Abstract
To study the spatiotemporal variability of particle-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and assess their carcinogenic potential in six contrasting urban environments in Greece, a total of 305 filter samples were collected and analyzed. Sampling sites included a variety of urban background, traffic (Athens, Ioannina and Heraklion), rural (Xanthi) and near-port locations (Piraeus and Volos). When considering the sum of 16 U.S. EPA priority PAHs, as well as that of the six EU-proposed members, average concentrations observed across locations during summer varied moderately (0.4–2.2 ng m−3) and independently of the population of each site, with the highest values observed in the areas of Piraeus and Volos that are affected by port and industrial activities. Winter levels were significantly higher and more spatially variable compared to summer, with the seasonal enhancement ranging from 7 times in Piraeus to 98 times in Ioannina, indicating the large impact of PAH emissions from residential wood burning. Regarding benzo(a)pyrene (BaP), an IARC Group 1 carcinogen and the only EU-regulated PAH, the winter/summer ratios were 24–33 in Athens, Volos, Heraklion and Xanthi; 60 in Piraeus; and 480 in Ioannina, which is afflicted by severe wood-burning pollution events. An excellent correlation was observed between organic carbon (OC) and benzo(a)pyrene (BaP) during the cold period at all urban sites (r2 > 0.8) with stable BaP/OC slopes (0.09–0.14 × 10−3), highlighting the potential use of OC as a proxy for the estimation of BaP in winter conditions. The identified spatiotemporal contrasts, which were explored for the first time for PAHs at such a scale in the Eastern Mediterranean, provide important insights into sources and controlling atmospheric conditions and reveal large deviations in exposure risks among cities that raise the issue of environmental injustice on a national level.
1. Introduction
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are toxic organic pollutants that have the potential to induce carcinogenic effects following chronic inhalation exposure [1,2]. PAHs in the atmosphere can be present either in the gaseous or in the particulate phase, and although semi-volatile PAHs have the potential to initiate genotoxic mechanisms at the cellular level, heavier and less volatile PAH members with more rings and bay- or fjord-like regions [3,4] in their structure are more susceptible to enzymatic metabolism, leading to DNA adduction and mutations. Besides their carcinogenic activity [5], PAHs are also related to a plethora of non-carcinogenic—e.g., cardiorespiratory—effects, which are mainly induced by oxidative stress and inflammatory responses [6,7]. Moreover, PAHs have been linked to neurodevelopmental effects following prenatal or early postnatal exposure, even at lower doses than those that induce carcinogenicity [8,9,10]. Regarding individual PAHs, naphthalene, benzo(a)anthracene, chrysene, benzo(b)fluoranthene, benzo(k)fluoranthene, Indeno(123cd)pyrene and dibenz(a,h)anthracene are classified as Group 1, 2A or 2B carcinogens by IARC (IARC Monographs 2010). Moreover, members like phenanthrene and benzo(ghi)perylene have been linked to cardiovascular and other systemic effects [7,11,12].
In 1976, the United States Environmental Protection Agency (U.S. EPA) established a list of 16 harmful PAH members that should be monitored regularly [13]. The European Union also moved to regulate atmospheric PAHs in 2004 (directive 2004/107/EC), setting an annual target value only for BaP (1 ng m−3) [14]. However, in the directive, it was proposed that PAH measurements should not be limited only to BaP but should also include benzo(a)anthracene, benzo(b)fluoranthene, benzo(j)fluoranthene, benzo(k)fluoranthene, indeno(1,2,3-cd)pyrene and dibenz(a,h)anthracene.
Fine particle-bound PAHs originate from a variety of anthropogenic activities, mostly related to incomplete combustion of fossil fuels and biomass [15,16], while fugitive emissions from fuel oil transport, use, storage and maturation can also be a factor in specific environments. These source categories can be classified as pyrogenic and petrogenic, respectively [17].
Recent studies have highlighted the connection of particle PAHs with residential biomass burning and have reported this source as abundantly present in European cities, where it frequently leads to the formation of winter haze events [18]. The use of biomass as a heating fuel alternative has increased dramatically in the last decade following the 2008 global recession and has persisted throughout the ongoing energy crisis, leading to an alarming increase of the fine particle carcinogenic potential [19,20].
In Greece, over the last few decades, research on PAHs and their sources has mostly been conducted through single-site measurements [18,21,22], hindering the study of contrasts between different site types and at the spatial scale (within-area or between-area), which has crucial implications for exposure assessment and also for informed policymaking. At present, spatial data regarding exposure to PAHs have to be mined from infrequent, fragmented and asynchronous observations. Furthermore, official PAH measurements according to the provisions of the EU directive in Greece are limited to a couple of monitoring sites in the Greater Athens Area and are reported only for BaP. Therefore, there is an urgent need for the longitudinal characterization of PAH levels in Greek cities, especially given the gravity of the residential wood-burning issue [18,23,24]. Moreover, measurements at different site types are needed to highlight the relative importance of residential against road and maritime transport sources.
Greece has been regularly reporting compliance with the BaP EU standard; however, this is assessed through measurements only at urban background sites around Athens, and it is unknown whether BaP annual mean concentrations remain- below the EU target value at traffic locations or in residential areas in cities with increased heating energy demand during the cold season. In this context, we investigated the seasonal pattern of PAH concentrations in six cities (Athens, Piraeus, Ioannina, Volos, Xanthi, Heraklion), using measurements at varying site types (traffic, urban, rural, port) [25].
The majority of these cities were previously characterized in terms of PM2.5 levels, sources and long-term variability in an overview study [26], which reported low and almost uniform PM2.5 levels over continental Greece during the warm period. Conversely, during the cold period, PM2.5 concentrations were largely increased in all areas, due to residential biomass burning. Specifically for the study sites, in Athens, the National Observatory of Athens (NOA) Thissio supersite has been well-characterized during the last decade in terms of toxic organic aerosol sources and chemical composition [18,23,27,28]. Ioannina is a medium-sized mountainous city impacted by intense residential biomass burning (BB), especially during winter nights. These emissions, in combination with the city’s climate and topography (mountainous basin, air mass stagnation, haze-promoting conditions), result in a large accumulation of organic aerosols, which is also due to local-scale secondary processing [29,30]. Organic aerosol sources were also recently characterized at the port of Piraeus [31]. Little is known about the organic aerosol composition in medium-sized peripheral Greek cities like Volos, Heraklion and Xanthi [26], although some results on PM concentration levels have been reported. Frequent exceedances of the PM10 daily limit values have been consistently reported in Volos [32]. In Heraklion, the frequency of exceedance of the PM10 limit value in summer and fall can be almost double compared to the other half of the year, despite a large number of spring exceedances due to dust transport [33]. In the near-city rural site of Xanthi, the aforementioned overview study indicated summer PM2.5 levels comparable to those measured in other urban background sites in Greece, while in winter, the mean concentration was 70% lower compared to the most polluted city (Ioannina) [26].
In this work, focus was placed on the specific PAH congeners regulated by the EPA and the EU. The selected measurement areas had different characteristics and populations, allowing to assess the impact of PAH sources and evaluate potential exposure risks on a national level. Τhis was performed for the first time at multiple sites across Greece, highlighting the importance of representative PAH measurements for a deeper understanding of their origin and consequently of mitigation possibilities. A key motivation of this work was to examine whether a potentially severe ambient PAH pollution issue in Greece is masked by the lenient macro-siting requirements foreseen in current environmental legislation. To our knowledge, this study is one of the few worldwide [34,35,36,37] to investigate the PAH spatial variability in national networks on a seasonal basis, while comparing different measurement area types (urban, rural) and site types (traffic, near-port, background). This comparison is expected to highlight environmental injustices regarding carcinogenic ambient exposure among areas that experience different climate but also socio-economic characteristics, especially when the option to use “clean” residential heating fuels is not available.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Filter Sampling
Measurements were conducted at sites in six Greek cities (Figure 1), namely Athens (3.5 M inhabitants, urban background site), Heraklion (0.2 M, traffic site), Ioannina (0.15 Μ, urban background site), Xanthi (0.05 M, rural background site), Piraeus (0.6 M, urban site near the port) and Volos (0.15 M, urban site near the port) (Figure 1, Table 1). Site characterizations are according to the 2008/50/EC directive and European Environmental Agency (EEA) guidelines [38].
Figure 1.
Map of Greece displaying the six cities where PAH measurements were conducted. The two sites in the Greater Area of Athens are shown in the insert panel.

Table 1.
Details of sampling sites.
Ambient particle samples were collected on quartz-fiber filters (Flex Tissuquartz, Pall Corporation, Port Washington, NY, USA) using high- or low-volume samplers, during winter (December and January) and summer (June to August) months. All used gravimetric samplers were reference-equivalent for PM measurement according to the EU standards. The sampling duration at all sites was 24 h. Sampling took place concurrently at Ioannina, Xanthi, Volos and Piraeus [31] in summer (June to August 2019) and winter (December 2019 to January 2020). In Athens, the same monthly periods were considered, but for summer 2017 and winter 2017–2018 instead [18]. In Heraklion, the same monthly periods were considered for summer 2022 and winter 2022–2023. This was necessary due to the lack of concurrent measurements with the other four sites and to ensure a degree of seasonal comparability. It is noted that a lack of significant interannual trend for black carbon (a pollutant strongly associated with primary PAHs) was reported for year 2015–2019 at the Athens Thissio site [39]. Moreover, the selected periods in Heraklion presented very similar meteorological conditions (temperature, wind speed) to the respective months in 2019–2020.
PM2.5 particles were collected at all sites, with the exception of Heraklion where a PM10 sampler was used, since the station is operated officially according to the provisions of the 2004/107/EC directive. Nevertheless, this is not anticipated to significantly influence the comparison with PAH concentrations measured in PM2.5, since the vast majority (85–95%) of PAH species determined in this study are expected to be present in the PM2.5 fraction [40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47]. Past measurements in Heraklion showed that 97% and 93% of total particle-bound Σ-PAH concentrations were encountered incomposed of particles smaller than 3 μm and 1.5 μm, respectively [48]. Similar results have been reported in Athens, with 98–99% of PM10 Σ-PAHs measured in the PM2.5 fraction [47]. The dominance of the fine mode in Σ-PAH concentrations has also been demonstrated in Thessaloniki, where 88–89% of mean ambient Σ-PAHs concentrations were attributed to particles up to 3 μm [44].
Filters were equilibrated pre-/post-sampling, and weighed under controlled temperature (20 ± 3 °C) and relative humidity (40 ± 5%) and were stored in a freezer until analysis. Field blanks and laboratory blanks were also kept and analyzed. A total of 305 samples were collected and analyzed (81 in Ioannina, 71 in Thissio, 62 in Xanthi, 38 in Piraeus, 29 in Volos, 23 in Heraklion). Details regarding measurements and meteorological data at the six sites are provided in Table 1 and Table 2.

Table 2.
Meteorological data by season for the six sampling sites.
2.2. Laboratory Analyses
PAHs in the filter samples were quantified by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS). An Agilent 6890N system (Agilent Technologies Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA) with a J&W DB-5MS capillary column and a 5973 mass selective detector was used for samples from Athens, Piraeus, Volos and Xanthi. For samples from Ioannina and Heraklion, an Agilent 7890 (Agilent Technologies Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA) system with an HP-5MS capillary column and an Agilent 5975C mass selective detector was used [18,49]. All quartz filter samples were extracted using an accelerated solvent extraction system (Dionex ASE 300; Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA). Prior to the analysis, samples were spiked with a mixture of deuterated internal standards for the identification of PAHs and calculation of recovery efficiencies (16 members, LGC Standards, Middlesex, UK). For the extraction, part of the quartz filter was extracted using a 50:50 n-hexane-dichloromethane (SupraSolv®, Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany) mixture, and obtained extracts were purified through a silica column. PAHs were eluted with a 10 mL n-hexane/ethyl acetate (9:1 v/v) mixture and placed into a glass vial for further concentration under a gentle nitrogen stream [18,50,51]. [2H12]perylene (LGC Standards, Middlesex, UK) used as an internal standard for the calculation of recovery efficiencies, was spiked into the vial before sealing and storage. On the day of the analysis, injections with internal standards were also run to calculate Relative Response Factors (RRF).
The identification of compounds was based on the retention time, mass fractionation and co-injection of standard mixtures. Information regarding the detected PAHs is provided in Table 3. PAH quantification was based on the calculation of RRF for every PAH member. The recovery efficiency of the method was calculated using 17 deuterated PAHs (16 deuterated EPA PAHs and [2H12]perylene), according to the equation provided by Mandalakis et al., 2001 [52]. The calculated average recoveries for the two GC-MS systems, Agilent 6890N and Agilent 7890, were 81 ± 10% and 75 ± 12%, respectively, in agreement with literature values [50,53].

Table 3.
Information about the PAH species presented in this study.
Limits of detection (LODs) were calculated as three times the standard deviation of blanks. All 16 EPA species were detected in blanks. For the summer period, mean blank concentrations were one order of magnitude lower than the mean measured concentrations, while during winter, they were almost two orders of magnitude lower. All data were corrected using the mean concentration of the blank samples, and correction for recoveries was also performed.
Organic and elemental carbon (OC, EC) concentrations were also determined by-the thermal–optical transmission (TOT) method, using a sunset carbon analyzer (Sunset Laboratory Inc., Portland, OR, USA) [54,55]. The LODs for OC and EC were estimated at 0.62 and 0.05 μg C m−3, respectively, with uncertainties of less than 10% and the final concentrations being blank corrected.
Meteorological data (temperature, relative humidity, wind speed and direction) were measured in situ at the Athens and Ioannina sites and were retrieved by the nearest stations of the automatic weather station network of the National Observatory of Athens (NOA) at the other four sites [56].
2.3. Carcinogenic Risk
It is well established that PAHs are strongly associated with increased carcinogenic risks. The carcinogenic risk from cumulative exposure to PAHs can be assessed by using the “toxicity equivalent factor” (TEF) approach, where the BaP equivalent concentration of each toxic PAH member is calculated based on its concentration and specific TEF conversion factors (Table 3) derived from toxicological studies [57,58]. The BaP-equivalent concentration (BaPeq) for the mixture of the 16 EPA PAHs (Σ16PAHs) was calculated according to the following equation:
where Ci is the concentration (in ng m−3) and TEFi is the toxicity equivalent factor for each member [57,59].
Having calculated the BaPeq, it is possible to estimate the incremental lifetime excess cancer risk (ILCR) from inhalation, based on the following equation:
where URBaP (unit risk) is an estimation of the increased cancer risk from inhalation exposure to a concentration of 1 ng m−3 of BaP over a lifetime of 70 years. For this estimation, two approaches are commonly used. The more conservative is the one proposed by the Office of Environmental Health Hazards Assessment (OEHHA) of the California Environmental Protection Agency (CalEPA), with an inhalation URBaP (IUR) of 1.1 × 10−6 (i.e., 0.11 cases per 100,000). The other has been suggested by the Word Health Organization (WHO), with an IUR equal to 8.7 × 10−5 (i.e., 8.7 cases per 100,000) [18,53,60].
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of PAH Levels
Table 4 presents the winter–summer mean concentrations of the 16 EPA PAH sum (Σ16PAHs) along with BaP at the six cities. Considering the average of winter and summer values as an approximation of the annual mean, the value in Ioannina stands out (2.4 ng m−3), being well above the EU annual target value of 1 ng m−3. The Σ16PAHs sum in Ioannina was more than two times higher compared to the second-highest measuring site (Athens). The only study that had reported PAH concentrations in Ioannina [61] was based on measurements in the late 90s, and presented annual BaP concentrations varying between 0.3 and 2.6 ng m−3. However, these high levels had been attributed to excessive emissions from old-technology cars in Greece (pre-Euro 2, most of which were not even equipped with catalytic converters) and to heating oil burning. This illustrates a long-term organic air pollution issue for the city, albeit due to changing environmental pressures. PAH levels of the magnitude observed in Ioannina are rarely observed in European cities, except in areas directly impacted by fossil fuel-burning for power production, like in Upper Silesia, Poland [62]. However, they are more comparable to concentrations reported in East Asian cities [63,64,65,66].

Table 4.
Seasonal levels of the sum of 16 EPA PAHs (Σ16PAHs) and benzo[a]pyrene (BaP) at the six sites.
At the Thissio urban background site in Athens, the annual approximation for BaP (0.76 ng m−3) was close to the EU target value of 1 ng m−3 (2004/107/EC directive). These levels are much higher than those measured (0.01–0.10 ng m−3) at the suburban background sites used in Greek reporting- to the EU. The concentrations observed at Thissio classify Athens among the upper tier of major European metropolitan areas reporting BaP concentrations at urban background sites [67]. BaP and Σ16PAH levels in winter appear similar to those recorded during the cold period in Southeastern-European capitals like Sofia [68], Zagreb [69], and Ljubljana [70].
At the two near-port sites (Piraeus and Volos), the estimated annual BaP concentration was also close to the EU target value of 1 ng m−3 (0.61 and 0.74 ng m−3, respectively), probably due to the proximity to shipping emissions and the increased traffic-related activity. Piraeus is the biggest port in Greece with more than 5.8 M passengers (at the central passenger terminal, within 200 m of the sampling site) and 600,000 tons of cargo annually [71]. In comparison to Piraeus, the port of Volos is much smaller, and its operation is concentrated on freight rather than on passenger transport. Similar annual BaP levels (0.60 ng m−3) were registered in Volos in 2015 [72]. Up to now, there has been no published record of PAH measurements in the port of Piraeus, but the estimated annual value for Σ16PAHs is close to the one reported in 2018–2019 (9.8 ng m−3) in the industrialized coastal area of the Thriassion plain (12 km to the NW of Piraeus), which is also affected by shipping emissions [73]. The summertime Σ16PAH levels in the two port areas (Piraeus and Volos) resemble those reported in other ports in the Mediterranean, like Venice [74], Brindisi [75], Bari and Taranto [76].
Mean annual estimates in Heraklion were 60% lower than the respective ones in Piraeus, in spite of the site’s traffic characterization. This can be attributed to the low winter levels due to the mild temperature conditions [77] and reduced heating needs. However, the traffic influence can be seen by comparison to the 2-year average background levels (0.08 ng m−3) outside the city, measured in 2012–2014 [78]. Heraklion is the only city in the study where vehicular traffic remains stable if not increased during the summer period due to the tourist activity (indicatively there were 1.9 million arrivals at the Heraklion international airport in July–August 2022) [79]. However, it should be noted that current information about the impact of direct road traffic on PAH levels in Greece is very limited, since the latest systematic PAH measurements at traffic sites were conducted more than 10 years in the past [42,80,81], and in the years between, there have been significant changes in the road transport sector, including the modernization passenger fleet and the increased participation of diesel cars.
The rural background site in the area of Xanthi expectedly registered the lowest winter–summer mean (0.17 ng m−3), given the relative absence of local sources. However, it is noteworthy that this value is considerably higher than the one (0.06 ng m−3) reported by 2-year measurements at a similar site in the same region of Greece (Thrace), near the city of Alexandroupolis, during 2009–2011 [82], i.e., prior to the onset of the Greek recession. This might signify that even the near-city background locations in Greece can be affected by the dramatically increased winter residential wood burning (RWB) emissions in the past decade. A similar impact of RWB on a nearby rural background location was reported for the research site at Melpitz, Germany [19].
3.2. Spatiotemporal Variability of PAH Groups
The seasonal variability of the 16 EPA PAHs (Σ16PAHs) and BaP in the six cities is presented, including statistical testing, in Figure 2a,b and Figure S1 and Table 4. The winter/summer ratios of mean Σ16PAHs concentrations were 21, 7, 98, 16, 10 and 8 in Athens, Piraeus, Ioannina, Volos, Xanthi and Heraklion, respectively. For BaP, the corresponding ratios were 29, 60, 479, 29, 33 and 24. All seasonal differences were statistically significant (Table S1) and were related to the decreased anthropogenic emissions during summer in Greece, especially in the vacation month of August [26], but also to the increased volatilization of LMW PAH congeners. In addition, the enhanced atmospheric reactivity during the warm period led to PAH substitution or degradation [83] (this was particularly visible for BaP, the levels of which collapsed in summer across the country). High seasonal differences were observed for Σ16PAHs at the two urban background sites, Athens and especially Ioannina, as a result of strong RWB emissions in limited dispersion conditions that favor the appearance of intense pollution events (IPEs) in winter [18,30].
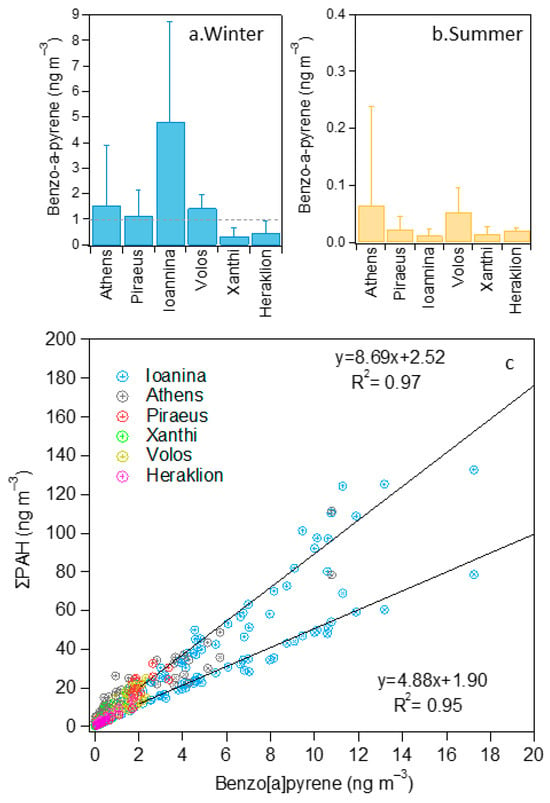
Figure 2.
Seasonal variability of BaP mean concentration (a,b) at the six sites (dashed line for the EU target value) and correlation between the 16 EPA (high slope) and the 6 EU-proposed (low slope) PAHs with BaP (c).
The lower ratio recorded in Piraeus (7 for Σ16PAHs), in spite of the very strong impact of winter RWB, which is comparable to the one at Athens—Thissio [31], indicates considerable PAH emissions from increased anthropogenic activity in the summer. This is related to the operation of the passenger port [31], as the sampling site is at a distance of approximately 150 m to the east of the port terminals (Figure S2a). The winter–summer gradient in Volos could also indicate increased emissions from the port area in summer (Figure S2c).
Heraklion also recorded a relatively low winter enhancement (ratio of 8 for Σ16PAHs), which should be related to the reduced RWB activity due to higher temperatures in winter but also to the local traffic source, which is associated with a more uniform emission profile throughout the year compared to residential heating. The rural background site in Xanthi also displayed a strong wintertime increase. This is expected since the site is affected mainly by regionally transported aerosol, which arrives at the site highly processed with respect to the source, and the majority of its original PAH content has been lost [84]. As discussed previously, an impact from RWB emissions in the city of Xanthi to the west is also possible (Figure S2b). Overall, the levels of both Σ16PAHs and BaP during summer were similar throughout Greece, with a Σ16PAHs range of 0.4–2.1 ng m−3 and a BaP range of 0.01–0.05 ng m−3, and the differences in the majority of the inter-site pairs were not statistically significant at the 99% confidence level (Table S2).
Figure S3 shows that during winter the PAH members with the highest concentrations at all sites were benzofluoranthenes (here presented as a BbjkF sum), followed by Chr in Ioannina, Xanthi and Volos, and by IP or BghiP in Athens, Piraeus and Heraklion. It can be observed that at the two sites in the Greater Athens Area (Athens and Piraeus), where a total of 3 million vehicles are circulating, the concentrations of high molecular weight (HMW) IP and BghiP were enhanced, indicating an important input from the road transport sector [85,86]. This was also the case for the traffic site in Heraklion. On the contrary, at the sites where in winter the RWB source dominates (especially in Ioannina), the Chr contribution to Σ16PAHs was stronger [87]. The third most abundant PAH members were IP, BghiP or BaP. It is noted that four of the five members (with the exception of BghiP), mentioned as the most abundant here, are found in the IARC list of carcinogenic agents.
The classification of PAHs by molecular weight is often used as indicative of their sources. For example, LMW PAHs (LMW: 128–178 gmol−1) and medium molecular weight PAHs (MMW: 202–228 gmol−1) have been used as indicators of heavy oil and diesel combustion emissions [88,89], while MMW and HMW (HMW: 252–300 gmol−1) PAH concentrations can be influenced by BB and road transport [90,91]. Also, it should be mentioned that the health impacts of PAHs are associated with their MW; for example, HMW member concentrations have been found to correlate with oxidative potential [92,93], while more volatile species have increased inhalation bio-accessibilities [94].
Figure 3 presents the seasonal and spatial variation of mean PAH concentrations by MW group (the respective relative fractions in Σ16PAHs are shown in Figure S5). At all sites during winter, HMW PAHs exhibited the highest contributions (>50%), mainly demonstrating the importance of BB and car traffic emissions. Biomass burning is known to contribute strongly to HWM but also to MMW PAH members [95]. Especially, in Ioannina, it has been estimated that RWB can be responsible for approximately 92% of OC concentrations in winter [29] and is anticipated to be the major contributor to PAH concentrations as well. The only site that showed a substantial contribution of LMW PAHs during winter was Athens (~10%). At the Thissio site, which is a receptor site [23], a high contribution to Σ16PAHs (~33%) has been estimated by source apportionment analysis for a diesel/oil source (vehicles, central heating, shipping) enriched in LMW PAHs [18].
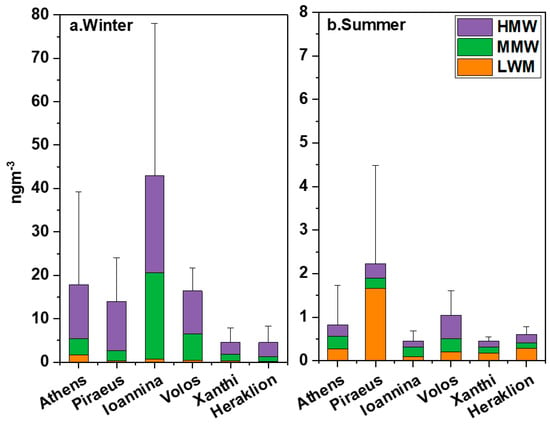
Figure 3.
Seasonal variability of Σ16PAH concentrations by MW group in (a) winter and (b) summer in the six cities. Different colors represent the low- (LMW), medium- (MMW) and high- (HMW) molecular weight fractions.
On the contrary, during summer, Piraeus was the only site exhibiting a majority contribution of LMW PAHs, which should be considered indicative of oil combustion in passenger ships navigating, calling at or hoteling in the port area [96,97]. Moreover, LMW PAH-emitting vehicular diesel emissions are an important contributor near the site in summer [98], with an increased number of heavy duty vehicles transporting goods to insular areas of Greece to accommodate tourist needs. The LMW PAH results in Piraeus during high temperature conditions, when a large part of LMW compounds volatilizes out of the particle phase [83,99], emphasize the strength of the source. Studies in other Mediterranean ports have presented similar summertime PAH levels and MW classification [75,100]. Even though LMW congeners such as Nap, Acy, Ace and Flu are volatile, they are regularly detected in the vast majority of PAH studies analyzing the PM2.5 phase and in comparable levels to the ones reported here [101,102]. In the present case, the highest concentrations of these LMW congeners were measured at the near-port site of Piraeus. It is characteristic that Tolis et al. in the port of Thessaloniki [103] reported six-fold higher levels of PM2.5-bound LMW members compared to Piraeus (e.g., mean annual Nap concentrations of 2.7 ng m−3).
In Ioannina, the mean summer concentrations of HMW and MMW species are more than two orders of magnitude lower compared to winter, due to the absence of the RWB source. Moreover, long-range transport might have had a lower effect in Ioannina as the area is shielded by high mountainous ranges. It is worth noting that the three sites that are more affected by combined port and traffic emissions (namely Piraeus, Volos and Heraklion) reported the highest summertime Σ16PAH levels, suggesting additional exposure risks for pedestrians, commuters and travelers [104].
For comparison reasons, the sum of the six PAHs proposed by the EU (Table S3) in its air quality directive is also included in Figure 2c. It can be observed that the average concentration difference when considering the 16 EPA and the 6 EU proposed PAHs is almost two-fold (Figure 2c and Figure S1). Furthermore, the excellent correlation seen between the Σ16PAHs (R2 = 0.97) and Σ6EU (R2 = 0.95) PAHs with BaP (Figure 2c) demonstrates that by determining the levels of BaP, a fair estimation of PAH sums can be provided for winter across Greece. It should be stressed that Σ16PAH levels presented some spatial variability during summer, in contrast to the sum of the six EU-suggested species - where this differentiation was not observed due to the non-inclusion of LMW PAHs that are increasingly present during the warm period mainly at the near-port sites. This within-area variability should be taken into consideration in the design of health studies aiming to characterize long-term PAH effects.
3.3. Diagnostic Ratios
Four diagnostic ratios (DR) were used, namely Ant/(Ant + Phe); Flt/(Flt + Pyr); BaA/(BaA + Chr); and IP/(IP + BghiP) (Figure S4). The first DR (Ant/(Ant + Phe)) involves LMW species and is useful for separation between petrogenic (<0.1) and pyrogenic (>0.1) origins [105,106]. The second DR (Flt/(Flt + Pyr)) includes MMW (202) PAHs and can suggest petrogenic (<0.4), non-solid fuel combustion (0.4–0.5) or biomass/coal burning (>0.5) sources [105,106]. BaA/(BaA + Chr) can indicate petroleum (<0.2), petroleum product combustion (0.2–0.35) and biomass/coal burning (>0.35) [34]. Finally, the ratio of the less volatile species (IP/(IP + BghiP)) is used in order to distinguish between petrogenic (<0.2), vehicular exhaust (0.2–0.5) and biomass/coal burning (>0.5) sources [107].
Τhe Ant/(Ant + Phe) ratio here indicated a predominantly pyrogenic origin in all cities, since its mean values were higher than 0.1. Only in Piraeus did the interquartile range (IQR) include the 0.1 cutoff, implying a potential influence of petrogenic PAHs deriving—from transport and storage activities of petroleum products in the port areas in Piraeus and the Elefsis bay [108]. Indicativly, 80% of ratio values below 0.1 in Piraeus were associated with prevailing winds from the port sectors (SW to NW). Both Athens and Piraeus presented wider IQRs compared to the other cities.
The Flt/(Flt + Pyr) ratio pointed to pyrogenic sources in all cities, registering mean values close to or above 0.4, again with the exception of Piraeus (although this discrepancy was marginal with a mean DR of 0.38). The mean DR in Ioannina appears to be lower than expected (<0.5) when considering the very large impact of RWB and the low temperatures that would ensure that the majority of the two MMW members were in the particle phase [83,109,110]. In addition, the ratio can be affected by the type of combustion appliance and the type of wood. In the region of Ioannina, hardwood is mostly used [29], and several studies have reported ratios smaller than 0.5 in hardwood burning emissions [111,112].
Conversely, the IP/(IP + BghiP) ratio, which depends on PAH members not being affected by volatilization for atmospheric chemical processing, verified the impact of RWB in Ioannina and Athens (mean values > 0.5), as it has already been hinted by the temporal variability characteristics. All other sites registered mean values within 0.45–0.5, indicating a mixed influence of wood and liquid fuel burning.
The BaA/(BaA + Chr) DR can also reveal the BB impact, as indicated by the >0.35 mean value in Ioannina, where in harsh winter conditions both species are found exclusively in the particle phase. Piraeus that was also affected by severe RWB episodes [31] had some very high daily DRs and a large IQR. Heraklion also had a high mean DR; however, this was affected by outlying values during festive days characterized by more intense BB emissions (e.g., Christmas).
Given that the ratios that involve volatile and reactive members [113] cannot fully represent the relative PAH abundances as they were during their emission, it is useful to examine DR cross-plots in order to reduce uncertainty. Figure 4 shows selected DR correlations for data-points from all sites combined during winter. The first cross-plot includes the ratios of BaA/(BaA + Chr) and Ant/(Ant + Phe) (Figure 4a) while the second presents IP/(IP + BghiP) vs. BaA/(BaA + Chr) (Figure 4b).
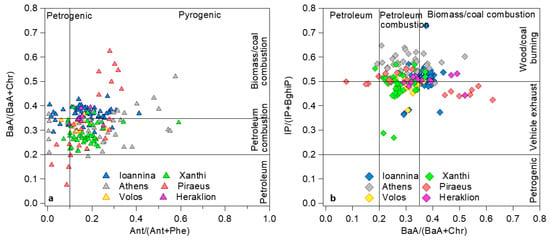
Figure 4.
Diagnostic ratio (DR) cross-plot diagrams, (a) BaA/(BaA + Chr) to Ant/(Ant + Phe) and (b) IP/(IP + BghiP) to BaA/(BaA + Chr), based on PAHs concentrations measured in the six cities. DR ranges delineate the impacts of potential PAH sources.
In Figure 4a, a petrogenic/petroleum origin is verified by both ratios only in the case of Piraeus. The majority of the data are associated with fuel burning, with a clear effect of BB being confirmed in Ioannina and also in Athens and Piraeus. There were, however, days in Ioannina that, despite high BaA/(BaA + Chr) ratios (>0.30), were classified as petrogenic by the Ant/(Ant + Phe) ratio. They all had Ant concentrations below the LOD and in their majority they were low-concentration days, which probably favored the almost complete degradation of Ant [30,114].
In the second cross-plot (Figure 4b), the impact of BB is confirmed for Ioannina [30,115], with the majority of points concentrated in the upper-right ninth of the grid. The important BB impact in Athens [18,116] was validated mainly by the HMW ratio, while the BaA/(BaA + Chr) was more balanced between vehicular and RWB emissions. Impacts from the use of both petroleum products and biomass can be deduced for Volos and Heraklion as well. In Piraeus, the large BaA/(BaA + Chr) ratios did not correspond to high IP/(IP + BghiP) values. Since the two HMW species are known to be enhanced by intense gasoline emissions, this behavior could indicate the coincidence of increased traffic and RWB in the holiday period [31]. In the rural background site, the impact of local BB emissions appears to be more limited, with the majority of the days linked to road fuel and oil combustion, although it should be noted that aerosols arrive at the Xanthi site highly processed and the typical ranges might not apply [117].
3.4. Associations of PAHs with Carbonaceous Compounds
PAH concentrations were also studied with respect to OC and EC measured concurrently at the same sites. The respective average OC and EC concentrations during winter and summer are listed in Table 5, along with their correlation coefficients with Σ16PAH concentrations.

Table 5.
Seasonal mean concentrations of organic and elemental carbon, and correlation coefficients for pairwise comparisons with mean concentrations for Σ16PAHs.
Regarding the spatiotemporal variability of the relative OC and EC levels, at urban sites the mean OC/EC ratios were higher in winter than in summer, with differences being statistically significant at the 95% confidence level (Table S3), especially at the locations that were highly affected by RWB (Athens, Ioannina and Volos). The winter enhancement of OC average concentration at these sites was from 3-fold in Piraeus to 10-fold in Ioannina. While higher summer OC/EC in the past were reported in Greece due to the photochemical production of secondary organic aerosol (SOA), in the present conditions, it is typical for urban sites to record higher ratios in winter due to RWB emissions (especially in smoldering conditions) and their nighttime processing [77]. Xanthi had similar OC and EC levels in the two seasons, with a 47% higher OC/EC summer ratio being compatible with sampling of processed aerosol. OC levels in summer were within a 2-fold range (2.8–4.2 μg m−3) [26] but EC showed marked inter-site differences, resembling those observed for Σ16PAHs, with very low levels in Ioannina and Xanthi where high OC/EC ratios were recorded. In the remaining sites, the summer ratio of mean OC to mean EC was around 3 (including at the Heraklion traffic site), mostly indicating the impact of the road transport sector and a moderate local production of SOA (in Heraklion, traffic emissions that would lead to a lower OC/EC ratio of 1 to 2 are probably counterbalanced by the more enhanced photochemical production of SOA) [118,119]. The seasonal persistence of EC concentrations in Volos is also notable.
When comparing OC concentrations with both Σ16PAHs and BaP during winter, very strong Pearson correlation coefficients were observed (r = 0.91 and 0.89, respectively, for the pooled dataset across all sites). The strong associations were driven by co-emission, especially during nighttime when atmospheric dispersion is reduced in a shallow boundary layer and also by limited PAH volatilization. It has been shown that atmospheric reactivity in Greek cities is favored even in winter conditions; therefore, it is possible that processing mechanisms at a local level are similar between OC and PAHs. This could be supported by the fact that winter correlations of Σ16PAHs with inert EC are lower in comparison to OC, at least in the three cities where wintertime atmospheric chemistry has been verified in Greece [27,29,31].
The correlations of Σ16PAHs with OC were statistically significantly lower (p-value < 0.01) during summer, given the different degrees and pathways of processing that they are undergoing. This was also evident in the case of EC that is not transformed following co-emission with PAHs. A notable exception was the traffic site of Heraklion and also Piraeus that is also influenced by near-port traffic emissions.
Figure 5 displays the associations of BaP with OC and EC. It is apparent that since the correlation between OC and BaP during winter is excellent when considering all the urban sites (and the fact that the slopes of the OC vs. BaP linear associations remain stable among sites), OC might be used as a proxy for the estimation of BaP levels if needed, since the analysis for the determination of PAHs is more complex compared to OC. This observation could also be of use for urban-scale chemical transport models [120] to simulate PAH fields in winter conditions.
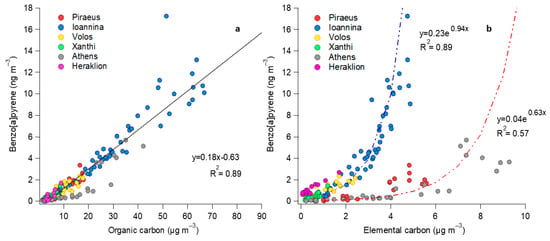
Figure 5.
Correlations of BaP with OC (a) and EC (b), including winter data from the six sites.
Figure 5b presents the association of BaP with EC across the cities in winter. In this case, the link was not linear, as with OC. Two patterns emerge, mostly influenced by the sites affected by winter smog events due to RWB. In Ioannina, the BaP/EC ratios during these events was lower than in the two sites in the area of Athens, where in spite of higher EC levels, BaP does not reach the high concentrations observed in Ioannina. The difference could be attributed either to differences in wood-burning type and conditions among the cities (it has been shown that while hardwood is mostly burned in Ioannina, in Athens, the biomass fuel mixture is more diversified), or to atmospheric conditions in Ioannina being more favorable for the conservation of BaP from atmospheric decay.
3.5. Aerosol Carcinogenic Risk
The BaPeq values for all sites were calculated for summer and winter, taking into account the average concentrations and TEFs of the 16 EPA members (Table 6).

Table 6.
Seasonal variability of BaPeq, and ILCR estimates in the six cities.
It is clear that the urban environment which exhibited the highest BaPeq values both during winter and overall was Ioannina. Athens, Piraeus and Volos experienced similar values in the range of 7–8 ng m−3, while the cities with the lowest values were Xanthi and Heraklion. Since these values are solely based on the 16 EPA components, they are expected to be significantly higher if other emerging PAHs are also taken into account [121]. At all sampling sites, benzofluoranthenes and dibenzo(ah)anthracene contributed the most to BaPeq (62–77%), while benzo(a)pyrene had smaller contributions (14–24%), highlighting the need to include more PAHs species to exposure studies for a more accurate estimation of risks.
Based on the estimated annual BaPeq values, the respective inhalation ILCR was calculated. As expected, the highest values were found for Ioannina, equal to 1.1 × 10−5 (OEHHA method) and 8.8 × 10−4 (WHO method). These values were well above the value of 10−6, which is considered a threshold above which carcinogenic risks become not acceptable, while the value calculated with the WHO method exceeded the 10−4 level, and have no alternatives for affordable residential heating other than biomass burning [122]. Athens, Piraeus and Volos were linked to similar ILCR values, in the order of 4.4–5.4 × 10−6 (OEHHA method) and 3.5–4.3 × 10−4 (WHO method). The lowest ILCR values were estimated for Xanthi, remaining, however, above the 10−6 lower acceptable threshold, while in Heraklion, values were 33% higher than Xanthi but not as high as in the other urban areas that are disproportionately impacted by RWB in winter. When comparing winter vs. summer BaPeq values, the risk in Athens was 44 times higher during winter, 35 times higher in Piraeus, a striking 78 times higher in Ioannina, 27 times higher in Volos, 24 times higher in Xanthi and merely 4 times higher in Heraklion. Comparing the values with other cities, the exposure levels were lower compared to Asian megacities like Xi’an (17 ng m−3) [123] and Taiyuan (28 ng m−3) [124]; however, the levels in Ioannina seemed to approach those extreme values. The other cities presented similar values to Zagreb, Croatia (4.5 ng m−3) [125], and Istanbul, Turkey (5.5 ng m−3) [126], but higher values than Gdynia, Poland (0.9 ng m−3) [127]; Győr, Hungary (1.4–2.2 ng m−3) [128]; southern Germany (2.7 ng m-3) [129]; Tuscany, Italy (0.1–0.8 ng m−3) [130]; and Santander, Spain (0.11–0.23 ng m−3) [131]. In conclusion, ILCR risks at all sites were above the minimum acceptable threshold, highlighting the significant impact of biomass burning on air quality and population exposure on a national level.
4. Conclusions
The levels of 16 EPA PAHs (Σ16PAHs) in six Greek cities were examined in two different periods (summer and winter) and were found to present substantial spatial (estimated annual means ranging between 2.5–21.7 ng m−3 among the cities) and temporal variability, driven by site type, local emissions and prevailing climatic conditions. Enhanced concentrations were observed during winter while in summer the levels remained uniformly low. Regarding estimated BaP mean annual levels, the EU target value is expected to be violated in Ioannina but also in other medium-sized cities in Northern Greece, which experience harsh winters and have no alternatives for affordable residential heating other than biomass burning.
Moreover, the separation of PAHs according to their molecular weight as well as diagnostic ratios of PAHs isomers and their cross-plots were used for the estimation of PAH sources. At all sites, the influence of local activities for residential heating was major during winter. During summer, PAH concentrations were mainly affected by fossil fuel emissions, linked to the road transport sector and to shipping in port areas (an observation that was verified for the first time by multi-site measurements in Greece), while the regional contribution was generally low. A direct correlation was observed for BaP and OC, while the correlation with EC presented patterns depending on the sampling site.
BaPeq estimates were used to evaluate the carcinogenic potency and estimate the incremental lifetime cancer risk from inhalation exposure to PAHs. The results indicate that there is a definite need to expand the range of PAHs (and their derivatives) that are presently considered in exposure and risk assessment studies, since there are members with recognized carcinogenic potential exceeding that of BaP and other IARC-listed species. The fact that five of the eight IARC-listed PAHs are in the HMW group indicates the large carcinogenic potential of the BB source, which needs to be regulated locally, if not nationally.
Among the six cities, the highest values were calculated in Ioannina, where the risks were found to be at alarming levels, with the severity of the issue being also intertwined with socioeconomic factors, given the low income in the region. This, on a national level, translates into substantial environmental injustice among regions and urban areas. Increased levels were recorded also in Athens, Piraeus and Volos. Despite the limitations of this study—mainly the unavailability of concurrent measurements at all sites, the use of different sampler types and the relatively small sample sizes in some cities—the results highlight the need to investigate PAH properties in more Greek cities and an urgent need for biomass burning regulations.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/toxics12040293/s1. Table S1: Statistical significance of seasonal differences in Σ16PAH concentrations measured at each site; Table S2: Statistical significance of inter-site differences in Σ16PAH concentrations during the warm season; Table S3: Statistical analysis between the OC/EC ratios during winter and summer at each site. Figure S1: Σ16-EPA PAHs and Σ6-EU PAHs mean concentrations at the six sampling sites (blue color for winter values; yellow for summer); Figure S2: Selected wind plots for Piraeus in summer (a), Xanthi in winter (b) and Volos in summer (c), associating wind direction with Σ16PAH concentration (ng m−3). The color scale indicates Σ16PAH levels and the radial axis shows their frequency of appearance by direction; Figure S3: PAH mean concentrations by member during winter (left) and summer (right) periods; Figure S4: Distribution of diagnostic ratio values calculated at the six sites; Figure S5: Seasonal variability of the relative contributions on LMW, MMW and HMW PAHs groups at the six sites.
Author Contributions
I.T.: conceptualization, methodology, data curation, investigation, formal analysis, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing; K.T.: data curation, investigation; G.G.: methodology, data curation, investigation, formal analysis, writing—review and editing; C.P.: data curation, writing—review and editing; K.P.: data curation; D.P.: data curation, writing—review and editing; E.L.: writing—review and editing; A.G.: writing—review and editing; A.B.: conceptualization, methodology, data curation, investigation, formal analysis, visualization, supervision, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing; M.K.: writing—review and editing; E.G.: writing—review and editing; N.M.: conceptualization, visualization, supervision, writing—review and editing, project administration, funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research work was supported by the Hellenic Foundation for Research and Innovation (H.F.R.I.) under the “First Call for H.F.R.I. Research Projects to support Faculty members and Researchers and the procurement of high-cost research equipment grant” (Project Number: 3232-Regenerate) by the General Secretariat for Research and Innovation (GSRI).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon request to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge support for sample collection and logistics from various colleagues, especially from N. Hatzianastasiou (Ioannina), K. Kourtidis (Xanthi), K. Eleftheriadis, E. Diapouli, A. Papayiannis (Volos), P. Kalkavouras, I. Stavroulas (Athens and Piraeus), N. Kalivitis and G. Kouvarakis (Heraklion).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Krzyszczak, A.; Czech, B. Occurrence and Toxicity of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Derivatives in Environmental Matrices. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, L.; Zhang, H.; Xing, W.; Wang, Y.; Bai, P.; Zhang, L.; Hayakawa, K.; Toriba, A.; Wei, Y.; et al. Assessing Approaches of Human Inhalation Exposure to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desler, C.; Johannessen, C.; Rasmussen, L.J. Repair of DNA Damage Induced by Anthanthrene, a Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon (PAH) without Bay or Fjord Regions. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2009, 177, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, B.; Albores, A. DNA Damage Caused by Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Mechanisms and Markers. Sel. Top. DNA Repair 2011, 201, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheurer, M.E.; Danysh, H.E.; Follen, M.; Lupo, P.J. Association of Traffic-Related Hazardous Air Pollutants and Cervical Dysplasia in an Urban Multiethnic Population: A Cross-Sectional Study. Environ. Health Glob. Access Sci. Source 2014, 13, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, K.; Wietzoreck, M.; Shahpoury, P.; Filippi, A.; Hildmann, S.; Lelieveld, S.; Berkemeier, T.; Tong, H.; Pöschl, U.; Lammel, G. Is the Oxidative Potential of Components of Fine Particulate Matter Surface-Mediated? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 16749–16755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marris, C.R.; Kompella, S.N.; Miller, M.R.; Incardona, J.P.; Brette, F.; Hancox, J.C.; Sørhus, E.; Shiels, H.A. Polyaromatic Hydrocarbons in Pollution: A Heart-Breaking Matter. J. Physiol. 2020, 598, 227–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollinger, C.E.; McCallister, M.; Clark, R.; Rhoades, R.; Maguire, M.; Savage, R.E.; Jiao, Y.; Harris, K.J.; Ramesh, A.; Lochotzki, H.; et al. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Implications for Developmental, Molecular, and Behavioral Neurotoxicity. In Handbook of Toxicology of Chemical Warfare Agents; Gupta, R.C., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 279–297. ISBN 9780128190906. [Google Scholar]
- Geier, M.C.; Chlebowski, A.C.; Truong, L.; Massey Simonich, S.L.; Anderson, K.A.; Tanguay, R.L. Comparative Developmental Toxicity of a Comprehensive Suite of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 571–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartaglione, A.M.; Racca, A.; Ricceri, L. Developmental Exposure to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs): Focus on Benzo[a]Pyrene Neurotoxicity. Reprod. Toxicol. 2023, 119, 108394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaragoza-Ojeda, M.; Eguía-Aguilar, P.; Perezpeña-Díazconti, M.; Arenas-Huertero, F. Benzo[Ghi]Perylene Activates the AHR Pathway to Exert Biological Effects on the NL-20 Human Bronchial Cell Line. Toxicol. Lett. 2016, 256, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaragoza-Ojeda, M.; Torres-Flores, U.; Rodríguez-Leviz, A.; Arenas-Huertero, F. Benzo[Ghi]Perylene Induces Cellular Dormancy Signaling and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in NL-20 Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2022, 439, 115925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keith, L.H. The Source of U.S. EPA’s Sixteen PAH Priority Pollutants. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 2015, 35, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Directive 2004/107/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 15 December 2004 Relating to Arsenic, Cadmium, Mercury, Nickel and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Ambient Air. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2004/107/oj (accessed on 11 March 2024).
- Lammel, G. Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds in the Atmosphere—A Review Identifying Research Needs. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 2015, 35, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.B.; Shaikh, S.; Jain, K.R.; Desai, C.; Madamwar, D. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Sources, Toxicity, and Remediation Approaches. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 562813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Shafy, H.I.; Mansour, M.S.M. A Review on Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Source, Environmental Impact, Effect on Human Health and Remediation. Egypt. J. Pet. 2016, 25, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiodra, I.; Grivas, G.; Tavernaraki, K.; Bougiatioti, A.; Apostolaki, M.; Paraskevopoulou, D.; Gogou, A.; Parinos, C.; Oikonomou, K.; Tsagkaraki, M.; et al. Annual Exposure to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Urban Environments Linked to Wintertime Wood-Burning Episodes. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 17865–17883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Pinxteren, D.; Engelhardt, V.; Mothes, F.; Poulain, L.; Fomba, K.W.; Spindler, G.; Cuesta-Mosquera, A.; Tuch, T.; Müller, T.; Wiedensohler, A.; et al. Residential Wood Combustion in Germany: A Twin-Site Study of Local Village Contributions to Particulate Pollutants and Their Potential Health Effects. ACS Environ. Au 2023, 4, 12–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.; Silvergren, S.; Spinicci, S.; Mashayekhy Rad, F.; Nilsson, U.; Westerholm, R.; Johansson, C. Contribution of Wood Burning to Exposures of PAHs and Oxy-PAHs in Eastern Sweden. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 11359–11379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iakovides, M.; Apostolaki, M.; Stephanou, E.G. PAHs, PCBs and Organochlorine Pesticides in the Atmosphere of Eastern Mediterranean: Investigation of Their Occurrence, Sources and Gas-Particle Partitioning in Relation to Air Mass Transport Pathways. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 244, 117931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffari, A.; Daher, N.; Samara, C.; Voutsa, D.; Kouras, A.; Manoli, E.; Karagkiozidou, O.; Vlachokostas, C.; Moussiopoulos, N.; Shafer, M.M.; et al. Increased Biomass Burning Due to the Economic Crisis in Greece and Its Adverse Impact on Wintertime Air Quality in Thessaloniki. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 13313–13320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Grivas, G.; Stavroulas, I.; Bougiatioti, A.; Liakakou, E.; Dumka, U.C.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Mihalopoulos, N. Apportionment of Black and Brown Carbon Spectral Absorption Sources in the Urban Environment of Athens, Greece, during Winter. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalkavouras, P.; Grivas, G.; Stavroulas, I.; Petrinoli, K. Science of the Total Environment Source Apportionment of Fine and Ultrafine Particle Number Concentrations in a Major City of the Eastern Mediterranean. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 915, 170042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EEA. Classification of Monitoring Stations and Criteria to Include Them in EEA’s Assessments Products. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/themes/air/air-quality-concentrations/classification-of-monitoring-stations-and (accessed on 11 March 2024).
- Dimitriou, K.; Stavroulas, I.; Grivas, G.; Chatzidiakos, C.; Kosmopoulos, G.; Kazantzidis, A.; Kourtidis, K.; Karagioras, A.; Hatzianastassiou, N.; Pandis, S.; et al. Intra- and Inter-City Variability of PM2.5 Concentrations in Greece as Determined with a Low-Cost Sensor Network. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 301, 119713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavroulas, I.; Bougiatioti, A.; Grivas, G.; Paraskevopoulou, D.; Tsagkaraki, M.; Zarmpas, P.; Liakakou, E.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Mihalopoulos, N. Sources and Processes That Control the Submicron Organic Aerosol Composition in an Urban Mediterranean Environment (Athens): A High Temporal-Resolution Chemical Composition Measurement Study. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 901–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liakakou, E.; Stavroulas, I.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Grivas, G.; Paraskevopoulou, D.; Dumka, U.C.; Tsagkaraki, M.; Bougiatioti, A.; Oikonomou, K.; Sciare, J.; et al. Long-Term Variability, Source Apportionment and Spectral Properties of Black Carbon at an Urban Background Site in Athens, Greece. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 222, 117137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Grivas, G.; Oikonomou, K.; Tavernaraki, P.; Papoutsidaki, K.; Tsagkaraki, M.; Stavroulas, I.; Zarmpas, P.; Paraskevopoulou, D.; Bougiatioti, A.; et al. Impacts of Severe Residential Wood Burning on Atmospheric Processing, Water-Soluble Organic Aerosol and Light Absorption, in an Inland City of Southeastern Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 280, 119139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraskevopoulou, D.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Grivas, G.; Bikkina, S.; Tsagkaraki, M.; Vrettou, I.M.; Tavernaraki, K.; Papoutsidaki, K.; Stavroulas, I.; Liakakou, E.; et al. Brown Carbon Absorption and Radiative Effects under Intense Residential Wood Burning Conditions in Southeastern Europe: New Insights into the Abundance and Absorptivity of Methanol-Soluble Organic Aerosols. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 860, 160434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavroulas, I.; Grivas, G.; Liakakou, E.; Kalkavouras, P.; Bougiatioti, A.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Lianou, M.; Papoutsidaki, K.; Tsagkaraki, M.; Zarmpas, P.; et al. Online Chemical Characterization and Sources of Submicron Aerosol in the Major Mediterranean Port City of Piraeus, Greece. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanouil, C.; Drositi, E.; Vasilatou, V.; Diapouli, E.; Krikonis, K.; Eleftheriadis, K.; Kungolos, A. Study on Particulate Matter Air Pollution, Source Origin, and Human Health Risk Based of PM10 Metal Content in Volos City, Greece. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2017, 99, 691–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasopoulos, E.; Kouvarakis, G.; Babasakalis, P.; Vrekoussis, M.; Putaud, J.P.; Mihalopoulos, N. Origin and Variability of Particulate Matter (PM10) Mass Concentrations over the Eastern Mediterranean. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 4679–4690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.B.; Masiol, M.; Bruno, C.; Pasqualetto, A.; Formenton, G.M.; Agostinelli, C.; Pavoni, B. Potential Sources and Meteorological Factors Affecting PM2.5-Bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Levels in Six Main Cities of Northeastern Italy: An Assessment of the Related Carcinogenic and Mutagenic Risks. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 31987–32000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eiguren-Fernandez, A.; Miguel, A.H.; Froines, J.R.; Thurairatnam, S.; Avol, E.L. Seasonal and Spatial Variation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Vapor-Phase and PM2.5 in Southern California Urban and Rural Communities. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, Z.; Zheng, M.; Schauer, J.J.; Sheesley, R.J.; Salmon, L.G.; Cass, G.R.; Russell, A.G. Speciation of Ambient Fine Organic Carbon Particles and Source Apportionment of PM2.5 in Indian Cities. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godec, R.; Jakovljević, I.; Šega, K.; Čačković, M.; Bešlić, I.; Davila, S.; Pehnec, G. Carbon Species in PM10 Particle Fraction at Different Monitoring Sites. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 700–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Environment Agency. Criteria for EUROAIRNET-The EEA Air Quality Monitoringand Information Network; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1999.
- Garcia-Marlès, M.; Lara, R.; Reche, C.; Pérez, N.; Tobías, A.; Savadkoohi, M.; Beddows, D.; Salma, I.; Vörösmarty, M.; Weidinger, T.; et al. Inter-Annual Trends of Ultrafine Particles in Urban Europe. Environ. Int. 2024, 185, 108510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manoli, E.; Voutsa, D.; Samara, C. Chemical Characterization and Source Identification/Apportionment of Fine and Coarse Air Particles in Thessaloniki, Greece. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 949–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, R.; Wang, Y.; Gao, W.; Cong, X.; Cheng, L.; Li, X. Size-Segregated Particulate Matter Bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) over China: Size Distribution, Characteristics and Health Risk Assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 685, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoli, E.; Kouras, A.; Karagkiozidou, O.; Argyropoulos, G.; Voutsa, D.; Samara, C. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) at Traffic and Urban Background Sites of Northern Greece: Source Apportionment of Ambient PAH Levels and PAH-Induced Lung Cancer Risk. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 3556–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saarnio, K.; Sillanpää, M.; Hillamo, R.; Sandell, E.; Pennanen, A.S.; Salonen, R.O. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Size-Segregated Particulate Matter from Six Urban Sites in Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 9087–9097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysikou, L.P.; Gemenetzis, P.G.; Samara, C.A. Wintertime Size Distribution of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs), Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) and Organochlorine Pesticides (OCPs) in the Urban Environment: Street- vs Rooftop-Level Measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysikou, L.P.; Samara, C.A. Seasonal Variation of the Size Distribution of Urban Particulate Matter and Associated Organic Pollutants in the Ambient Air. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 4557–4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besis, A.; Gallou, D.; Avgenikou, A.; Serafeim, E.; Samara, C. Size-Dependent In Vitro Inhalation Bioaccessibility of PAHs and O/N PAHs—Implications to Inhalation Risk Assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 301, 119045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreou, G.; Rapsomanikis, S. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Their Oxygenated Derivatives in the Urban Atmosphere of Athens. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavouras, I.G.; Stephanou, E.G. Particle Size Distribution of Organic Primary and Secondary Aerosol Constituents in Urban, Background Marine, and Forest Atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2002, 107, AAC 7-1–AAC 7-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parinos, C.; Skylaki, E.; Hatzianestis, I.; Gogou, A. Occurrence, Sources and Water Column Distribution Trends of Suspended Particle-Associated Aliphatic and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Open Northeastern Mediterranean Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 914, 169685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogou, A.I.; Apostolaki, M.; Stephanou, E.G. Determination of Organic Molecular Markers in Marine Aerosols and Sediments: One-Step Flash Chromatography Compound Class Fractionation and Capillary Gas Chromatographic Analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 1998, 799, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parinos, C.; Gogou, A.; Bouloubassi, I.; Hatzianestis, I.; Rousakis, G. Occurrence, Sources and Transport Pathways of Natural and Anthropogenic Hydrocarbons in Deep-Sea Sediments of the Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 6069–6089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandalakis, M.; Tsapakis, M.; Stephanou, E.G. Optimization and Application of High-Resolution Gas Chromatography with Ion Trap Tandem Mass Spectrometry to the Determination of Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Atmospheric Aerosols. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 925, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iakovides, M.; Iakovides, G.; Stephanou, E.G. Atmospheric Particle-Bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons, n-Alkanes, Hopanes, Steranes and Trace Metals: PM2.5 Source Identification, Individual and Cumulative Multi-Pathway Lifetime Cancer Risk Assessment in the Urban Environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, F.; Viana, M.; Yttri, K.E.; Genberg, J.; Putaud, J. Toward a Standardised Thermal-Optical Protocol for Measuring Atmospheric Organic and Elemental Carbon: The EUSAAR Protocol. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2009, 2, 2321–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraskevopoulou, D.; Liakakou, E.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Theodosi, C.; Mihalopoulos, N. Long-Term Characterization of Organic and Elemental Carbon in the PM2.5 Fraction: The Case of Athens, Greece. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 13313–13325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagouvardos, K.; Kotroni, V.; Bezes, A.; Koletsis, I.; Kopania, T.; Lykoudis, S.; Mazarakis, N.; Papagiannaki, K.; Vougioukas, S. The Automatic Weather Stations NOANN Network of the National Observatory of Athens: Operation and Database. Geosci. Data J. 2017, 4, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Su, W.; Zhong, L.; Liang, W.; Feng, X.; Zhu, B.; Ruan, T. An Integrated Workflow Assisted by In Silico Predictions To Expand the List of Priority Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 20854–20863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghvaee, S.; Sowlat, M.H.; Hassanvand, M.S.; Yunesian, M.; Naddafi, K.; Sioutas, C. Source-Specific Lung Cancer Risk Assessment of Ambient PM2.5-Bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Central Tehran. Environ. Int. 2018, 120, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisbet, I.C.T.; LaGoy, P.K. Toxic Equivalency Factors (TEFs) for Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs). Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 1992, 16, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, C.A.; Vicente, A.M.; Custódio, D.; Cerqueira, M.; Nunes, T.; Pio, C.; Lucarelli, F.; Calzolai, G.; Nava, S.; Diapouli, E.; et al. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Their Derivatives (Nitro-PAHs, Oxygenated PAHs, and Azaarenes) in PM2.5 from Southern European Cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikalos, T.I.; Paleologos, E.K.; Karayannis, M.I. Monitoring of Time v Ariation and Effect of Some Meteorological Parameters in Polynuclear Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Ioannina, Greece with the Aid of HPLC-Fluorescence Analysis. Talanta 2002, 58, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozielska, B.; Klejnowski, K. Seasonal Variations in Health Hazards from Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Bound to Submicrometer Particles at Three Characteristic Sites in the Heavily Polluted Polish Region. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Kang, S.; Li, C.; Li, Q.; Yan, F.; Guo, J.; Ji, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, Z.; Tripathee, L.; et al. Source Apportionment and Risk Assessment of Atmospheric Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Lhasa, Tibet, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 1294–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, T.; Kong, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Niu, X.; Huang, S.; Xu, H.; Ho, K.F.; et al. A Comprehensive Evaluation of PM2.5-Bound PAHs and Their Derivative in Winter from Six Megacities in China: Insight the Source-Dependent Health Risk and Secondary Reactions. Environ. Int. 2022, 165, 107344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, S.; Du, W.; Shen, G.; Li, B.; Liu, J.; Cheng, H.; Xing, B.; Tao, S. Estimating Relative Contributions of Primary and Secondary Sources of Ambient Nitrated and Oxygenated Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 159, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Chen, Y.; Xu, X. Health Risk Assessment of PM2.5-Bound Components in Beijing, China during 2013–2015. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 1938–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EEA. EEA Europe’s Air Quality Status 2023. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/europes-air-quality-status-2023 (accessed on 11 March 2024).
- Hristova, E.; Georgieva, E.; Veleva, B. Temporal Variations of Black Carbon in the Urban Air Particulate Matter of Sofia–Observed and Modelled; Dobrinkova, N., Nikolov, O., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; ISBN 9783031267536. [Google Scholar]
- Jakovljević, I.; Štrukil, Z.S.; Godec, R.; Bešlić, I.; Davila, S.; Lovrić, M.; Pehnec, G. Pollution Sources and Carcinogenic Risk of PAHs in Pm1 Particle Fraction in an Urban Area. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drventić, I.; Glumac, M.; Carev, I.; Kroflič, A. Seasonality of Polyaromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) and Their Derivatives in PM2.5 from Ljubljana, Combustion Aerosol Source Apportionment, and Cytotoxicity of Selected Nitrated Polyaromatic Hydrocarbons (NPAHs). Toxics 2023, 11, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. EMODnet Map Viewer. Available online: https://emodnet.ec.europa.eu/geoviewer/# (accessed on 8 March 2024).
- Manoli, E.; Chelioti-Chatzidimitriou, A.; Karageorgou, K.; Kouras, A.; Voutsa, D.; Samara, C.; Kampanos, I. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Trace Elements Bounded to Airborne PM10 in the Harbor of Volos, Greece: Implications for the Impact of Harbor Activities. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 167, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanellopoulos, P.G.; Verouti, E.; Chrysochou, E.; Koukoulakis, K.; Bakeas, E. Primary and Secondary Organic Aerosol in an Urban/Industrial Site: Sources, Health Implications and the Role of Plastic Enriched Waste Burning. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 99, 222–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregoris, E.; Barbaro, E.; Morabito, E.; Toscano, G.; Donateo, A.; Cesari, D.; Contini, D.; Gambaro, A. Impact of Maritime Traffic on Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons, Metals and Particulate Matter in Venice Air. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 6951–6959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donateo, A.; Gregoris, E.; Gambaro, A.; Merico, E.; Giua, R.; Nocioni, A.; Contini, D. Contribution of Harbour Activities and Ship Traffic to PM2.5, Particle Number Concentrations and PAHs in a Port City of the Mediterranean Sea (Italy). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 9415–9429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amodio, M.; Caselli, M.; de Gennaro, G.; Tutino, M. Particulate PAHs in Two Urban Areas of Southern Italy: Impact of the Sources, Meteorological and Background Conditions on Air Quality. Environ. Res. 2009, 109, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Grivas, G.; Theodosi, C.; Tsagkaraki, M.; Paraskevopoulou, D.; Stavroulas, I.; Liakakou, E.; Gkikas, A.; Hatzianastassiou, N.; Wu, C.; et al. Carbonaceous Aerosols in Contrasting Atmospheric Environments in Greek Cities: Evaluation of the EC-Tracer Methods for Secondary Organic Carbon Estimation. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iakovides, M.; Stephanou, E.G.; Apostolaki, M.; Hadjicharalambous, M.; Evans, J.S.; Koutrakis, P.; Achilleos, S. Study of the Occurrence of Airborne Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Associated with Respirable Particles in Two Coastal Cities at Eastern Mediterranean: Levels, Source Apportionment, and Potential Risk for Human Health. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 213, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logothetis, I.; Antonopoulou, C.; Sfetsioris, K.; Mitsotakis, A.; Grammelis, P. Comparison Analysis of the Effect of High and Low Port Activity Seasons on Air Quality in the Port of Heraklion. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2021, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pateraki, S.; Fameli, K.M.; Assimakopoulos, V.; Bougiatioti, A.; Maggos, T.; Mihalopoulos, N. Levels, Sources and Health Risk of PM2.5 and PM1-Bound PAHs across the Greater Athens Area: The Role of the Type of Environment and the Meteorology. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedynska, A.; Hoek, G.; Wang, M.; Eeftens, M.; Cyrys, J.; Keuken, M.; Ampe, C.; Beelen, R.; Cesaroni, G.; Forastiere, F.; et al. Development of Land Use Regression Models for Elemental, Organic Carbon, PAH, and Hopanes/Steranes in 10 ESCAPE/TRANSPHORM European Study Areas. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 14435–14444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karali, D.; Loupa, G.; Rapsomanikis, S. Origins of Regulated Semi-Volatile PAHs and Metals near an Industrial Area and a Highway in the Region of Alexandroupolis, Greece. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2019, 12, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achten, C.; Andersson, J.T. Overview of Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds (PAC). Polycycl Aromat. Compd. 2015, 35, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passig, J.; Schade, J.; Irsig, R.; Kroger-Badge, T.; Czech, H.; Adam, T.; Fallgren, H.; Moldanova, J.; Sklorz, M.; Streibel, T.; et al. Single-Particle Characterization of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Background Air in Northern Europe. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 1495–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callén, M.S.; López, J.M.; Iturmendi, A.; Mastral, A.M. Nature and Sources of Particle Associated Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAH) in the Atmospheric Environment of an Urban Area. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 183, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javed, W.; Iakovides, M.; Garaga, R.; Euripides, G.; Kota, S.H.; Ying, Q.; Wolfson, J.M.; Koutrakis, P.; Guo, B. Source Apportionment of Organic Pollutants in Fine and Coarse Atmospheric Particles in Doha, Qatar. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2019, 69, 1277–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassura, I.; Venturini, E.; Marchetti, S.; Piazzalunga, A.; Bernardi, E.; Fermo, P.; Passarini, F. Markers and in Fl Uence of Open Biomass Burning on Atmospheric Particulate Size and Composition during a Major Bon Fi Re Event. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 82, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, C.V.; Corrêa, S.M. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Diesel Emission, Diesel Fuel and Lubricant Oil. Fuel 2016, 185, 925–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Hu, J.; Zhang, K.M.; Li, Z.; He, L.; Hao, J. Characterizing Particulate Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Emissions from Diesel Vehicles Using a Portable Emissions Measurement System. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Bai, P.; Hayakawa, K.; Zhang, L.; Tang, N. Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Emitted from Open Burning and Stove Burning of Biomass: A Brief Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samburova, V.; Connolly, J.; Gyawali, M.; Yatavelli, R.L.N.; Watts, A.C.; Chakrabarty, R.K.; Zielinska, B.; Moosmüller, H.; Khlystov, A. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Biomass-Burning Emissions and Their Contribution to Light Absorption and Aerosol Toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Ding, X.; Turap, Y.; Tursun, Y.; Abulizi, A.; Wang, X.; Shao, L.; Talifu, D.; An, J.; Zhang, X.; et al. Distribution, Sources, Risks, and Vitro DNA Oxidative Damage of PM2.5-Bound Atmospheric Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Urumqi, NW China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsey, S.P.; Thomson, N.R.; Barker, J.F. Oxidation Kinetics of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons by Permanganate. Chemosphere 2010, 79, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahpoury, P.; Wnorowski, A.; Harner, T.; Saini, A.; Halappanavar, S. A Method for Measuring the Bioaccessibility of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Cell Culture Media. Chemosphere 2024, 351, 141257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, X.; Zhao, Q.; Shen, X.; Cao, X.; Feng, S.; Li, X.; Yao, X.; Wang, P.; Yao, Z. Emissions of PAHs From Crop Residues Burning in Domestic Stoves in Rural China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 883576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Huang, Q.; Qi, A.; Zhang, W.; Gao, H.; Duan, S.; Yang, L.; Wang, W. Investigation of PM2.5-Bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) and Their Derivatives (Nitrated-PAHs and Oxygenated-PAHs) in the Roadside Environment at the Eastern Coastal Region of China: Characterization, Source Identification, and Toxicity Evalua. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2023, 16, 1257–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Sun, L.; Yang, Z.; Lin, Y.; Chen, Y.; Mao, H. Characterization of PM2.5-Bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Their Derivatives (Nitro-and Oxy-PAHs) Emissions from Two Ship Engines under Different Operating Conditions. Chemosphere 2019, 225, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyte, I.J.; Albinet, A.; Harrison, R.M. On-Road Traffic Emissions of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Their Oxy- and Nitro- Derivative Compounds Measured in Road Tunnel Environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 1131–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjan, M.; Presto, A.A.; May, A.A.; Robinson, A.L. Temperature Dependence of Gasparticle Partitioningof Primary Organic Aerosol Emissions from a Small Diesel Engine. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Romagnoli, P.; Balducci, C.; Perilli, M.; Perreca, E.; Cecinato, A. Particulate PAHs and N-Alkanes in the Air over Southern and Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Chemosphere 2016, 159, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Lin, T.; Syed, J.H.; Cheng, Z.; Xu, Y.; Li, K.; Zhang, G.; Li, J. Concentration, Source Identification, and Exposure Risk Assessment of PM2.5-Bound Parent PAHs and Nitro-PAHs in Atmosphere from Typical Chinese Cities. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Błaszczyk, E.; Rogula-Kozłowska, W.; Klejnowski, K.; Fulara, I.; Mielżyńska-Švach, D. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Bound to Outdoor and Indoor Airborne Particles (PM2.5) and Their Mutagenicity and Carcinogenicity in Silesian Kindergartens, Poland. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2017, 10, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolis, E.I.; Saraga, D.E.; Filiou, K.F.; Tziavos, N.I.; Tsiaousis, C.P.; Dinas, A.; Bartzis, J.G. One-Year Intensive Characterization on PM2.5 Nearby Port Area of Thessaloniki, Greece. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 6812–6826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karageorgou, K.; Manoli, E.; Kouras, A.; Samara, C. Commuter Exposure to Particle-Bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Thessaloniki, Greece. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 59119–59130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yunker, M.B.; Macdonald, R.W.; Vingarzan, R.; Mitchell, H.; Goyette, D.; Sylvestre, S. PAHs in the Fraser River basin: A critical appraisal of PAH ratios as indicators of PAH source and composition. Org. Geochem. 2002, 33, 489–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsoyiannis, A.; Sweetman, A.J.; Jones, K.C. PAH Molecular Diagnostic Ratios Applied to Atmospheric Sources: A Critical Evaluation Using Two Decades of Source Inventory and Air Concentration Data from the UK. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 8897–8906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunker, M.B.; Perreault, A.; Lowe, C.J. Source Apportionment of Elevated PAH Concentrations in Sediments near Deep Marine Outfalls in Esquimalt and Victoria, BC, Canada: Is Coal from an 1891 Shipwreck the Source? Org. Geochem. 2012, 46, 12–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigas, F.; Sklavounos, S. Major Hazards Analysis for Populations Adjacent to Chemical Storage Facilities. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2004, 82, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finardi, S.; Radice, P.; Cecinato, A.; Gariazzo, C.; Gherardi, M.; Romagnoli, P. Seasonal Variation of PAHs Concentration and Source Attribution through Diagnostic Ratios Analysis. Urban Clim. 2017, 22, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaz, S.; Shahpoury, P.; Jaffrezo, J.L.; Lammel, G.; Perraudin, E.; Villenave, E.; Albinet, A. One-Year Study of Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds at an Urban Site in Grenoble (France): Seasonal Variations, Gas/Particle Partitioning and Cancer Risk Estimation. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 1071–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvorská, A.; Lammel, G.; Klánová, J. Use of Diagnostic Ratios for Studying Source Apportionment and Reactivity of Ambient Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons over Central Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avagyan, R.; Nyström, R.; Lindgren, R.; Boman, C.; Westerholm, R. Particulate Hydroxy-PAH Emissions from a Residential Wood Log Stove Using Different Fuels and Burning Conditions. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 140, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyte, I.J.; Harrison, R.M.; Lammel, G. Chemical Reactivity and Long-Range Transport Potential of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons-a Review. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 9333–9391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobiszewski, M.; Namie, J. PAH Diagnostic Ratios for the Identi Fi Cation of Pollution Emission Sources. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 162, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desservettaz, M.; Pikridas, M.; Stavroulas, I.; Bougiatioti, A.; Liakakou, E.; Hatzianastassiou, N.; Sciare, J.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Bourtsoukidis, E. Emission of Volatile Organic Compounds from Residential Biomass Burning and Their Rapid Chemical Transformations. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 903, 166592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fourtziou, L.; Liakakou, E.; Stavroulas, I.; Theodosi, C.; Zarmpas, P.; Psiloglou, B.; Sciare, J.; Maggos, T.; Bairachtari, K.; Bougiatioti, A.; et al. Multi-Tracer Approach to Characterize Domestic Wood Burning in Athens (Greece) during Wintertime. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 148, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kumfer, B.M.; Anastasio, C.; Kennedy, I.M.; Young, T.M. Environmental Aging of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons on Soot and Its Effect on Source Identification. Chemosphere 2009, 76, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pio, C.; Cerqueira, M.; Harrison, R.M.; Nunes, T.; Mirante, F.; Alves, C.; Oliveira, C.; Sanchez de la Campa, A.; Artíñano, B.; Matos, M. OC/EC Ratio Observations in Europe: Re-Thinking the Approach for Apportionment between Primary and Secondary Organic Carbon. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 6121–6132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivas, G.; Cheristanidis, S.; Chaloulakou, A. Elemental and Organic Carbon in the Urban Environment of Athens. Seasonal and Diurnal Variations and Estimates of Secondary Organic Carbon. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 414, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myriokefalitakis, S.; Karl, M.; Weiss, K.A.; Karagiannis, D.; Athanasopoulou, E.; Kakouri, A.; Bougiatioti, A.; Liakakou, E.; Stavroulas, I.; Papangelis, G.; et al. Analysis of Secondary Inorganic Aerosols over the Greater Area of Athens Using the EPISODE-CityChem Source Dispersion and Photochemistry Model. EGUsphere 2024, 2024, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samburova, V.; Zielinska, B.; Khlystov, A. Do 16 Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Represent PAH Air Toxicity? Toxics 2017, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. EPA. Exposure Factors Handbook 2011 Edition (Final Report); EPA/600/R-09/052F; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2011.
- Bandowe, B.A.M.; Meusel, H.; Huang, R.J.; Ho, K.; Cao, J.; Hoffmann, T.; Wilcke, W. PM2.5-Bound Oxygenated PAHs, Nitro-PAHs and Parent-PAHs from the Atmosphere of a Chinese Megacity: Seasonal Variation, Sources and Cancer Risk Assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473–474, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.J.; Kou, X.J.; Geng, H.; Dong, C.; Cai, Z.W. Pollution Characteristics of Ambient PM2.5-Bound PAHs and NPAHs in a Typical Winter Time Period in Taiyuan. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2014, 25, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pehnec, G.; Jakovljević, I.; Godec, R.; Štrukil, Z.S.; Žero, S.; Huremović, J.; Džepina, K. Carcinogenic Organic Content of Particulate Matter at Urban Locations with Different Pollution Sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 734, 139414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, R.M.; Özdemir, H.; Ünal, A.; Tayanç, M. Distribution and Sources of SVOCs in Fine and Coarse Aerosols in the Megacity of Istanbul. Atmos. Res. 2022, 271, 106100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skalska, K.; Lewandowska, A.U.; Staniszewska, M.; Reindl, A.; Witkowska, A.; Falkowska, L. Sources, Deposition Flux and Carcinogenic Potential of PM2.5-Bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Coastal Zone of the Baltic Sea (Gdynia, Poland). Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2019, 12, 1291–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, A.S.; Szabó, J. Characterization of PM2.5-Bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Ambient Air of Győr, Hungary. Polycycl Aromat. Compd. 2019, 39, 332–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, M.A.; Baumbach, G.; Kuch, B.; Scheffknecht, G. Particle-Phase Concentrations of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Ambient Air of Rural Residential Areas in Southern Germany. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2010, 3, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martellini, T.; Giannoni, M.; Lepri, L.; Katsoyiannis, A.; Cincinelli, A. One Year Intensive PM2.5 Bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Monitoring in the Area of Tuscany, Italy. Concentrations, Source Understanding and Implications. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 164, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arruti, A.; Fernández-Olmo, I.; Irabien, Á. Evaluation of the Urban/Rural Particle-Bound PAH and PCB Levels in the Northern Spain (Cantabria Region). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 6513–6526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).