Prediction of Soil Pollution Risk Based on Machine Learning and SHAP Interpretable Models in the Nansi Lake, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
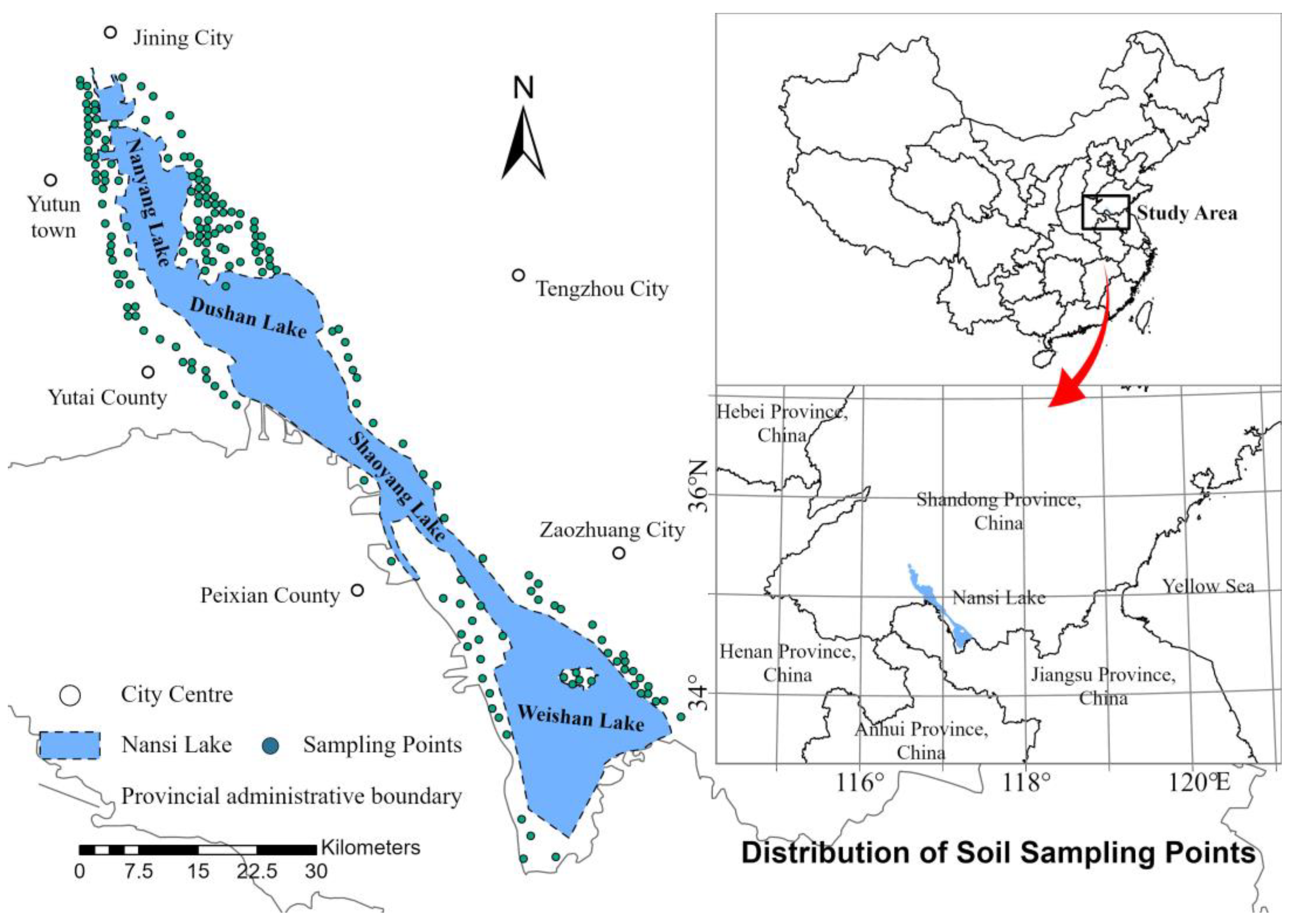
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Processing
2.3. Potential Ecological Risk Index
2.4. Pollution Load Index
2.5. Support Vector Machine (SVM) Model
2.6. Decision Tree and Random Forestx
2.7. Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost)
2.8. Synthetic Minority Over-Sampling Technique
2.9. Evaluation of Predictive Performance
2.10. SHapley Additive exPlanations Interpretation Frameworkx
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Statistical Analysis of Soil Sample Characteristics
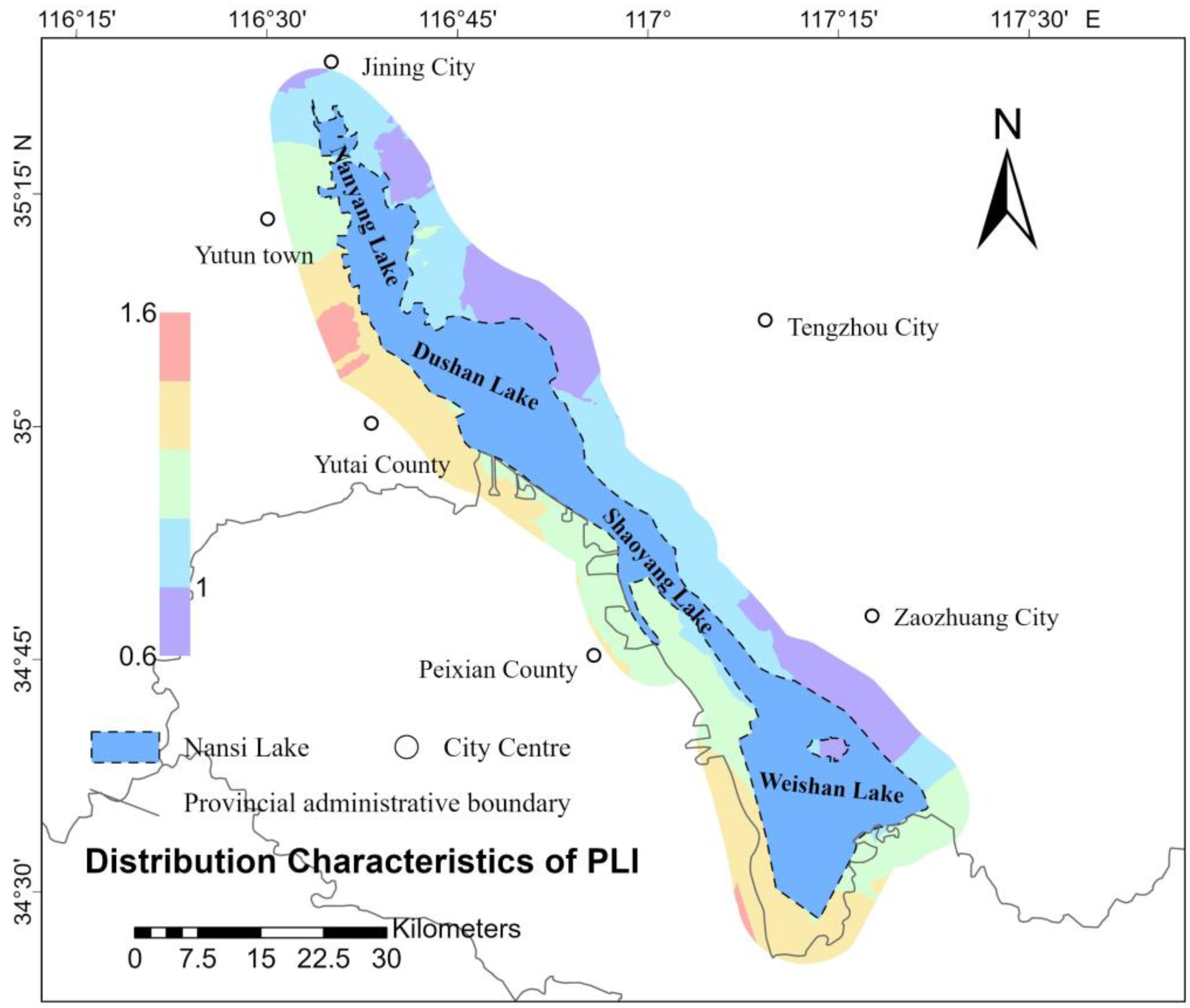
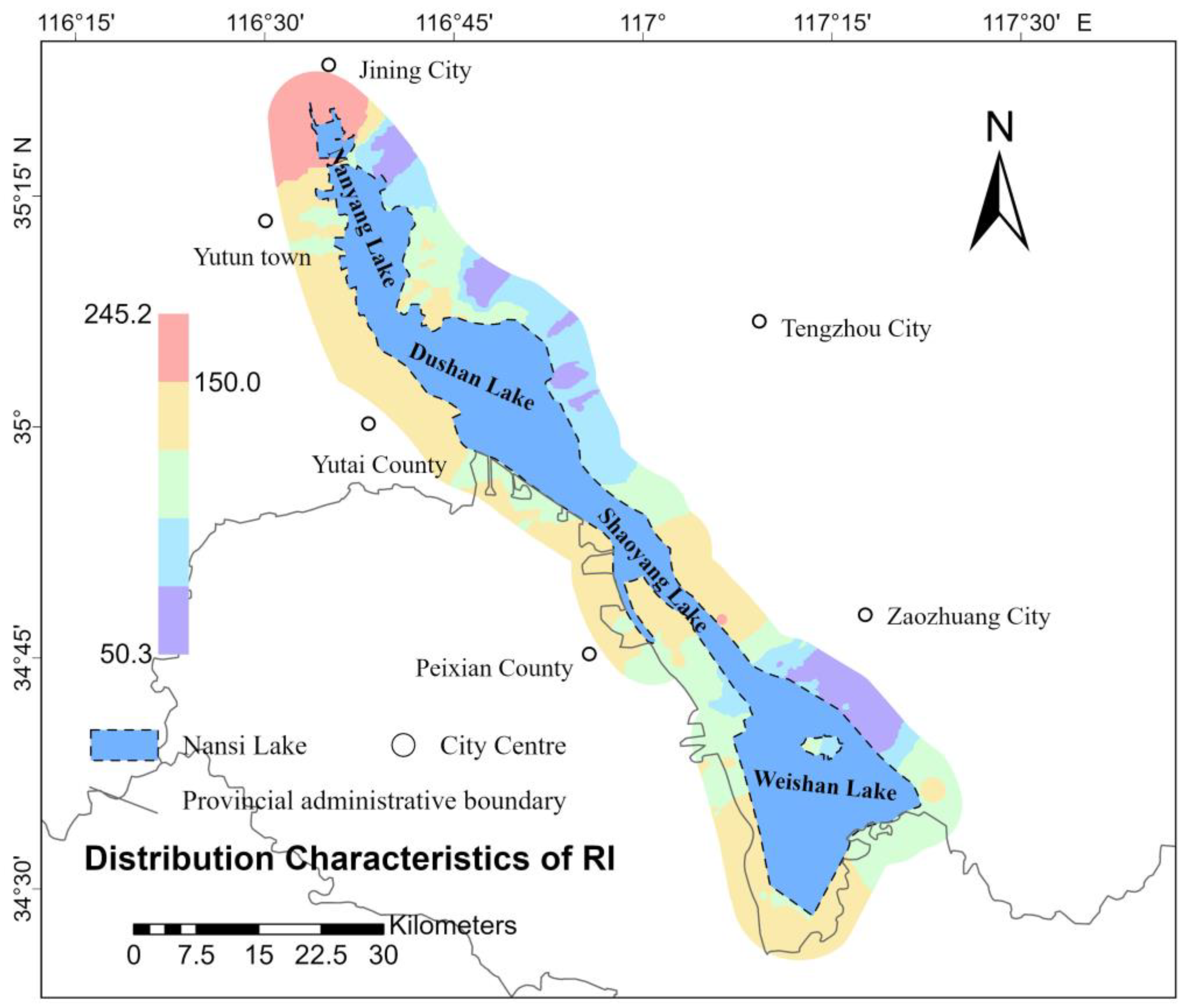
3.2. Spatial Distribution of Soil PLI and PERI
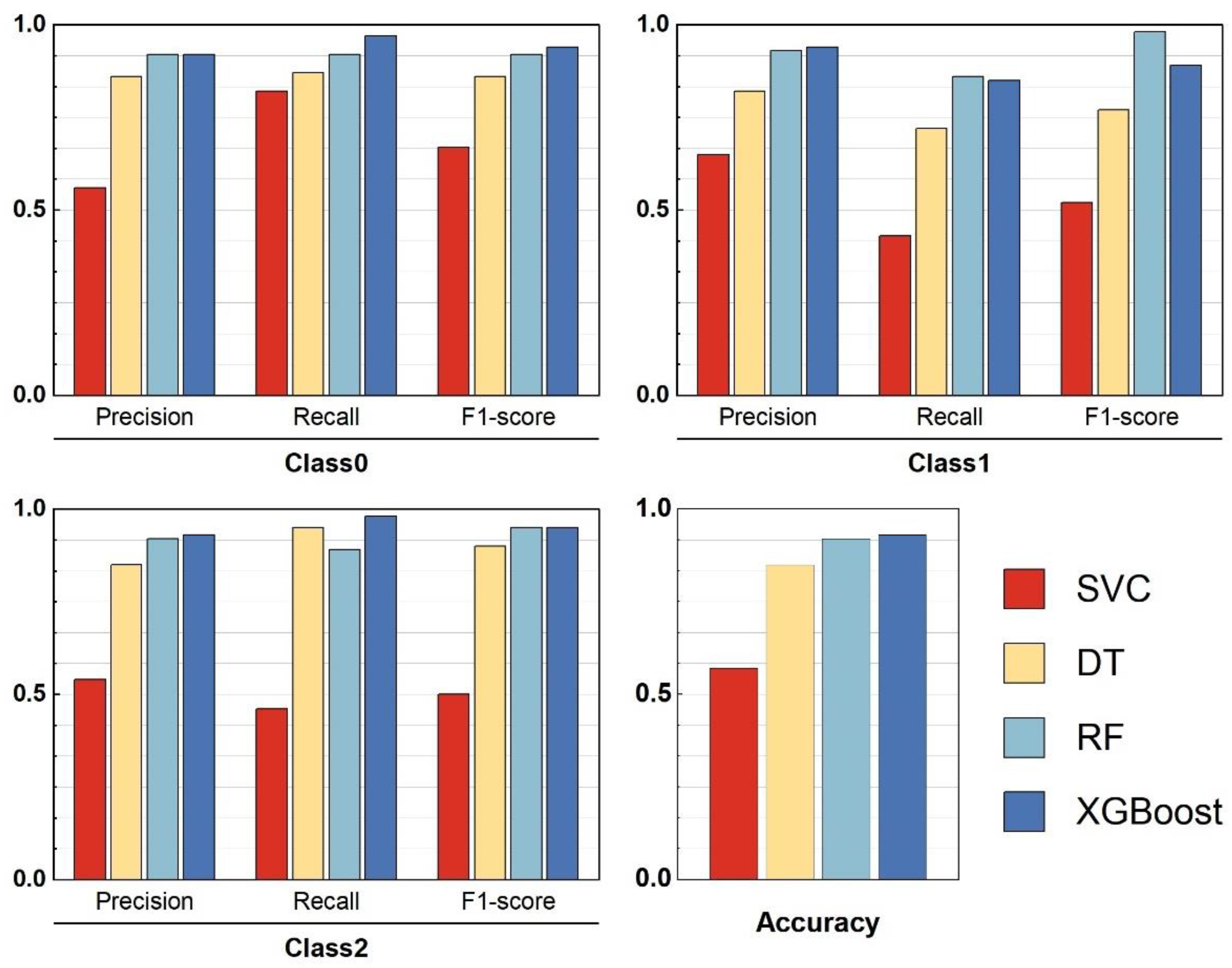
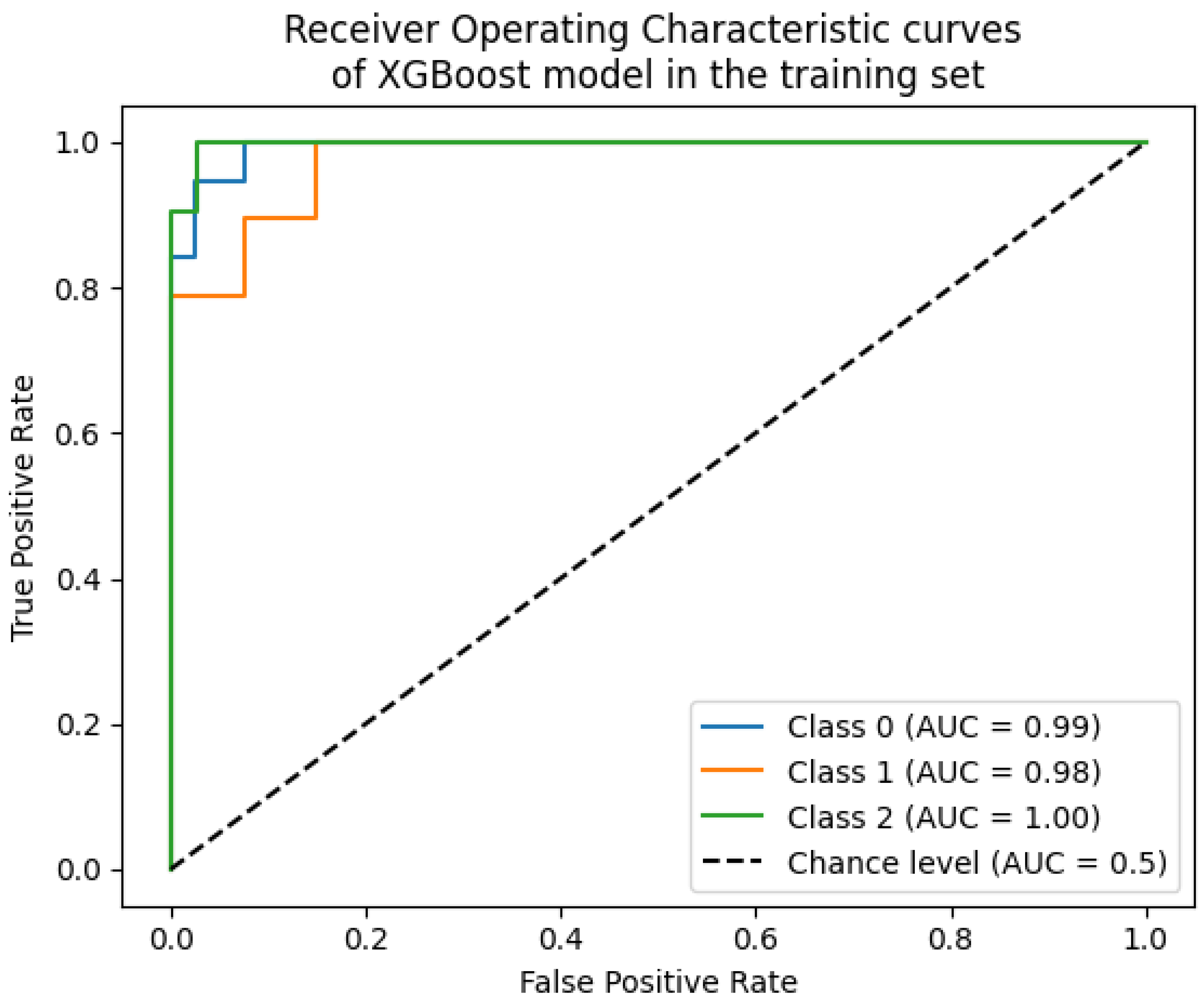
3.3. Training and Selection of Machine Learning Classification Models
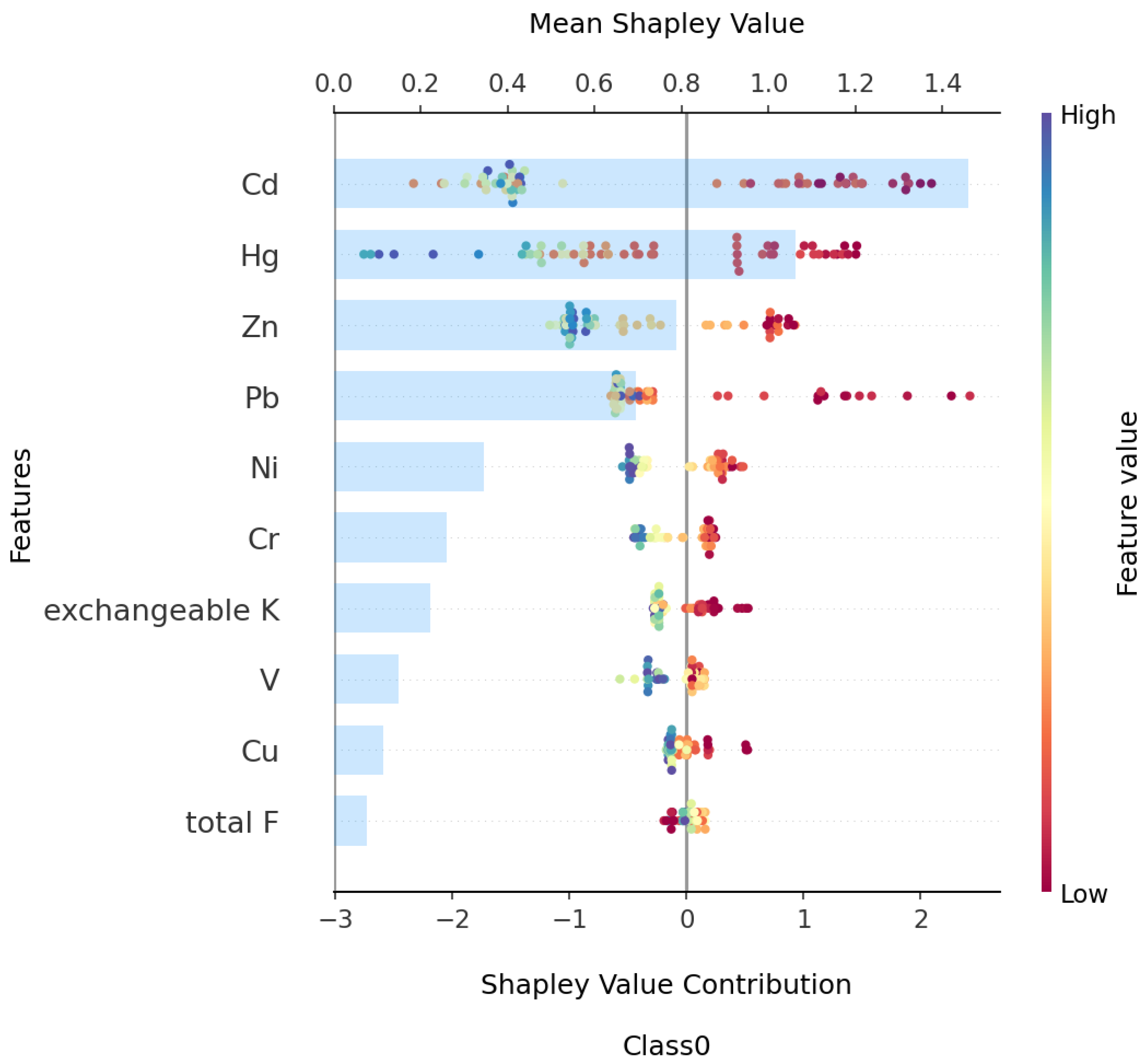
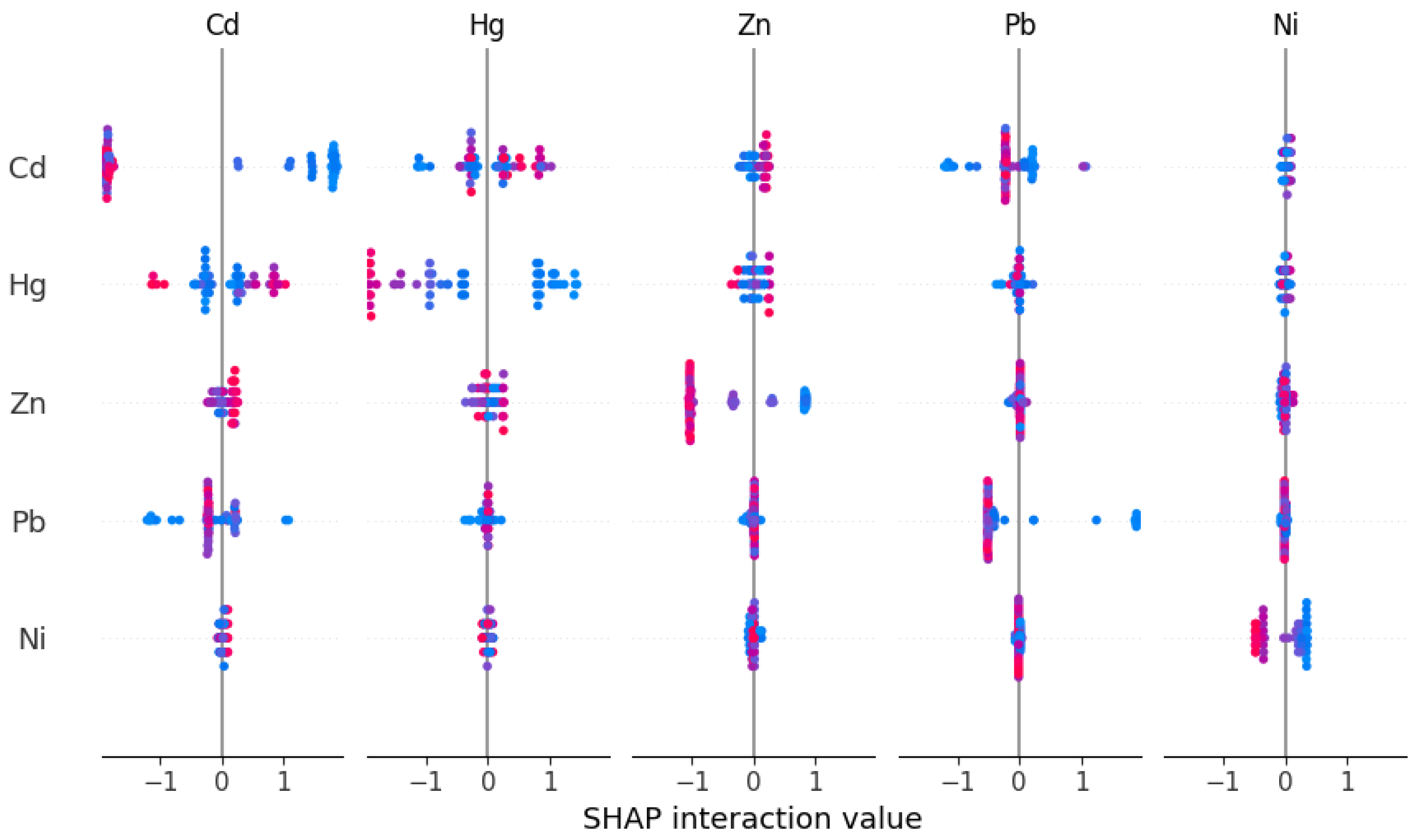
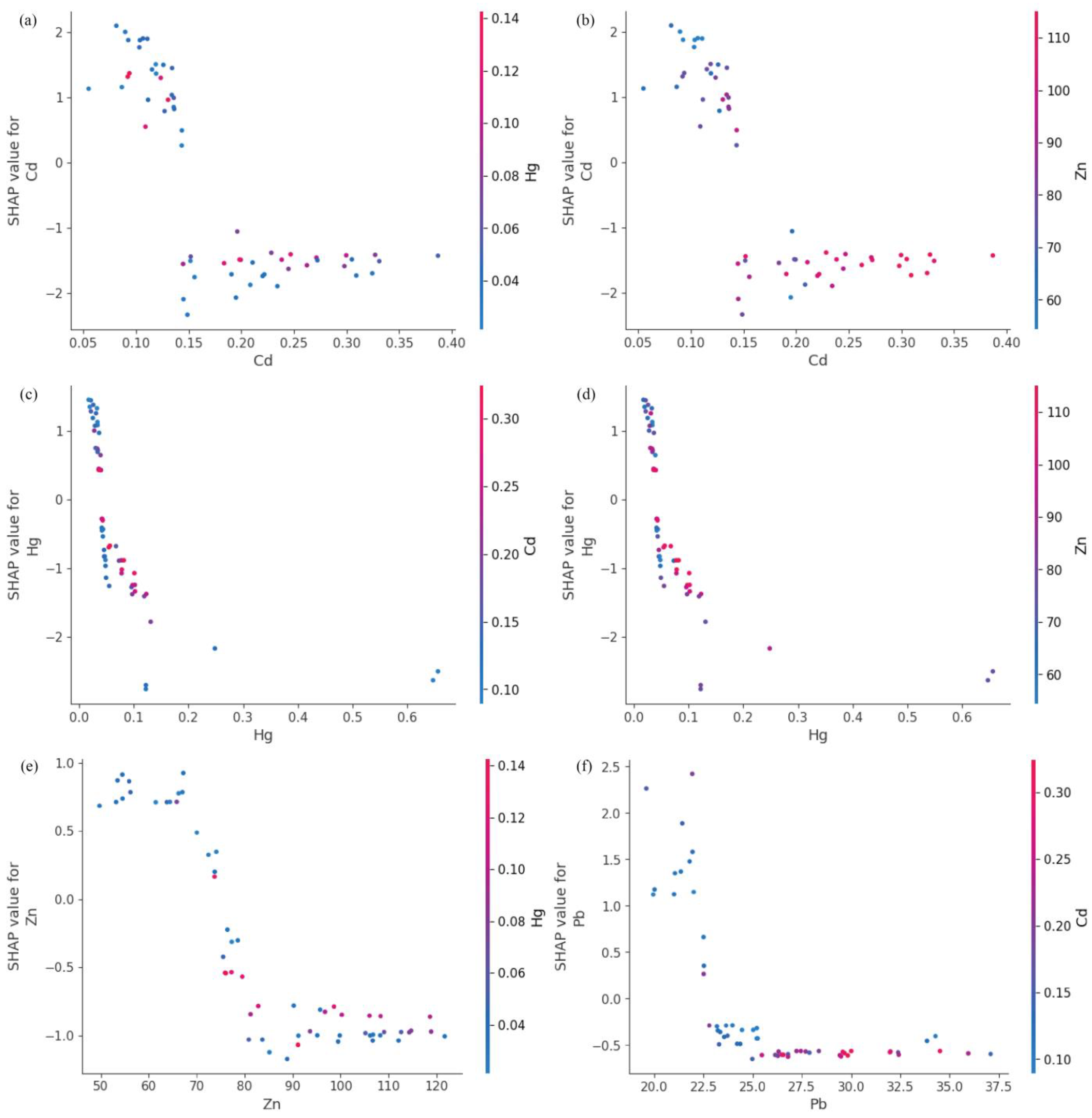
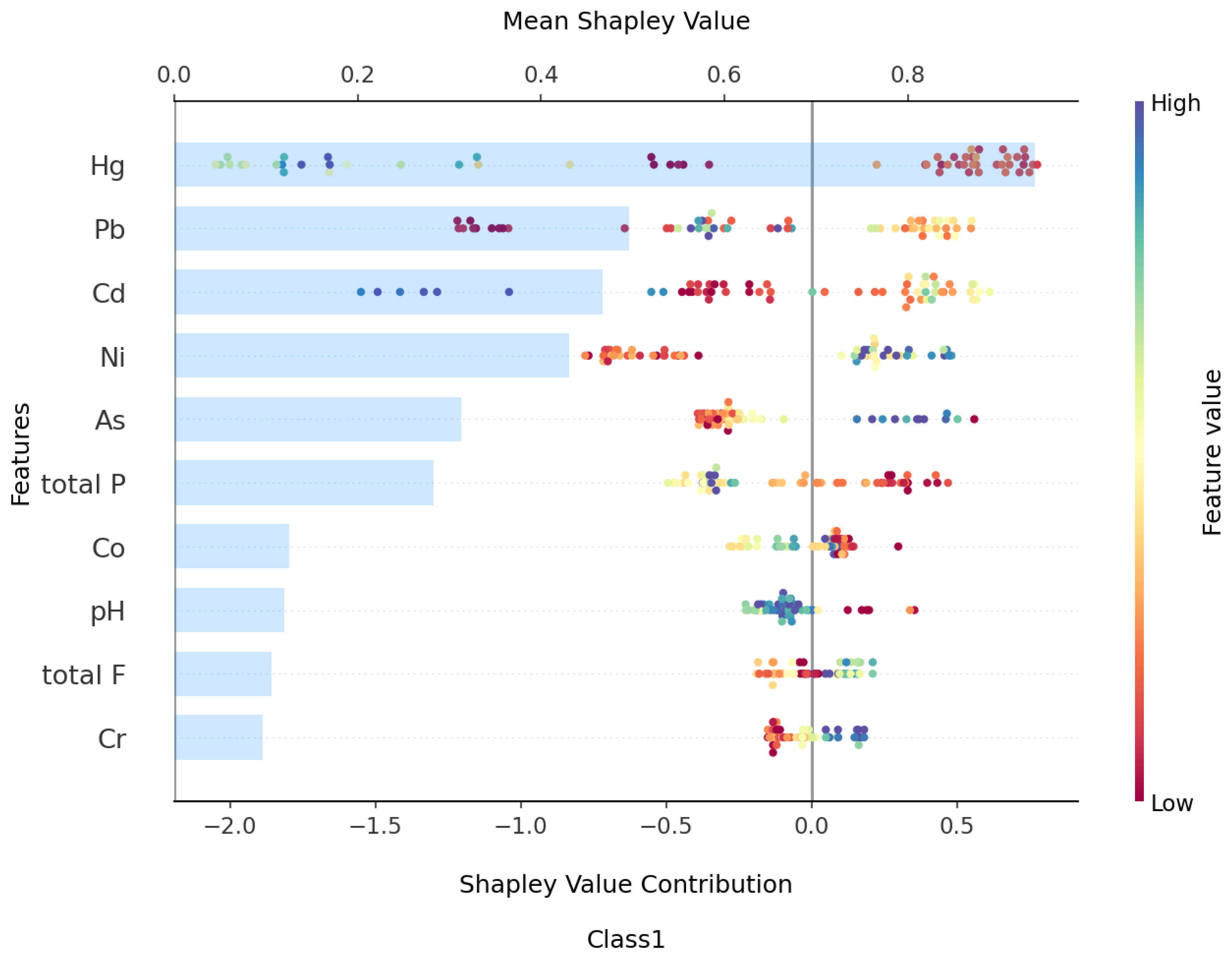
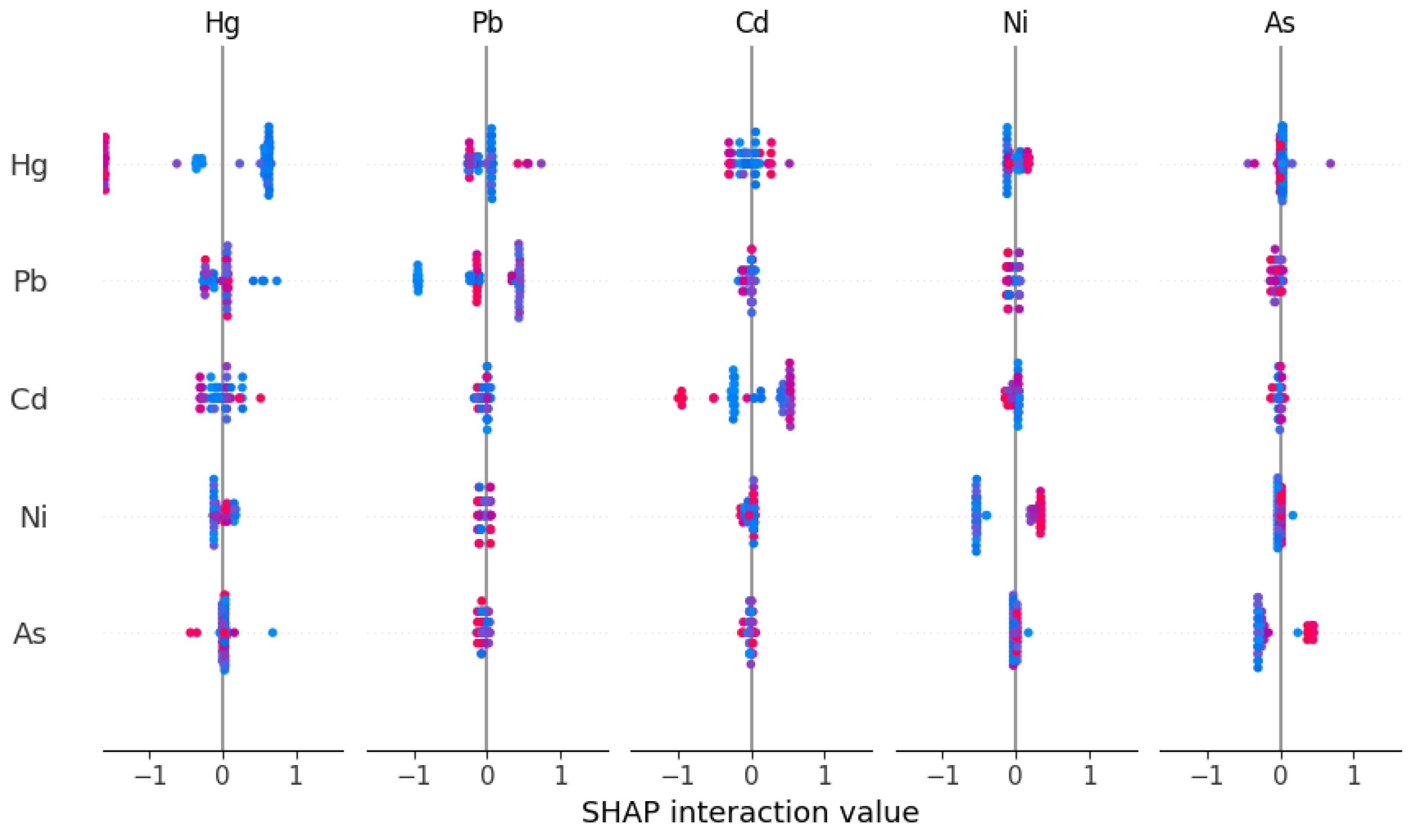
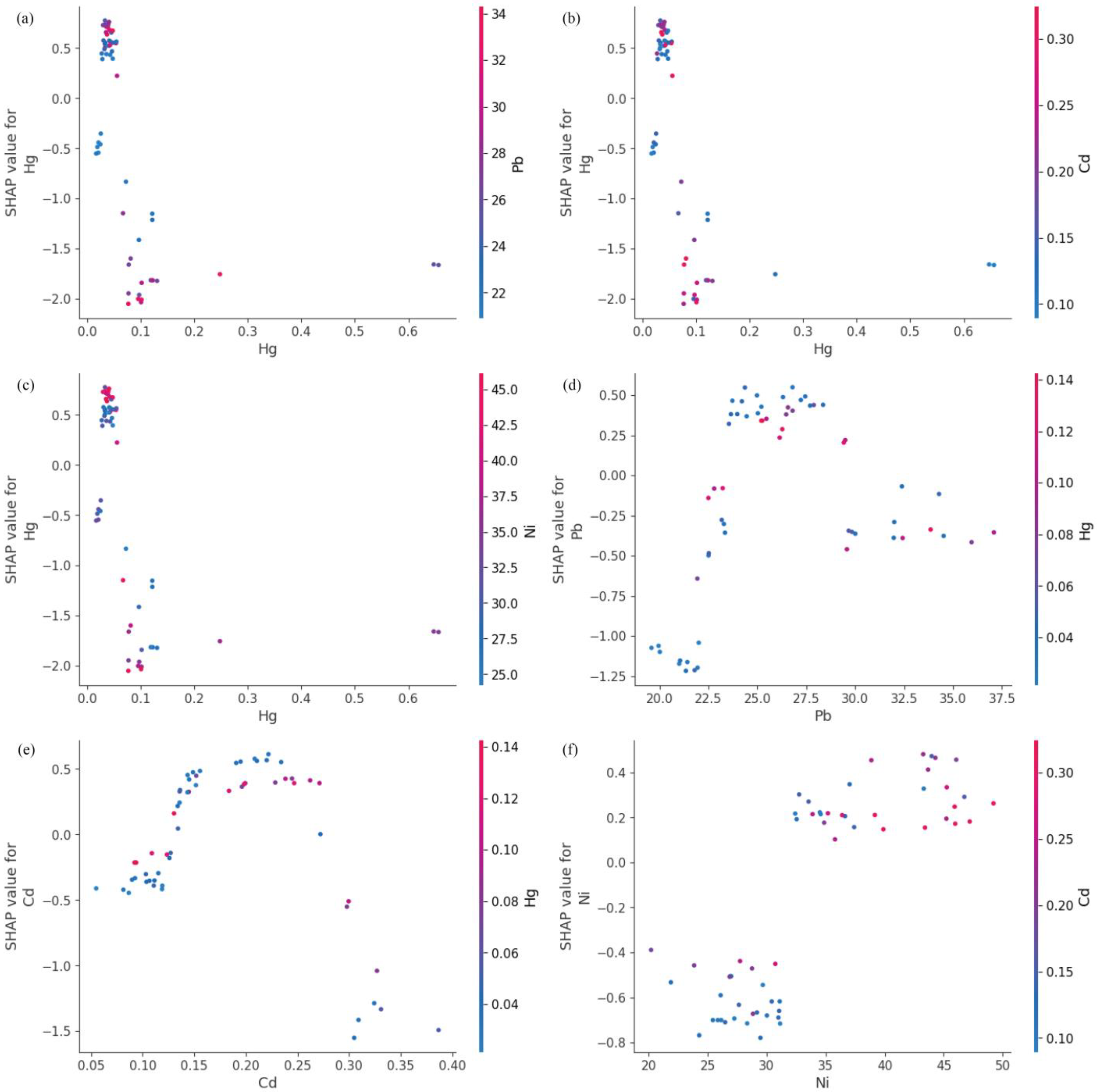
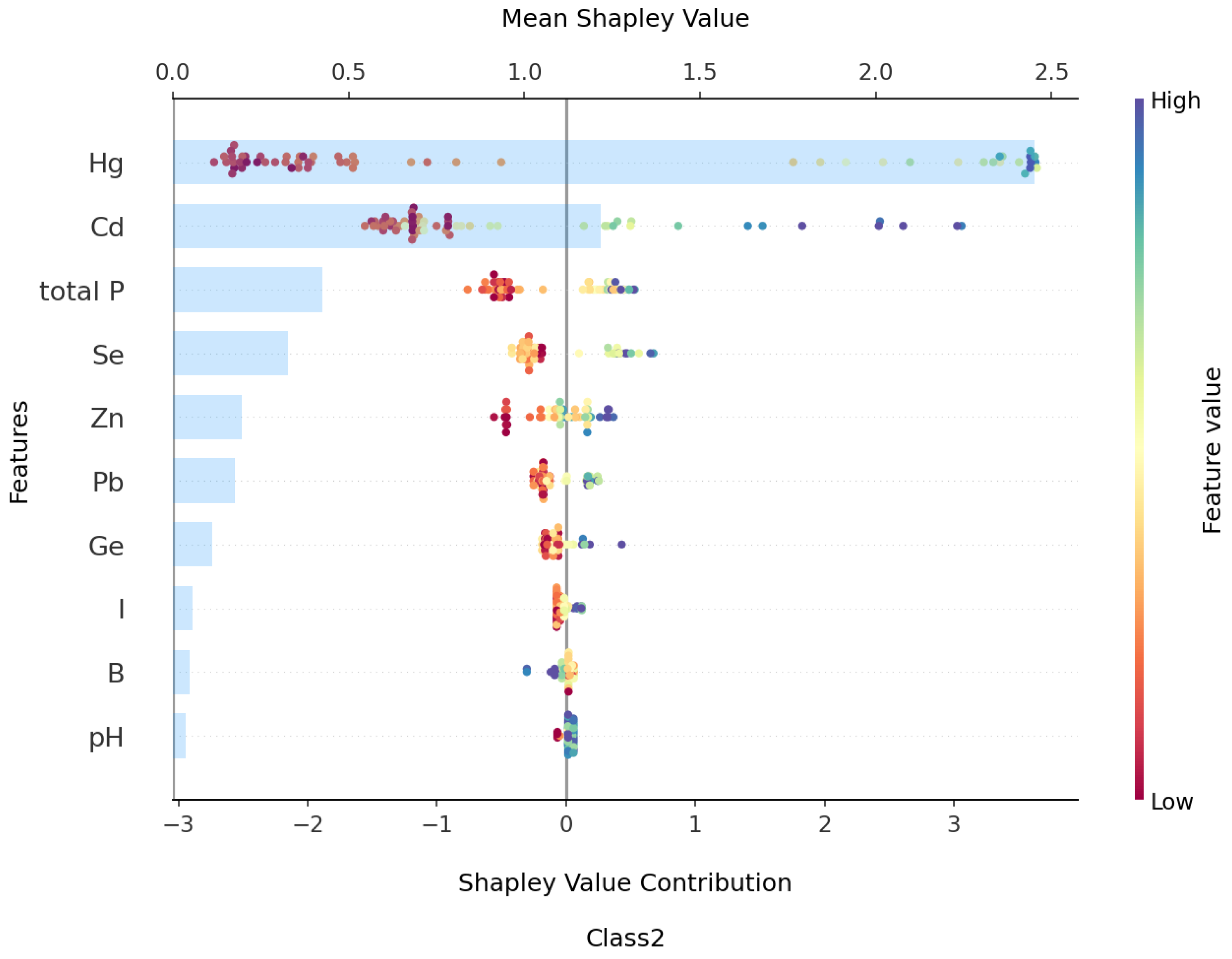
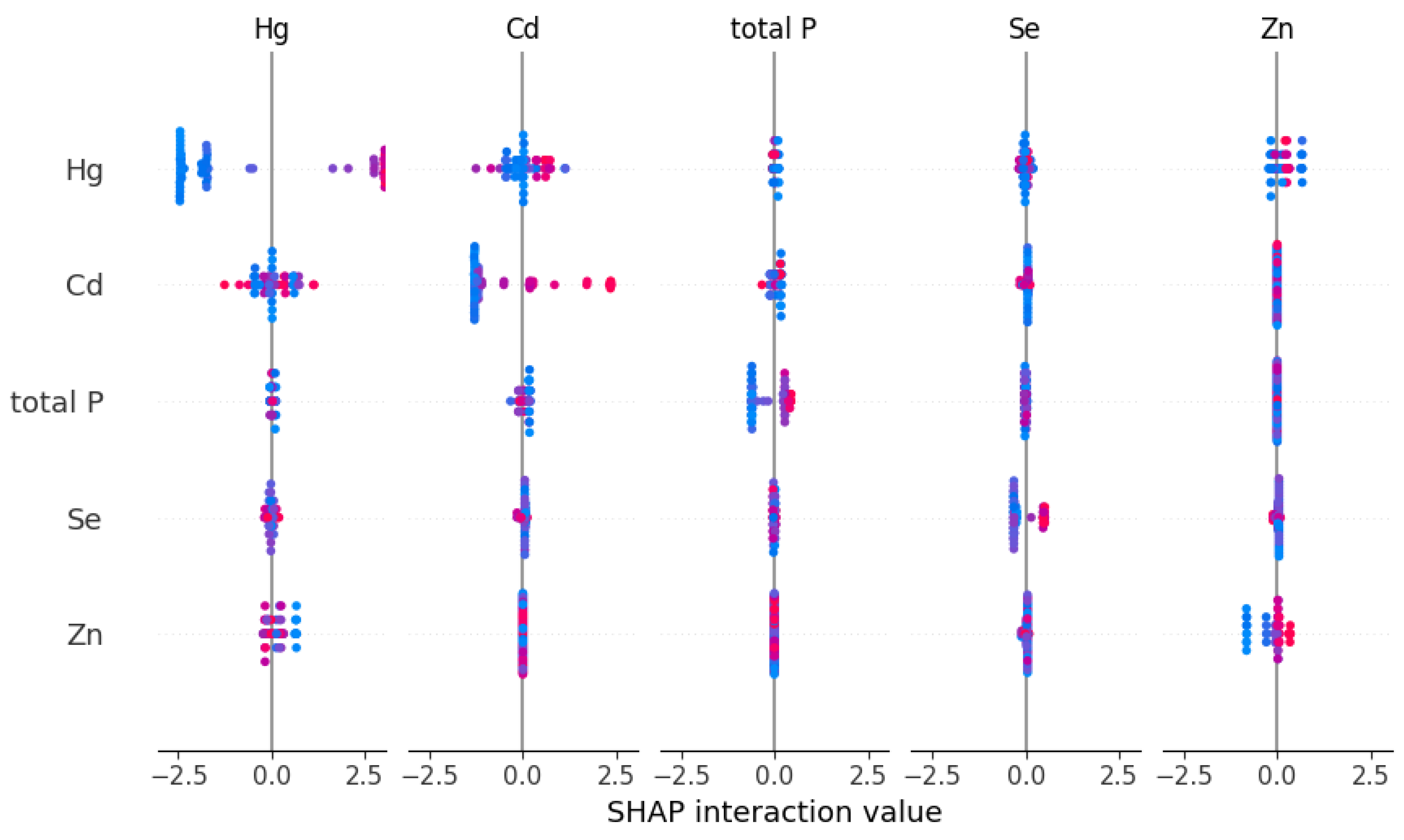
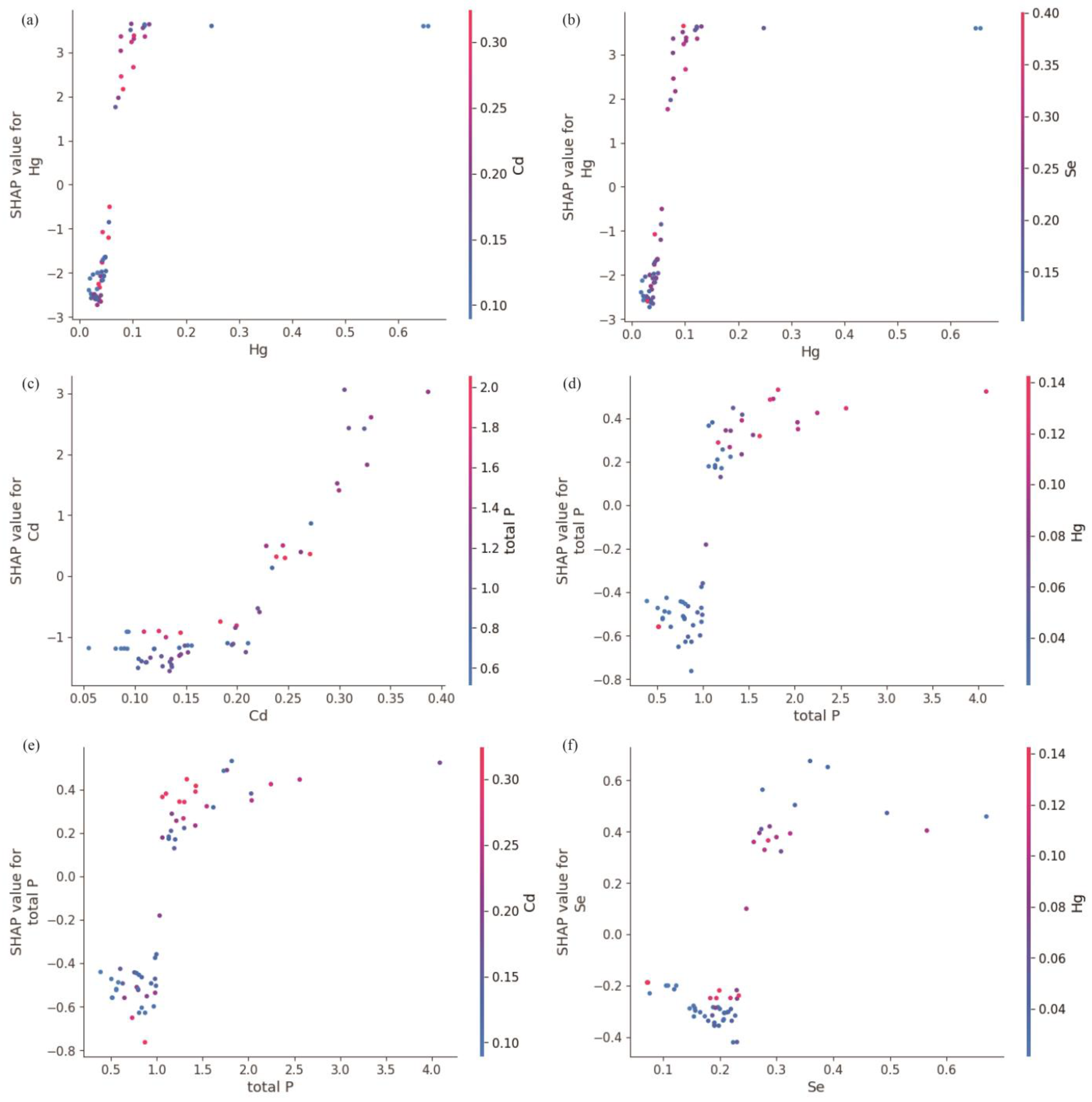
3.4. Explanatory Analysis Based on SHAP
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yan, D. Study on the Remediation Effects and Mechanisms of Alternanthera Philoxeroides on Cd and Pb Contaminated Sediments in Nansi Lake. Master’s Thesis, Shandong Jianzhu University, Jinan, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, F.; Lv, S.; Hu, S.; Wang, G.; Liu, J.; Hou, G.; Liu, A. Spatial Variation Characteristics of Farmland Soil Nutrients in the Nansi Lake Basin. Shandong Agric. Sci. 2023, 55, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Fang, J. Study on the Current Situation and Control of Agricultural Non-point Source Pollution in the Nansi Lake Basin: A Case Study of Yutai County, Jining City. Environ. Prot. Circ. Econ. 2024, 44, 52–55. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=52O9CKbg8L5nkQuE3k4MB0ldf9XKFnDQfUgo6AVXDWJjJRFNnbE9jeKsuv6uqOzdJKXGdgvtPF-YnOekgq5uK1K4GnTCwGGY_iMB0FNZGpPQicZKx_aL0FWxZkPy--Wj82xMyeYtaQZ9enSPr4sLW3QE_9Te6uR9hj7HPxm2xOXRMsLgvO2aB9Cq3drrC6PLu-0pfHdvBqQ (accessed on 18 October 2024).
- Zhong, X.; Luo, L.; Song, X.; Wang, W. Evaluation of soil pollution ecological risk. Guizhou Sci. 2025, 43, 66–69. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=52O9CKbg8L7F6fM4P5Tk9HYU3AC2aF_YCReVr1LDMQQFOw2VbDha2GEI1Kd8SwU0_zs8dl1MGCsV6YE7XfGrhwmil51BrsCUof26gFE00daQe6Q6Ljxs8UAAOaotKeydAo__wdlDmMGRHRosBJcTPZ8nZ_Q7sZz6JLgC-TDXdWI_BLYhUMbOLoOgsQ6woiCD (accessed on 19 February 2025).
- Zhao, T.; Liu, S.; Xu, J.; He, H.; Wang, D.; Horton, R.; Liu, G. Comparative Analysis of Seven Machine Learning Algorithms and Five Empirical Models to Estimate Soil Thermal Conductivity. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2022, 323, 109080. [Google Scholar]
- Mannaa, A.A.; Khan, A.A.; Haredy, R.; Al-Zubieri, A.G. Contamination Evaluation of Heavy Metals in a Sediment Core from the Al-Salam Lagoon, Jeddah Coast, Saudi Arabia. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y. Research and Application of Prediction Model for Regional Soil Heavy Metal Pollution. Master’s Thesis, Beijing Information Science and Technology University, Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Shen, C.; Tang, H.; Huang, Y. Soil Type Data Provide New Methods and Insights for Heavy Metal Pollution Assessment and Driving Factors Analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 135868. [Google Scholar]
- Jas, K.; Dodagoudar, G.R. Explainable Machine Learning Model for Liquefaction Potential Assessment of Soils Using XGBoost-SHAP. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2023, 165, 107662. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Dong, C.; Sun, S.; Peng, S.; Mu, L.; Zhang, N.; Bao, L. Characteristics and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination in Arable Soils Developed from Different Parent Materials. Agriculture 2024, 14, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xi, Z. Application of Delphi Method in Screening of Indexes for Measuring Soil Pollution Value Evaluation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 6561–6571. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, H.; Zhou, J.; Li, Z.; Gu, C. Soil and Sediment Pollution, Processes and Remediation. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 822355. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, L.; Liang, J.; Song, W.; Li, Y.; Tao, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yao, Y. Comprehensive evaluation of ecological health of key rivers and lakes in the Yellow River and Nansi Lake basins in Shandong Province. J. Beijing Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2025, 1–10. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.1991.N.20250306.1119.005 (accessed on 6 March 2025).
- Jiao, P.; Jiang, D.; Xu, P.; Wang, S.; Wu, H.; Shi, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Z. Spatial and temporal characteristics of agricultural non-point source pollution in the Nansi Lake Basin of Shandong Province and its prevention and control strategies. China South. Agric. Mach. 2025, 56, 17–24+45. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=52O9CKbg8L5DkLZTVybIi5iccb70zPEoEYVDrWI_HAr62RMVLdS_MsIWjOZ5RC-El_gjDxTXcHEH9bJo4Qn0Jp3VdWo0_VWBYv1fuCdMUEsbtIoZvvofPJ3V9v0QNi08O4XoYEKDpzQf0q7_ETZy79FDbGP1c3jlrJnN7G1CPWfChrJQVAh925hThO3OFLnO9L5nF3JpQvs (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, G.; He, L.; Sun, J. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in the Water and Sediments of the Nansi Lake and The Assessment of Ecological Risk. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2024, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ/T 166-2004; Technical Specification for Soil Environmental Monitoring. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2004.
- DZ/T 0295-2016; Specification of Land Quality Geochemical Assessment. Ministry of Land and Resources of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- HJ 1019-2019; Technical Guideline for Site Soil and Groundwater Sampling of Volatile Organic Compounds. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2019.
- HJ 962-2018; Soil—Determination of pH—Potentiometry. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- HJ 1315-2023; Soil and Sediment—Determination of 19 Total Metal Elements—Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2023.
- DB12/T 1022-2022; Determination of Available Boron in Soil—Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2022.
- DZ/T 0279.16—2016; Determination of Germanium Contents by Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Ministry of Land and Resources of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB/T 42333-2023; Soil and Stream Sediment—Determination of Iodine Content—Pressurized Ammonia Extraction Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2023.
- HJ 680-2013; Soil and Sediment—Determination of Mercury, Arsenic, Selenium, Bismuth, and Antimony—Microwave Digestion/Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2013.
- HJ 873-2017; Soil—Determination of Water-Soluble Fluoride and Total Fluoride—Ion Selective Electrode Method. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Chen, L.; Wu, J.; Xia, C.; Gong, L.; Xu, Z. Chemical Speciation and Potential Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Volcanic Rocks of Southern Qinghai, China. Chem. Ecol. 2019, 35, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Gallagher, F.; Deng, Y.; Wu, M.; Feng, H. Risk Assessment and Interpretation of Heavy Metal Contaminated Soils on an Urban Brownfield Site in New York Metropolitan Area. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 23549–23558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, C.; Guo, J.; Pan, J.; Qi, J.; Zhou, W. Potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in sediments of the Yangtze River within the Wanzhou section, China. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2009, 129, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, X. Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Potential Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Sludge of Shanghai Sewage Treatment Plant: A Case Study. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalçın, M.G.; Mutlu, E.; Olguner, C.; Atakoğlu, Ö.Ö.; Bat, L.; Özkan, E.Y. Spatial Geochemical Structure of Soft Sediment on Shallow Littoral of the Gulf of Antalya, the Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 193, 115155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Cui, X.; Feng, H.; Yan, S. Environmental Background Values and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Watershed Sediments: A Comparison of Assessment Methods. Water 2021, 14, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, V.; Maiti, S.K.; Jagadevan, S. Ecological Risk Assessment of Metals Contamination in the Sediments of Natural Urban Wetlands in Dry Tropical Climate. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 97, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeilzadeh, M.; Mahmodpor, E.; Haghighat, S.; Esmaeilzadeh, S.; Aliani, H.; Yazdanfar, N. Contamination and Ecological Risk Assessment of Trace Elements in Sediments of the Anzali Wetland, Northern Iran. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 2578–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Wang, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, X.; Hu, Q. Regression-Based Hyperparameter Learning for Support Vector Machines. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 35, 18799–18813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.K.; Kumar, D.; Kashyap, P.S.; Singh, P.K.; Kumar, A.; Singh, S.K. Modelling of Soil Permeability Using Different Data Driven Algorithms Based on Physical Properties of Soil. J. Hydrol. 2020, 580, 124223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estévez, V.; Beucher, A.; Mattbäck, S.; Boman, A.; Auri, J.; Björk, K.-M.; Österholm, P. Machine Learning Techniques for Acid Sulfate Soil Mapping in Southeastern Finland. Geoderma 2022, 406, 115446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, A.B.; Iversen, B.V.; Beucher, A.; Greve, M.H. Prediction of Soil Drainage Classes in Denmark by Means of Decision Tree Classification. Geoderma 2019, 352, 314–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, T.; Chen, D.; Zhang, X. Identification of Potential Sources of Mercury (Hg) in Farmland Soil Using a Decision Tree Method in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabameri, A.; Sadhasivam, N.; Turabieh, H.; Mafarja, M.; Rezaie, F.; Pal, S.C.; Santosh, M. Credal Decision Tree Based Novel Ensemble Models for Spatial Assessment of Gully Erosion and Sustainable Management. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.; Cao, M.; Wang, C.; Yu, N.; Qing, H. Research on Mining Maximum Subsidence Prediction Based on Genetic Algorithm Combined with XGBoost Model. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi-Termeh, S.V.; Sadeghi-Niaraki, A.; Abba, S.I.; Ali, F.; Choi, S.-M. Enhancing Spatial Prediction of Groundwater-Prone Areas through Optimization of a Boosting Algorithm with Bio-Inspired Metaheuristic Algorithms. Appl. Water Sci. 2024, 14, 244. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.; Chen, H.; Dong, X.; Zhou, K.; Xu, Z. Research on Prediction of Multi-Class Theft Crimes by an Optimized Decomposition and Fusion Method Based on XGBoost. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 207, 117943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niazkar, M.; Menapace, A.; Brentan, B.; Piraei, R.; Jimenez, D.; Dhawan, P.; Righetti, M. Applications of XGBoost in Water Resources Engineering: A Systematic Literature Review (Dec 2018–May 2023). Environ. Model. Softw. 2024, 174, 105971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi-Termeh, S.V.; Seo, M.; Sadeghi-Niaraki, A.; Choi, S.-M. Flash Flood Detection and Susceptibility Mapping in the Monsoon Period by Integration of Optical and Radar Satellite Imagery Using an Improvement of a Sequential Ensemble Algorithm. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2023, 41, 100595. [Google Scholar]
- Aydın, Y.; Işıkdağ, Ü.; Bekdaş, G.; Nigdeli, S.M.; Geem, Z.W. Use of Machine Learning Techniques in Soil Classification. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, L. Building Vulnerability Assessment in Seismic Areas Using Ensemble Learning: A Nepal Case Study. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 350, 131418. [Google Scholar]
- Bammou, Y.; Benzougagh, B.; Abdessalam, O.; Brahim, I.; Kader, S.; Spalevic, V.; Sestras, P.; Ercişli, S. Machine Learning Models for Gully Erosion Susceptibility Assessment in the Tensift Catchment, Haouz Plain, Morocco for Sustainable Development. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2024, 213, 105229. [Google Scholar]
- Nishitsuji, Y.; Exley, R. Elastic Impedance Based Facies Classification Using Support Vector Machine and Deep Learning. Geophys. Prospect. 2019, 67, 1040–1054. [Google Scholar]
- Shayilan, A.; Chen, Y. A SMOTified Extreme Learning Machine for Identifying Mineralization Anomalies from Geochemical Exploration Data: A Case Study from the Yeniugou Area, Xinjiang, China. Earth Sci. Inform. 2024, 17, 1329–1343. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Zhu, M.; Feng, Z.; Stanković, L. Manifold-Based Shapley Explanations for High Dimensional Correlated Features. Neural Netw. 2024, 180, 106634. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, N.; Zhang, D.; Feng, S.; Ding, K.; Tan, L.; Wang, B.; Chen, T.; Li, W.; Dai, X.; Pan, J. Rapid Landslide Extraction from High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images Using SHAP-OPT-XGBoost. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Dai, J.; Chen, L.; Liu, H.; Yu, C.; Han, L.; Ren, T.; Hu, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z. Soil Geochemical Background Value of 17 Cities in Shandong Province. Shandong Land Resour. 2019, 35, 46–56. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=52O9CKbg8L7_ZHKqHlG7zlYVkNoIpb-GJr4x3KaGJswYq2N5c4kKRyTgKXML5IWFXp1aGgegDN5hJHqIhhVmMdxkoUvgHOheb9DGVgnDj69WfmKCFuxd7OcwScs1E9hJdySfRXk0Pj29clQp9QZN5lxmRonRzmcOFRxixfeFZLTRdlHqLsnn9RaZSb6OyjbqIhE70LGUiCQ (accessed on 16 January 2019).
- Hou, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, Q. Pollution Characteristics and Source Apportionment of Heavy Metals in Topsoil of Counties Along the Shandong Section of the Yellow River. Environ. Sci. 2024, 45, 5485–5493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Li, Z.; Wu, L.; Ni, C.; Luo, Y. Preliminary Study on Cadmium and Lead Stabilization in Soil Highly Polluted with Heavy Metals Using Different Stabilizing Agents. Soils 2019, 51, 752–759. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, F.; Ali, S.; Zhang, H.; Ouyang, Y.; Qiu, B.; Wu, F.; Zhang, G. The Influence of pH and Organic Matter Content in Paddy Soil on Heavy Metal Availability and Their Uptake by Rice Plants. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Min | Max | Mean | Standard Deviation | Coefficient of Variance | Kurtosis | Skewness | Background Value 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | 3.75 | 25.65 | 12.70 | 3.60 | 0.28 | −0.05 | 0.49 | 10.40 |
| B | 25.83 | 145.65 | 50.20 | 10.91 | 0.22 | 20.00 | 2.58 | 2.58 |
| Cr | 24.67 | 96.38 | 65.15 | 12.91 | 0.20 | −0.65 | 0.18 | 66.00 |
| Cd | 0.04 | 0.41 | 0.18 | 0.08 | 0.43 | −0.22 | 0.67 | 0.16 |
| Cu | 11.50 | 76.01 | 31.33 | 7.36 | 0.23 | 3.49 | 0.90 | 28.80 |
| Co | 6.98 | 24.19 | 12.98 | 2.65 | 0.20 | 0.95 | 0.67 | 0.67 |
| Ge | 1.06 | 3.51 | 1.56 | 0.34 | 0.22 | 9.29 | 2.73 | 1.33 |
| Hg | 0.01 | 0.66 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 1.07 | 46.95 | 6.00 | 0.04 |
| I | 0.47 | 6.44 | 2.23 | 1.13 | 0.51 | 0.39 | 0.88 | 0.88 |
| Mn | 353.04 | 2481.23 | 770.16 | 272.91 | 0.35 | 9.95 | 2.59 | 2.59 |
| Mo | 0.26 | 2.36 | 0.66 | 0.26 | 0.39 | 10.07 | 2.24 | 0.64 |
| Ni | 12.84 | 153.25 | 35.36 | 10.27 | 0.29 | 58.72 | 5.23 | 30.80 |
| Pb | 14.08 | 44.60 | 26.40 | 4.35 | 0.16 | 0.69 | 0.63 | 23.30 |
| Se | 0.03 | 1.24 | 0.25 | 0.17 | 0.68 | 12.75 | 3.20 | 3.20 |
| V | 42.56 | 116.67 | 80.43 | 15.11 | 0.19 | −0.88 | 0.16 | 0.16 |
| Zn | 37.89 | 162.22 | 85.36 | 20.29 | 0.24 | −0.50 | 0.13 | 72.20 |
| total F | 331.54 | 1372.39 | 661.08 | 158.61 | 0.24 | 0.72 | 0.60 | - |
| total K | 15.29 | 30.54 | 21.44 | 3.31 | 0.15 | 0.21 | 0.93 | - |
| exchangeable K | 62.00 | 1438.00 | 237.38 | 123.99 | 0.52 | 30.66 | 3.70 | - |
| total N | 0.26 | 3.85 | 1.56 | 0.67 | 0.43 | 0.17 | 0.75 | - |
| hydrolyzable N | 4.80 | 317.62 | 119.16 | 56.01 | 0.47 | 1.73 | 1.22 | - |
| total P | 0.35 | 4.09 | 1.12 | 0.56 | 0.50 | 8.41 | 2.27 | - |
| available P | 2.82 | 379.05 | 47.82 | 53.08 | 1.11 | 8.54 | 2.54 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; Zhang, R.; Yan, B.; Song, C.; Lv, Y.; Zhao, H. Prediction of Soil Pollution Risk Based on Machine Learning and SHAP Interpretable Models in the Nansi Lake, China. Toxics 2025, 13, 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040278
Wang M, Zhang R, Yan B, Song C, Lv Y, Zhao H. Prediction of Soil Pollution Risk Based on Machine Learning and SHAP Interpretable Models in the Nansi Lake, China. Toxics. 2025; 13(4):278. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040278
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Min, Ruilin Zhang, Beibei Yan, Chengyuan Song, Yang Lv, and Hengyi Zhao. 2025. "Prediction of Soil Pollution Risk Based on Machine Learning and SHAP Interpretable Models in the Nansi Lake, China" Toxics 13, no. 4: 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040278
APA StyleWang, M., Zhang, R., Yan, B., Song, C., Lv, Y., & Zhao, H. (2025). Prediction of Soil Pollution Risk Based on Machine Learning and SHAP Interpretable Models in the Nansi Lake, China. Toxics, 13(4), 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040278





