DGT-Based Assessment of Antibiotics and Hormones in a Typical Wastewater Treatment Plant and Its Receiving Water in Shanghai: Implications for Aquaculture Reuse
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Equipment and Reagents
2.2. Sampling Sites in Different Compartments of the WWTP and Its Receiving Water Body
2.3. DGT Devices Application
2.4. Sample Extraction and Analytical Analysis
2.5. Data Analysis
2.5.1. DGT-Based Concentration Calculation
2.5.2. DGT-Derived Risk Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Applicability of DGT in the Wastewater and Its Receiving Water Body
3.2. Assessment of the Environmental Hormones and Antibiotics Removal in WWTP Based on the XAD-DGT Technique
3.2.1. Environmental Hormones and Antibiotics in the Influent in WWTP
3.2.2. XAD-DGT Derived Removal Efficiency
3.3. Feasibility of Using WWTP Effluent and Receiving Water for Aquaculture: From Bioavailable Perspectives
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, H. Spatial and seasonal distributions of estrogens and bisphenol A in the Yangtze River Estuary and the adjacent East China Sea. Chemosphere 2014, 111, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mair, G.C.; Halwart, M.; Derun, Y.; Costa-Pierce, B.A. A decadal outlook for global aquaculture. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2023, 54, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaibel, I.; Arnon, S.; Zilberg, D. Treated municipal wastewater as a water source for sustainable aquaculture: A review. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 14, 62–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S. Waste Water Management Through Aquaculture. J. Environ. Manag. 2006, 1, 339–350. [Google Scholar]
- US Environmental Protection Agency. Evaluation of Filter Feeding Fishes for Removing Excessive Nutrients and Algae from Wastewater; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washinton, DC, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, M.T.; Hussein, H.A. Use of waste water for aquaculture: An experimental field study at a sewage-treatment plant, Egypt. Aquac. Res. 1997, 28, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahbub, P.; Sharma, A. Investigation of alternative water sources for fish farming using life cycle costing approach: A case study in North West Tasmania. J. Hydrol. 2019, 579, 124215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaibel, I.; Dagan, G.; Arnon, S.; Schwartsburd, F.; Britzi, M.; Snyder, S.A.; Zilberg, D. Tertiary-treated wastewater as a potential water source for sustainable aquaculture: A laboratory-scale experiment with Cyprinus carpio. Aquaculture 2020, 522, 735161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobling, S.; Nolan, M.; Tyler, C.R.; Brighty, G.; Sumpter, J.P. Widespread sexual disruption in wild fish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 2498–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.Y.; Zou, H.Y.; Gao, J.; Wang, T.; Bu, Q.W.; Wang, Z.L.; Hu, M.; Wang, Z.Y. A critical review on the distribution and ecological risk assessment of steroid hormones in the environment in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 786, 147452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegg, C.E.; Zaichick, S.V.; Bomba-Warczak, E.; Jovasevic, V.; Kim, D.; Kharkwal, H.; Wilson, D.W.; Walsh, D.; Sollars, P.J.; Pickard, G.E. Herpesviruses assimilate kinesin to produce motorized viral particles. Nature 2021, 599, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Hernández, J.A.; Araújo, R.G.; López-Pacheco, I.Y.; Rodas-Zuluaga, L.I.; González-González, R.B.; Parra-Arroyo, L.; Sosa-Hernández, J.E.; Melchor-Martínez, E.M.; Martínez-Ruiz, M.; Barceló, D. Environmental persistence, detection, and mitigation of endocrine disrupting contaminants in wastewater treatment plants–a review with a focus on tertiary treatment technologies. Environ. Sci. Adv. 2022, 1, 680–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Lu, C.; Huang, N.; Zhong, M.; Teng, Y.; Tian, Y.; Ye, K.; Liang, L.; Hu, Z. Exploration of the effect of simultaneous removal of EDCs in the treatment process of different types of wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 87, 436–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Ngasepam, J.; Dhangar, K.; Mahlknecht, J.; Manna, S. Critical review on negative emerging contaminant removal efficiency of wastewater treatment systems: Concept, consistency and consequences. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 352, 127054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.-M.; Lu, X.-M.; Jia, J.-W.; Xing, D.-F.; Li, Y.-F.; Cao, G.-L.; Zhang, Z.-F. Comprehensive assessment of 45 antibiotics in ten urban wastewater treatment plants in Northeastern China: Terminal treatment is not a reliable guard. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 489, 137755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stasinakis, A.S.; Thomaidis, N.S.; Arvaniti, O.S.; Asimakopoulos, A.G.; Samaras, V.G.; Ajibola, A.; Mamais, D.; Lekkas, T.D. Contribution of primary and secondary treatment on the removal of benzothiazoles, benzotriazoles, endocrine disruptors, pharmaceuticals and perfluorinated compounds in a sewage treatment plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.F.; Qiang, Z.M.; Zhang, H.Q.; Ben, W.W. Fate and seasonal variation of endocrine-disrupting chemicals in a sewage treatment plant with A/A/O process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 84, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Lam, J.C.W.; Kwok, K.Y.; Tsui, M.M.P.; Lam, P.K.S. Occurrence and fate of endogenous steroid hormones, alkylphenol ethoxylates, bisphenol A and phthalates in municipal sewage treatment systems. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 61, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onchoke, K.K.; Fateru, O.O. Evaluating bioavailability of elements in municipal wastewater sludge (Biosolids) from three rural wastewater treatment plants in East Texas (USA) by a sequential extraction procedure. Results Chem. 2021, 3, 100211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yin, R.; Yu, X.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y. Occurrence, removal, and ecological risk assessment of Emerging organic contaminants in an industrial WWTP. Water Resour. Ind. 2025, 34, 100308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorell, T.; McEvoy, K. Incorporating Bioavailability Considerations into the Evaluation of Contaminated Sediment Sites. Remediat. J. 2013, 23, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.L.L.; Hawker, D.W.; Müller, J.F.; Leusch, F.D.L.; Tremblay, L.A.; Chapman, H.F. Comprehensive study of endocrine disrupting compounds using grab and passive sampling at selected wastewater treatment plants in South East Queensland, Australia. Environ. Int. 2007, 33, 654–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, D. Dissolved organic carbon concentration and biodegradability across the global rivers: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 818, 151828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, A.; Candolfi, M.; Kimmel, S.; Poulsen, V. The challenge: Pollinator risk assessment—Past, present, and future. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, J.; Özkan, A.; Oh, C.; Mahajan, G.; Prantil-Baun, R.; Ingber, D.E. Simulating drug concentrations in PDMS microfluidic organ chips. Lab A Chip 2021, 21, 3509–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnier, A.; Bancon-Montigny, C.; Delpoux, S.; Spinelli, S.; Avezac, M.; Gonzalez, C. Study of passive sampler calibration (Chemcatcher®) for environmental monitoring of organotin compounds: Matrix effect, concentration levels and laboratory vs in situ calibration. Talanta 2020, 219, 121316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Y.; Ji, X.; Zhang, D.; Xu, G.; Wu, D.; Li, A.; Xie, X. Validation and application of diffusive gradient in thin-film (DGT) equipped novel cyclodextrin polymer gels for monitoring endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) and environmental risk assessment in the Taihu lake basin. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Chen, S. Organic diffusive gradients in thin films (o-DGT) for determining environmental behaviors of antibiotics: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 459, 132279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Pan, S.; Cheng, H.; Sweetman, A.J.; Zhang, H.; Jones, K.C. Diffusive gradients in thin-films (DGT) for in situ sampling of selected endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) in waters. Water Res. 2018, 137, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Bu, Q.; Li, Q.; Gao, X.; Xie, H.; Gong, W.; Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Tang, J. Development and applications of diffusive gradients in thin films for monitoring pharmaceuticals in surface waters. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 311, 119979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Yan, L.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Li, D.; Chen, S. MOF-Derived DGT for Selective Monitoring of Quinolones and Tetracyclines: Tracking Antibiotics Risks in Urban Wastewater Treatment Plant. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 498, 139936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins de Barros, R.; Lissalde, S.; Guibal, R.; Guibaud, G. Development of a multi-hormone analysis method by LC-MS/MS for environmental water application using diffusive gradient in thin films. Talanta 2022, 243, 123390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Su, Y.; Jiang, L.; Peng, K.; Li, J.; Liu, S.; Sun, Y.; Chen, C.-E.; Luo, C. Assessing the bioavailability of antibiotics in soil with the diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT). J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 448, 130935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xu, H.; Gan, S.; Sun, R.; Zheng, Y.; Craig, N.J.; Sheng, W.; Li, J.-Y. Antibiotics and endocrine disrupting chemicals in effluent from wastewater treatment plants of a mega-city affected the water quality of juvenile Chinese sturgeon habitat: Upgrades to wastewater treatment processes are needed. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 215, 117840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Liu, M.; Nie, M.; Shi, H.; Gu, L. Antibiotics in the surface water of the Yangtze Estuary: Occurrence, distribution and risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 175, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhong, J.; Lou, Q. Occurrence, distribution, and risk assessment of antibiotics in the surface water of Poyang Lake, the largest freshwater lake in China. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guérit, I.; Bocquené, G.; James, A.; Thybaud, E.; Minier, C. Environmental risk assessment: A critical approach of the European TGD in an in situ application. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2008, 71, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-C.; Jiang, L.-Y.; Kuo, Y.-L.; Chen, C.-Y.; Hsieh, C.-Y.; Hung, C.-F.; Tien, C.-J. Characteristics of nonylphenol and bisphenol A accumulation by fish and implications for ecological and human health. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 502, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright-Walters, M.; Volz, C.; Talbott, E.; Davis, D. An updated weight of evidence approach to the aquatic hazard assessment of Bisphenol A and the derivation a new predicted no effect concentration (Pnec) using a non-parametric methodology. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 676–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, R.; Liu, J.; Huang, B.; Wang, X.; Luan, T.; Yuan, K. Assessment of the potential ecological risk of residual endocrine-disrupting chemicals from wastewater treatment plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Lin, C.; Lei, K.; Xin, M.; Wang, B.; Ouyang, W.; Liu, X.; He, M. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals in a typical urbanized bay of Yellow Sea, China: Distribution, risk assessment, and identification of priority pollutants. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czarny, K.; Szczukocki, D.; Krawczyk, B.; Skrzypek, S.; Zieliński, M.; Gadzała-Kopciuch, R. Toxic effects of single animal hormones and their mixtures on the growth of Chlorella vulgaris and Scenedesmus armatus. Chemosphere 2019, 224, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhu, Y.; Zhong, G.; Huang, Y.; Jones, K.C. Comprehensive Assessment of Environmental Emissions, Fate, and Risks of Veterinary Antibiotics in China: An Environmental Fate Modeling Approach. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 5534–5547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Wang, K.; Yang, F.; Zhuang, T. Antibiotic pollution of the Yellow River in China and its relationship with dissolved organic matter: Distribution and Source identification. Water Res. 2023, 235, 119867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernando, M.D.; Mezcua, M.; Fernández-Alba, A.R.; Barceló, D. Environmental risk assessment of pharmaceutical residues in wastewater effluents, surface waters and sediments. Talanta 2006, 69, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahnke, A.; MacLeod, M.; Wickström, H.; Mayer, P. Equilibrium Sampling to Determine the Thermodynamic Potential for Bioaccumulation of Persistent Organic Pollutants from Sediment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 11352–11359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neale, P.A.; Antony, A.; Gernjak, W.; Leslie, G.; Escher, B.I. Natural versus wastewater derived dissolved organic carbon: Implications for the environmental fate of organic micropollutants. Water Res. 2011, 45, 4227–4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; He, X.; Xiong, H.; Chen, Y.; Huang, L. Structure, mechanism, and toxicity in antibiotics metal complexation: Recent advances and perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 848, 157778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulikova, N.A.; Solovyova, A.A.; Perminova, I.V. Interaction of Antibiotics and Humic Substances: Environmental Consequences and Remediation Prospects. Molecules 2022, 27, 7754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.; Lu, L.; Meng, F. DOM-mediated membrane retention of fluoroquinolone as revealed by fluorescence quenching properties. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, T.F.; Lach, J.L. Drug diffusion and bioavailability: Tetracycline metallic chelation. Am. J. Hosp. Pharm. 1975, 32, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavumiragira, J.P.; Yin, H.; Jin, W.; Fangninou, F.F.; Eheneden, I. Influence of Seasonal Variation in Antibiotic Concentration on the Fate and Transport of Antibiotics Within an Artificial Pond System. Water 2025, 17, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Bao, Y.; Xu, B. Seasonal variation of antibiotics in surface water of Pudong New Area of Shanghai, China and the occurrence in typical wastewater sources. Chemosphere 2020, 239, 124816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Hofstra, N.; van de Schans, M.G.M.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, L.; Strokal, M.; Kroeze, C.; Chen, X. Riverine Antibiotics from Animal Production and Wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2023, 10, 1059–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkow, I.S.; Oswald, S.E.; Lensing, H.J.; Munz, M. Seasonal dynamics modifies fate of oxygen, nitrate, and organic micropollutants during bank filtration—Temperature-dependent reactive transport modeling of field data. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 9682–9700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Yang, T.; Huang, B.; Zhu, B.; Xing, Z.; Zhan, G. The operating temperature affects the efficiency and pathogenic risk of wastewater treatment enhanced by slurry. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 188, 1306–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoso-Bravo, A.; Retamal, C.; Carballa, M.; Ruiz-Filippi, G.; Chamy, R. Influence of temperature on the hydrolysis, acidogenesis and methanogenesis in mesophilic anaerobic digestion: Parameter identification and modeling application. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 60, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.B.; Qiu, S.M.; Dai, L.Y.; Zhang, L.H.; Meng, L.W.; Liu, M.W.; Yao, H. The occurrence and removal of steroid estrogens in a full-scale anaerobic/anoxic/aerobic-membrane bioreactor process and the implication of the bacterial community dynamics. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Eichhorn, P.; Jensen, J.N.; Weber, A.S.; Aga, D.S. Removal of antibiotics in wastewater: Effect of hydraulic and solid retention times on the fate of tetracycline in the activated sludge process. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 5816–5823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Maniquiz-Redillas, M.C.; Kim, L.-H. Settling basin design in a constructed wetland using TSS removal efficiency and hydraulic retention time. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 1791–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.; Tsezos, M. Removal of Hazardous Organic Pollutants by Adsorption on Microbial Biomass. Water Sci. Technol. 1987, 19, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, M.; Combalbert, S.; Delgenès, N.; Bergheaud, V.; Rocher, V.; Benoît, P.; Delgenès, J.P.; Patureau, D.; Hernandez-Raquet, G. Occurrence of estrogens in sewage sludge and their fate during plant-scale anaerobic digestion. Chemosphere 2010, 81, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency. Guideline on the Environmental Risk Assessment of Medicinal Products for Human Use; European Medicines Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.-G.; Gao, Y.-P.; Jiang, S.-J.; Jordan, R.W.; Yang, Y.-F. Ecotoxicological risk of antibiotics and their mixtures to aquatic biota with the DGT technique in sediments. Ecotoxicology 2023, 32, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
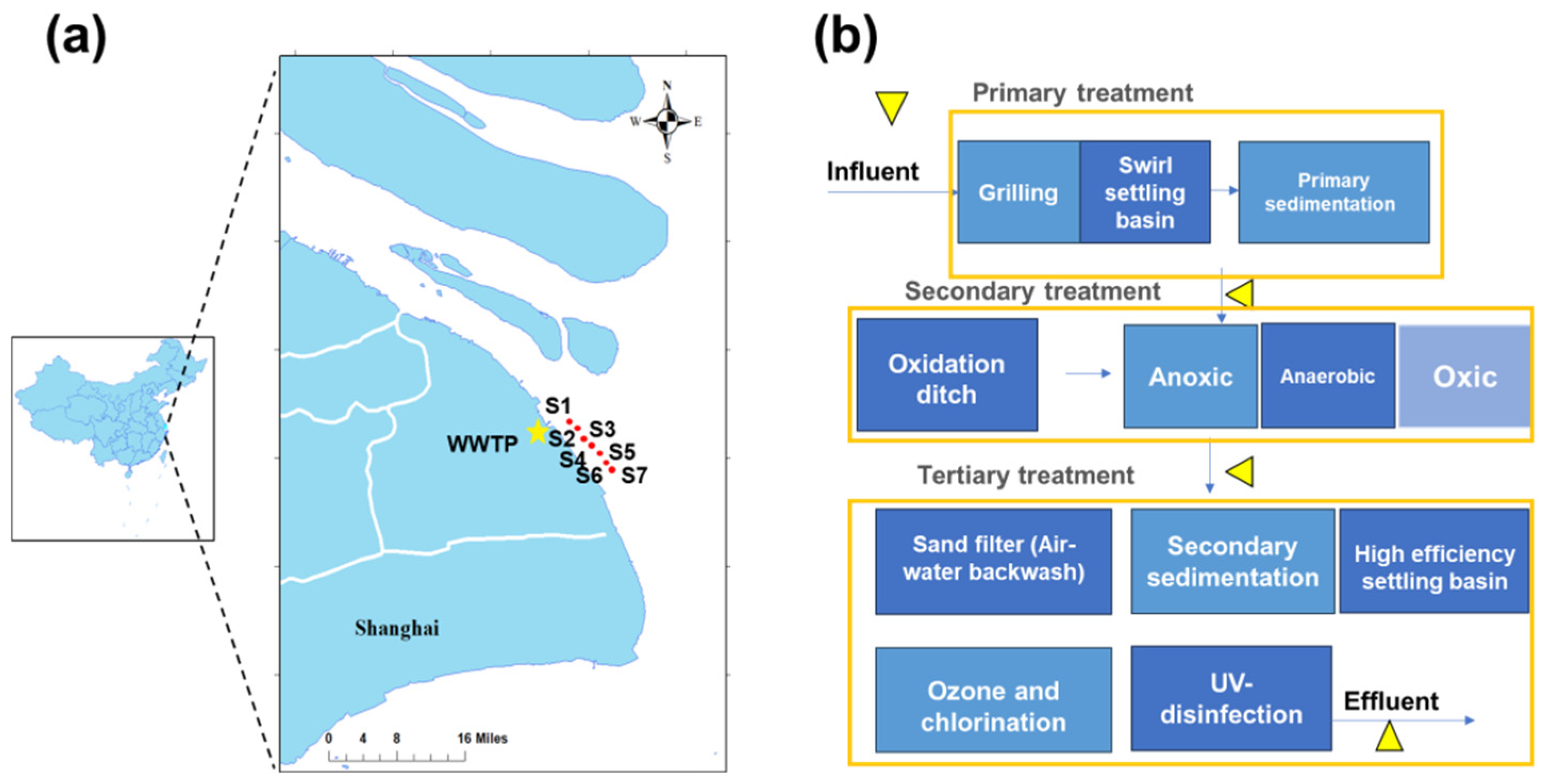
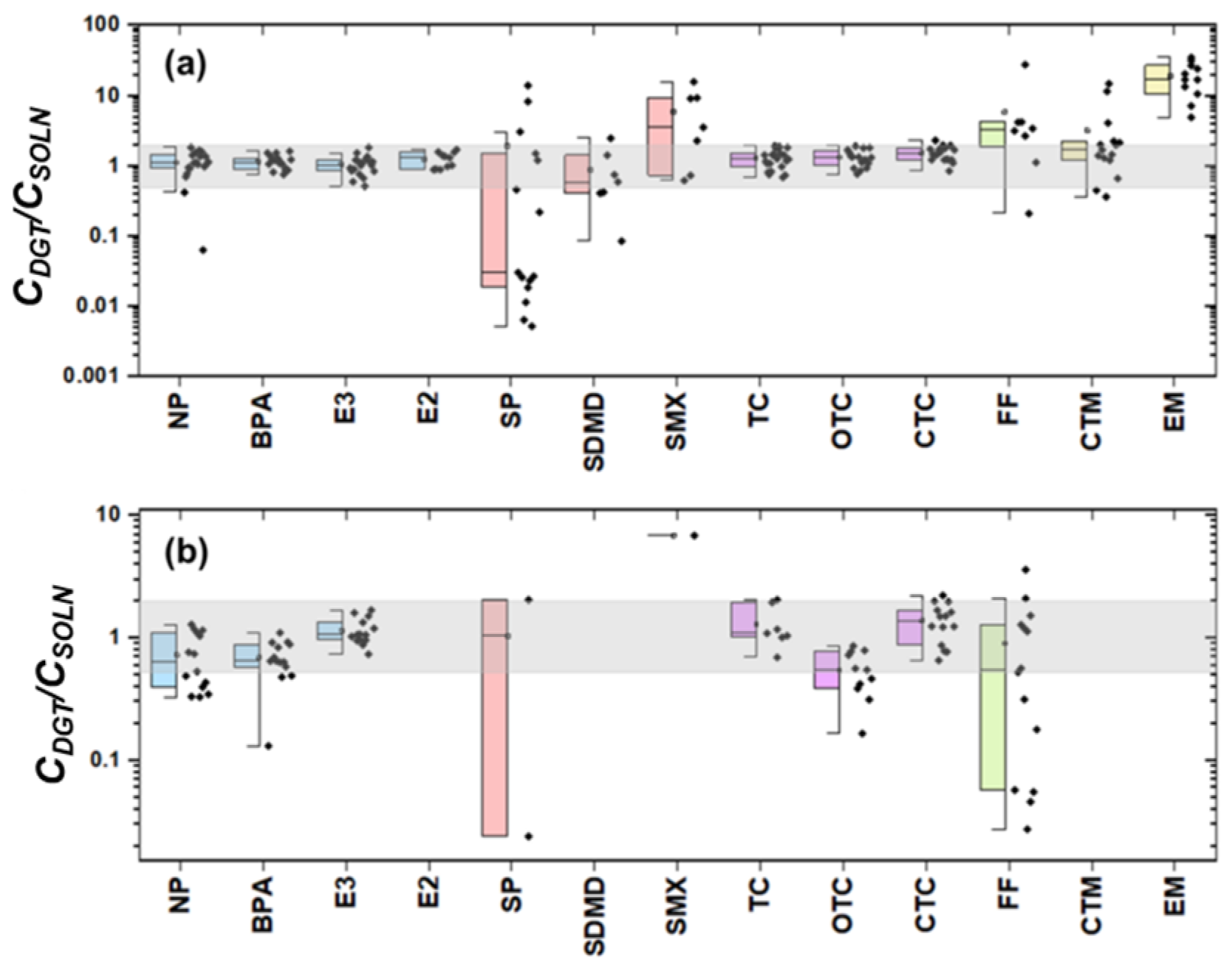
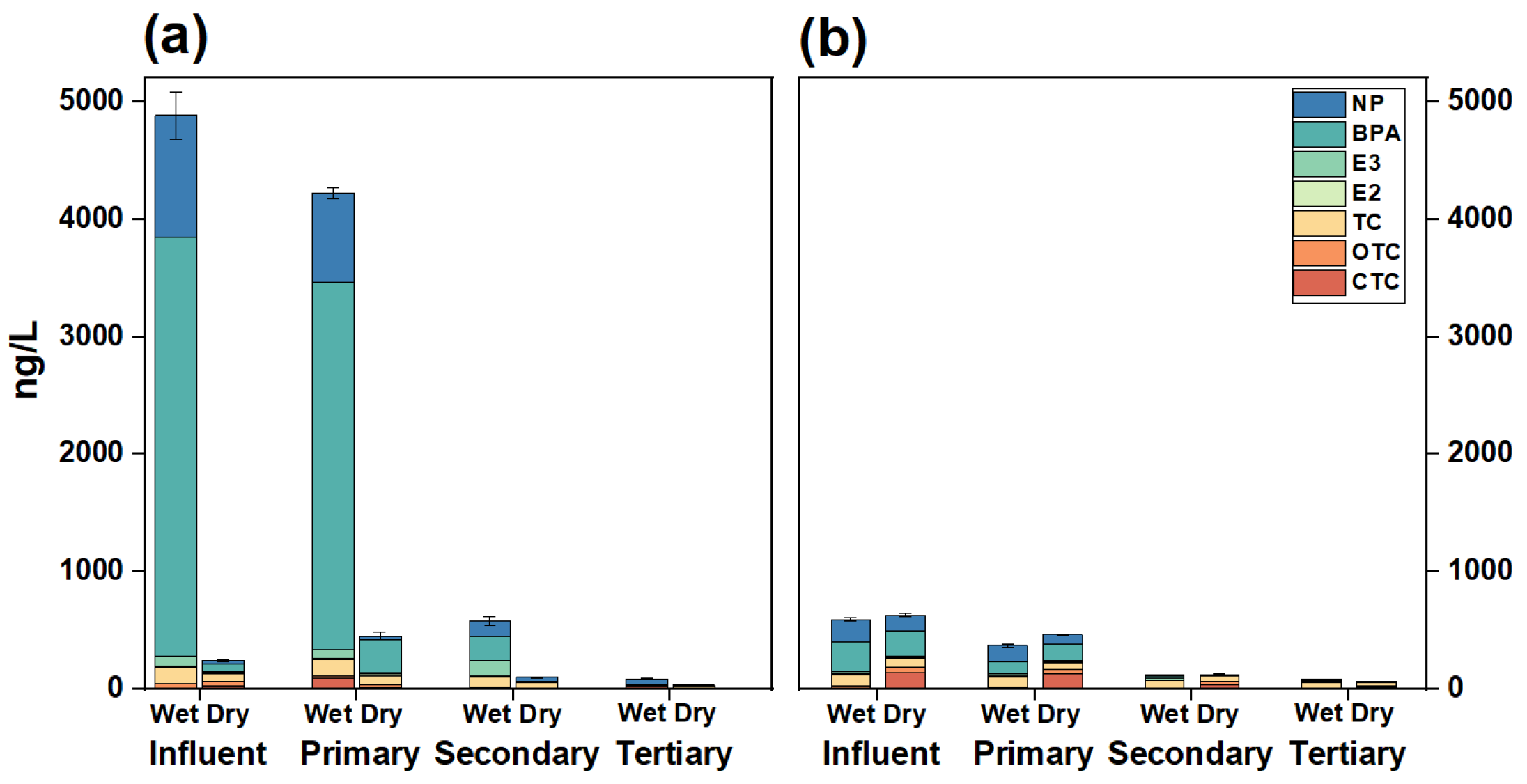

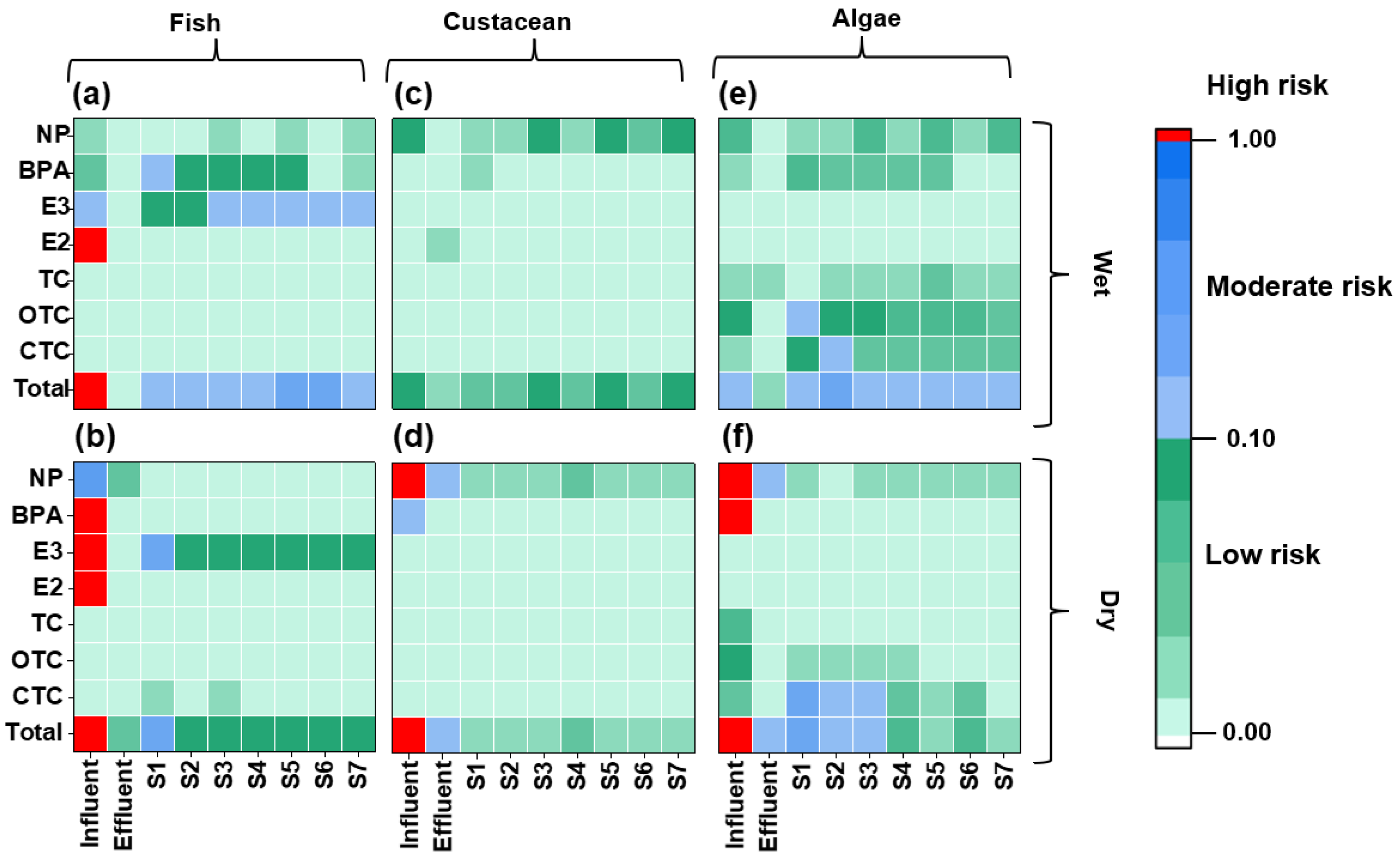
| Chemicals | Influent | Primary Treatment Effluent | Secondary Treatment Effluent | Tertiary Treatment Effluent |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wet Season | ||||
| BPA | 3571.53 ± 198.19 | 3122.52 ± 43.43 | 210.75 ± 33.39 | 10.69 ± 0.69 |
| NP | 1033.2 ± 41.44 | 760.42 ± 22.92 | 130.53 ± 2.57 | 49.45 ± 2.67 |
| E2 | 8.66 ± 0.05 | 7.01 ± 0.08 | 4.75 ± 0.61 | / |
| E3 | 80.53 ± 4.13 | 74.95 ± 4.55 | 128.43 ± 1.16 | / |
| ∑EDCs | 4693.92 ± 202.52 | 3964.9 ± 49.32 | 474.45 ± 33.512 | 60.14 ± 2.76 |
| TC | 144.44 | 144.85 ± 1.7 | 86.03 ± 2.44 | 0.17 |
| OTC | 33.9 ± 0.11 | 20.53 ± 0.25 | 5.99 ± 0.11 | / |
| CTC | 134.12 ± 12.67 | 92.05 ± 5.18 | 14.91 ± 1.44 | 26.63 |
| ∑Antibiotics | 312.46 ± 12.67 | 257.43 ± 5.46 | 106.93 ± 2.84 | 26.8 |
| ∑EOCs | 5006.38 ± 203.31 | 4365.43 ± 49.92 | 843.26 ± 33.75 | 86.94 ± 2.76 |
| Dry Season | ||||
| BPA | 68.9 ± 0.46 | 283.59 ± 5.93 | 3.54 ± 0.06 | 1.76 ± 0.08 |
| NP | 23.84 ± 0.09 | 26.58 ± 0.01 | 29.78 ± 2.73 | 1.02 ± 0.12 |
| E2 | 6.78 ± 0.77 | 12.92 ± 1.28 | 0.82 ± 0.12 | / |
| E3 | 14.91 ± 0.78 | 13.23 ± 0.84 | 5.26 ± 0.42 | 0.2 |
| ∑EDCs | 114.43 ± 1.19 | 336.32 ± 6.12 | 39.39 ± 2.77 | 2.78 ± 0.14 |
| TC | 64.26 ± 10.5 | 78.58 ± 16.35 | 49.68 ± 3.27 | 30.7 ± 0.77 |
| OTC | 34.08 ± 0.55 | 0.83 ± 0.83 | 0.83 ± 0.83 | 0.83 ± 0.83 |
| CTC | 31.52 ± 5.39 | 0.83 ± 0.83 | 0.83 ± 0.83 | 0.83 ± 0.83 |
| ∑Antibiotics | 129.86 ± 11.82 | 80.24 ± 16.40 | 51.34 ± 3.47 | 32.36 ± 1.40 |
| ∑EOCs | 244.29 ± 16.75 | 416.56 ± 17.50 | 843.26 ± 5.64 | 86.94 ± 1.99 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, C.; Wen, L.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Y. DGT-Based Assessment of Antibiotics and Hormones in a Typical Wastewater Treatment Plant and Its Receiving Water in Shanghai: Implications for Aquaculture Reuse. Toxics 2025, 13, 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110970
Huang Y, Zhang Z, Sun C, Wen L, Wang Q, Yang Y. DGT-Based Assessment of Antibiotics and Hormones in a Typical Wastewater Treatment Plant and Its Receiving Water in Shanghai: Implications for Aquaculture Reuse. Toxics. 2025; 13(11):970. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110970
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Yin, Zheng Zhang, Chaofeng Sun, Luting Wen, Qian Wang, and Yanhao Yang. 2025. "DGT-Based Assessment of Antibiotics and Hormones in a Typical Wastewater Treatment Plant and Its Receiving Water in Shanghai: Implications for Aquaculture Reuse" Toxics 13, no. 11: 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110970
APA StyleHuang, Y., Zhang, Z., Sun, C., Wen, L., Wang, Q., & Yang, Y. (2025). DGT-Based Assessment of Antibiotics and Hormones in a Typical Wastewater Treatment Plant and Its Receiving Water in Shanghai: Implications for Aquaculture Reuse. Toxics, 13(11), 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110970








