Heavy Metal Pollution and Health-Ecological Risk Assessment in Agricultural Soils: A Case Study from the Yellow River Bend Industrial Parks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3. Pollution Assessment
2.3.1. Geoaccumulation Index
2.3.2. Potential Ecological Risk Index
2.3.3. Source Apportionment
2.3.4. Health Risk Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Descriptive Statistics of Heavy Metals in Soils of Agricultural Lands
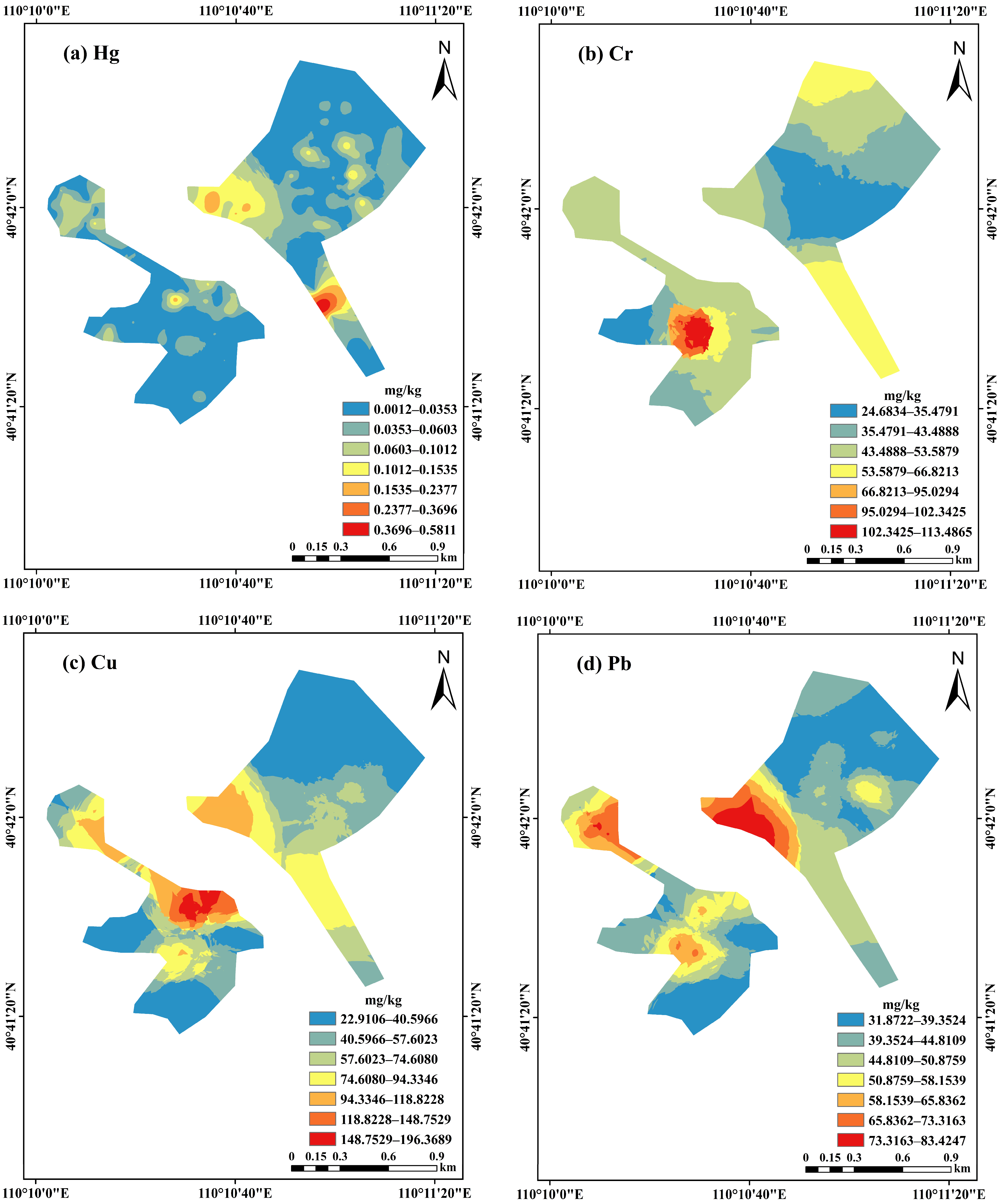
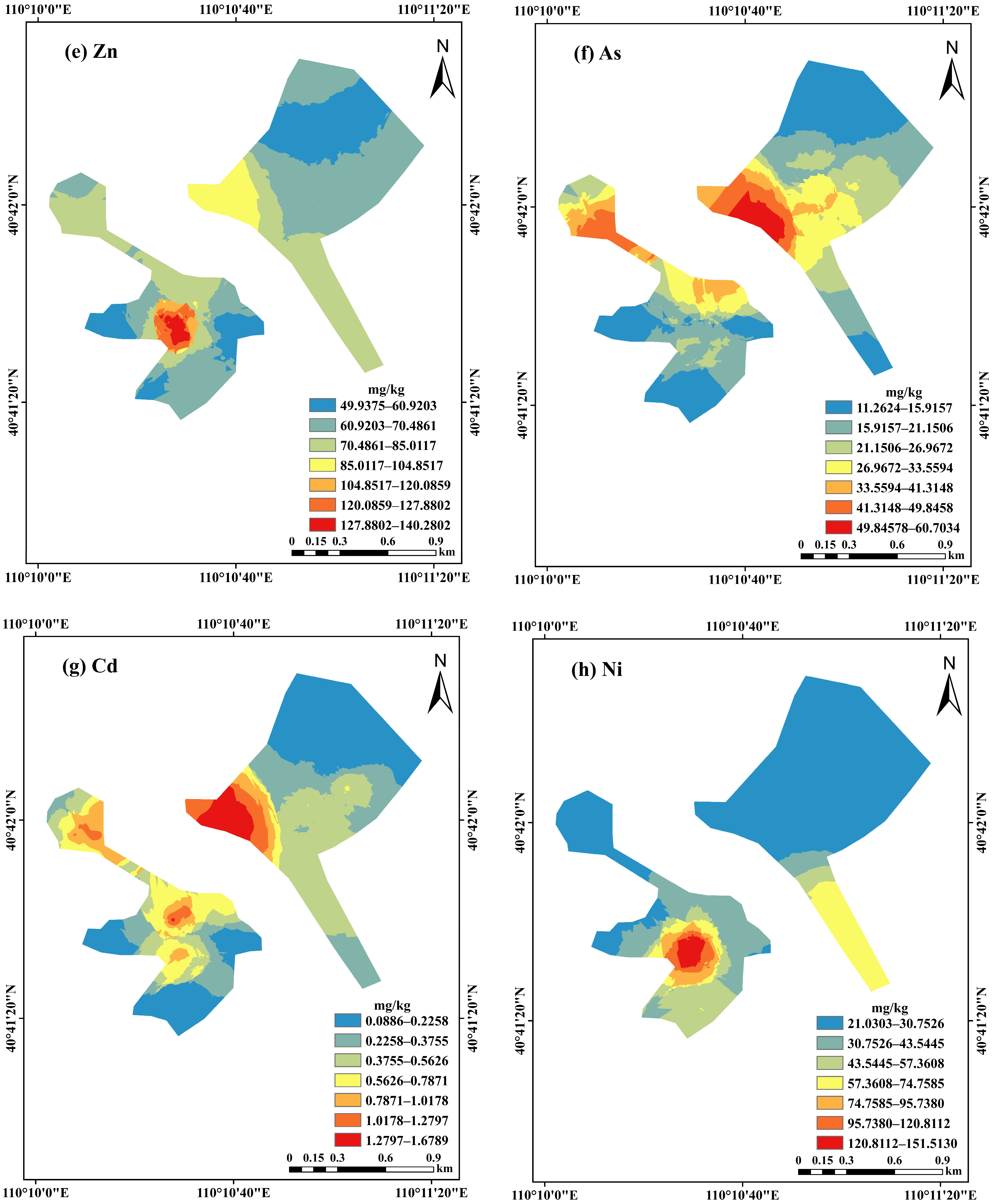
3.2. Spatial Distribution of Heavy Metals in Soils
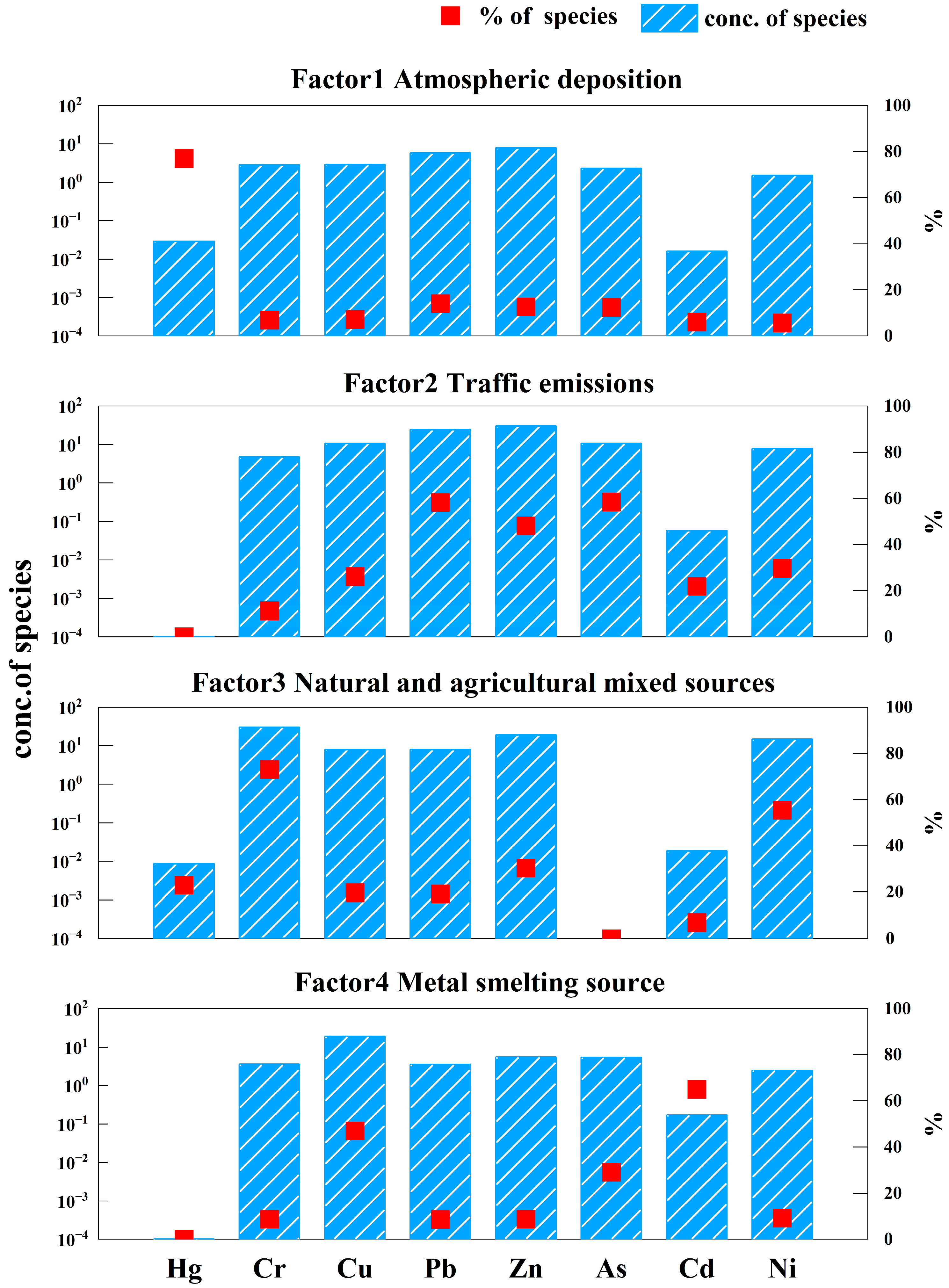
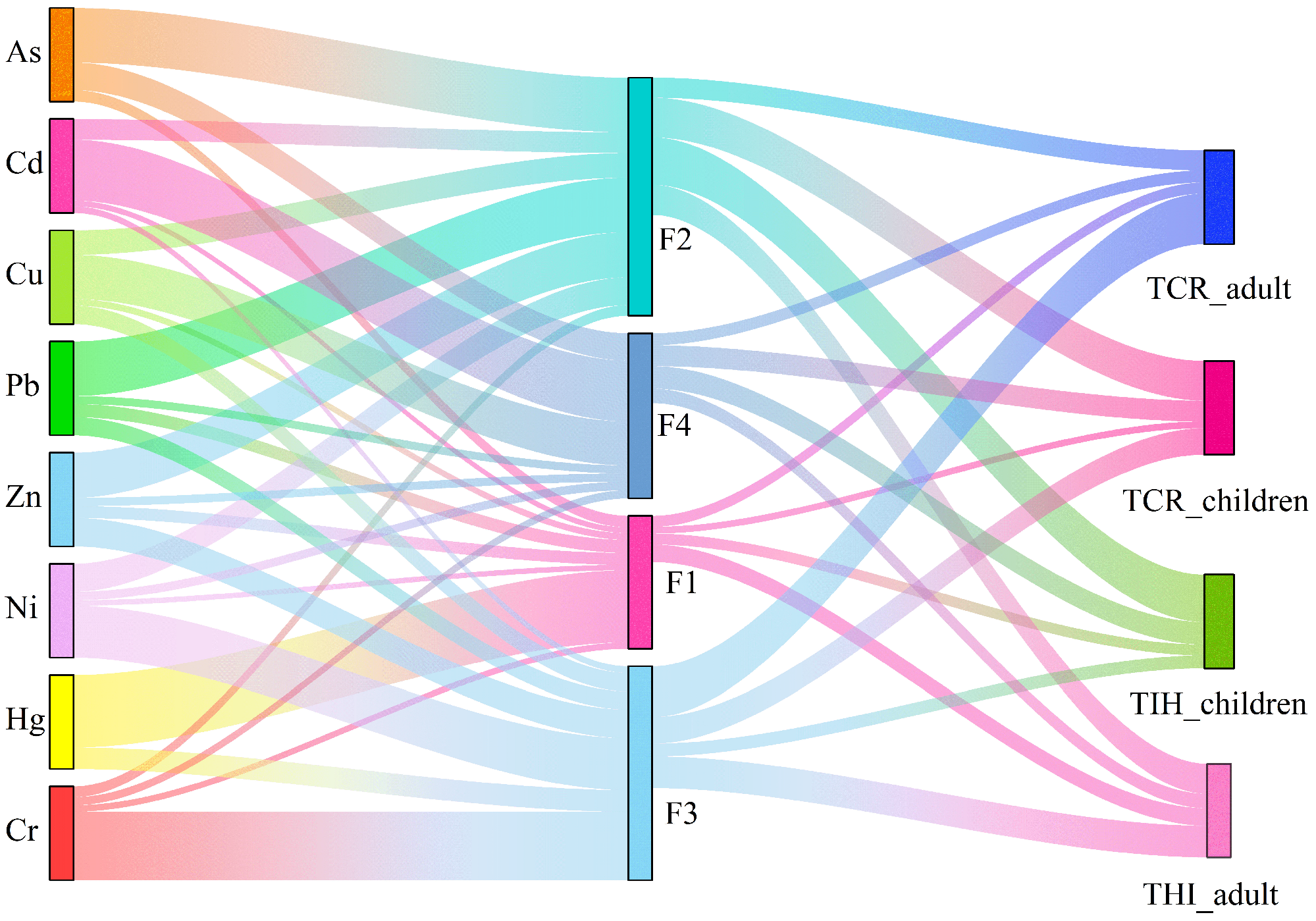
3.3. Combining PCA and PMF Models to Jointly Identify the Sources of Heavy Metals
3.4. Risk Assessment
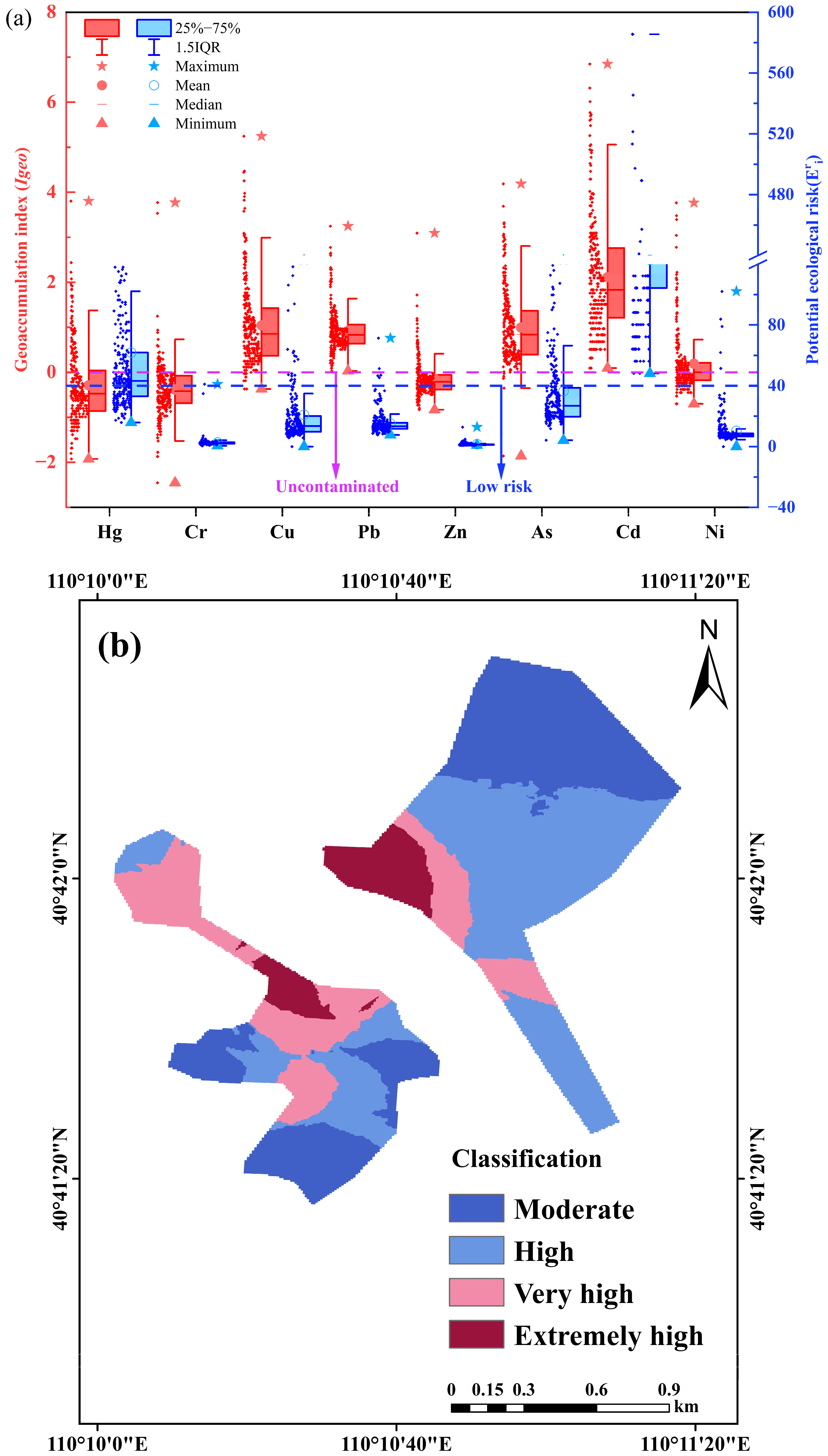
3.4.1. Assessment of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution and Potential Ecological Risks
3.4.2. Integrated Metal-Source-Risk Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, X. Agricultural Land Soil Health Risk Assessment, China. Agric. Eng. 2024, 14, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Luo, M.; Xiang, L.; Zha, L. Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Farmland Soils and Crops Around Metal Mines. Environ. Sci. 2024, 45, 2461–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Li, J.; Li, K.; Hu, J.; Tang, Z.; Xie, J.; Ding, L. Heavy Metal Pollution and Risk Assessment of Soils around a Tin Mining Area in Guangxi. Geol. China 2025, 1–12. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.1167.P.20250902.1625.010 (accessed on 2 September 2025).
- Dai, C. Ecological Behavior and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Soil-Different Crop Systems in the Indigenous Zinc Refining Area of Northwest Guizhou Province. Master’s Thesis, Guizhou Normal University, Guiyang, China, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Qin, R.; Si, Q.; Xu, L.; Wang, H.; Cong, L.; Liu, Z. Assessment of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution in the Dump of a Western Inner Mongolian Coal Mine. J. Resour. Ecol. 2023, 14, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Qi, S.; Wang, Q.; Wang, W.; Tian, X.; Xu, Y.; Xie, W.; Zhang, R.; Wang, K.; et al. Vertical Distribution Characteristics of Soil Elements and Enrichment Ability of Crop Elements in Ancient Volcanic Areas in Shandong Province. Shandong Land Resour. 2023, 39, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, G.; Meng, L.; Tan, L.; Ning, M.; Duan, J.; Deng, S.; Chen, J.; Tian, X.; Xie, T.; Liu, Y. Enrichment Characteristics and Pollution Risks of Heavy Metals in Soils with High Geochemical Background in Chongqing City. Earth Environ. 2023, 51, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cai, S.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, X.; Miao, Y.; Su, P.; Wang, S. The Heavy Metals Pollution Assessment of Farmland Soil around Thel Ead-Zinc Mine and Characteristics of Agricultural Product Pollution. J. Henan Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2025, 53, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Li, H.; Lv, L.; Liang, G.; Wu, T. Distributions and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Solid Waste in Lead-Zinc Mining Areas and across the Soil Water Body Sediment Agricultural Product Ecosystem in Their Surrounding Areas. China Geol. 2025, 8, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravchenko, E.; Minkina, T.; Mandzhieva, S.; Bauer, T.; Lacynnik, E.; Wong, M.H.; Nazarenko, O. Ecological and Health Risk Assessments of Heavy Metal Contamination in Soils Surrounding a Coal Power Plant. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 484, 136751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Gopalakrishnan, G.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y. Characteristics, Source Apportionment, and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution in Soil of Jiangmen, China. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 31578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, X.; Lou, Z.; Xiao, R.; Lv, X.; Christakos, G. Contamination and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution in Soils Developed from Different Soil Parent Materials. Expo. Health 2023, 15, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, X.; He, M.; Christakos, G. Beyond Mere Pollution Source Identification: Determination of Land Covers Emitting Soil Heavy Metals by Combining PCA/APCS, GeoDetector and GIS Analysis. Catena 2020, 185, 104297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, T.; Wu, C.; He, Z.; Japenga, J.; Deng, M.; Yang, X. An Integrated Approach to Assess Heavy Metal Source Apportionment in Peri-Urban Agricultural Soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 299, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Hao, M.; Li, Y.; Li, S. Contamination, Sources and Health Risks of Toxic Elements in Soils of Karstic Urban Parks Based on Monte Carlo Simulation Combined with a Receptor Model. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 839, 156223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, T.K.; Islam, M.S.; Ghosh, G.C.; Ghosh, P.; Zaman, S.; Hossain, M.R.; Habib, A.; Nice, M.S.; Rahman, M.S.; Islam, K.R.; et al. Receptor Model-Based Sources and Risks Appraisal of Potentially Toxic Elements in the Urban Soils of Bangladesh. Toxicol. Rep. 2023, 10, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ/T 166-2004; Technical Specifications for Soil Environmental Monitoring. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2004.
- China National Environmental Monitoring Centre. Background Values of Soil Elements in China; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- HJ/T 962-2018; Soil-Determination of pH- Potentiometry. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. Soil Quality—Determination of Total Mercury—Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2008.
- HJ/T 781-2016; Soil and Sediment—Determination of 22 Metal Elements—Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Chai, L.; Wang, Y.H.; Wang, X.; Ma, L.; Cheng, Z.X.; Su, L.M. Pollution Characteristics, Spatial Distributions, and Source Apportionment of Heavy Metals in Cultivated Soil in Lanzhou, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhou, H.; Qi, Z. Assessment of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution with Principal Component Analysis and Geoaccumulation Index. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 10, 1946–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An Ecological Risk Index for Aquatic Pollution Control. A Sedimentological Approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wang, L. Ecological and Human Health Risk Assessments in the Context of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution in a Typical Industrial Area of Shanghai, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 27090–27105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.; Hu, W.; Wang, H.; Tian, K.; Huang, B. Comprehensive Assessment of Heavy Metal Risk in Soil-Crop Systems along the Yangtze River in Nanjing, Southeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Chen, Y.; Yue, X.; Ren, D.; Liu, Y.; Yang, K. Identification and Hazard Analysis of Heavy Metal Sources in Agricultural Soils in Ancient Mining Areas: A quantitative method based on the receptor model and risk assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 445, 130528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paatero, P.; Hopke, P.K.; Hoppenstock, J.; Eberly, S.I. Advanced Factor Analysis of Spatial Distributions of PM2.5 in the Eastern United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 2460–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Teng, Y.; Lu, S.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, J. Source Apportionment and Health Risk Assessment of Trace Metals in Surface Soils of Beijing Metropolitan, China. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 1002–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C. Sources of Heavy Metals in Soils in Densely Populated Areas Based on the UNMIX Model. Environ. Forensics 2021, 23, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund, Volume I (Part A: Human Health Evaluation Manual; Part E, Supplemental Guidance for Dermal Risk Assessment; Part F. Supplemental Guidance for Inhalation Risk Assessment); United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1999.
- MEP (Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China). Handbook of Exposure Parameters for Chinese Population (Adults); China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2014.
- Hu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Ji, W.; Fu, Z.; Shao, S.; Li, S.; Huang, M.; Zhou, L.; Shi, Z. Spatio-Temporal Variation and Source Changes of Potentially Toxic Elements in Soil on a Typical Plain of the Yangtze River Delta, China (2002–2012). J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 271, 110943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.F.; Zhao, X.L.; Meng, Y.B.; Fei, Y.; Teng, M.M.; Song, F.H.; Wu, F.C. Identification Priority Source of Soil Heavy Metals Pollution Based on Source-specific Ecological and Human Health Risk Analysis in a Typical Smelting and Mining Region of South China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 242, 113864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 15618-2018; Soil Environmental Quality Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Chen, T.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, J.; Xu, J.; Shi, J.; Dahlgren, R.A. Heavy Metal Sources Identification and Sampling Uncertainty Analysis in a Field-Scale Vegetable Soil of Hangzhou, China. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manta, D.S.; Angelone, M.; Bellanca, A.; Neri, R.; Sprovieri, M. Heavy Metals in Urban Soils: A Case Study from the City of Palermo (Sicily), Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 300, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimyan, K.; Alimohammadi, M.; Maleki, A.; Yunesian, M.; Nodehi, R.N.; Foroushani, A.R. Human Health and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal(Loid)s in Agricultural Soils of Rural Areas: A Case Study in Kurdistan Province, Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2020, 18, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Pan, A.; Ma, R.; Wang, H. Distribution Characteristics, Source Analysis and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Farmland Soil in Shiquan County, Shaanxi Province. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 171, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, X.; Lou, Z.; Xiao, R.; Ren, Z.; Lv, X. Contamination Assessment and Source Apportionment of Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soil through the Synthesis of PMF and GeogDetector Models. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 747, 141293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco-Uría, A.; López-Mateo, C.; Roca, E.; Fernández-Marcos, M.L. Source Identification of Heavy Metals in Pastureland by Multivariate Analysis in NW Spain. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micó, C.; Recatalá, L.; Peris, M.; Sánchez, J. Assessing Heavy Metal Sources in Agricultural Soils of an European Mediterranean Area by Multivariate Analysis. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sungur, A.; Soylak, M.; Yilmaz, E.; Yilmaz, S.; Ozcan, H. Characterization of Heavy Metal Fractions in Agricultural Soils by Sequential Extraction Procedure: The Relationship Between Soil Properties and Heavy Metal Fractions. Soil Sediment Contam. 2015, 24, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, H. Soil Heavy Metal(Loid) Pollution and Health Risk Assessment of Farmlands Developed on Two Different Terrains on the Tibetan Plateau, China. Chemosphere 2023, 335, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Rathore, D. Role of Transitory Starch on Growth, Development and Metal Accumulation of Triticum Aestivum Cultivars Grown under Textile Effluent Fertilization. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 24201–24217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, H. Source Analysis and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Development Zones: A Case Study in Rizhao, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Li, P.; Fu, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Lin, C. Mercury Pollution in China: Implications on the Implementation of the Minamata Convention. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2022, 5, 634–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Fu, Q.; Gao, S.; Zhang, X.; Feng, J.; Chen, X. Investigate the Impact of Local Iron–Steel Industrial Emission on Atmospheric Mercury Concentration in Yangtze River Delta, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 5862–5872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Liu, Z.; Tian, Y.; Shi, H.; Fei, Y.; Qi, J.; Mo, L. Research on Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Soil Based on Multi-Factor Source Apportionment: A Case Study in Guangdong Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Wang, Q.; Wen, H.; Luo, J.; Wang, S. Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils from a Typical Township in Guangdong Province, China: Occurrences and Spatial Distribution. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 168, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Guo, D.; Liu, K.; Meng, H.; Zheng, Y.; Yuan, F.; Zhu, G. Levels, Sources, and Spatial Distribution of Heavy Metals in Soils from a Typical Coal Industrial City of Tangshan, China. Catena 2019, 175, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Poon, C.; Liu, P.S. Heavy Metal Contamination of Urban Soils and Street Dusts in Hong Kong. Appl. Geochem. 2001, 16, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Lu, W.; Long, Y.; Bao, X.; Yang, Q. Assessment of Heavy Metals Contamination in Urban Topsoil from Changchun City, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2011, 108, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Yu, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, Y.; Pu, S. Source-Pathway-Sink Analysis and Health Risk Zoning of Heavy Metal Groundwater Pollution in Karst Chemical Park. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 382, 126716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Liang, J.; Shi, H.; Yan, T.; He, Z.; Li, L.; Hu, H. Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals Based on Source Analysis and Monte Carlo in the Downstream Basin of the Zishui. Environ. Res. 2024, 245, 117975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Islam, M.A. Concentrations and Health Risk Assessment of Trace Elements in Cereals, Fruits, and Vegetables of Bangladesh. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 191, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, P.; Wang, M.; Liu, J.; Gong, L.; Xia, S. Spatial Distribution, Source Identification, and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Riparian Soils of the Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Res. 2023, 237, 116977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.Y.; Xie, L.L.; Jin, D.C.; Mi, B.B.; Wang, D.H.; Li, X.F.; Dai, X.Z.; Zou, X.X.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, Y.Q.; et al. Bacterial Community Response to Cadmium Contamination of Agricultural Paddy Soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 139, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | pH | w/mg·kg−1 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hg | Cr | Cu | Pb | Zn | As | Cd | Ni | ||
| Min | 6.5 | 0.01 | 10 | 15 | 23 | 41 | 2.6 | 0.06 | 16 |
| Max | 8.9 | 0.58 | 748 | 734 | 214 | 622 | 172 | 6.5 | 353 |
| Mean | 7.7 | 0.04 | 48.3 | 54.3 | 45.7 | 70.0 | 22.9 | 0.42 | 35.7 |
| SD | 0.58 | 0.05 | 57.6 | 70.2 | 21.9 | 40.7 | 19.1 | 0.7 | 36.9 |
| CV/% | 8 | 107 | 119 | 129 | 48 | 58 | 83 | 166 | 103 |
| >background value/% a | - | 61.5 | 66.3 | 99.6 | 100 | 94.1 | 99.6 | 100 | 98.9 |
| >risk screening value/% b | - | 0 | 1.1 | 7.7 | 0.73 | 0.73 | 11.7 | 11.4 | 2.9 |
| >intervention value/% b | - | 0 | 0 | - | 0 | - | 0.37 | 1.1 | - |
| Elements | PC | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Cd | 0.917 | 0.155 | 0.143 |
| Hg | 0.233 | 0.043 | 0.959 |
| As | 0.877 | 0.007 | 0.178 |
| Pb | 0.871 | 0.242 | 0.177 |
| Cr | −0.125 | 0.877 | 0.075 |
| Cu | 0.830 | 0.099 | 0.012 |
| Ni | 0.231 | 0.754 | −0.078 |
| Zn | 0.301 | 0.884 | 0.102 |
| Characteristic value | 3.858 | 1.817 | 0.837 |
| Variance contribution rate (%) | 48.23 | 22.71 | 10.46 |
| Cumulative variance contribution rate (%) | 48.23 | 70.94 | 81.39 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Mo, L.; Liang, J.; Shi, H.; Yao, J.; Lun, X. Heavy Metal Pollution and Health-Ecological Risk Assessment in Agricultural Soils: A Case Study from the Yellow River Bend Industrial Parks. Toxics 2025, 13, 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13100834
Liu Z, Mo L, Liang J, Shi H, Yao J, Lun X. Heavy Metal Pollution and Health-Ecological Risk Assessment in Agricultural Soils: A Case Study from the Yellow River Bend Industrial Parks. Toxics. 2025; 13(10):834. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13100834
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zang, Li Mo, Jiahui Liang, Huading Shi, Jingjing Yao, and Xiaoxiu Lun. 2025. "Heavy Metal Pollution and Health-Ecological Risk Assessment in Agricultural Soils: A Case Study from the Yellow River Bend Industrial Parks" Toxics 13, no. 10: 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13100834
APA StyleLiu, Z., Mo, L., Liang, J., Shi, H., Yao, J., & Lun, X. (2025). Heavy Metal Pollution and Health-Ecological Risk Assessment in Agricultural Soils: A Case Study from the Yellow River Bend Industrial Parks. Toxics, 13(10), 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13100834









