Serum miRNA and Metabolomic Signatures of Residential Radon Exposure in Chiang Mai, Thailand
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Site Selection
2.2. Participant Eligibility and Recruitment
2.3. Blood Collection and Processing
2.4. Small RNA Sequencing
2.5. RT-qPCR Validation of Selected miRNAs
2.6. Untargeted Serum Metabolomics Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Household Radon Concentrations and Selection of Study Participants
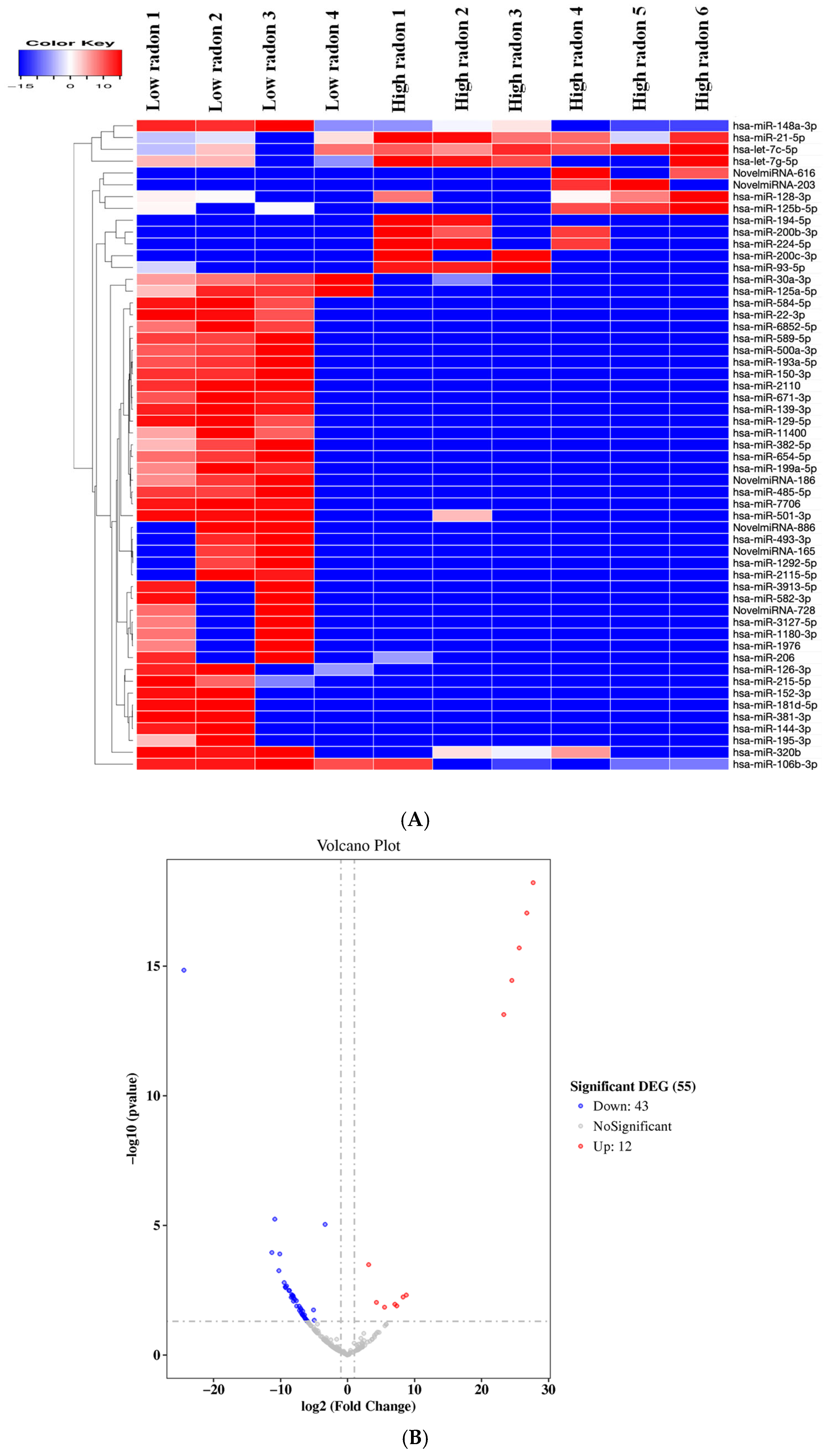
3.2. Differential Expression of miRNAs Between Low and High Radon Exposure
3.3. RT-qPCR Validation of Radon-Responsive miRNAs
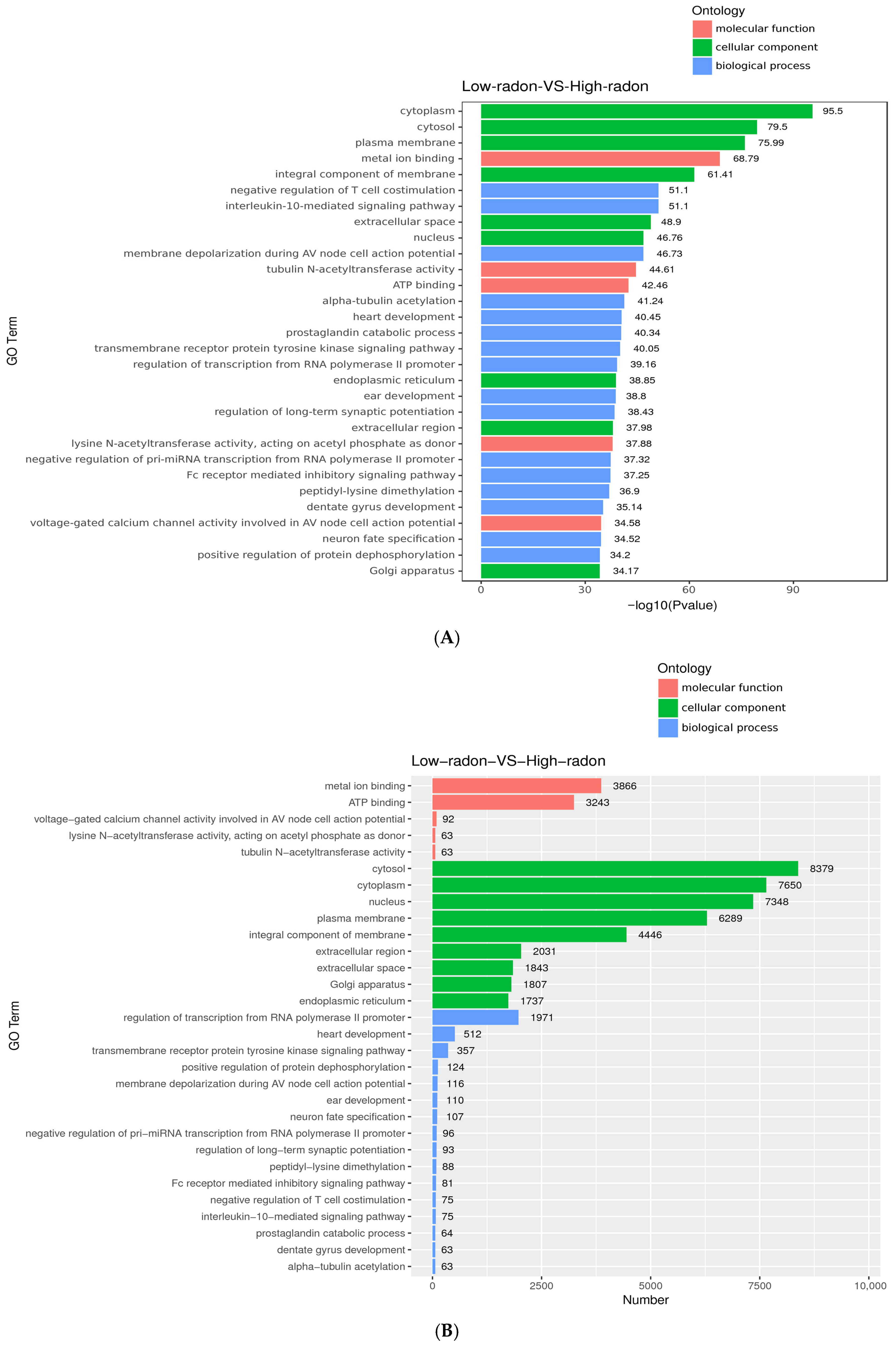
3.4. Gene Ontology (GO) Enrichment Analysis
3.5. KEGG Enrichment of Targets of Radon-Responsive miRNAs
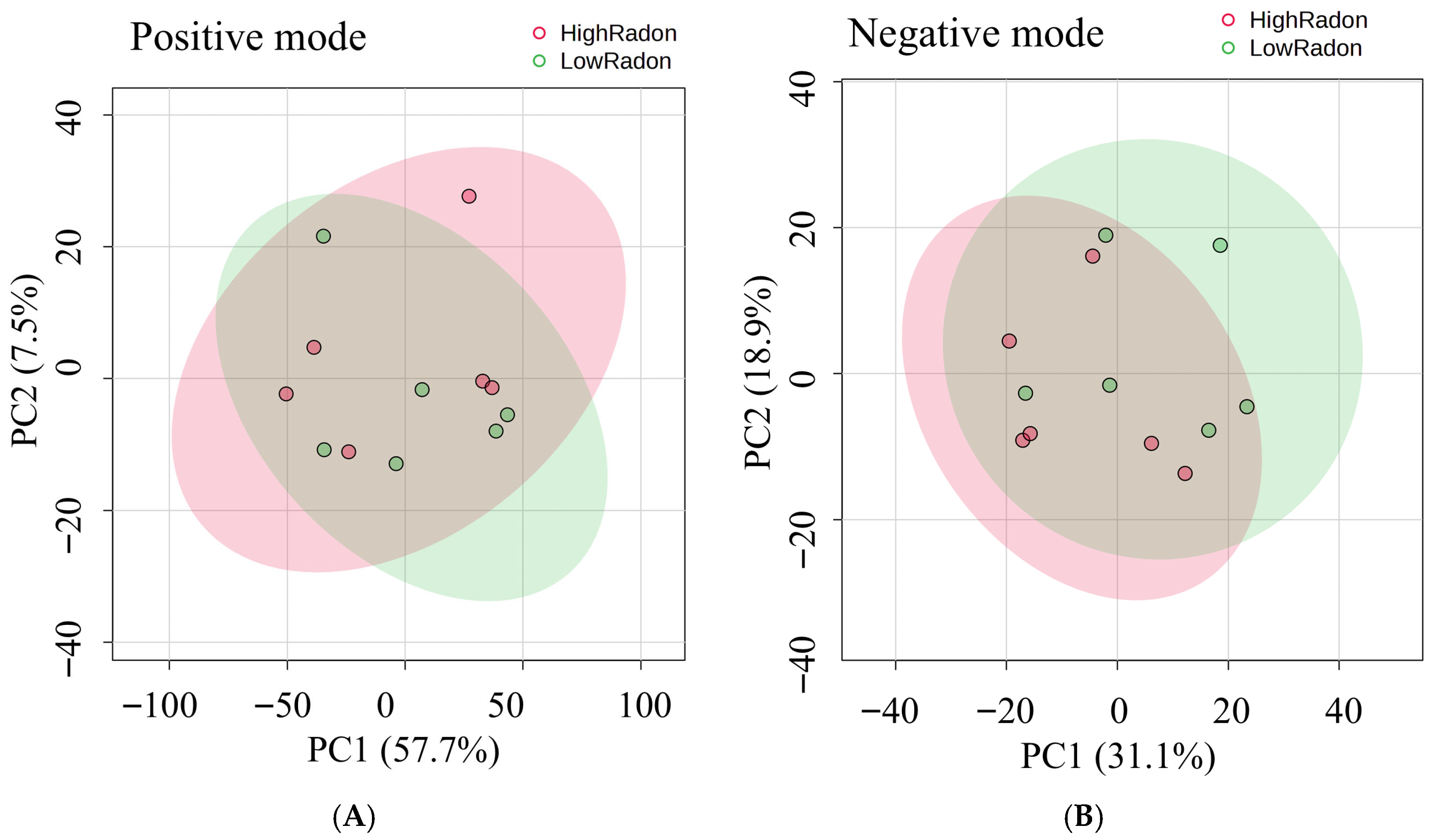
3.6. Global Metabolomic Profiling of High- and Low-Radon Groups
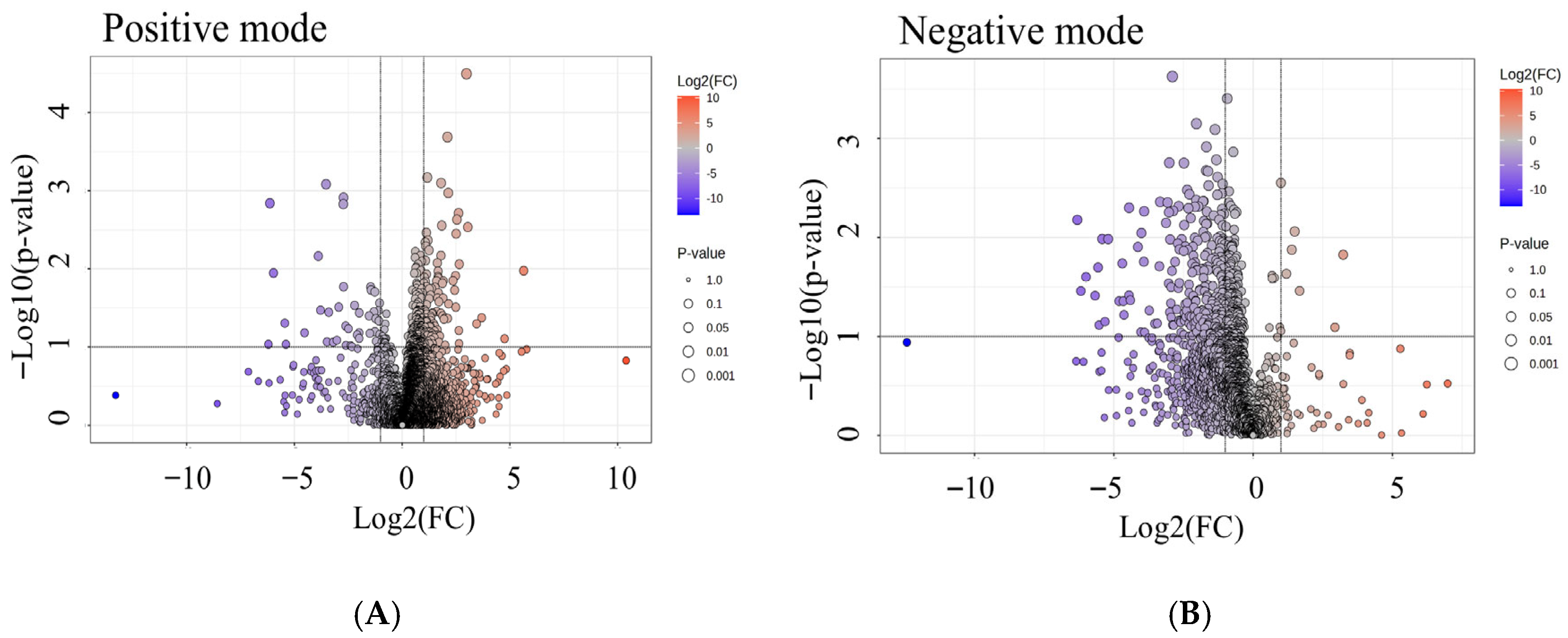
3.7. Differential Metabolites Associated with Radon Exposure
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AA | arachidonic acid |
| AC | acyl-carnitine |
| AKT | protein kinase B |
| ATM | ataxia telangiectasia mutated |
| Bq/m3 | becquerels per cubic meter |
| CCL5 (RANTES) | C-C motif chemokine ligand 5 |
| COX | cyclooxygenase |
| DDR | DNA-damage response |
| DESeq2 | Differential Expression analysis for sequence count data |
| DHA | docosahexaenoic acid |
| DiHETE | dihydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid |
| DNA | deoxyribonucleic acid |
| DNMT3A | DNA methyltransferase 3A |
| EGFR-TKI | epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor |
| EMT | epithelial–mesenchymal transition |
| EPA | eicosapentaenoic acid |
| ESI | electrospray ionization |
| EV | extracellular vesicle |
| FDR | false discovery rate |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| HEPE | hydroxyeicosapentaenoic acid |
| HETE | hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid |
| HIF-1α | hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha |
| HODE | 9-hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid |
| IGSF11 | immunoglobulin superfamily member 11 |
| JAK–STAT | Janus kinase–signal transducer and activator of transcription |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| LC–MS | liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry |
| LET | linear energy transfer |
| log2FC | log2 fold change |
| LOX | lipoxygenase |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MS1 | precursor (MS1) scan |
| MS2 | fragment (MS2) scan |
| mSv·y−1 | millisieverts per year |
| MMP | matrix metalloproteinase |
| mTOR | mechanistic/mammalian target of rapamycin |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| NGS | next-generation sequencing |
| nt | nucleotides |
| padj | FDR-adjusted p-value |
| PCA | principal component analysis |
| PC | phosphatidylcholine |
| PI3K | phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| PLA2 | phospholipase A2 |
| PM2.5 | fine particulate matter ≤2.5 μm |
| PUFA | polyunsaturated fatty acid |
| q value | FDR-adjusted p-value |
| RT-qPCR | reverse transcription quantitative PCR |
| RAC1 | Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 |
| RAD9 | cell-cycle checkpoint protein RAD9A |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| RT (chromatography) | retention time |
| S1P | sphingosine-1-phosphate |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
| VSIG3 | V-set and immunoglobulin domain-containing 3 |
| Wnt | wingless-related integration site pathway |
| YKT6 | vesicle SNARE protein YKT6 |
| ZEB1 | zinc finger E-box-binding homeobox 1 |
| ZEB2 | zinc finger E-box-binding homeobox 2 |
References
- LoPiccolo, J.; Gusev, A.; Christiani, D.C.; Janne, P.A. Lung cancer in patients who have never smoked—An emerging disease. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 21, 121–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- World Health Organization. Radon Geneva: World Health Organization. 2023. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/radon-and-health (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- Xiong, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Peng, J.; Liang, J.; Lian, D.; Zhao, X.; Wang, L.; Lu, T.; Li, Y. Epidemiological trends of lung cancer attributed to residential radon exposure at global, regional, and national level: A trend analysis study from 1990 to 2021. Front. Public Health 2025, 13, 1593415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Thumvijit, T.; Chanyotha, S.; Sriburee, S.; Hongsriti, P.; Tapanya, M.; Kranrod, C.; Tokonami, S. Identifying indoor radon sources in Pa Miang, Chiang Mai, Thailand. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rankantha, A.; Chitapanarux, I.; Pongnikorn, D.; Prasitwattanaseree, S.; Bunyatisai, W.; Sripan, P.; Traisathit, P. Risk patterns of lung cancer mortality in northern Thailand. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mayes, C.; Houston, R.; Seashols-Williams, S.; LaRue, B.; Hughes-Stamm, S. The stability and persistence of blood and semen mRNA and miRNA targets for body fluid identification in environmentally challenged and laundered samples. Leg. Med. 2019, 38, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Dominguez, M.V.; Zottel, A.; Samec, N.; Jovcevska, I.; Dincer, C.; Kahlert, U.D.; Nickel, A.C. Current Technologies for RNA-Directed Liquid Diagnostics. Cancers 2021, 13, 5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hollis, R.; Aziz, M.; Jacob, A.; Wang, P. Harnessing Extracellular microRNAs for Diagnostics and Therapeutics in Acute Systemic Inflammation. Cells 2024, 13, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Aljani, B.; Lindner, A.; Weigelt, M.; Zhao, M.; Sharma, V.; Bonifacio, E.; Jones, P.; Eugster, A. Small RNA-Seq and real time rt-qPCR reveal islet miRNA released under stress conditions. Islets 2024, 16, 2392343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, Z.; Han, S.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, P.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, G. Metabolomics screening of serum biomarkers for occupational exposure of titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Nanotoxicology 2021, 15, 832–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Lai, Y.; Chi, L.; Tu, P.; Leng, J.; Liu, C.W.; Ru, H.; Lu, K. Serum Metabolomics Reveals That Gut Microbiome Perturbation Mediates Metabolic Disruption Induced by Arsenic Exposure in Mice. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 1006–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zheng, J.; Johnson, M.; Mandal, R.; Cruz, M.; Martinez-Huelamo, M.; Andres-Lacueva, C.; Wishart, D.S. A Comprehensive LC-MS Metabolomics Assay for Quantitative Analysis of Serum and Plasma. Metabolites 2024, 14, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kumar, P.; Wang, P.; Farese, A.M.; MacVittie, T.J.; Kane, M.A. Metabolomics of Multiorgan Radiation Injury in Non-human Primate Model Reveals System-wide Metabolic Perturbations. Health Phys. 2021, 121, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarigiannis, D.; Karakitsios, S.; Anesti, O.; Stem, A.; Valvi, D.; Sumner, S.C.J.; Chatzi, L.; Snyder, M.P.; Thompson, D.C.; Vasiliou, V. Advancing translational exposomics: Bridging genome, exposome and personalized medicine. Hum. Genom. 2025, 19, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Thumvijit, T.; Somboon, S.; Tapanya, M.; Ruktinnakorn, K.; Kranrod, C.; Tokonami, S.; Chanyotha, S.; Sriburee, S. Assessment of annual effective doses from indoor radon and thoron in Doi Lo, Chiang Mai, Thailand. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2024, 200, 1715–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somsunun, K.; Prapamontol, T.; Pothirat, C.; Liwsrisakun, C.; Pongnikorn, D.; Fongmoon, D.; Chantara, S.; Wongpoomchai, R.; Naksen, W.; Autsavapromporn, N.; et al. Estimation of lung cancer deaths attributable to indoor radon exposure in upper northern Thailand. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ngansom, W.; Rodphothong, D.; Itthipoonthanakorn, T.; Niyomdecha, S.; Durrast, H.; Yongprawat, M. Hydrogeological environments and radon activities of saline geothermal hot spring sites located along eastern and western coastlines of southern Thailand. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2023, 253, 104105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ausoodkij, B.; Polpong, P.; Bovornkitti, S. Indoor radon in Thailand: A study with particular reference to its sources. J. Med. Assoc. Thail. 1996, 79, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rattanapongs, C.P.; Kranrod, C.; Jitpakdee, M.; Tokonami, S.; Chanyotha, S. Internal Exposure from Indoor Radon, Thoron and Their Progeny in Residence around High Background Radiation Area, Phang Nga Province, Thailand. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2022, 198, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polpong, P.; Aranyakananda, P.; Bovornkitti, S. A preliminary study of indoor radon in Thailand. J. Med. Assoc. Thail. 1994, 77, 652–656. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Riudavets, M.; Garcia de Herreros, M.; Besse, B.; Mezquita, L. Radon and Lung Cancer: Current Trends and Future Perspectives. Cancers 2022, 14, 3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, X.; Shan, S.; Wang, A.; Tu, C.; Wan, J.; Hong, C.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Yin, J.; Tong, J.; et al. Repeated radon exposure induced ATM kinase-mediated DNA damage response and protective autophagy in mice and human bronchial epithelial cells. Toxicol. Res. 2024, 13, tfae165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, X.; Peng, Y.; Chen, R.; Zhou, Y.; Zou, X.; Xia, M.; Wu, X.; Yu, M. Transcriptomic analysis reveals transcription factors implicated in radon-induced lung carcinogenesis. Toxicol. Res. 2024, 13, tfae161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Aksamitiene, E.; Kiyatkin, A.; Kholodenko, B.N. Cross-talk between mitogenic Ras/MAPK and survival PI3K/Akt pathways: A fine balance. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2012, 40, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Huang, B.; Li, G.; Zeng, S. Apatinib affect VEGF-mediated cell proliferation, migration, invasion via blocking VEGFR2/RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT pathways in cholangiocarcinoma cell. BMC Gastroenterol. 2018, 18, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, Q.; Li, Z.; Luo, T.; Shi, H. Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR and RAF/MEK/ERK pathways for cancer therapy. Mol. Biomed. 2022, 3, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xu, W.; He, Z.; Fu, C.; Du, F. Radon and lung cancer: Current status and future prospects. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2024, 198, 104363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, P.A.; Bert, A.G.; Paterson, E.L.; Barry, S.C.; Tsykin, A.; Farshid, G.; Vadas, M.A.; Khew-Goodall, Y.; Goodall, G.J. The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korpal, M.; Lee, E.S.; Hu, G.; Kang, Y. The miR-200 family inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer cell migration by direct targeting of E-cadherin transcriptional repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 14910–14914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shan, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, A.; Yan, W.; Wu, Q.; Wan, J.; Hong, C.; Wang, Y.; Tong, J.; Tian, H.; et al. Repeated radon exposure induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition-like transformation via disruption of p53-dependent mitochondrial function. Toxicol. Res. 2023, 12, 1143–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, H.; Chen, N.; Li, F.; Sun, L.; Du, J.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, F.; Li, Y.; Tian, S.; Jiang, Q.; et al. Repeated radon exposure induced lung injury and epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in human bronchial epithelial cells and mice. Toxicol. Lett. 2020, 334, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortez, M.A.; Valdecanas, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhan, Y.; Bhardwaj, V.; Calin, G.A.; Komaki, R.; Giri, D.K.; Quini, C.C.; Wolfe, T.; et al. Therapeutic delivery of miR-200c enhances radiosensitivity in lung cancer. Mol. Ther. 2014, 22, 1494–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xia, M.; Sheng, L.; Qu, W.; Xue, X.; Chen, H.; Zheng, G.; Chen, W. MiR-194-5p enhances the sensitivity of nonsmall-cell lung cancer to doxorubicin through targeted inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor-1. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 19, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lee, S.B.; Park, Y.S.; Sung, J.S.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, B.; Kim, Y.H. Tumor Suppressor miR-584-5p Inhibits Migration and Invasion in Smoking Related Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells by Targeting YKT6. Cancers 2021, 13, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wei, D.; Yu, G.; Zhao, Y. MicroRNA-30a-3p inhibits the progression of lung cancer via the PI3K/AKT by targeting DNA methyltransferase 3a. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 7015–7024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yang, X.; Su, W.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Shan, H.; Han, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Q.; Bai, Y.; et al. MiR-22-3p suppresses cell growth via MET/STAT3 signaling in lung cancer. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 1221–1232. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, X.; Chen, C.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Sun, W.; Shen, K.; Lv, Y.; Zhu, S.; Zhan, P.; Lv, T.; et al. Elevated exosome-derived miRNAs predict osimertinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tomasini, S.; Vigo, P.; Margiotta, F.; Scheele, U.S.; Panella, R.; Kauppinen, S. The Role of microRNA-22 in Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Autsavapromporn, N.; Duangya, A.; Klunklin, P.; Chitapanarux, I.; Kranrod, C.; Jaikang, C.; Monum, T.; Paemanee, A.; Tokonami, S. Serum Metabolomics Study to Screen Potential Biomarkers of Lung Cancer Risk in High Natural Background Radiation Areas of Thailand: A Pilot Study. Cancers 2024, 16, 4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ghandhi, S.A.; Ponnaiya, B.; Panigrahi, S.K.; Hopkins, K.M.; Cui, Q.; Hei, T.K.; Amundson, S.A.; Lieberman, H.B. RAD9 deficiency enhances radiation induced bystander DNA damage and transcriptomal response. Radiat. Oncol. 2014, 9, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Subsomwong, P.; Kranrod, C.; Sakai, Y.; Asano, K.; Nakane, A.; Tokonami, S. Impact of intermittent high-dose radon exposures on lung epithelial cells: Proteomic analysis and biomarker identification. J. Radiat. Res. 2025, 66, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ma, L.; Wang, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhang, X.; Xing, S.; Liu, B.; Chen, G.; Wang, X.; Hu, J.; Li, G.; et al. C-C motif chemokine ligand 5 contributes to radon exposure-induced lung injury by recruiting dendritic cells to activate effector T helper cells. Toxicology 2025, 511, 154044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakeel, S.; Sabir, S.; Parklak, W.; Kawichai, S.; Kijkuokool, P.; Khiaolaongam, W.; Ngamsang, P.; Jiraya, P.; Chuljerm, H.; Fakfum, P.; et al. Impact of Seasonal PM2.5 Exposure on Metabolic and Hormonal Profiles in Healthy Individuals and Individuals with Metabolic Syndrome in Chiang Mai, Thailand. Toxics 2025, 13, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kliengchuay, W.; Niampradit, S.; Sahanavin, N.; Mueller, W.; Steinle, S.; Loh, M.; Johnston, H.J.; Vardoulakis, S.; Suwanmanee, S.; Phonphan, W.; et al. Seasonal analysis of indoor and outdoor ratios of PM2.5 and PM10 in Bangkok and Chiang Mai: A comparative study of haze and non-haze episodes. Heliyon 2025, 11, e42261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
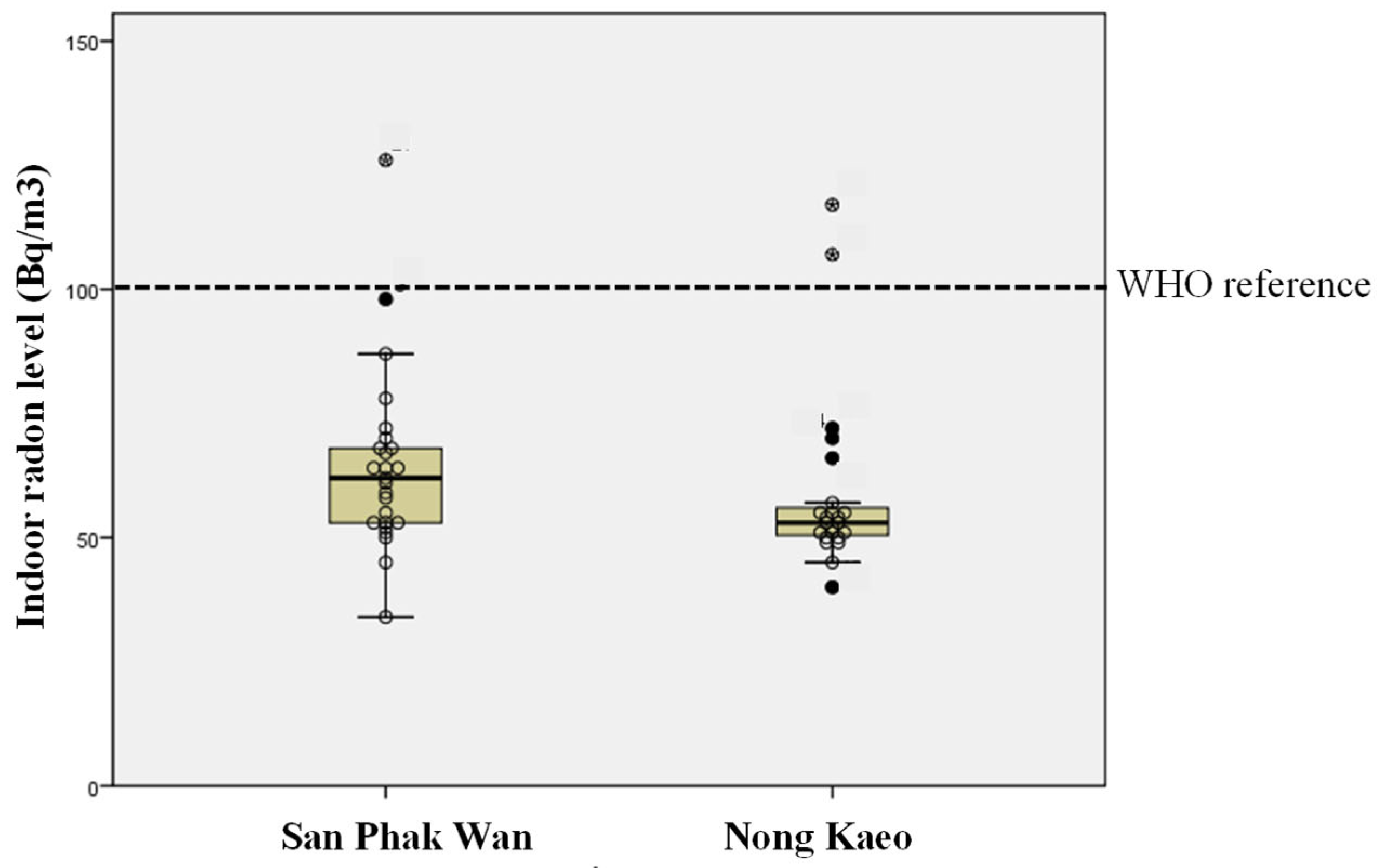


| Area | N | Mean ± SD | Min–Max | No. of House Classified According to Radon Level (Bq/m3) WHO Reference = 100 Bq/m3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <100 | ≥100 | ||||
| San Phak Wan | 25 | 64.5 ± 18.42 | 34–125 | 24 | 1 |
| Nong Kaeo | 23 | 60.0 ± 18.26 | 40–117 | 21 | 2 |
| Both area | 48 | 61.8 ± 18.36 | 34–125 | 45 | 3 |
| Gene_id | log2 Fold Change | padj |
|---|---|---|
| miRNA significantly up-regulated | ||
| 27.7 | 9.34 × 10−17 |
| 26.7 | 6.88 × 10−16 |
| 25.6 | 1.02 × 10−14 |
| 24.5 | 1.10 × 10−13 |
| 23.3 | 1.88 × 10−12 |
| 8.7 | 0.034468 |
| 8.2 | 0.034885 |
| 7.3 | 0.057078 |
| 7.0 | 0.052435 |
| 5.5 | 0.060395 |
| 4.3 | 0.045629 |
| 3.1 | 0.004513 |
| miRNA significantly down-regulated | ||
| −24.4 | 5.52 × 10−14 |
| −11.3 | 0.001881 |
| −10.9 | 0.000125 |
| −10.3 | 0.00707 |
| −10.1 | 0.00192 |
| −9.5 | 0.018719 |
| −9.3 | 0.02387 |
| −9.2 | 0.023942 |
| −9.1 | 0.023685 |
| −8.8 | 0.027473 |
| −8.7 | 0.027473 |
| −8.4 | 0.034885 |
| −8.3 | 0.034468 |
| −8.2 | 0.034885 |
| −8.2 | 0.034468 |
| −8.2 | 0.034468 |
| −8.1 | 0.034468 |
| −8.1 | 0.042125 |
| −8.0 | 0.035285 |
| −7.9 | 0.039445 |
| −7.6 | 0.042125 |
| −3.4 | 0.000174 |
| Met ID | RT (min) | m/z | Met Name | p-Value | q-Value (FDR-BH) | Low Radon (avg) | High Radon (avg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2946 | 12.231 | 334.2 | resorcinol (pregnenolone) | 0.0001 | 0.011 | 7444 | 8000 |
| 3117 | 10.175 | 343.2 | (Resolvin D5 | 0.0006 | 0.011 | 340,426 | 375,290 |
| 7656 | 9.5 | 584.3 | Shearinine F (PC20:4/2:0) | 0.0008 | 0.0012 | 41,331 | 48,311 |
| 2688 | 8.1 | 316.2 | Decanoyl-L-Carnitine | 0.0026 | 0.0036 | 874,330 | 1,922,109 |
| 1292 | 4.0 | 211.1 | Cyclo (Leu-Pro) | 0.0103 | 0.0032 | 46,651 | 205,776 |
| 2867 | 12.9 | 329.2 | Docosahexaenoic acid | 0.006 | 0.0078 | 37,253 | 33,172 |
| 2130 | 10.7 | 279.2 | Gamma-Linolenic acid | 0.0254 | 0.0206 | 10,057 | 32,302 |
| 2833 | 13.2 | 327.2 | Arachidonic acid | 0.0266 | 0.0144 | 130,013 | 174,315 |
| 970 | 2.1 | 181.0 | Theobromine | 0.0337 | 0.0435 | 122,185 | 388,356 |
| 1011 | 12.7 | 184.0 | Phosphocholine | 0.0367 | 0.0399 | 640,531 | 988,649 |
| 3147 | 9.5 | 344.2 | Lauroyl carnitine | 0.0491 | 0.0436 | 274,556 | 420,792 |
| Met ID | RT (min) | m/z | Met Name | p-Value | q-Value (FDR-BH) | Low Radon (avg) | High Radon (avg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2130 | 13.0 | 301.2 | Eicosapentaenoic acid | 0.0062 | 0.0103 | 247,489 | 322,314 |
| 2335 | 13.6 | 317.2 | 9-HEPE | 0.0043 | 0.0103 | 48,350 | 79,112 |
| 2356 | 13.0 | 319.2 | 8-HETE | 0.005 | 0.0103 | 1,853,013 | 2,266,134 |
| 1746 | 1.3 | 267.0 | Inosine | 0.0041 | 0.0103 | 300,249 | 683,873 |
| 2336 | 12.2 | 317.2 | 5-HEPE | 0.0056 | 0.0103 | 125,978 | 149,332 |
| 2552 | 10.5 | 335.2 | 5,12-DiHETE | 0.0032 | 0.0103 | 3,379,115 | 4,049,347 |
| 2059 | 12.2 | 295.2 | 9-HODE | 0.0115 | 0.0164 | 1,091,002 | 1,395,424 |
| 4088 | 11.7 | 455.3 | Ursolic acid | 0.0375 | 0.0422 | 29,786 | 39,853 |
| 442 | 0.89 | 135.0 | Hypoxanthine | 0.038 | 0.0422 | 76,322 | 153,048 |
| 1872 | 12.2 | 277.2 | γ-Linolenic acid | 0.0517 | 0.0517 | 53,311 | 76,549 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, M.T.T.; Thumvijit, T.; Kranrod, C.; Tokonami, S.; Choocheep, K.; Kumsaiyai, W.; Wuttiin, Y.; Punturee, K.; Pornprasert, S.; Chiampanichayakul, S.; et al. Serum miRNA and Metabolomic Signatures of Residential Radon Exposure in Chiang Mai, Thailand. Toxics 2025, 13, 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13121021
Han MTT, Thumvijit T, Kranrod C, Tokonami S, Choocheep K, Kumsaiyai W, Wuttiin Y, Punturee K, Pornprasert S, Chiampanichayakul S, et al. Serum miRNA and Metabolomic Signatures of Residential Radon Exposure in Chiang Mai, Thailand. Toxics. 2025; 13(12):1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13121021
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Moe Thi Thi, Tarika Thumvijit, Chutima Kranrod, Shinji Tokonami, Kanyamas Choocheep, Warunee Kumsaiyai, Yupanun Wuttiin, Khanittha Punturee, Sakorn Pornprasert, Sawitree Chiampanichayakul, and et al. 2025. "Serum miRNA and Metabolomic Signatures of Residential Radon Exposure in Chiang Mai, Thailand" Toxics 13, no. 12: 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13121021
APA StyleHan, M. T. T., Thumvijit, T., Kranrod, C., Tokonami, S., Choocheep, K., Kumsaiyai, W., Wuttiin, Y., Punturee, K., Pornprasert, S., Chiampanichayakul, S., & Cressey, R. (2025). Serum miRNA and Metabolomic Signatures of Residential Radon Exposure in Chiang Mai, Thailand. Toxics, 13(12), 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13121021










