The Associations between Organophosphate Pesticides (OPs) and Respiratory Disease, Diabetes Mellitus, and Cardiovascular Disease: A Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy for the Studies Included
2.2. Criteria for Study Selection
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Quality Assessment
2.5. Search Strategy for the Included Studies
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. The Association between OP Exposure and Respiratory Diseases
3.4. The Association between OP Exposure and DM
3.5. The Association between OP Exposure and CVD
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ye, J.; Zhao, M.; Liu, J.; Liu, W. Enantioselectivity in environmental risk assessment of modern chiral pesticides. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 2371–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Antary, T.M.; Alawi, M.A.; Othman, M.A.; Haddad, N. Persistent Organochlorine Pesticides in Mother’s Milk from the Northern Governorates of Jordan in 2014/2015. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2018, 27, 7685–7690. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Sun, M.L.; Barr, D.B. Exposure to organophosphorus insecticides and increased risks of health and cancer in US women. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 80, 103474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veludo, A.F.; Figueiredo, D.M.; Degrendele, C.; Masinyana, L.; Curchod, L.; Kohoutek, J.; Kukučka, P.; Martiník, J.; Přibylová, P.; Klánová, J.; et al. Seasonal variations in air concentrations of 27 organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) and 25 current-use pesticides (CUPs) across three agricultural areas of South Africa. Chemosphere 2021, 289, 133162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, W.; Shao, H.; Jin, W.; Xiong, Y.; Xu, B.; Chen, B. Determination of OCPs, OPPs, and 21 SVOCs in water and sediment samples in five rivers of Shenzhen, China, during the period of 2017 and 2018. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 42444–42457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khammanee, N.; Qiu, Y.; Kungskulniti, N.; Bignert, A.; Meng, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Teffera, Z.L. Presence and Health Risks of Obsolete and Emerging Pesticides in Paddy Rice and Soil from Thailand and China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidhu, G.K.; Singh, S.; Kumar, V.; Dhanjal, D.S.; Datta, S.; Singh, J. Toxicity, monitoring and biodegradation of organophosphate pesticides: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 1135–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkhondeh, T.; Mehrpour, O.; Forouzanfar, F.; Roshanravan, B.; Samarghandian, S. Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in organophosphate pesticide-induced neurotoxicity and its amelioration: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 24799–24814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashutosh, K. Mitochondrial dysfunction & neurological disorders. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016, 6, 565–566. [Google Scholar]
- Ratanachina, J.; De Matteis, S.; Cullinan, P.; Burney, P. Pesticide exposure and lung function: A systematic review and me-ta-analysis. Occup. Med. Oxf. 2020, 70, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evangelou, E.; Ntritsos, G.; Chondrogiorgi, M.; Kavvoura, F.K.; Hernandez, A.F.; Ntzani, E.E.; Tzoulaki, I. Exposure to pesti-cides and diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Int. 2016, 91, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zago, A.M.; Faria, N.M.X.; Fávero, J.L.; Meucci, R.D.; Woskie, S.; Fassa, A.G. Pesticide exposure and risk of cardiovascular disease: A systematic review. Glob. Public Health 2020, 17, 3944–3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, M.P.; Kamel, F.; Saldana, T.M.; Alavanja, M.C.R.; Sandler, D.P. Incident Diabetes and Pesticide Exposure among Licensed Pesticide Applicators: Agricultural Health Study, 1993-2003. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2008, 167, 1235–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolaos, G.; Tsarouhas, K.; Tsitsimpikou, C.; Vardavas, A.; Rezaee, R.; Gerrnanakis, I.; Tsatsakis, A.; Stagos, D.; Kouretas, D. Pesticides and Cardiotoxicity. Where Do We Stand? Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2018, 353, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, D.-Z.; Yang, H.-J.; Li, Y.-F.; Lin, C.-L.; Chang, S.-Y.; Sung, F.-C.; Tai, S.C.W. The Long-Term Effects of Organophos-phates Poisoning as a Risk Factor of Cvds: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matome, S.; Monyeki, K.D.; Sibuyi, M.E. Exposure to Agrochemicals and Cardiovascular Disease: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 229. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.; Barr, D.B.; Pearson, M.A.; Waller, L.A. Dietary Intake and Its Contribution to Longitudinal Organophosphorus Pesticide Exposure in Urban/Suburban Children. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Roychoudhury, S.; Siddique, S.; Lahiri, T.; Ray, M.R. Chronic exposures to cholinesterase-inhibiting pesticides adversely affect respiratory health of agricultural workers in India. J. Occup. Health 2009, 51, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razavi, B.M.; Hosseinzadeh, H.; Imenshahidi, M.; Malekian, M.; Ramezani, M.; Abnous, K. Evaluation of Protein Ubiq-uitylation in Heart Tissue of Rats Exposed to Diazinon (an Organophosphate Insecticide) and Crocin (an Active Saffron In-gredient): Role of Hif-1alpha. Drug Res. 2015, 65, 561–566. [Google Scholar]
- Raja, R.; Mornagui, B.; El-Fazaa, S.; Gharbi, N. Organophosphorus Pesticides as Food Chain Contami-nants and Type 2 Diabetes: A Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 21, 345–357. [Google Scholar]
- Raanan, R.; Balmes, J.R.; Harley, K.G.; Gunier, R.B.; Magzamen, S.; Bradman, A.; Eskenazi, B. Decreased lung function in 7-year-old children with early-life organophosphate exposure. Thorax 2016, 71, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fieten, K.B.; Kromhout, H.; Heederik, D.; Joode, B.v.W.d. Pesticide Exposure and Respiratory Health of Indigenous Women in Costa Rica. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2009, 169, 1500–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crofton, K.M. Thyroid disrupting chemicals: Mechanisms and mixtures. Int. J. Androl. 2008, 31, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutoluk, Z.; Kekec, Z.; Daglioglu, N.; Hant, I. Association of Chronic Pesticide Exposure with Serum Cholinesterase Levels and Pulmonary Functions. Arch. Environ. Occup. Health 2011, 66, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu Sham’A, F.; Skogstad, M.; Nijem, K.; Bjertness, E.; Kristensen, P. Lung Function and Respiratory Symptoms in Male Palestinian Farmers. Arch. Environ. Occup. Health 2010, 65, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perla, M.E.; Rue, T.; Cheadle, A.; Krieger, J.; Karr, C.J. Biomarkers of Insecticide Exposure and Asthma in Children: A National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 1999–2008 Analysis. Arch. Environ. Occup. Health 2015, 70, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seesen, M.; Lucchini, R.G.; Siriruttanapruk, S.; Sapbamrer, R.; Hongsibsong, S.; Woskie, S.; Kongtip, P. Association between Organophosphate Pesticide Exposure and Insulin Resistance in Pesticide Sprayers and Nonfarmworkers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahsa, R.; Rotondi, M.A.; Ardern, C.I.; Kuk, J.L. The Influence of Urinary Concentrations of Or-ganophosphate Metabolites on the Relationship between Bmi and Cardiometabolic Health Risk. J. Obes. 2015, 2015, 687914. [Google Scholar]
- Warembourg, C.; Basagaña, X.; Seminati, C.; de Bont, J.; Granum, B.; Lyon-Caen, S.; Manzano-Salgado, C.B.; Pin, I.; Sakhi, A.K.; Siroux, V.; et al. Exposure to phthalate metabolites, phenols and organophosphate pesticide metabolites and blood pressure during pregnancy. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2019, 222, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; the PRISMA Group. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The Prisma Statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, 264–269. [Google Scholar]
- Stang, A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 25, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atieh, M.; Daneshzad, E.; Moradi, S.; Abaj, F.; Mehranfar, S.; Asbaghi, O.; Clark, C.C.T.; Mirzaei, K. The Association between Urinary Metabolites of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (Pahs) and Cardio-vascular Diseases and Blood Pressure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 1712–1728. [Google Scholar]
- Hoppin, J.A.; Umbach, D.M.; London, S.J.; Lynch, C.F.; Alavanja, M.C.R.; Sandler, D.P. Pesticides and Adult Respiratory Outcomes in the Agricultural Health Study. In Living in a Chemical World: Framing the Future in Light of the Past; Mehlman, M.A., Soffritti, M., Landrigan, P., Bingham, E., Belpoggi, F., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 343–354. [Google Scholar]
- Hoppin, J.A.; Umbach, D.M.; London, S.J.; Alavanja, M.C.R.; Sandler, D.P. Chemical Predictors of Wheeze among Farmer Pesticide Applicators in the Agricultural Health Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoppin, J.A.; Umbach, D.M.; London, S.J.; Lynch, C.F.; Alavanja, M.C.R.; Sandler, D.P. Pesticides associated with Wheeze among Commercial Pesticide Applicators in the Agricultural Health Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 163, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahakoon, C.; Dassanayake, T.L.; Gawarammana, I.B.; Weerasinghe, V.S.; Buckley, N.A. Differences between organophosphates in respiratory failure and lethality with poisoning post the 2011 bans in Sri Lanka. Clin. Toxicol. 2020, 58, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppin, J.A.; Umbach, D.M.; London, S.J.; Henneberger, P.K.; Kullman, G.J.; Alavanja, M.C.R.; Sandler, D.P. Pesticides and Atopic and Nonatopic Asthma among Farm Women in the Agricultural Health Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 177, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppin, J.A.; Umbach, D.M.; London, S.J.; Henneberger, P.K.; Kullman, G.J.; Coble, J.; Alavanja, M.C.R.; Freeman, L.E.B.; Sandler, D.P. Pesticide use and adult-onset asthma among male farmers in the Agricultural Health Study. Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 34, 1296–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinsky, J.L.; Richardson, D.B.; Kreiss, K.; Nylander-French, L.; Freeman, L.E.B.; London, S.J.; Henneberger, P.K.; Hoppin, J.A. Animal production, insecticide use and self-reported symptoms and diagnoses of COPD, including chronic bronchitis, in the Agricultural Health Study. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starling, A.P.; Umbach, D.M.; Kamel, F.; Long, S.; Sandler, D.P.; Hoppin, J.A. Pesticide use and incident diabetes among wives of farmers in the Agricultural Health Study. Occup. Environ. Med. 2014, 71, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.T.; Blair, A.; Freeman, L.E.B.; Sandler, D.P.; Hoppin, J.A. Pesticides and Myocardial Infarction Incidence and Mortality Among Male Pesticide Applicators in the Agricultural Health Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2009, 170, 892–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fareed, M.; Pathak, M.K.; Bihari, V.; Kamal, R.; Srivastava, A.K.; Kesavachandran, C.N. Adverse Respiratory Health and Hematological Alterations among Agricultural Workers Occupationally Exposed to Organophosphate Pesticides: A Cross-Sectional Study in North India. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, K.; Thangavel, G. Pesticides and human diabetes: A pilot project to explore a possible link. Pract. Diabetes 2015, 32, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.-P.; Lin, C.-L.; Hung, D.-Z.; Ma, W.-C.; Lin, Y.-N.; Kao, C.-H. Increased Risk of Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Thromboembolism in Patients with Organophosphate Intoxication a Nationwide Prospective Cohort Study. Medicine 2015, 94, e341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Quezada, M.T.; Lucero, B.; Iglesias, V.; Levy, K.; Muñoz, M.P.; Achú, E.; Cornejo, C.; Concha, C.; Brito, A.M.; Villalobos, M. Exposure to organophosphate (OP) pesticides and health conditions in agricultural and non-agricultural workers from Maule, Chile. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2017, 27, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juntarawijit, C.; Juntarawijit, Y. Association between diabetes and pesticides: A case-control study among Thai farmers. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2018, 23, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, J.V.; Jerobin, J.; Nair, A.; Bennett, A.; Samuel, P.; Chrispal, A.; Abraham, O.C.; Mathews, K.P.; Fleming, J.J.; Oommen, A. Clinical profile and outcome of patients hospitalized with dimethyl and diethyl organophosphate poisoning. Clin. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robyn, G.; Friedmann, E.; Holmes, K.; Yolton, K.; Xu, Y.; Lanphear, B.; Chen, A.; Braun, J.; Spanier, A. Gestational Pesticide Exposure and Child Respiratory Health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7165. [Google Scholar]
- Buralli, R.J.; Dultra, A.F.; Ribeiro, H. Respiratory and Allergic Effects in Children Exposed to Pesticides—A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattila, T.; Santonen, T.; Andersen, H.R.; Katsonouri, A.; Szigeti, T.; Uhl, M.; Wąsowicz, W.; Lange, R.; Bocca, B.; Ruggieri, F.; et al. Scoping Review—The Association between Asthma and Environmental Chemicals. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, J.L.; Dunn, C.; Gaspari, R.J. Central respiratory failure during acute organophosphate poisoning. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2013, 189, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullmann, R.; Reinsberg, J.; Amirmanssouri, M. Regional blood flow during paraoxon infusion in rabbits. Arch. Toxicol. 1982, 50, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, T.; Tsuda, S.; Shirasu, Y. Non-Cholinergic Mechanisms Underlying the Acute Lethal Effects of P = S Type Or-ganophosphorus Insecticides in Rats. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 1992, 54, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadia, R.S.; Chitra, S.; Amin, R.B.; Kiwalkar, R.S.; Sardesai, H.V. Electrophysiological studies in acute organophosphate poisoning. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1987, 50, 1442–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, A.; Seidler, F.J.; Slotkin, T.A. Developmental effects of chlorpyrifos extend beyond neurotoxicity: Critical periods for immediate and delayed-onset effects on cardiac and hepatic cell signaling. Environ. Health Perspect. 2004, 112, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassiter, T.L.; Ryde, I.T.; MacKillop, E.A.; Brown, K.K.; Levin, E.D.; Seidler, F.J.; Slotkin, T.A. Exposure of Neonatal Rats to Parathion Elicits Sex-Selective Reprogramming of Metabolism and Alters the Response to a High-Fat Diet in Adulthood. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 1456–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chung, Y.-L.; Hou, Y.-C.; Wang, I.-K.; Lu, K.-C.; Yen, T.-H. Organophosphate pesticides and new-onset diabetes mellitus: From molecular mechanisms to a possible therapeutic perspective. World J. Diabetes 2021, 12, 1818–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, S.; Nanda, R.; Mangaraj, M.; Rathod, P.K.; Mishra, P.K. Glycemic Status in Organophosphorus Poisoning. J. Nepal Health Res. Counc. 2015, 13, 214–219. [Google Scholar]
- Javeres, M.N.L.; Raza, S.; Judith, N.; Anwar, F.; Habib, R.; Batool, S.; Nurulain, S.M. Mixture of Organophosphates Chronic Exposure and Pancreatic Dysregulations in Two Different Population Samples. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 534902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, A.; Pasalar, P.; Abdollahi, M. Induction of Oxidative Stress and Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition in Organo-phosphorous Pesticide Manufacturing Workers. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2002, 21, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morino, K.; Petersen, K.F.; Shulman, G.I. Molecular Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance in Humans and Their Potential Links with Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Diabetes 2006, 55, S9–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allon, N.; Rabinovitz, I.; Manistersky, E.; Weissman, B.A.; Grauer, E. Acute and Long-Lasting Cardiac Changes Following a Single Whole-Body Exposure to Sarin Vapor in Rats. Toxicol. Sci. 2005, 87, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clement, E.F. Genetic Variability in the Cytochrome P450-Paraoxonase 1 (Pon1) Pathway for Detoxication of Organ-ophosphorus Compounds. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2007, 21, 197–205. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao-Ming, X.; Dai, W.; Li, P.; Wu, S.-J.; Hu, M.; Liu, L.-Y. Subchronic Toxicity Organophosphate Insecticide-Induced Damages on Endothelial Function of Vessels in Rabbits by Inhibiting Antioxidases. Prog. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 37, 1232–1239. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Z.J.; Chen, J.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, Z.Y. Lack of Association between the Paraoxonase 1 Q/R192 Single Nucleotide Poly-morphism and Stroke in a Chinese Cohort. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2009, 109, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



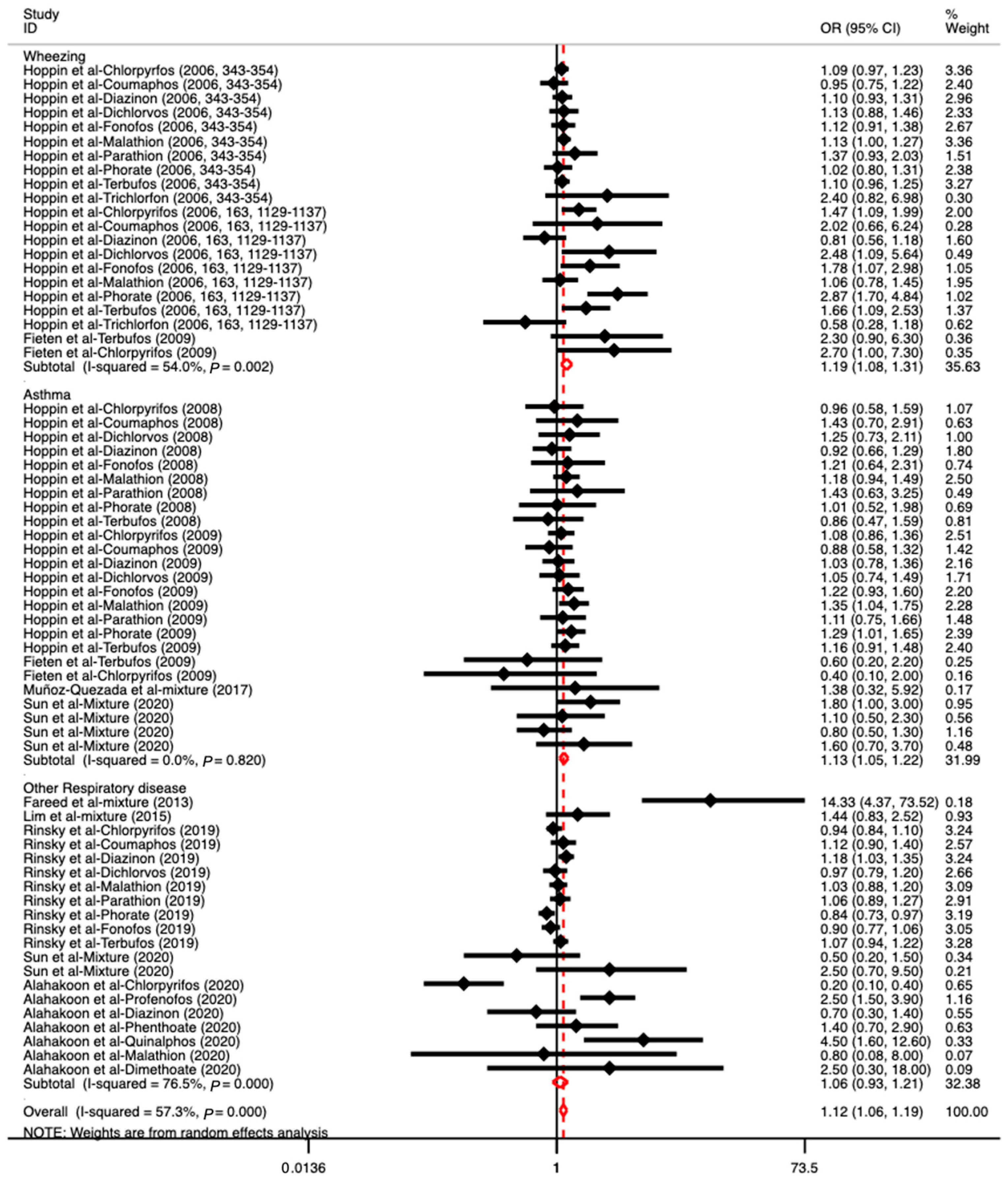
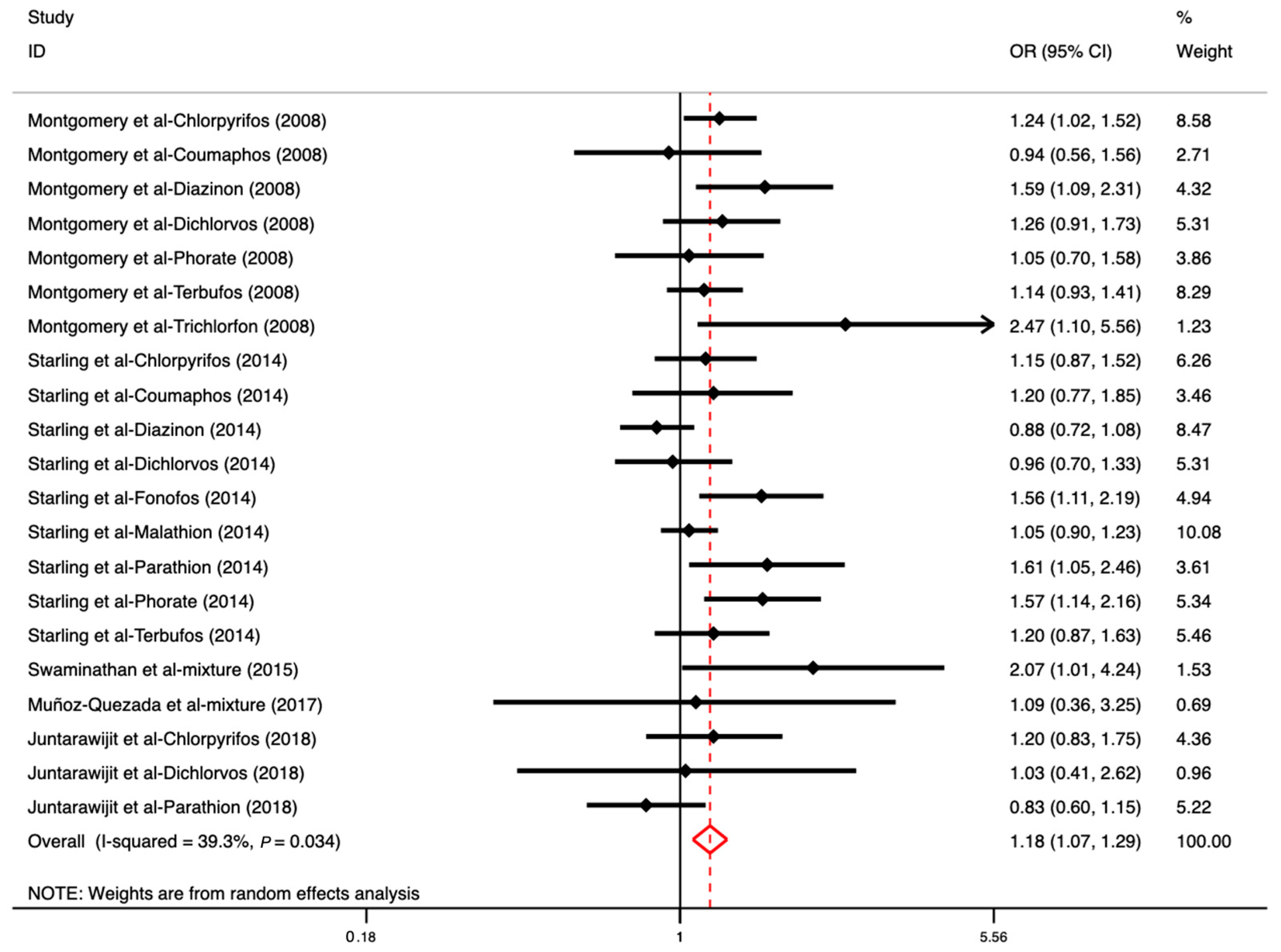
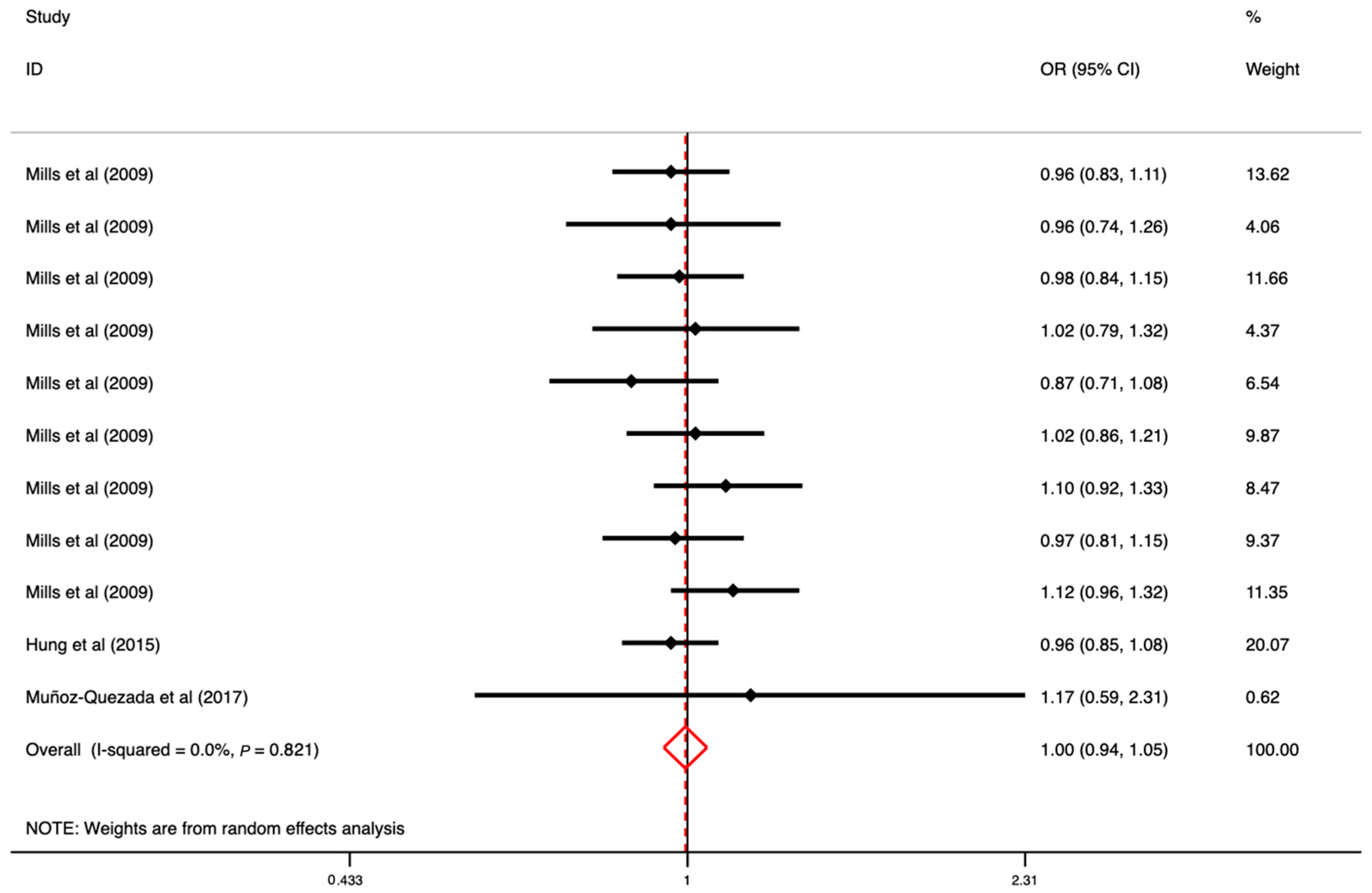
| Author (Year) | Country | Age (Range or Mean ± SD) | Sample Size | Study Design | Outcome | Exposure | Comparison | OR (95% CI) | Adjustment | Quality Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hoppin et al., 2006 [33] | USA | 18–88 | 17,920 (F: 538, M: 17,382) | Cohort | Respiratory disease (wheezing) | Chlorpyrifos Coumaphos Diazinon Dichlorvos Fonofos Malathion Parathion Phorate Terbufos Trichlorfon | Population who never reported using OPs | 1.09 (0.97–1.23) 0.95 (0.75–1.22 1.10 (0.93–1.31) 1.13 (0.88–1.46) 1.12 (0.91–1.38) 1.13 (1.00–1.27) 1.37 (0.93–2.03) 1.02 (0.80–1.31) 1.10 (0.96–1.25) 2.40 (0.82–6.98) | Age, BMI, smoking, asthma/atopy status, and previous use of pesticide | 7 |
| Hoppin et al., 2006 [35] | USA | 17–83 | 2255 (F: 114, M: 2141) | Cohort | Respiratory disease (wheezing) | Chlorpyrifos Coumaphos Diazinon Dichlorvos Fonofos Malathion Phorate Terbufos Trichlorfon | The group “Never use” was the reference category | 1.47 (1.09–1.99) 2.02 (0.66–6.24) 0.81 (0.56–1.18) 2.48 (1.09–5.64) 1.78 (1.07–2.98) 1.06 (0.78–1.45) 2.87 (1.70–4.84) 1.66 (1.09–2.53) 0.58 (0.28–1.18) | Age, BMI, smoking status, asthma/atopy status | 7 |
| Hoppin et al., 2008 [37] | USA | 20–88 | 25,814 (F) | Cohort | Respiratory disease (asthma) | Chlorpyrifos Coumaphos Dichlorvos Diazinon Fonofos Malathion Parathion Phorate Terbufos | Nonexposed population as the reference | 0.96 (0.58–1.59) 1.43 (0.70–2.91) 1.25 (0.73–2.11) 0.92 (0.66–1.29) 1.21 (0.64–2.31) 1.18 (0.94–1.49) 1.43 (0.63–3.25) 1.01 (0.52–1.98) 0.86 (0.47–1.59) | Age, state, BMI, smoking status, and “grew up on farm” | 7 |
| Hoppin et al., 2009 [38] | USA | ≥20 | 19,704 (M) | Cohort | Respiratory disease (asthma) | Chlorpyrifos Coumaphos Diazinon Dichlorvos Fonofos Malathion Parathion Phorate Terbufos | Never-users were the reference group | 1.08 (0.86–1.36) 0.88 (0.58–1.32) 1.03 (0.78–1.36) 1.05 (0.74–1.49) 1.22 (0.93–1.60) 1.35 (1.04–1.75) 1.11 (0.75–1.66) 1.29 (1.01–1.65) 1.16 (0.91–1.48) | Age, state, BMI, smoking, high pesticide exposure events | 7 |
| Fieten et al., 2009 [22] | Costa Rica | 20–58 | 127 (M) | Cross-sectional study | Respiratory disease (wheezing) | Chlorpyrifos Terbufos | Unexposed participants who worked on organic banana plantations or at other locations (home, school, etc.) | 2.70 (1.00–7.30) 2.30 (0.90–6.30) | Age and atopic symptoms, defined as self-reported symptoms of rhinitis, eczema, or both, during the last year. | 7 |
| Respiratory disease (asthma) | Chlorpyrifos Terbufos | 0.40 (0.10–2.00) 0.60 (0.20–2.20) | ||||||||
| Fareed et al., 2013 [42] | India | 38.12 ± 15.39 | 243 (M) | Cross-sectional study | Respiratory disease | Mixed OPs (such as monocrotphos, dichlorvos, malathion, parathion) | Participants who did not handle pesticides and had a similar socioeconomic status and age group to the exposed subjects | 14.33 (4.37–73.52) | Smoking habits | 6 |
| Lim et al., 2015 [44] | China | 53.40 ± 16.50 | 46,115 (F: 13,810, M: 32,305) | Cohort | Respiratory disease (COPD) | Mixed OPs | Population without OP poisoning | 1.44 (0.83–2.52) | Age and comorbidities of atrial fibrillation, hypertension, diabetes, CVA, and heart failure. | 8 |
| Muñoz-Quezada et al., 2017 [45] | Chile | 49.00 ± 12.60 | 207 (F: 102, M: 105) | Cross-sectional study | Respiratory disease (asthma) | Mixed OPs | Non-agricultural workers (non-exposed) | 1.38 (0.32–5.92) | - | 7 |
| Rinsky et al., 2019 [39] | USA | 27–97 | 22,491 (F: 621, M: 21,870) | Cohort | Respiratory disease (COPD) | Chlorpyrifos Coumapphos Diazinon Dichlorovs Malathion Parathion Phorate Fonofos Terbufos | Farmers who did not report a diagnosis or symptoms consistent with chronic bronchitis | 0.94 (0.84–1.10) 1.12 (0.90–1.40) 1.18 (1.03–1.35) 0.97 (0.79–1.20) 1.03 (0.88–1.20) 1.06 (0.89–1.27) 0.84 (0.73–0.97) 0.90 (0.77–1.06) 1.07 (0.94–1.22) | Using stabilized inverse probability of exposure weights (IPEWs) to address confounding factors | 6 |
| Sun et al., 2020 [3] | USA | 6–19 | 1830 (F) | Cross-sectional study | Respiratory disease (asthma) | Mixed OPs | Participants who had the lowest OP metabolite levels | 1.80 (1.00–3.00) | BMI, creatinine, and races | 7 |
| 20–39 | 1181 (F) | Respiratory disease (asthma) | 1.10 (0.50–2.30) | |||||||
| 40–59 | 1036 (F) | Respiratory disease (chronic bronchitis) | 0.50 (0.20–1.50) | |||||||
| 60–85 | 1056 (F) | Respiratory disease (chronic bronchitis) | 2.50 (0.70–9.50) | |||||||
| 6–19 | 1794 (M) | Respiratory disease (asthma) | 0.80 (0.50–1.30) | |||||||
| 20–39 | 1079 (M) | Respiratory disease (asthma) | 1.60 (0.70–3.70) | |||||||
| Alahakoon et al., 2020 [36] | Sri Lanka | 25–49 | 540 (F: 166, M: 374) | Cohort | Respiratory disease | Chlorpyrifos Profenofos Diazinon Phenthoate Quinalphos Malathion Dimethoate | Comparing the odds of one OP with the odds for all other confirmed OPs combined | 0.20 (0.10–0.40) 2.50 (1.50–3.90) 0.70 (0.30–1.40) 1.40 (0.70–2.90) 4.50 (1.60–12.60) 0.80 (0.08–8.00) 2.50 (0.30–18.00) | - | 5 |
| Montgomery et al., 2008 [13] | USA | <40, 40–49, 50–59, 60–69, ≥70 | 37,787 (F: 832, M: 30,955) | Cohort | DM | Chlorpyrifos Coumaphos Diazinon Dichlorvos Phorate Terbufos Trichlorfon | Participants who never used OPs were the reference category | 1.24 (1.02–1.52) 0.94 (0.56–1.56) 1.59 (1.09–2.31) 1.26 (0.91–1.73) 1.05 (0.70–1.58) 1.14 (0.93–1.41) 2.47 (1.10–5.56) | Age, BMI, and state | 7 |
| Starling et al., 2014 [40] | USA | 17–88 | 13,637 (F) | Cohort | DM | Chlorpyrifos Coumaphos Diazinon Dichlorvos Fonofos Malathion Parathion Phorate Terbufos | Participants who reported no diabetes | 1.15 (0.87–1.52) 1.20 (0.77–1.85) 0.88 (0.72–1.08) 0.96 (0.70–1.33) 1.56 (1.11–2.19) 1.05 (0.90–1.23) 1.61 (1.05–2.46) 1.57 (1.14–2.16) 1.20 (0.87–1.63) | BMI and state at enrollment | 7 |
| Swaminathan et al., 2015 [43] | India | >18 | 260 (F and M) | Cross-sectional study | DM | Mixed OPs | No or minimal exposure group (participants working in offices or people at home) | 2.07 (1.01–4.24) | - | 5 |
| Muñoz-Quezada et al., 2017 [45] | Chile | 49.00 ± 12.60 | 207 (F: 102, M: 105) | Cross-sectional study | DM | Mixed OPs | Non-agricultural workers (non-exposed) | 1.09 (0.36–3.25) | - | 7 |
| Juntarawijit et al., 2018 [46] | Thailand | 15–86 | 1,887 (F: 1244, M: 643) | Case-control study | DM | Chlorpyrifos Dichlorvos Parathion | For each specific pesticide, exposure was categorized as ever vs. never used. | 1.20 (0.83–1.75) 1.03 (0.41–2.62) 0.83 (0.60–1.15) | Age, gender, BMI, smoking status, alcohol consumption, family history of diabetes, and occupation | 8 |
| Mills et al., 2009 [41] | USA | <50, 50–59, 60–69, >69 | 32,024 (M) | Cohort | CVD | Chlorpyrifos Coumaphos Diazinon Dichlorvos Fonofos Malathion Parathion Phorate Terbufos | Participants with no exposure to each individual pesticide | 0.96 (0.83–1.11) 0.96 (0.74–1.26) 0.98 (0.84–1.15) 1.02 (0.79–1.32) 0.87 (0.71–1.08) 1.02 (0.86–1.21) 1.10 (0.92–1.33) 0.97 (0.81–1.15) 1.12 (0.96–1.32) | Age, BMI, state, and smoking status | 7 |
| Hung et al., 2015 [15] | China | 39.0–63.6 | 37,805 (F: 11,010, M: 26,795) | Cohort | CVD (coronary artery disease) | Mixed OPs | Population without OP poisoning | 0.96 (0.85–1.08) | Age, gender, and comorbidities of diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and COPD | 7 |
| Muñoz-Quezada et al., 2017 [45] | Chile | 49.00 ± 12.60 | 207 (F: 102, M: 105) | Cross-sectional study | CVD (hypertension) | Mixed OPs | Non-agricultural workers (non-exposed) | 1.17 (0.59–2.31) | - | 7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, L.; Liu, Q.; Jia, Y.; Lin, H.; Yu, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, W.; Fang, T.; Jiang, W.; et al. The Associations between Organophosphate Pesticides (OPs) and Respiratory Disease, Diabetes Mellitus, and Cardiovascular Disease: A Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Toxics 2023, 11, 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11090741
Zhao L, Liu Q, Jia Y, Lin H, Yu Y, Chen X, Liu Z, Li W, Fang T, Jiang W, et al. The Associations between Organophosphate Pesticides (OPs) and Respiratory Disease, Diabetes Mellitus, and Cardiovascular Disease: A Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Toxics. 2023; 11(9):741. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11090741
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Lei, Qisijing Liu, Yaning Jia, Huishu Lin, Yuanyuan Yu, Xuemei Chen, Ziquan Liu, Weixia Li, Tao Fang, Wenbing Jiang, and et al. 2023. "The Associations between Organophosphate Pesticides (OPs) and Respiratory Disease, Diabetes Mellitus, and Cardiovascular Disease: A Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies" Toxics 11, no. 9: 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11090741
APA StyleZhao, L., Liu, Q., Jia, Y., Lin, H., Yu, Y., Chen, X., Liu, Z., Li, W., Fang, T., Jiang, W., Zhang, J., Cui, H., Li, P., Li, H., Hou, S., & Guo, L. (2023). The Associations between Organophosphate Pesticides (OPs) and Respiratory Disease, Diabetes Mellitus, and Cardiovascular Disease: A Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Toxics, 11(9), 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11090741







