Deciphering Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Mechanistic Insights and Environmental Risks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Understanding Multidrug-Resistance Mechanisms in P. aeruginosa
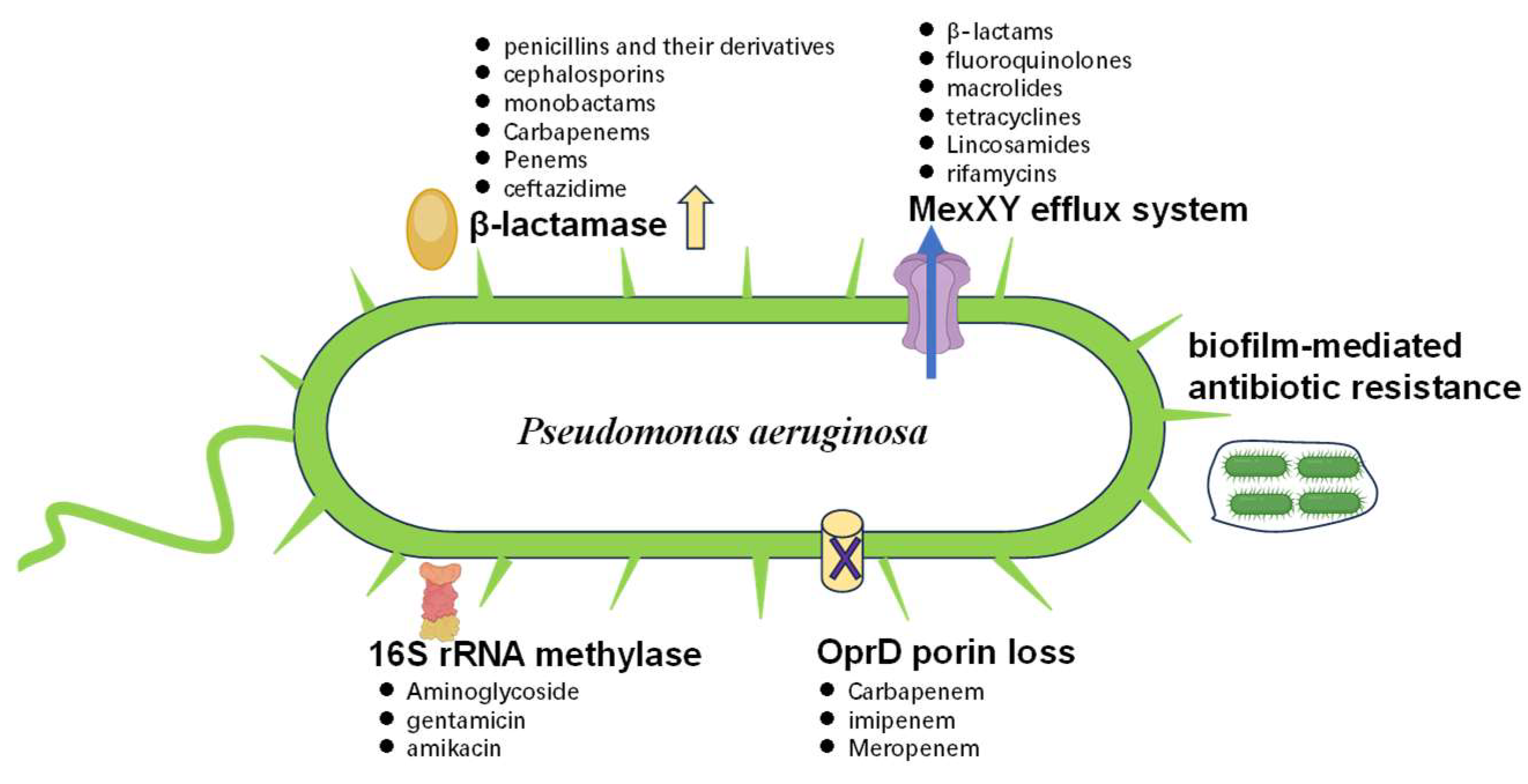
2.1. Main Factors Involved in MDR
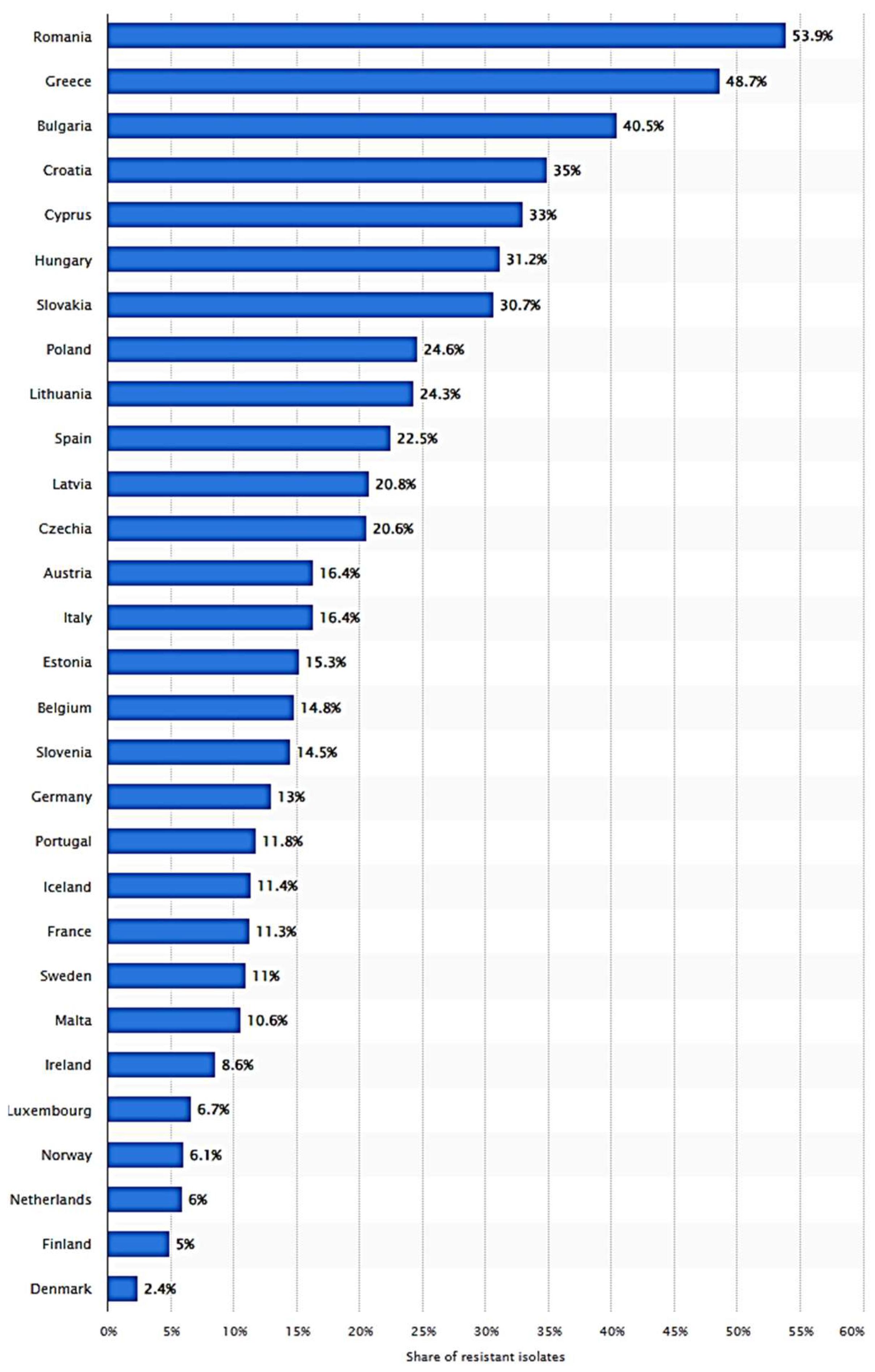
2.2. Improper Use of Antibiotics in Spreading MDR
3. The Contribution of Evolutionary Dynamics in Shaping Resistance
3.1. Co-Evolution of Virulence Factors and ARGs
3.2. MDR-Related Genes and Gene Regulatory Mechanisms
4. MDR Detection Methods in P. aeruginosa
4.1. Traditional Bacteriological Detection Methods
4.2. Molecular Biology Detection Methods
5. Treatment Strategies for MDR in P. aeruginosa
5.1. Current Treatment Strategies
5.2. New Treatment Strategies and Drugs
5.3. Antibiotic Combination Therapy
5.4. Treatment Methods Targeting Resistance Mechanisms
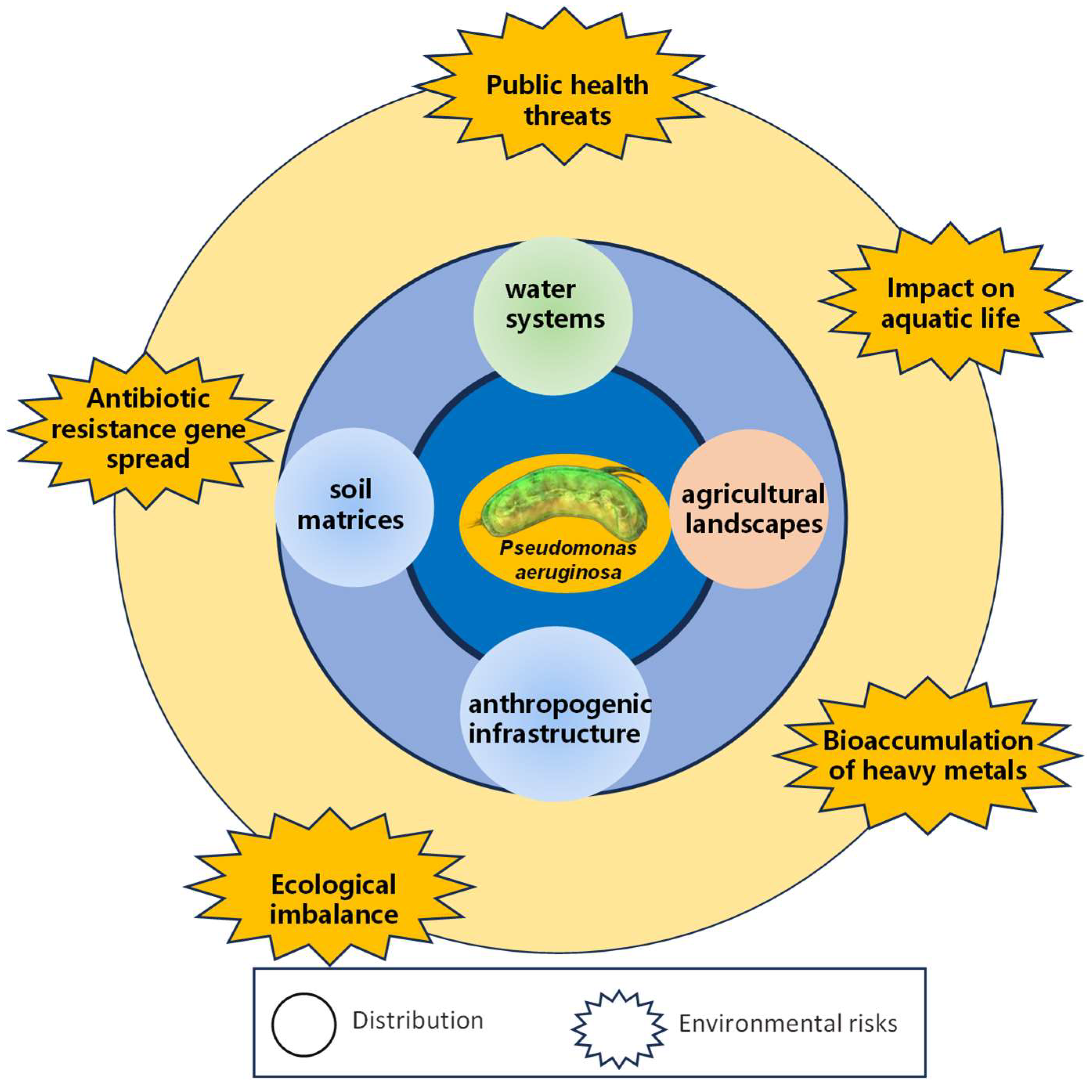
6. Distribution, Migration, and Risks of MDR P. aeruginosa in the Environment
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weimann, A.; Dinan, A.M.; Ruis, C.; Bernut, A.; Pont, S.; Brown, K.; Ryan, J.; Santos, L.; Ellison, L.; Ukor, E.; et al. Evolution and host-specific adaptation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Science 2024, 385, eadi0908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, B.; Klamer, K.; Zimmerman, J.; Kale-Pradhan, P.B.; Bhargava, A. Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Clinical Settings: A Review of Resistance Mechanisms and Treatment Strategies. Pathogens 2024, 13, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leoni Swart, A.; Laventie, B.J.; Sütterlin, R.; Junne, T.; Lauer, L.; Manfredi, P.; Jakonia, S.; Yu, X.; Karagkiozi, E.; Okujava, R.; et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa breaches respiratory epithelia through goblet cell invasion in a microtissue model. Nat. Microbiol. 2024, 9, 1725–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köhler, T.; Luscher, A.; Falconnet, L.; Resch, G.; McBride, R.; Mai, Q.A.; Simonin, J.L.; Chanson, M.; Maco, B.; Galiotto, R.; et al. Personalized aerosolised bacteriophage treatment of a chronic lung infection due to multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsilipounidaki, K.; Gkountinoudis, C.G.; Florou, Z.; Fthenakis, G.C.; Petinaki, E. In Silico Molecular Analysis of Carbapenemase-Negative Carbapenem-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strains in Greece. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Alam, M.Z.; Fallon, J.T.; Huang, W. Advances in Development of Novel Therapeutic Strategies against Multi-Drug Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karruli, A.; Catalini, C.; D’Amore, C.; Foglia, F.; Mari, F.; Harxhi, A.; Galdiero, M.; Durante-Mangoni, E. Evidence-Based Treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections: A Critical Reappraisal. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Hong, X.; Chen, S.; He, Y.; Xie, L.; Gao, F.; Zhu, C.; Jin, X.; Yan, H.; Ye, Y.; et al. Biomimetic Metal-Organic Framework Gated Nanoplatform for Sonodynamic Therapy against Extensively Drug Resistant Bacterial Lung Infection. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2402473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, N.A.; Tohamy, S.T.; Alshahrani, M.Y.; Aboshanab, K.M. Evaluation of fortimicin antibiotic combinations against MDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa and resistome analysis of a whole genome sequenced pan-drug resistant isolate. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosentino, F.; Viale, P.; Giannella, M. MDR/XDR/PDR or DTR? Which definition best fits the resistance profile of Pseudomonas aeruginosa? Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 36, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Raudonis, R.; Glick, B.R.; Lin, T.J.; Cheng, Z. Antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Mechanisms and alternative therapeutic strategies. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partridge, S.R.; Kwong, S.M.; Firth, N.; Jensen, S.O. Mobile Genetic Elements Associated with Antimicrobial Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00088-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chebotar, I.; Savinova, T.; Bocharova, J.; Korostin, D.; Evseev, P.; Mayanskiy, N. Genetic Alternatives for Experimental Adaptation to Colistin in Three Pseudomonas aeruginosa Lineages. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefi, S.; Nazari, M.; Ramazanzadeh, R.; Sahebkar, A.; Safarzadeh, E.; Khademi, F. Association of carbapenem and multidrug resistance with the expression of efflux pump-encoding genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates. Acta Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 2023, 70, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawadi, P.; Khadka, C.; Shyaula, M.; Syangtan, G.; Joshi, T.P.; Pepper, S.H.; Kanel, S.R.; Pokhrel, L.R. Prevalence of metallo-β-lactamases as a correlate of multidrug resistance among clinical Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates in Nepal. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 850, 157975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qader, G.M.; Jarjees, K.K.; Jarjees, R.K. Molecular detection of Metallo-Beta-Lactamase and alginate in multidrug resistance Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from the clinical specimen. J. Med. Life 2022, 15, 1105–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teran, N.; Egge, S.L.; Phe, K.; Baptista, R.P.; Tam, V.H.; Miller, W.R. The emergence of cefiderocol resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa from a heteroresistant isolate during prolonged therapy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2024, 68, e0100923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddamsetti, R.; Yao, Y.; Wang, T.; Gao, J.; Huang, V.T.; Hamrick, G.S.; Son, H.I.; You, L. Duplicated antibiotic resistance genes reveal ongoing selection and horizontal gene transfer in bacteria. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishbein, S.R.S.; Mahmud, B.; Dantas, G. Antibiotic perturbations to the gut microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 772–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, F.; Imtiaz, M.; Haq, I.U. Emergent crisis of antibiotic resistance: A silent pandemic threat to 21st century. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 174, 105923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Wei, X.; Yin, J.; Haley, D.R.; Sun, Q.; Lundborg, C.S. Interventions to optimize the use of antibiotics in China: A scoping review of evidence from humans, animals, and the environment from a One Health perspective. One Health 2022, 14, 100388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, D.G.J.; Flach, C.F. Antibiotic resistance in the environment. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulingam, T.; Parumasivam, T.; Gazzali, A.M.; Sulaiman, A.M.; Chee, J.Y.; Lakshmanan, M.; Chin, C.F.; Sudesh, K. Antimicrobial resistance: Prevalence, economic burden, mechanisms of resistance and strategies to overcome. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 170, 106103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, A.F.; Huang, V.; Samaroo-Campbell, J.; Augenbraun, M. Multi-drug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A 2019–2020 single center retrospective case control study. Infect. Prev. Pract. 2023, 5, 100296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.K.; Hussein, S.; Qurbani, K.; Ibrahim, R.H.; Fareeq, A.; Mahmood, K.A.; Mohamed, M.G. Antimicrobial resistance: Impacts, challenges, and future prospects. J. Med. Surg. Public Health 2024, 2, 100081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Xiao, W.; Zhou, C.; Pu, Q.; Deng, X.; Lan, L.; Liang, H.; Song, X.; Wu, M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Pathogenesis, virulence factors, antibiotic resistance, interaction with host, technology advances and emerging therapeutics. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidar, A.; Muazzam, A.; Nadeem, A.; Atique, R.; Saeed, H.A.; Naveed, A.; Sharif, J.; Perveen, A.; Fatima, H.R.; Samad, A. Biofilm formation and antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbe 2024, 3, 100078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, M.W.; Khan, A.U. Updates on the pathogenicity status of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horna, G.; López, M.; Guerra, H.; Saénz, Y.; Ruiz, J. Interplay between MexAB-OprM and MexEF-OprN in clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salleh, M.Z.; Nik Zuraina, N.M.N.; Deris, Z.Z.; Mohamed, Z. Current Trends in the Epidemiology of Multidrug-Resistant and Beta-Lactamase-Producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Asia and Africa: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Peer J. 2025, 13, e18986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zeng, J.; Li, L.; Yang, J.; Tang, Z.; Xiong, W.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Zeng, Z. Coexistence of Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Virulence Factors Deciphered by Large-Scale Complete Genome Analysis. mSystems 2020, 5, e00821-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Huang, X.; Wang, Q.; Yao, D.; Lu, W. Virulence Factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Antivirulence Strategies to Combat Its Drug Resistance. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 926758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darby, E.M.; Trampari, E.; Siasat, P.; Gaya, M.S.; Alav, I.; Webber, M.A.; Blair, J.M.A. Molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance revisited. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 280–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Chen, D.Q.; Hong, J.; Huang, H.; Xu, X. Prevalence of qnrVC Genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Clinical Isolates from Guangdong, China. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 1532–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerminiaux, N.A.; Cameron, A.D.S. Horizontal transfer of antibiotic resistance genes in clinical environments. Can. J. Microbiol. 2019, 65, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Ali, Z.; Zou, J.; Jin, G.; Zhu, J.; Yang, J.; Dai, J. Detection methods for Pseudomonas aeruginosa: History and future perspective. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 51789–51800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capatina, D.; Feier, B.; Hosu, O.; Tertis, M.; Cristea, C. Analytical methods for the characterization and diagnosis of infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A critical review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1204, 339696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ye, Q.; Jiang, A.; Zhang, J.; Shang, Y.; Li, F.; Zhou, B.; Xiang, X.; Gu, Q.; Pang, R.; et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Detection Using Conventional PCR and Quantitative Real-Time PCR Based on Species-Specific Novel Gene Targets Identified by Pangenome Analysis. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 820431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Liu, X.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Huang, G.; Wu, J. Rapid and sensitive detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by isothermal amplification combined with Cas12a-mediated detection. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatami, S.H.; Karami, S.; Siahkouhi, H.R.; Taheri-Anganeh, M.; Fathi, J.; Aghazadeh Ghadim, M.B.; Taghvimi, S.; Shabaninejad, Z.; Tondro, G.; Karami, N.; et al. Aptamer-based biosensors for Pseudomonas aeruginosa detection. Mol. Cell. Probes 2022, 66, 101865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Ye, Q.; Zhang, J.; Pang, R.; Gu, Q.; Ding, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wang, J. Multiplex PCR identification of the major Pseudomonas aeruginosa serogroups using specific novel target genes. LWT 2022, 163, 113567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Pan, Y.; Yu, H.; Chen, X. Simple and sensitive detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in neonatal infection based on a both-end blocked peroxidase-mimicking DNAzyme. BioTechniques 2024, 76, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, F.; Hilal, A.; Thirugnanasampanthar, M.; Tremblay, D.; Filipe, C.D.M.; Moineau, S.; Didar, T.F.; Hosseinidoust, Z. High throughput platform technology for rapid target identification in personalized phage therapy. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Qu, H.; Wu, X.; Shi, J.; Wang, X. Rapid, sensitive, and user-friendly detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa using the RPA/CRISPR/Cas12a system. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, R.; Ma, X.; Han, L.; Yao, J.; Li, Z. Accurate, Sensitive, and Rapid Detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Based on CRISPR/Cas12b with One Fluid-Handling Step. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0352322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Zhai, L.; Wang, J.; Sun, X.; Wang, B.; Wei, Z. An Evaluation of the Sensitivity and Applicability of a Droplet Digital Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay to Simultaneously Detect Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas fragi in Foods. Foods 2024, 13, 1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, W.R.; Arias, C.A. ESKAPE pathogens: Antimicrobial resistance, epidemiology, clinical impact and therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 598–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizza, B.D.; Betthauser, K.D.; Ritchie, D.J.; Micek, S.T.; Kollef, M.H. New Perspectives on Antimicrobial Agents: Ceftolozane-Tazobactam. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e0231820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albin, O.R.; Pogue, J.M.; Wunderink, R.G.; Kaye, K.S. Which trial do we need? Combination antimicrobial therapy for hospital-acquired bacterial pneumonia caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2024, 30, 162–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferous, S.; Anastassopoulou, C.; Pitiriga, V.; Vrioni, G.; Tsakris, A. Antimicrobial and diagnostic stewardship of the novel β-lactam/β-lactamase inhibitors for infections due to car-bapenem-resistant enterobacterales species and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfieri, A.; Di Franco, S.; Donatiello, V.; Maffei, V.; Fittipaldi, C.; Fiore, M.; Coppolino, F.; Sansone, P.; Pace, M.C.; Passavanti, M.B. Plazomicin against multidrug-resistant bacteria: A scoping review. Life 2022, 12, 1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi, T.S.; Behrouz, B.; Mousavi Gargari, S.L. Polyclonal anti-whole cell IgY passive immunotherapy shields against P. aeruginosa-induced acute pneumonia and burn wound infections in murine models. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, J.A.; Garnier, N.E.; Pei, Y.; Yates, J.G.E.; Campbell, E.S.B.; Goens, M.M.; Hughes, M.E.; Rghei, A.D.; Stevens, B.A.Y.; Guilleman, M.M.; et al. AAV-vectored expression of monospecific or bispecific monoclonal antibodies protects mice from lethal Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia. Gene Ther. 2024, 31, 400–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moule, M.G.; Benjamin, A.B.; Burger, M.L.; Herlan, C.; Lebedev, M.; Lin, J.S.; Koster, K.J.; Wavare, N.; Adams, L.G.; Bräse, S.; et al. Peptide-Mimetic treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a mouse model of respiratory infection. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, A.; Khalid, N.A.; Zafar, S.; Majid, A.; Shahzadi, M.; Saleem, S.; Shah, A.A.; Badshah, M.; Khan, S. Phage therapy as a revolutionary treatment for multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections: A narrative review. Microbe 2024, 2, 100030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chang, R.Y.K.; Lin, Y.; Morales, S.; Kutter, E.; Chan, H.-K. Phage cocktail powder for Pseudomonas aeruginosa respiratory infections. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 596, 120200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manohar, P.; Loh, B.; Nachimuthu, R.; Leptihn, S. Phage-antibiotic combinations to control Pseudomonas aeruginosa-Candida two-species biofilms. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, T.; Kolenda, C.; Laurent, F.; Leboucher, G.; Merabischvilli, M.; Djebara, S.; Gustave, C.A.; Perpoint, T.; Barrey, C.; Pirnay, J.P.; et al. Personalized bacteriophage therapy to treat pandrug-resistant spinal Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, P.; Fahimi, H.; Khaleghi, S. Novel Chimeric Endolysin Conjugated Chitosan Nanocomplex as a Potential Inhibitor Against Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2024, 196, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardakas, K.Z.; Tansarli, G.S.; Bliziotis, I.A.; Falagas, M.E. β-Lactam plus aminoglycoside or fluoroquinolone combination versus β-lactam monotherapy for Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2013, 41, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Zhong, L.; Weng, Y.; Peng, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, X.-J. Therapeutic siRNA: State of the art. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pankratz, D.; Gomez, N.O.; Nielsen, A.; Mustafayeva, A.; Gür, M.; Arce-Rodriguez, F.; Nikel, P.I.; Häussler, S.; Arce-Rodriguez, A. An expanded CRISPR–Cas9-assisted recombineering toolkit for engineering genetically intractable Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates. Nat. Protoc. 2023, 18, 3253–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durrant, M.G.; Perry, N.T.; Pai, J.J.; Jangid, A.R.; Athukoralage, J.S.; Hiraizumi, M.; McSpedon, J.P.; Pawluk, A.; Nishimasu, H.; Konermann, S.; et al. Bridge RNAs direct programmable recombination of target and donor DNA. Nature 2024, 630, 984–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uribe, R.V.; Rathmer, C.; Jahn, L.J.; Ellabaan, M.M.H.; Li, S.S.; Sommer, M.O.A. Bacterial resistance to CRISPR-Cas antimicrobials. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraizumi, M.; Perry, N.T.; Durrant, M.G.; Soma, T.; Nagahata, N.; Okazaki, S.; Athukoralage, J.S.; Isayama, Y.; Pai, J.J.; Pawluk, A.; et al. Structural mechanism of bridge RNA-guided recombination. Nature 2024, 630, 994–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.S.; Gustavo, L.; Rajkumar, V.C.; Swe-Han, K.S. Antimicrobial stewardship approach: Prevalence of antimicrobial resistant bacteria at a regional hospital in South Africa. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2019, 13, 748–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, B.; Moustafa, S.; Shata, R.; Sayed-Ahmed, M.Z.; Alqahtani, S.S.; Ali, M.S.; Alam, N.; Ahmad, S.; Kasem, N.; Elbaz, E.; et al. Prevalence of Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolated from Dairy Cattle, Milk, Environment, and Workers’ Hands. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crone, S.; Vives-Flórez, M.; Kvich, L.; Saunders, A.M.; Malone, M.; Nicolaisen, M.H.; Martínez-García, E.; Rojas-Acosta, C.; Gomez-Puerto, M.C.; Calum, H.; et al. The environmental occurrence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. APMIS Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Immunol. Scandinavica 2020, 128, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Elez, R.M.M.; Zahra, E.M.F.; Gharieb, R.M.A.; Mohamed, M.E.M.; Samir, M.; Saad, A.M.A.; Merwad, A.M.A. Resistance patterns, virulence determinants, and biofilm genes of multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from fish and fish handlers. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 24063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denissen, J.; Reyneke, B.; Waso-Reyneke, M.; Havenga, B.; Barnard, T.; Khan, S.; Khan, W. Prevalence of ESKAPE pathogens in the environment: Antibiotic resistance status, community-acquired infection and risk to human health. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2022, 244, 114006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pei, Y.; Hamar, P.; Pei, D.-S. Deciphering Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Mechanistic Insights and Environmental Risks. Toxics 2025, 13, 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040303
Pei Y, Hamar P, Pei D-S. Deciphering Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Mechanistic Insights and Environmental Risks. Toxics. 2025; 13(4):303. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040303
Chicago/Turabian StylePei, Yang, Péter Hamar, and De-Sheng Pei. 2025. "Deciphering Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Mechanistic Insights and Environmental Risks" Toxics 13, no. 4: 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040303
APA StylePei, Y., Hamar, P., & Pei, D.-S. (2025). Deciphering Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Mechanistic Insights and Environmental Risks. Toxics, 13(4), 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040303





