Preliminary Identification of PFAS and Other Emerging Contaminants in the French Broad River, NC Post-Hurricane Helene
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
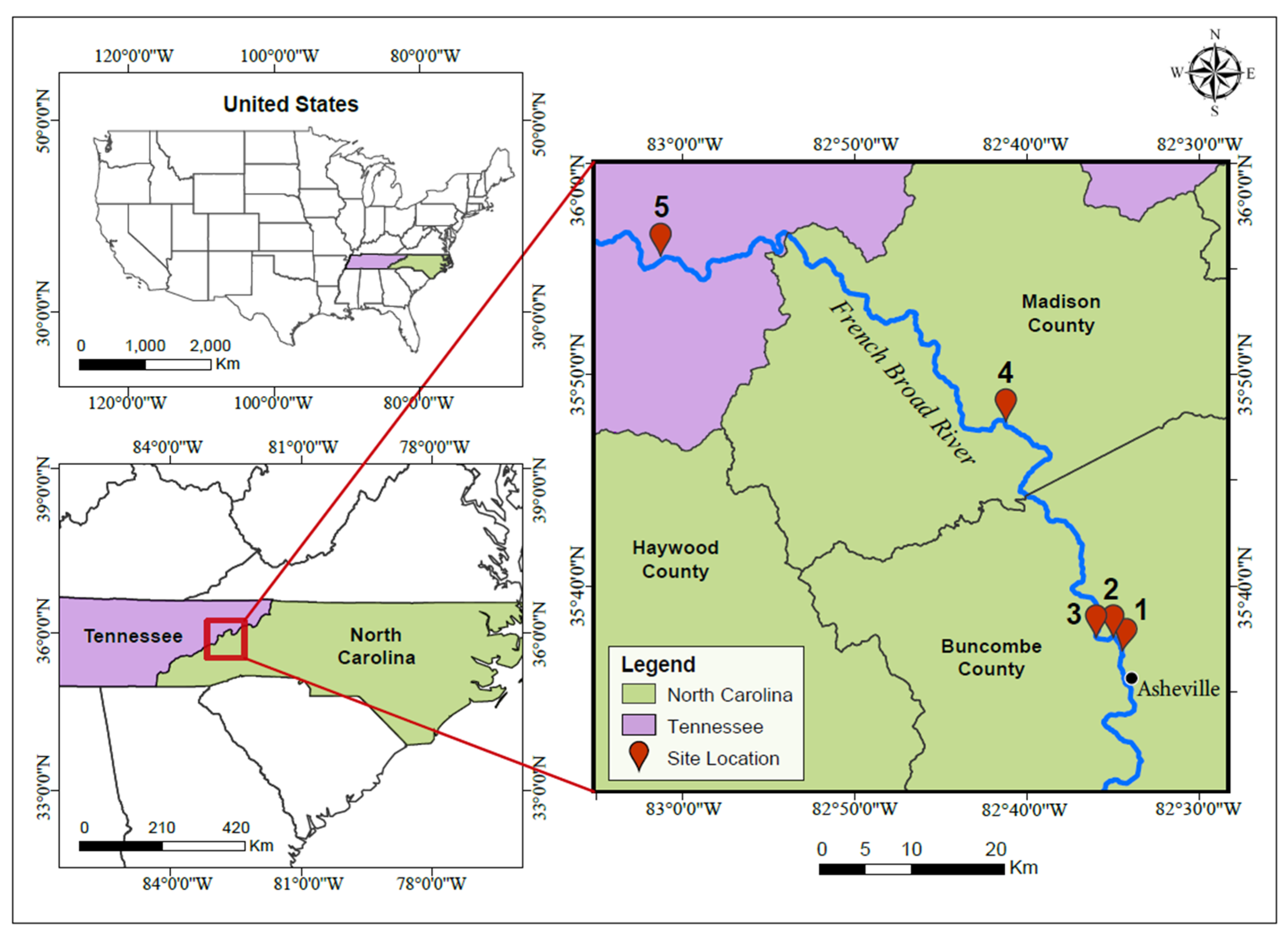
2.1. Site Locations and Sample Collection
2.2. Materials
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. Sample Analysis
2.5. Hazard Classifications of Annotations
3. Results and Discussion
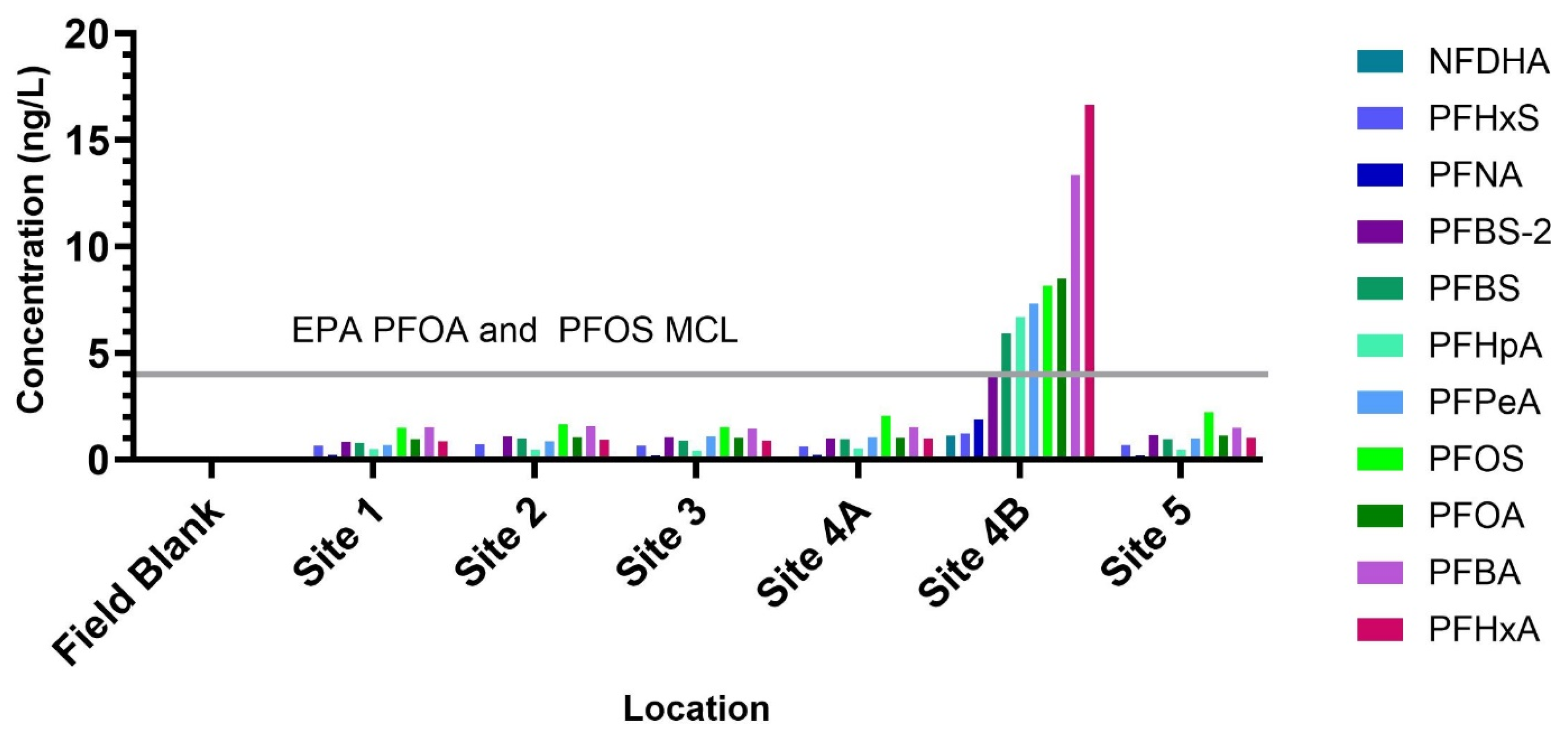
3.1. Targeted PFAS Analysis
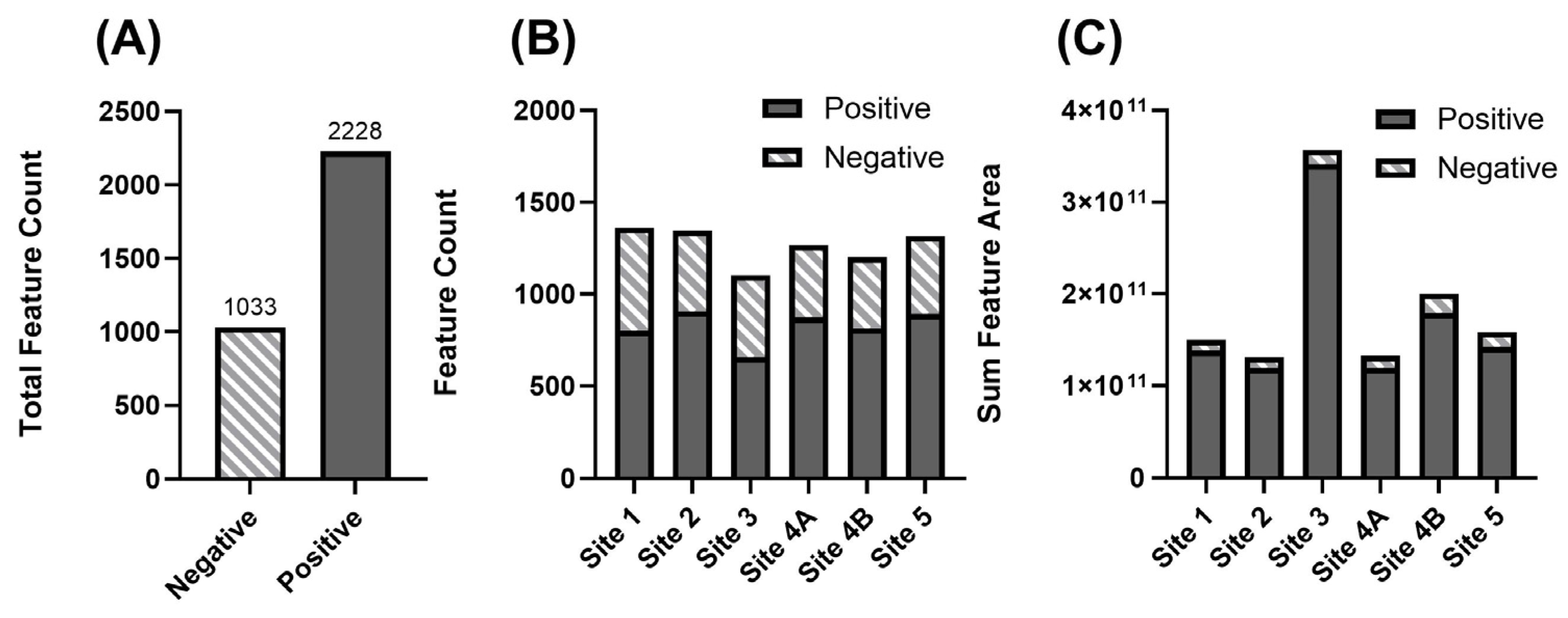
3.2. Overview of Detected Chemical Features
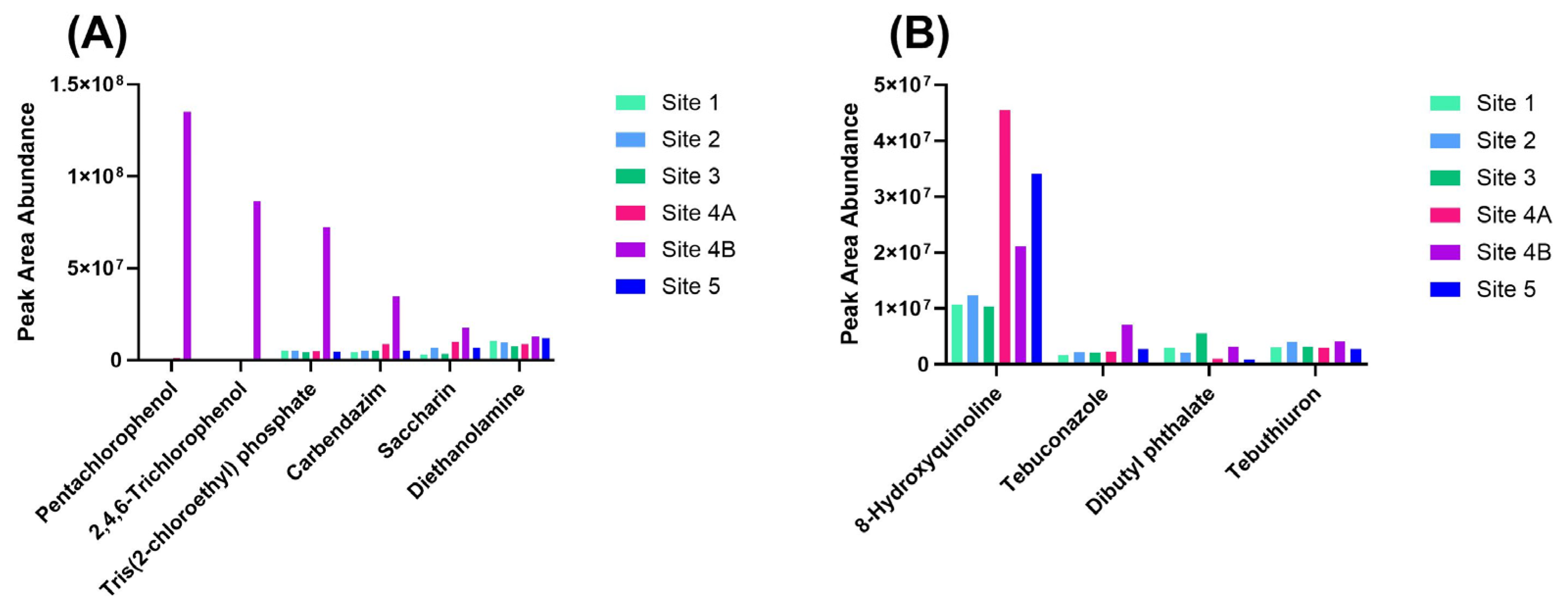
3.3. High-Risk Compounds Annotated via Suspect Screening and Hazard Screening
3.4. Spatial Distribution of Key Contaminant Classes
3.5. Limitations and Contextual Considerations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DBP | Dibutyl phthalate |
| EPA | United States Environmental Protection Agency |
| FBR | French Broad River |
| LC-HRMS | Liquid Chromatography–High Resolution Mass Spectrometry |
| MCL | Maximum contaminant level |
| PFAS | Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances |
| QAS | Quaternary ammonium salt |
| WNC | Western North Carolina |
References
- French Broad River Partnership. About the French Broad River. Available online: https://frenchbroadriver.org/about-the-french-broad-river/ (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- Ansari, R.A.; Esimaje, T.; Ibrahim, O.M.; Mulrooney, T. Analysis of Forest Change Detection Induced by Hurricane Helene Using Remote Sensing Data. Forests 2025, 16, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FEMA. North Carolina Tropical Storm Helene. Available online: https://www.fema.gov/disaster/4827 (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- Hertelendy, A.J.; Ciottone, G.R. Averting flood-related deaths and injuries from hurricanes: Enhancing hospital resilience. Lancet Reg. Health–Am. 2024, 40, 100930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Wang, W.; Zhang, K. Beyond wind and rainfall: Insights into Hurricane Helene fatalities with the National Risk Index. NPJ Nat. Hazards 2025, 2, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, Z. Post-Hurricane Helene Landslide Detection and Slope Analysis in Western North Carolina Using Google Earth Engine. 2024. Available online: https://digitalcommons.murraystate.edu/scholarsweek/Fall2024/EES/2/ (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- Welsh, W.; Bassett, H.; Fitzgerald, K.; Hanson, K.; Maher, A.; Carroll, C.; Averyt, K.; Gunter-Bassett, M.; Daniels, B.; Wegener, C. Rapid Site Report: Potential Impacts to Cultural Heritage Sites from Hurricane Helene, Western North Carolina, USA. 2024. Available online: https://smithsonian.figshare.com/articles/report/Rapid_Site_Report_Potential_Impacts_to_Cultural_Heritage_Sites_from_Hurricane_Helene_Western_North_Carolina_USA/27558057?file=50360079 (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- Amorim, R.; Villarini, G.; Czajkowski, J.; Smith, J. Flooding from Hurricane Helene and associated impacts: A historical perspective. J. Hydrol. X 2025, 27, 100204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS. Hurricane Helene Flooding on French Broad River in Asheville, North Carolina. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/media/images/hurricane-helene-flooding-french-broad-river-asheville-north-carolina#:~:text=An%20image%20of%20a%20USGS,USGS%20image (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- Keenum, I.; Medina, M.C.; Garner, E.; Pieper, K.J.; Blair, M.F.; Milligan, E.; Pruden, A.; Ramirez-Toro, G.; Rhoads, W.J. Source-to-Tap Assessment of Microbiological Water Quality in Small Rural Drinking Water Systems in Puerto Rico Six Months After Hurricane Maria. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 3775–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunderland, E.M.; Hu, X.C.; Dassuncao, C.; Tokranov, A.K.; Wagner, C.C.; Allen, J.G. A review of the pathways of human exposure to poly-and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) and present understanding of health effects. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2019, 29, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsan, M.N.; Riza, M.; Pervez, M.N.; Khyum, M.M.O.; Liang, Y.; Naddeo, V. Environmental and health impacts of PFAS: Sources, distribution and sustainable management in North Carolina (USA). Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 878, 163123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panieri, E.; Baralic, K.; Djukic-Cosic, D.; Buha Djordjevic, A.; Saso, L. PFAS molecules: A major concern for the human health and the environment. Toxics 2022, 10, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Sevillano-Rivera, M.; Jiang, T.; Li, G.; Cotto, I.; Vosloo, S.; Carpenter, C.M.G.; Larese-Casanova, P.; Giese, R.W.; Helbling, D.E.; et al. Impact of Hurricane Maria on Drinking Water Quality in Puerto Rico. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 9495–9509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiller, A.M.; Shim, M.-J.; Guo, L.; Bianchi, T.S.; Smith, R.W.; Duan, S. Hurricane Katrina impact on water quality in the East Pearl River, Mississippi. J. Hydrol. 2012, 414, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagy, J.D.; Lehrter, J.C.; Murrell, M.C. Effects of hurricane Ivan on water quality in Pensacola Bay, Florida. Estuaries Coasts 2006, 29, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schymanski, E.L.; Jeon, J.; Gulde, R.; Fenner, K.; Ruff, M.; Singer, H.P.; Hollender, J. Identifying small molecules via high resolution mass spectrometry: Communicating confidence. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 2097–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedgespeth, M.L.; McCord, J.P.; Phillips, K.A.; Strynar, M.J.; Shea, D.; Nichols, E.G. Suspect-screening analysis of a coastal watershed before and after Hurricane Florence using high-resolution mass spectrometry. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 782, 146862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newmeyer, M.N.; Lyu, Q.; Sobus, J.R.; Williams, A.J.; Nachman, K.E.; Prasse, C. Combining nontargeted analysis with computer-based hazard comparison approaches to support prioritization of unregulated organic contaminants in biosolids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 12135–12146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Getzinger, G.J.; Ferguson, P.L. Illuminating the exposome with high-resolution accurate-mass mass spectrometry and nontargeted analysis. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2020, 15, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruff, M.; Mueller, M.S.; Loos, M.; Singer, H.P. Quantitative target and systematic non-target analysis of polar organic micro-pollutants along the river Rhine using high-resolution mass-spectrometry–identification of unknown sources and compounds. Water Res. 2015, 87, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schymanski, E.L.; Singer, H.P.; Slobodnik, J.; Ipolyi, I.M.; Oswald, P.; Krauss, M.; Schulze, T.; Haglund, P.; Letzel, T.; Grosse, S. Non-target screening with high-resolution mass spectrometry: Critical review using a collaborative trial on water analysis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 6237–6255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, I.; Whitworth, K.W.; Christensen, B.; Afshar, M.; Han, H.A.; Rammah, A.; Oluwadairo, T.; Symanski, E. Heavy metal pollution of soils and risk assessment in Houston, Texas following Hurricane Harvey. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 296, 118717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reible, D. Hurricane Katrina: Environmental hazards in the disaster area. Cityscape 2007, 9, 53–68. [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker, J.S.; Hrabak, R.B.; Ramos, M.; Neslund, C.; Li, Y. An interlaboratory study on EPA methods 537.1 and 533 for per-and polyfluoroalkyl substance analyses. AWWA Water Sci. 2021, 3, e1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, B.; Jeon, Y.; Kaserzon, S.; Heffernan, A.L.; Dewapriya, P.; O’Brien, J.; Ramos, M.J.G.; Gorji, S.G.; Mueller, J.F.; Thomas, K.V. An assessment of quality assurance/quality control efforts in high resolution mass spectrometry non-target workflows for analysis of environmental samples. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 133, 116063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Place, B.J.; Ulrich, E.M.; Challis, J.K.; Chao, A.; Du, B.; Favela, K.; Feng, Y.-L.; Fisher, C.M.; Gardinali, P.; Hood, A. An introduction to the benchmarking and publications for non-targeted analysis working group. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 16289–16296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- mzCloud. Advanced Mass Spectral Database. 2015. Available online: https://www.mzcloud.org/ (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- BP4NTA. NTA Study Reporting Tool. 2022. Available online: https://figshare.com/articles/online_resource/NTA_Study_Reporting_Tool_Excel_/19763503?file=47020795 (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- Vegosen, L.; Martin, T.M. An automated framework for compiling and integrating chemical hazard data. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2020, 22, 441–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA). Design for the Environment Program Alternatives Assessment Criteria for Hazard Evaluation; US Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA): Washington, DC, USA, 2011.
- Glüge, J.; Scheringer, M.; Cousins, I.T.; DeWitt, J.C.; Goldenman, G.; Herzke, D.; Lohmann, R.; Ng, C.A.; Trier, X.; Wang, Z. An overview of the uses of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2020, 22, 2345–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, Z.; Song, M.; Ikram, S.; Zahra, Z. Overview of Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS), Their Applications, Sources, and Potential Impacts on Human Health. Pollutants 2024, 4, 136–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, B.; Da Silva, B.F.; Aristizabal-Henao, J.J.; Denslow, N.D.; Osborne, T.Z.; Morrison, E.S.; Bianchi, T.S.; Bowden, J.A. Increased levels of perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS) during Hurricane Dorian on the east coast of Florida. Environ. Res. 2022, 208, 112635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mišľanová, C.; Valachovičová, M. Health Impacts of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs): A Comprehensive Review. Life 2025, 15, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North Carolina Department of Environmental Quality Division of Water Resource Water Sciences Section. Identification of Select Emerging PFAS Compounds in Public Water Supply Reservoirs of the Catawba, French Broad, and Tar River Basins in 2022. 2024. Available online: https://www.deq.nc.gov/water-resources/almp2022ecreportfinalcjsignpdf/open (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- Penland, T.N.; Cope, W.G.; Kwak, T.J.; Strynar, M.J.; Grieshaber, C.A.; Heise, R.J.; Sessions, F.W. Trophodynamics of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in the Food Web of a Large Atlantic Slope River. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6800–6811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASHEVILLE, Co. PFAS Mitigation Efforts; ASHEVILLE, Co.: Asheville, NC, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Koelmel, J.P.; Stelben, P.; McDonough, C.A.; Dukes, D.A.; Aristizabal-Henao, J.J.; Nason, S.L.; Li, Y.; Sternberg, S.; Lin, E.; Beckmann, M.; et al. FluoroMatch 2.0-making automated and comprehensive non-targeted PFAS annotation a reality. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 1201–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, K.A.; Wambaugh, J.F.; Grulke, C.M.; Dionisio, K.L.; Isaacs, K.K. High-throughput screening of chemicals as functional substitutes using structure-based classification models. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 1063–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandra, V.J.; Kouskoura, M.G.; Markopoulou, C.K. Using the partial least squares method to model the electrospray ionization response produced by small pharmaceutical molecules in positive mode. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 29, 1661–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.J.; Lambert, J.C.; Thayer, K.; Dorne, J.-L.C. Sourcing data on chemical properties and hazard data from the US-EPA CompTox Chemicals Dashboard: A practical guide for human risk assessment. Environ. Int. 2021, 154, 106566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temple, A.J.; Murphy, B.R.; Cheslak, E.F. Effects of tebuthiuron on aquatic productivity. Hydrobiologia 1991, 224, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, J. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) General Permit for Waste Discharge Requirements (WDRs) for Storm Water Discharges from Small Municipal Separate Storm Sewer Systems (MS4s) Water Quality (WQ) Order 2013-0001-DWQ NPDES NO. CAS000004. 2014. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/npdes (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- Crawford, S.E.; Brinkmann, M.; Ouellet, J.D.; Lehmkuhl, F.; Reicherter, K.; Schwarzbauer, J.; Bellanova, P.; Letmathe, P.; Blank, L.M.; Weber, R. Remobilization of pollutants during extreme flood events poses severe risks to human and environmental health. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwanen, C.A.; Müller, J.; Schulte, P.; Schwarzbauer, J. Distribution, remobilization and accumulation of organic contaminants by flood events in a meso-scaled catchment system. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2023, 35, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rager, J.E.; Strynar, M.J.; Liang, S.; McMahen, R.L.; Richard, A.M.; Grulke, C.M.; Wambaugh, J.F.; Isaacs, K.K.; Judson, R.; Williams, A.J. Linking high resolution mass spectrometry data with exposure and toxicity forecasts to advance high-throughput environmental monitoring. Environ. Int. 2016, 88, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahony, A.K.; McNamara, P.J.; Arnold, W.A. Quaternary ammonium compounds (QACs) in wastewater influent and effluent throughout the COVID-19 pandemic. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 20148–20158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zhou, Z.-C.; Zhu, L.; Wei, Y.-Y.; Feng, W.-Q.; Xu, L.; Liu, Y.; Lin, Z.-J.; Shuai, X.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-J. The impact and mechanism of quaternary ammonium compounds on the transmission of antibiotic resistance genes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 28352–28360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Cui, F.; Zeng, G.-M.; Jiang, M.; Yang, Z.-Z.; Yu, Z.-G.; Zhu, M.-Y.; Shen, L.-Q. QUATERNARY ammonium compounds (QACs): A review on occurrence, fate and toxicity in the environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 518, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; LaVergne, J.M.; Carpenter, C.M.; Desai, R.; Zhang, X.; Gray, K.; Helbling, D.E.; Wells, G.F. Exploring co-occurrence patterns between organic micropollutants and bacterial community structure in a mixed-use watershed. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2019, 21, 867–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, B.; Walker, I.; Lassiter, R.; Lassiter, V.; Gibson, J.M.; Ferguson, P.L.; Deshusses, M.A. Evaluation of private well contaminants in an underserved North Carolina community. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 147823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The United States Geological Survey (USGS). National Water Information System Dataset for French Broad River. Available online: https://waterdata.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 11 July 2025).
- Fisher, S.C.; Phillips, P.J.; Brownawell, B.J.; Browne, J.P. Comparison of wastewater-associated contaminants in the bed sediment of Hempstead Bay, New York, before and after Hurricane Sandy. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 107, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| # | Name [Common Name or Abbreviation] | PU | CASRN | Formula | Max Peak Area Abund. | Site 1 | Site 2 | Site 3 | Site 4A | Site 4B | Site 5 | AMT Oral | Carc | Dev | AAT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Dodecyltrimethylammonium | PCP | 10182-91-9 | C15 H33 N | 1.20 × 109 | I | L | I | |||||||
| 2 | (Z)-octadec-9-enamide [Oleamide] | PA | 301-02-0 | C18 H35 N O | 1.14 × 109 | L | I | H | H | ||||||
| 3 | Pentaethylene glycol [PEG n5] | PA | 4792-15-8 | C10 H22 O6 | 5.33 × 108 | L | L | L | |||||||
| 4 | Hexaethylene glycol [PEG n6] | PA | 2615-15-8 | C12 H26 O7 | 5.01 × 108 | L | L | L | |||||||
| 5 | Heptaethylene glycol [PEG n7] | PA | 5617-32-3 | C14 H30 O8 | 4.38 × 108 | L | L | L | |||||||
| 6 | Octaethylene glycol [PEG n8] | PA | 5117-19-1 | C16 H34 O9 | 3.46 × 108 | L | L | L | |||||||
| 7 | Tris(1-chloro-2-propanyl) phosphate | FR | 13674-84-5 | C9 H18 Cl3 O4 P | 2.63 × 108 | M | I | M | M | ||||||
| 8 | 4-Dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid | PCP | 121-65-3 | C18 H30 O3 S | 2.63 × 108 | M | H | L | |||||||
| 9 | Xylenesulfonate | PCP | 25241-16-1 | C8 H10 O3 S | 2.43 × 108 | L | H | M | |||||||
| 10 | Diethyltoluamide (DEET) | PE | 134-62-3 | C12 H17 N O | 1.92 × 108 | M | I | M | M | ||||||
| 11 | N-Methyldioctylamine | PCP | 4455-26-9 | C17 H37 N | 1.87 × 108 | M | L | H | |||||||
| 12 | 2-Naphthalenesulfonic acid | PA | 120-18-3 | C10 H8 O3 S | 1.49 × 108 | M | H | M | |||||||
| 13 | 2-Methoxy-4,6-bis(isopropylamino)triazine [Prometon] | PE | 1610-18-0 | C10 H19 N5 O | 1.41 × 108 | M | I | H | M | ||||||
| 14 | 2,3,4,5,6-pentachlorophenol | PE | 87-86-5 | C6 H Cl5 O | 1.35 × 108 | H | VH | H | VH | ||||||
| 15 | Dodecyl sulfate | PCP | 151-41-7 | C12 H26 O4 S | 1.31 × 108 | M | L | ||||||||
| 16 | N,N′-Dicyclohexylurea | NP | 2387-23-7 | C13 H24 N2 O | 1.29 × 108 | L | H | M | |||||||
| 17 | 1,3,7-trimethylpurine-2,6-dione [Caffeine] | WT | 58-08-2 | C8 H10 N4 O2 | 1.21 × 108 | H | I | H | L | ||||||
| 18 | azepan-2-one [Caprolactam] | PA | 105-60-2 | C6 H11 N O | 1.17 × 108 | M | L | L | L | ||||||
| 19 | N,N-Dimethyldecylamine N-oxide | PCP | 2605-79-0 | C12 H27 N O | 9.72 × 107 | M | I | L | H | ||||||
| 20 | 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol | PE | 88-06-2 | C6 H3 Cl3 O | 8.64 × 107 | M | VH | I | VH |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Walker-Franklin, I.; Blake, S.; Thorp, E.; Tuberty, S. Preliminary Identification of PFAS and Other Emerging Contaminants in the French Broad River, NC Post-Hurricane Helene. Toxics 2025, 13, 905. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110905
Walker-Franklin I, Blake S, Thorp E, Tuberty S. Preliminary Identification of PFAS and Other Emerging Contaminants in the French Broad River, NC Post-Hurricane Helene. Toxics. 2025; 13(11):905. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110905
Chicago/Turabian StyleWalker-Franklin, Imari, Samantha Blake, Evan Thorp, and Shea Tuberty. 2025. "Preliminary Identification of PFAS and Other Emerging Contaminants in the French Broad River, NC Post-Hurricane Helene" Toxics 13, no. 11: 905. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110905
APA StyleWalker-Franklin, I., Blake, S., Thorp, E., & Tuberty, S. (2025). Preliminary Identification of PFAS and Other Emerging Contaminants in the French Broad River, NC Post-Hurricane Helene. Toxics, 13(11), 905. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110905








