Investigating the Use of Diagnostic Genes in Integrated Monitoring with a Laboratory and Field Study on Flounder (Platichthys flesus)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. In Vivo Fish Exposure
2.2. Sampling and Survey Information for Field Samples
2.3. Determination of Contaminant Concentrations and Biological Effects in Field-Caught Fish
2.4. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis for Laboratory and Field-Exposed Fish
2.5. Quantitative PCR (q-PCR)
2.6. Gene Expression
2.7. Assessment Procedure and Scoring Index
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
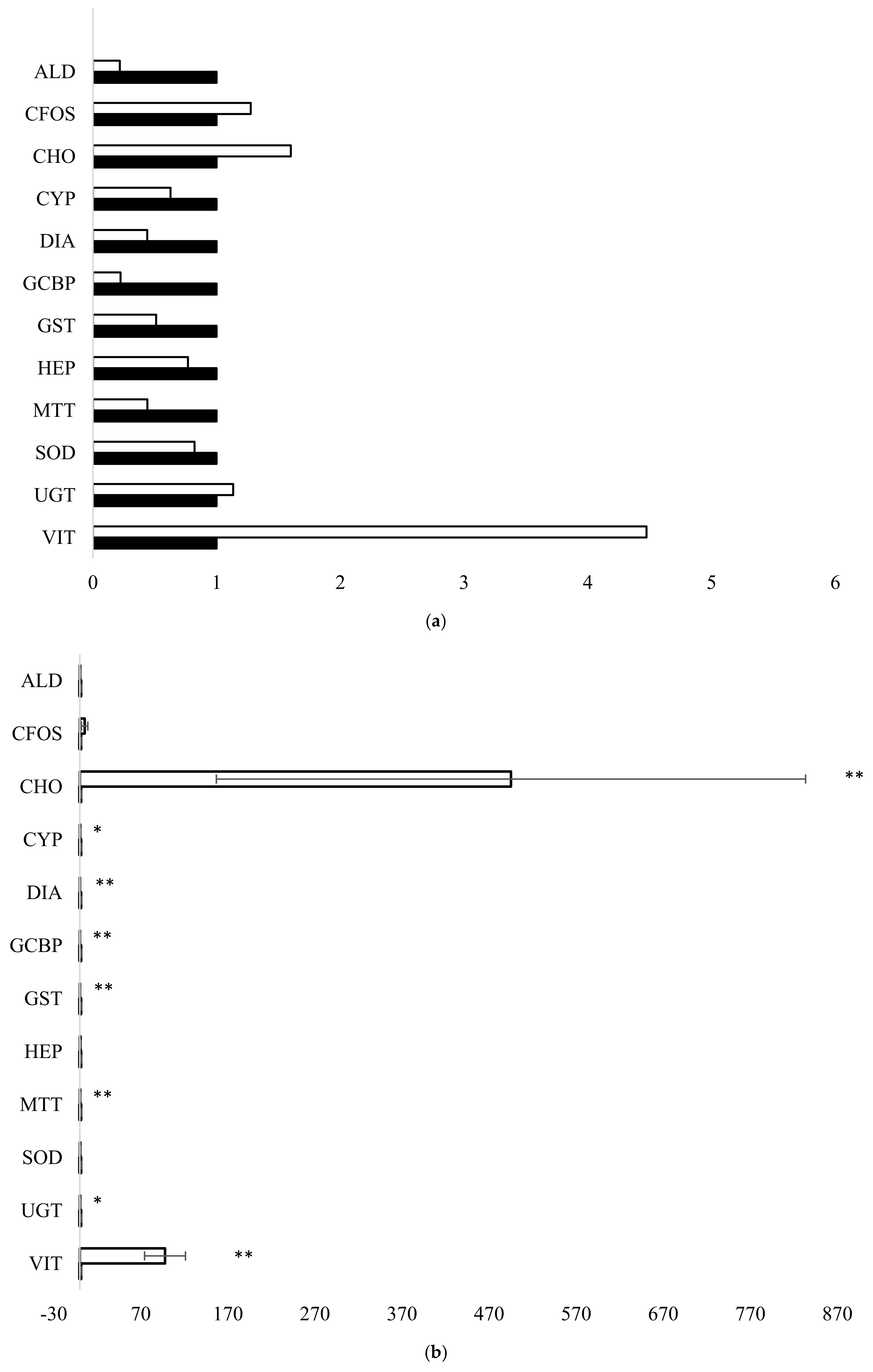
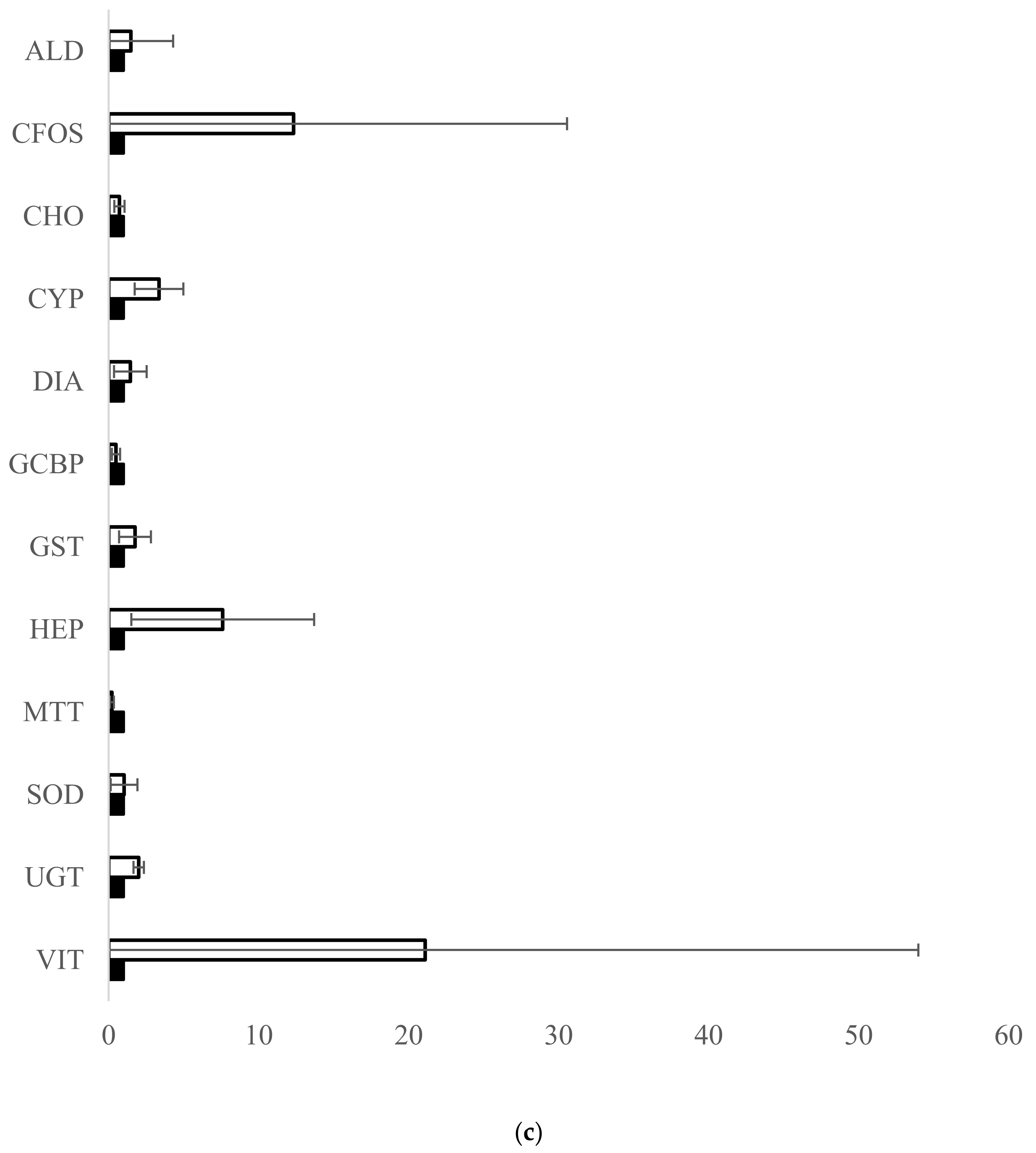
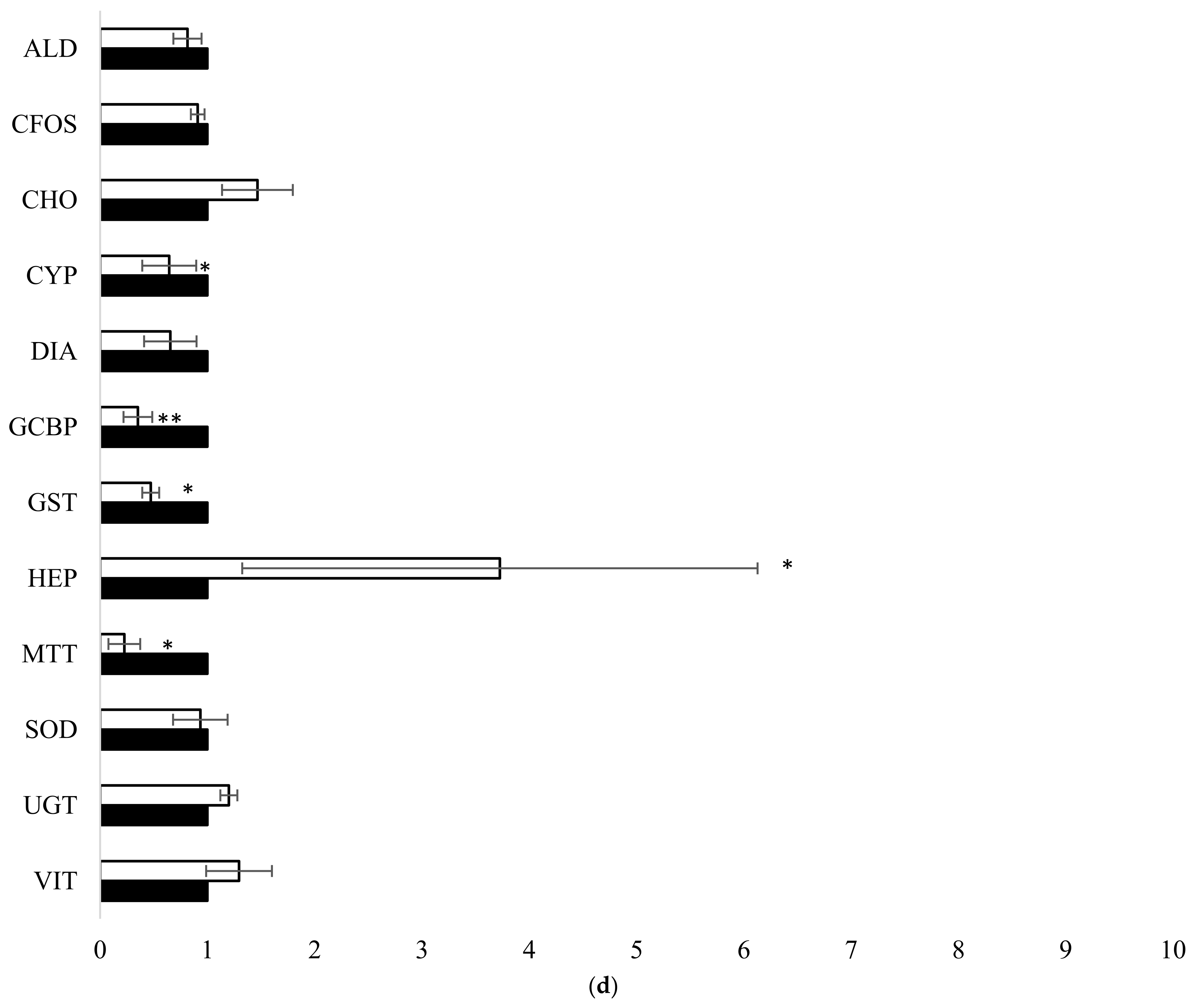
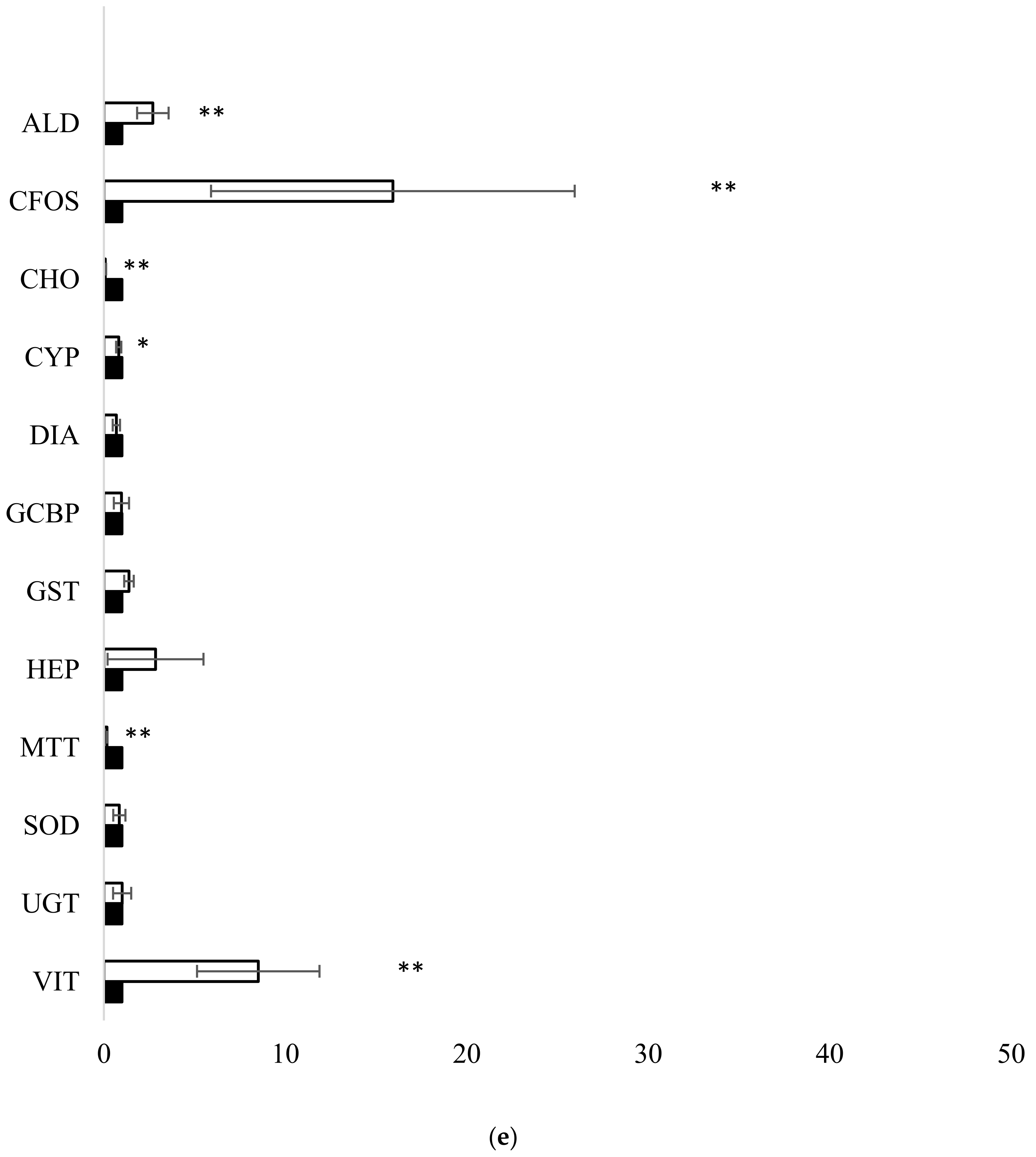
3.1. Fish Exposure and Diagnostic Genes
3.2. Contaminants in Wild-Caught Fish
3.3. Biomarkers and Supporting Parameters in Wild-Caught Fish
3.4. Multivariate Analysis of Contaminants in Flounder
3.5. Multivariate Analysis of Biological Effects in Wild-Caught Fish
3.6. Biomarkers, Contaminants, and Gene Expression in Wild-Caught Fish
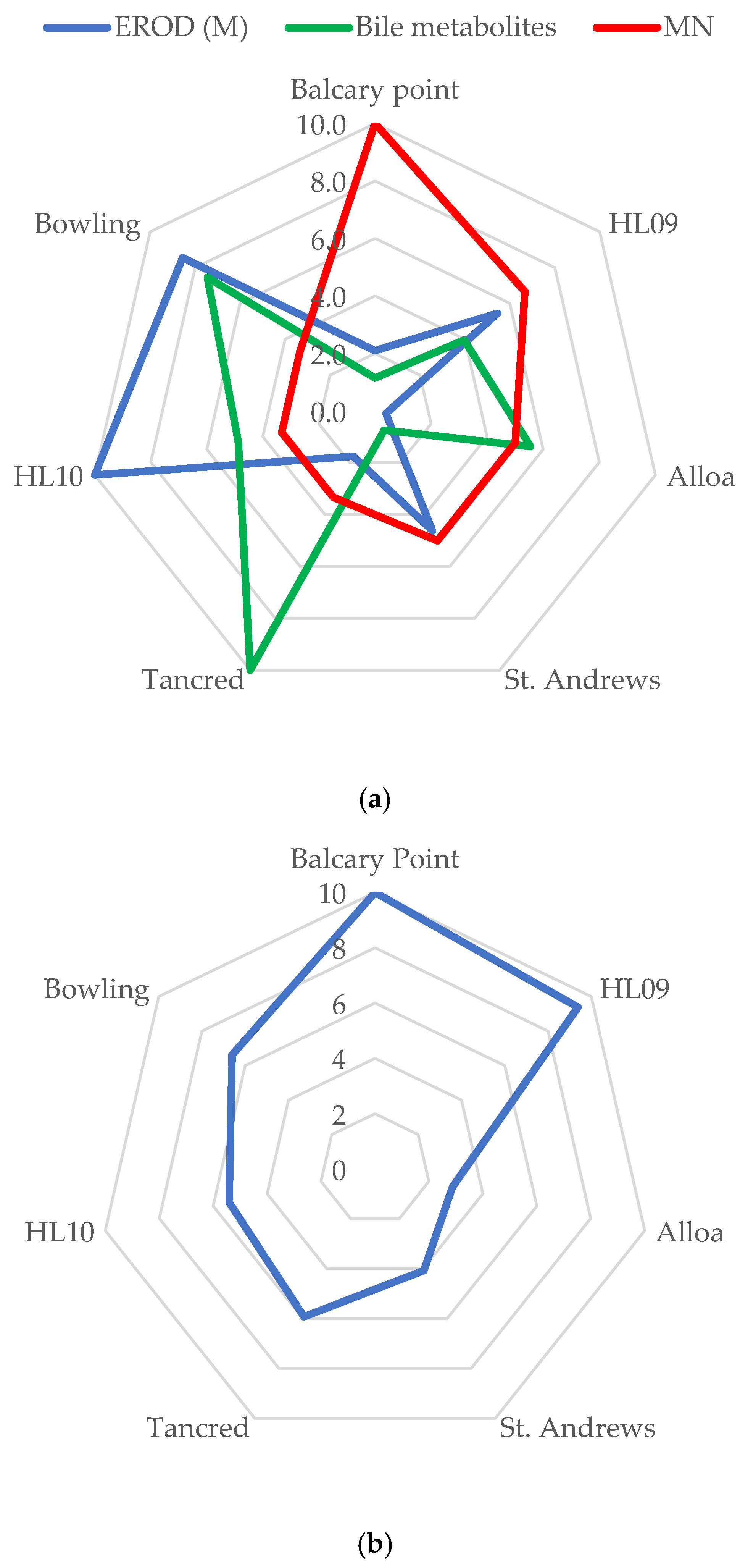
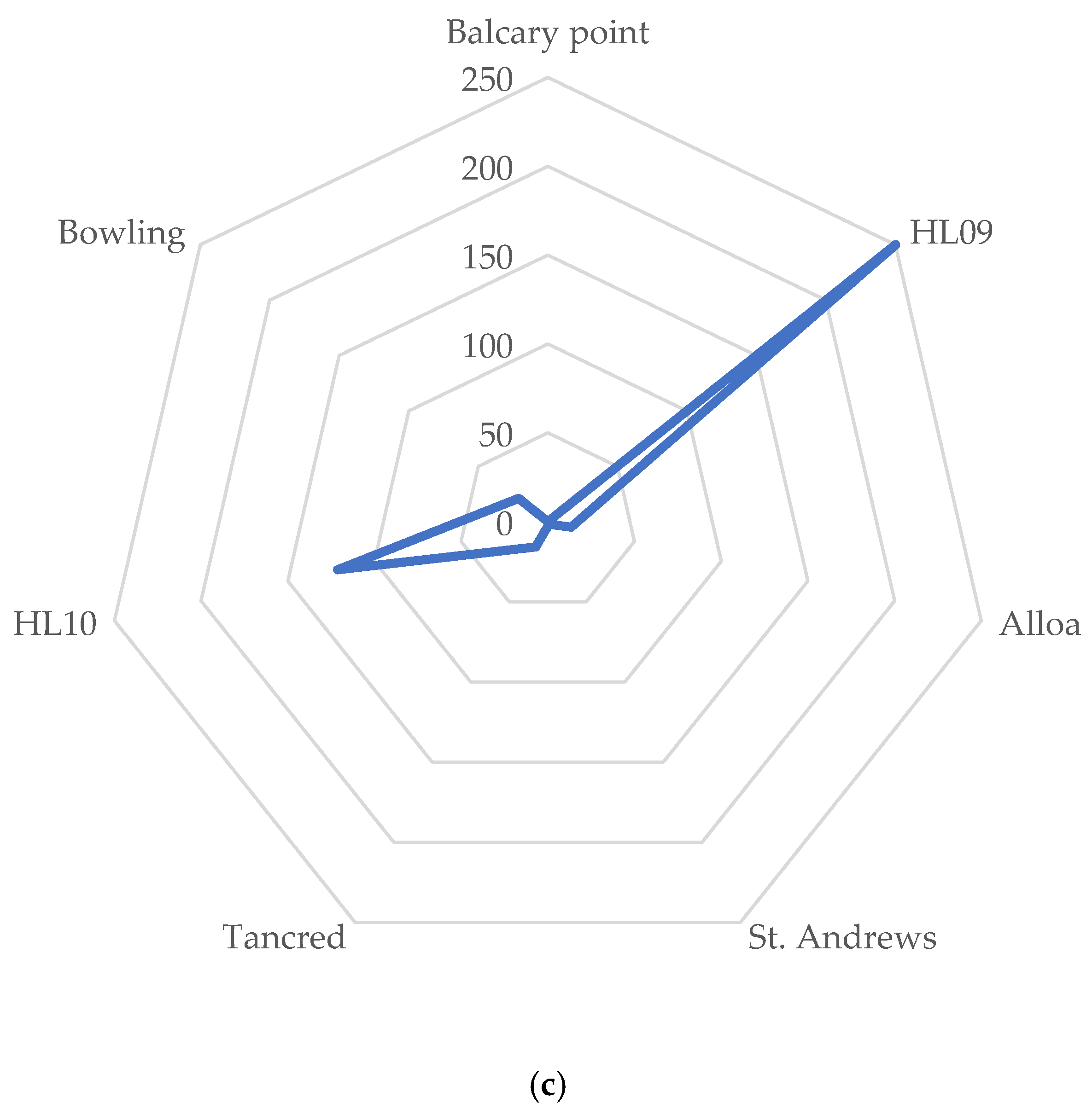
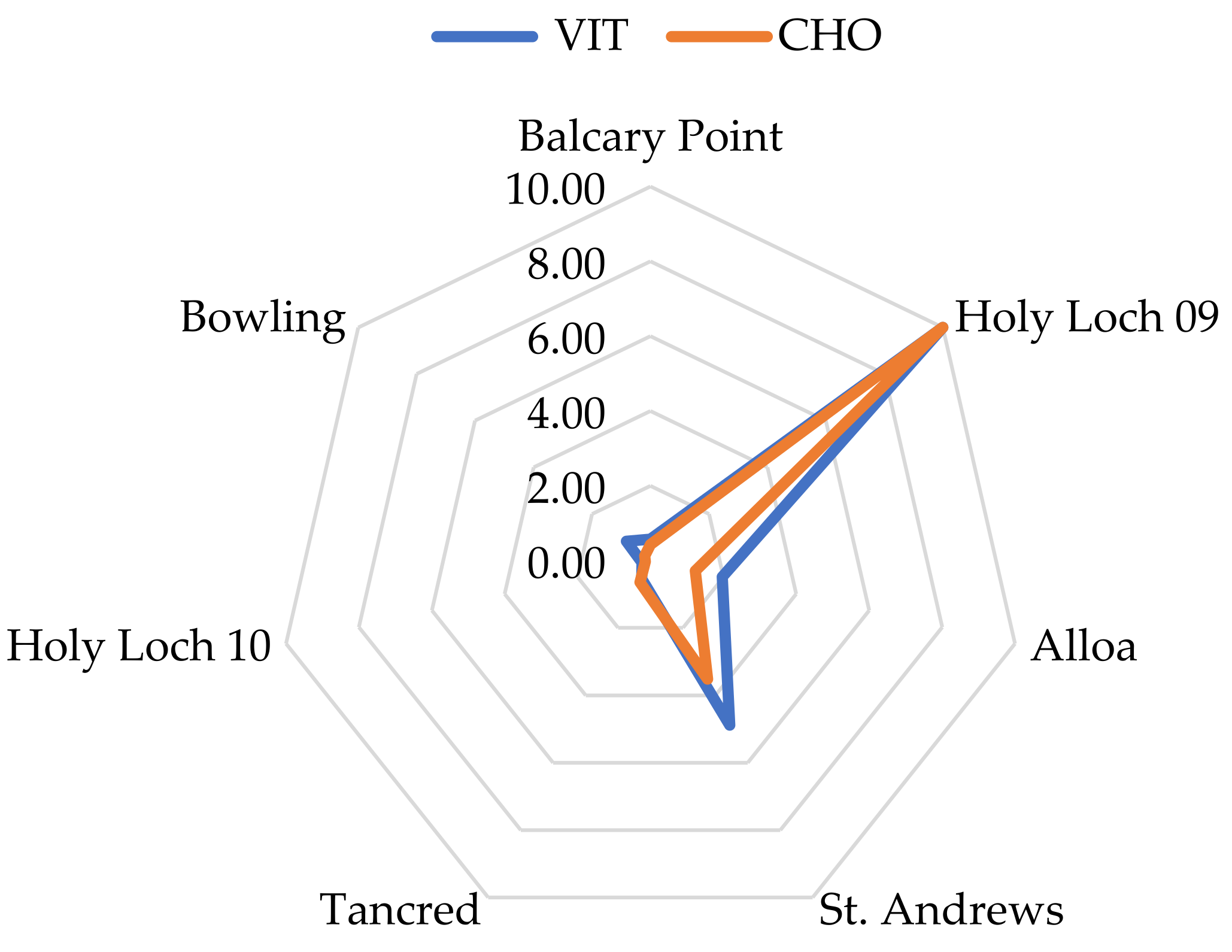
3.7. Scoring and Star Plots
4. Discussion
4.1. Fish Exposure
4.2. Wild-Caught Fish
4.3. Multivariate Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Commission. Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 establishing a framework for Community action in the field of water policy. Off. J. Eur. Communities 2000, 327, 1–72. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Directive 2008/56/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 17 June 2008, establishing a framework for community action in the field of marine environmental policy (Marine Strategy Framework Directive). Off. J. Eur. Union 2008, L164, 19–40. [Google Scholar]
- Matthiessen, P.; Law, R.J. Contaminants and their effects on estuarine and coastal organisms in the United Kingdom in the late twentieth century. Environ. Pollut. 2002, 120, 739–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennish, M.J. Ecology of estuaries: Anthropogenic effects. In Marine Science Series; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Thain, J.E.; Vethaak, A.D.; Hylland, K. Contaminants in marine ecosystems: Developing an integrated indicator framework using biological-effect techniques. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2008, 65, 1508–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lye, C.M.; Frid, C.L.J.; Gill, M.E.; McCormick, D. Abnormalities in the reproductive health of flounder Platichthys flesus exposed to effluent from a sewage treatment works. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1997, 34, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pes, K.; Ortiz-Delgado, J.B.; Sarasquete, C.; Laizé, V.; Fernández, I. Short-term exposure to pharmaceuticals negatively impacts marine flatfish species: Histological, biochemical and molecular clues for an integrated ecosystem risk assessment. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 90, 103822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vethaak, A.D. Disease prevalence in flounder (Platichthys flesus) from the Dutch Wadden Sea as indicator of environmental quality: A summary of 1988–2005 surveys. J. Sea Res. 2013, 82, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stentiford, G.D.; Bignell, J.P.; Lyons, B.P.; Feist, S.W. Site-specific disease profiles in fish and their use in environmental monitoring. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 381, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Davies, I.M.; Vethaak, D. Integrated Marine Environmental Monitoring of Chemicals and Their Effects; International Council for the Exploration of the Sea: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2012; Volume 315. [Google Scholar]
- Kesheri, M.; Kanchan, S.; Srivastava, U.; Chittoori, B.; Ratna-Raj, R.; Sinha, R.P.; Vaishampayan, A.; Rastogi, R.P.; Primerano, D.A. Chapter 19—Ecology and environmental omic. In Integrative Omics; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 315–331. ISBN 9780443160929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander-Dann, B.; Pruteanu, L.L.; Oerton, E.; Sharma, N.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Módos, D.; Bender, A. Developments in toxicogenomics: Understanding and predicting compound-induced toxicity from gene expression data. Mol. Omics 2018, 14, 213–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Horng, J.; Tong, S.; Cherng, B.; Liao, B.; Lin, L.; Chou, M. Exposure to silver impairs learning and social behaviors in adult zebrafish. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 124031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehinto, A.C.; Hampton, L.; Vidal-Dorsch, D.E.; Garcia-Reyero, N.; Arick, M.A.; Maruya, K.A.; Lao, W.; Vulpe, C.D.; Brown-Augustine, M.; Loguinov, A.; et al. Transcriptomic response patterns of hornyhead turbot (Pleuronichthys verticalis) dosed with polychlorinated biphenyls and polybrominated diphenyl ethers. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2021, 38, 100822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, P.; Sabo-Attwood, T.; Kelso, J.; Denslow, N.D. Analysis of gene expression profiles in largemouth bass exposed to 17-beta-estradiol and to anthropogenic contaminants that behave as estrogens. Ecotoxicology 2003, 12, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, T.D.; Gensberg, K.; Minchin, S.D.; Chipman, J.K. A DNA expression array to detect toxic stress response in European flounder (Platichthys flesus). Aquat. Toxicol. 2003, 65, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falciani, F.; Diab, A.M.; Sabine, V.; Williams, T.D.; Ortega, F.; George, S.G.; Chipman, J.K. Hepatic transcriptomic profiles of European flounder (Platichthys flesus) from field sites and computational approaches to predict site from stress gene responses following exposure to model toxicants. Aquat. Toxicol. 2008, 90, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Aggelen, G.; Ankley, G.T.; Baldwin, W.S.; Bearden, D.W.; Benson, W.H.; Chipman, J.K.; Collette, T.W.; Craft, J.A.; Denslow, N.D.; Embry, M.R.; et al. Integrating omic technologies into aquatic ecological risk assessment and environmental monitoring: Hurdles, achievements, and future outlook. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leaver, M.J.; Diab, A.; Boukouvala, E.; Williams, T.D.; Chipman, J.K.; Moffat, C.F.; Robinson, C.D.; George, S.G. Hepatic gene expression in flounder chronically exposed to multiply polluted estuarine sediment: Absence of classical exposure ‘biomarker’ signals and induction of inflammatory, innate immune and apoptotic pathways. Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 96, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, T.D.; Diab, A.M.; George, S.G.; Sabine, V.; Chipman, J.K. Gene expression responses of European flounder (Platichthys flesus) to 17-β estradiol. Toxicol. Lett. 2007, 168, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepp, T.; Baines, C.; Kreitsberg, R.; Scharsack, J.P.; Nogueira, P.; Lang, T.; Fort, J.; Sild, E.; Clarke, J.T.; Tuvikene, A.; et al. Differences on the level of hepatic transcriptome between two flatfish species in response to liver cancer and environmental pollution levels. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2024, 275, 109781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-López, E.; Panzera, Y.; Bessonart, M.; Marandino, A.; Féola, F.; Gadea JMagnone, L.; Salhi, M. Effect of salinity on fads2 and elovl gene expression and fatty acid profile of the euryhaline flatfish Paralichthys orbignyanus. Aquaculture 2024, 583, 740585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, T.; Diab, A.; Ortegaa, F.; Sabine, V.S.; Godfreya, R.E.; Falciani, F.; Chipman, J.K.; George, S.G. Transcriptomic responses of European flounder (Platichthys flesus) to model toxicants. Aquat. Toxicol. 2008, 90, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, L.; Russell, M.; Walsham, P.; Robinson, C.; Phillips, L.A.; Hussy, I.; Packer, G.; Rose, M.; Dalgarno, E.J.; Devalla, S.; et al. Regional assessment of hazardous substances in coastal and offshore marine environments: 1999–2009. Scott. Mar. Freshw. Sci. 2010, 1, 89. Available online: https://webarchive.nrscotland.gov.uk/20200114184812/http:/www2.gov.scot/Topics/marine/science/Publications/publicationslatest/Science/SMFS/2010Reports/SMFS0117 (accessed on 20 February 2015).
- Robinson, C.D.; Webster, L.; Martínez-Gómez, C.; Burgeot, T.; Gubbins, M.J.; Thain, J.E.; McIntosh, A.D.; Vethaak, A.D.; Hylland, K. Assessment of contaminant concentrations in sediments, fish and mussels sampled from the North Atlantic and European regional seas within the ICON project. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 124, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, L.; Tronczynski, J.; Bersuder, P.; Vorkamp, K.; Lepom, P. Determination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in sediment and biota. ICES Tech. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2009, 49, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, L.; Roose, P.; Bersuder, B.; Kotterman, M.; Haarich, M.; Vorkamp, K. Determination of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in sediment and biota. ICES Tech. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2013, 53, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Stagg, R.; McIntosh, A. Biological effects of contaminants: Determination of CYP1A-dependent mono-oxygenase activity in dab by fluorimetric measurement of EROD activity. ICES Tech. Mar. Environ. Sci. 1998, 23, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Stagg, R.; McIntosh, A.; Gubbins, M.J. Determination of CYP1A-dependent mono-oxygenase activity in dab by fluorimetric measurement of EROD activity in S9 or microsomal liver fractions. ICES Tech. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2016, 57, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariese, F.; Beyer JJonsson, G.; Porte, C.; Krahn, M.M. Review of analytical methods for determining metabolites of polycyclic aromatic compounds (PACs) in fish bile. ICES Tech. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2005, 39, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Baršiene, J.; Lethonen, K.K.; Koehler, A.; Broeg, K.; Vuorinen, P.J.; Lang, T.; Pemkowiak, J.; Syvokiene, J.; Dedonyte, V.; Rybakovas, A.; et al. Biomarker responses in flounder (Platichthys flesus) and mussel (Mytilus edulis) in the Klaipeda-Butinge area (Baltic Sea). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2006, 53, 422–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.P.; Hylland, K. Biological effects of contaminants: Radioimmunoassay (RIA) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) techniques for the measurement of marine fish vitellogenins. ICES Tech. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2002, 31, 27. [Google Scholar]
- ISO/IEC 17025:2017; Requirements. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT–PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OSPAR. CEMP Assessment Report: 2008/2009 Assessment of Trends and Concentrations of Selected Hazardous Substances in Sediments and Biota. 2009. Available online: http://qsr2010.ospar.org/media/assessments/p00390_2009_CEMP_assessment_report.pdf (accessed on 21 February 2014).
- Giltrap, M.; Ronan, J.; Bignell, J.P.; Lyons, B.P.; Collins, E.; Rochford, H.; McHugh, B.; McGovern, E.; Bull, L.; Wilson, J. Integration of biological effects, fish histopathology and contaminant measurements for the assessment of fish health: A pilot application in Irish marine waters. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 129, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beliaeff, B.; Burgeot, T. Integrated biomarker response: A useful tool for ecological risk assessment. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. Int. J. 2002, 21, 1316–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Commission regulation (EC) No. 1881/2006 of 20 December 2006. Off. J. Eur. Communities 2006, L364, 5–24. [Google Scholar]
- Maguire, A.; Vega-Carrascal, I.; Bryant, J.; White, L.; Howe, O.; Lyng, F.M.; Meade, A.D. Competitive evaluation of data mining algorithms for use in classification of leukocyte subtypes with Raman microspectroscopy. Analyst 2015, 140, 2473–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.P.; Sanders, M.; Stentiford, G.D.; Reese, R.A.; Katsiadaki, I. Evidence for estrogenic endocrine disruption in an offshore flatfish, the dab (Limanda limanda L.). Mar. Environ. Res. 2007, 64, 128–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, M.F.; Allen, Y.T.; Dyer, R.A.; Feist, S.W.; Katsiadaki, I.; Matthiessen, P.; Scott, A.P.; Smith, A.; Stentiford, G.D.; Thain, J.E.; et al. Surveys of plasma vitellogenin and intersex in male flounder (Platichthys flesus) as measures of endocrine disruption by estrogenic contamination in United Kingdom estuaries: Temporal trends, 1996 to 2001. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2004, 23, 748–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, M.F.; Smith, A.J.; Rooke, J.; Neall, P.; Scott, A.P.; Katsiadaki, I. Ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase (EROD) and vitellogenin (VTG) in flounder (Platichthys flesus): System interaction, crosstalk and implications for monitoring. Aquat. Toxicol. 2007, 81, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, N.; Williams, T.D.; Chipman, K. Functional analysis of xenobiotic response elements (XREs) in CYP 1A of the European Flounder (Platichthys flesus). Mar. Environ. Res. 2004, 58, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.A.; Blaney, S.C.; Houlihan, D.F.; Secombes, C.J. Transcriptome response following administration of a live bacterial vaccine in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Mol. Immunol. 2006, 43, 1900–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.C.; Osborne, J.A.; Tsoi, S.C.; Brown, L.L.; Johnson, S.C. Expressed sequence tags analysis of Atlantic halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus) liver, kidney and spleen tissues following vaccination against Vibrio anguillarum and Aeromonas salmonicida. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2005, 18, 393–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cañizares-Martínez, M.A.; Quintanilla-Mena, M.A.; Árcega-Cabrera, F.; Ceja-Morena, V.; Del Río-García, M.; Reyes-Solian, S.G.; Rivas-Reyes, I.; Rivera-Bustamante, R.F.; Puch-Hau, C.A. Transcriptional Response of Vitellogenin Gene in Flatfish to Environmental Pollutants from Two Regions of the Gulf of Mexico. Bull. Environ. Contam Toxicol. 2024, 112, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hylland, K.; Sandvik, M.; Skaare, J.U.; Beyer, J.; Egaas, E.; Goksøyr, A. Biomarkers in flounder (Platichthys flesus): An evaluation of their use in pollution monitoring. Mar. Environ. Res. 1996, 42, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotchell, J.M.; Clarke, K.R.; Newton, L.C.; Bird, D.J. Hepatic metallothionein as a biomarker for metal contamination: Age effects and seasonal variation in European flounders (Pleuronectes flesus) from the Severn Estuary and Bristol Channel. Mar. Environ. Res. 2001, 52, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrulis, J.R.; Bunce, N.J. Competitive inhibition by inducer as a confounding factor in the use of the ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase (EROD) assay to estimate exposure to dioxin-like compounds. Toxicol. Lett. 1999, 105, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Acronym | Gene | Function |
|---|---|---|
| ALD | Aldehyde dehydrogenase 9A1 | Xenobiotic metabolism, oxidises amino aldehydes |
| UGT | UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1B | Xenobiotic metabolism, detoxification of organics |
| SOD | Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase | Xenobiotic metabolism, detoxification of superoxide radicals |
| GST | Glutathione S-transferase rho class | Xenobiotic metabolism, detoxification of organics |
| MTT | Metallothionein | Xenobiotic metabolism, toxic metal defense |
| CYP1A | Cytochrome P4501A | Xenobiotic metabolism, metabolises polyaromatic hydrocarbons |
| CFOS | C-fos | Stress response, multifunctional transcription factor |
| HEP | Hepcidin | Stress response, regulates iron distribution |
| VIT | Vitellogenin | Endocrine disruption, egg protein induced in male fish by estrogens |
| CHO | Choriogenin L | Endocrine disruption, egg protein induced in male fish by estrogens |
| DIA | Diablo1 | Apoptosis regulator, increases sensitivity to apototic signals |
| GCBP | Cytosolic non-specific dipeptidase | Glutathione synthesis but function uncertain |
| Elongation factor alpha | Reference gene | |
| Alpha tubulin | Reference gene |
| <BAC | <EACpassive | <ECa | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metals | ||||
| Cd | 26 | X | X | |
| Hg | 35 | X | 500 (a) | |
| Pb | 26 | X | X | |
| PCBs | ||||
| CB 28 | 0.1 | 64 | X | |
| CB52 | 0.08 | 108 | X | |
| CB101 | 0.08 | 120 | X | |
| CB118 | 0.1 | 24 | X | |
| CB138 | 0.09 | 316 | X | |
| CB153 | 0.1 | 1600 | X | |
| CB180 | 0.11 | 480 | X | |
| Biomarkers | Species | Sex | <BAC | <EAC |
| EROD (pmol min−1 mg protein−1) | Flounder | M | 24 | X |
| PAH bile metabolites (pyrene type ng mL−1); synchronous scan fluorescence | Flounder | M&F | 16 | X |
| VTG plasma (μg mL−1) | Flounder | M | 0.13 | X |
| Micronuclei frequency in erythrocytes | Flounder | M&F | 0–0.3 | X |
| Balcary Point | Holy Loch 2009 | Alloa | St. Andrews | Tancred | Holy Loch 2010 | Bowling | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 307.9 ± 81.9 | 57.6 ± 8 | 107.6 ± 10 | 236.8 ± 107 | 95.8 ± 12.5 | 76.5 ± 42.7 | 53.3 ± 6.5 |
| Hg | 102.9 ± 24.1 | 26.3 ± 3.3 | 114.6 ± 20.9 | 61.6 ± 86.1 | 121.5 ± 23.6 | 42.8 ± 15 | 57.4 ± 9.9 |
| Pb | 46.8 ± 27.4 | 31.3 ± 18 | 61.8 ± 5.3 | 140 ± 28.5 | 150 ± 50.3 | ||
| CB28 | ND | 49.5 ± 23.5 | 3.4 ± 2 | 0.1 ± 0.9 | 2.7 ± 0.9 | 13 ± 8.9 | 7.3 ± 2.5 |
| CB52 | ND | 78.6 ± 44.2 | 4.4 ± 2.7 | 0.1 ± 1.1 | 5.8 ± 2 | 24.8 ± 15.3 | 12.7 ± 3.8 |
| CB101 | TR | 77.3 ± 39.4 | 9.2 ± 5 | 0.5 ± 2.9 | 10.7 ± 4.7 | 32.2 ± 9.4 | 5.8 ± 1.5 |
| CB118 | TR | 63.9 ± 35.1 | 7.2 ± 3.7 | 5.4 ± 1.9 | 8.2 ± 3.6 | 32.5 ± 7.7 | 8.3 ± 2.1 |
| CB138 | TR | 59 ± 29.8 | 13.3 ± 7.6 | 5.8 ± 3.7 | 16.9 ± 7.1 | 45.9 ± 12.9 | 10.8 ± 2 |
| CB153 | 103 ± 4.2 | 122.8 ± 64.2 | 22.5 ± 10.1 | 7 ± 4.2 | 24.9 ± 12 | 75.9 ± 20 | 15.2 ± 2.6 |
| CB180 | TR | 66.1 ± 33.4 | 21.8 ± 13 | 3.8 ± 4.3 | 19 ± 9.6 | 43 ± 20.5 | 11.4 ± 3 |
| Gender | Balcary Pt. | HL09 | Alloa | St. Andrews | Tancred | HL10 | Bowling | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Condition index (K) | Mixed | 1.19 ± 0.07 | 1.24 ± 0.05 | 1.01 ± 0.05 | 1.03 ± 0.05 | 1.07 ± 0.04 | 1.15 ± 0.08 | 1.07 ± 0.04 |
| Gonadal somatic index (GSI) | Mixed | 7.37 ± 1.94 | 1.79 ± 0.7 | 0.45 ± 0.36 | 1.35 ± 0.38 | 0.82 ± 0.27 | 1.52 ± 0.51 | 0.9 ± 0.37 |
| Liver somatic index (LSI) | Mixed | 1.99 ± 0.31 | 1.59 ± 0.2 | 1.19 ± 0.08 | 1.46 ± 0.18 | 1.0 ± 0.09 | 1.45 ± 0.21 | 1.3 ± 0.15 |
| EROD | Male | 16.22 ± 25.92 | 42.17 ± 18.3 | 3 ± 1.17 | 35.7 ± 9.7 | 13.5 ± 6.7 | 77.35 ± 33.9 | 66.2 ± 13.1 |
| Female | 3 ± 0 | 13.2 ± 7.72 | 3 | 18 ± 25.18 | 12.9 ± 12.3 | 52 ± 30.3 | 48.5 ± 31.4 | |
| Bile metabolites | Mixed | 247.7 ± 58.4 | 857.6 ± 1108 | 1201 ± 418 | 159.72 ± 28.1 | 2163.3 ± 2066.8 | 1055.3 ± 1036.2 | 1614.4 ± 464 |
| Vitellogenin (Vtg) | Male | none | none | 0.2 ± 1.45 × 10−17 | 0.2 ± 1.4 × 10−17 | 0.2 ± 0.04 | 0.2 ± 11.4 | 0.2 ± 0 |
| Micronucleus (MN) | Mixed | 0.6 ± 0.4 | 0.4 ± 0.27 | 0.3 ± 0.2 | 0.3 ± 0.22 | 0.2 ± 0.13 | 0.2 ± 0.23 | 0.2 ± 0.36 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giltrap, M.C.; Leaver, M.J.; White, K.; Wilson, J.G.; Rahman, A.; Maguire, A.; Meade, A.D.; Baršiene, J.; Robinson, C.D. Investigating the Use of Diagnostic Genes in Integrated Monitoring with a Laboratory and Field Study on Flounder (Platichthys flesus). Toxics 2025, 13, 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13030203
Giltrap MC, Leaver MJ, White K, Wilson JG, Rahman A, Maguire A, Meade AD, Baršiene J, Robinson CD. Investigating the Use of Diagnostic Genes in Integrated Monitoring with a Laboratory and Field Study on Flounder (Platichthys flesus). Toxics. 2025; 13(3):203. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13030203
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiltrap, Michelle C., Michael J. Leaver, Kelly White, James G. Wilson, Atiqur Rahman, Adrian Maguire, Aidan D. Meade, Janina Baršiene, and Craig D. Robinson. 2025. "Investigating the Use of Diagnostic Genes in Integrated Monitoring with a Laboratory and Field Study on Flounder (Platichthys flesus)" Toxics 13, no. 3: 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13030203
APA StyleGiltrap, M. C., Leaver, M. J., White, K., Wilson, J. G., Rahman, A., Maguire, A., Meade, A. D., Baršiene, J., & Robinson, C. D. (2025). Investigating the Use of Diagnostic Genes in Integrated Monitoring with a Laboratory and Field Study on Flounder (Platichthys flesus). Toxics, 13(3), 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13030203







