Heavy Metals in the Soil–Coffee System of Pu’er, China, a Major Coffee Producing Region in China: Distribution and Health Risks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
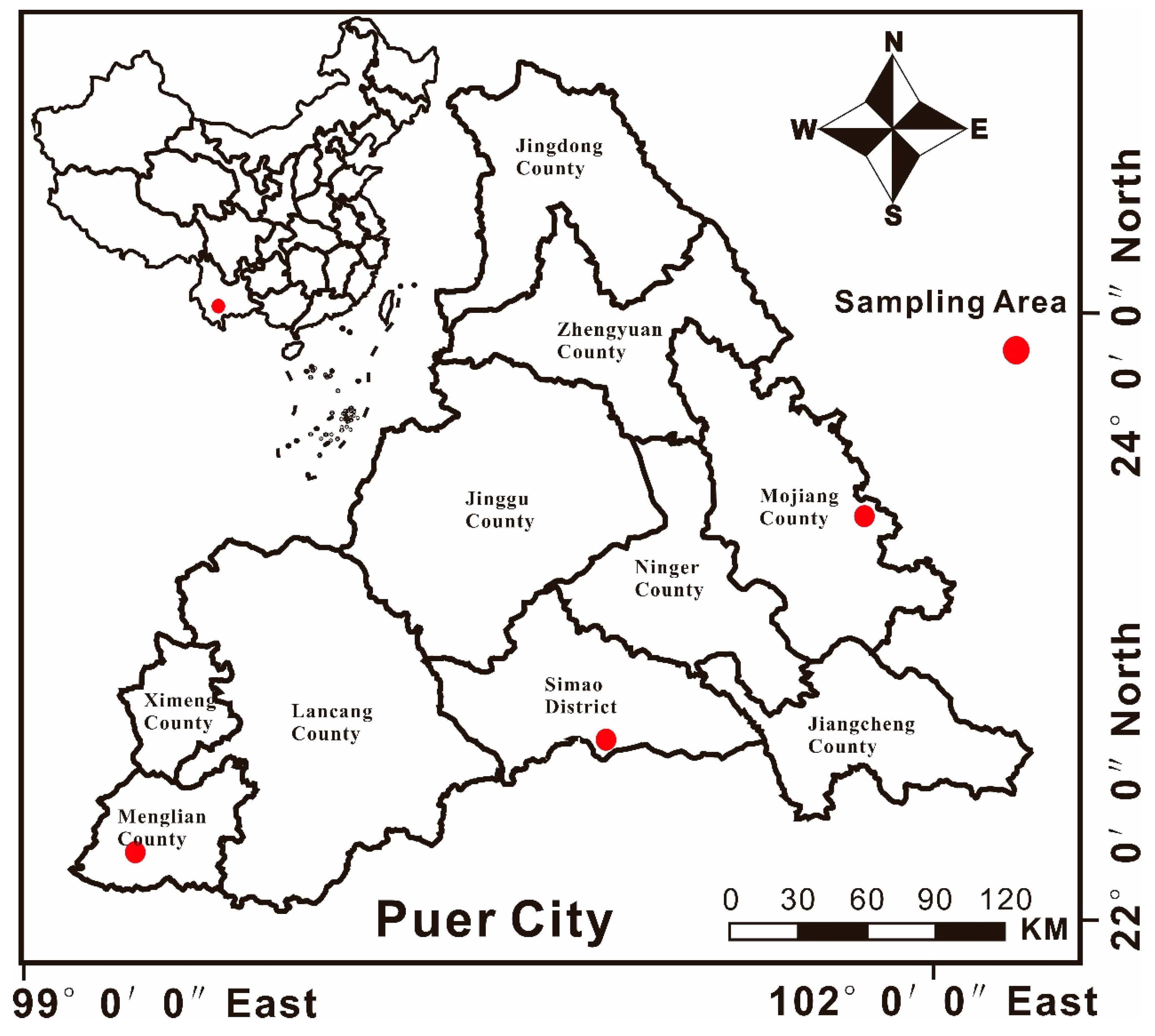
2.1. Description of the Study Area and Field Sampling
2.2. Sample Preparation and Analysis
2.3. Quality Assurance and Quality Control
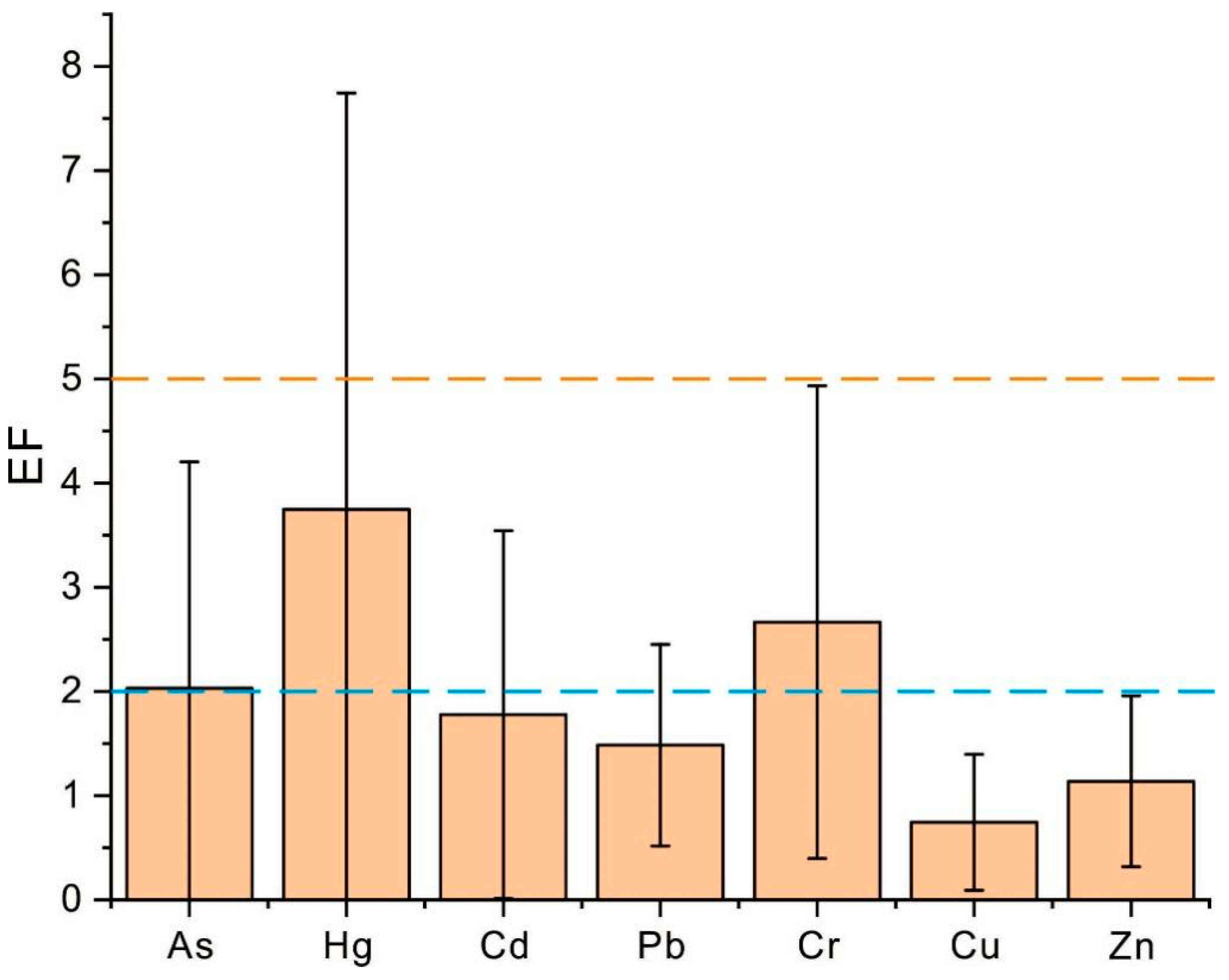
2.4. Enrichment Factor Index
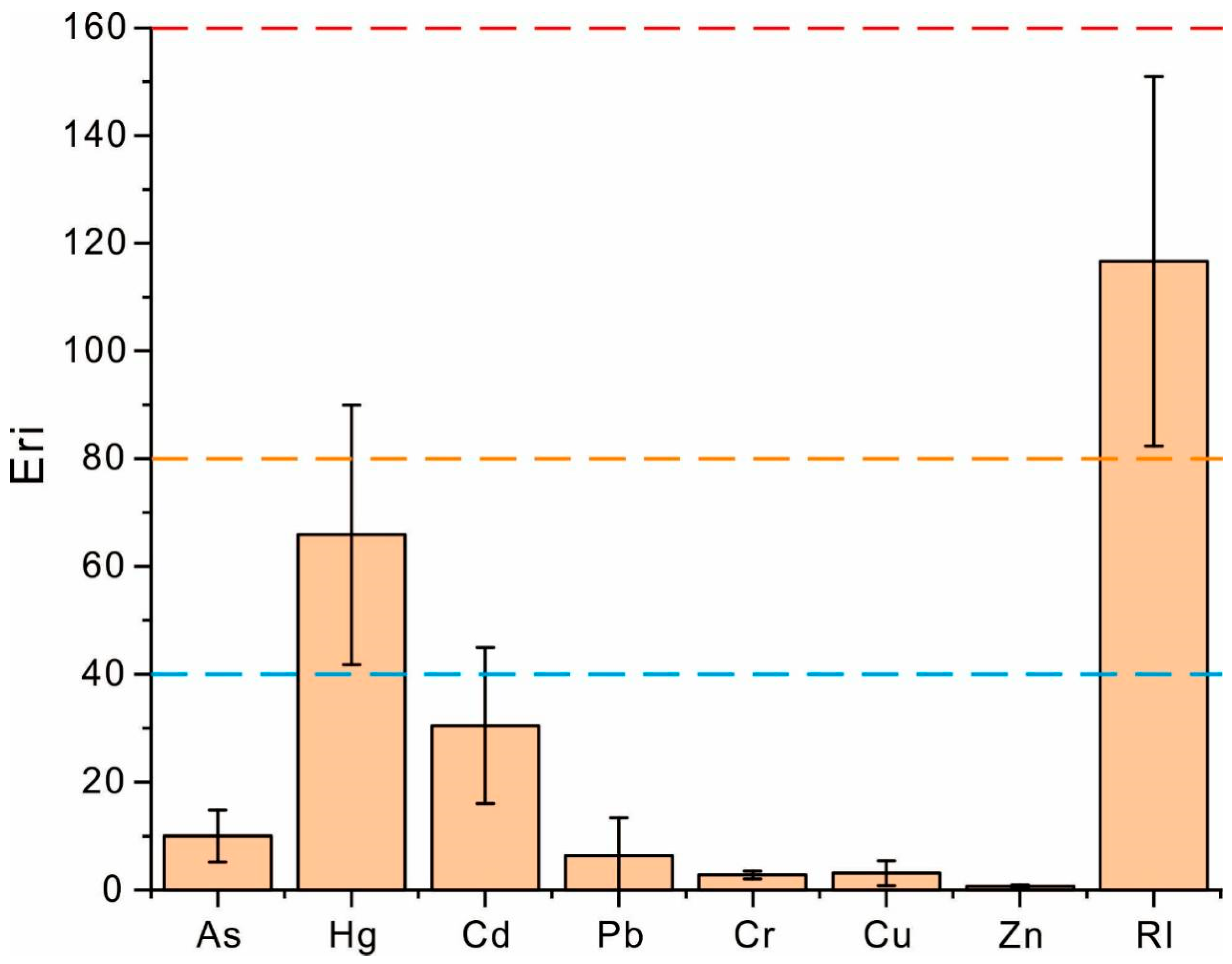
2.5. Potential Ecological Risk Index for Heavy Metals
2.6. Calculation of Heavy Metal Bioconversion
2.7. Assessment of Health Risk of HMs in Coffee Fruit
TLTR = LCR
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Content of Heavy Metals in Soil of Coffee-Growing Areas
3.2. Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination in Soils of Coffee-Growing Areas
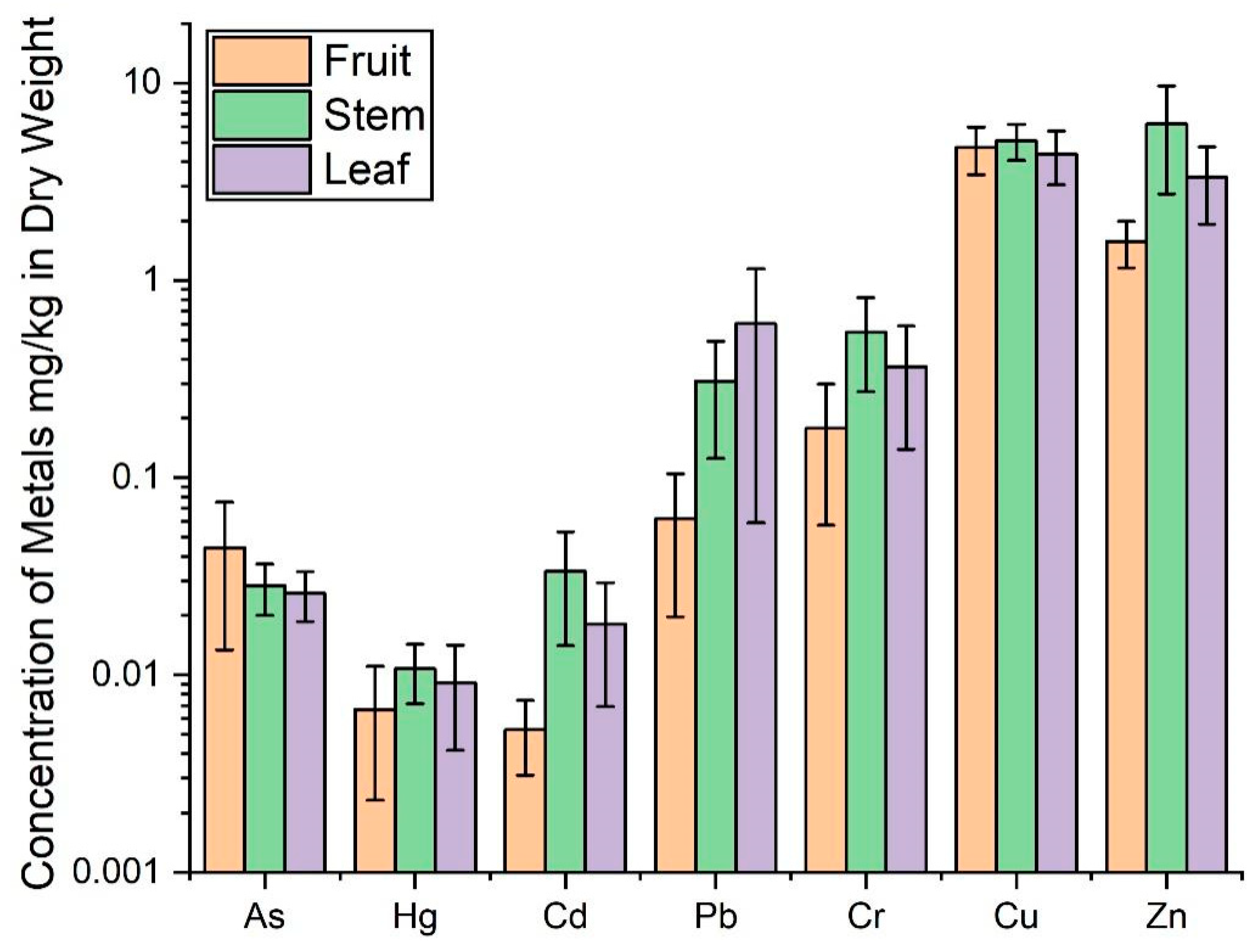
3.3. Distribution of Heavy Metals in Coffee Plants
| Fruit | As | Hg | Cd | Pb | Cr | Cu | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min–Max | 0.01–0.13 | N.D.–0.02 | N.D.–0.01 | 0.02–0.16 | 0.05–0.38 | 3.06–7.43 | 1.02–2.35 |
| Mean | 0.04 | 0.007 | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.18 | 4.71 | 1.57 |
| MRL | - | 0.05 a | 0.3 b | 0.10 c | 0.05 d | - | - |
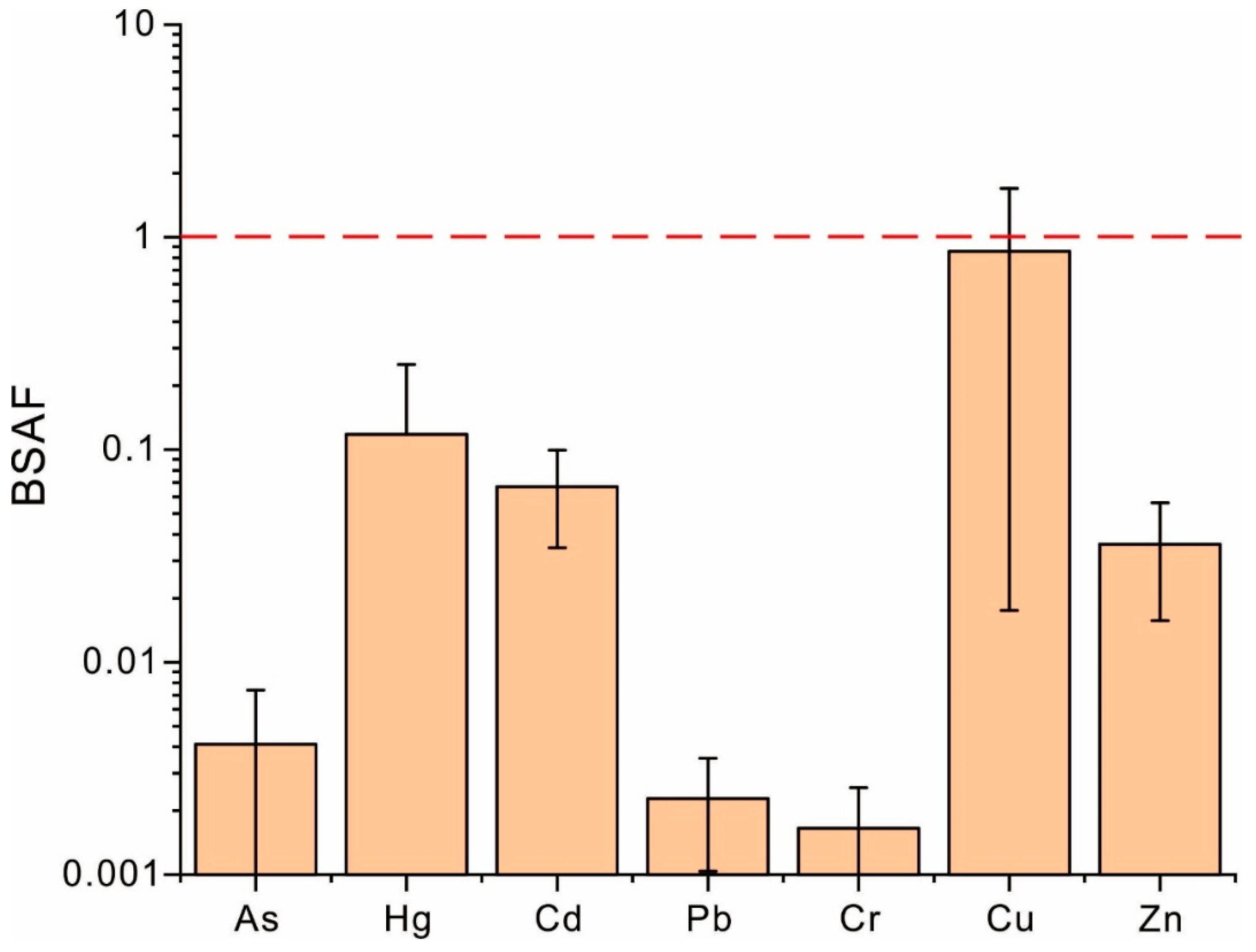
3.4. Bioconversion of Heavy Metals Within Soil–Coffee System
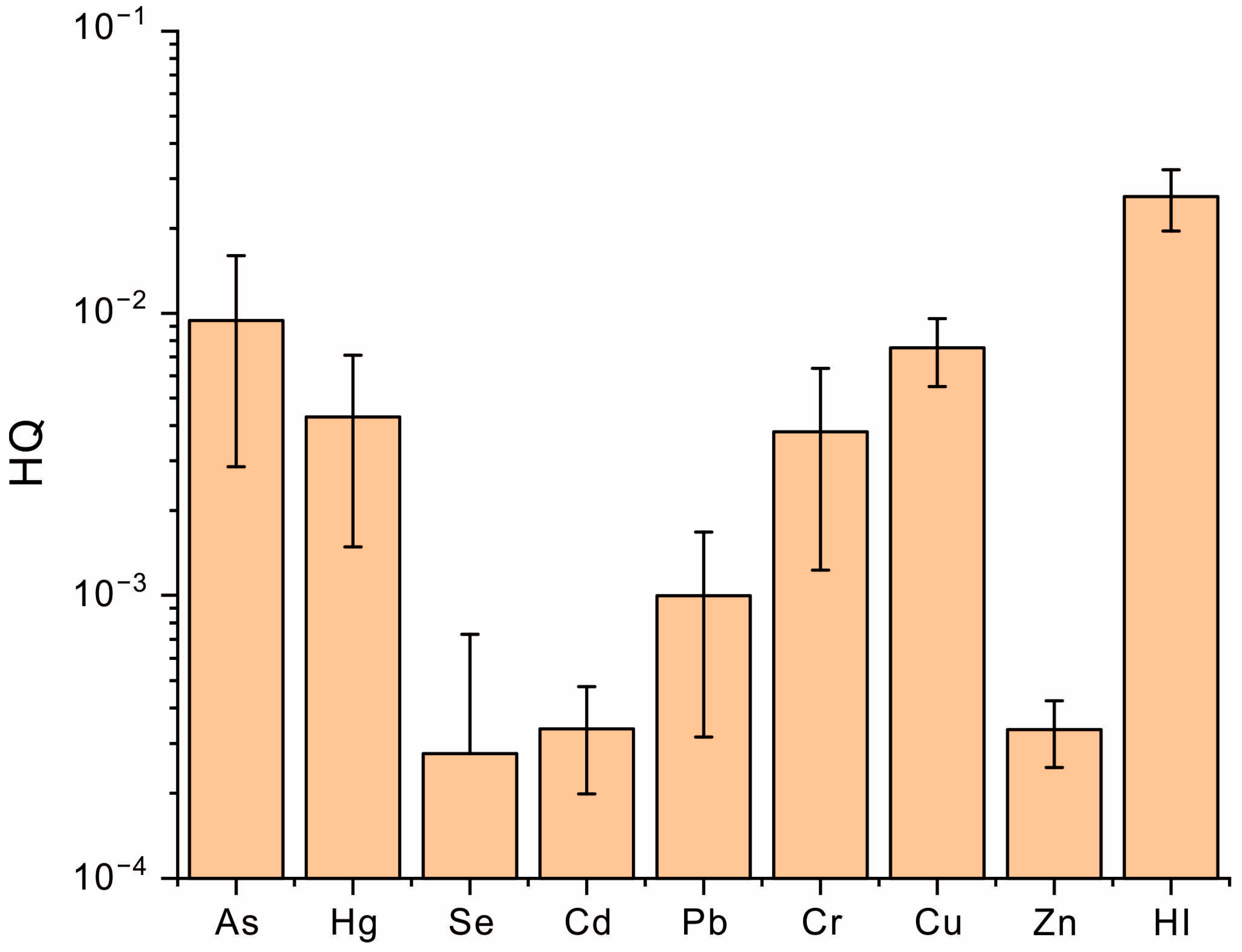
3.5. Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Coffee
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cai, L.-M.; Quan, K.; Wen, H.-H.; Luo, J.; Wang, S.; Chen, L.-G.; Song, H.; Wang, A. A comprehensive approach for quantifying source-specific ecological and health risks of potentially toxic elements in agricultural soil. Environ. Res. 2024, 263 Pt 2, 120163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, M.; Ma, Y. Mitigation of heavy metal stress in the soil through optimized interaction between plants and microbes. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, X.; Wei, X.; Hao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, X. The sources of bioavailable toxic metals in sediments regulated their aggregated form, environmental responses and health risk-a case study in Liujiang River Basin, China. Water Res. 2025, 278, 123369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Miao, X.; Liu, H.; Miao, D. The Variation of Heavy Metals Bioavailability in Sediments of Liujiang River Basin, SW China Associated to Their Speciations and Environmental Fluctuations, a Field Study in Typical Karstic River. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misic, I.D.R.; Tosic, S.B.; Pavlovic, A.N.; Pecev-Marinkovic, E.T.; Mrmosanin, J.M.; Mitic, S.S.; Stojanovic, G.S. Trace element content in commercial complementary food formulated for infants and toddlers: Health risk assessment. Food Chem. 2022, 378, 132113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gall, J.E.; Boyd, R.S.; Rajakaruna, N. Transfer of heavy metals through terrestrial food webs: A review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.H.; Zhong, Z.Y.; Hong-Mei, L.I.; Wang, H.B. Heavy-metal pollution in-situ in farming soil-crop system in multi-metal mining area—A case study of Zhadian Town, Gejiu City, Yunnan. J. Saf. Environ. 2012, 12, 138–146. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Wang, Z.; Williams, G.D.Z.; Dwyer, G.S.; Gatiboni, L.; Duckworth, O.W.; Vengosh, A. Evidence for the accumulation of toxic metal(loid)s in agricultural soils impacted from long-term application of phosphate fertilizer. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 167863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Das, B.K.; Sarkar, D.J.; Samanta, S.; Vijaykumar, M.E.; Khan, M.F.; Kayal, T.; Jana, C.; Kumar, V.; Gogoi, P.; et al. Trace metals and pesticides in water-sediment and associated pollution load indicators of Netravathi-Gurupur estuary, India: Implications on coastal pollution. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 199, 115950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Othman, Z.A.; Ali, R.; Al-Othman, A.M.; Ali, J.; Habila, M.A. Assessment of toxic metals in wheat crops grown on selected soils, irrigated by different water sources. Arab. J. Chem. 2016, 9 (Suppl. 2), S1555–S1562. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Bi, L.; Jin, L.; Peng, R. Understanding the mechanistic roles of microplastics combined with heavy metals in regulating ferroptosis: Adding new paradigms regarding the links with diseases. Environ. Res. 2024, 2024, 117732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Chen, F.; Ma, J.; Khan, Z.I.; Hussain, M.I.; Javaid, I.; Ahmad, K.; Nazar, S.; Akhtar, S.; Ejaz, A.; et al. Comparative evaluation of groundwater, wastewater and canal water for irrigation on toxic metal accumulation in soil and vegetable: Pollution load and health risk assessment. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 264, 107515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Miao, D.; Hao, Y.; Xie, Z.; Zou, S. Potential health risks associated to heavy metal contamination of soils in the Yellow River Delta, China. J. Coast. Conserv. 2019, 23, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, M.W.D.; Pereira, W.V.D.S.; Souza, E.S.D.; Teixeira, R.A.; Palheta, D.D.C.; Faial, K.D.C.F.; Costa, H.F.; Fernandes, A.R. Bioaccumulation and human health risks of potentially toxic elements in fish species from the southeastern Carajás Mineral Province, Brazil. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Liang, J.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, H. The Influence of the Reduction in Clay Sediments in the Level of Metals Bioavailability—An Investigation in Liujiang River Basin after Wet Season. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Chen, L.; Hao, Y.; An, J.; Xu, T.; Bao, W.; Chen, X.; Liao, X.; Xie, Y. The variations of heavy metals sources varied their aggregated concentration and health risk in sediments of karst rivers—A case study in Liujiang River Basin, Southwest China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 201, 116171. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Y.; Wei, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; Cai, J.; Song, Z.; Liao, X.; Chen, X.; Miao, X. Bioaccumulation, contamination and health risks of trace elements in wild fish in Chongqing City, China: A consumer guidance regarding fish size. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Miao, X.; Song, M.; Zhang, H. The Bioaccumulation and Health Risk Assessment of Metals among Two Most Consumed Species of Angling Fish (Cyprinus carpio and Pseudohemiculter dispar) in Liuzhou (China): Winter Should Be Treated as a Suitable Season for Fish Angling. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Wei, X.; Zhao, X.; Hao, Y.; Bao, W. The Bioaccumulation, Fractionation and Health Risk of Rare Earth Elements in Wild Fish of Guangzhou City, China. Animals 2024, 14, 3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wu, P.; Yin, A.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Gao, C. Distribution and source analysis of heavy metals in soils and sediments of Yueqing Bay basin, East China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 115, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Hu, Y.; Su, B.; Fang, G.; Wang, L.; Xiang, B. A review of heavy metal pollution levels and health risk assessment of urban soils in Chinese cities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 25, 1055–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Chen, M.; Ding, L.; Zhao, Y.; Man, Y.; Feng, L.; Li, P.; Zhang, L.; Feng, X. Fish, rice, and human hair mercury concentrations and health risks in typical Hg-contaminated areas and fish-rich areas, China. Environ. Int. 2021, 154, 106561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Yi, G.; Hao, Y.; Li, L.; Shen, L.; Zhang, Q. The effect of combined application of biochar and phosphate fertilizers on phosphorus transformation in saline-alkali soil and its microbiological mechanism. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khelfi, A.; Azzouz, M. Evaluation of EDCs (phthalates, bisphenols, parabens, and benzophenones) in coffee: Cross-sectional study in Algiers. Food Chem. 2025, 495 Pt 2, 146465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Lu, K.; He, Y.; Mao, X.; Liu, L.; Li, H.; Hu, Y. Integrated multi-omics analysis to reveal roles of fungal and bacterial microbiota in regulating the taste compounds of sun-dried processing coffee in Baoshan of Yunnan province, China. J. Future Foods 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Huang, S.; Dong, S.; Zheng, W.; Tong, S. Intake of Coffee and Blood Pressure: A Mendelian Randomized Study. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2025, 104273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Lin, J.; Hu, S.; Wang, G.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, D.; Yi, L.; Li, S. Exploring the impacts and mechanisms of water on the taste extractions and perceptions of coffee brews: A case study in filter brewing. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 146, 107987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, S.J.; Pereira, G.d.B.; Martins, P.M.M.; Batista, N.N.; Dias, D.R.; Schwan, R.F. The origin of culture starters influences the chemical and sensory quality of coffee. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2025, 443, 111433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EL-Araby, E.H.; Azazi, A.; Hassani, R.; Shabaan, D.H.; El-Barbary, A.; El-Bialy, E.; Dhawale, S.P. Assessment of naturally occurring radionuclides and radiation safety in coffee samples from Saudi markets. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 147, 107996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, E.; Caldeirão, L.; Oliveira, W.d.S.; Garcia, A.d.O.; Filho, J.T.; Hantao, L.W.; Godoy, H.T. Analysis of PAHs in Brazilian coffee by combining QuEChERS and LD-DLLME. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 148 Pt 2, 108327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Chen, X.; Sun, J.; Chen, H.; Sun, B. Unveiling key aroma compounds formation during the roasting process of Yunnan Arabica coffee using molecular sensory science approaches. Food Chem. 2025, 494, 145853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Wang, J.; Mu, L.; Peng, S.; Li, A.; Zhang, N.; Bao, L. Source-risk-driver analysis of heavy metal pollution in karst soils: An integrated assessment in eastern Yunnan, China. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 176, 113699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Li, W.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Ji, J. Enrichment and source identification of Cd and other heavy metals in soils with high geochemical background in the karst region, Southwestern China. Chemosphere 2020, 245, 125620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Lin, T.; Tian, H.; Du, L.; Li, K.; Cao, Q.; Liu, H.; Pang, G.; Chang, Q. Kinetics, pathways, mechanism and toxicity evaluation of chiral pesticide Paichongding during the fermentation of Puer tea. Food Chem. X 2025, 26, 102300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, X.; Hao, Y.; Liu, H.; Xie, Z.; Miao, D.; He, X. Effects of heavy metals speciations in sediments on their bioaccumulation in wild fish in rivers in Liuzhou—A typical karst catchment in southwest China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 214, 112099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, X.; Song, M.; Xu, G.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, H. The Accumulation and Transformation of Heavy Metals in Sediments of Liujiang River Basin in Southern China and Their Threatening on Water Security. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahjahan, M.; Taslima, K.; Rahman, M.S.; Al-Emran, M.; Alam, S.I.; Faggio, C. Effects of heavy metals on fish physiology—A review. Chemosphere 2022, 300, 134519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xie, E.; Luo, Y.; Xiong, X.; He, X. Correlation Analysis between the Basic Physical and Chemical Properties of Pu’er Coffee Soil and Sensory Quality of Coffee. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2021, 1, 131–134. [Google Scholar]
- Feifei, G.; Jiahua, L.; Ping, Z.; Wanfang, S.; Kunming, M.; Ping, Z. Analysis on Soil Nutrients of Tea Gardens in Pu′er City of Yunnan Province. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2013, 2, 398–402. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, A.; Meng, X.; Xu, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Huang, W.; Xu, F. Distribution, sources, and contamination evaluation of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Qizhou Island sea area in Hainan, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 208, 116933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Hao, Y.; He, X.; Luo, S. The human impacts level and migration of heavy metals in original inshore sediments of Dongying, China. J. Coast. Conserv. 2020, 24, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Luo, T.-C.; Zhang, B.-R.; Zhang, H.-F.; Han, Y.-W.; Zhao, Z.-D.; Hu, Y.-K. Chemical composition of the continental crust as revealed by studies in East China. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1998, 62, 1959–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control-a sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Miao, X.; Hao, Y.; Xie, Z.; Zou, S.; Zhou, C. Health Risk Assessment of Metals (Cu, Pb, Zn, Cr, Cd, As, Hg, Se) in AnglingFish with Different Lengths Collected from Liuzhou, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherlad, R. Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environ. Geol. 2000, 39, 611–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zou, S.; Ye, S.; Xie, Z. Spatial distribution of heavy metals and their potential sources in the soil of Yellow River Delta: A traditional oil field in China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 42, 7–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yin, P.; Chen, B.; Gao, F.; Song, H.; Li, M. Distribution and contamination assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Luanhe River Estuary, northwest of the Bohai Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 109, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, J.; Yan, Y.; Dai, Y.Y.; Gan, Z. Distribution and risk assessment of metals in water, sediments, and wild fish from Jinjiang River in Chengdu, China. Chemosphere 2017, 196, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CNEMC. The Background Values of Soil Elements in China; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Jolaosho, T.L.; Elegbede, I.O.; Akintola, S.L.; Jimoh, A.A.; Ndimele, P.E.; Mustapha, A.A.; Adukonu, J.D. Bioaccumulation dynamics, noncarcinogenic and carcinogenic risks of heavy metals in commercially valuable shellfish and finfish species from the world largest floating slum, Makoko, Nigeria. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 207, 116807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekperusi, A.O.; Asiwa, D.O. Trophodynamics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in seafood from a tropical estuary in the gulf of Guinea. Environ. Res. 2024, 252 Pt 2, 118977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USEPA. Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund (RAGS). Vol. III-Part A, Process for Conducting Probabilistic Risk Assessment; EPA 540-R-02-002; Office of Emergency and Remedial Response, US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2001.
- Hamrah, R.P.; Rahimi, A.; Yarahmadi, M.; Talebi-Ghane, E.; Mehri, F. Health risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in coffee-based products: A meta-analysis study and systematic review. J. Agric. Food Res. 2024, 18, 101508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamal, A.; Abdel-Megeed, M.; Mahmoud, H.; Soliman, M.; Al-Anany, M.; Eissa, F. Pesticide residues in Green, roasted, and capsule coffee from the Egyptian market: Occurrence, processing effects, and health risk assessment. Food Chem. 2025, 486, 144671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Luo, L.; Chen, Y.; He, Q.; Zhan, L. The characteristics and potential risk of heavy metals pollution in farmland soil of an agricultural land in the Three Gorges Reservoir area. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2018, 12, 2711–2717. [Google Scholar]
- Gitet, H.; Hilawie, M.; Muuz, M.; Weldegebriel, Y.; Gebremichael, D.; Gebremedhin, D. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in crop plants grown near Almeda Textile Factory, Adwa, Ethiopia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.K. Heavy metals in water, sediments and wetland plants in an aquatic ecosystem of tropical industrial region, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 158, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Tian, M.; Ding, W.; Cisse, E.-H.M.; Miao, L.; Ye, B.; Li, M.; Long, Y.; Yang, F. Dissecting possible correlations between leaf functional traits and heavy metal accumulation in two contrasting mangrove species across tidal gradients. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2025, 238, 106234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Htwe, H.Z.; Zhu, Y.; Christakos, G.; Wu, J. An assessment of metal concentrations in leaves, roots, and associated sediments of mangrove plant (Avicennia marina) in the Myeik area, Myanmar. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 216, 117973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, T.; Zhou, D.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, C. The release and transformation mechanisms of heavy metals from the vanadium-titanium magnetite tailings: Role of organic acids and light exposure. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 118726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hu, T.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Mei, Y.; Zhou, X. A key heavy metal-binding protein orchestrates plant resistance against a geminivirus. Fundam. Res. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-F.; Ju, Y.-R.; Chen, C.-W.; Dong, C.-D. Changes in the total content and speciation patterns of metals in the dredged sediments after ocean dumping: Taiwan continental slope. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2019, 181, 104893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, N.; Leng, H.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Wang, Q.; Xue, Q.; Chen, T.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, C.; et al. Mechanisms of heavy metal toxicity mitigation by polysaccharides from Camellia oleifera leaves. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 236, 121904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Yang, S.; Han, H.; Bai, Y.; Luo, W.; Wang, Q. Is biomagnetic leaf monitoring still an effective method for monitoring the heavy metal pollution of atmospheric particulate matter in clean cities? Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gültekin, Y.; Bayraktar, M.K.; Sevik, H.; Cetin, M.; Bayraktar, T. Optimal vegetable selection in urban and rural areas using artificial bee colony algorithm: Heavy metal assessment and health risk. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 139, 107169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, A.K.M.M.; Hamed, M.; Hasan, J.; Martyniuk, C.J.; Niyogi, S.; Chivers, D.P. A review of the neurobehavioural, physiological, and reproductive toxicity of microplastics in fishes. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 282, 116712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, D.M.; Martín-Liñares, V.; Piñeiro, V.; Barral, M.T. Arsenic Transfer from As-Rich Sediments to River Water in the Presence of Biofilms. J. Chem. 2016, 2016, 6092047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Zhou, A.; Li, X.; Zhou, J.; Pan, G.; He, N. Response of antimony and arsenic in karst aquifers and groundwater geochemistry to the influence of mine activities at the world’s largest antimony mine, central China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603 Pt C, 127131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albarico, F.P.J.B.; Lim, Y.C.; Chen, C.-W.; Chen, C.-F.; Wang, M.-H.; Dong, C.-D. Linking seasonal plankton succession and cellular trace metal dynamics in marine assemblages. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 167805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Han, C.; Liu, Z.; Wei, Y.; Ma, S.; Bao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, H. Nutrient limitations on primary productivity and phosphorus removal by biological carbon pumps in dammed karst rivers: Implications for eutrophication control. J. Hydrol. 2022, 607, 127480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ding, S.; Ma, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Q.; Zhong, Z.; Chen, M.; Fan, X. Sediment arsenic remediation by submerged macrophytes via root-released O2 and microbe-mediated arsenic biotransformation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 449, 131006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 2762-2022; National Food Safety Standard—Maximum Levels of Pollutants in Foods. National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China & State Administration for Market Regulation: Beijing, China, 2022.
- EC No. 1881/2006; Commission Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 of 19 December 2006 Setting Maximum Levels for Certain Contaminants in Foodstuffs. Official Journal of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2006.
- CODEX STAN 193-1995; General Standard for Contaminants and Toxins in Food and Feed. Codex Alimentarius Commission, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) & World Health Organization (WHO): Rome, Italy, 1995; (Amended 2019).
- Food Sanitation Act (Act No. 233 of 1947); Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare: Tokyo, Japan, 1947; (Latest Revision).
- Yao, X.; Xiao, R.; Ma, Z.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yu, F. Distribution and contamination assessment of heavy metals in soils from tidal flat, oil exploitation zone and restored wetland in the Yellow River Estuary. Wetlands 2016, 36, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Guo, J.; Yu, K. Distribution, speciation, environmental risk, and source identification of heavy metals in surface sediments from the karst aquatic environment of the Lijiang River, Southwest China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 9122–9133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Xie, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhou, X.; Miao, X. Seasonal variation characteristics and environmental risk assessmentof heavy metals in sediments of the Liujiang River Basin. China Geol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Miao, X.; Guo, Q. Decline in Soil Nitrogen Retention Capacity After Converting Subtropical Forest Land to Tea Plantations in China. Soil Fertil. Sci. China 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Class | EF | Level of Enrichment |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.5 < EF < 2 | No Enrichment |
| 2 | 2 ≤ EF < 5 | Moderate Enrichment |
| 3 | 5 ≤ EF < 20 | Significant Enrichment |
| 4 | 20 ≤ EF < 40 | Severe Enrichment |
| 5 | EF < 40 | Extremely Severe Enrichment |
| Item | Cr | Cu | Zn | Pb | Cd | As | Hg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mg/kg) | 69.6 | 37.6 | 88.8 | 36.5 | 0.08 | 14.9 | 0.05 |
| 2 | 5 | 1 | 5 | 30 | 10 | 40 |
| Grade | Eri | Ecological Risk Level |
| 1 | <40 | Low |
| 2 | 40–80 | Moderate |
| 3 | 80–160 | Considerable |
| 4 | 160–320 | High |
| 5 | >320 | Very high |
| Grade | RI | Ecological risk level |
| 1 | <150 | Low |
| 2 | 150–300 | Moderate |
| 3 | 300–600 | Considerable |
| 4 | >600 | Very high |
| Parameter | Unit | Definition | Value | Reference | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | µg kg−1 | Metal content | - | - | ||||
| BW | kg | Average body weight | 70 | [16] | ||||
| ED | year | Exposure duration | 30 | [52] | ||||
| EF | d yr−1 | Exposure frequency | 350 | [52] | ||||
| IngR | g d−1 | Ingestion rate | 5 | |||||
| ATnc | d | Averaging times for non-carcinogenic effects | 9125 | [17] | ||||
| ATca | d | Averaging times for carcinogenic effects | 26,280 | [17] | ||||
| CF | kg mg−1 | Conversion factor | 10−6 | [18] | ||||
| Ingestion | Metal | Pb | Cd | Cr | Hg | As | Zn | Cu |
| RfD | 3.50 × 10−3 | 1.00 × 10−3 | 3.00 × 10−3 | 3.00 × 10−4 | 3.00 × 10−4 | 3.00 × 10−1 | 4.00 × 10−2 | |
| SF | 8.50 × 10−3 | 6.10 × 100 | 5.01 × 10−1 | - | 1.50 × 100 | - | - | |
| As | Hg | Cd | Pb | Cr | Cu | Zn | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pu’er City | Min–Max | 3.41–30.65 | 0.02–0.17 | 0.03–0.17 | 9.89–193 | 65.1–157 | 1.32–60.2 | 14.8–118 |
| Mean | 14.96 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 46.97 | 98.47 | 23.68 | 62.50 | |
| Soil Baseline for Yunnan Province [7] | Median | 13 | 0.0875 | 0.07 | 22.35 | 88.7 | 24.75 | 63.2 |
| Risk Screening Value for Agricultural Land [55] | 14.9 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 36.5 | 69.6 | 37.6 | 88.8 |
| BSAF | As | Hg | Cd | Pb | Cr | Cu | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content in soil | −0.467 | −0.875 ** | −0.381 | −0.551 * | 0.755 ** | −0.686 ** | −0.891 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, X.; Yang, T.; Hao, Y.; Li, J.; Du, B.; Yang, S.; Miao, X. Heavy Metals in the Soil–Coffee System of Pu’er, China, a Major Coffee Producing Region in China: Distribution and Health Risks. Toxics 2025, 13, 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110944
Zhou X, Yang T, Hao Y, Li J, Du B, Yang S, Miao X. Heavy Metals in the Soil–Coffee System of Pu’er, China, a Major Coffee Producing Region in China: Distribution and Health Risks. Toxics. 2025; 13(11):944. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110944
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Xiaohua, Tianyao Yang, Yupei Hao, Jing Li, Bai Du, Sheping Yang, and Xiongyi Miao. 2025. "Heavy Metals in the Soil–Coffee System of Pu’er, China, a Major Coffee Producing Region in China: Distribution and Health Risks" Toxics 13, no. 11: 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110944
APA StyleZhou, X., Yang, T., Hao, Y., Li, J., Du, B., Yang, S., & Miao, X. (2025). Heavy Metals in the Soil–Coffee System of Pu’er, China, a Major Coffee Producing Region in China: Distribution and Health Risks. Toxics, 13(11), 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110944





