QTAIM Based Computational Assessment of Cleavage Prone Bonds in Highly Hazardous Pesticides
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Pesticide Classification
2.2. Computational Details
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Topological Analyses of Thiophosphate Molecules
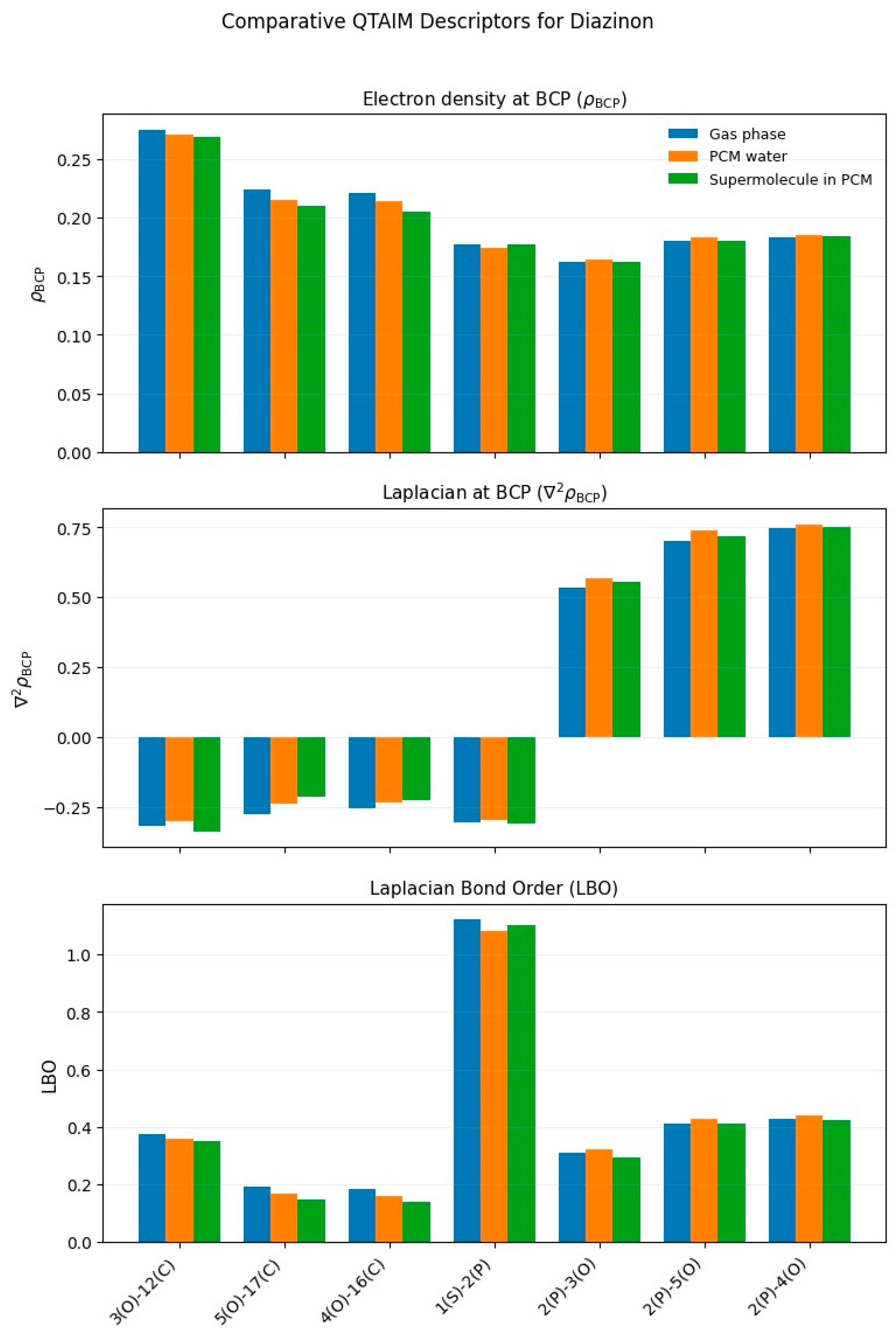
3.1.1. Diazinon
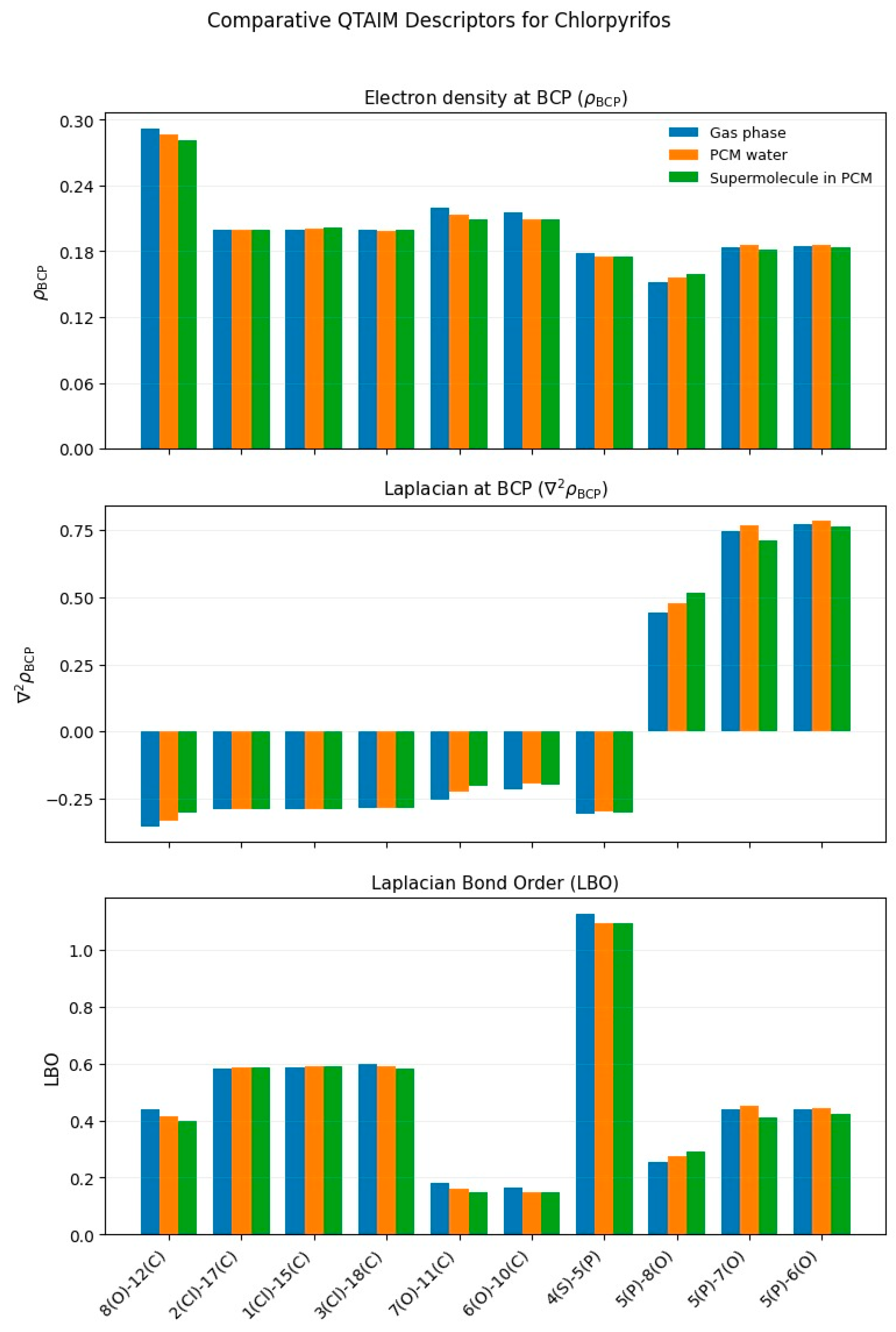
3.1.2. Chlorpyriphos
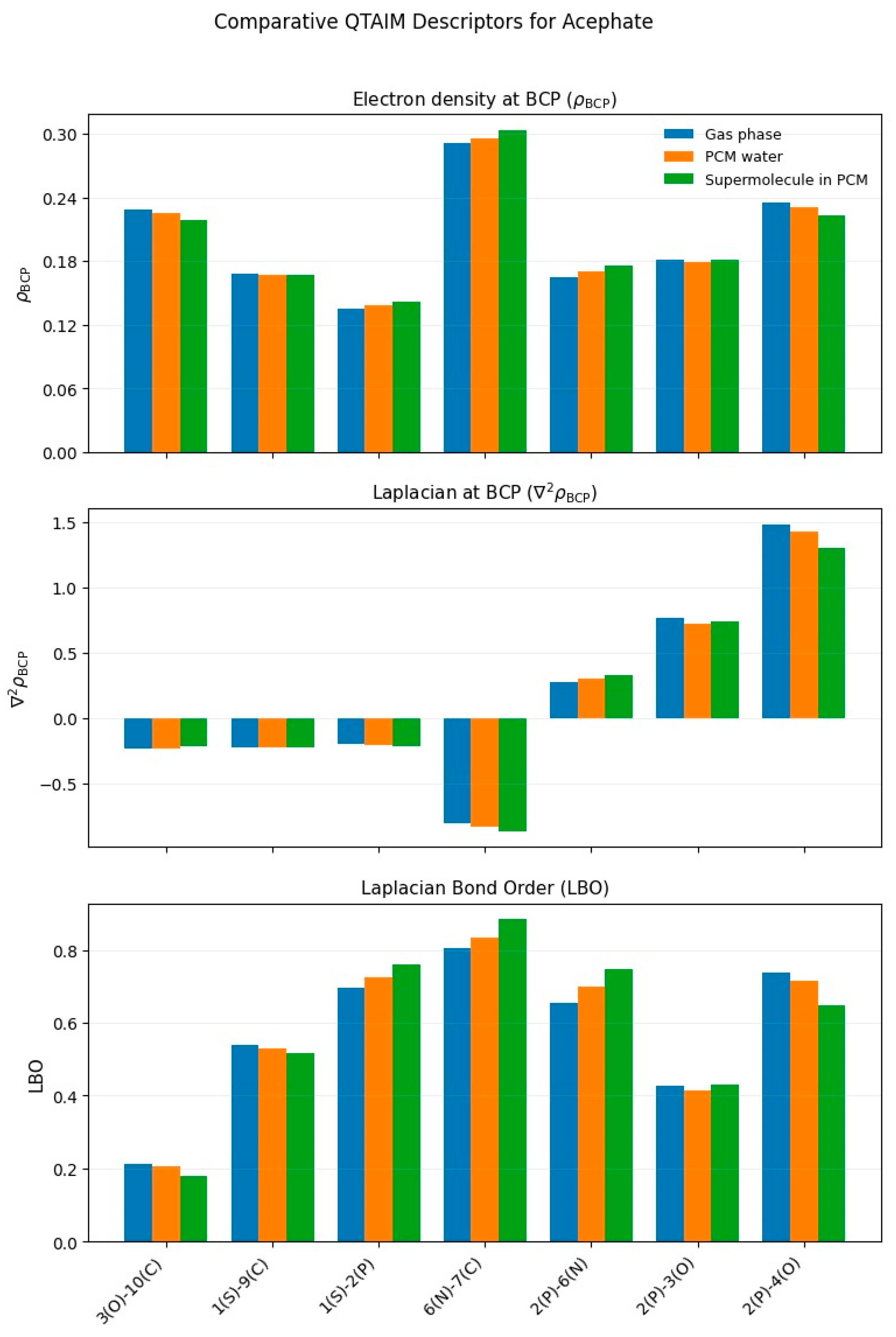
3.1.3. Acephate
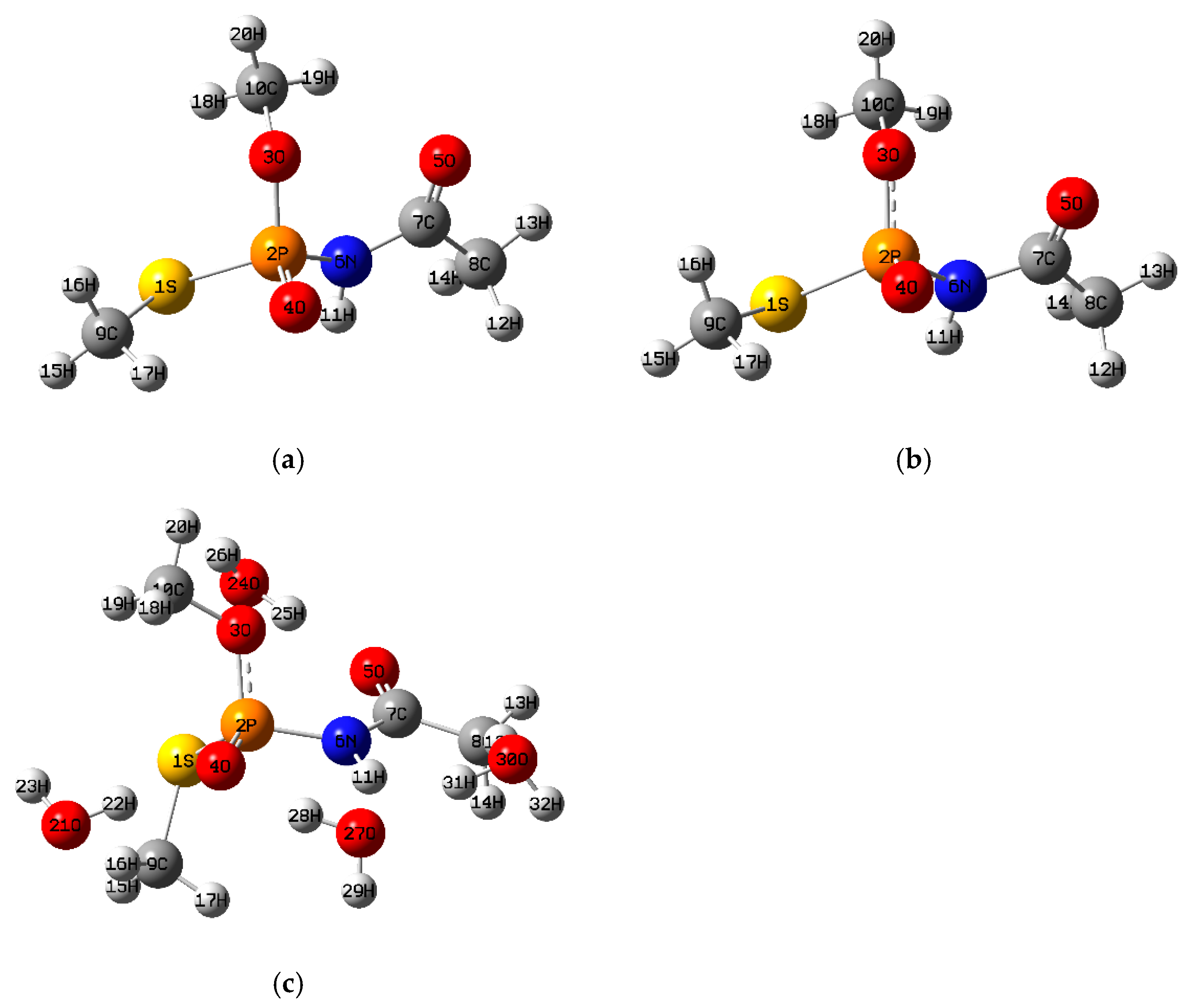
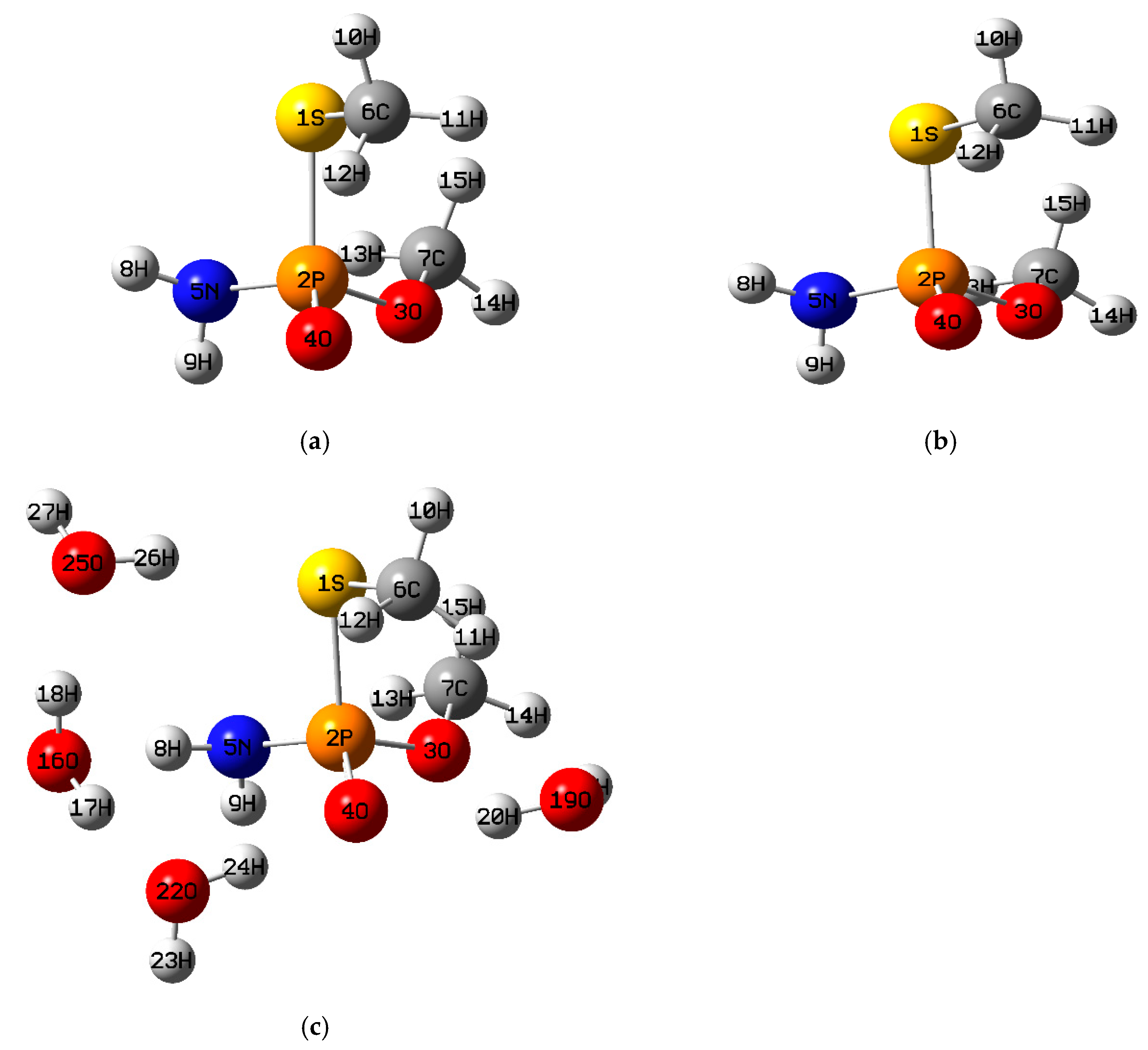
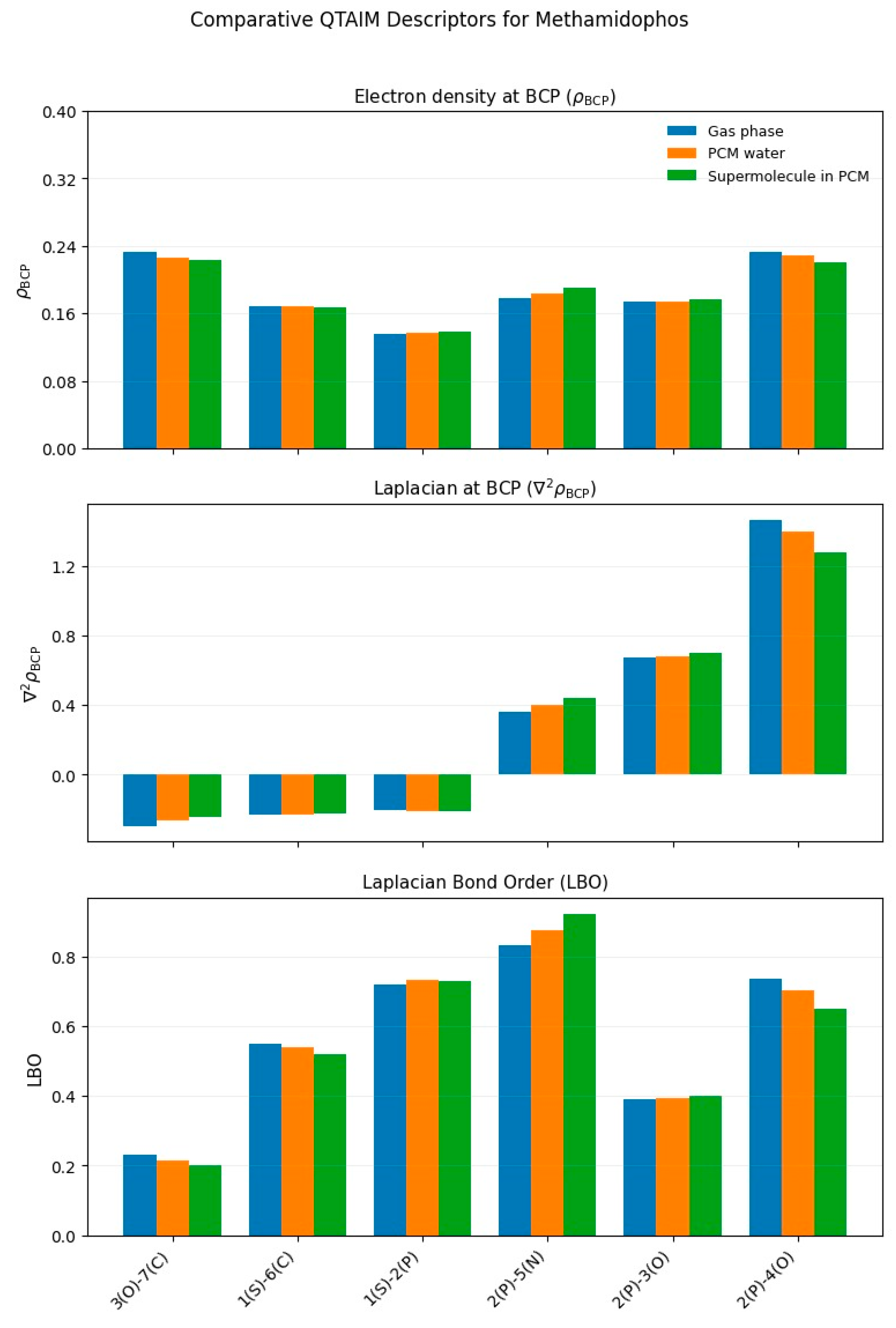
3.1.4. Methamidophos
3.2. Comparative Analysis Across Pesticides
4. Global and Local Reactivity Descriptors
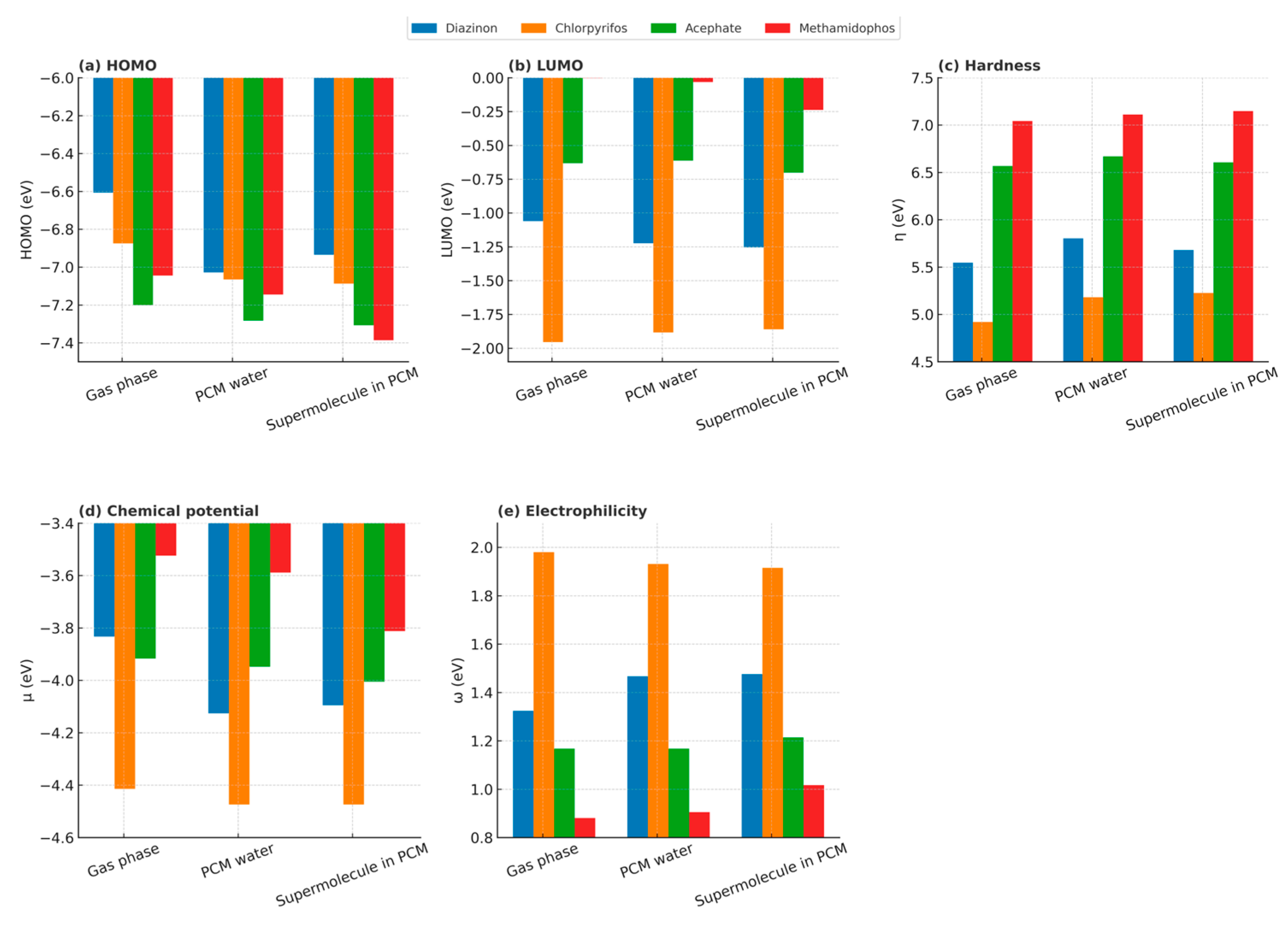
4.1. Influence of Solvation on Frontier Molecular Orbitals and Global Reactivity Descriptors
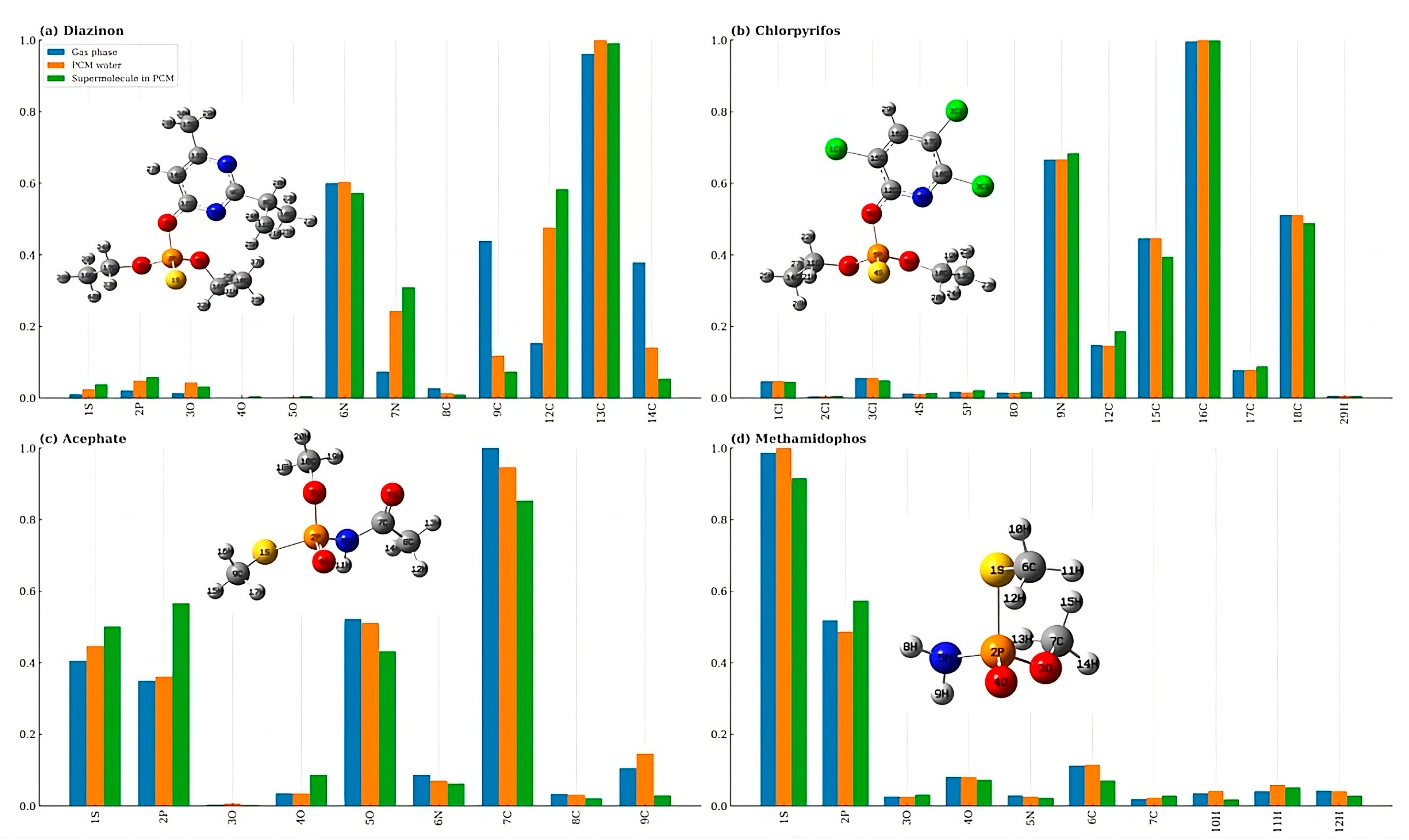
4.2. The Condensed Electrophilic Fukui Functions (f+) and Solvent Effects
4.3. Topological Analysis of the Fukui Function (TAFF)
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Elgueta, S.; Valenzuela, M.; Fuentes, M.; Ulloa, P.; Ramos, C.; Correa, A.; Molinett, S. Analysis of multi-pesticide residues and dietary risk assessment in fresh tomatoes (Lycopersicum esculentum) from local supermarkets of the metropolitan region, Chile. Toxics 2021, 9, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inostroza, P.A.; Elgueta, S.; Krauss, M.; Brack, W.; Backhaus, T. A multi-scenario risk assessment strategy applied to mixtures of chemicals of emerging concern in the River Aconcagua basin in Central Chile. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 921, 171054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conejo-Bolaños, L.D.; Mora, A.M.; Hernández-Bonilla, D.; Cano, J.C.; Menezes-Filho, J.A.; Eskenazi, B.; Lindh, C.H.; van Wendel de Joode, B. Prenatal current-use pesticide exposure and children’s neurodevelopment at one year of age in the Infants’ Environmental Health (ISA) birth cohort, Costa Rica. Environ. Res. 2024, 249, 118222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Peer review of the pesticide risk assessment of the active substance chlorpyrifos. EFSA J. 2019, 17, e05790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, D.L.; Daroff, R.B.; Autrup, H.; Bridges, J.; Buffler, P.; Costa, L.G.; Coyle, J.; McKhann, G.; Mobley, W.C.; Nadel, L.; et al. Review of the toxicology of chlorpyrifos with an emphasis on human exposure and neurodevelopment. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2008, 38, 1–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauh, V.; Arunajadai, S.; Horton, M.; Perera, F.; Hoepner, L.; Barr, D.B.; Whyatt, R. Seven-Year Neurodevelopmental Scores and Prenatal Exposure to Chlorpyrifos, a Common Agricultural Pesticide. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1196–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkey, A.B.; Pippen, E.; Kenou, B.; Holloway, Z.; Slotkin, T.A.; Seidler, F.J.; Levin, E.D. Persistent Neurobehavioral and Neurochemical Anomalies in Middle-Aged Rats after Maternal Diazinon Exposure. Toxicology 2022, 472, 153189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Targeted review of maximum residue levels (MRLs) for diazinon. EFSA J. 2023, 21, 8426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, C.S.; Dutra-Tavares, A.C.; Nunes, F.; Nunes-Freitas, A.L.; Ribeiro-Carvalho, A.; Filgueiras, C.C.; Manhães, A.C.; Meyer, A.; Abreu-Villaça, Y. Exposure to methamidophos at adulthood elicits depressive-like behavior in mice. Neurotoxicology 2009, 30, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, C.S.; Dutra-Tavares, A.C.; Nunes, F.; Nunes-Freitas, A.L.; Ribeiro-Carvalho, A.; Filgueiras, C.C.; Manhães, A.C.; Meyer, A.; Abreu-Villaça, Y. Methamidophos Exposure During the Early Postnatal Period of Mice: Immediate and Late-Emergent Effects on the Cholinergic and Serotonergic Systems and Behavior. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 134, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, R.K.; Rodrigues, T.C.; Júnior, W.D.; Mota, G.M.P.; Andersen, M.L.; Mazaro, E.C.; Costa, R. Short- and long-term exposure to methamidophos impairs spermatogenesis in mice. Reprod. Biol. 2020, 20, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, A.T.; Eweidah, M.H.; El-Okazy, A.M. Reproductive toxicology of acephate in male mice. Reprod. Toxicol. 2000, 14, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, A.T.; Eweidah, M.H.; El-Sebae, A.H. Developmental toxicity of acephate by gavage in mice. Reprod. Toxicol. 2000, 14, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilber, I.; Bahena-Juárez, F.; Chiaia-Hernández, A.C.; Elgueta, S.; Escobar-Medina, A.; Friedrich, K.; González-Curbelo, M.Á.; Grob, Y.; Martín-Fleitas, M.; Miglioranza, K.S.B.; et al. Pesticides in soil, groundwater and food in Latin America as part of one health. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 14333–14345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO); World Health Organization (WHO). International Code of Conduct on Pesticide Management: Guidelines on Highly Hazardous Pesticides; FAO/WHO: Rome, Italy, 2016; Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/i5566e/i5566e.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2016).
- World Health Organization (WHO). The WHO Recommended Classification of Pesticides by Hazard and Guidelines to Classification 2019; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240005662 (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Bader, R.F.W. Atoms in molecules. Acc. Chem. Res. 1985, 18, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, R.F.W. A Quantum Theory of Molecular Structure and Its Applications. Chem. Rev. 1991, 91, 893–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.S.V.; Raghavendra, V.; Subramanian, V. Bader’s Theory of Atoms in Molecules (AIM) and its Applications to Chemical Bonding. J. Chem. Sci. 2016, 128, 1527–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klyukin, I.N.; Kolbunova, A.V.; Novikov, A.S.; Zhizhin, K.Y.; Kuznetsov, N.T. Theoretical Investigation of Bond Dissociation Energies of exo-Polyhedral B–H and B–F Bonds of closo-Borate Anions [BnHn−1X]2− (n = 6, 10, 12; X = H, F). Computation 2025, 13, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, F.; Wang, B.; Cao, Z. Degradation of pesticides diazinon and diazoxon by phosphotriesterase: Insight into divergent mechanisms from QM/MM and MD simulations. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2022, 24, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Wu, W.; Zhu, Z.; Zhu, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Fan, Z.; Chen, Y. Structure identification and toxicity evaluation of one newly-discovered dechlorinated photoproducts of chlorpyrifos. Chemosphere 2022, 301, 134822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, J.; Wu, N.; Xu, X.; Qi, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z. Oxidative degradation of chlorpyrifos using ferrate(VI): Kinetics and reaction mechanism. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 170, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, C.; Wang, L.; Du, X.; Zhu, L.; Wang, J.; Mo Kim, Y.; Wang, J. Biodegradation mechanism of chlorpyrifos by Bacillus sp. H27: Degradation enzymes, products, pathways and whole genome sequencing analysis. Environ. Res. 2023, 239, 117315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Sun, X.; Gao, R.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, W. Mechanism study on OH-initiated atmospheric degradation of the organophosphorus pesticide chlorpyrifos. J. Mol. Struct. THEOCHEM 2010, 952, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.L.; Chang, C.M. Quantum Chemical Approach to the Adsorption of Chlorpyrifos and Fenitrothion on the Carbon-Doped Boron Nitride Nanotube Decorated with Tetrapeptide. Crystals 2022, 12, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyguda-Kazimierowicz, E.; Roszak, S.; Sokalski, W.A. Alkaline hydrolysis of organophosphorus pesticides: The dependence of the reaction mechanism on the incoming group conformation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 7277–7289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, S.; Sun, J.; Lu, C.; Tang, Y. A new theoretical investigation on ·OH initiated oxidation of acephate in the environment: Mechanism, kinetics, and toxicity. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2022, 24, 1912–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; White, T.; Spassova, D.; Jiang, Y. Physicochemical, Molecular-Orbital and Electronic Properties of Acephate and Methamidophos. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Pharmacol. Toxicol. Endocrinol. 1998, 119, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zhang, L.; Luo, X.; Liang, G. Hydrolysis of an organophosphorus pesticide: A theoretical investigation of the reaction mechanism for acephate. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2018, 137, 2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zhang, K.; Lu, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhang, H. Theoretical study on the degradation mechanism of methamidophos and chloramine phosphorus with OH radicals. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2015, 115, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rifai, A.; Bourcier, S.; Jaber, F.; Bouchoux, G. Structures and dissociation mechanisms of protonated and electron ionized methamidophos. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2013, 339–340, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khavidaki, H.D.; Soleymani, M.; Shirzadi, S. A DFT study on adsorption of diazinon and fenitrothion on nanocages B12N12 and B12P12. Struct. Chem. 2022, 34, 1133–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-H.; Huang, W.-J.; Xu, T.-L.; Kirk, S.R.; Jenkins, S. Stress Tensor Eigenvector Following with Next-Generation Quantum Theory of Atoms in Molecules. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1809.06732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Chen, D.; Parales, R.E.; Jiang, J. Oxygenases as Powerful Weapons in the Microbial Degradation of Pesticides. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 76, 325–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, S.; Gee, W.; Alexandrova, A. High-throughput quantum theory of atoms in molecules (QTAIM) for geometric deep learning of molecular and reaction properties. Digit. Discov. 2024, 3, 987–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodakarami, M.; Rahman, M.H.; Misra, M.; Menezes, P. Structure-property-biodegradability relationships in phosphonium-based ionic liquids: Experimental investigation and DFT computations. J. Mol. Struct. 2025, 1349, 143764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Martínez, C.; Zárate-Hernández, L.; Camacho-Mendoza, R.; González-Montiel, S.; Meneses-Viveros, A.; Cruz-Borbolla, J. The use of global and local reactivity descriptors of conceptual DFT to describe toxicity of benzoic acid derivatives. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2023, 1226, 114211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PPDB: Pesticide Properties DataBase. University of Hertfordshire. Available online: https://sitem.herts.ac.uk/aeru/ppdb/ (accessed on 15 August 2025).
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16, Revision C.01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, T.; Chen, F. Multiwfn: A multifunctional wavefunction analyzer. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 33, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Chen, F. Bond Order Analysis Based on the Laplacian of Electron Density in Fuzzy Overlap Space. J. Phys. Chem. A. 2013, 117, 3100–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matta, C.F.; Boyd, R.J. The Quantum Theory of Atoms in Molecules: From Solid State to DNA and Drug Design; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2007; pp. 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasi, J.; Mennucci, B.; Cammi, R. Quantum Mechanical Continuum Solvation Models. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 2999–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelsky, S.I. AOMix: Program for Molecular Orbital Analysis. 2012. Available online: https://www.sg-chem.net/aomix.html (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Pino-Rios, R.; Yañez, O.; Inostroza, D.; Ruiz, L.; Cardenas, C.; Fuentealba, P.; Tiznado, W. Proposal of a simple and effective local reactivity descriptor through a topological analysis of an orbital weighted Fukui function. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2017, 38, 481–488. Available online: https://github.com/HumanOsv/TAFF (accessed on 22 October 2015). [CrossRef]
- Shemer, H.; Linden, K.G. Degradation and by-product formation of diazinon in water during UV and UV/H2O2 treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari, G.; Seidmohammadi, A.; Esrafili, A.; Faradmal, J.; Noori Sepehr, M.; Jafarinia, M. The catalytic ozonation of diazinon using nano-MgO@CNT@Gr as a new heterogenous catalyst: The optimization of effective factors by response surface methodology. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 7718–7731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishido, T.; Usui, K.; Sato, M.; Fukaixi, J.-I. Enzymatic Conjugation of Diazinon with Glutathione in Rat and American Cockroach. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 1972, 2, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, J.; Zhou, Z.; Lin, Z.; Pang, S.; Bhatt, P.; Mishra, S.; Chen, S. Environmental Occurrence, Toxicity Concerns, and Degradation of Diazinon Using a Microbial System. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 717286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Pehkonen, S.O. Oxidation of diazinon by aqueous chlorine: Kinetics, mechanisms, and product studies. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 1760–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bempelou, E.D.; Vontas, J.G.; Liapis, K.S.; Ziogas, V.N. Biodegradation of chlorpyrifos and 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol by the epiphytic yeasts Rhodotorula glutinis and Rhodotorula rubra. Ecotoxicology 2018, 27, 1368–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basfar, A.A.; Mohamed, K.A.; Al-Abduly, A.J.; Al-Kuraiji, T.S.; Al-Shahrani, A.A. Degradation of diazinon contaminated waters by ionizing radiation. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2007, 76, 1474–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Chen, F.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Hu, X. The degradation of chlorpyrifos and diazinon in aqueous solution by ultrasonic irradiation: Effect of parameters and degradation pathway. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duirk, S.E.; Tarr, J.C.; Collette, T.W. Chlorpyrifos transformation by aqueous chlorine in the presence of bromide and natural organic matter. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 1328–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ying, R.; Wang, G.; Long, T.; Li, J.; Lin, Y. Thermoactivated persulfate oxidation of pesticide chlorpyrifos in aquatic system: Kinetic and mechanistic investigations. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 11549–11558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, L.G.; Murthy, B.N.; Kumar, S.G. Photocatalytic activity of V5+, Mo6+ and Th4+ doped polycrystalline TiO2 for the degradation of chlorpyrifos under UV/solar light. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2009, 308, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nthumbi, R.M.; Ngila, J.C. Electrospun and functionalized PVDF/PAN nanocatalyst-loaded composite for dechlorination and photodegradation of pesticides in contaminated water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 20214–20231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Fang, L.; Qin, H.; Chen, Y.; Wu, X.; Hua, R. Rapid biodegradation of the organophosphorus insecticide chlorpyrifos by Cupriavidus nantongensis x1T. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiny Raj, R.; Anoop Krishnan, K. A comprehensive review on the impact of emerging organophosphorous pesticides and their remedial measures: Special focus on acephate. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2023, 20, 100813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Chen, W.J.; Lin, Z.; Huang, Y.; el Sebai, T.N.M.; Alansary, N.; El-Hefny, D.E.; Mishra, S.; Bhatt, P.; Lü, H.; et al. Rapid Biodegradation of the Organophosphorus Insecticide Acephate by a Novel Strain Burkholderia sp. A11 and Its Impact on the Structure of the Indigenous Microbial Community. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 5261–5274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phugare, S.S.; Gaikwad, Y.B.; Jadhav, J.P. Biodegradation of acephate using a developed bacterial consortium and toxicological analysis using earthworms (Lumbricus terrestris) as a model animal. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2012, 69, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Wang, C.; Huhetaoli; Li, C.; Fan, B.; Niu, D. Biodegradation of acephate by Bacillus paramycoides NDZ and its degradation pathway. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 36, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Pang, S.; Zhang, W.; Mishra, S.; Bhatt, P.; Chen, S. Degradation of Acephate and Its Intermediate Methamidophos: Mechanisms and Biochemical Pathways. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyugi, A.M.; Kibet, J.K.; Adongo, J.O. A review on the biodegradation of acephate insecticides widely used in khat farming and horticultural crops. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2024, 105, 2513–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Kumar, V.; Singla, S.; Sharma, M.; Singh, D.P.; Prasad, R.; Thakur, V.K.; Singh, J. Kinetic study of the biodegradation of acephate by indigenous soil bacterial isolates in the presence of humic acid and metal ions. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wen, Y.; Guo, X.; Wang, G.; Li, S.; Jiang, J. Degradation of methamidophos by Hyphomicrobium species MAP-1 and the biochemical degradation pathway. Biodegradation 2010, 21, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentealba, P.; Florez, E.; Tiznado, W. Topological Analysis of the Fukui Function. Chem. Theory Comput. 2010, 6, 1470–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aracena, A.; Elgueta, S.; Pizarro, S.; Zúñiga, C. QTAIM Based Computational Assessment of Cleavage Prone Bonds in Highly Hazardous Pesticides. Toxics 2025, 13, 839. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13100839
Aracena A, Elgueta S, Pizarro S, Zúñiga C. QTAIM Based Computational Assessment of Cleavage Prone Bonds in Highly Hazardous Pesticides. Toxics. 2025; 13(10):839. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13100839
Chicago/Turabian StyleAracena, Andrés, Sebastián Elgueta, Sebastián Pizarro, and César Zúñiga. 2025. "QTAIM Based Computational Assessment of Cleavage Prone Bonds in Highly Hazardous Pesticides" Toxics 13, no. 10: 839. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13100839
APA StyleAracena, A., Elgueta, S., Pizarro, S., & Zúñiga, C. (2025). QTAIM Based Computational Assessment of Cleavage Prone Bonds in Highly Hazardous Pesticides. Toxics, 13(10), 839. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13100839








