Characteristics of the Chemical Components of PM2.5 in the Dangjin Region, South Korea, and Evaluation of Emission Source Contributions During High-Concentration Events
Highlights
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Monitoring Site
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Gravimetric Analysis
2.4. Ionic Composition Analysis
2.5. Carbon Component Analysis
2.6. Trace Elemental Composition Analysis
2.7. Quality Control (QA/QC)
2.8. Statistical Analysis
2.9. Weather Information Processing and the Hybrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory (HYSPLIT) Model
3. Results
3.1. Meteorological Data
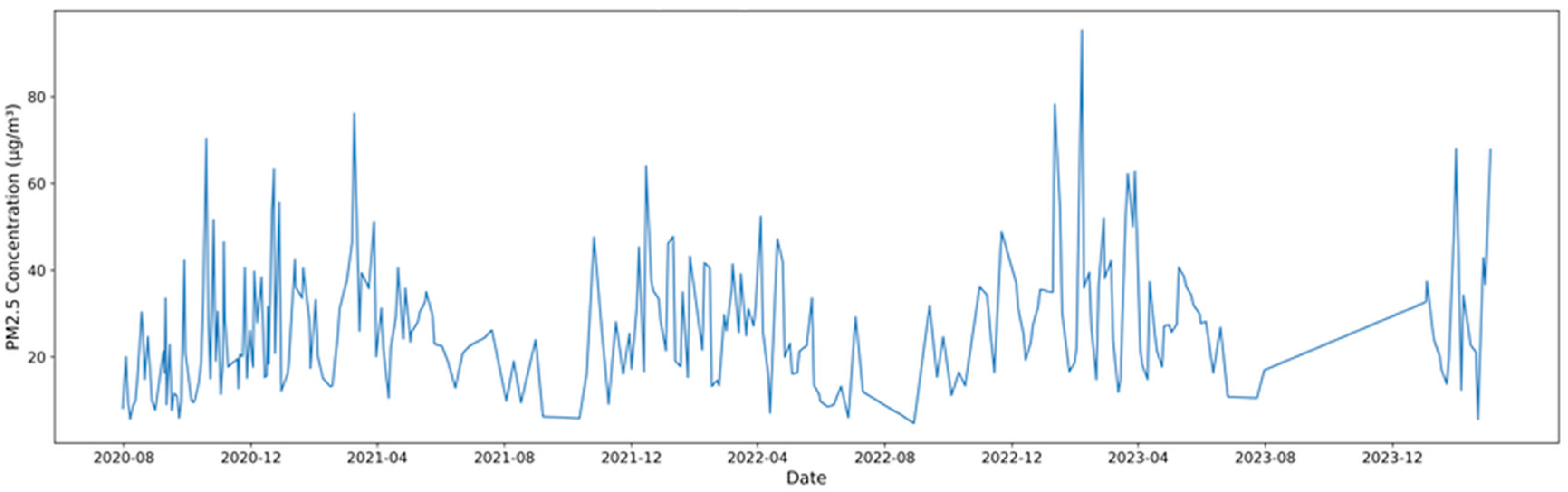
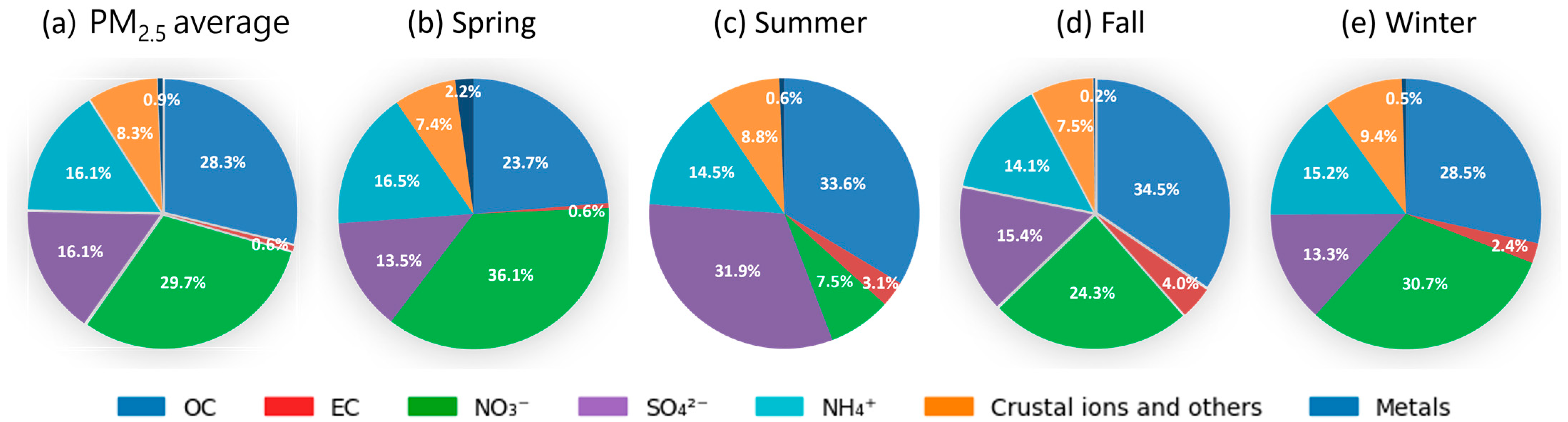
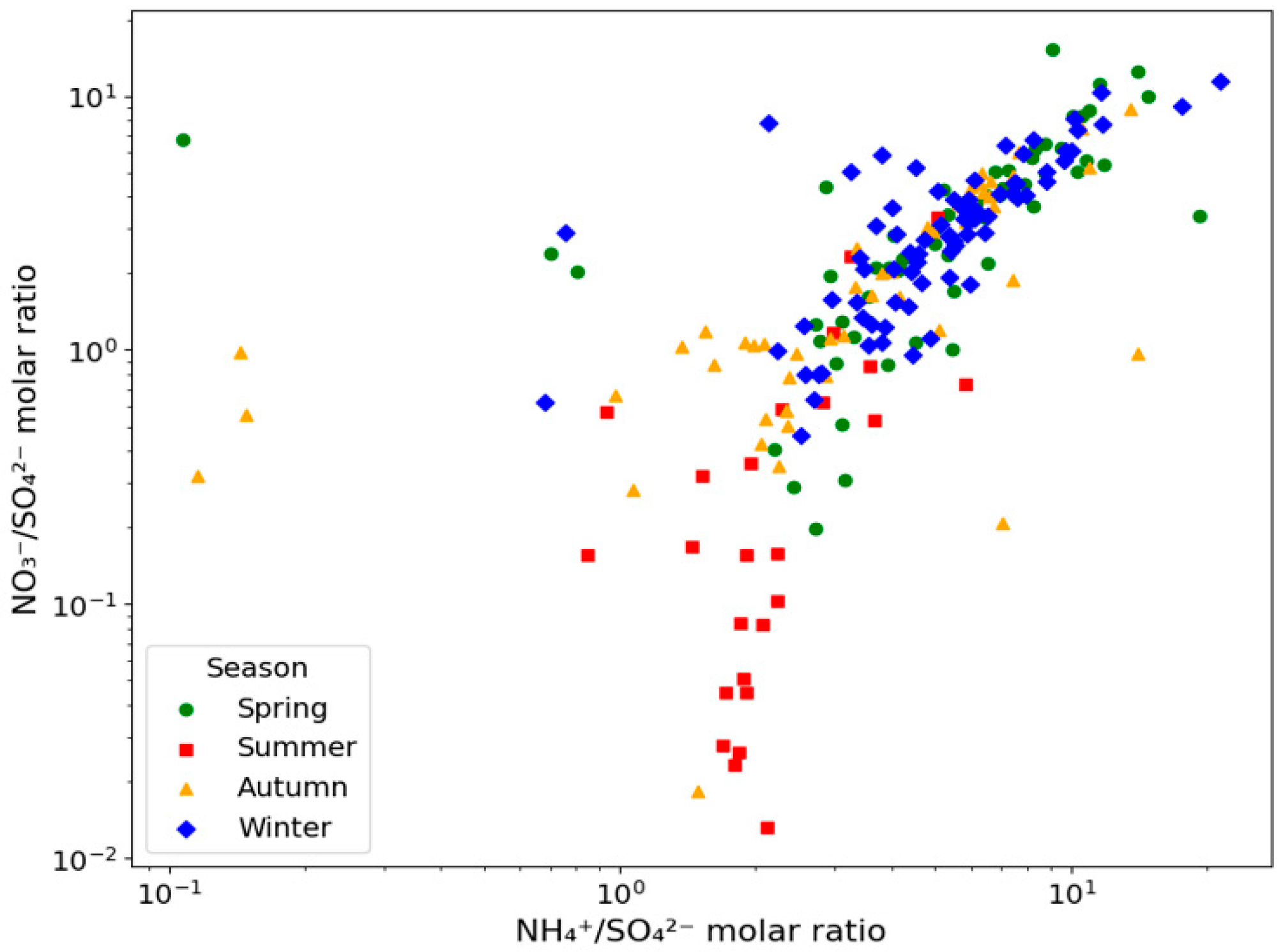
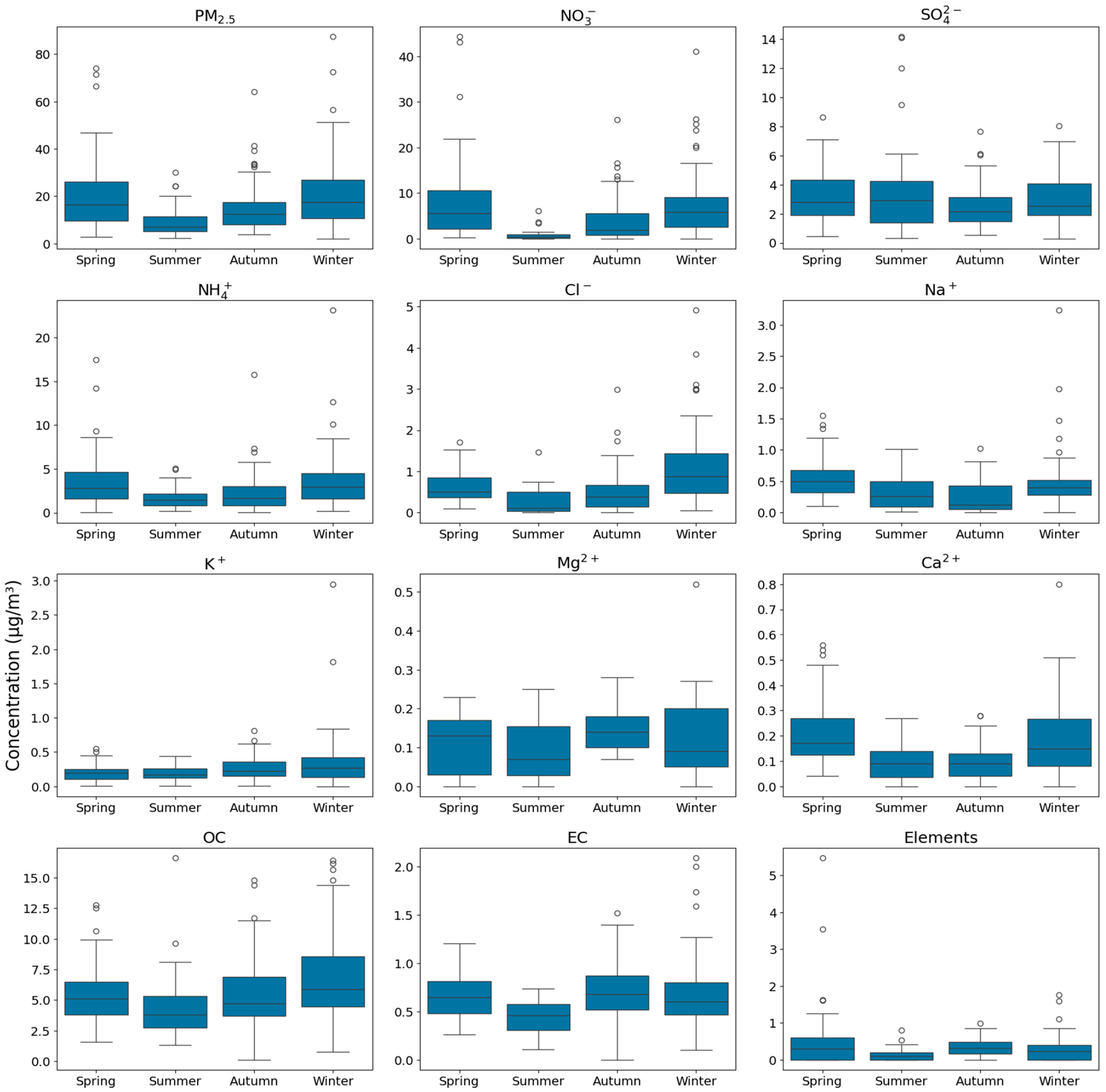
3.2. PM2.5 Seasonal Distribution and Chemical Components
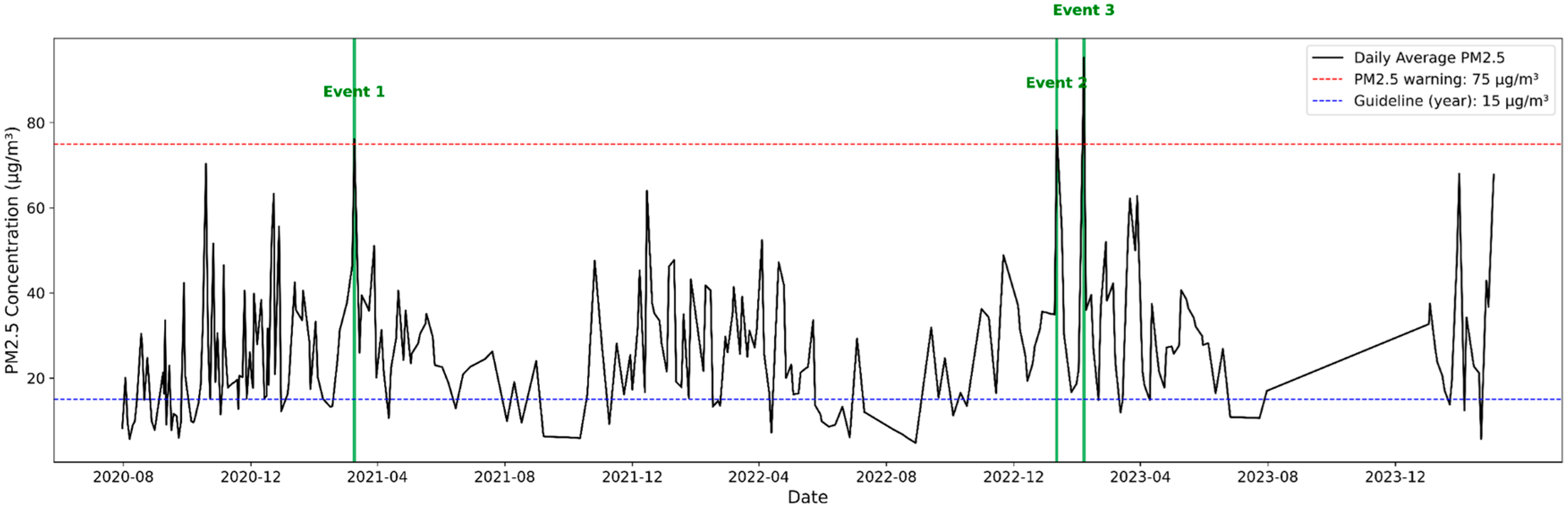
3.3. Characteristics of High-Concentration PM2.5 Components
4. Causes of High-Concentration Occurrences
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saini, P.; Sharma, M. Cause and age-specific premature mortality attributable to PM2.5 exposure: An analysis for million-plus Indian cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 135230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Guo, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, L. Spatiotemporal patterns and equity analysis of premature mortality due to ischemic heart disease attributable to PM2.5 exposure in China: 2007–2022. Toxics 2024, 12, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines: Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10), Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/345329 (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- Fortoul, T.I.; Rodriguez-Lara, V.; Gonzalez-Villalva, A.; Rojas-Lemus, M.; Colin-Barenque, L.; Bizarro-Nevares, P.; García-Peláez, I.; Ustarroz-Cano, M.; López-Zepeda, S.; Cervantes-Yépez, S.; et al. Health Effects of Metals in Particulate Matter. In Current Air Quality Issues; Nejadkoorki, F., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, Y.; Xu, L.; Chen, Y.; Du, W.; Chen, J. Optical properties of PM2.5 and the impacts of chemical compositions in the coastal city Xiamen in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 557–558, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamra, G.B.; Guha, N.; Cohen, A.; Laden, F.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; Samet, J.M.; Vineis, P.; Forastiere, F.; Saldiva, P.; Yorifuji, T.; et al. Outdoor particulate matter exposure and lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 906–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Ho, C.-H.; Choi, Y.-S. High-PM10 concentration episodes in Seoul, Korea: Background sources and related meteorological conditions. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 7240–7247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.-Y.; Lee, D.-W.; Lee, H.; Kim, J.; Le, S.; Liu, Y. Assessment of long-range transboundary aerosols in Seoul, South Korea from geostationary ocean color imager (GOCI) and ground-based observations. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 115924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute of Environmental Research (NIER). Summary Report of the 4th Stage (2013–2017) LTP Project; National Institute of Environmental Research: Incheon, Republic of Korea, 2019.
- Kim, S.; Kim, O.; Kim, B.U.; Kim, H.C. Impact of emissions from major point sources in Chungcheongnam-do on surface fine particulate matter concentration in the surrounding area. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 33, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.C.; Park, S.S.; Bae, M.A.; Kim, S.T. A study on characteristics of high PM2.5 pollution observed around large-scale stationary sources in Chungcheongnam-do Province. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 36, 669–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.I.; Jung, J.Y.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, H.W.; Lee, J.I.; Lee, C.M. A comparison of health risks from PM2.5 and heavy metal exposure in industrial complexes in Dangjin and Yeosu·Gwangyang. Toxics 2024, 12, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chungcheongnam-do Provincial Government. Current Status of Industrial Complexes in Chungcheongnam-do. 2024. Available online: https://www.chungnam.go.kr/cnportal/main/contents.do?menuNo=501062 (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- Korea Industrial Complex Corporation (KICOX). Status of Tenant Companies in Industrial Complexes in Dangjin-Si, Chungcheongnam-do (as of 5 July 2024). 2024. Available online: https://www.kicox.or.kr (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- Park, S.; Shin, H. Analysis of the factors influencing PM2.5 in Korea: Focusing on seasonal factors. J. Environ. Policy 2017, 25, 227–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myong, J.-P. Health effects of particulate matter. Korean J. Med. 2016, 91, 106–113, (In Korean with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Park, S.Y.; Jang, H.; Lee, C.M. Spatiotemporal distribution characterization and source estimation of PM2.5 components in the Ulsan Industrial Complex. Asian J. Atmos. Environ. 2025, 19, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute of Environmental Research (NIER). Air Pollution Monitoring Network Installation and Operation Guidelines; Ministry of the Environment: Sejong, Republic of Korea, 2021.
- Qiu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Man, R.; Zong, T.; Liu, Y.; Meng, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, S.; Yang, S.; Yuan, B.; et al. Secondary aerosol formation drives atmospheric particulate matter pollution over megacities (Beijing and Seoul) in East Asia. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 301, 119702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Wu, L.; Guo, J.; Chen, W.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; et al. Measurement report: Vertical distribution of atmospheric particulate matter within the urban boundary layer in southern China—Size-segregated chemical composition and secondary formation through cloud processing and heterogeneous reactions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 6435–6453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, N.; Xu, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, G.; Liu, W.; Zhuoga, D.; Xiao, D.; Yao, J. Characteristics of size distributions and sources of water-soluble ions in Lhasa during monsoon and non-monsoon seasons. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 82, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Qiu, R.; Chan, C.K.; Ravi Kant, P.R. Evidence of high PM2.5 strong acidity in ammonia-rich atmosphere of Guangzhou, China: Transition in pathways of ambient ammonia to form aerosol ammonium at [NH4+]/[SO42−] = 1.5. Atmos. Res. 2011, 99, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Ding, S.Y.; Ji, C.W.; Li, Q.K.; Li, X.D. Combustion related ammonia promotes PM2.5 accumulation in autumn in Tianjin, China. Atmos. Res. 2022, 275, 106225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lu, X.; Zhai, J.; Chen, H.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Fu, Q.; Sha, F.; Jin, J. Insights into the formation of secondary organic carbon in the summertime in urban Shanghai. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 72, 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Schnelle-Kreis, J.; Abbaszade, G.; Zimmermann, R.; Zotter, P.; Shen, R.R.; Schäfer, K.; Shao, L.; Prévôt, A.S.H.; Szidat, S. Source apportionment of elemental carbon in Beijing, China: Insights from radiocarbon and organic marker measurements. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8408–8415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Ni, H.; Cao, J.; Han, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.W.A.; Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Wei, C.; et al. Characteristics of carbonaceous particles from residential coal combustion and agricultural biomass burning in China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2017, 8, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Huang, R.J.; Cao, J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, T.; Wang, M.; Meijer, H.A.J.; Dusek, U. Source apportionment of carbonaceous aerosols in Xi’an, China: Insights from a full year of measurements of radiocarbon and the stable isotope 13C. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 16363–16383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Guo, L.; Wang, Z.; Tian, Y.; Yue, C.; Zhou, X.; Wang, W.; Xin, J.; Lü, C. Geochemical characteristics and socioeconomic associations of carbonaceous aerosols in coal-fueled cities with significant seasonal pollution pattern. Environ. Int. 2023, 179, 108179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, T.; Wang, Y. Nationwide summer peaks of OC/EC ratios in the contiguous United States. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; He, K.B.; Duan, F.K.; Zheng, M.; Du, Z.Y.; Ma, Y.L.; Tan, J.H. Ambient Organic Carbon to Elemental Carbon Ratios: Influences of the Measurement Methods and Implications. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2060–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute of Environmental Research (NIER). Annual Report of Intensive Air Quality Monitoring Station; National Institute of Environmental Research: Incheon, Republic of Korea, 2018.
- Shi, X.; Nenes, A.; Xiao, Z.; Song, S.; Yu, H.; Shi, G.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, K.; Feng, Y.; Russell, A.G. High-resolution data sets unravel the effects of sources and meteorological conditions on nitrate and its gas-particle partitioning. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 3048–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, N.D.; Hieu, B.T.; Hiep, N.H. Contrasting seasonal pattern between ground-based PM2.5 and MODIS satellite-based aerosol optical depth (AOD) at an urban site in Hanoi, Vietnam. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 41971–41982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.S.; Flechard, C.R.; Dämmgen, U.; Vidic, S.; Djuricic, V.; Mitosinkova, M.; Uggerud, H.T.; Sanz, M.J.; Simmons, I.; Dragosits, U.; et al. Pan-European rural monitoring network shows dominance of NH3 gas and NH4NO3 aerosol in inorganic atmospheric pollution load. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 875–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, L.; Yu, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y. Impact of precursor gases and meteorological variables on satellite-estimated near-surface sulfate and nitrate concentrations over the North China Plain. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 199, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, T.; Xia, M.; Gao, X.; Li, Q.; Zhang, N.; Gao, Y.; Lee, S.; Wang, X.; Xue, L.; et al. Abundance and origin of fine particulate chloride in continental China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 624, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatoutsidou, S.E.; Lazaridis, M. Mass concentrations and elemental analysis of PM2.5 and PM10 in a coastal Mediterranean site: A holistic approach to identify contributing sources and varying factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 155980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Sarin, M.M. Atmospheric water-soluble constituents in fine and coarse mode aerosols from high-altitude site in western India: Long-range transport and seasonal variability. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 1245–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Yang, Y.; Luo, H.; Zhao, R.; Pan, N.; Lin, J.; Yang, L. Transport pathways of PM10 during the spring in northwest China and its characteristics of potential dust sources. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 237, 117746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhan, Y.; Li, J.; Chao, C.Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, C.; Jia, S.; Ma, L.; Biswas, P. Using Kriging Incorporated with Wind Direction to Investigate Ground-Level PM2.5 Concentration. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 141813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, M.; Guan, H.; Luo, L.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, Z. Using Nitrogen and Oxygen Stable Isotopes to Analyze the Major NOx Sources to Nitrate of PM2.5 in Lanzhou, Northwest China, in Winter–Spring Periods. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 276, 119036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhang, C.; Xue, C.; Mu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, D.; Ye, C.; Zhang, H.; Guan, J. The Contribution of Residential Coal Combustion to Atmospheric PM2.5 in Northern China during Winter. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 11503–11520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Li, Q.; Xiong, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, S.; Ding, Y. Enhanced Secondary Organic Aerosol Formation during Dust Episodes by Photochemical Reactions in the Winter in Wuhan. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 133, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, W.; Chen, Z.; Zeng, G.; Hu, C.; León, T.; Liang, J.; Huang, G.; Gao, Z.; Li, Z.; et al. The Application of Semicircular-Buffer-Based Land Use Regression Models Incorporating Wind Direction in Predicting Quarterly NO2 and PM10 Concentrations. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 103, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Han, Y.; Shi, A.; Sun, X.; Yan, X.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y. Characteristics of Ambient Ammonia and Its Effects on Particulate Ammonium in Winter of Urban Beijing, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 62828–62838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Substance (Unit) | N | Mean | S.D. | Max | p-Value a | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 (μg/m3) | 245 | 26.22 | 15.29 | 95.31 | 0.047 | |
| Ion (μg/m3) | Cl− | 245 | 0.66 | 0.68 | 4.91 | 0.000 |
| NO3− | 245 | 5.69 | 7.02 | 44.29 | 0.058 | |
| SO42− | 245 | 2.90 | 2.12 | 14.18 | 0.002 | |
| Na+ | 245 | 0.37 | 0.36 | 3.23 | 0.000 | |
| NH4+ | 245 | 2.82 | 2.93 | 23.08 | 0.023 | |
| K+ | 209 | 0.27 | 0.27 | 3.00 | 0.000 | |
| Mg2+ | 127 | 0.11 | 0.08 | 1.00 | 0.078 | |
| Ca2+ | 245 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.80 | 0.000 | |
| Carbon (μg/m3) | EC | 280 | 0.64 | 0.29 | 2.09 | 0.060 |
| OC | 280 | 5.58 | 2.95 | 16.62 | 0.448 | |
| Elements (ng/m3) | Al | 51 | 324.74 | 627.24 | 3680 | 0.027 |
| Ti | 245 | 8.31 | 12.23 | 140.61 | 0.000 | |
| V | 245 | 1.10 | 1.22 | 6.48 | 0.000 | |
| Mn | 245 | 17.12 | 15.48 | 78.68 | 0.000 | |
| Fe | 245 | 193.80 | 186.70 | 1549.08 | 0.000 | |
| Ni | 245 | 1.54 | 1.91 | 20.09 | 0.000 | |
| Co | 245 | 1.01 | 1.04 | 8.22 | 0.000 | |
| Cu | 245 | 7.27 | 7.68 | 42.44 | 0.000 | |
| Zn | 245 | 62.24 | 51.21 | 234.06 | 0.000 | |
| As | 225 | 3.28 | 4.95 | 37.00 | 0.000 | |
| Sr | 245 | 0.65 | 1.02 | 6.33 | 0.000 | |
| Mo | 140 | 1.35 | 1.98 | 12.00 | 0.000 | |
| Cd | 245 | 1.82 | 3.34 | 22.09 | 0.000 | |
| Ba | 245 | 5.36 | 7.06 | 39.82 | 0.000 | |
| Pb | 245 | 23.31 | 49.52 | 621.90 | 0.003 | |
| P | 245 | 5.69 | 8.32 | 54.80 | 0.000 | |
| S | 245 | 928.19 | 962.45 | 4909.62 | 0.000 | |
| Cr | 245 | 2.43 | 2.72 | 22.85 | 0.000 | |
| Si | 245 | 302.29 | 563.26 | 6458.81 | 0.000 | |
| Spring | NO3− | SO42− | NH4+ | OC | Summer | NO3− | SO42− | NH4+ | OC |
| SO42− | 0.51 | SO42− | –0.15 | ||||||
| NH4+ | 0.85 | 0.67 | NH4+ | 0.15 | 0.92 | ||||
| OC | 0.55 | 0.34 | 0.62 | OC | 0.79 | –0.07 | 0.19 | ||
| EC | 0.47 | 0.26 | 0.46 | 0.78 | EC | 0.52 | 0.09 | 0.27 | 0.50 |
| Fall | NO3− | SO42− | NH4+ | OC | Winter | NO3− | SO42− | NH4+ | OC |
| SO42− | 0.64 | SO42− | 0.74 | ||||||
| NH4+ | 0.92 | 0.73 | NH4+ | 0.94 | 0.76 | ||||
| OC | 0.62 | 0.31 | 0.54 | OC | 0.69 | 0.48 | 0.62 | ||
| EC | 0.41 | 0.26 | 0.41 | 0.87 | EC | 0.32 | 0.12 | 0.26 | 0.72 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.-h.; Park, S.-Y.; Jang, H.; Moon, J.-E.; Lee, C.-M. Characteristics of the Chemical Components of PM2.5 in the Dangjin Region, South Korea, and Evaluation of Emission Source Contributions During High-Concentration Events. Toxics 2025, 13, 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13100869
Kim Y-h, Park S-Y, Jang H, Moon J-E, Lee C-M. Characteristics of the Chemical Components of PM2.5 in the Dangjin Region, South Korea, and Evaluation of Emission Source Contributions During High-Concentration Events. Toxics. 2025; 13(10):869. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13100869
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Young-hyun, Shin-Young Park, Hyeok Jang, Ji-Eun Moon, and Cheol-Min Lee. 2025. "Characteristics of the Chemical Components of PM2.5 in the Dangjin Region, South Korea, and Evaluation of Emission Source Contributions During High-Concentration Events" Toxics 13, no. 10: 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13100869
APA StyleKim, Y.-h., Park, S.-Y., Jang, H., Moon, J.-E., & Lee, C.-M. (2025). Characteristics of the Chemical Components of PM2.5 in the Dangjin Region, South Korea, and Evaluation of Emission Source Contributions During High-Concentration Events. Toxics, 13(10), 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13100869






