Clinical and Epidemiological Characteristics of Severe Acute Adult Poisonings in French Amazonia: Urgent Need for a Toxicovigilance Monitoring Framework
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area Description
2.2. Data Collection Procedures
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
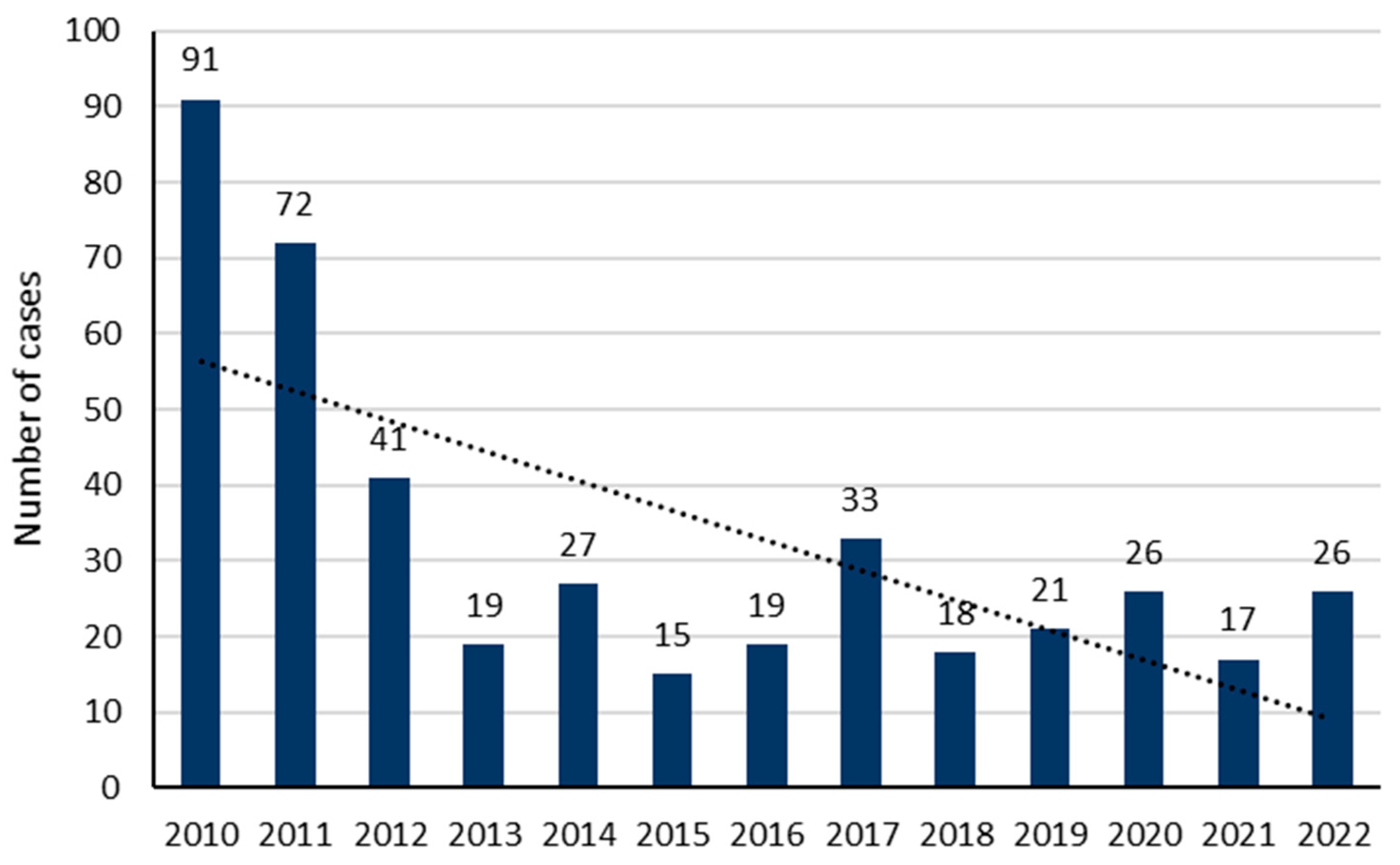
3.1. Sociodemographic Characteristics of the Included Cases
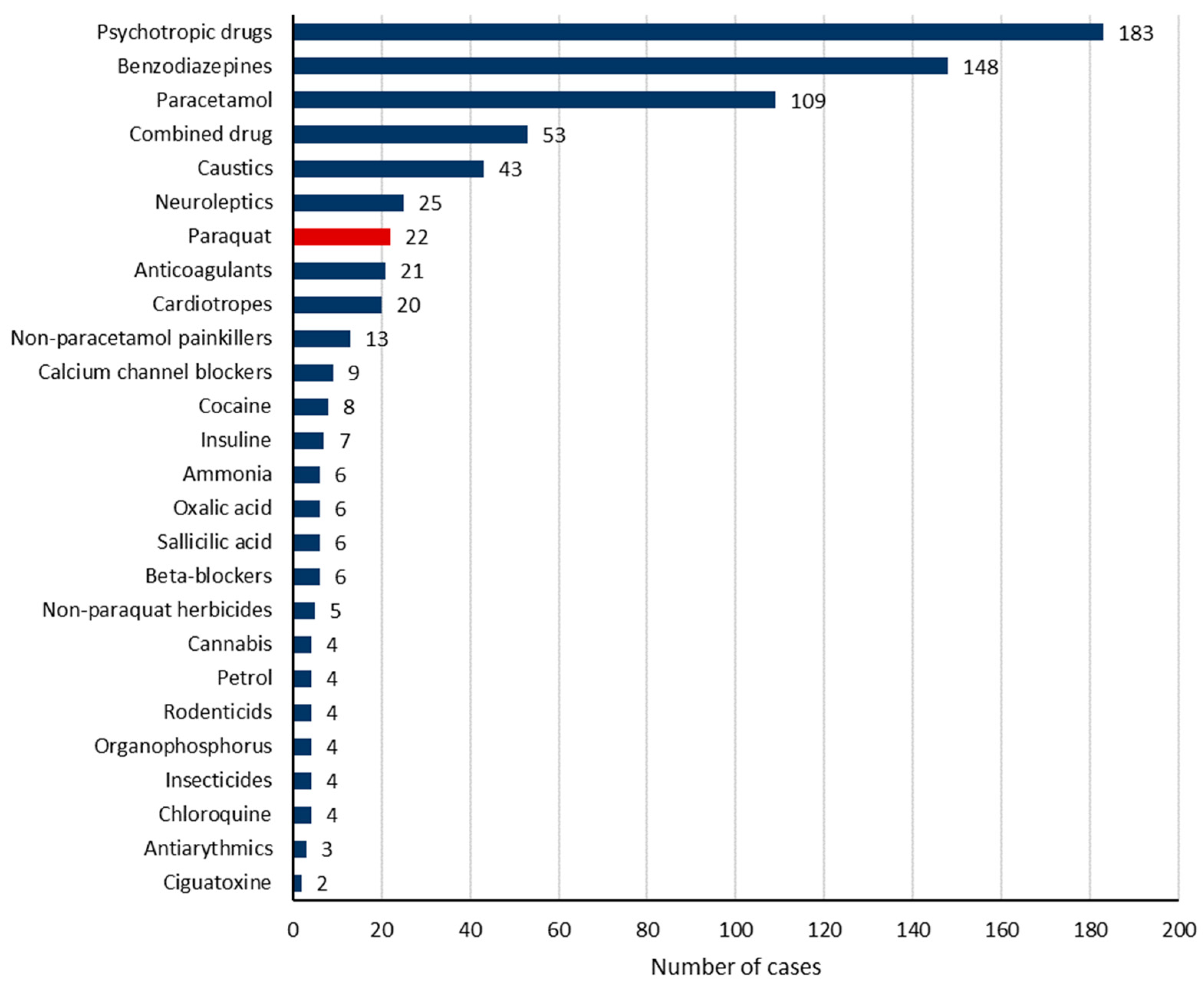
3.2. Implicated Toxic Substances
3.3. Clinical Manifestations at Admission to the Emergency Department
3.4. Management of Acute Poisoning Cases
3.5. Outcome of Poisoned Cases
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, B.; Wang, N.; Li, T. Acute Poisoning in Shenyang, China: A Retrospective and Descriptive Study from 2012 to 2016. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e021881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resiere, D.; Kallel, H.; Oxybel, O.; Chabartier, C.; Florentin, J.; Brouste, Y.; Gueye, P.; Megarbane, B.; Mehdaoui, H. Clinical and Epidemiological Characteristics of Severe Acute Adult Poisoning Cases in Martinique: Implicated Toxic Exposures and Their Outcomes. Toxics 2020, 8, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getie, A.; Belayneh, Y.M. A Retrospective Study of Acute Poisoning Cases and Their Management at Emergency Department of Dessie Referral Hospital, Northeast Ethiopia. Drug Healthc. Patient Saf. 2020, 12, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.P.; Aggarwal, A.D.; Oberoi, S.S.; Aggarwal, K.K.; Thind, A.S.; Bhullar, D.S.; Walia, D.S.; Chahal, P.S. Study of Poisoning Trends in North India—A Perspective in Relation to World Statistics. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2013, 20, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baud, F.; Garnier, R. Toxicologie Clinique, 6th ed.; Lavoisier Médecine-sciences: Paris, France, 2017; ISBN 978-2-257-20480-6. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Poison Control and Unintentional Poisoning. Available online: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/topics/indicator-groups/poison-control-and-unintentional-poisoning (accessed on 14 January 2024).
- Islambulchilar, M.; Islambulchilar, Z.; Kargar-Maher, M.H. Acute Adult Poisoning Cases Admitted to a University Hospital in Tabriz, Iran. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2009, 28, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albano, G.D.; Malta, G.; La Spina, C.; Rifiorito, A.; Provenzano, V.; Triolo, V.; Vaiano, F.; Bertol, E.; Zerbo, S.; Argo, A. Toxicological Findings of Self-Poisoning Suicidal Deaths: A Systematic Review by Countries. Toxics 2022, 10, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesslin, J.; Adepu, R.; Churi, S. Assessment of Prevalence and Mortality Incidences Due to Poisoning in a South Indian Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 72, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teklemariam, E.; Tesema, S.; Jemal, A. Pattern of Acute Poisoning in Jimma University Specialized Hospital, South West Ethiopia. World J. Emerg. Med. 2016, 7, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baydin, A.; Yardan, T.; Aygun, D.; Doganay, Z.; Nargis, C.; Incealtin, O. Retrospective Evaluation of Emergency Service Patients with Poisoning: A 3-Year Study. Adv. Ther. 2005, 22, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, A.; Cochet, A.; Guyodo, G. Poison episodes reported to French poison control centers in 2006. Rev. Prat. 2008, 58, 825–831. [Google Scholar]
- Boedeker, W.; Watts, M.; Clausing, P.; Marquez, E. The Global Distribution of Acute Unintentional Pesticide Poisoning: Estimations Based on a Systematic Review. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Daghastani, T.; Naser, A.Y. Hospital Admission Profile Related to Poisoning by, Adverse Effect of and Underdosing of Psychotropic Drugs in England and Wales: An Ecological Study. Saudi Pharm. J. 2022, 30, 1262–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuolo, M.; Frizzell, L.C.; Kelly, B.C. Trends in Psychotropic-Drug-Implicated Mortality: Psychotropic Drugs as a Contributing but Non-Underlying Cause of Death. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2021, 226, 108843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coben, J.H.; Davis, S.M.; Furbee, P.M.; Sikora, R.D.; Tillotson, R.D.; Bossarte, R.M. Hospitalizations for Poisoning by Prescription Opioids, Sedatives, and Tranquilizers. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2010, 38, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, T.M.; Davies, M.S.; Kitching, G.; Waring, W.S. Comparative Drug Dose and Drug Combinations in Patients That Present to Hospital Due to Self-Poisoning. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2012, 111, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, F.; Murray, M.L.; Byrne, P.J.; Wong, I.C.K. Epidemiologic Features of Antipsychotic Prescribing to Children and Adolescents in Primary Care in the United Kingdom. Pediatrics 2008, 121, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschtritt, M.E.; Slama, N.; Sterling, S.A.; Olfson, M.; Iturralde, E. Psychotropic Medication Prescribing during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Medicine 2021, 100, e27664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulose-Ram, R.; Jonas, B.S.; Orwig, D.; Safran, M.A. Prescription Psychotropic Medication Use among the U.S. Adult Population: Results from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988–1994. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2004, 57, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, A.; Ormseth, G.; Seifi, A. Gender and Psychotropic Poisoning in the USA. J. Neurol. Res. 2020, 10, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CIM-10 Version: 2008. Available online: https://icd.who.int/browse10/2008/fr (accessed on 18 November 2020).
- Cairns, R.; Buckley, N.A. The Poisoning Severity Score: If It Did Not Exist, We Would Have to Invent It. J. Med. Toxicol. 2017, 13, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khwaja, A. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Acute Kidney Injury. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2012, 120, c179–c184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gummin, D.D.; Mowry, J.B.; Spyker, D.A.; Brooks, D.E.; Beuhler, M.C.; Rivers, L.J.; Hashem, H.A.; Ryan, M.L. 2018 Annual Report of the American Association of Poison Control Centers’ National Poison Data System (NPDS): 36th Annual Report. Clin. Toxicol. 2019, 57, 1220–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tooplate NPIS. Available online: https://www.npis.org/index.html (accessed on 22 September 2023).
- Sorge, M.; Weidhase, L.; Bernhard, M.; Gries, A.; Petros, S. Self-Poisoning in the Acute Care Medicine 2005–2012. Anaesthesist 2015, 64, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindqvist, E.; Edman, G.; Hollenberg, J.; Nordberg, P.; Ösby, U.; Forsberg, S. Intensive Care Admissions Due to Poisoning. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2017, 61, 1296–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maignan, M.; Pommier, P.; Clot, S.; Saviuc, P.; Debaty, G.; Briot, R.; Carpentier, F.; Danel, V. Deliberate Drug Poisoning with Slight Symptoms on Admission: Are There Predictive Factors for Intensive Care Unit Referral? A Three-Year Retrospective Study. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2014, 114, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, A.; Wright, M.; Pond, S.M. Experience with 732 Acute Overdose Patients Admitted to an Intensive Care Unit over Six Years. Med. J. Aust. 1993, 158, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapur, N.; House, A.; Creed, F.; Feldman, E.; Friedman, T.; Guthrie, E. Management of Deliberate Self Poisoning in Adults in Four Teaching Hospitals: Descriptive Study. BMJ 1998, 316, 831–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liisanantti, J.H.; Ohtonen, P.; Kiviniemi, O.; Laurila, J.J.; Ala-Kokko, T.I. Risk Factors for Prolonged Intensive Care Unit Stay and Hospital Mortality in Acute Drug-Poisoned Patients: An Evaluation of the Physiologic and Laboratory Parameters on Admission. J. Crit. Care 2011, 26, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Neelanjana; Rawat, N.; Panwar, N. Mortality and Morbidity Associated with Acute Poisoning Cases in North-East India: A Retrospective Study. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2019, 8, 2068–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prashar, A.; Ramesh, M. Assessment of Pattern and Outcomes of Pesticides Poisoning in a Tertiary Care Hospital. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2018, 23, 1401–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ling, L.; Ma, J.; Yuan, H.; Guo, Z.; Feng, Q.; Xia, X. Trends and Profiles of Acute Poisoning Cases: A Retrospective Analysis. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1235304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, A.; Pakravan, N.; Ghazizadeh, Z. Pattern of Acute Food, Drug, and Chemical Poisoning in Sari City, Northern Iran. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2010, 29, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apata, J.; Pennap, D.; Ma, Y.; Mosholder, A. Suicide Poisoning Mortality: A Comparison of the National Poison Data System and Centers for Disease Control National Dataset. Inj. Prev. 2023, 30, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jelaify, M.; AlHomidah, S. The Individualized Management Approach for Acute Poisoning. Adv. Pharmacol. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 2021, 9926682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veale, D.J.H.; Wium, C.A.; Müller, G.J. Toxicovigilance. II: A Survey of the Spectrum of Acute Poisoning and Current Practices in the Initial Management of Poisoning Cases Admitted to South African Hospitals. S. Afr. Med. J. 2013, 103, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burillo-Putze, G.; Munne, P.; Dueñas, A.; Pinillos, M.A.; Naveiro, J.M.; Cobo, J.; Alonso, J.; Clinical Toxicology Working Group, Spanish Society of Emergency Medicine (SEMESTOX). National Multicentre Study of Acute Intoxication in Emergency Departments of Spain. Eur. J. Emerg. Med. 2003, 10, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandenburg, R.; Brinkman, S.; de Keizer, N.F.; Meulenbelt, J.; de Lange, D.W. In-Hospital Mortality and Long-Term Survival of Patients with Acute Intoxication Admitted to the ICU*. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 42, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- [Multisource observatory of acute intoxications in Île-de-France: An exploratory study]. Available online: https://www.santepubliquefrance.fr/notices/observatoire-multisources-des-intoxications-aigues-en-ile-de-france-une-etude-exploratoire (accessed on 25 October 2022).
- WHO. Suicide (2023). Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/suicide (accessed on 4 December 2023).
- Graafsma, T.; Kerkhof, A.; Gibson, D.; Badloe, R.; van de Beek, L.M. High Rates of Suicide and Attempted Suicide Using Pesticides in Nickerie, Suriname, South America. Crisis 2006, 27, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elenga, N.; Merlin, C.; Le Guern, R.; Kom-Tchameni, R.; Ducrot, Y.-M.; Pradier, M.; Ntab, B.; Dinh-Van, K.-A.; Sobesky, M.; Mathieu, D.; et al. Clinical Features and Prognosis of Paraquat Poisoning in French Guiana: A Review of 62 Cases. Medicine 2018, 97, e9621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaher, S.E.; Van den Hurk, P. Ecotoxicology of the Herbicide Paraquat: Effects on Wildlife and Knowledge Gaps. Ecotoxicology 2023, 32, 1187–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari-Nozad, A.M.; Jafari, A.; Aschner, M.; Farkhondeh, T.; Samarghandian, S. Curcumin Combats against Organophosphate Pesticides Toxicity: A Review of the Current Evidence and Molecular Pathways. Curr. Med. Chem. 2023, 30, 2312–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- [Senate bans use of the herbicide Paraquat in France]. Available online: https://www.senat.fr/questions/base/2004/qSEQ040712949.html (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Flechel, A.; Jolivet, A.; Boukhari, R.; Misslin-Tritsch, C.; Manca, M.F.; Wiel, E.; Megarbane, B.; Pousset, F. Paraquat Poisoning in Western French Guyana: A Public Health Problem Persisting Ten Years after Its Withdrawal from the French Market. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 7034–7038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kervégant, M.; Schmitt, C.; Martin, E.; Merigot, L.; Tichadou, L.; Bonnet, P.; De Haro, L. Intoxications Au Paraquat En Guyane Française: Utilisation Persistante Lors de Comportements Suicidaires En Outre-Mer. Ann. Toxicol. Anal. 2013, 25, 71–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Boucaud-Maitre, D.; Rambourg, M.-O.; Sinno-Tellier, S.; Puskarczyk, E.; Pineau, X.; Kammerer, M.; Bloch, J.; Langrand, J. Human Exposure to Banned Pesticides Reported to the French Poison Control Centers: 2012–2016. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 69, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, C.; Villers, A.; Balent, G.; Bar-Hen, A.; Chadoeuf, J.; Cylly, D.; Cluzeau, D.; Fried, G.; Guillocheau, S.; Pillon, O.; et al. A Real-World Implementation of a Nationwide, Long-Term Monitoring Program to Assess the Impact of Agrochemicals and Agricultural Practices on Biodiversity. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 3771–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bismuth, C.; Garnier, R.; Baud, F.J.; Muszynski, J.; Keyes, C. Paraquat Poisoning: An Overview of the Current Status. Drug Saf. 1990, 5, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilks, M.F.; Fernando, R.; Ariyananda, P.L.; Eddleston, M.; Berry, D.J.; Tomenson, J.A.; Buckley, N.A.; Jayamanne, S.; Gunnell, D.; Dawson, A. Improvement in Survival after Paraquat Ingestion Following Introduction of a New Formulation in Sri Lanka. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddleston, M. Evidence for the Efficacy of the Emetic PP796 in Paraquat SL20 Formulations–a Narrative Review of Published and Unpublished Evidence. Clin. Toxicol. 2022, 60, 1163–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myung, W.; Lee, G.-H.; Won, H.-H.; Fava, M.; Mischoulon, D.; Nyer, M.; Kim, D.K.; Heo, J.-Y.; Jeon, H.J. Paraquat Prohibition and Change in the Suicide Rate and Methods in South Korea. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, E.R.; Zapiola, M.L.; de Avila, L.A.; Garcia, M.A.; Plaza, G.; Gazziero, D.; Hoyos, V. Current Situation Regarding Herbicide Regulation and Public Perception in South America. Weed Sci. 2020, 68, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, V.M.; Verma, V.K.; Rawat, B.S.; Kaur, B.; Babu, N.; Sharma, A.; Dewali, S.; Yadav, M.; Kumari, R.; Singh, S.; et al. Current Status of Pesticide Effects on Environment, Human Health and It’s Eco-Friendly Management as Bioremediation: A Comprehensive Review. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 962619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, V.; Paul, B.; Falade, T.; Moodley, A.; Ramankutty, N.; Olawoye, J.; Djouaka, R.; Lekei, E.; de Haan, N.; Ballantyne, P.; et al. A One Health Approach to Plant Health. CABI Agric. Biosci. 2022, 3, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Ibáñez, A.; Ugalde-Herrá, R.; Rodríguez-Getino, J.Á.; García Casas, J.B.; Díaz-Suárez, J.C. Epidemiology of Acute Poisoning by Substances of Abuse in the Emergency Department. Descriptive Study in District IV of Asturias. Adicciones 2021, 33, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léon, C.; Chan-Chee, C.; du Roscoät, E. Santé Publique France Health Barometer 2017: Suicidal Attempts and Suicidal Ideation among the 18–75 Years-Old. Bull. Épidémiologique Hebd. 2019, 3–4, 38–47. [Google Scholar]
- Suicide Acts in 8 States: Incidence and Case Fatality Rates by Demographics and Method–PMC. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1446422/ (accessed on 16 August 2023).
- Bertolote, J.M.; Fleischmann, A.; De Leo, D.; Bolhari, J.; Botega, N.; De Silva, D.; Tran Thi Thanh, H.; Phillips, M.; Schlebusch, L.; Värnik, A.; et al. Suicide Attempts, Plans, and Ideation in Culturally Diverse Sites: The WHO SUPRE-MISS Community Survey. Psychol. Med. 2005, 35, 1457–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarmit, B.; Brousse, P.; Lucarelli, A.; Donutil, G.; Cropet, C.; Mosnier, E.; Travers, P.; Nacher, M. Descriptive Epidemiology of Suicide Attempts and Suicide in the Remote Villages of French Guiana. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2018, 53, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collados-Ros, A.; Torres-Sánchez, C.; Pérez-Cárceles, M.D.; Luna, A.; Legaz, I. Suicidal Behavior and Its Relationship with Postmortem Forensic Toxicological Findings. Toxics 2022, 10, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacot, R.; Garmit, B.; Pradem, M.; Nacher, M.; Brousse, P. The Problem of Suicide among Amerindians in Camopi-Trois Sauts, French Guiana 2008–2015. BMC Psychiatry 2018, 18, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.N.; Kumpati, R.K.; Ramavath, P.N.; Sangaraju, R.; Gouda, B.; Chougule, P. Investigation of Acute Organophosphate Poisoning in Humans Based on Sociodemographic and Role of Neurotransmitters with Survival Study in South India. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilón-Leiva, J.J.; Tejada-Garrido, C.I.; Echániz-Serrano, E.; Mir-Ramos, E.; Torres-Pérez, A.M.; Lafuente-Jiménez, A.; Martínez-Soriano, M.; Santolalla-Arnedo, I.; Czapla, M.; Smereka, J.; et al. Clinical and Sociodemographic Profile of Acute Intoxications in an Emergency Department: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 990262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhaboob, A.A. Sociodemographic Characteristics and Risk Factors for Childhood Poisoning Reported by Parents at a Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital. Cureus 2021, 13, e13313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Total | PSS 1 or 2 | PSS 3 or 4 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nb | Result | Nb | Result | Nb | Result | p | |
| Male sex | 425 | 146 (34.4%) | 357 | 117 (32.8%) | 68 | 29 (42.6%) | 0.116 |
| Age (years) | 425 | 34 (25–47) | 357 | 32 (24–45) | 68 | 41 (31–58) | 0.001 |
| Personal medical history | |||||||
| Psychiatric disorders | 425 | 178 (41.9%) | 357 | 152 (42.6%) | 68 | 26 (38.2%) | 0.506 |
| Voluntary medical intoxication | 425 | 145 (34.1%) | 357 | 123 (34.5%) | 68 | 22 (32.4%) | 0.738 |
| Alcohol abuse | 425 | 54 (12.7%) | 357 | 46 (12.9%) | 68 | 8 (11.8%) | 0.799 |
| Poisoning characteristics | |||||||
| Pharmaceutical drug | 425 | 334 (78.6%) | 357 | 286 (80.1%) | 68 | 48 (70.6%) | 0.079 |
| Combined drug | 425 | 55 (12.9%) | 357 | 43 (12%) | 68 | 12 (17.6%) | 0.207 |
| Caustic | 425 | 70 (16.5%) | 357 | 50 (14%) | 68 | 20 (29.4%) | 0.002 |
| Alcohol | 425 | 53 (12.5%) | 357 | 45 (12.6%) | 68 | 8 (11.8%) | 0.848 |
| Intentional self-poisoning | 425 | 358 (84.2%) | 357 | 305 (85.4%) | 68 | 53 (77.9%) | 0.120 |
| Unintentional poisoning | 395 | 321 (81.3%) | 331 | 274 (82.8%) | 64 | 47 (73.4%) | 0.080 |
| Management | |||||||
| Hospitalization | 425 | 265 (62.4%) | 357 | 215 (60.2%) | 68 | 50 (73.5%) | 0.038 |
| Hospital length of stay (days) | 425 | 2 (2–3) | 357 | 2 (2–3) | 68 | 3 (2–5) | 0.012 |
| Total | PSS 1 or 2 | PSS 3 or 4 | p | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toxic Agent | Nb | Result | Nb | Result | Nb | Result | |
| Pharmaceutical (drug) | 425 | 322 (75.8%) | 357 | 277 (77.6%) | 68 | 45 (66.2%) | 0.044 |
| Psychotropic drugs | 425 | 183 (43.1%) | 357 | 152 (42.6%) | 68 | 31 (45.6%) | 0.646 |
| Benzodiazepines | 425 | 148 (34.8%) | 357 | 122 (34.2%) | 68 | 26 (38.2%) | 0.519 |
| Analgesics | 425 | 122 (28.7%) | 357 | 113 (31.7%) | 68 | 9 (13.2%) | 0.002 |
| Paracetamol | 425 | 109 (25.6%) | 357 | 102 (28.6%) | 68 | 7 (10.3%) | 0.002 |
| Neuroleptics | 425 | 25 (5.9%) | 357 | 17 (4.8%) | 68 | 8 (11.8%) | 0.024 |
| Anticoagulants | 425 | 21 (4.9%) | 357 | 19 (5.3%) | 68 | 2 (2.9%) | 0.551 |
| Cardiotropic drugs | 425 | 20 (4.7%) | 357 | 14 (3.9%) | 68 | 6 (8.8%) | 0.080 |
| Calcium channel blockers | 425 | 9 (2.1%) | 357 | 7 (2%) | 68 | 2 (2.9%) | 0.641 |
| Insulin | 425 | 7 (1.6%) | 357 | 4 (1.1%) | 68 | 3 (4.4%) | 0.085 |
| Beta-blockers | 425 | 6 (1.4%) | 357 | 5 (1.4%) | 68 | 1 (1.5%) | 1.000 |
| Salicylic acid | 425 | 6 (1.4%) | 357 | 5 (1.4%) | 68 | 1 (1.5%) | 1.000 |
| Chloroquine | 425 | 4 (0.9%) | 357 | 1 (0.3%) | 68 | 3 (4.4%) | 0.014 |
| Antiarrhythmics | 425 | 3 (0.7%) | 357 | 2 (0.6%) | 68 | 1 (1.5%) | 0.408 |
| Barbiturates | 425 | 1 (0.2%) | 357 | 1 (0.3%) | 68 | 0 (0%) | 1.000 |
| Non-pharmaceutical (toxics) | 425 | 103 (24.2%) | 357 | 80 (22.4%) | 68 | 23 (33.8%) | 0.044 |
| Caustic | 425 | 43 (10.1%) | 357 | 37 (10.4%) | 68 | 6 (8.8%) | 0.699 |
| Herbicide | 425 | 27 (6.4%) | 357 | 12 (3.4%) | 68 | 15 (22.1%) | 0.000 |
| Paraquat | 425 | 22 (5.2%) | 357 | 7 (2%) | 68 | 15 (22.1%) | 0.000 |
| Cocaine | 425 | 8 (1.9%) | 357 | 8 (2.2%) | 68 | 0 (0%) | 0.365 |
| Oxalic acid | 424 | 6 (1.4%) | 356 | 6 (1.7%) | 68 | 0 (0%) | 0.596 |
| Ammonia | 425 | 6 (1.4%) | 357 | 5 (1.4%) | 68 | 1 (1.5%) | 1.000 |
| Rodenticide | 280 | 4 (1.4%) | 231 | 3 (1.3%) | 49 | 1 (2%) | 0.539 |
| Insecticide | 425 | 4 (0.9%) | 357 | 4 (1.1%) | 68 | 0 (0%) | 1.000 |
| Organophosphorus | 425 | 4 (0.9%) | 357 | 3 (0.8%) | 68 | 1 (1.5%) | 0.503 |
| Petroleum product | 425 | 4 (0.9%) | 357 | 4 (1.1%) | 68 | 0 (0%) | 1.000 |
| Cannabis | 425 | 4 (0.9%) | 357 | 4 (1.1%) | 68 | 0 (0%) | 1.000 |
| Ciguatoxin | 425 | 2 (0.5%) | 357 | 2 (0.6%) | 68 | 0 (0%) | 1.000 |
| Aldicarbe | 425 | 1 (0.2%) | 357 | 1 (0.3%) | 68 | 0 (0%) | 1.000 |
| Ethylene-glycol | 425 | 1 (0.2%) | 357 | 1 (0.3%) | 68 | 0 (0%) | 1.000 |
| Crack | 425 | 1 (0.2%) | 357 | 1 (0.3%) | 68 | 0 (0%) | 1.000 |
| Plants | 425 | 1 (0.2%) | 357 | 1 (0.3%) | 68 | 0 (0%) | 1.000 |
| Total | PSS 1 or 2 | PSS 3 or 4 | p | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nb | Result | Nb | Result | Nb | Result | ||
| Temperature (°C) | 382 | 36.8 (36.5–37.1) | 323 | 36.8 (36.5–37.1) | 59 | 36.7 (36.4–37.2) | 0.799 |
| Hypothermia | 382 | 8 (2.1%) | 323 | 3 (0.9%) | 59 | 5 (8.5%) | 0.003 |
| Fever | 382 | 5 (1.3%) | 323 | 3 (0.9%) | 59 | 2 (3.4%) | 0.172 |
| Respiratory rate (cycles/min) | 312 | 16 (12–22) | 259 | 16 (12–21) | 53 | 20 (12–24) | 0.028 |
| Bradypnea | 307 | 92 (30%) | 257 | 78 (30.4%) | 50 | 14 (28%) | 0.740 |
| Heart rate (beats/min) | 422 | 86 (74–99) | 355 | 86 (74–99) | 67 | 85 (74–103) | 0.849 |
| Bradycardia | 422 | 2 (0.5%) | 355 | 2 (0.6%) | 67 | 0 (0%) | 1.000 |
| Tachycardia | 422 | 104 (24.6%) | 355 | 84 (23.7%) | 67 | 20 (29.9%) | 0.281 |
| Circulatory shock | 423 | 16 (3.8%) | 355 | 0 (0%) | 68 | 16 (26.5%) | 0.000 |
| Glasgow coma scale | 423 | 15 (12–15) | 355 | 15 (13–15) | 68 | 13 (7–15) | 0.000 |
| Coma | 423 | 41 (9.7%) | 355 | 10 (2.8%) | 68 | 31 (45.6%) | 0.000 |
| Seizures | 423 | 6 (1.4%) | 355 | 1 (0.3%) | 68 | 5 (7.4%) | 0.000 |
| Digestive disorders | 424 | 211 (49.8%) | 356 | 181 (50.8%) | 68 | 30 (44.1%) | 0.309 |
| Conjunctivitis | 423 | 5 (1.2%) | 355 | 5 (1.4%) | 68 | 0 (0%) | 1.000 |
| Total | PSS 1 or 2 | PSS 3 or 4 | p | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nb | Result | Nb | Result | Nb | Result | ||
| pH | 85 | 7.38 (7.35–7.42) | 57 | 7.4 (7.37–7.42) | 28 | 7.36 (7.31–7.41) | 0.012 |
| Alkaline reserve (mmol/L) | 389 | 24 (22–26) | 321 | 24 (22.6–26) | 68 | 22.6 (18.1–25.3) | 0.000 |
| Metabolic acidosis | 388 | 113 (29.1%) | 321 | 80 (24.9%) | 67 | 33 (49.3%) | 0.000 |
| Lactates (mmol/L) | 93 | 2 (1–3.2) | 70 | 1.9 (1–2.9) | 23 | 3.7 (1.4–7) | 0.022 |
| Hyperlactatemia | 93 | 0 (0–1) | 70 | 31 (44.3%) | 23 | 13 (56.5%) | 0.308 |
| Venous glycemia (mmol/L) | 368 | 5.2 (4.6–6.1) | 309 | 5.2 (4.6–6) | 59 | 5.6 (4.6–8.3) | 0.023 |
| Hypoglycemia | 368 | 18 (4.9%) | 309 | 15 (4.9%) | 59 | 3 (5.1%) | 1.000 |
| Hyperglycemia | 368 | 41 (11.1%) | 309 | 24 (7.8%) | 59 | 17 (28.8%) | 0.000 |
| Natremia (mmol/L) | 421 | 138 (136–141) | 353 | 138 (136–140) | 68 | 139 (137–141) | 0.543 |
| Hyponatremia | 421 | 52 (12.4%) | 353 | 43 (12.2%) | 68 | 9 (13.2%) | 0.809 |
| Kalemia (mmol/L) | 404 | 3.7 (3.4–4.0) | 339 | 3.7 (3.4–4.1) | 65 | 3.8 (3.4–4) | 0.862 |
| Hypokalemia | 404 | 107 (26.5%) | 339 | 88 (26%) | 65 | 19 (29.2%) | 0.584 |
| Hyperkalemia | 404 | 7 (1.7%) | 339 | 0 (0%) | 65 | 7 (10.8%) | 0.000 |
| Calcemia (mmol/L) | 416 | 2.3 (2.2–2.5) | 348 | 2.3 (2.2–2.5) | 68 | 2.29 (2.2–2.4) | 0.013 |
| Magnesemia (mmol/L) | 11 | 0.7 (0.7–0.9) | 5 | 0.7 (0.7–0.9) | 6 | 0.7 (0.7–1) | 0.848 |
| Phosphoremia (mmol/L) | 13 | 0.9 (0.7–1.2) | 5 | 1.1 (0.9–1.2) | 8 | 0.9 (0.7–1.4) | 0.825 |
| Creatinine (µmol/L) | 420 | 69 (58–85) | 352 | 68 (57–81) | 68 | 81 (66–125) | 0.000 |
| Acute renal failure | 420 | 42 (10%) | 352 | 23 (6.5%) | 68 | 18 (26.5%) | 0.000 |
| Aspartate aminotransferase (IU/L) | 381 | 16 (12–25) | 320 | 16 (11–24) | 61 | 21 (12–42) | 0.009 |
| Alanine aminotransferase (IU/L) | 370 | 21 (16–28) | 310 | 21 (16–27) | 60 | 25 (18–51) | 0.013 |
| Hepatic cytolysis | 381 | 45 (11.8%) | 320 | 29 (9.1%) | 61 | 16 (26.2%) | 0.000 |
| Creatinine phosphokinase (IU/L) | 266 | 92 (65–192) | 221 | 92 (65–186) | 45 | 92 (66–262) | 0.470 |
| Rhabdomyolysis | 264 | 19 (7.2%) | 220 | 11 (5%) | 44 | 8 (18.2%) | 0.002 |
| Troponin (µg/L) | 40 | 0.01 (0.005–0.028) | 28 | 0.006 (0.005–0.011) | 12 | 0.017 (0.011–0.06) | 0.016 |
| Platelets (G/L) | 414 | 264 (219–321) | 347 | 270 (220–324) | 67 | 249 (217–283) | 0.027 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 413 | 15 (3.6%) | 347 | 9 (2.6%) | 66 | 6 (9.1%) | 0.020 |
| Prothrombin rate (%) | 322 | 87 (77–96) | 267 | 88 (79–97) | 55 | 80 (69–89) | 0.000 |
| Total | PSS 1 or 2 | PSS 3 or 4 | p | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nb | Result | Nb | Result | Nb | Result | ||
| Activated charcoal | 425 | 119 (28%) | 357 | 102 (28.6%) | 68 | 17 (25%) | 0.548 |
| Gastric lavage | 425 | 50 (11.8%) | 357 | 32 (9%) | 68 | 18 (26.5%) | 0.000 |
| Antidotes | 425 | 191 (44.9%) | 357 | 165 (46.2%) | 68 | 26 (38.2%) | 0.225 |
| Mechanical ventilation (MV) | 425 | 15 (3.5%) | 357 | 0 (0%) | 68 | 15 (22.1%) | 0.000 |
| Duration of MV (days) | 15 | 4 (1–9) | - | - | 15 | 4 (1–9) | - |
| Vasopressors | 425 | 18 (4.2%) | 357 | 0 (0%) | 68 | 18 (26.5%) | 0.000 |
| Dialysis | 425 | 3 (0.7%) | 357 | 0 (0%) | 68 | 3 (4.4%) | 0.004 |
| p | OR | 95% CI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||
| Paracetamol | 0.036 | 0.324 | 0.113 | 0.931 |
| Choroquine | 0.017 | 18.274 | 1.665 | 200.561 |
| Neuroleptics | 0.009 | 3.893 | 1.409 | 10.753 |
| Paraquat | 0.012 | 5.472 | 1.452 | 20.618 |
| Metabolic acidosis | 0.048 | 2.109 | 1.005 | 4.424 |
| Hyperglycemia (>5.5 mmol/L) | 0.049 | 2.404 | 1.002 | 5.766 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pujo, J.M.; Simon, Y.; Lontsi Ngoulla, G.R.; Signaté, B.; Mutricy, R.; Frémery, A.; Burin, A.; Toffol, B.d.; Ben Amara, I.; Houcke, S.; et al. Clinical and Epidemiological Characteristics of Severe Acute Adult Poisonings in French Amazonia: Urgent Need for a Toxicovigilance Monitoring Framework. Toxics 2024, 12, 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12030200
Pujo JM, Simon Y, Lontsi Ngoulla GR, Signaté B, Mutricy R, Frémery A, Burin A, Toffol Bd, Ben Amara I, Houcke S, et al. Clinical and Epidemiological Characteristics of Severe Acute Adult Poisonings in French Amazonia: Urgent Need for a Toxicovigilance Monitoring Framework. Toxics. 2024; 12(3):200. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12030200
Chicago/Turabian StylePujo, Jean Marc, Yann Simon, Guy Roger Lontsi Ngoulla, Boubacar Signaté, Rémi Mutricy, Alexis Frémery, Antoine Burin, Bertrand de Toffol, Ibtissem Ben Amara, Stephanie Houcke, and et al. 2024. "Clinical and Epidemiological Characteristics of Severe Acute Adult Poisonings in French Amazonia: Urgent Need for a Toxicovigilance Monitoring Framework" Toxics 12, no. 3: 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12030200
APA StylePujo, J. M., Simon, Y., Lontsi Ngoulla, G. R., Signaté, B., Mutricy, R., Frémery, A., Burin, A., Toffol, B. d., Ben Amara, I., Houcke, S., Nasri, A., Resiere, D., & Kallel, H. (2024). Clinical and Epidemiological Characteristics of Severe Acute Adult Poisonings in French Amazonia: Urgent Need for a Toxicovigilance Monitoring Framework. Toxics, 12(3), 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12030200






