Spatiotemporal Trends and Drivers of PM2.5 Concentrations in Shandong Province from 2014 to 2023 Under Socioeconomic Transition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
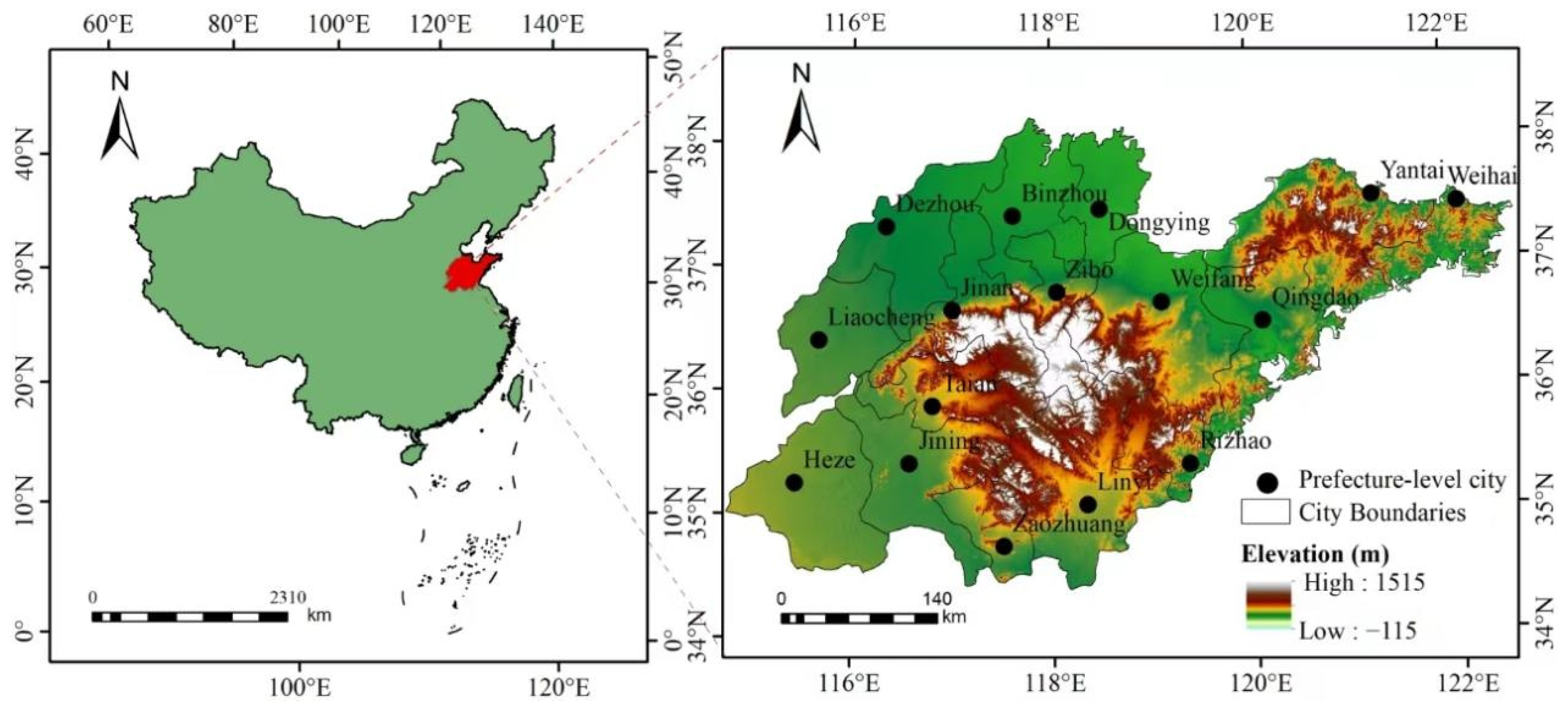
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection and Processing
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.3.1. Spatial Interpolation and Cluster Analysis
2.3.2. Statistical Analysis
2.3.3. Geodetector Analysis
3. Results
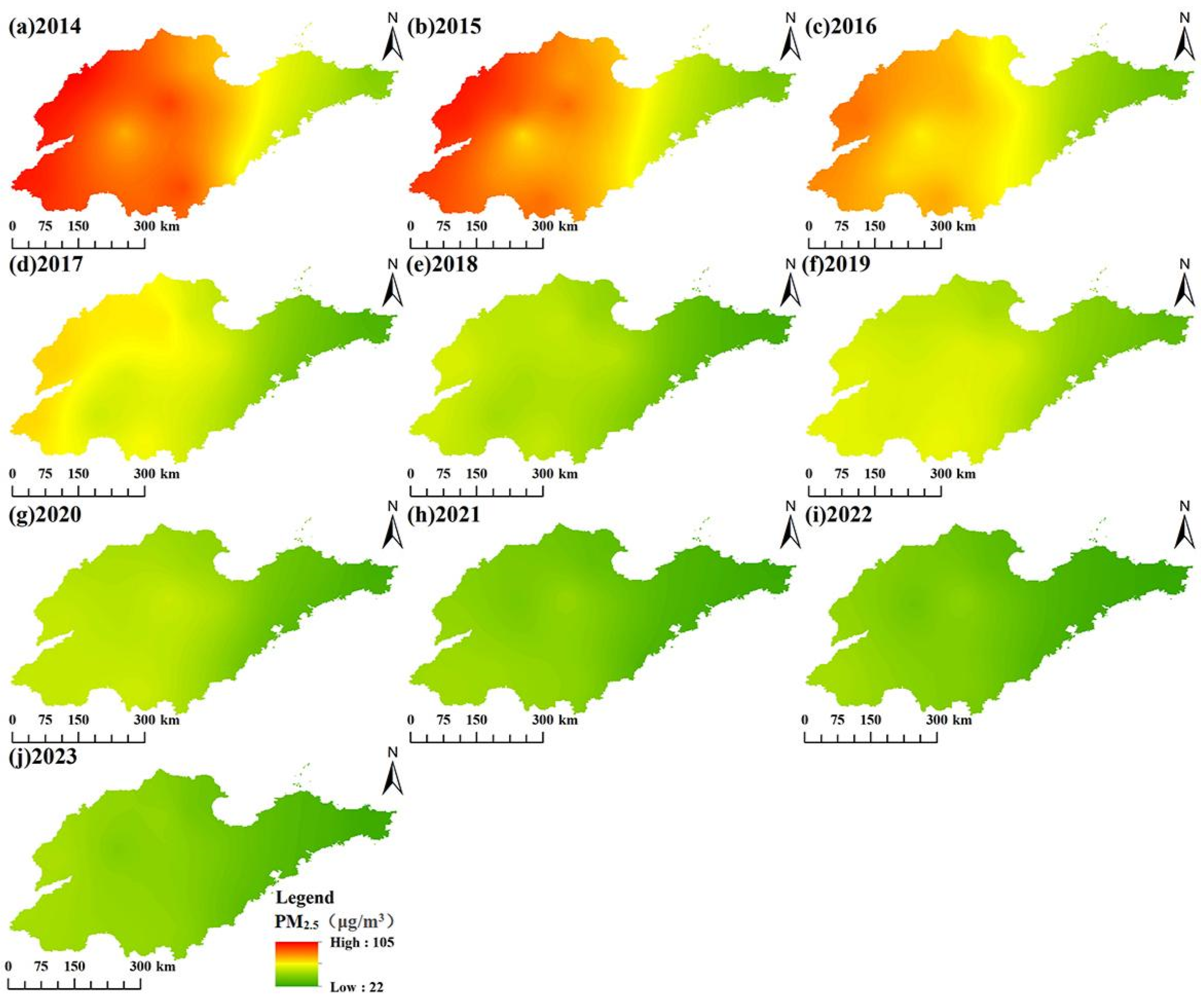
3.1. Annual Spatiotemporal Variation Characteristics of PM2.5 Concentrations
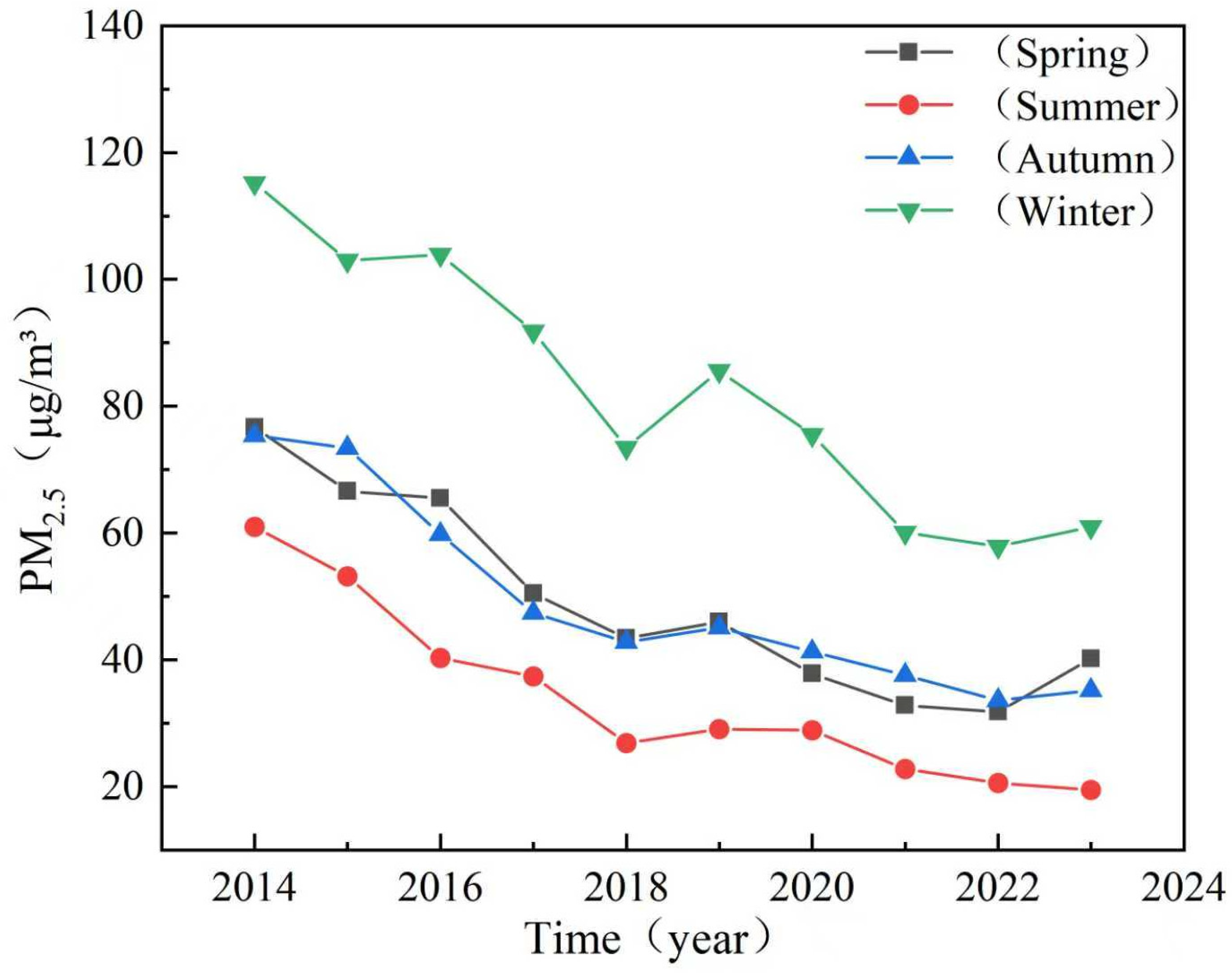
3.2. Seasonal Spatiotemporal Variation Characteristics of PM2.5 Concentrations
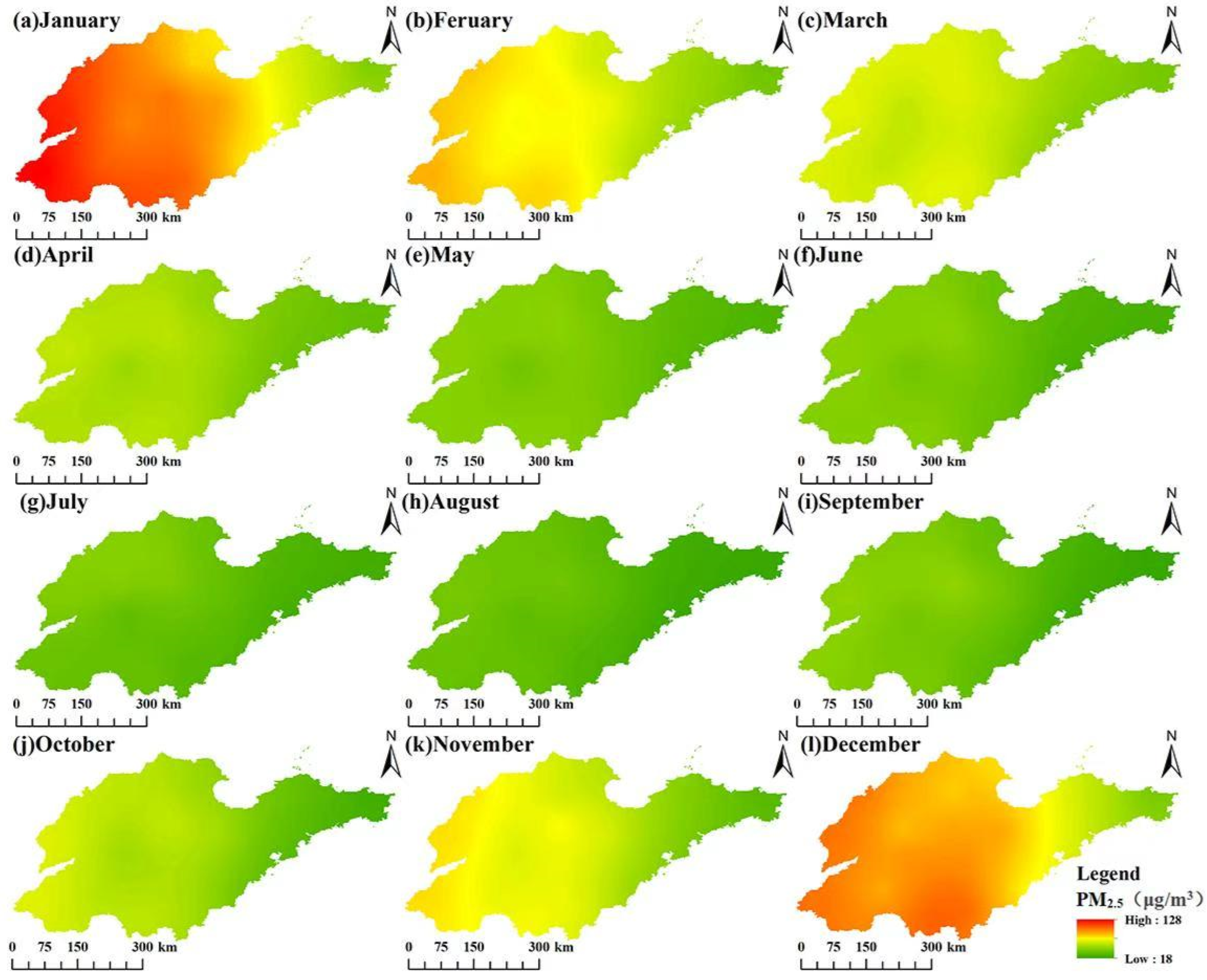
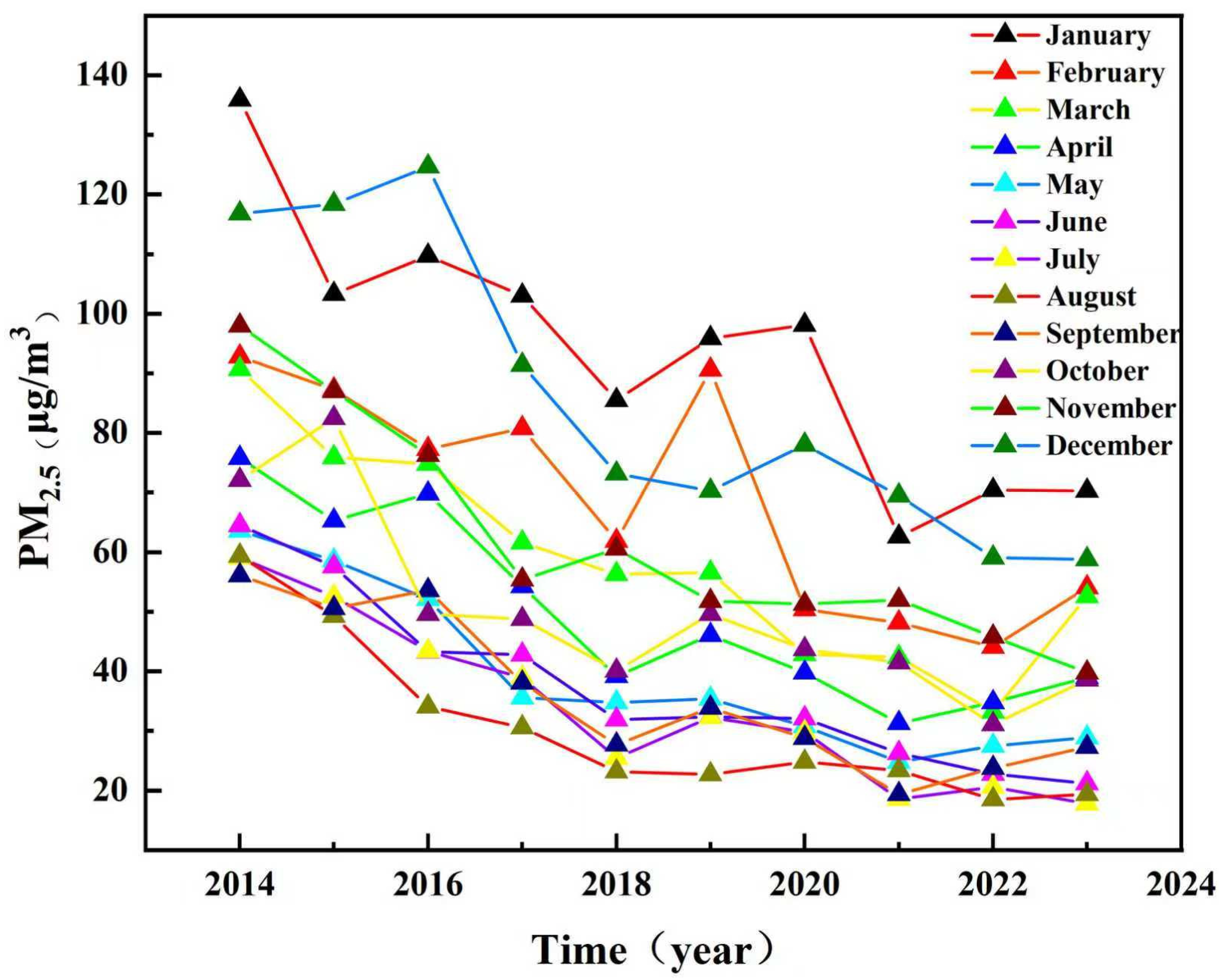
3.3. Monthly Spatiotemporal Variation Characteristics of PM2.5 Concentrations
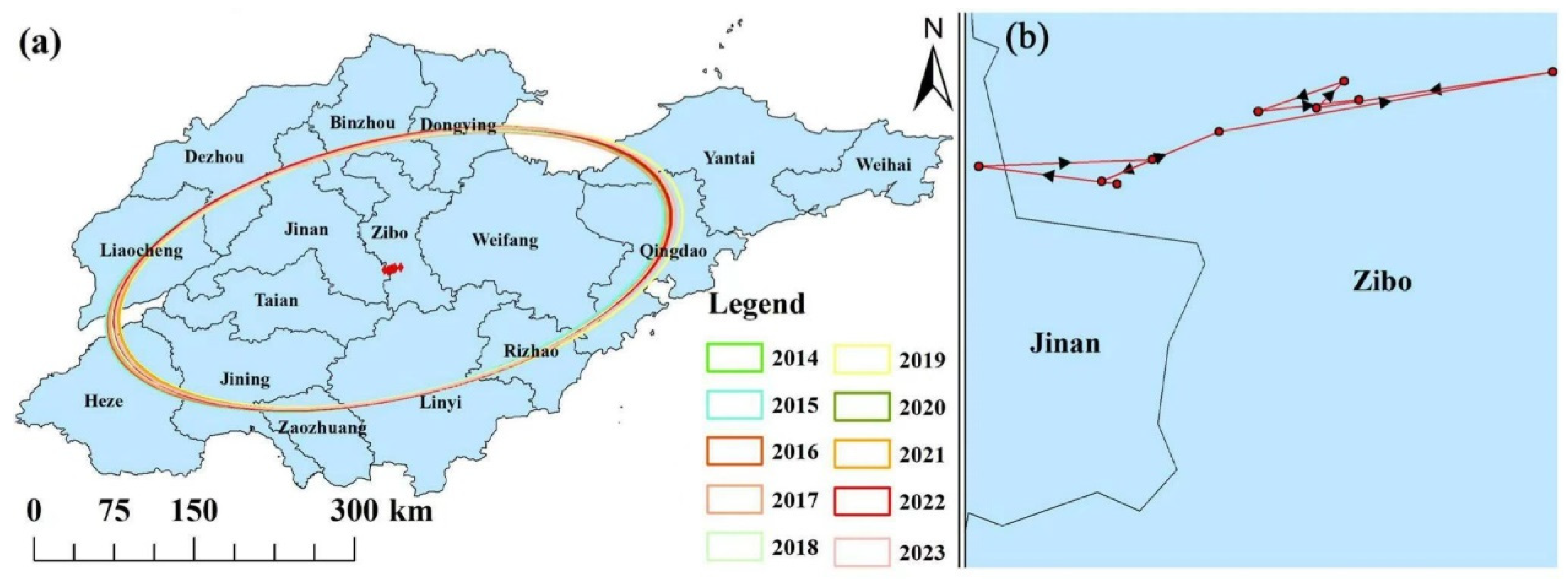
3.4. Variation Characteristics in the Centers of Gravity of PM2.5 Concentrations
3.5. Interaction Effects of Meteorological Factors on PM2.5 Concentrations
3.6. Interaction Effects of Socioeconomic Factors on PM2.5 Concentrations
4. Discussion
4.1. Policy Impact
4.2. Relationship Between Meteorological Factors and PM2.5
4.3. Relationship Between Socio-Economic Factors and PM2.5
5. Conclusions and Future Work
5.1. Summary of Findings
5.2. Limitations and Future Research Directions
- (1)
- Data uncertainty
- (2)
- Limits of correlation interpretation
- (3)
- Impact of data quality from environmental sensors
- (4)
- Future Research directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Geng, G.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xue, T.; Zhao, H.; Tong, D.; Zheng, B.; Li, M.; Liu, F.; Hong, C.; et al. Drivers of PM2.5 air pollution deaths in China 2002–2017. Nat. Geosci. 2021, 14, 645–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, S.; Jacob, D.J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Wen, T.; Shah, V.; Li, K.; Moch, J.M.; Bates, K.H.; Song, S.; et al. Control of particulate nitrate air pollution in China. Nat. Geosci. 2021, 14, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Wu, D.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Jin, L.N.; Zhao, B.; Li, S.; Sun, Y.; Dong, Z.; Wu, Q.; et al. Control of toxicity of fine particulate matter emissions in China. Nature 2025, 643, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Yang, J.; Yung, Y.L.; Li, G.; Seinfeld, J.H. Unexpected air pollution with marked emission reductions during the COVID-19 outbreak in China. Science 2020, 369, 702–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Bozzetti, C. High secondary aerosol contribution to particulate pollution during haze events in China. Nature 2014, 514, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Mahendran, R.; Yu, P.; Xu, R.; Yu, W.; Godellawattage, S.; Li, S.; Guo, Y. Health Effects of Long-Term Exposure to Ambient PM2.5 in Asia-Pacific: A Systematic Review of Cohort Studies. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2022, 9, 130–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelieveld, J.; Klingmüller, K.; Pozzer, A.; Pöschl, U.; Fnais, M.; Daiber, A.; Münzel, T. Cardiovascular disease burden from ambient air pollution in Europe reassessed using novel hazard ratio functions. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 1590–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidell, M.A.; Chen, Z.; Huang, B.Z.; Chow, T.; Eckel, S.P.; Martinez, M.P.; Lurmann, F.; Thomas, D.C.; Gilliland, F.D.; Xiang, A.H. Ambient air pollution and COVID-19 incidence during four 2020–2021 case surges. Environ. Res. 2022, 208, 112758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Zhang, Z.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Huang, J.; Li, F.; He, Y.; Lu, S.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, W.; et al. Inter- and trans-generational impacts of real-world PM2.5 exposure on male-specific primary hypogonadism. Cell Discov. 2024, 10, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Wu, B.; Liu, J. PM2.5 pollution-related health effects and willingness to pay for improved air quality: Evidence from China’s prefecture-level cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 273, 122876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Zhao, C.; Yang, Y. A comprehensive analysis of the spatio-temporal variation of urban air pollution in China during 2014–2018. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 220, 117066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Tong, D.; Shao, M.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, J.; He, H.; Liu, W.; et al. Drivers of improved PM2.5 air quality in China from 2013 to 2017. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 24463–24469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Guo, J.; Liu, S.; Liu, H.; Zhang, G.; Yan, Y.; He, J. Relay transport of aerosols to Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region by multi-scale atmospheric circulations. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 165, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H. Spatio-temporal variation of the coupling relationship between urbanization and air quality: A case study of Shandong Province. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 272, 122812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.-y.; Cao, Y.-q. Do smart cities have lower particulate matter 2.5 (PM2.5)? Evidence from China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 86, 104082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Wang, X.; Yu, M.; Yuan, Y.; Li, B. PM2.5 reduces the daytime/nighttime urban heat island intensity over mainland China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 118, 106001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.-Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, J.-Q.; Lu, X.-C.; Xing, H.-Q.; Ma, M.-L. Geographic Detector-Based Spatiotemporal Variation and Influence Factors Analysis of PM2.5 in Shandong, China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Yao, L.; Li, T.; Fu, X. Spatiotemporal heterogeneity of PM2.5 and its driving difference comparison associated with urbanization in China’s multiple urban agglomerations. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 29689–29703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Guo, Q.; Wang, Z.; Li, X. A Hybrid Wavelet-Based Deep Learning Model for Accurate Prediction of Daily Surface PM2.5 Concentrations in Guangzhou City. Toxics 2025, 13, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, T.; Wang, P.; Yu, W.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, D.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, H. Drivers of alleviated PM2.5 and O3 concentrations in China from 2013 to 2020. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 197, 107110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wen, W.; Ma, X.; Qian, D.; Zhang, W.; Wang, S. Air Pollution in a Northwest Chinese Valley City (2020–2024): Integrated WRF-HYSPLIT Modeling of Pollution Characteristics, Meteorological Drivers, and Transport Pathways in Yining. Toxics 2025, 13, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, Z.; Cui, L.; Fu, H.; Zhang, L.; Kong, L.; Chen, W.; Chen, J. Air pollution characteristics in China during 2015–2016: Spatiotemporal variations and key meteorological factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 902–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; He, Z.; Wang, Z. The Characteristics of Air Quality Changes in Hohhot City in China and their Relationship with Meteorological and Socio-economic Factors. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2024, 24, 230274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Yuan, Q.; Li, T.; Shen, H.; Zhang, L. The Relationships between PM2.5 and Meteorological Factors in China: Seasonal and Regional Variations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, C.; Qin, C.; Li, Z.; Li, K. Spatiotemporal variations of PM2.5 pollution and its dynamic relationships with meteorological conditions in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Chemosphere 2022, 301, 134640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munyati, C.; Sinthumule, N.I. Comparative suitability of ordinary kriging and Inverse Distance Weighted interpolation for indicating intactness gradients on threatened savannah woodland and forest stands. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2021, 12, 100151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Guo, Q.; Yin, Z.; Luo, X.; Sun, M. Evolution and driving mechanisms of eco-environmental quality across different urbanization stages. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 22101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Xu, C. Knowledge diffusion of Geodetector: A perspective of the literature review and Geotree. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Kong, S.; Chen, N.; Yan, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhu, B.; Xu, K.; Cao, W.; Ding, Q.; Lan, B.; et al. Significant changes in the chemical compositions and sources of PM2.5 in Wuhan since the city lockdown as COVID-19. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 140000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Sun, J.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, X. Spatiotemporal variation and socioeconomic drivers of air pollution in China during 2005–2016. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 245, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Shahbaz, M. The existence of environmental Kuznets curve: Critical look and future implications for environmental management. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fang, X.; Ji, H.; Li, X.; Zhao, Z. Spatiotemporal patterns of recent PM2.5 concentrations over typical urban agglomerations in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Yang, X.; Ma, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, T. Integrating explainable AI and causal inference to unveil regional air quality drivers in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 390, 126270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girotti, C.; Fernando Kowalski, L.; Silva, T.; Correia, E.; Shimomura, A.R.P.; Akira Kurokawa, F.; Lopes, A. Air pollution Dynamics: The role of meteorological factors in PM10 concentration patterns across urban areas. City Environ. Interact. 2025, 25, 100184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; He, Z.; Wang, Z. Change in Air Quality during 2014–2021 in Jinan City in China and Its Influencing Factors. Toxics 2023, 11, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, L.; Wang, T.; Liu, J.; Chen, Z.; Wu, H.; Qu, Y.; Li, M.; Xie, M. Elucidating drivers of severe wintertime fine particulate matter pollution episodes in the Yangtze River Delta region of eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, N.; Wang, G.; Li, G.; Lang, J. Trends in Air Pollutant Concentrations and the Impact of Meteorology in Shandong Province, Coastal China, during 2013–2019. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2021, 21, 200545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, G.T.H.; La, L.T.; Hoang-Cong, H.; Le, A.H. An exploration of meteorological effects on PM2.5 air quality in several provinces and cities in Vietnam. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 145, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, G.; Kong, F.; Zhao, N.; Gao, W.; Zhang, H. PM2.5 pollution characteristics, drivers, and regional transport during different pollution levels in Linyi, China: An integrated PMF-ML-SHAP framework and transport models. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 494, 138534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Cheng, J.; Yan, L.; Wu, N.; Hu, H.; Tong, D.; Zheng, B.; et al. Efficacy of China’s clean air actions to tackle PM2.5 pollution between 2013 and 2020. Nat. Geosci. 2024, 17, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano-Monserrate, M.A.; Subramaniam, Y.; Adnan, N.; Bergougui, B.; Adebayo, T.S. Dynamic factors driving PM2.5 concentrations: Fresh evidence at the global level. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 362, 124940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Zhang, M.; Chen, S.; Wang, W.; Nie, R. The environmental Kuznets curve for PM2.5 pollution in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region of China: A spatial panel data approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 984–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.; Cui, X.; Chu, L.; Wang, H.; Xi, Z.; Deng, Y. Nonlinear effects of environmental regulation on PM2.5 and CO2 in China: Evidence from a quantile-on-quantile approach. Energy 2024, 292, 130456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Hunt, A.; Morley, B. The Effectiveness of Environmental Spending in China and the Environmental Kuznets Curve. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Method | Key Parameters | Quality Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| Ordinary Kriging | Semivariogram Model: Spherical, Nugget: 0.339, Step size: 0.572 | Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) |
| Geodetector | Interaction Detector | q-statistic: [0–1], p < 0.05 |
| Interpolation Method | Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) | Slope of the Regression Function |
|---|---|---|
| Ordinary Kriging (OK) | 6.2079 | 0.8342 |
| Inverse Distance Weighting (IDW) | 7.4733 | 0.4779 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiao, S.; Guo, Q.; He, Z.; Feng, G.; Wang, Z.; Li, X. Spatiotemporal Trends and Drivers of PM2.5 Concentrations in Shandong Province from 2014 to 2023 Under Socioeconomic Transition. Toxics 2025, 13, 978. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110978
Qiao S, Guo Q, He Z, Feng G, Wang Z, Li X. Spatiotemporal Trends and Drivers of PM2.5 Concentrations in Shandong Province from 2014 to 2023 Under Socioeconomic Transition. Toxics. 2025; 13(11):978. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110978
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiao, Shuaisen, Qingchun Guo, Zhenfang He, Genyue Feng, Zhaosheng Wang, and Xinzhou Li. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Trends and Drivers of PM2.5 Concentrations in Shandong Province from 2014 to 2023 Under Socioeconomic Transition" Toxics 13, no. 11: 978. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110978
APA StyleQiao, S., Guo, Q., He, Z., Feng, G., Wang, Z., & Li, X. (2025). Spatiotemporal Trends and Drivers of PM2.5 Concentrations in Shandong Province from 2014 to 2023 Under Socioeconomic Transition. Toxics, 13(11), 978. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110978








