Cellular Impact of Micro(nano)plastics on Human Health: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
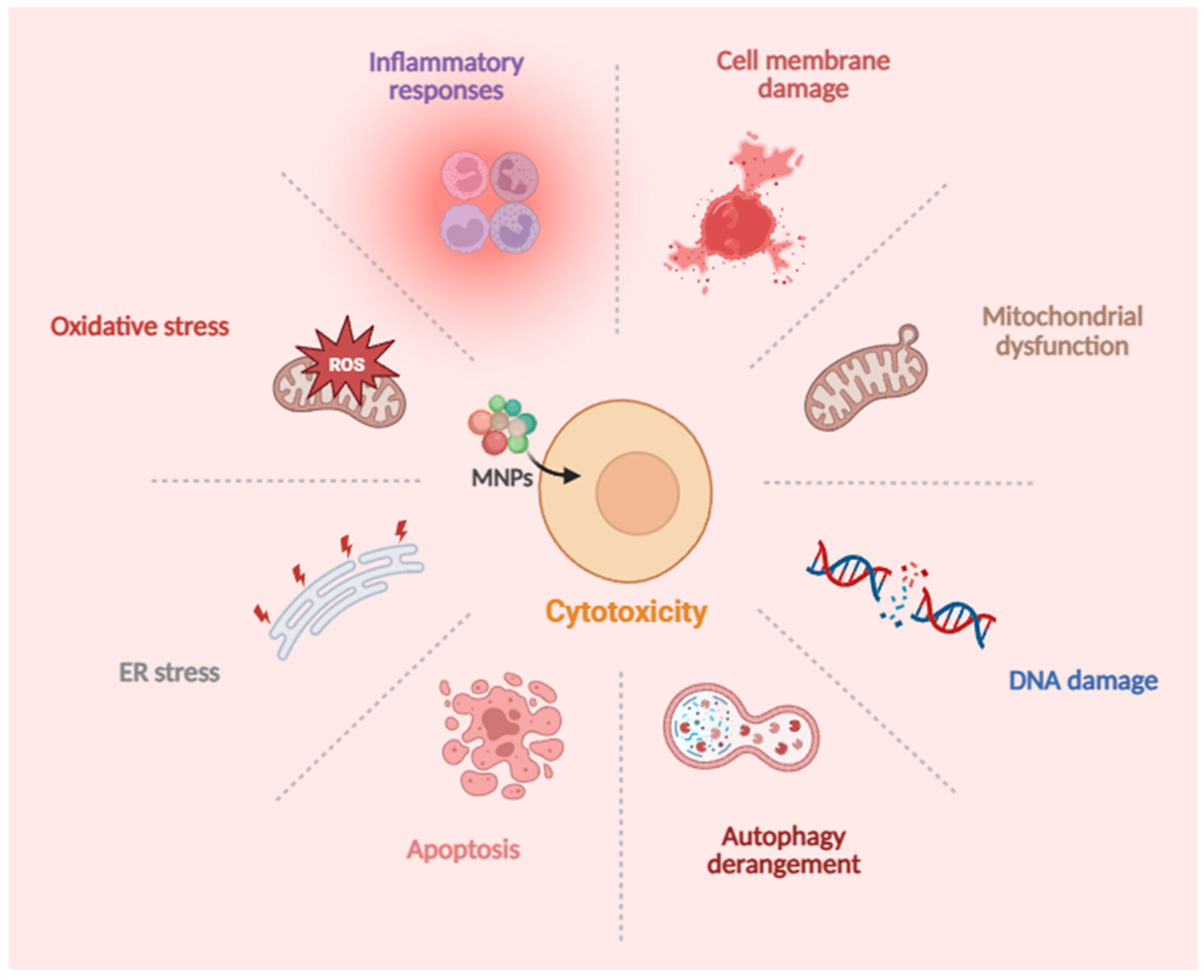
2. Toxic Effects and Molecular Mechanisms of MNPs on Human Cells
2.1. Respiratory System
2.2. Digestive System
2.3. Cardiovascular System
2.4. Reproductive System
2.5. Urinary System
2.6. Nervous System
2.7. Immune System
3. Limitations of Human Cell Models
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.; Shi, H.; Chen, L.; Teng, X.; Xue, C.; Li, Z. An Overview of Microplastics in Oysters: Analysis, Hazards, and Depuration. Food Chem. 2023, 422, 136153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Hamidian, A.H.; Tubić, A.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, J.K.H.; Wu, C.; Lam, P.K.S. Understanding Plastic Degradation and Microplastic Formation in the Environment: A Review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 274, 116554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.C.; Olsen, Y.; Mitchell, R.P.; Davis, A.; Rowland, S.J.; John, A.W.G.; McGonigle, D.; Russell, A.E. Lost at Sea: Where Is All the Plastic? Science 2004, 304, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, P.D.; Kim, S.; Sarkar, B.; Oleszczuk, P.; Sang, M.K.; Haque, M.N.; Ahn, J.H.; Bank, M.S.; Ok, Y.S. Effects of Microplastics on the Terrestrial Environment: A Critical Review. Environ. Res. 2022, 209, 112734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskar, N.; Kumar, U. Plastics and Microplastics: A Threat to Environment. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2019, 14, 100352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigault, J.; Halle, A.T.; Baudrimont, M.; Pascal, P.-Y.; Gauffre, F.; Phi, T.-L.; El Hadri, H.; Grassl, B.; Reynaud, S. Current Opinion: What Is a Nanoplastic? Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 1030–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrano, D.M.; Wick, P.; Nowack, B. Placing Nanoplastics in the Context of Global Plastic Pollution. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Che, R.; Zong, X.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, F. A Comprehensive Review on the Source, Ingestion Route, Attachment and Toxicity of Microplastics/Nanoplastics in Human Systems. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 352, 120039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Qu, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, L.; Xiong, F.; Wang, D.; Liu, M.; Sun, R. Research Progress on the Cellular Toxicity Caused by Microplastics and Nanoplastics. J Appl. Toxicol. 2023, 43, 1576–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Shelver, W.L. Micro- and Nanoplastic Induced Cellular Toxicity in Mammals: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Halimu, G.; Zhang, Q.; Song, Y.; Fu, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H. Internalization and Toxicity: A Preliminary Study of Effects of Nanoplastic Particles on Human Lung Epithelial Cell. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Wang, X.; Huang, R.; Tang, C.; Hu, C.; Ning, P.; Wang, F. Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity of Polystyrene Micro- and Nanoplastics with Different Size and Surface Modification in A549 Cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 4509–4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halimu, G.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Gu, W.; Zhang, B.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, C.; et al. Toxic Effects of Nanoplastics with Different Sizes and Surface Charges on Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in A549 Cells and the Potential Toxicological Mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 430, 128485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Tang, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, R. Ultraviolet-Induced Photodegradation Elevated the Toxicity of Polystyrene Nanoplastics on Human Lung Epithelial A549 Cells. Environ. Sci. Nano 2021, 8, 2660–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Duan, Z.; Wang, L. Pulmonary Toxicology Assessment of Polyethylene Terephthalate Nanoplastic Particles in Vitro. Environ. Int. 2022, 162, 107177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.-D.; Chen, C.-W.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chen, H.-H.; Lee, J.-S.; Lin, C.-H. Polystyrene Microplastic Particles: In Vitro Pulmonary Toxicity Assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, T.; Yin, L.; Pu, Y.; Liang, G. In Vitro Evaluation of Nanoplastics Using Human Lung Epithelial Cells, Microarray Analysis and Co-Culture Model. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 226, 112837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, M.S.; Kim, J.W.; Han, Y.B.; Jeong, M.H.; Kim, H.R.; Sik Kim, H.; Park, Y.J.; Chung, K.H. Polystyrene Microplastic Particles Induce Autophagic Cell Death in BEAS-2B Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells. Environ. Toxicol. 2023, 38, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annangi, B.; Villacorta, A.; López-Mesas, M.; Fuentes-Cebrian, V.; Marcos, R.; Hernández, A. Hazard Assessment of Polystyrene Nanoplastics in Primary Human Nasal Epithelial Cells, Focusing on the Autophagic Effects. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annangi, B.; Villacorta, A.; Vela, L.; Tavakolpournegari, A.; Marcos, R.; Hernández, A. Effects of True-to-Life PET Nanoplastics Using Primary Human Nasal Epithelial Cells. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 100, 104140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, S.; Geng, H.; Tan, X.-D. Cell Death of Intestinal Epithelial Cells in Intestinal Diseases. Sheng Li Xue Bao 2020, 72, 308. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Wu, M.; Tian, D.; Qiu, L.; Li, T. Effects of Polystyrene Microbeads on Cytotoxicity and Transcriptomic Profiles in Human Caco-2 Cells. Environ. Toxicol. 2020, 35, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Ma, Y.; Han, X.; Chen, Y. Systematic Toxicity Evaluation of Polystyrene Nanoplastics on Mice and Molecular Mechanism Investigation about Their Internalization into Caco-2 Cells. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 126092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés, C.; Domenech, J.; Salazar, M.; Pastor, S.; Marcos, R.; Hernández, A. Nanoplastics as a Potential Environmental Health Factor: Effects of Polystyrene Nanoparticles on Human Intestinal Epithelial Caco-2 Cells. Environ. Sci. Nano 2020, 7, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Koh, J.Y.C.; Lim, H.K.; Shi, P.; Tay, C.Y. Elucidating the Size-Dependency of In Vitro Digested Polystyrene Microplastics on Human Intestinal Cells Health and Function. Macro Chem. Phys. 2022, 223, 2100454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenech, J.; De Britto, M.; Velázquez, A.; Pastor, S.; Hernández, A.; Marcos, R.; Cortés, C. Long-Term Effects of Polystyrene Nanoplastics in Human Intestinal Caco-2 Cells. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Vercauteren, M.; Grootaert, C.; Rajkovic, A.; Boon, N.; Janssen, C.; Asselman, J. Cellular and Bioenergetic Effects of Polystyrene Microplastic in Function of Cell Type, Differentiation Status and Post-Exposure Time. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 337, 122550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Billey, L.O.; McGarvey, A.M.; Shelver, W.L. Effects of Polystyrene Micro/Nanoplastics on Liver Cells Based on Particle Size, Surface Functionalization, Concentration and Exposure Period. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 836, 155621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Olga, V.; Xue, Y.; Lv, S.; Diao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, Q.; Zhou, H. The Potential Effects of Microplastic Pollution on Human Digestive Tract Cells. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Wu, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L. Size-Dependent Effects of Polystyrene Microplastics on Cytotoxicity and Efflux Pump Inhibition in Human Caco-2 Cells. Chemosphere 2019, 221, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inkielewicz-Stepniak, I.; Tajber, L.; Behan, G.; Zhang, H.; Radomski, M.W.; Medina, C.; Santos-Martinez, M.J. The Role of Mucin in the Toxicological Impact of Polystyrene Nanoparticles. Materials 2018, 11, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Xia, P.-F.; Yuan, X.-Z.; Wang, S.-G. Chlorine Disinfection Elevates the Toxicity of Polystyrene Microplastics to Human Cells by Inducing Mitochondria-Dependent Apoptosis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 127842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Lang, M.; Huang, D.; Yang, C.; Ouyang, Z.; Guo, X. Photo-Transformation of Microplastics and Its Toxicity to Caco-2 Cells. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oddone, E. Occupational Exposures and Colorectal Cancers: A Quantitative Overview of Epidemiological Evidence. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 12431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brynzak-Schreiber, E.; Schögl, E.; Bapp, C.; Cseh, K.; Kopatz, V.; Jakupec, M.A.; Weber, A.; Lange, T.; Toca-Herrera, J.L.; Del Favero, G.; et al. Microplastics Role in Cell Migration and Distribution during Cancer Cell Division. Chemosphere 2024, 353, 141463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Liu, M.; Xiong, F.; Xu, K.; Huang, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, D.; Pu, Y. Polystyrene Micro- and Nanoplastics Induce Gastric Toxicity through ROS Mediated Oxidative Stress and P62/Keap1/Nrf2 Pathway. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhang, R.; Li, B.; Du, Y.; Li, J.; Tong, X.; Wu, Y.; Ji, X.; Zhang, Y. Tissue Distribution of Polystyrene Nanoplastics in Mice and Their Entry, Transport, and Cytotoxicity to GES-1 Cells. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 280, 116974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, M.; Iachetta, G.; Tussellino, M.; Carotenuto, R.; Prisco, M.; De Falco, M.; Laforgia, V.; Valiante, S. Polystyrene Nanoparticles Internalization in Human Gastric Adenocarcinoma Cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2016, 31, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.-C.; Zhang, Q.-B.; Qiao, L. Pathogenesis of Liver Cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 7312–7324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Yu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Yin, Q.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yue, R.; Xiong, X. Polystyrene Microplastics-Triggered Mitophagy and Oxidative Burst via Activation of PERK Pathway. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 781, 146753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ma, Y.; Ye, S.; Tang, S.; Liang, N.; Liang, Y.; Xiao, F. Polystyrene Microplastics Trigger Hepatocyte Apoptosis and Abnormal Glycolytic Flux via ROS-Driven Calcium Overload. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 126025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, M.; Ma, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, S.; Wang, K.; Tian, H.; Cui, J. Enhanced Hepatic Cytotoxicity of Chemically Transformed Polystyrene Microplastics by Simulated Gastric Fluid. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 410, 124536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, R.; Yang, K.; Cheng, X.; Guo, C.; Xing, X.; Sun, H.; Liu, D.; Liu, X.; Wang, D. Accumulation of Polystyrene Microplastics Induces Liver Fibrosis by Activating cGAS/STING Pathway. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 300, 118986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barshtein, G.; Arbell, D.; Yedgar, S. Hemolytic Effect of Polymeric Nanoparticles: Role of Albumin. IEEE Trans. Nanobiosci. 2011, 10, 259–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuinnes, C.; Duffin, R.; Brown, S.; Mills, N.L.; Megson, I.L.; MacNee, W.; Johnston, S.; Lu, S.L.; Tran, L.; Li, R.; et al. Surface Derivatization State of Polystyrene Latex Nanoparticles Determines Both Their Potency and Their Mechanism of Causing Human Platelet Aggregation In Vitro. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 119, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Choi, D.; Han, S.; Jung, S.Y.; Choi, J.; Hong, J. Potential Toxicity of Polystyrene Microplastic Particles. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.-H.; Choi, S.; Kim, D.; Park, H.J.; Bian, Y.; Choi, S.H.; Chung, H.Y.; Bae, O.-N. Amine-Modified Nanoplastics Promote the Procoagulant Activation of Isolated Human Red Blood Cells and Thrombus Formation in Rats. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2022, 19, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lett, Z.; Hall, A.; Skidmore, S.; Alves, N.J. Environmental Microplastic and Nanoplastic: Exposure Routes and Effects on Coagulation and the Cardiovascular System. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 291, 118190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.-Y.; Li, H.; Ren, H.; Zhang, X.; Huang, F.; Zhang, D.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, X. Size-Dependent Effects of Polystyrene Nanoplastics on Autophagy Response in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Cao, M.; Tian, M.; Huang, Q. Internalization and Cytotoxicity of Polystyrene Microplastics in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2023, 43, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-S.; Amarakoon, D.; Wei, C.; Choi, K.Y.; Smolensky, D.; Lee, S.-H. Adverse Effect of Polystyrene Microplastics (PS-MPs) on Tube Formation and Viability of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 154, 112356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Li, Y.; Lee, M.; Andrikopoulos, N.; Lin, S.; Chen, C.; Leong, D.T.; Ding, F.; Song, Y.; Ke, P.C. Anionic Nanoplastic Exposure Induces Endothelial Leakiness. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Du, Y.; Li, P.; Guan, C.; Zhou, M.; Wu, L.; Liu, Z.; Huang, Z. Microplastics Accelerates the Premature Aging of Blood Vessels Though ROS-Mediated CDK5 Signaling Pathway. Preprint 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contino, M.; Ferruggia, G.; Indelicato, S.; Pecoraro, R.; Scalisi, E.M.; Bracchitta, G.; Dragotto, J.; Salvaggio, A.; Brundo, M.V. In Vitro Nano-Polystyrene Toxicity: Metabolic Dysfunctions and Cytoprotective Responses of Human Spermatozoa. Biology 2023, 12, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, L.; Zhou, C.; Xu, W.; Huang, Y.; Wang, W.; Ma, Z.; Huang, J.; Li, J.; Hu, L.; Xue, Y.; et al. The Ovarian-Related Effects of Polystyrene Nanoplastics on Human Ovarian Granulosa Cells and Female Mice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 257, 114941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zou, L.; Bao, M.; Feng, Q.; Xia, W.; Zhu, C. Toxicity of Polystyrene Nanoparticles for Mouse Ovary and Cultured Human Granulosa Cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 249, 114371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Li, D.; Guo, J.; Chen, J. Mechanistic Toxicity Assessment of Differently Sized and Charged Polystyrene Nanoparticles Based on Human Placental Cells. Water Res. 2022, 223, 118960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dusza, H.M.; Katrukha, E.A.; Nijmeijer, S.M.; Akhmanova, A.; Vethaak, A.D.; Walker, D.I.; Legler, J. Uptake, Transport, and Toxicity of Pristine and Weathered Micro- and Nanoplastics in Human Placenta Cells. Environ. Health Perspect. 2022, 130, 097006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-L.; Lee, Y.-H.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Chiu, I.-J.; Huang, C.C.-Y.; Huang, C.-C.; Chia, Z.-C.; Lee, C.-P.; Lin, Y.-F.; Chiu, H.-W. The Kidney-Related Effects of Polystyrene Microplastics on Human Kidney Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cells HK-2 and Male C57BL/6 Mice. Environ. Health Perspect. 2021, 129, 057003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, J.; Xing, B. Environmental Source, Fate, and Toxicity of Microplastics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, K.E.; Hua, T.; Sang, Q.-X.A. Effects of Polystyrene Microplastics on Human Kidney and Liver Cell Morphology, Cellular Proliferation, and Metabolism. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 34136–34153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-L.; Huang, C.C.-Y.; Zheng, C.-M.; Liu, W.-C.; Lee, Y.-H.; Chiu, H.-W. Polystyrene Microplastic-Induced Extracellular Vesicles Cause Kidney-Related Effects in the Crosstalk between Tubular Cells and Fibroblasts. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 273, 116098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Chen, K.-F.; Lin, K.-Y.A.; Chen, J.-K.; Jiang, X.-Y.; Lin, C.-H. The Nephrotoxic Potential of Polystyrene Microplastics at Realistic Environmental Concentrations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 427, 127871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-R.; Men, S.-H.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Liu, C.; Zhou, G.-R.; Yan, Z.-G. The Application of Human-Derived Cell Lines in Neurotoxicity Studies of Environmental Pollutants. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 168839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Ji, J.; Sun, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Z. Blood-Brain Barrier Damage Accelerates the Accumulation of Micro- and Nanoplastics in the Human Central Nervous System. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Folgar, R.; González-Caballero, M.C.; Torres-Ruiz, M.; Cañas-Portilla, A.I.; De Alba González, M.; Liste, I.; Morales, M. Molecular Effects of Polystyrene Nanoplastics on Human Neural Stem Cells. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0295816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Caballero, M.C.; De Alba González, M.; Torres-Ruiz, M.; Iglesias-Hernández, P.; Zapata, V.; Terrón, M.C.; Sachse, M.; Morales, M.; Martin-Folgar, R.; Liste, I.; et al. Internalization and Toxicity of Polystyrene Nanoplastics on Inmortalized Human Neural Stem Cells. Chemosphere 2024, 355, 141815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban, M.; Shimoda, R.; Chen, J. Investigation of Nanoplastic Cytotoxicity Using SH-SY5Y Human Neuroblastoma Cells and Polystyrene Nanoparticles. Toxicol. Vitr. 2021, 76, 105225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Liang, B.; Li, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, B.; Du, J.; Ye, R.; Xian, H.; Min, W.; et al. Polystyrene Nanoplastic Exposure Induces Excessive Mitophagy by Activating AMPK/ULK1 Pathway in Differentiated SH-SY5Y Cells and Dopaminergic Neurons in Vivo. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2023, 20, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, K.; Chen, Z.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liang, Y.; Esteban, M.A.; Zhou, Y.; et al. TDP-43 Aggregation Induced by Oxidative Stress Causes Global Mitochondrial Imbalance in ALS. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2021, 28, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Yang, B.; Li, Q.; Zhu, X.; Song, E.; Liu, C.; Song, Y.; Jiang, G. Polystyrene Nanoparticles Trigger Aberrant Condensation of TDP-43 and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis-like Symptoms. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2024, 19, 1354–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, W.; Kim, D.; Kim, H.-Y.; Jeong, S.W.; Lee, S.-G.; Kim, H.-C.; Lee, Y.-J.; Kwon, M.K.; Hwang, J.-S.; Han, J.E.; et al. Microglial Phagocytosis of Polystyrene Microplastics Results in Immune Alteration and Apoptosis in Vitro and in Vivo. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosal, S.; Bag, S.; Bhowmik, S. Insights into the Binding Interactions between Microplastics and Human α-Synuclein Protein by Multispectroscopic Investigations and Amyloidogenic Oligomer Formation. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2024, 15, 6560–6567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Sokratian, A.; Duda, A.M.; Xu, E.; Stanhope, C.; Fu, A.; Strader, S.; Li, H.; Yuan, Y.; Bobay, B.G.; et al. Anionic Nanoplastic Contaminants Promote Parkinson’s Disease–Associated α-Synuclein Aggregation. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadi8716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, A.; Park, S.J.; Lee, E.J.; Kim, K.W. Nanoplastics Exacerbate Parkinson’s Disease Symptoms in C. Elegans and Human Cells. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.; Lee, D.-K.; Jeong, J.; Yang, S.I.; Kim, J.-S.; Kim, J.; Cho, W.-S. The Reactive Oxygen Species as Pathogenic Factors of Fragmented Microplastics to Macrophages. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 281, 117006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koner, S.; Florance, I.; Mukherjee, A.; Chandrasekaran, N. Cellular Response of THP-1 Macrophages to Polystyrene Microplastics Exposure. Toxicology 2023, 483, 153385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, M.; Bredeck, G.; Waag, F.; Rahimi, K.; Ramachandran, H.; Bessel, T.; Barcikowski, S.; Herrmann, A.; Rossi, A.; Schins, R.P.F. Assessing the NLRP3 Inflammasome Activating Potential of a Large Panel of Micro- and Nanoplastics in THP-1 Cells. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florance, I.; Chandrasekaran, N.; Gopinath, P.M.; Mukherjee, A. Exposure to Polystyrene Nanoplastics Impairs Lipid Metabolism in Human and Murine Macrophages in Vitro. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 238, 113612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, V.; Böhmert, L.; Lisicki, E.; Block, R.; Cara-Carmona, J.; Pack, L.K.; Selb, R.; Lichtenstein, D.; Voss, L.; Henderson, C.J.; et al. Uptake and Effects of Orally Ingested Polystyrene Microplastic Particles in Vitro and in Vivo. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 1817–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, D.K.; Dubey, R.; Samarth, R.M.; Shubham, S.; Chowdhury, P.; Kumawat, M.; Verma, V.; Tiwari, R.R.; Kumar, M. The Biological Effects of Polystyrene Nanoplastics on Human Peripheral Blood Lymphocytes. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çobanoğlu, H.; Belivermiş, M.; Sıkdokur, E.; Kılıç, Ö.; Çayır, A. Genotoxic and Cytotoxic Effects of Polyethylene Microplastics on Human Peripheral Blood Lymphocytes. Chemosphere 2021, 272, 129805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salimi, A.; Alavehzadeh, A.; Ramezani, M.; Pourahmad, J. Differences in Sensitivity of Human Lymphocytes and Fish Lymphocytes to Polyvinyl Chloride Microplastic Toxicity. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2022, 38, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Bang, J.; Choi, D.; Hwang, J.; Kim, T.; Oh, Y.; Hwang, Y.; Choi, J.; Hong, J. Surface Pattern Analysis of Microplastics and Their Impact on Human-Derived Cells. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 4541–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Bang, J.; Kim, T.; Oh, Y.; Hwang, Y.; Hong, J. In Vitro Chemical and Physical Toxicities of Polystyrene Microfragments in Human-Derived Cells. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Choi, D.; Han, S.; Choi, J.; Hong, J. An Assessment of the Toxicity of Polypropylene Microplastics in Human Derived Cells. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 684, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Hwang, J.; Bang, J.; Han, S.; Kim, T.; Oh, Y.; Hwang, Y.; Choi, J.; Hong, J. In Vitro Toxicity from a Physical Perspective of Polyethylene Microplastics Based on Statistical Curvature Change Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 142242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, A.; Schwiebs, A.; Solhaug, H.; Stenvik, J.; Nilsen, A.M.; Wagner, M.; Relja, B.; Radeke, H.H. Nanoplastics Affect the Inflammatory Cytokine Release by Primary Human Monocytes and Dendritic Cells. Environ. Int. 2022, 163, 107173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezet, M.G.; Torres, J.A.; Thimraj, T.A.; Matkovic, I.; Schrode, N.; Murray, J.W.; Saqi, A.; Beaumont, K.G.; Snoeck, H.-W. Human Respiratory Airway Progenitors Derived from Pluripotent Cells Generate Alveolar Epithelial Cells and Model Pulmonary Fibrosis. Nat. Biotechnol. 2025, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Yang, S.; Ge, Y.; Yin, L.; Pu, Y.; Gu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Liang, G. Unveiling the Heart’s Hidden Enemy: Dynamic Insights into Polystyrene Nanoplastic-Induced Cardiotoxicity Based on Cardiac Organoid-on-a-Chip. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 31569–31585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgeman, L.; Pamies, D.; Frangiamone, M. Human Organoids to Assess Environmental Contaminants Toxicity and Mode of Action: Towards New Approach Methodologies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 497, 139562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Bai, C.; Xuan, L.; Yi, W.; Luo, J.; Pan, H.; Chen, W.; Guan, H.; Zhou, P.; Huang, R. Toxicological Assessments Based on Intestine 3D Organoids Reveal Environmental Low-Dose Nanosized Microplastics (NPs) Exposure Aggravates Radiation-Induced Intestine Injury. Chemosphere 2025, 370, 143922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okkelman, I.A.; Zhou, H.; Borisov, S.M.; Debruyne, A.C.; Lefebvre, A.E.Y.T.; Leomil Zoccoler, M.; Chen, L.; Devriendt, B.; Dmitriev, R.I. Visualizing the Internalization and Biological Impact of Nanoplastics in Live Intestinal Organoids by Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy (FLIM). Light Sci. Appl. 2025, 14, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.; Luo, Y.; Su, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, S.; Xu, M.; Yao, R. Distinct Toxicity of Microplastics/TBBPA Co-Exposure to Bioprinted Liver Organoids Derived from hiPSCs of Healthy and Patient Donors. Int. J. Bioprint. 2024, 10, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Chen, H.; Zhou, Y.; You, Y.; Lei, D.; Li, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Y. Aged Fragmented-Polypropylene Microplastics Induced Ageing Statues-Dependent Bioenergetic Imbalance and Reductive Stress: In Vivo and Liver Organoids-Based in Vitro Study. Environ. Int. 2024, 191, 108949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.B.; Jo, J.H.; Kim, S.S.; Jung, W.H.; Bae, M.A.; Koh, B.; Kim, K.Y. Microplastics Accumulation Induces Kynurenine-Derived Neurotoxicity in Cerebral Organoids and Mouse Brain. Biomol. Ther. 2025, 33, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; You, H.; Tang, X.; Su, Y.; Peng, H.; Li, H.; Wei, Z.; Hua, J. Early-Life Exposure to Polypropylene Nanoplastics Induces Neurodevelopmental Toxicity in Mice and Human iPSC-Derived Cerebral Organoids. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2025, 23, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Liang, T.; Chen, L.; Feng, S.; Zhao, Z.; Jing, Z.; Lv, J.; Xie, J.; Zhou, B. Polystyrene Microplastics Induce Nephrotoxicity through DDIT4-Mediated Autophagy and Apoptosis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 294, 118066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Wei, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, A.; Liang, T.; Low, J.H.; Liu, Z.; He, S.; Guo, Z.; Xie, J. Microplastics Exposure Disrupts Nephrogenesis and Induces Renal Toxicity in Human iPSC-Derived Kidney Organoids. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 360, 124645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, J.; Wu, J.; Fang, Y.; Wang, J.; Kong, X.; Wang, L.; Duan, Z. Application of Organoid Technology in the Human Health Risk Assessment of Microplastics: A Review of Progresses and Challenges. Environ. Int. 2024, 188, 108744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cell Model | MNP Type | Size | Dose | Time | Toxic Effect | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A549 | PS | 25, 75 nm | 2.5–300 μg/mL | 12 h | Cell viability ↓ Inflammatory responses ↑ Cell apoptosis ↑ Cell cycle S-phase arrest Disturb gene transcription and protein expression | [11] |
| PS, NH2-PS, COOH-PS | 2 μm, 80 nm | 0–400 μg/mL | 24 h | Cell viability ↓ Genotoxicity ↑ Oxidative stress ↑ | [12] | |
| PS | 20, 50 nm | 10–160 μg/mL | 24 h | Cell viability ↓ ROS generation ↑ MMP ↓ ER stress ↑ Mitochondrial dysfunction | [13] | |
| PS, UV PS | 100 nm | 5–100 μg/mL | 24 h | Cell viability ↓ Oxidative stress ↑ Membrane damage ↑ Mitochondrial dysfunction Genotoxic and oxidative DNA damage | [14] | |
| PET | 164, 190 nm | 0.10–300 μg/mL | 24 h | Cell viability (0.10–0.98 μg/mL ↑ 4.92–196.79 μg/mL ↓) Oxidative stress ↑ MMP ↓ Cell apoptosis ↑ | [15] | |
| BEAS-2B | PS | 1.72 ± 0.26 μm | 1–1000 μg/cm2 | 24, 48 h | Cytotoxicity ↑ Inflammatory responses ↑ ROS accumulation ↑ Barrier dysfunction | [16] |
| PS, NH2-PS, COOH-PS | 100 nm | 25–400 μg/mL | 24 h | Cell viability (NH2-PS-MPs) ↓ ROS generation ↑ ER stress ↑ Inflammatory responses ↑ Autophagic cell death ↑ | [18] | |
| HPAEpiC, BEAS-2B | PS | 40 nm | 24, 48, 96 μg/mL | 24 h | Cell viability ↓ Oxidative Stress ↑ Inflammatory adverse response ↑ Cell apoptosis ↑ Alter the gene expression Alveolar Epithelial Barrier damage Pulmonary dysfunction | [17] |
| HNEpCs | PS | 50, 500 nm | 0.5–100 μg/mL | 24 h | Oxidative Stress ↑ Loss of MMP Disturbance to the autophagy pathway | [19] |
| PET | 62.38 nm ± 3.51 | 0–100 μg/mL | 24 h | iROS generation ↑ Loss of MMP Alter the autophagy pathway | [20] |
| Cell Model | MNP Type | Size | Dose | Time | Toxic Effect | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caco-2 | PS | 5 μm | 10−1–10−5 mg/mL 12.5, 25, 50 mg/L | 24, 48 h | Cell viability ↓ Oxidative Stress ↑ Epithelial cell injury and alterations to intestinal barrier function Change the transcription level of genes | [22] |
| PS, PS-COOH, PS-NH2 | 100 nm | 30, 60, 120, 240, 480 μg/mL | 24, 48, 96 h | Cell proliferation ↓ Cell apoptosis ↑ Autophagic cell death ↑ Disrupt the intestinal barrier function | [23] | |
| PS | 0.1, 5 μm | 1, 10, 20, 40, 50, 80, 200 μg/mL | 12 h | ROS generation ↑ Mitochondrial depolarization | [30] | |
| PS | 1.0–1.9 μm | 0, 50, 500, 1000 μg/mL | 24 h | Cell viability ↓ Cell membrane damage ↑ | [33] | |
| HepG2 | PS(amine, carboxyl and non-functionalize) | 50–5000 nm | 0.1–100 μg/mL | 1–24 h | Cell viability ↓ Inflammatory response ↑ Cell apoptosis↑ | [28] |
| CCD841CoN HIEC-6 | PS | 0.1–5 μm | 0, 12.5, 25, 50, 100 μg/mL | 0.5, 1, 4, 8, 12, 24 h | Oxidative Stress ↑ Membrane damage ↑ Mitochondrial depolarization | [29] |
| GES-1 | PS, Cl2-PS | 213.7 ± 8.2 nm | 1, 10, 20, 50, 100 mg/L | 48 h | Cell viability ↓ Mitochondria-dependent apoptosis ↑ Cell membrane damage ↑ Oxidative stress ↑ Inflammatory response ↑ Mitochondrial dysfunction Alter cell morphology | [32] |
| PS | 50, 250 nm | 0, 20, 40, 80 μg/mL | 24, 48 h | Cell viability ↓ Oxidative Stress ↑ MMP and ATP level ↓ Mitochondria-dependent apoptosis ↑ Inhibit gastric juice secretion and mucus secretion Disrupt gastric barrier function Mitochondria dysfunction | [36] | |
| PS | 60 nm | 50 μg/mL | 2, 4, 6, 12, 24, 48 h | Cell proliferation ↓ Apoptosis ↑ Autophagy ↑ | [37] | |
| LO2 | PS | 5 μm | 0.5 mg/mL | 24 h | ER stress ↑ Oxidative Stress ↑ Apoptosis ↑ MMP ↓ Mitochondrial fission, apoptosis, and mitophagy ↑ | [40] |
| PS | 5, 10 μm | 0.2, 0.4, 0.6 mg/mL | 24 h | ROS ↑ Apoptosis↑ S phase arrest | [41] | |
| SMMC-7721 | PS | 500 nm, 50 μm | 2, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100 μg/mL | 24 h | Cell viability ↓ Cell membrane damage and apoptosis ↑ Cell morphological alteration | [42] |
| HL7702 | PS | 0.1, 1 μm | 0.1, 1 mg/L | 24 h | Nucleus damage and micronucleus formation Mitochondria DNA damage | [43] |
| Cell Model | MNP Type | Size | Dose | Time | Toxic Effect | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RBC | PS | 50, 107, 250 nm | 50, 150, 250, 350, 500 μg/mL | 1 h | Hemolysis ↑ | [44] |
| PS | 50 nm | 0–1000 μg/mL | 20 min | Platelet aggregation ↑ | [45] | |
| PS | 50, 100, 1000 nm | 10–500 μg/mL | 3, 24 h | Hemolysis ↑ Cell adhesion and thrombin generation ↑ Morphological and membrane changes | [47] | |
| HUVEC | PS | 100, 500 nm | 0, 5, 10, 25, 50, 100 μg/mL | 0–48 h | Cell viability ↓ Lysosomal damage Autophagosomes accumulation Cell membrane damage | [49] |
| PS | 0.5, 1, 5 μm | 0, 20, 40, 60, 80, 100 μg/mL | 24, 48, 72 h | Cell viability ↓ Angiogenic signaling pathway ↓ Wound healing and cell migration ↓ Cell senescence ↑ Autophagy and necrosis ↑ Angiogenic tube formation ↓ | [51] | |
| PS | 21.2 ± 3.5 nm | 0–0.5 mg/mL | 1, 3, 6 h | Endothelial leakiness ↑ | [52] | |
| PS | 1 μm | 0, 5, 10, 25, 100 μg/mL | 48 h | Cell viability (100 μg/mL ↓) | [50] | |
| HCAECs, HUVEC | PS | 1 μm | 0.1, 0.3, 0.6, 0.9 mg/mL | 90 min | Cell senescence ↑ Oxidative Stress ↑ Lamin A ↓ | [53] |
| Cell Model | MNP Type | Size | Dose | Time | Toxic Effect | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Semen | PS | 50, 100 nm | 0.1, 0.5, 1 μg/mL | 30 min | Motility ↓ Acrosomal damage ↑ Oxidative stress ↑ DNA fragmentation ↑ Mitochondrial activity ↓ | [54] |
| KGN | PS | 15–38 nm | 50, 100, 200 μg/mL | 24, 48, 72 h | Cell proliferation ↓ Oxidative stress ↑ Cell apoptosis ↑ | [55] |
| COV434 | PS | 50 nm | 50, 100, 150, 200 μg/mL | 24 h | Cell viability ↓ MMP ↓ Oxidative stress ↑ Cell apoptosis ↑ | [56] |
| JEG-3 | PS, PS-NH2, PS-COOH | 25, 50, 100, 500 nm | 0, 20, 39, 78, 156, 313, 625, 1250, 2500, 5000 μg/mL | 24 h | Cell viability ↓ PKA activity ↓ Oxidative stress ↑ DNA damage ↑ Inflammation and apoptosis ↑ Cell cycle arrest | [57] |
| BeWo b30 | PS, HDPE | PS: 0.05–10 μm HDPE: 0–80 μm | 0.1–100 μg/mL | 1–48 h | Membrane damage (100 μg/mL) Alter gene expression | [58] |
| Cell Model | MNP Type | Size | Dose | Time | Toxic Effect | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HK-2 | PS | 2 μm | 0.025, 0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 0.8 mg/mL | 0–48 h | Mitochondrial ROS ↑ ER Stress ↑ Inflammation ↑ Autophagy ↑ Apoptosis ↑ Mitochondrial Dysfunction | [59] |
| HEK 293 | PS | 1 μm | 0.05, 5, 10, 25, 50, 75, 100 μg/mL | 0–72 h | Cell Morphological Changes Cellular Proliferation ↓ Metabolic Activity ↓ ROS Levels ↑ | [61] |
| HK-2 | PS | Water: 2121.3 nm K-SFM: 2209.0 nm | 0.4, 0.8 mg/ml | 0–24 h | Extracellular vesicle production ↑ ER stress-related proteins ↑ ROS production ↑ Fibrosis-related proteins ↑ | [62] |
| HEK293 | PS | 3.54 ± 0.39 μm | 3–300 ng/mL | 24 h | Inflammatory responses ↑ Apoptosis and autophagy ↑ Barrier integrity ↓ Oxidative and inflammatory ↑ | [63] |
| Cell Model | MNP Type | Size | Dose | Time | Toxic Effect | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hNS1 | PS | 30 nm | 0.5, 2.5, 10 μg/mL | 4 days | Oxidative stress ↑ Cellular Stress ↑ DNA Damage ↑ Inflammatory response ↑ Apoptotic ↑ | [66] |
| NSCs | PS | 30 nm | 0.5, 2.5, 10 μg/mL | 1–4 days | Apoptosis ↑ Cell proliferation ↓ | [67] |
| SH-SY5Y | PS | 50 nm | 27.6, 138, 690 μg/mL | 24 h | Neurite outgrowth ↓ Morphology alteration and swelling of the nuclei Spilling of intracellular components | [68] |
| PS | 50 nm | 0.5, 5, 50, 500 μg/mL | 48 h | ROS levels ↑ Cell death ↑ Dopaminergic neuron ↓ Mitophagy ↓ Mitochondrial dysfunction Disrupt mitochondrial respiration | [69] | |
| HMC-3 | PS | 0.2, 2, 10 μm | 1, 5, 10 μg/mL | 24, 48, 72 h | Microglial activation ↑ Apoptosis ↑ Immune responses ↑ Microglial morphological change | [72] |
| Cell Model | MNP Type | Size | Dose | Time | Toxic Effect | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| THP-1 | PP, PS | 100 μm | 625–20,000 particles/mL | 24 h | ROS generation ↑ Inflammation ↑ | [76] |
| PS | 100–450 nm | 50–500 μg/mL | 4, 24, 48, 72, 96 h | Cell viability and proliferation ↓ Oxidative stress ↑ Apoptosis ↑ DNA damage ↑ Morphology changes Mitochondrial membrane damage | [77] | |
| Peripheral lymphocytes | PS | 50 nm | 500, 1000, 2000 μg/mL | 48 h | Cell viability ↓ Hemolysis ↑ Mitotic Index and nuclear division index ↓ Micronuclei frequency and cytostasis ↑ | [81] |
| PE | 10–45 μm | 25, 50, 100, 250, 500 μg/mL | 48 h | DNA Damage ↑ Micronucleus formantion ↑ Nucleoplasmic bridge formation ↑ Nuclear bud formation ↑ | [82] | |
| Human lymphocytes | PVC | 0.16–1.82 μm | 24, 48, 96 μg/mL | 3 h | ROS formation ↑ Lysosomal membrane injury ↑ GSH ↓ Lipid peroxidation ↑ MMP collapse | [83] |
| PBMCs | PVC, ABS | 25–75, 75–200 μm | 10, 100, 1000 μg/mL | 1–5 days | Immune responses ↑ | [84] |
| PS | 5–25, 25–75, 75–200 μm | 5, 25, 75, 200 μg/mL | 1–4 days | Immune responses ↑ Inflammation ↑ Cell death ↑ Cell membrane damage ↑ Hemolysis ↑ | [85] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, L.; Tu, P.; Niu, H.; Li, X.; Gong, X.; Chen, Z.; Xing, M.; Wu, L.; Lou, X. Cellular Impact of Micro(nano)plastics on Human Health: A Review. Toxics 2025, 13, 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110913
Liu L, Tu P, Niu H, Li X, Gong X, Chen Z, Xing M, Wu L, Lou X. Cellular Impact of Micro(nano)plastics on Human Health: A Review. Toxics. 2025; 13(11):913. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110913
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Longxiao, Pengcheng Tu, Huixia Niu, Xueqing Li, Xin Gong, Zhijian Chen, Mingluan Xing, Lizhi Wu, and Xiaoming Lou. 2025. "Cellular Impact of Micro(nano)plastics on Human Health: A Review" Toxics 13, no. 11: 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110913
APA StyleLiu, L., Tu, P., Niu, H., Li, X., Gong, X., Chen, Z., Xing, M., Wu, L., & Lou, X. (2025). Cellular Impact of Micro(nano)plastics on Human Health: A Review. Toxics, 13(11), 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110913








