Mechanistic Studies on the Role of IL-17/NLRP3 in Arsenic-Induced Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells Through Hepatocyte Proptosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Instruments and Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. NaAsO2 Treated Cell
2.4. Inhibitor Treatment of Cells
2.5. Conditioned Culture
2.6. CCK8 for Cell Viability
2.7. Western Blot
2.8. qPCR
2.9. ELISA
2.10. Analyze Statistics
3. Results
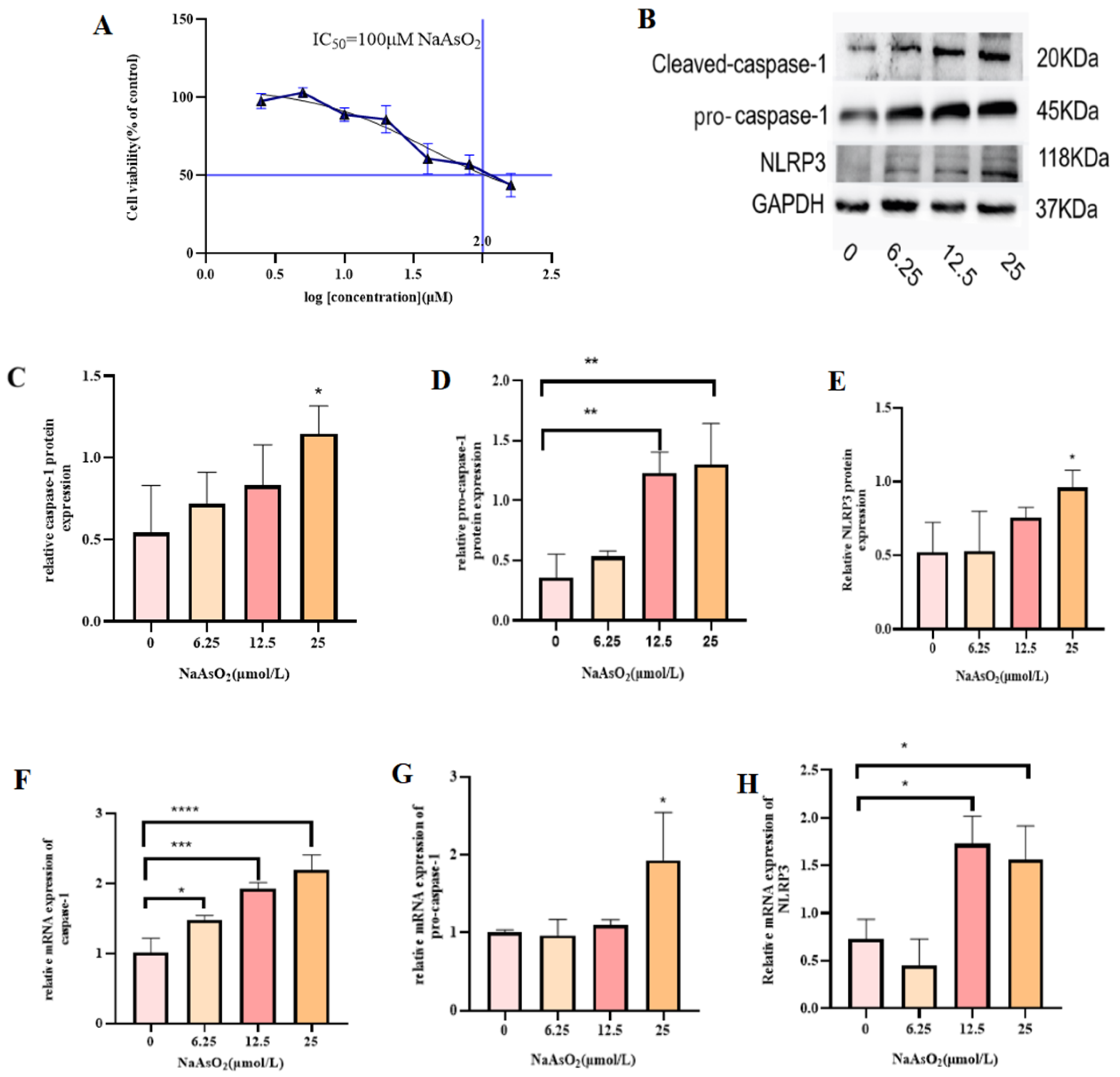
3.1. Effect of Different Concentrations of Sodium Arsenite on MIHA Cell Viability
3.2. NaAsO2 Induces Inflammation and Proptosis in MIHA Cells
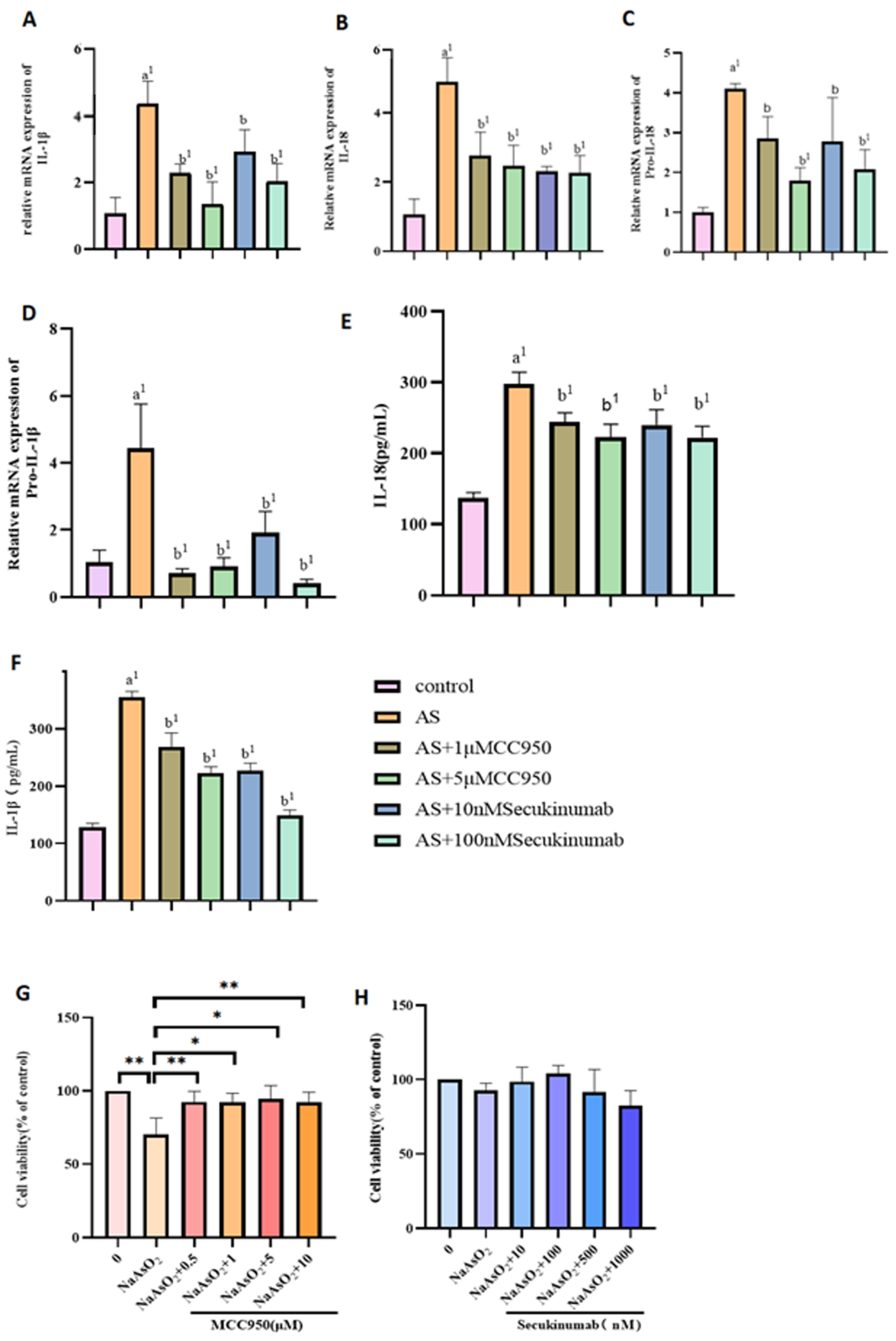
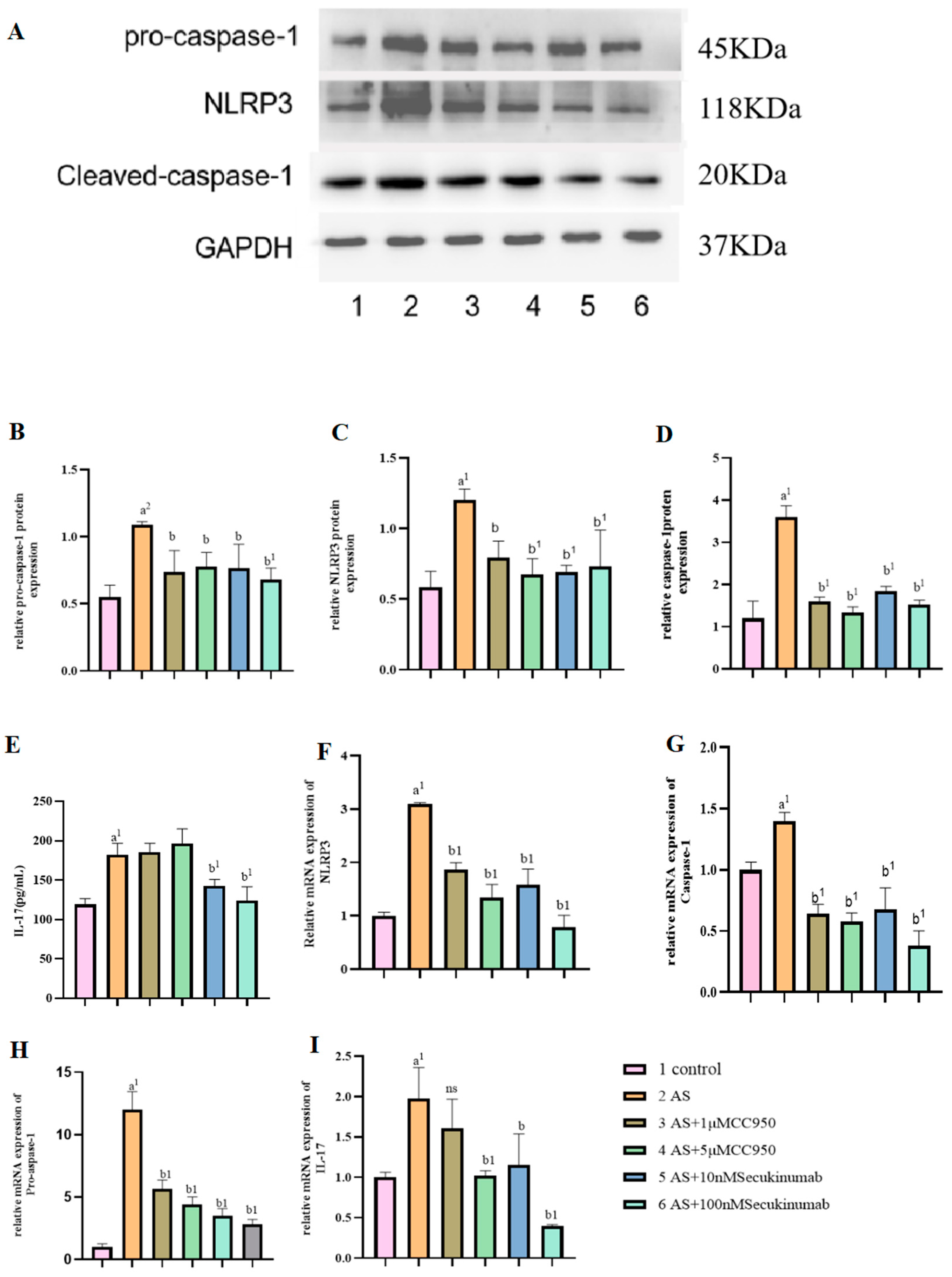
3.3. Pre-Treatment of NaAsO2 with Different Concentrations of the Inhibitors MCC950 and Secukinumab Induced the Pyroptotic Effects of Related Genes and Proteins in MIHA Cells
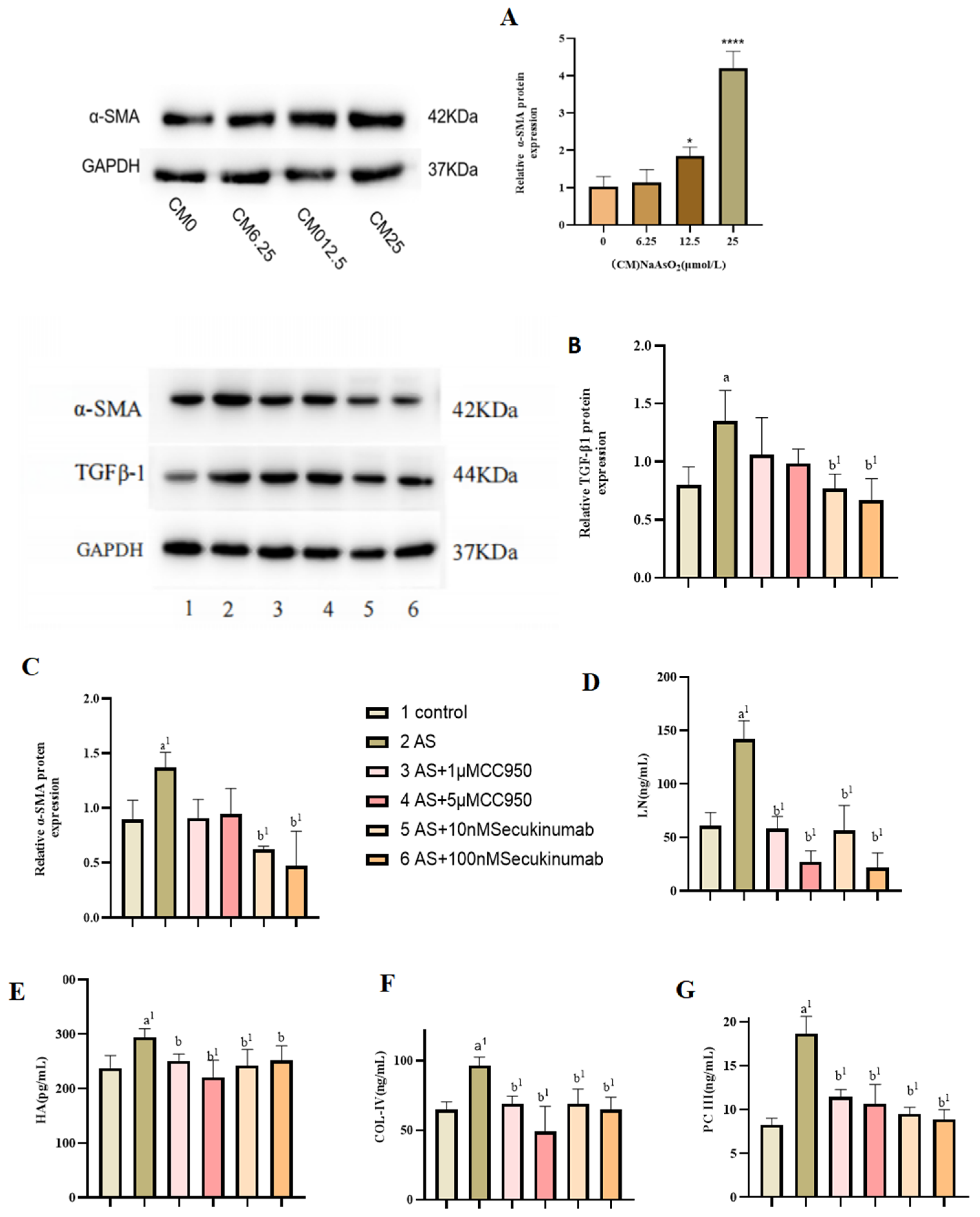
3.4. Effect of Conditioned Medium on LX-2 Cell Activation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El-Ghiaty, M.A.; El-Kadi, A.O.S. The Duality of Arsenic Metabolism: Impact on Human Health. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2023, 63, 341–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, R.; Wang, Z. Research progress on arsenic, arsenic-containing medicinal materials, and arsenic-containing preparations: Clinical application, pharmacological effects, and toxicity. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1338725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jin, P.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Xi, S. sEcad and EGF Levels Increased in Urine of Non-ferrous Metal Workers and Medium of Uroepithelial Cell Line Treated by Arsenic. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2018, 183, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Machado-Neves, M. Effect of heavy metals on epididymal morphology and function: An integrative review. Chemosphere 2022, 291 Pt 2, 133020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Centeno, J.A.; Patlolla, A.K. Arsenic toxicity, mutagenesis, and carcinogenesis—A health risk assessment and management approach. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2004, 255, 47–55. [Google Scholar]
- Si-Tayeb, K.; Lemaigre, F.P.; Duncan, S.A. Organogenesis and development of the liver. Dev. Cell 2010, 18, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Xu, G.; Li, J.; Yan, N.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Li, B. Arsenic Induces Continuous Inflammation and Regulates Th1/Th2/Th17/Treg Balance in Liver and Kidney In Vivo. Mediat. Inflamm. 2022, 2022, 8414047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreval, K.; Tryndyak, V.; Kindrat, I.; Twaddle, N.C.; Orisakwe, O.E.; Mudalige, T.K.; Beland, F.A.; Doerge, D.R.; Pogribny, I.P. Cellular and Molecular Effects of Prolonged Low-Level Sodium Arsenite Exposure on Human Hepatic HepaRG Cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 162, 676–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, K.; Suzuki, T.; Nohara, K. Gestational arsenite exposure augments hepatic tumors of C3H mice by promoting senescence in F1 and F2 offspring via different pathways. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020, 408, 115259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taru, V.; Szabo, G.; Mehal, W.; Reiberger, T. Inflammasomes in chronic liver disease: Hepatic injury, fibrosis progression and systemic inflammation. J. Hepatol. 2024, 81, 895–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Gea, V.; Friedman, S.L. Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2011, 6, 425–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elpek, G. Cellular and molecular mechanisms in the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis: An update. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 7260–7276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roehlen, N.; Crouchet, E.; Baumert, T.F. Liver Fibrosis: Mechanistic Concepts and Therapeutic Perspectives. Cells 2020, 9, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammerich, L.; Tacke, F. Hepatic inflammatory responses in liver fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 20, 633–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Huang, D.; Weng, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Mai, Z.; Gu, W. Effect of reversine on cell cycle, apoptosis, and activation of hepatic stellate cells. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2016, 423, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, N.M.; McCulloch, C.A. Mechanical signaling through the discoidin domain receptor 1 plays a central role in tissue fibrosis. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2018, 12, 348–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, P.; Tacke, F. Metabolic reprogramming in liver fibrosis. Cell Metab. 2024, 36, 1439–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahid, R.M.; Hassan, N.H.; Samy, W.; Abdelhadi, A.A.; Saadawy, S.F.; Elsayed, S.F.; Seada, S.G.; Mohamed, S.R.A. Unraveling the hepatic stellate cells mediated mechanisms in aging’s influence on liver fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskunpinar, E.; Islamzade, F.; Yilmaz, E.P.; Ors, C.H.; Adak, H.; Yesiltepe, A.; Turksoylu, S.; Dural, A.C. The Importance of Fecal Transplantation in Personalized Medicine. Bezmialem Sci. 2018, 6, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Liu, M.; Jiang, M.; Li, Z.; Chen, W.; Wang, W.; Fu, X.; Qi, M.; Ali, M.H.; Zou, N.; et al. Isoliquiritigenin alleviates the development of alcoholic liver fibrosis by inhibiting ANXA2. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 159, 114173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhao, C.; Tai, Y.; Li, B.; Lan, T.; Lai, E.; Dai, W.; Guo, Y.; Gan, C.; Kostallari, E.; et al. STING mediates hepatocyte pyroptosis in liver fibrosis by Epigenetically activating the NLRP3 inflammasome. Redox Biol. 2023, 62, 102691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.; Cai, Q.; Tang, C.; Gao, J. Inflammasomes and Pyroptosis of Liver Cells in Liver Fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 896473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho Ribeiro, M.; Szabo, G. Role of the Inflammasome in Liver Disease. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2022, 17, 345–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inzaugarat, M.E.; Johnson, C.D.; Holtmann, T.M.; McGeough, M.D.; Trautwein, C.; Papouchado, B.G.; Schwabe, R.; Hoffman, H.M.; Wree, A.; Feldstein, A.E. NLR Family Pyrin Domain-Containing 3 Inflammasome Activation in Hepatic Stellate Cells Induces Liver Fibrosis in Mice. Hepatology 2019, 69, 845–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, S.; Li, B.; Du, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.; Song, M.; Li, Y. Dibutyl phthalate induces liver fibrosis via p38MAPK/NF-κB/NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 897, 165500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A.H. Chronic arsenic poisoning. Toxicol. Lett. 2002, 128, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Kamli, M.R.; Ali, A. Role of arsenic and its resistance in nature. Can. J. Microbiol. 2011, 57, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganie, S.Y.; Javaid, D.; Hajam, Y.A.; Reshi, M.S. Arsenic toxicity: Sources, pathophysiology and mechanism. Toxicol. Res. 2024, 13, tfad111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantoni, O.; Zito, E.; Guidarelli, A.; Fiorani, M.; Ghezzi, P. Mitochondrial ROS, ER Stress, and Nrf2 Crosstalk in the Regulation of Mitochondrial Apoptosis Induced by Arsenite. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajam, Y.A.; Rani, R.; Ganie, S.Y.; Sheikh, T.A.; Javaid, D.; Qadri, S.S.; Pramodh, S.; Alsulimani, A.; Alkhanani, M.F.; Harakeh, S.; et al. Oxidative Stress in Human Pathology and Aging: Molecular Mechanisms and Perspectives. Cells 2022, 11, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, S.; Ghosh, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Gupta, P.; Bhattacharya, S.; Adhikary, A.; Chattopadhyay, S. Pomegranate protects against arsenic-induced p53-dependent ROS-mediated inflammation and apoptosis in liver cells. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2016, 38, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, R.L.; Jiang, B.H. Roles of EGFR, PI3K, AKT, and mTOR in heavy metal-induced cancer. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2013, 13, 252–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.B.; Vahter, M.; Concha, G.; Broberg, K. Environmental arsenic exposure and DNA methylation of the tumor suppressor gene p16 and the DNA repair gene MLH1: Effect of arsenic metabolism and genotype. Metallomics 2012, 4, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balali-Mood, M.; Naseri, K.; Tahergorabi, Z.; Khazdair, M.R.; Sadeghi, M. Toxic Mechanisms of Five Heavy Metals: Mercury, Lead, Chromium, Cadmium, and Arsenic. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 643972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, K.; Haque, A.; Fau-Karim, R.; Karim, R.; Fau-Fajol, A.; Fajol, A.; Fau-Hossain, E.; Hossain, E.; Fau-Salam, K.A.; Salam Ka Fau-Ali, N.; et al. Dose-response relationship between arsenic exposure and the serum enzymes for liver function tests in the individuals exposed to arsenic: A cross sectional study in Bangladesh. Environ. Health 2011, 10, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yao, X.; Qiu, T.; Jiang, L.; Wang, N.; Shi, Y.; Wu, C.; Yuan, W.; Yang, G.; et al. Ubiquitinated gasdermin D mediates arsenic-induced pyroptosis and hepatic insulin resistance in rat liver. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 160, 112771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhu, K.; Zhang, A. SIRT1-mediated tunnelling nanotubes may be a potential intervention target for arsenic-induced hepatocyte senescence and liver damage. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 947, 174502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Q.; Song, D.; Wang, Q.; Wang, D.; Chen, X.; Zhang, A.; Ma, L. Resveratrol Alleviates Arsenic Exposure-Induced Liver Fibrosis in Rats by Inhibiting Hepatocyte Senescence. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2025, 203, 1528–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, G.; Rao, G.; Tang, L.; Wu, S.; Tang, Z.; Huang, R.; Ruan, Z.; Hu, L. Combined effect of arsenic and polystyrene-nanoplastics at environmentally relevant concentrations in mice liver: Activation of apoptosis, pyroptosis and excessive autophagy. Chemosphere 2022, 300, 134566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chang, L.H.; Huang, W.Q.; Bao, H.W.; Li, X.; Chen, X.H.; Wu, H.T.; Yao, Z.Z.; Huang, Z.Z.; Weinberg, S.E.; et al. IL-17A mediates pyroptosis via the ERK pathway and contributes to steroid resistance in CRSwNP. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 150, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Zhang, X.; Liu, N.; Tang, L.; Peng, C.; Chen, X. Pyroptosis: Mechanisms and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, P.; Chen, Z.; Xia, Y.; Qiao, C.; Liu, W.; Deng, H.; Li, J.; Ning, P.; et al. Pyroptosis in inflammatory diseases and cancer. Theranostics 2022, 12, 4310–4329. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, E.I.; Sutterwala, F.S. Initiation and perpetuation of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and assembly. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 265, 35–52. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, D.; Liwinski, T.; Elinav, E.A.-O. Inflammasome activation and regulation: Toward a better understanding of complex mechanisms. Cell Discov. 2020, 6, 36. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Yang, S.; Guo, Y.; Sun, G.; Li, B. Chronic arsenic exposure in drinking water interferes with the balances of T lymphocyte subpopulations as well as stimulates the functions of dendritic cells in vivo. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 71, 115–131. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, C.; Wu, L.; Fau-Li, X.; Li, X. IL-17 family: Cytokines, receptors and signaling. Cytokine 2013, 64, 477–485. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, L.; Sun, J.; Han, J.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L. Interleukin-17 induces pyroptosis in osteoblasts through the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway in vitro. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 96, 107781. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Dai, M.Y.; Huang, R.Y.; Duan, J.Y.; Zhang, T.; Bao, W.M.; Zhang, J.Y.; Gui, S.Q.; Xia, S.M.; Dai, C.T.; et al. Parabacteroides distasonis ameliorates hepatic fibrosis potentially via modulating intestinal bile acid metabolism and hepatocyte pyroptosis in male mice. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1829. [Google Scholar]
- Hammerich, L.; Tacke, F. Role of gamma-delta T cells in liver inflammation and fibrosis. World J. Gastrointest. Pathophysiol. 2014, 5, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, C.; Jia, Z.; Xiaoli, W.; Na, Z.; He, W.; Hao, J. New Aspect of Liver IL-17(+)γδ T Cells. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 107, 41–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| pro-caspase-1F | TGAAGGACAAACCGAAGG |
| pro-caspase-1R | GAAGAGCAGAAAGCGATA |
| pro-IL-18F | CATTGACCAAGGAAATCGGCC |
| pro-IL-18R | TAAATATGGTCCGGGGTGCA |
| pro-IL-1βF | GCTTGGTGATGTCTGGTCCA |
| pro-IL-1βR | TCAACACGCAGGACAGGTAC |
| IL-18 F | ATCGCTTCCTCTCGCAACAA |
| IL-18 R | TCCAGGTTTTCATCATCTTCAGC |
| IL-1beta F | ATCAGCACCTCTCAAGCAG |
| IL-1beta R | AGTCCACATTCAGCACAGG |
| NLRP3 F | GACCATCCTCGGCATGT |
| NLRP3 R | CACGATCCAGCAGACCA |
| IL-17F | AGATTACTACAACCGATCCACCT |
| IL-17R | GGGGACAGAGTTCATGTGGTA |
| Caspase-1F | GAAAAGCCATGGCCGACAGA |
| Caspase-1R | GCCCCTTTCATGGGTGAAGG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, T.; Chen, M.; Tian, S.; Luo, P.; Zhang, J. Mechanistic Studies on the Role of IL-17/NLRP3 in Arsenic-Induced Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells Through Hepatocyte Proptosis. Toxics 2025, 13, 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040287
Hu T, Chen M, Tian S, Luo P, Zhang J. Mechanistic Studies on the Role of IL-17/NLRP3 in Arsenic-Induced Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells Through Hepatocyte Proptosis. Toxics. 2025; 13(4):287. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040287
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Ting, Mei Chen, Sai Tian, Peng Luo, and Jiangping Zhang. 2025. "Mechanistic Studies on the Role of IL-17/NLRP3 in Arsenic-Induced Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells Through Hepatocyte Proptosis" Toxics 13, no. 4: 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040287
APA StyleHu, T., Chen, M., Tian, S., Luo, P., & Zhang, J. (2025). Mechanistic Studies on the Role of IL-17/NLRP3 in Arsenic-Induced Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells Through Hepatocyte Proptosis. Toxics, 13(4), 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040287





