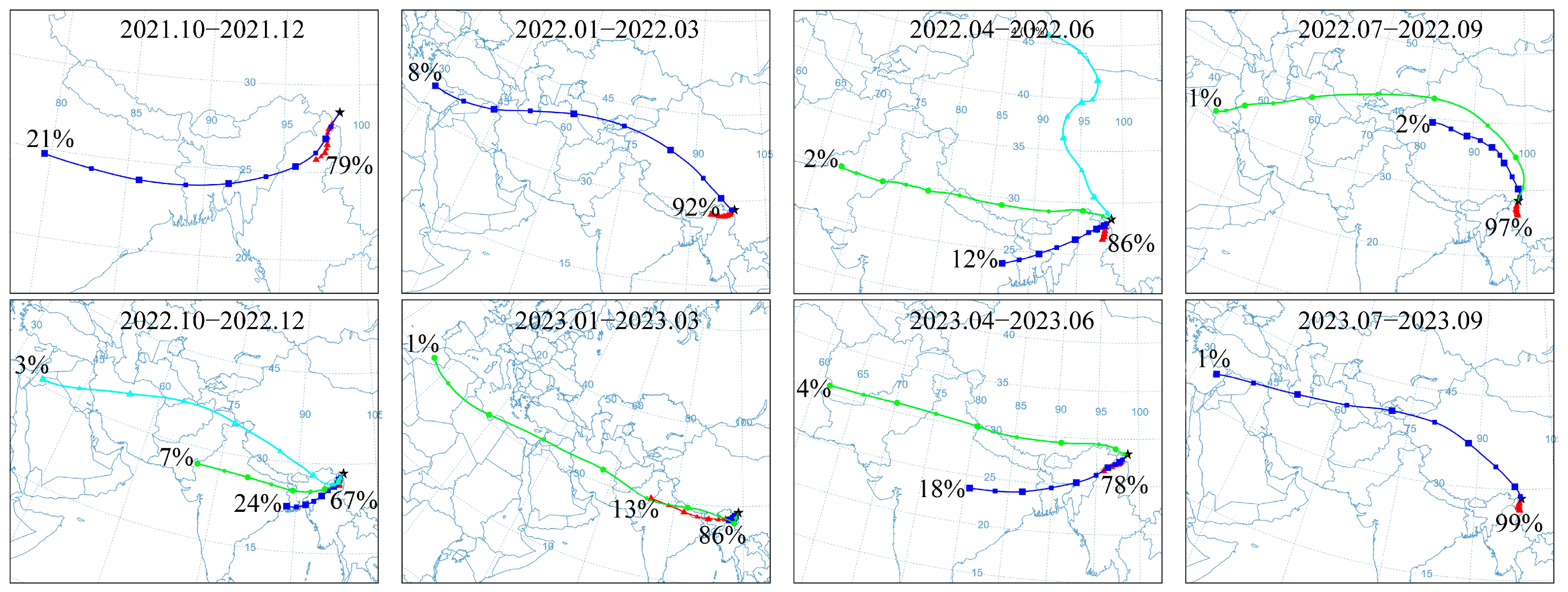
3.4. Air Masses Backward Trajectories
4. Discussion
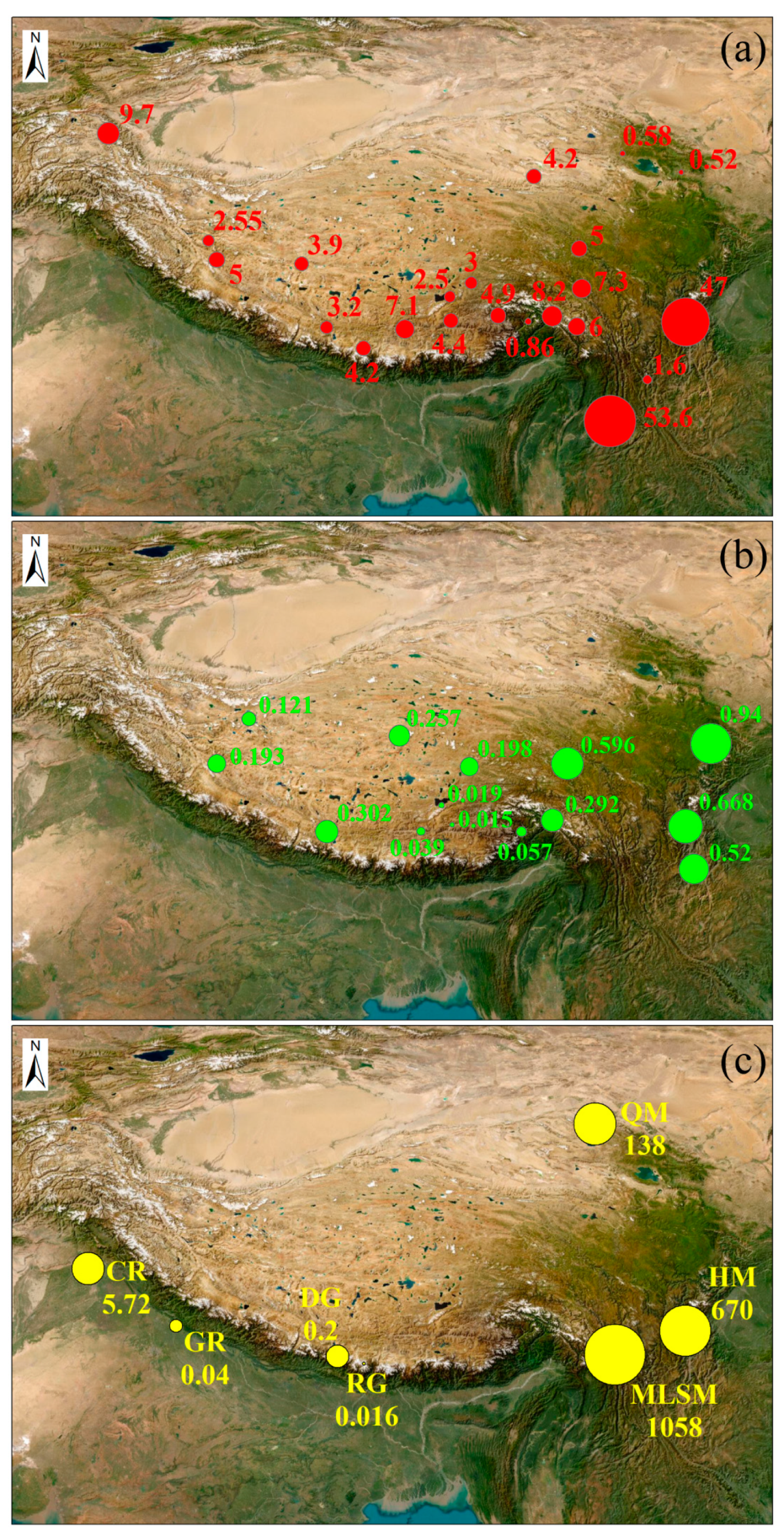
4.1. Comparison with Global Related Studies
4.2. Factors Influencing PCB Distribution
4.2.1. Local Environment Driven Pattern
4.2.2. Regional Atmospheric Origins
4.2.3. Impact of Melting Glaciers
4.3. Potential Sources
4.4. Ecotoxicological Risk
4.5. Health Risk Assessment
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PCBs | Polychlorinated biphenyls |
| POPs | Persistent organic pollutants |
| TP | Tibetan Plateau |
| US EPA | United States Environmental Protection Agency |
| LRAT | Long-range atmospheric transport |
| TEQs | Toxic equivalency concentrations |
| DL PCBs | Dioxin-like PCBs |
| non-DL PCBs | Non-dioxin-like PCBs |
| LoD | Limit of detection |
| HQ | Hazard quotient |
| ILCR | Incremental lifetime cancer risk |
| TEF | Toxic equivalency factor |
| CSF | Carcinogenic slope factor |
| NOAA | National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration |
| HYSPLIT | Hybrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory |
| CMC | Criterion maximum concentration |
| CCC | Criterion continuous concentration |
| AhR | Aryl hydrocarbon receptor |
References
- Sun, R.; Yu, J.; Liao, Y.; Chen, J.; Wu, Z.; Mai, B. Geographical Distribution and Risk Assessment of Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane and Its Metabolites in Perna Viridis Mussels from the Northern Coast of the South China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 151, 110819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, R.; Asghar, R.; Baqar, M.; Mahmood, A.; Alamdar, A.; Qadir, A.; Sohail, M.; Schäfer, R.B.; Musstjab Akber Shah Eqani, S.A. Assessment of Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) in the Himalayan Riverine Network of Azad Jammu and Kashmir. Chemosphere 2020, 240, 124762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouch, A.; Zaborska, A.; Mazurkiewicz, M.; Winogradow, A.; Pazdro, K. PCBs, HCB and PAHs in the Seawater of Arctic Fjords—Distribution, Sources and Risk Assessment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 164, 111980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, S.N.; Huber, C.; Asimakopoulos, A.G.; Steinnes, E.; Mikkelsen, Ø. Trace Elements and Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) in Terrestrial Compartments of Svalbard, Norwegian Arctic. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 685, 1127–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermanson, M.H.; Isaksson, E.; Hann, R.; Teixeira, C.; Muir, D.C.G. Atmospheric Deposition of Organochlorine Pesticides and Industrial Compounds to Seasonal Surface Snow at Four Glacier Sites on Svalbard, 2013–2014. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 9265–9273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravanipour, M.; Nabipour, I.; Yunesian, M.; Rastkari, N.; Mahvi, A.H. Exposure Sources of Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) and Health Risk Assessment: A Systematic Review in Iran. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 55437–55456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, D.O. Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs): Routes of Exposure and Effects on Human Health. Rev. Environ. Health 2006, 21, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Mao, S.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, C.; Sun, X.; Sun, J.; Liu, W. Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) in Soils from Typical Paddy Fields of China: Occurrence, Influencing Factors and Human Health Risks. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 307, 119567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, R.; Li, B.; Zhong, S.; Peng, G.; Li, J.; Ma, R.; Chen, Q.; Ni, J. Distribution, Source Identification, and Health Risk of Emerging Organic Contaminants in Groundwater of Xiong’an New Area, Northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 893, 164786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Dong, Z.; Baccolo, G.; Gao, W.; Li, Q.; Wei, T.; Qin, X. Distribution, Composition and Risk Assessment of PAHs and PCBs in Cryospheric Watersheds of the Eastern Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 890, 164234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Gong, P.; Yao, T. Long-Term Trends of Atmospheric Organochlorine Pollutants and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons over the Southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 624, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Yuan, H.; Jin, J.; Li, P.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y. Polychlorinated Biphenyl Concentrations in Pooled Serum from People in Different Age Groups from Five Chinese Cities. Chemosphere 2018, 198, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, J.; Yan, Z.; Liu, X.; Men, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Chao, W.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, X. Health Risk Assessment and Development of Human Health Ambient Water Quality Criteria for PCBs in Taihu Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 920, 170669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lušnic Polak, M.; Zlatić, E.; Demšar, L.; Žlender, B.; Polak, T. Degradation of PCBs in Dry Fermented Sausages during Drying/Ripening. Food Chem. 2016, 213, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnar, A.A.; Desor, F.; Marin, F.; Soulimani, R.; Nemos, C. Lactational Exposure to Low Levels of the Six Indicator Non-Dioxin-like Polychlorinated Biphenyls Induces DNA Damage and Repression of Neuronal Activity, in Juvenile Male Mice. Toxicology 2015, 328, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Wan, M.; Lin, K.; Chen, Y.; Wang, R.; Tan, L.; Wang, J. Spatiotemporal Distribution, Source Analysis and Ecological Risk Assessment of Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) in the Bohai Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 198, 115780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, S.; Liu, S.; Zhou, Y.; An, Q.; Zhou, X.; Mao, Z.; Wu, Y.; Liu, W. The Occurrence and Sources of Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) in Agricultural Soils across China with an Emphasis on Unintentionally Produced PCBs. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 271, 116171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Jones, K.C.; Li, J.; Sweetman, A.J.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lin, T.; Mao, S.; Li, K.; et al. Evidence for Major Contributions of Unintentionally Produced PCBs in the Air of China: Implications for the National Source Inventory. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 2163–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M.; Kawser Ahmed, M.; Saiful Islam, M.; Tokumura, M.; Masunaga, S. Occurrence, Distribution and Possible Sources of Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) in the Surface Water from the Bay of Bengal Coast of Bangladesh. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 167, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans: Polychlorinated Biphenyls and Polybrominated Biphenyls; IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans: Lyon, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Yan, S.; Chang, C.; Qu, C.; Tian, Y.; Song, J.; Guo, J. Occurrence, Potential Risk Assessment, and Source Apportionment of Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Water from Beiluo River. Water 2023, 15, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolska, L.; Mechlińska, A.; Rogowska, J.; Namieśnik, J. Sources and Fate of PAHs and PCBs in the Marine Environment. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 42, 1172–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, R.O.; Bermudez, B.S.; Tolentino, R.G.; Gonzalez, G.D.; León, S.V.y. Presence of Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) in Bottled Drinking Water in Mexico City. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 85, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragab, S.; El Sikaily, A.; El Nemr, A. Concentrations and Sources of Pesticides and PCBs in Surficial Sediments of the Red Sea Coast, Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2016, 42, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Masson-Delmotte, V.; Gao, J.; Yu, W.; Yang, X.; Risi, C.; Sturm, C.; Werner, M.; Zhao, H.; He, Y.; et al. A Review of Climatic Controls on Δ18O in Precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau: Observations and Simulations. Rev. Geophys. 2013, 51, 525–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Gong, P.; Yao, T. Atmospheric Processes of Organic Pollutants over a Remote Lake on the Central Tibetan Plateau: Implications for Regional Cycling. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 1401–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Xie, T.; Wang, P.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, G. Historical Trends of PCBs and PBDEs as Reconstructed in a Lake Sediment from Southern Tibetan Plateau. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 98, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, B.M.; Bharat, G.K.; Tayal, S.; Nizzetto, L.; Larssen, T. The Legal Framework to Manage Chemical Pollution in India and the Lesson from the Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs). Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 733–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) Learn About Polychlorinated Biphenyls. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/pcbs/learn-about-polychlorinated-biphenyls (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Exposure Factors Handbook; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2011.
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). National Primary Drinking Water Standards; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2001.
- Van den Berg, M.; Birnbaum, L.S.; Denison, M.; De Vito, M.; Farland, W.; Feeley, M.; Fiedler, H.; Hakansson, H.; Hanberg, A.; Haws, L.; et al. The 2005 World Health Organization Reevaluation of Human and Mammalian Toxic Equivalency Factors for Dioxins and Dioxin-Like Compounds. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 93, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) CASRN 1336-36-3; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1996.
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund (Volume 1) Human Health Evaluation Manual; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1989.
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Characterizing Risk and Hazard. In Human Health Risk Assessment Protocol; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.; Cao, S.; Yan, F.; Qin, N.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, K.; El-maleh, C.A.; Duan, X. Health Risks and Source Identification of Dietary Exposure to Indicator Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) in Lanzhou, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gong, P.; Yao, T.; Jones, K.C. Passive Air Sampling of Organochlorine Pesticides, Polychlorinated Biphenyls, and Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers Across the Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 2988–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.-X.; He, C.; Ma, Z.-H.; Ma, L.-H.; Zhaxi, Z.-M.; Wang, Y.; Jin, J. Levels and distribution of organochlorine pesticides and dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls in atmospheric particulates in Xining and Tianjun, Qinghai province, China. Chin. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 36, 402–407. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Gong, P.; Wang, C.; Sun, D. Seasonal Variation and Source Analysis of Persistent Organic Pollutants in the Atmosphere over the Western Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 24052–24063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Schramm, K.-W.; Wang, T.; Henkelmann, B.; Zheng, X.; Fu, J.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, G. Environmental Fate and Behavior of Persistent Organic Pollutants in Shergyla Mountain, Southeast of the Tibetan Plateau of China. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 191, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Li, J.; Zheng, Q.; Bing, H.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Luo, C.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Pan, S.; et al. Forest Filter Effect versus Cold Trapping Effect on the Altitudinal Distribution of PCBs: A Case Study of Mt. Gongga, Eastern Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 14377–14385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Li, J.; Chakraborty, P.; Li, H.; Liu, X. Long-Range Atmospheric Transport of Persistent Organochlorinated Compounds from South and Mainland South-Eastern Asia to a Remote Mountain Site in South-Western China. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 3119–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Wang, X.; Sheng, J.; Wang, H.; Yuan, X.; He, Y.; Qian, Y.; Yao, T. Seasonal Variations and Sources of Atmospheric Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Organochlorine Compounds in a High-Altitude City: Evidence from Four-Year Observations. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 233, 1188–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Nizzetto, L.; Mulder, M.D.; Sáňka, O.; Lammel, G.; Li, J.; Bing, H.; Liu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Luo, C.; et al. Does an Analysis of Polychlorinated Biphenyl (PCB) Distribution in Mountain Soils across China Reveal a Latitudinal Fractionation Paradox? Environ. Pollut. 2014, 195, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, N.; Pan, J.; Tang, H.; Chen, S.; Chen, D.; Zhu, X.; Lu, G.; Yang, Y. Organochlorine Pesticides and Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Surface Soils from Ruoergai High Altitude Prairie, East Edge of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 478, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Li, H.; Xie, H.; Tang, C.; Han, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, W. Polychlorinated Dibenzo-p-Dioxins and Dibenzofurans and Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Surface Soil from the Tibetan Plateau. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 2041–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sheng, J.; Gong, P.; Xue, Y.; Yao, T.; Jones, K.C. Persistent Organic Pollutants in the Tibetan Surface Soil: Spatial Distribution, Air-Soil Exchange and Implications for Global Cycling. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 170, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Schramm, K.-W.; Wang, T.; Henkelmann, B.; Fu, J.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, G. Lichen, Moss and Soil in Resolving the Occurrence of Semi-Volatile Organic Compounds on the Southeastern Tibetan Plateau, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 518–519, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yao, T.; Wang, P.; Wei-Yang; Tian, L. The Recent Deposition of Persistent Organic Pollutants and Mercury to the Dasuopu Glacier, Mt. Xixiabangma, Central Himalayas. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 394, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.-H.; Choi, S.-D.; Park, H.; Baek, S.-Y.; Hong, S.; Chang, Y.-S. Atmospheric Deposition of Persistent Organic Pollutants to the East Rongbuk Glacier in the Himalayas. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 408, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, A.; Malik, R.N.; Li, J.; Zhang, G. Levels, Distribution Profile, and Risk Assessment of Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) in Water and Sediment from Two Tributaries of the River Chenab, Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 7847–7855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, B.M.; Nizzetto, L.; Bharat, G.K.; Tayal, S.; Melymuk, L.; Sáňka, O.; Přibylová, P.; Audy, O.; Larssen, T. Melting Himalayan Glaciers Contaminated by Legacy Atmospheric Depositions Are Important Sources of PCBs and High-Molecular-Weight PAHs for the Ganges Floodplain during Dry Periods. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 206, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Wu, L.; Sun, Y.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Wang, G. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Soils of the Central Tibetan Plateau, China: Distribution, Sources, Transport and Contribution in Global Cycling. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 203, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Liu, W.; Liu, X.; Westgate, J.N.; Wania, F. Cold-Trapping of Persistent Organic Pollutants in the Mountain Soils of Western Sichuan, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 9086–9091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, K.; Kozioł, K.; Luks, B.; Chmiel, S.; Ruman, M.; Marć, M.; Namieśnik, J.; Polkowska, Ż. The Role of Atmospheric Precipitation in Introducing Contaminants to the Surface Waters of the Fuglebekken Catchment, Spitsbergen. Polar Res. 2015, 34, 24207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Chakraborty, P.; Li, J.; Sampathkumar, P.; Balasubramanian, T.; Kathiresan, K.; Takahashi, S.; Subramanian, A.; Tanabe, S.; Jones, K.C. Passive Atmospheric Sampling of Organochlorine Pesticides, Polychlorinated Biphenyls, and Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers in Urban, Rural, and Wetland Sites along the Coastal Length of India. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 8218–8223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurl, O.; Potter, J.R.; Obbard, J.P.; Durville, C. Persistent Organic Pollutants in the Equatorial Atmosphere over the Open Indian Ocean. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 1454–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioia, R.; Nizzetto, L.; Lohmann, R.; Dachs, J.; Temme, C.; Jones, K.C. Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) in Air and Seawater of the Atlantic Ocean: Sources, Trends and Processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 1416–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gioia, R.; Lohmann, R.; Dachs, J.; Temme, C.; Lakaschus, S.; Schulz-Bull, D.; Hand, I.; Jones, K.C. Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Air and Water of the North Atlantic and Arctic Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manodori, L.; Gambaro, A.; Piazza, R.; Ferrari, S.; Stortini, A.M.; Moret, I.; Capodaglio, G. PCBs and PAHs in Sea-Surface Microlayer and Sub-Surface Water Samples of the Venice Lagoon (Italy). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2006, 52, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioia, R.; Dachs, J.; Nizzetto, L.; Lohmann, R.; Jones, K.C. Atmospheric Transport, Cycling and Dynamics of Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) from Source Regions to Remote Oceanic Areas. In Occurrence, Fate and Impact of Atmospheric Pollutants on Environmental and Human Health; ACS Symposium Series; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; Volume 1149, pp. 1–3. ISBN 9780841228900. [Google Scholar]
- Falconer, R.L.; Bidleman, T.F. Vapor Pressures and Predicted Particle/Gas Distributions of Polychlorinated Biphenyl Congeners as Functions of Temperature and Ortho-Chlorine Substitution. Atmos. Environ. 1994, 28, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górski, J.; Bąk, Ł.; Sałata, A.; Górska, K.; Rabajczyk, A. Changes of Heavy Metal Concentration in Rainfall Wastewater in Urban Catchment. Desalin. Water Treat. 2018, 117, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Lin, Z.; Wu, X.; Shen, Z.; Yuan, F.; Huang, C.; Li, C. Climate of Tibet; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1984; pp. 112–114. [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald, R.W.; Harner, T.; Fyfe, J. Recent Climate Change in the Arctic and Its Impact on Contaminant Pathways and Interpretation of Temporal Trend Data. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 342, 5–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Wang, N.; Wu, X.; Xie, J.; He, J.; Jiang, X. Aliphatic and Polyaromatic Hydrocarbons in Snow/Ice and Glacier Meltwater in the Qiyi Glacier, Qilian Mountains: Sources and Distribution. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2010, 32, 706–713. [Google Scholar]
- Bogdal, C.; Schmid, P.; Zennegg, M.; Anselmetti, F.S.; Scheringer, M.; Hungerbühler, K. Blast from the Past: Melting Glaciers as a Relevant Source for Persistent Organic Pollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 8173–8177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Lin, L.; He, J.; Pan, X.; Wu, X.; Yang, Y.; Jing, Z.; Zhang, S.; Yin, G. PAHs in the Surface Water and Sediments of the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Han River, China: Occurrence, Source, and Probabilistic Risk Assessment. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 164, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jianrong, C.; Yanjun, L.; Sujie, Y. The Concentrations and Sources of PAHs and PCBs in Soil from an Oil Field and Estuary in the Yellow River Delta, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1028299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Lu, Y.; Dawson, R.W.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, T.; Liu, W.; Ren, H. A Spatial Temporal Assessment of Pollution from PCBs in China. Chemosphere 2005, 60, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Miao, Q.; Pei, G.; Nan, Y.; Yu, S.; Mei, X.; Feng, W. Distribution, Sources, and Risk of Polychlorinated Biphenyls in the Largest Irrigation Area in the Yellow River Basin. Water 2022, 14, 3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Hirai, Y.; Kato, M.; Urano, K.; Masunaga, S. Detailed PCB Congener Patterns in Incinerator Flue Gas and Commercial PCB Formulations (Kanechlor). Chemosphere 2004, 55, 539–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tongu, S.M.; Sha’Ato, R.; Wase, G.A.; Okonkwo, J.O.; Vesuwe, R.N. Organochlorine Pesticides and Polychlorinated Biphenyls in City Drains in Makurdi, Central Nigeria: Seasonal Variations, Source Apportionment and Risk Assessment. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Dong, J.; Huang, Z.; Liu, C.; Qiao, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Zheng, B.; Shen, J. Polychlorinated Biphenyls in the Drinking Water Source of the Yangtze River: Characteristics and Risk Assessment. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, A.; Liu, X.; Bidegain, G.; Zong, H.; Guan, C.; Song, M.; Qu, L.; Huang, W.; et al. Levels, Sources and Potential Risks of Polychlorinated Biphenyls and Organochlorine Pesticides in Sediments of Qingduizi Bay, China: Does Developing Mariculture Matter? Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Xu, S.; Song, W.; Ye, H.; Huang, J.; Liu, B.; Dong, B.; Xu, Z. Trace Metals, Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Polychlorinated Biphenyls in the Surface Sediments from Sanya River, China: Distribution, Sources and Ecological Risk. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 294, 118614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Li, J.; Albanese, S.; Lima, A.; Wang, M.; Sacchi, M.; Molisso, F.; De Vivo, B. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Sediments of the Gulfs of Naples and Salerno, Southern Italy: Status, Sources and Ecological Risk. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 161, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desforges, J.-P.; Hall, A.; McConnell, B.; Rosing-Asvid, A.; Barber, J.L.; Brownlow, A.; De Guise, S.; Eulaers, I.; Jepson, P.D.; Letcher, R.J.; et al. Predicting Global Killer Whale Population Collapse from PCB Pollution. Science. 2018, 361, 1373–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 3838-2002; Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water. Beijing, China, 2002.
- Chakraborty, P.; Khuman, S.N.; Selvaraj, S.; Sampath, S.; Devi, N.L.; Bang, J.J.; Katsoyiannis, A. Polychlorinated Biphenyls and Organochlorine Pesticides in River Brahmaputra from the Outer Himalayan Range and River Hooghly Emptying into the Bay of Bengal: Occurrence, Sources and Ecotoxicological Risk Assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 998–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Government of Japan. Dioxins; Government of Japan: Tokyo, Japan, 2012.
- Omar, W.A.; Mahmoud, H.M. Risk Assessment of Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) and Trace Metals in River Nile up- and Downstream of a Densely Populated Area. Environ. Geochem. Health 2017, 39, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Berg, M.; Birnbaum, L.; Bosveld, A.T.; Brunström, B.; Cook, P.; Feeley, M.; Giesy, J.P.; Hanberg, A.; Hasegawa, R.; Kennedy, S.W.; et al. Toxic Equivalency Factors (TEFs) for PCBs, PCDDs, PCDFs for Humans and Wildlife. Environ. Health Perspect. 1998, 106, 775–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, T.R.; DeVito, M.J. Non-Dioxin-Like PCBS: Effects and Consideration in Ecological Risk Assessment; USEPA: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Goudarzi, G.; Idani, E.; Alavi, N.; Salmanzadeh, S.; Babaei, A.A.; Geravandi, S.; Mohammadi, M.J.; Mahboubi, M.; Moradi, M. Association of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons of the Outdoor Air in Ahvaz, Southwest Iran during Warm-Cold Season. Toxin Rev. 2017, 36, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerzynska, J.; Podlecka, D.; Polanska, K.; Hanke, W.; Stelmach, I.; Stelmach, W. Prenatal and Postnatal Exposure to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Allergy Symptoms in City Children. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2017, 45, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameter | Meaning | Unit | Selected Values | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Infants | Toddlers | Children | Adolescents | Adults | |||
| IR | Ingestion rate of water | L/d | 0.911 | 0.861 | 1.28 | 1.414 | 1.85 |
| EF | Exposure frequency | Ds/yr | 365 | ||||
| ED | Exposure duration | Yrs | 1 | 2 | 8 | 16 | 40 |
| BW | Body weight | kg | 6.8 | 12.6 | 24.1 | 51.1 | 63.1 |
| AT | Average time for carcinogenic/non-carcinogenic effect | Ds | 25,550/10,950 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Yao, Y.; Wen, X.; Zhang, R.; Liu, R. Glacial Waters Under Threat: Risk Assessment and Source Identification of Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Meili Snow Mountains, Southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Toxics 2025, 13, 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050391
Zhang H, Yao Y, Wen X, Zhang R, Liu R. Glacial Waters Under Threat: Risk Assessment and Source Identification of Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Meili Snow Mountains, Southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Toxics. 2025; 13(5):391. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050391
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Huawei, Yan Yao, Xinyu Wen, Rui Zhang, and Rui Liu. 2025. "Glacial Waters Under Threat: Risk Assessment and Source Identification of Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Meili Snow Mountains, Southeastern Tibetan Plateau" Toxics 13, no. 5: 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050391
APA StyleZhang, H., Yao, Y., Wen, X., Zhang, R., & Liu, R. (2025). Glacial Waters Under Threat: Risk Assessment and Source Identification of Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Meili Snow Mountains, Southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Toxics, 13(5), 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050391






