Ellagic Acid Alleviates Imidacloprid-Induced Thyroid Dysfunction via PI3K/Akt/mTOR-Mediated Autophagy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Network Pharmacology and Toxicology
2.2.1. Acquisition of “Ellagic Acid”, “Imidacloprid”, and “Thyroid Dysfunction” Targets
2.2.2. Identification of Shared Targets and Construction of Protein–Protein Interactions
2.2.3. Network Construction and Examination
2.3. Preparation and Characterization of Ellagic Acid-Loaded Novasomes
2.4. Animals and Ethics
2.4.1. Experimental Design
2.4.2. Specimen and Serum Collection
2.4.3. Biochemical Analyses
Assessment of Thyroid Function
Estimation of Oxidative Stress Markers
Estimation of Inflammatory Mediators
2.4.4. Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qPCR) Analysis of mRNA Expression
RNA Extraction
SYBR Green RT-PCR
Analysis of the SYBR Green RT-PCR Results
2.4.5. Histopathological Technique
2.4.6. Immunohistochemical Study
2.4.7. Morphometric Study
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
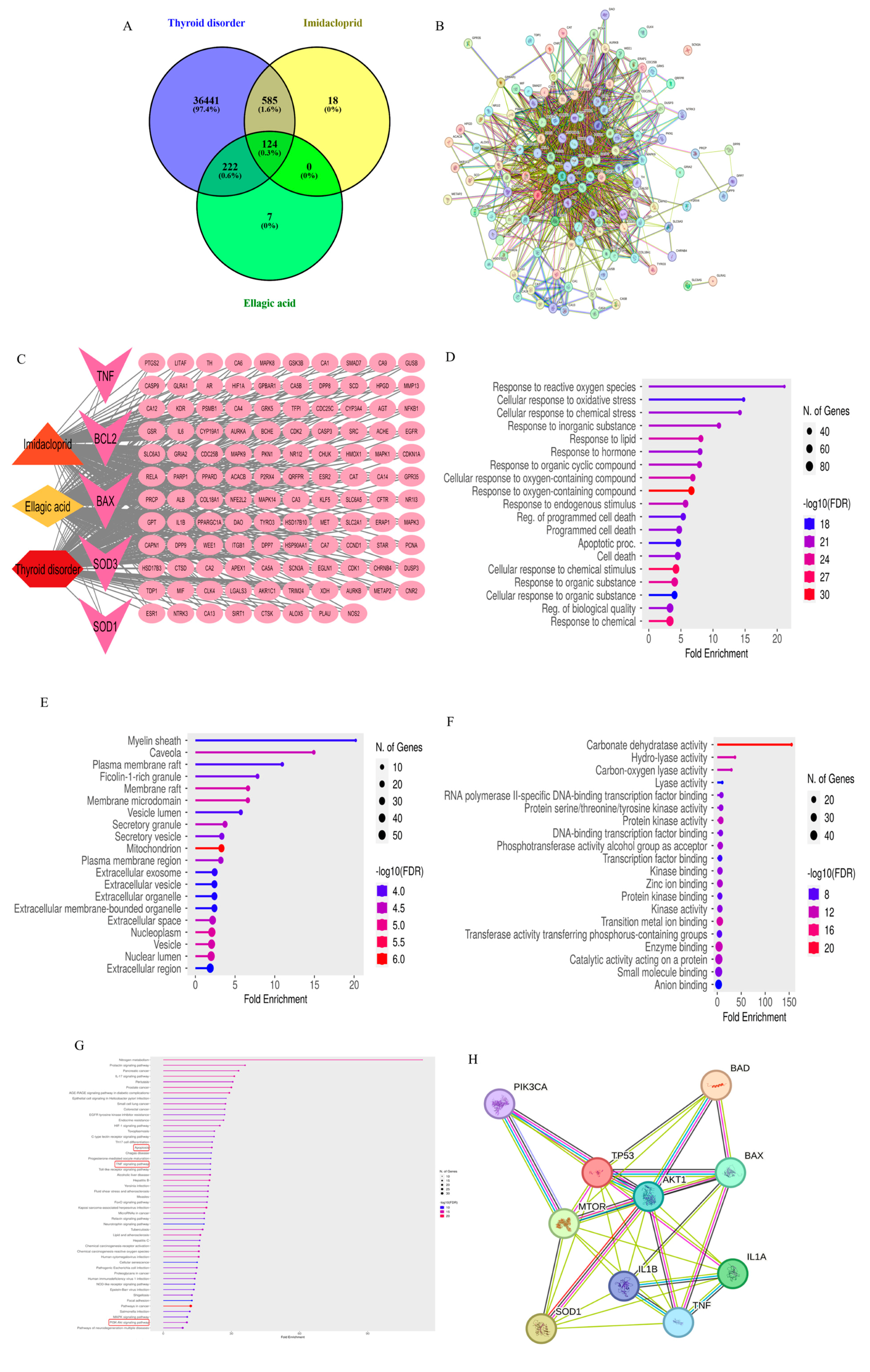
3.1. Network Pharmacology
3.1.1. Pharmacokinetics, Drug-Likeness, and Physicochemical Property Estimation
3.1.2. Target Collection and Network Construction
3.2. Preparation and Characterization of Ellagic Acid-Loaded Novasomes
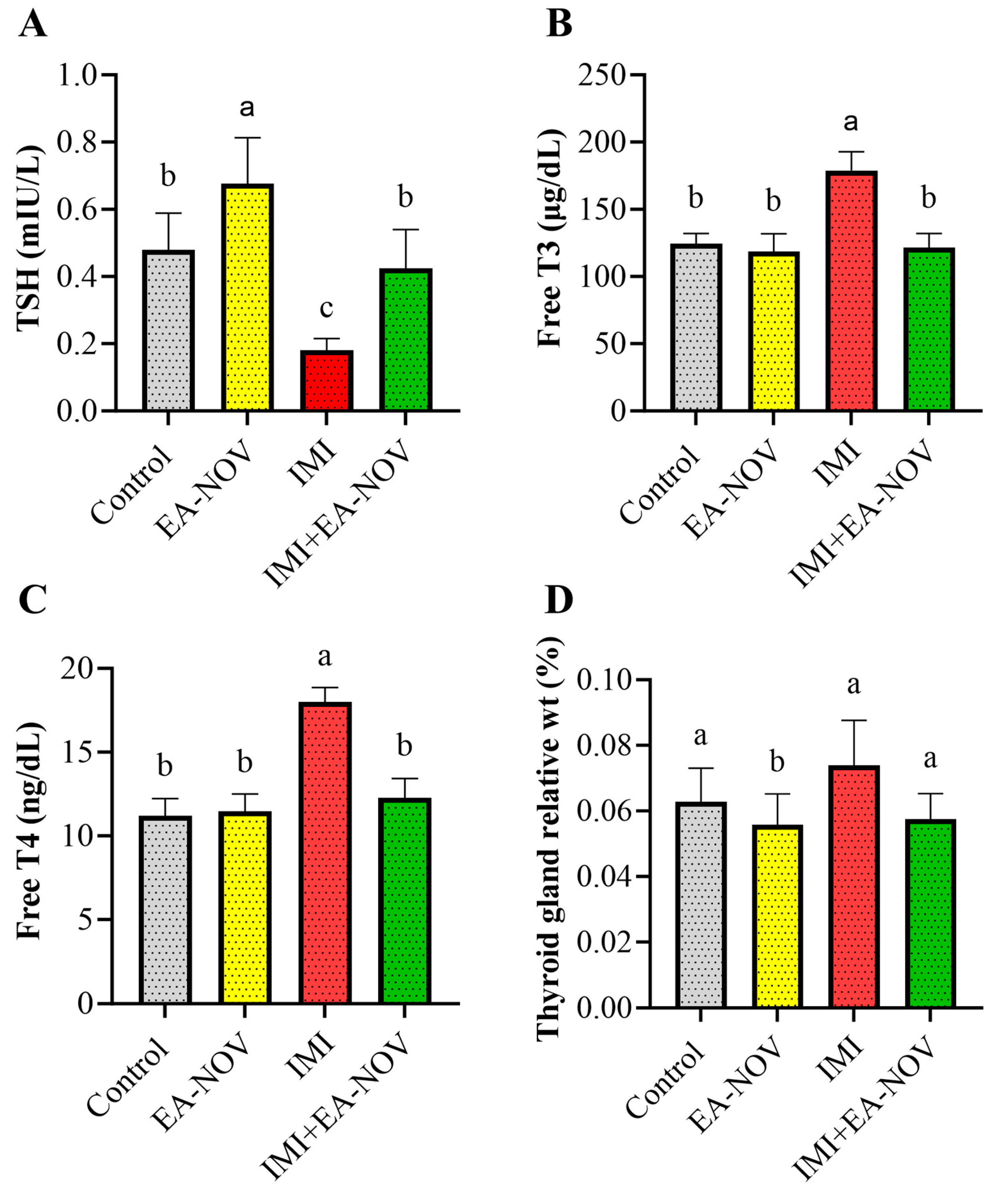
3.3. Effect of EA-NOV Administration on Serum TSH, Free T3, and Free T4 Levels in IMI-Intoxicated Rats
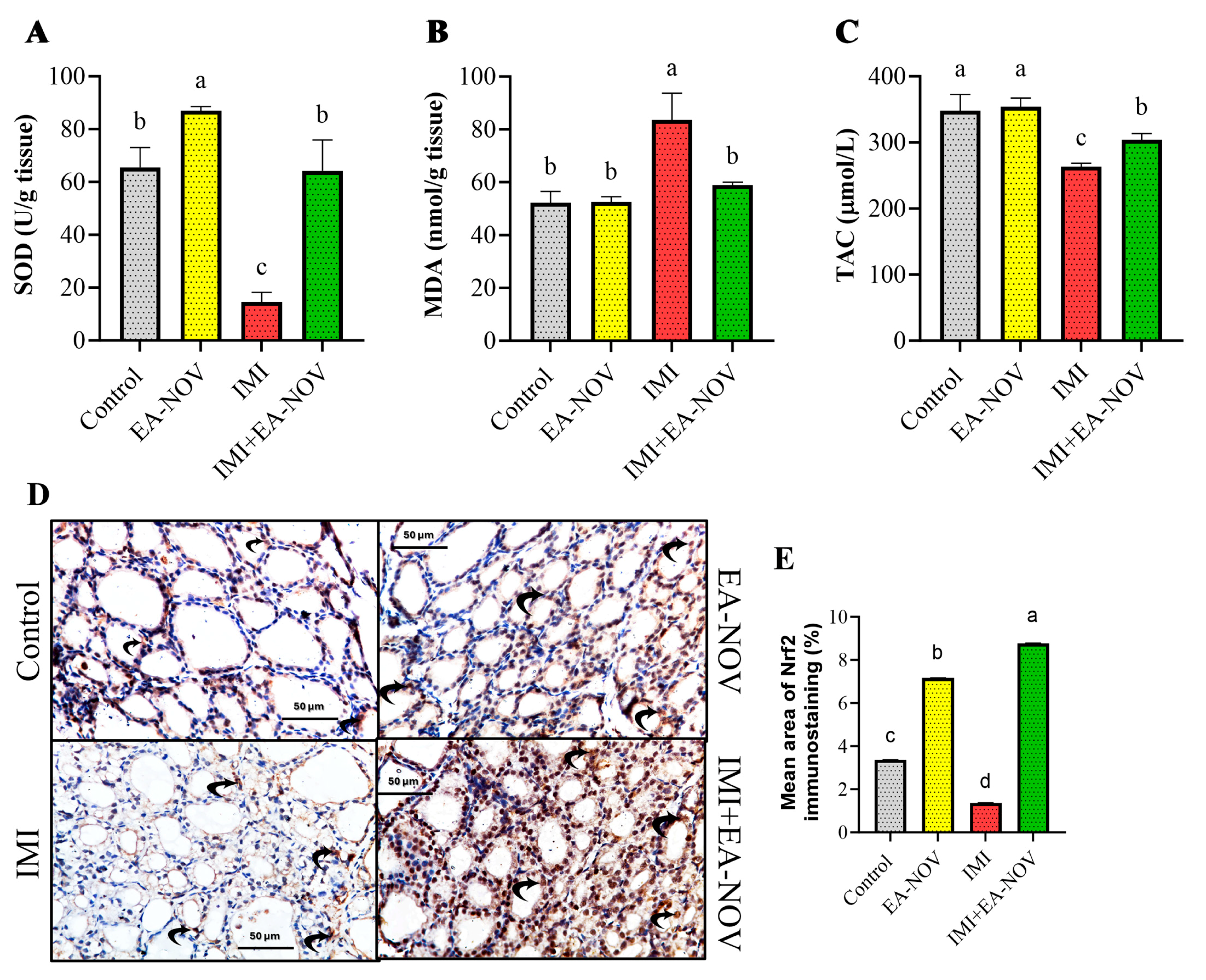
3.4. Effect of EA-NOV Administration on the Antioxidant Capacity of the Thyroid Gland in IMI-Intoxicated Rats
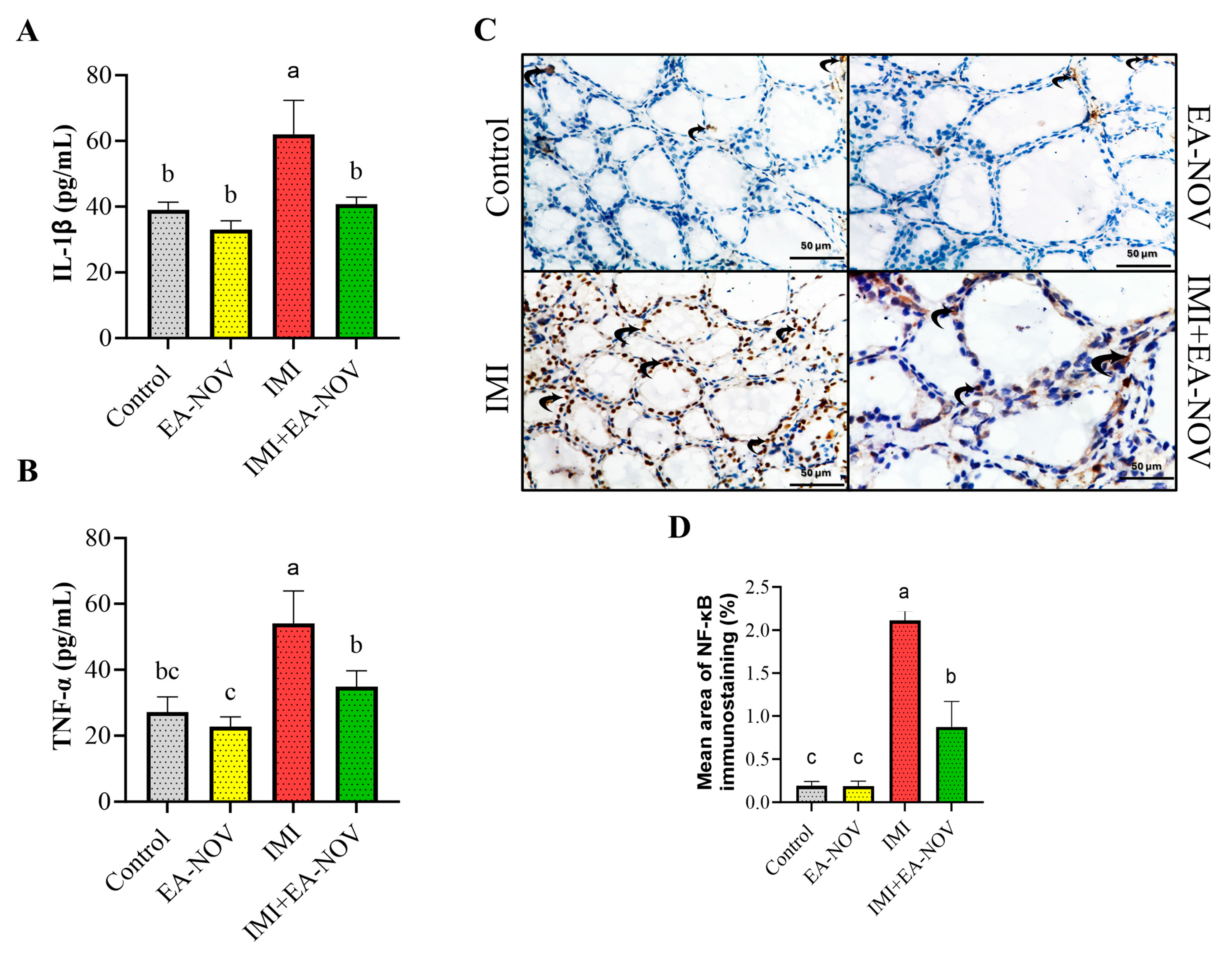
3.5. Effect of EA-NOV Administration on Thyroid Tissue Inflammation Markers in IMI-Intoxicated Rats
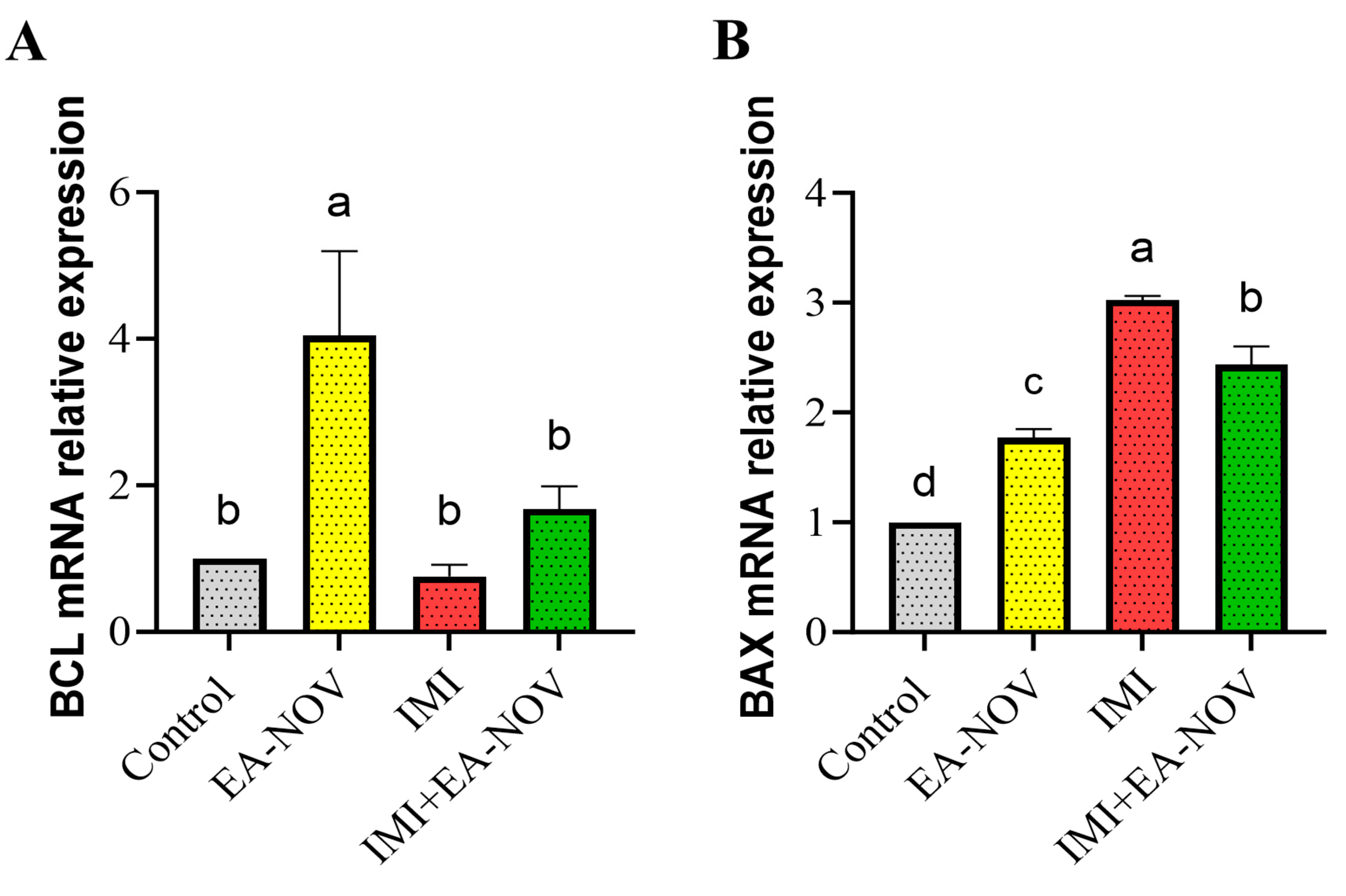
3.6. Effect of EA-NOV Administration on the Expression of Apoptosis-Related Genes of the Thyroid Gland in IMI-Intoxicated Rats
3.7. Effect of EA-NOV Administration on the Expression of Autophagy-Related Genes of the Thyroid Gland in IMI-Intoxicated Rats
3.7.1. Autophagy-Inhibitory Mechanisms
3.7.2. Autophagy-Induction Mechanisms
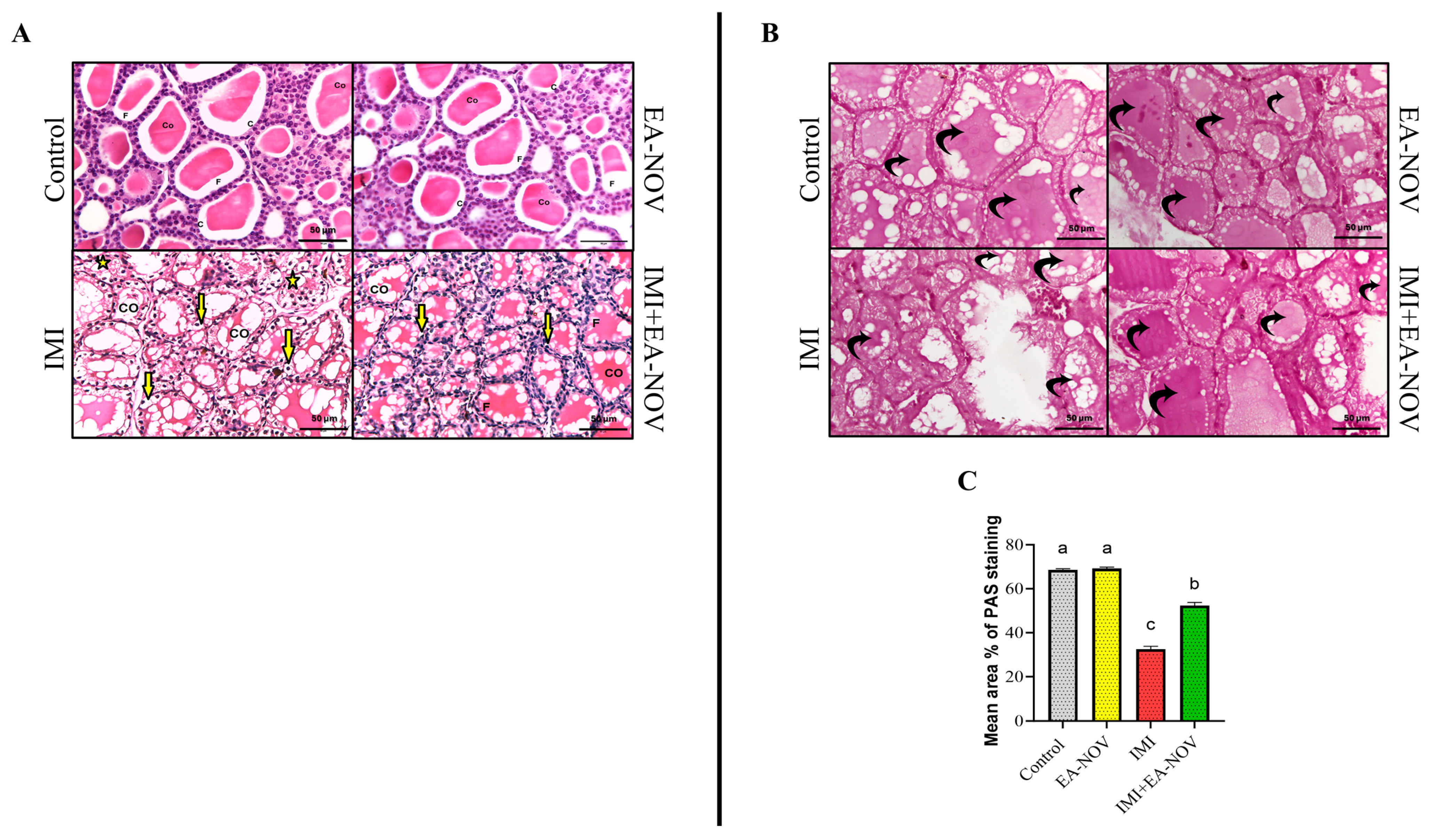
3.8. Histological Findings
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vohra, P.; Khera, K. A Three Generation Study with Effect of Imidacloprid in Rats: Biochemical and Histopathological Investigation. Toxicol. Int. 2015, 22, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, P.; Chang, J.; Li, W.; Yang, L.; Tian, H. Unraveling the toxic effects of neonicotinoid insecticides on the thyroid endocrine system of lizards. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.-P.; Li, J.-W.; Yang, F.-W.; Yin, X.-F.; Ren, F.-Z.; Fang, B.; Pang, G.-F. Spermiogenesis toxicity of imidacloprid in rats, possible role of CYP3A4. Chemosphere 2021, 282, 131120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, X.; Zhang, C.; Liu, H.; Wu, R.; Tian, D.; Ruan, J.; Zhang, T.; Huang, M.; Ying, G. Occurrence and distribution of neonicotinoid insecticides in surface water and sediment of the Guangzhou section of the Pearl River, South China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 251, 892–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, A.F.; Bennekou, S.H.; Hart, A.; Mohimont, L.; Wolterink, G. Mechanisms underlying disruptive effects of pesticides on the thyroid function. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2020, 19, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochman, J.; Jakubczyk, K.; Bargiel, P.; Janda-Milczarek, K. The Influence of Oxidative Stress on Thyroid Diseases. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.; Kar, A.; Singh, M.; Singh, R.K.; Ganeshpurkar, A. Syringic acid, a novel thyroid hormone receptor-β agonist, ameliorates propylthiouracil-induced thyroid toxicity in rats. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, e22814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Miao, Z.; Wang, S.; Wu, H.; Xu, S. Exposure to imidacloprid induce oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, inflammation, apoptosis and mitophagy via NF-kappaB/JNK pathway in grass carp hepatocytes. Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2022, 120, 674–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qumsani, A.T. Exploring the Effects of Imidacloprid on Liver Health and the Microbiome in Rats: A Comprehensive Study. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Huang, X.; Lu, S.; Deng, H.; Gan, H.; Huang, R.; Zhang, B. miRNA-125a modulates autophagy of thyroiditis through PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 17, 2465–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.; Wei, X.; Ju, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Li, X.; Song, Z.; Luo, L.; et al. Protective Effect of Photobiomodulation against Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Oxidative Damage by Promoting Autophagy through Inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway in MC3T3-E1 Cells. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 7223353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, C.; Cheng, B.; Xiong, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Wan, E.; He, Y. Genipin promotes the apoptosis and autophagy of neuroblastoma cells by suppressing the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 20231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.-Y.; Hsieh, Y.-H.; Ting, Y.-H.; Lee, C.-C.; Tsai, J.-P. Ellagic acid ameliorates renal fibrogenesis by blocking epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Tzu Chi Med. J. 2024, 36, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannino, F.; Imbesi, C.; Bitto, A.; Minutoli, L.; Squadrito, F.; D’Angelo, T.; Booz, C.; Pallio, G.; Irrera, N. Anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of ellagic and punicic acid in an in vitro model of cardiac fibrosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 162, 114666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadinejad, A.; Mohajeri, T.; Aleyaghoob, G.; Heidarian, F.; Oskuee, R.K. Ellagic acid as a potent anticancer drug: A comprehensive review on in vitro, in vivo, in silico, and drug delivery studies. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2022, 69, 2323–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, W.S.; Alkarim, S.; Moulay, M.; Alrefeai, G.; Alkudsy, F.; Hakeem, K.R.; Iskander, A. Modulation of the Tumor Microenvironment by Ellagic Acid in Rat Model for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Potential Target against Hepatic Cancer Stem Cells. Cancers 2023, 15, 4891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, A.; Gok, O.; Beyaz, S.; Arslan, E.; Erman, O.; Ağca, C.A. The preventive effect of ellagic acid on brain damage in rats via regulating of Nrf-2, NF-kB and apoptotic pathway. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warpe, V.S.; Mali, V.R.; Bodhankar, S.L.; Mahadik, K.R. Cardioprotective effect of ellagic acid on doxorubicin induced cardiotoxicity in wistar rats. J. Acute Med. 2015, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, M.; Bayrami, D.; Moghadam, A.A.; Jamali, Z.; Salimi, A. Pretreatment of ellagic acid protects ifosfamide-induced acute nephrotoxicity in rat kidneys: A mitochondrial, histopathological and oxidative stress approaches. Toxicol. Rep. 2023, 10, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, M.; Ying, X.; Zhou, C. Ellagic acid protects rats from chronic renal failure via MiR-182/FOXO3a axis. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 138, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramec Skledar, D.; Tomašič, T.; Dolenc, M.S.; Mašič, L.P.; Zega, A. Evaluation of endocrine activities of ellagic acid and urolithins using reporter gene assays. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Dalmazi, G.; Giuliani, C. Plant constituents and thyroid: A revision of the main phytochemicals that interfere with thyroid function. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 152, 112158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, S.M.; Measer, A.A. Effect of Hyperthyroidism on Lipid Metabolism and Evaluation of the Protective Role of Pomegranate Juice against the Risk of Oxidative Stress in Albino Rats. Int. J. Drug Deliv. Technol. 2022, 12, 373–378. [Google Scholar]
- González-Sarrías, A.; García-Villalba, R.; Núñez-Sánchez, M.Á.; Tomé-Carneiro, J.; Zafrilla, P.; Mulero, J.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A.; Espín, J.C. Identifying the limits for ellagic acid bioavailability: A crossover pharmacokinetic study in healthy volunteers after consumption of pomegranate extracts. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 19, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, A.B.; Salama, A.; Al-Samadi, I.E.I. Formulation, optimisation, and evaluation of Lornoxicam-loaded Novasomes for targeted ulcerative colitis therapy: In vitro and in vivo investigations. J. Drug Target. 2025; accepted. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 5281855, E.A. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Ellagic-Acid (accessed on 31 January 2025).
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 86287518, I.P. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Imidacloprid (accessed on 31 January 2025).
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.P.; Wiegers, T.C.; Johnson, R.J.; Sciaky, D.; Wiegers, J.; Carolyn, J. Mattingly Comparative Toxicogenomics Database (CTD): Update 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D1257–D1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissTargetPrediction: Updated data and new features for efficient prediction of protein targets of small molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W357–W364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickel, J.; Gohlke, B.-O.; Erehman, J.; Banerjee, P.; Rong, W.W.; Goede, A.; Dunkel, M.; Preissner, R. SuperPred: Update on drug classification and target prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W26–W31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.; Arndt, D.; Pon, A.; Sajed, T.; Guo, A.C.; Djoumbou, Y.; Knox, C.; Wilson, M.; Liang, Y.; Grant, J.; et al. T3DB: The toxic exposome database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D928–D934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelzer, G.; Rosen, N.; Plaschkes, I.; Zimmerman, S.; Twik, M.; Fishilevich, S.; Stein, T.I.; Nudel, R.; Lieder, I.; Mazor, Y.; et al. The GeneCards Suite: From Gene Data Mining to Disease Genome Sequence Analyses. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2016, 54, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochoa, D.; Hercules, A.; Carmona, M.; Suveges, D.; Baker, J.; Malangone, C.; Lopez, I.; Miranda, A.; Cruz-Castillo, C.; Fumis, L.; et al. McDonagh The next-generation Open Targets Platform: Reimagined, redesigned, rebuilt. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D1353–D1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The UniProt, C. UniProt: The Universal Protein Knowledgebase in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D523–D531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardou, P.; Mariette, J.; Escudié, F.; Djemiel, C.; Klopp, C. jvenn: An interactive Venn diagram viewer. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Gable, A.L.; Fang, T.; Doncheva, N.T.; Pyysalo, S.; et al. The STRING database in 2023: Protein–protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T.J.G.R. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.X.; Jung, D.; Yao, R. ShinyGO: A graphical gene-set enrichment tool for animals and plants. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 2628–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Emam, M.M.; Behairy, A.; Mostafa, M.; Khamis, T.; Osman, N.M.S.; Alsemeh, A.E.; Mansour, M.F. Chrysin-loaded PEGylated liposomes protect against alloxan-induced diabetic neuropathy in rats: The interplay between endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy. Biol. Res. 2024, 57, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosallam, S.; Ragaie, M.H.; Moftah, N.H.; Elshafeey, A.H.; Abdelbary, A.A. Use of Novasomes as a Vesicular Carrier for Improving the Topical Delivery of Terconazole: In Vitro Characterization, In Vivo Assessment and Exploratory Clinical Experimentation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornélio Favarin, D.; Teixeira, M.M.; de Andrade, E.L.; de Freitas Alves, C.; Chica, J.E.L.; Sorgi, C.A.; Faccioli, L.H.; Paula, A.P. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Ellagic Acid on Acute Lung Injury Induced by Acid in Mice. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 164202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aishwarya, V.; Solaipriya, S.; Sivaramakrishnan, V. Role of ellagic acid for the prevention and treatment of liver diseases. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 2925–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. The WHO Recommended Classification of Pesticides by Hazard and Guidelines to Classification 2009. WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mikolić, A.; Karačonji, I.B. Imidacloprid as reproductive toxicant and endocrine disruptor: Investigations in laboratory animals. Arch. Ind. Hyg. Toxicol. 2018, 69, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomlin, C.D.S. The pesticides manual: A world compendium. Br. Crop Prot. Counc. 2006, 14, 351. [Google Scholar]
- Pardridge, W.M.; Mietus, L.J. Influx of Thyroid Hormones into Rat Liver In Vivo: Differential Availability of Thyroxine and Triiodothyronine Bound by Plasma Proteins. J. Clin. Investig. 1980, 66, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.S.; Reed, A.; Chen, F.; Stewart, C.N. Statistical analysis of real-time PCR data. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, L.T. 7—Microtomy for paraffin and frozen sections. In Bancroft’s Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques, 8th ed.; Suvarna, S.K., Layton, C., Bancroft, J.D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplin, A.J. Manual of histological techniques. J. D. Bancroft and H. C. Cook. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, London, Melbourne, New York, 1984. No. of pages: Ii + 274. Price: £12.50. ISBN: 0 443 02870 2. J. Pathol. 1985, 145, 355–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, F.; Xiao, Y.; Shi, L. Inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway promotes autophagy and relieves hyperalgesia in diabetic rats. NeuroReport 2020, 31, 644–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.P.; Mohanty, B. The neonicotinoid pesticide imidacloprid and the dithiocarbamate fungicide mancozeb disrupt the pituitary–thyroid axis of a wildlife bird. Chemosphere 2015, 122, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Gazzar, W.B.; Bayoumi, H.; Youssef, H.S.; Ibrahim, T.A.; Abdelfatah, R.M.; Gamil, N.M.; Iskandar, M.K.; Abdel-Kareim, A.M.; Abdelrahman, S.M.; Gebba, M.A.; et al. Role of IRE1α/XBP1/CHOP/NLRP3 Signalling Pathway in Neonicotinoid Imidacloprid-Induced Pancreatic Dysfunction in Rats and Antagonism of Lycopene: In Vivo and Molecular Docking Simulation Approaches. Toxics 2024, 12, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samala, S.; Mekala, L.; Doppalapudi, M.; Alla, G.R.; Rao, R. Evaluation of Imidacloprid Induced Changes in Thyroid Gland and its Amelioration with Withania somnifera in Wistar Rats. J. Vet. Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 19, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Kumar, R.; Ganguly, R.; Singh, A.K.; Rana, H.K.; Pandey, A.K. Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and hepatoprotective activities of Terminalia bellirica and its bioactive component ellagic acid against diclofenac induced oxidative stress and hepatotoxicity. Toxicol. Rep. 2021, 8, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Huang, H.; Yu, Y.; Li, L.; Shi, X.; Wang, F. Exploring the mechanism of ellagic acid against gastric cancer based on bioinformatics analysis and network pharmacology. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2023, 27, 3878–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, C.E.D.; Pérez, M.R.; Acayaba, R.D.A.; Raimundo, C.C.M.; Martinez, C.B.D.R. DNA damage and oxidative stress induced by imidacloprid exposure in different tissues of the Neotropical fish Prochilodus lineatus. Chemosphere 2018, 195, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farag, A.A.; Bayoumi, H.; Radwaan, S.E.; El Gazzar, W.B.; Youssef, H.S.; Nasr, H.E.; Badr, A.M.; Mansour, H.M.; Elalfy, A.; Sayed, A.E.-D.H.; et al. Melatonin counteracts polyethylene microplastics induced adreno-cortical damage in male albino rats. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 279, 116499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, K.; El-Desouky, M.; Abou-Yousef, H.; Gabrowny, K.; El-Sayed, A.J. Imidacloprid and/or esfenvalerate induce apoptosis and disrupt thyroid hormones in neonatal rats. Glob. J. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2015, 10, 106–112. [Google Scholar]
- Alfei, S.; Marengo, B.; Zuccari, G. Oxidative Stress, Antioxidant Capabilities, and Bioavailability: Ellagic Acid or Urolithins? Antioxidants 2020, 9, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrak, J.K. Effect of Ellagic Acid Extracted from Pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) on Thyroid and Parathyroid Gland of Adult Rats Exposed to Lead Acetate. Kufa J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2010, 1, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Emam, M.M.; Mostafa, M.; Farag, A.A.; Youssef, H.S.; El-Demerdash, A.S.; Bayoumi, H.; Gebba, M.A.; El-Halawani, S.M.; Saleh, A.M.; Badr, A.M.; et al. The Potential Effects of Quercetin-Loaded Nanoliposomes on Amoxicillin/Clavulanate-Induced Hepatic Damage: Targeting the SIRT1/Nrf2/NF-κB Signaling Pathway and Microbiota Modulation. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altamimi, J.Z.; AlFaris, N.A.; Alshammari, G.M.; Alagal, R.I.; Aljabryn, D.H.; Aldera, H.; Alrfaei, B.M.; Alkhateeb, M.A.; Yahya, M.A. Ellagic acid protects against diabetic nephropathy in rats by regulating the transcription and activity of Nrf2. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 79, 104397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Botchway, B.O.A.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X. Ellagic acid activates the Keap1-Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway in improving Parkinson’s disease: A review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 156, 113848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.-z.; Zhu, G.-F.; Zheng, C.-Q.; Li, J.-J.; Sheng, S.; Li, D.-D.; Wang, G.-Q.; Zhang, F. Ellagic acid protects dopamine neurons from rotenone-induced neurotoxicity via activation of Nrf2 signalling. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 9446–9456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelombitko, M.A. Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in Inflammation: A Minireview. Mosc. Univ. Biol. Sci. Bull. 2018, 73, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Chen, F.; Zhou, B. Antioxidative, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects of ellagic acid in liver and brain of rats treated by D-galactose. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd-Elhakim, Y.M.; Mohammed, H.H.; Mohamed, W.A.M. Imidacloprid Impacts on Neurobehavioral Performance, Oxidative Stress, and Apoptotic Events in the Brain of Adolescent and Adult Rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 13513–13524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harakeh, S.; Almuhayawi, M.; Jaouni, S.A.; Almasaudi, S.; Hassan, S.; Amri, T.A.; Azhar, N.; Abd-Allah, E.; Ali, S.; El-Shitany, N.; et al. Antidiabetic effects of novel ellagic acid nanoformulation: Insulin-secreting and anti-apoptosis effects. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 3474–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, A.; Vakili, S.; Koohpeyma, F.; Jahromi, B.N.; Aghajari, Z.A.; Mahmoudikohani, F.; Saki, F.; Mahmoodi, M.; Jaberi, K.R.; Movahedpour, A.; et al. Ellagic acid effects on testis, sex hormones, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in the relative sterility rat model following busulfan administration. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2022, 22, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, Z.M.; Khattab, M.I.; Khorshid, N.E.; Salem, A.E. Ellagic acid and cilostazol ameliorate amikacin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats by downregulating oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0271591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Chen, C.; Li, H.; Tu, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Lin, Z.; Cai, Z. Imidacloprid-induced lung injury in mice: Activation of the PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling pathway via TLR4 receptor engagement. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 931, 172910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, H.; Fang, S.; Xu, C. Roles of endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy on H2O2-induced oxidative stress injury in HepG2 cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 4163–4174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, M.R.; CFisher, R.; Kapphahn, R.J.; Polanco, J.R.; Ferrington, D.A. Investigating AKT activation and autophagy in immunoproteasome-deficient retinal cells. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z. The FoxO-Autophagy Axis in Health and Disease. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 30, 658–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deleyto-Seldas, N.; Efeyan, A. The mTOR–Autophagy Axis and the Control of Metabolism. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 655731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ren, F.; Li, B.; Song, Z.; Chen, P.; Ouyang, L. Ellagic acid exerts antitumor effects via the PI3K signaling pathway in endometrial cancer. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 3303–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Song, S.; Jiao, J.; Liu, X.; Zhu, H.; Xiu, L.; Sun, D.; Li, Q.; Yue, X. ZiYinHuaTan Recipe Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Promotes Apoptosis in Gastric Cancer by Suppressing PI3K/AKT Pathway. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 2018162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, K.; Liu, X.; Ruan, H.; Ma, L.; Liang, J.; Cui, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Li, H.; et al. Ellagic Acid Attenuates BLM-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis via Inhibiting Wnt Signaling Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 639574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, E. Autophagy and p53. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a026120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.-J.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, C.-H.; Jang, J.-Y.; Chung, J.; Kwon, M.-H.; Kim, Y.-S. Upregulation of Beclin-1 expression and phosphorylation of Bcl-2 and p53 are involved in the JNK-mediated autophagic cell death. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 382, 726–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiuri, M.C.; Zalckvar, E.; Kimchi, A.; Kroemer, G. Self-eating and self-killing: Crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, S.; Fairlie, W.D.; Lee, E.F. BECLIN1: Protein Structure, Function and Regulation. Cells 2021, 10, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeeri, M.; Momtaz, S.; Navaei-Nigjeh, M.; Niaz, K.; Rahimifard, M.; Ghasemi-Niri, S.F.; Sanadgol, N.; Hodjat, M.; Sharifzadeh, M.; Abdollahi, M. Molecular evidence on the protective effect of ellagic acid on phosalone-induced senescence in rat embryonic fibroblast cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 100, 8–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.-C.; Ye, L.-X.; Zhu, J.-H.; Bai, J.-J.; Zeng, S.-S.; Chen, S.-Q.; Lin, Z.-L. Ellagic acid attenuates hypoxic-ischemic brain injury by alleviating autophagy. Chin. J. Pathophysiol. 2019, 12, 311–319. [Google Scholar]


| Target Gene | Primer Sequences | Accession Number | Amplicon Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| B-actin | CGGTCAGGTCATCACTATCG | NM_031144.3 | 79 |
| TAGTTTCATGGATGCCACAG | |||
| PI3K | CGTATCCACCTGTCCTCTCC | NM_001371300.3 | 199 |
| CTCCTTCCAAGCCTCAGTGA | |||
| Akt1 | CTGCCCTTCTACAACCAGGA | NM_033230.3 | 177 |
| GTGCTGCATGATCTCCTTGG | |||
| mTOR | TCTGCACTTGTTGTTGCCT | NM_019906.2 | 150 |
| ACAATCGGGTGAATGATGCG | |||
| BAX | CAGCTCTGAACAGATCAT | NM_017059.2 | 218 |
| AGTCTGTATCCACATCAG | |||
| Bcl | AGGGATGGAGGAGGAGCTTA | NM_022698.2 | 175 |
| TTGTCGCATCTGTGTTGC | |||
| P53 | GGCTCCGACTATACCACTATCCAC | U07020.1 | 129 |
| GTCCCGTCCCAGAAGATTC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farag, A.A.; Mostafa, M.; Abdelfatah, R.M.; ELdahshan, A.E.; Gad, S.F.; Mohamed, S.K.; Alawam, M.K.; Elzeer, A.A.; Ismail, N.S.; Elsharkawey, S.; et al. Ellagic Acid Alleviates Imidacloprid-Induced Thyroid Dysfunction via PI3K/Akt/mTOR-Mediated Autophagy. Toxics 2025, 13, 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050355
Farag AA, Mostafa M, Abdelfatah RM, ELdahshan AE, Gad SF, Mohamed SK, Alawam MK, Elzeer AA, Ismail NS, Elsharkawey S, et al. Ellagic Acid Alleviates Imidacloprid-Induced Thyroid Dysfunction via PI3K/Akt/mTOR-Mediated Autophagy. Toxics. 2025; 13(5):355. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050355
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarag, Amina A., Mahmoud Mostafa, Reham M. Abdelfatah, Alshimaa Ezzat ELdahshan, Samar Fawzy Gad, Shimaa K. Mohamed, Mona K. Alawam, Aya Aly Elzeer, Nesma S. Ismail, Sally Elsharkawey, and et al. 2025. "Ellagic Acid Alleviates Imidacloprid-Induced Thyroid Dysfunction via PI3K/Akt/mTOR-Mediated Autophagy" Toxics 13, no. 5: 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050355
APA StyleFarag, A. A., Mostafa, M., Abdelfatah, R. M., ELdahshan, A. E., Gad, S. F., Mohamed, S. K., Alawam, M. K., Elzeer, A. A., Ismail, N. S., Elsharkawey, S., Al-Mazroua, H. A., Alomar, H. A., Sarawi, W. S., & Youssef, H. S. (2025). Ellagic Acid Alleviates Imidacloprid-Induced Thyroid Dysfunction via PI3K/Akt/mTOR-Mediated Autophagy. Toxics, 13(5), 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050355









