Immunological Effects of Diesel Particles in a Murine Model of Healthy Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Diesel Exhaust Particles (DEP)
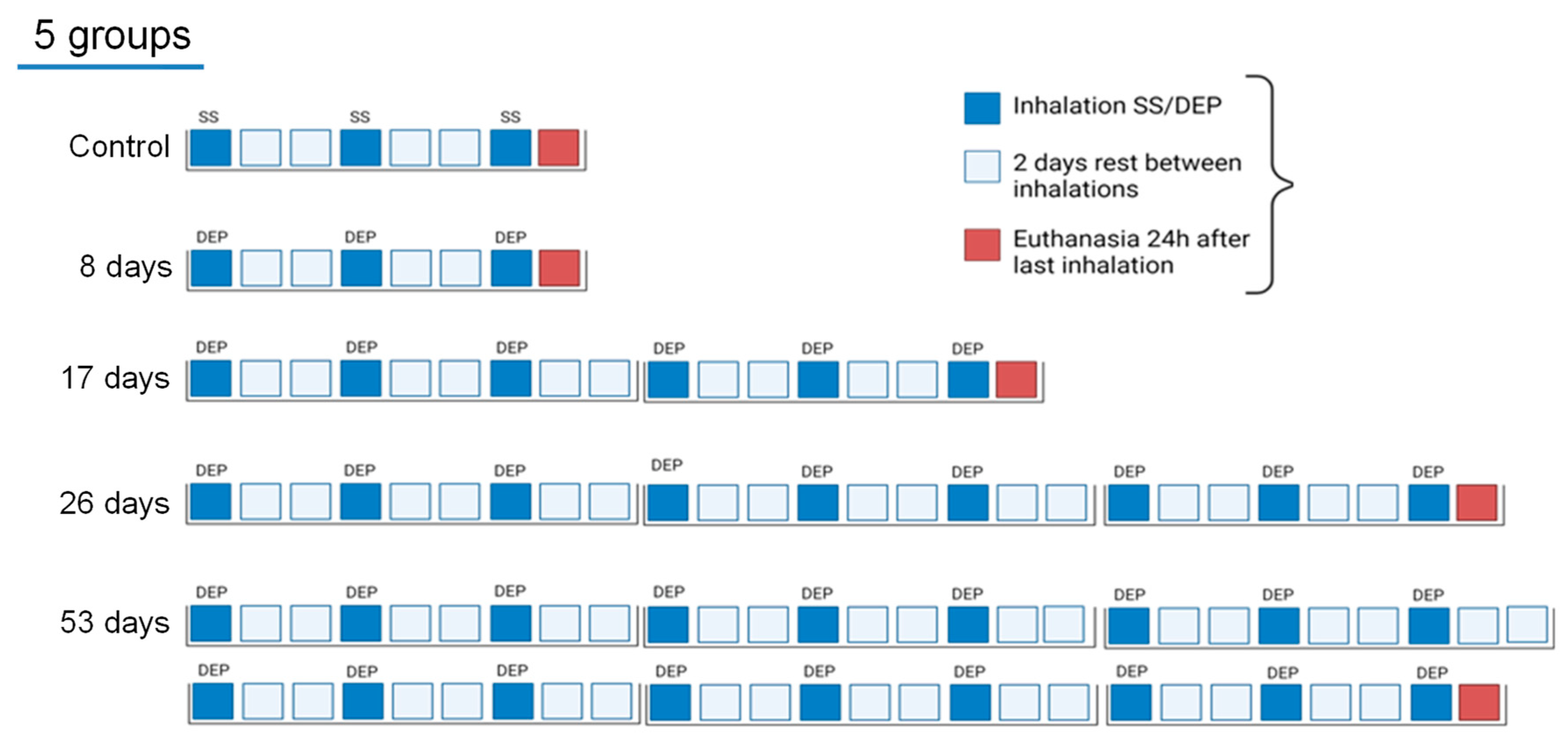
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Lung Function Assessment
2.5. Bronchoalveolar Lavage
2.6. DEP-Uptake Analysis
2.7. Flow Cytometry
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
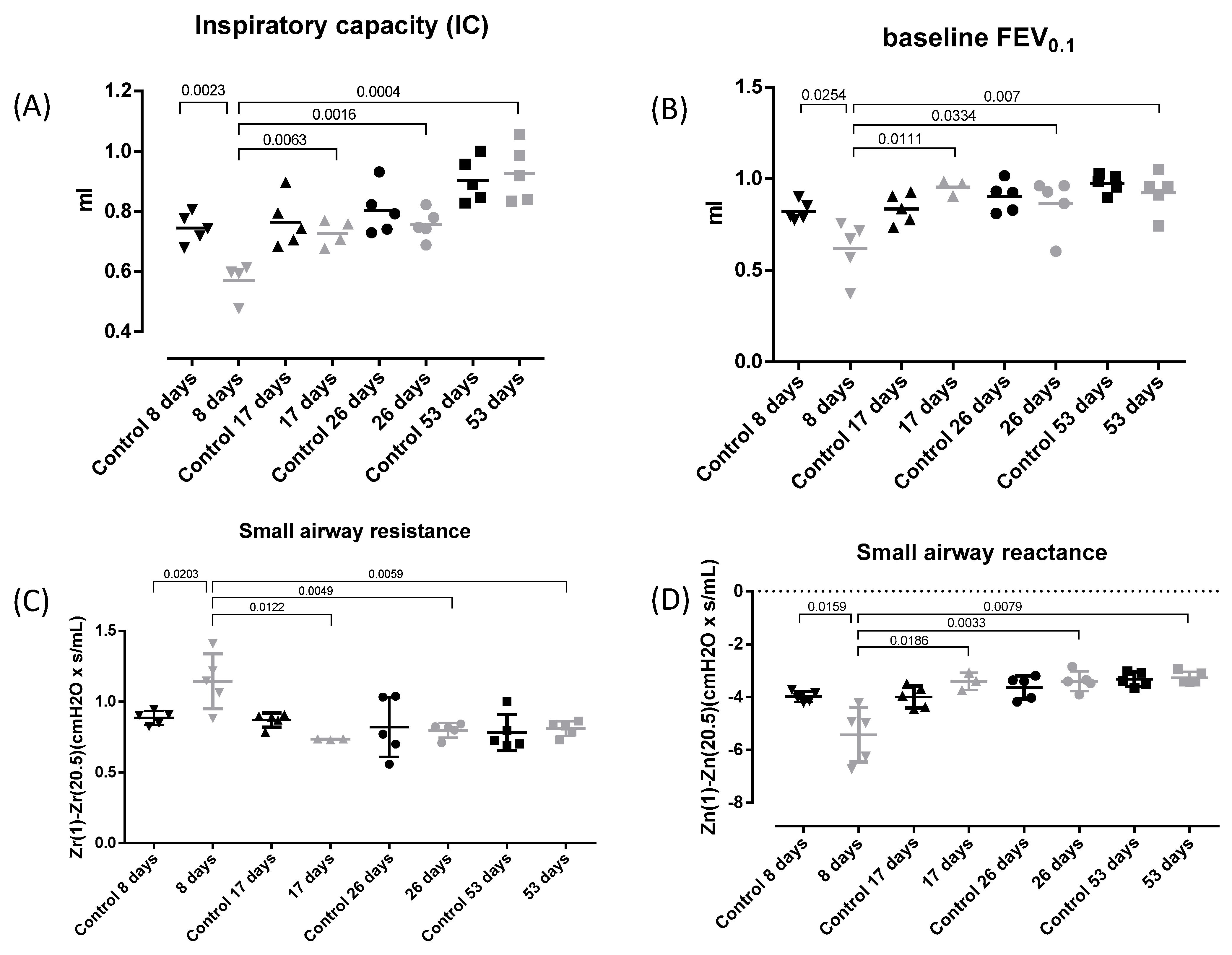
3.1. Lung Function Assessment
3.2. Bronchoalveolar Lavage
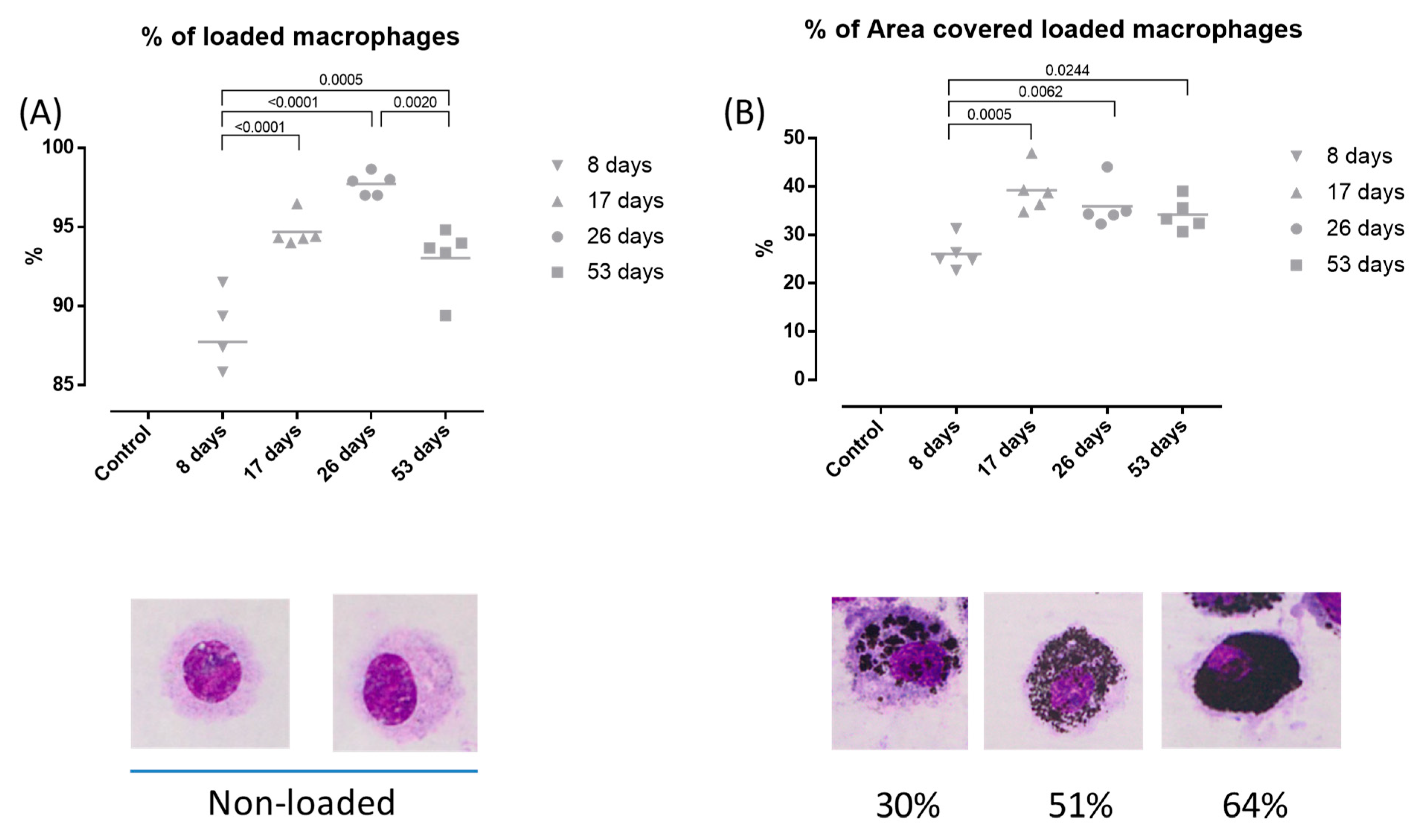
3.3. DEP-Uptake Analysis
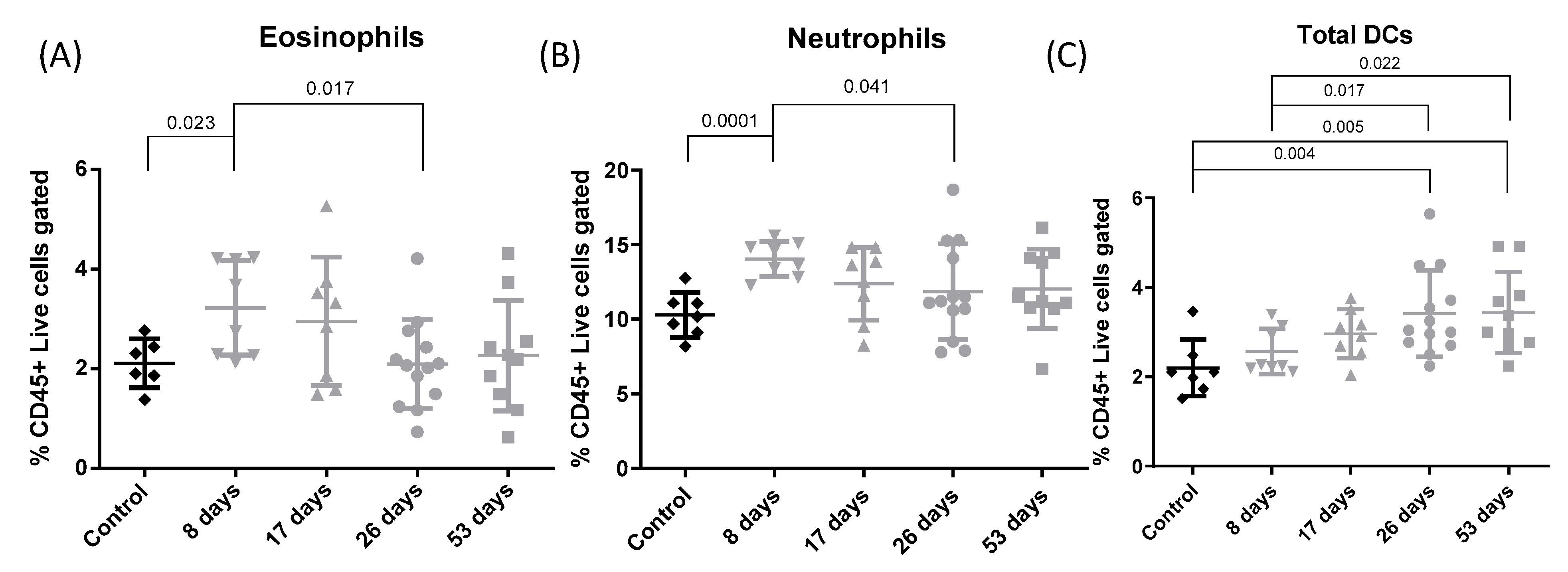
3.4. Flow Cytometry
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Health Impacts of Air Pollution in Europe, 2022—European Environment Agency [Internet]. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/air-quality-in-europe-2022/health-impacts-of-air-pollution (accessed on 3 March 2023).
- Liu, C.; Chen, R.; Sera, F.; Vicedo-Cabrera, A.M.; Guo, Y.; Tong, S.; Coelho, M.S.Z.S.; Saldiva, P.H.N.; Lavigne, E.; Matus, P.; et al. Ambient Particulate Air Pollution and Daily Mortality in 652 Cities. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendtsen, K.M.; Gren, L.; Malmborg, V.B.; Shukla, P.C.; Tunér, M.; Essig, Y.J.; Krais, A.M.; Clausen, P.A.; Berthing, T.; Loeschner, K.; et al. Particle characterization and toxicity in C57BL/6 mice following instillation of five different diesel exhaust particles designed to differ in physicochemical properties. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schraufnagel, D.E.; Balmes, J.R.; Cowl, C.T.; De Matteis, S.; Jung, S.H.; Mortimer, K.; Perez-Padilla, R.; Rice, M.B.; Riojas-Rodriguez, H.; Sood, A.; et al. Air Pollution and Noncommunicable Diseases: A Review by the Forum of International Respiratory Societies’ Environmental Committee, Part 1: The Damaging Effects of Air Pollution. Chest 2019, 155, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shears, R.K.; Jacques, L.C.; Naylor, G.; Miyashita, L.; Khandaker, S.; Lebre, F.; Lavelle, E.C.; Grigg, J.; French, N.; Neill, D.R.; et al. Exposure to diesel exhaust particles increases susceptibility to invasive pneumococcal disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 1272–1284.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.H.; Kim, B.G.; Park, M.K.; Hong, J.; Lee, Y.G.; Jang, A.S. The impact of diesel exhaust particles on tight junctional proteins on nose and lung in a mouse model. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2020, 13, 350–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatkin, J.; Correa, L.; Santos, U. External Environmental Pollution as a Risk Factor for Asthma. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2021, 62, 72–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, T.G.; Kesavalu, B.; Bernstein, C.K.; Ryan, P.H.; Bernstein, J.A.; Zimmermann, N.; Lummus, Z.; Villareal, M.S.; Smith, A.M.; Lenz, P.H.; et al. Chronic traffic pollution exposure is associated with eosinophilic, but not neutrophilic inflammation in older adult asthmatics. J. Asthma 2013, 50, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitehouse, A.L.; Mushtaq, N.; Miyashita, L.; Barratt, B.; Khan, A.; Kalsi, H.; Koh, L.; Padovan, M.G.; Brugha, R.; Balkwill, F.R.; et al. Airway dendritic cell maturation in children exposed to air pollution. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, E.; Carlsten, C. Controlled human exposure to diesel exhaust: Results illuminate health effects of traffic-related air pollution and inform future directions. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2022, 19, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, X.; Barreiro, E.; Bustamante, V.; Lopez-Campos, J.L.; González-Barcala, F.J.; Cruz, M.J. Diesel exhausts particles: Their role in increasing the incidence of asthma. Reviewing the evidence of a causal link. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, D.; Forsberg, B.; Bråbäck, L.; Geels, C.; Brandt, J.; Christensen, J.H.; Frohn, L.M.; Oudin, A. Early childhood exposure to ambient air pollution is associated with increased risk of paediatric asthma: An administrative cohort study from Stockholm, Sweden. Environ. Int. 2021, 155, 106667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, P.; Bernstein, D.; Levin, L.; Burkle, J.; Villareal, M.; Kalra, H.; Lockey, J.; Khuranahershey, G.; Lemasters, G. Exposure to Diesel Exhaust Particles and Indoor Endotoxin During Early Childhood Increases the Risk for Persistent Wheeze at Age Three. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 121, S65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.I. Particulate matter and childhood allergic diseases. Korean J. Pediatr. 2019, 62, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenfors, N.; Nordenhäll, C.; Salvi, S.S.; Mudway, I.; Söderberg, M.; Blomberg, A.; Helleday, R.; Levin, J.-O.; Holgate, S.; Kelly, F.; et al. Different airway inflammatory responses in asthmatic and healthy humans exposed to diesel. Eur. Respir. J. 2004, 23, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behndig, A.F.; Larsson, N.; Brown, J.L.; Stenfors, N.; Helleday, R.; Duggan, S.T.; Dove, R.E.; Wilson, S.J.; Sandstrom, T.; Kelly, F.J.; et al. Proinflammatory doses of diesel exhaust in healthy subjects fail to elicit equivalent or augmented airway inflammation in subjects with asthma. Thorax 2011, 66, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dauchet, L.; Hulo, S.; Cherot-Kornobis, N.; Matran, R.; Amouyel, P.; Edmé, J.L.; Giovannelli, J. Short-term exposure to air pollution: Associations with lung function and inflammatory markers in non-smoking, healthy adults. Environ. Int. 2018, 121, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, M.B.; Ljungman, P.L.; Wilker, E.H.; Gold, D.R.; Schwartz, J.D.; Koutrakis, P.; Washko, G.R.; O’connor, G.T.; Mittleman, M.A. Short-term exposure to air pollution and lung function in the framingham heart study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 1351–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalaby, K.H.; Gold, L.G.; Schuessler, T.F.; Martin, J.G.; Robichaud, A. Combined forced oscillation and forced expiration measurements in mice for the assessment of airway hyperresponsiveness. Respir. Res. 2010, 11, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decaesteker, T.; Vanhoffelen, E.; Trekels, K.; Jonckheere, A.C.; Cremer, J.; Vanstapel, A.; Dilissen, E.; Bullens, D.; Dupont, L.J.; Vanoirbeek, J.A. Differential effects of intense exercise and pollution on the airways in a murine model. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2021, 18, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Homdedeu, M.; Cruz, M.; Sánchez-Díez, S.; Gómez-Ollés, S.; Ojanguren, I.; Ma, D.; Muñoz, X. Role of diesel exhaust particles in the induction of allergic asthma to low doses of soybean. Environ. Res. 2021, 196, 110337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gie, A.G.; Regin, Y.; Salaets, T.; Casiraghi, C.; Salomone, F.; Deprest, J.; Muñoz, X. Intratracheal budesonide/surfactant attenuates hyperoxia-induced lung injury in preterm rabbits. Am. J. Physiol.—Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2020, 319, L949–L956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, R.; van Eeden, S.F. The innate and adaptive immune response induced by alveolar macrophages exposed to ambient particulate matter. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2011, 257, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzarella, G.; Ferraraccio, F.; Prati, M.V.; Annunziata, S.; Bianco, A.; Mezzogiorno, A.; Liguori, G.; Angelillo, I.; Cazzola, M. Effects of diesel exhaust particles on human lung epithelial cells: An in vitro study. Respir. Med. 2007, 101, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Champion, J.A.; Mitragotri, S. Shape induced inhibition of phagocytosis of polymer particles. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaguin, M.; Fardel, O.; Lecureur, V. Exposure to diesel exhaust particle extracts (DEPe) impairs some polarization markers and functions of human macrophages through activation of AhR and Nrf2. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.M.; Antonini, J.M.; Barger, M.W.; Butterworth, L.; Roberts, J.R.; Ma, J.K.H.; Castranova, V.; Ma, J.Y. Diesel exhaust particles suppress macrophage function and slow the pulmonary clearance of Listeria monocytogenes in rats. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawal, A.O. Diesel Exhaust Particles and the Induction of Macrophage Activation and Dysfunction. Inflammation 2018, 41, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewhurst, J.A.; Lea, S.; Hardaker, E.; Dungwa, J.V.; Ravi, A.K.; Singh, D. Characterisation of lung macrophage subpopulations in COPD patients and controls. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desch, A.N.; Gibbings, S.L.; Goyal, R.; Kolde, R.; Bednarek, J.; Bruno, T.; Slansky, J.E.; Jacobelli, J.; Mason, R.; Ito, Y.; et al. Flow cytometric analysis of mononuclear phagocytes in nondiseased human lung and lung-draining lymph nodes. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 193, 614–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeffel, G.; Chen, J.; Lavin, Y.; Low, D.; Almeida, F.F.; See, P.; Beaudin, A.E.; Lum, J.; Low, I.; Forsberg, E.C.; et al. C-Myb+ Erythro-Myeloid Progenitor-Derived Fetal Monocytes Give Rise to Adult Tissue-Resident Macrophages. Immunity 2015, 42, 665–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zasłona, Z.; Przybranowski, S.; Wilke, C.; van Rooijen, N.; Teitz-Tennenbaum, S.; Osterholzer, J.J.; Wilkinson, J.E.; Moore, B.B.; Peters-Golden, M. Resident Alveolar Macrophages Suppress, whereas Recruited Monocytes Promote, Allergic Lung Inflammation in Murine Models of Asthma. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 4245–4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, F.; Xiao, K.; Tang, L.; Xie, L. Diversity of Macrophages in Lung Homeostasis and Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 753940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coillard, A.; Segura, E. In vivo differentiation of human monocytes. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynn, T.A.; Vannella, K.M. Macrophages in Tissue Repair, Regeneration, and Fibrosis. Immunity 2016, 44, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguíluz-Gracia, I.; Bosco, A.; Dollner, R.; Melum, G.R.; Lexberg, M.H.; Jones, A.C.; Dheyauldeen, S.A.; Holt, P.G.; Bækkevold, E.S.; Jahnsen, F.L. Rapid recruitment of CD14+ monocytes in experimentally induced allergic rhinitis in human subjects. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 1872–1881.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, G.R.; Bain, C.C.; Fenton, T.M.; Kelly, A.; Brown, S.L.; Ivens, A.C.; Travis, M.A.; Cook, P.C.; MacDonald, A.S. Dynamics of colon monocyte and macrophage activation during colitis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonato, M.; Gallo, E.; Bazzan, E.; Marson, G.; Zagolin, L.; Cosio, M.G.; Barbato, A.; Saetta, M.; Gregori, D.; Baraldo, S. Air pollution relates to airway pathology in children with wheezing. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2021, 18, 2033–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellman, I. Dendritic cells: Master regulators of the immune response. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2013, 1, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fucikova, J.; Palova-Jelinkova, L.; Bartunkova, J.; Spisek, R. Induction of tolerance and immunity by dendritic cells: Mechanisms and clinical applications. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda, A.; Pinkerton, K.; Bein, K.; Magaña-Méndez, A.; Yang, H.; Ashwood, P.; Vogel, C.F.A. Ambient particulate matter activates the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in dendritic cells and enhances Th17 polarization Alejandro. Physiol. Behav. 2018, 292, 85–96. [Google Scholar]
- Brandt, E.B.; Kovacic, M.B.; Lee, G.B.; Aaron, M.; Acciani, T.H.; Le Cras, T.D.; Ryan, P.H.; Budelsky, A.L.; Hershey, G.K.K. Diesel exhaust particle induction of IL17A contributes to severe asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 1194–1204.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collin, M.; Bigley, V. Human dendritic cell subsets: An update. Immunology 2018, 154, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubesch, N.J.; De Nazelle, A.; Westerdahl, D.; Martinez, D.; Carrasco-Turigas, G.; Bouso, L.; Guerra, S.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J. Respiratory and inflammatory responses to short-term exposure to traffic-related air pollution with and without moderate Physical activity. Occup. Environ. Med. 2015, 72, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.P.; Zhang, X.; Duan, H.W.; Meng, T.; Niu, Y. Long-term exposure to diesel engine exhaust induced lung function decline in a cross sectional study. Ind. Health 2017, 55, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulin, L.; Hansel, N. Particulate air pollution and impaired lung function. F1000Research 2016, 5, F1000 Faculty Rev-201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egger, C.; Gerard, C.; Vidotto, N.; Accart, N.; Cannet, C.; Dunbar, A.; Tigani, B.; Piaia, A.; Jarai, G.; Jarman, E.; et al. Lung volume quantified by MRI reflects extracellular-matrix deposition and altered pulmonary function in bleomycin models of fibrosis: Effects of SOM230. Am. J. Physiol.—Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2014, 306, L1064–L1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southam, D.S.; Dolovich, M.; O’Byrne, P.M.; Inman, M.D. Distribution of intranasal instillations in mice: Effects of volume, time, body position, and anesthesia. Am. J. Physiol.—Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2002, 282, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soler-Segovia, D.; de Homdedeu, M.; Sánchez-Díez, S.; Romero-Mesones, C.; Espejo, D.; Marain, F.; Vanoirbeek, J.; Munoz, X.; Cruz, M.-J. Immunological Effects of Diesel Particles in a Murine Model of Healthy Mice. Toxics 2024, 12, 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12080530
Soler-Segovia D, de Homdedeu M, Sánchez-Díez S, Romero-Mesones C, Espejo D, Marain F, Vanoirbeek J, Munoz X, Cruz M-J. Immunological Effects of Diesel Particles in a Murine Model of Healthy Mice. Toxics. 2024; 12(8):530. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12080530
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoler-Segovia, David, Miquel de Homdedeu, Silvia Sánchez-Díez, Christian Romero-Mesones, David Espejo, Fopke Marain, Jeroen Vanoirbeek, Xavier Munoz, and María-Jesús Cruz. 2024. "Immunological Effects of Diesel Particles in a Murine Model of Healthy Mice" Toxics 12, no. 8: 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12080530
APA StyleSoler-Segovia, D., de Homdedeu, M., Sánchez-Díez, S., Romero-Mesones, C., Espejo, D., Marain, F., Vanoirbeek, J., Munoz, X., & Cruz, M.-J. (2024). Immunological Effects of Diesel Particles in a Murine Model of Healthy Mice. Toxics, 12(8), 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12080530








