Thioredoxin 1 and Thioredoxin Reductase 1 Redox System Is Dysregulated in Neutrophils of Subjects with Autism: In Vitro Effects of Environmental Toxicant, Methylmercury
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Study Measurements
2.3. Separation of Blood Neutrophils
2.4. Trx Activity Measurement in Neutrophils
2.5. Flow Cytometry
2.6. Neutrophil Cell Culture
2.7. Nrf2 Trans-Activation ELISA Assay in the Neutrophils
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
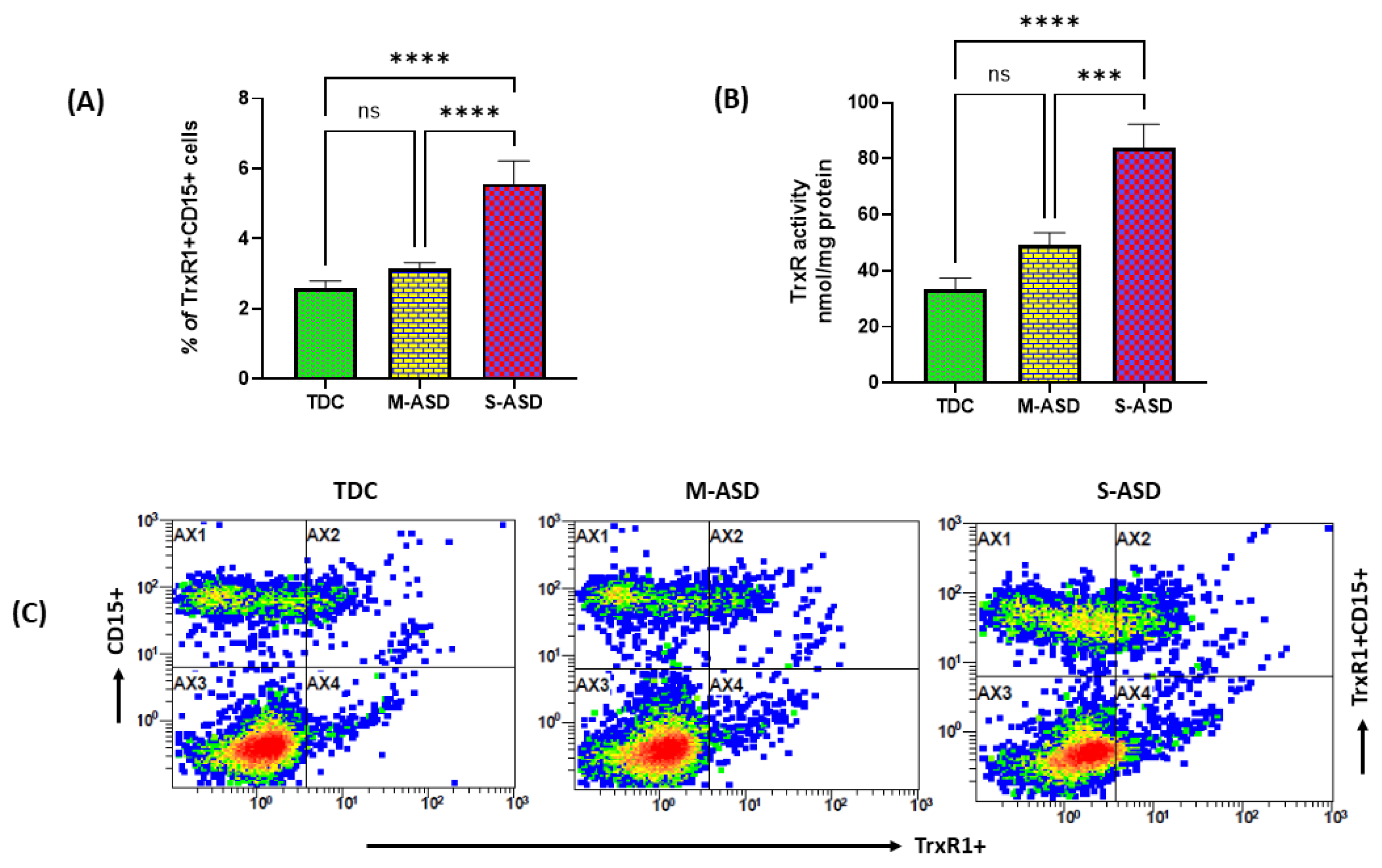
3.1. TrxR1 Expression and Trx Activity in ASD and TDC Neutrophils
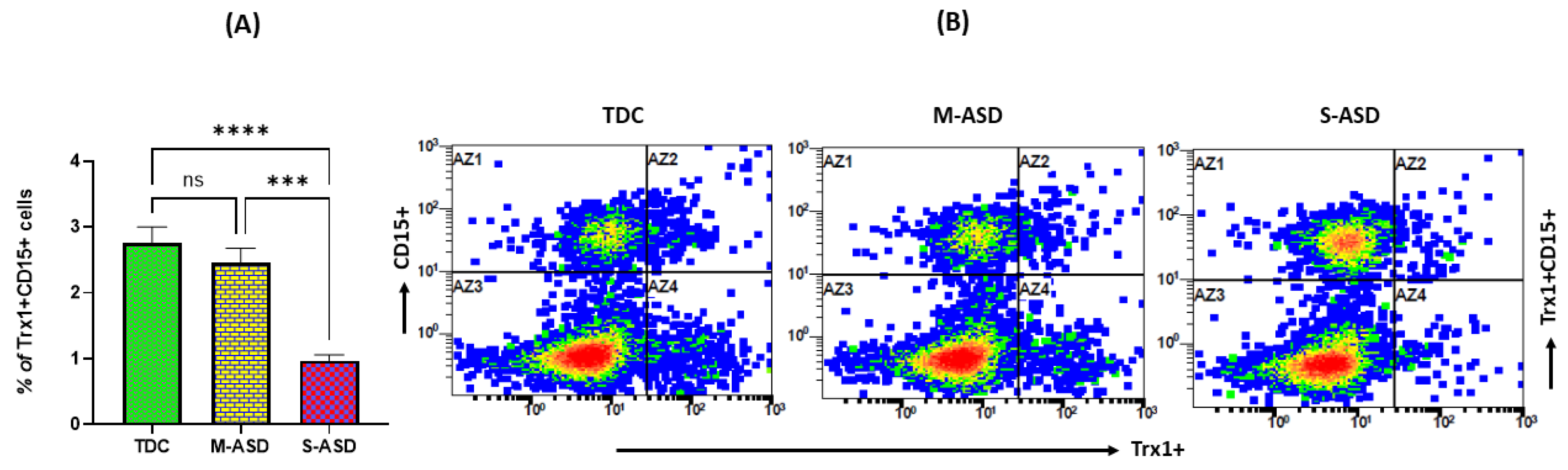
3.2. Trx1 Expression in ASD and TDC Neutrophils
3.3. Effect of MethylMercury on TrxR/Trx Redox Couple in ASD and TDC Neutrophils
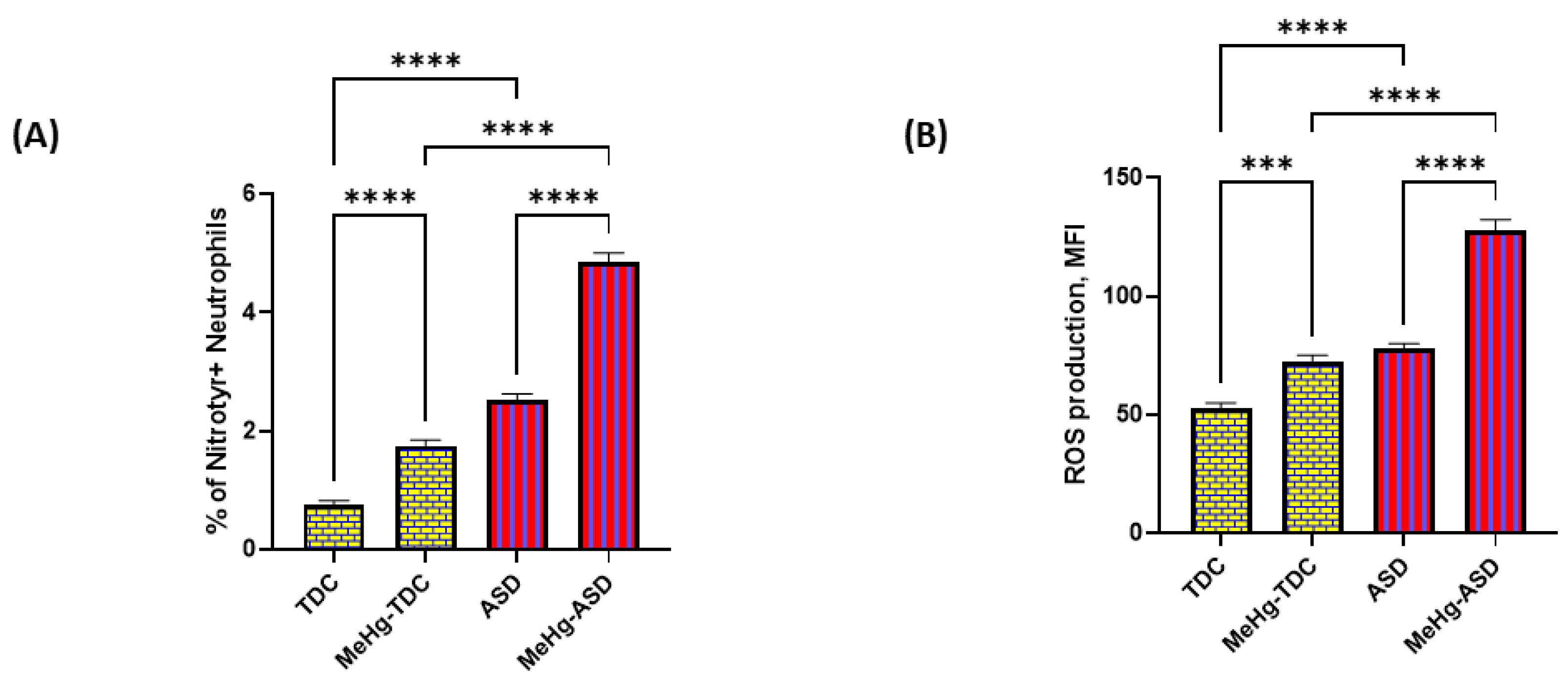
3.4. Effect of MethylMercury on Oxidative Stress Markers in ASD and TDC Neutrophils
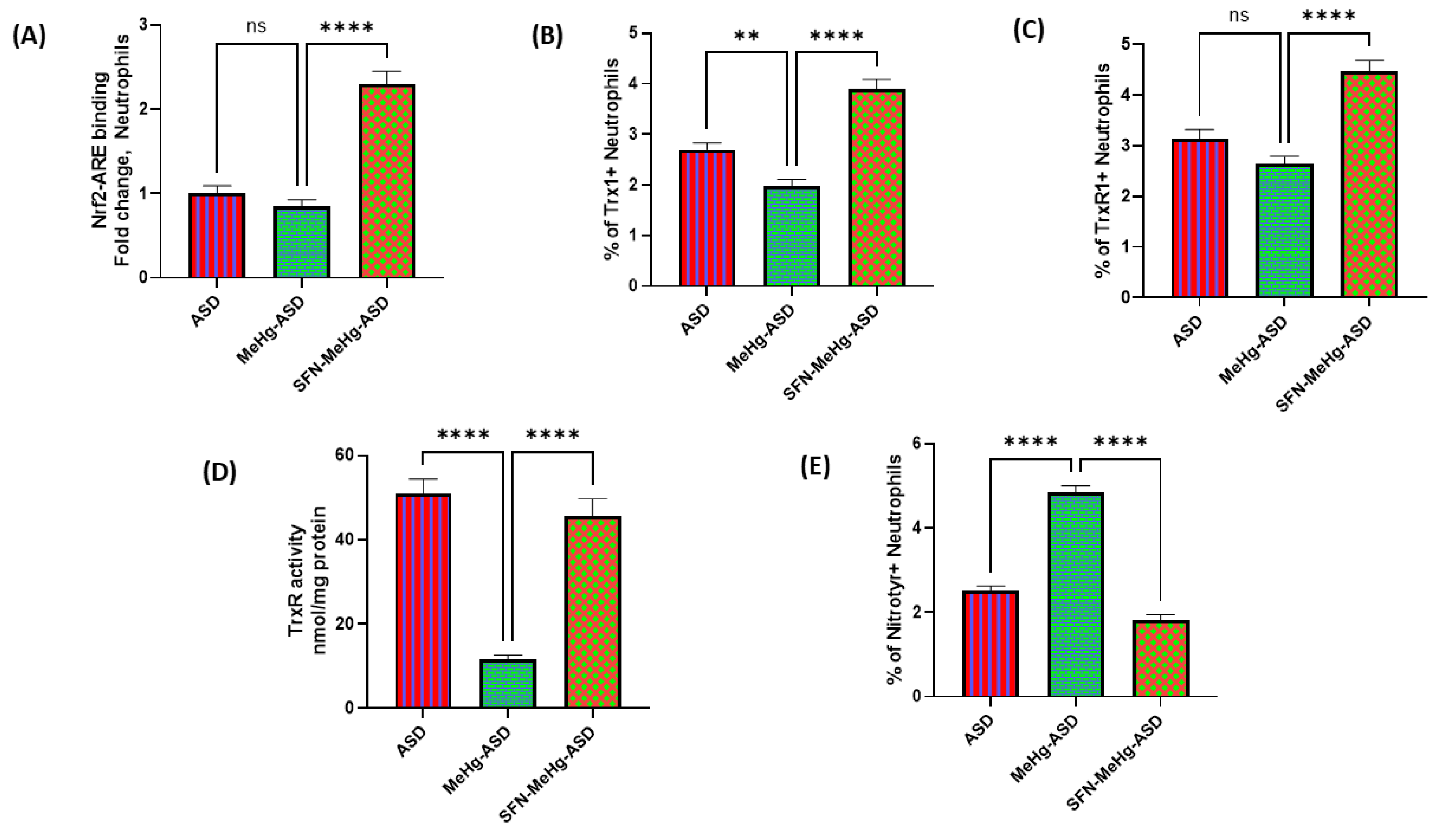
3.5. Effect of Sulforaphane on MethylMercury-Induced Changes in Trx1/TrxR1 System in ASD and TDC Neutrophils
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kern, J.K.; Geier, D.A.; Sykes, L.K.; Haley, B.E.; Geier, M.R. The relationship between mercury and autism: A comprehensive review and discussion. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2016, 37, 8–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsabbagh, M.; Divan, G.; Koh, Y.-J.; Kim, Y.S.; Kauchali, S.; Marcín, C.; Montiel-Nava, C.; Patel, V.; Paula, C.S.; Wang, C.; et al. Global Prevalence of Autism and Other Pervasive Developmental Disorders. Autism Res. 2012, 5, 160–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzzo, E.K.; Pérez-Cano, L.; Jung, J.Y.; Wang, L.K.; Kashef-Haghighi, D.; Hartl, C.; Singh, C.; Xu, J.; Hoekstra, J.N.; Leventhal, O.; et al. Inherited and De Novo Genetic Risk for Autism Impacts Shared Networks. Cell 2019, 178, 850–866.e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.-C.; Lin, L.-S.; Long, S.; Ke, X.-Y.; Fukunaga, K.; Lu, Y.-M.; Han, F. Signalling pathways in autism spectrum disorder: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, I.; Huang, B.; Mousavi, N.; Ma, N.; Lamkin, M.; Yanicky, R.; Shleizer-Burko, S.; Lohmueller, K.E.; Gymrek, M. Patterns of de novo tandem repeat mutations and their role in autism. Nature 2021, 589, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, A.; Butler, M.G. Clinical Assessment, Genetics, and Treatment Approaches in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khogeer, A.A.; AboMansour, I.S.; Mohammed, D.A. The Role of Genetics, Epigenetics, and the Environment in ASD: A Mini Review. Epigenomes 2022, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, L.A.; LaSalle, J.M. Future Prospects for Epigenetics in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2022, 26, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modabbernia, A.; Velthorst, E.; Reichenberg, A. Environmental risk factors for autism: An evidence-based review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Mol. Autism 2017, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.X.; Rasga, C.; Marques, A.R.; Martiniano, H.; Asif, M.; Vilela, J.; Oliveira, G.; Sousa, L.; Nunes, A.; Vicente, A.M. A Role for Gene-Environment Interactions in Autism Spectrum Disorder Is Supported by Variants in Genes Regulating the Effects of Exposure to Xenobiotics. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 862315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, R.; Wang, M.; Ren, X. Exposure to Aluminum, Cadmium, and Mercury and Autism Spectrum Disorder in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2020, 33, 2699–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadabadi, H.J.; Rahmatian, A.; Sayehmiri, F.; Rafiei, M. The Relationship Between the Level of Copper, Lead, Mercury and Autism Disorders: A Meta-Analysis. Pediatr. Heal. Med. Ther. 2020, 11, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Shi, S.; Qie, S.; Li, J.; Xi, X. Association between heavy metals exposure (cadmium, lead, arsenic, mercury) and child autistic disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11, 1169733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, S.M.; Lee, R.T. Thioredoxin and Thioredoxin Target Proteins: From Molecular Mechanisms to Functional Significance. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2013, 18, 1165–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjørklund, G.; Zou, L.; Peana, M.; Chasapis, C.T.; Hangan, T.; Lu, J.; Maes, M. The Role of the Thioredoxin System in Brain Diseases. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forrester, S.J.; Kikuchi, D.S.; Hernandes, M.S.; Xu, Q.; Griendling, K.K. Reactive Oxygen Species in Metabolic and Inflammatory Signaling. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 877–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanschmann, E.M.; Godoy, J.R.; Berndt, C.; Hudemann, C.; Lillig, C.H. Thioredoxins, glutaredoxins, and peroxiredoxins—Molecular mechanisms and health significance: From cofactors to antioxidants to redox signaling. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 1539–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, G.; Koshiba, M.; Nakamura, H.; Kosaka, H.; Hatachi, S.; Kurimoto, C.; Kurosaka, M.; Hayashi, Y.; Yodoi, J.; Kumagai, S. Thioredoxin protects against joint destruction in a murine arthritis model. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2006, 40, 1721–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sato, A.; Hoshino, Y.; Hara, T.; Muro, S.; Nakamura, H.; Mishima, M.; Yodoi, J. Thioredoxin-1 Ameliorates Cigarette Smoke-Induced Lung Inflammation and Emphysema in Mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 325, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Tabrizi, Z.; Bhatt, N.N.; Franciosa, S.A.; Bracko, O. A Brief Overview of Neutrophils in Neurological Diseases. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amulic, B.; Cazalet, C.; Hayes, G.L.; Metzler, K.D.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil Function: From Mechanisms to Disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 30, 459–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araźna, M.; Pruchniak, M.P.; Demkow, U. Reactive Oxygen Species, Granulocytes, and NETosis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 836, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Yin, Y.; Gong, D.; Hong, L.; Wu, G.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, C.; Blinder, P.; Long, S.; Han, F.; et al. Cathepsin B inhibition ameliorates leukocyte-endothelial adhesion in the BTBR mouse model of autism. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2019, 25, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.; Gevezova, M.; Sarafian, V.; Maes, M. Redox regulation of the immune response. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2022, 19, 1079–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manivasagam, T.; Arunadevi, S.; Essa, M.M.; Saravanababu, C.; Borah, A.; Thenmozhi, A.J.; Qoronfleh, M.W. Role of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Autism. Adv. Neurobiol. 2020, 24, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, A.; Ahmad, S.F.; Al-Harbi, N.O.; Al-Ayadhi, L.Y.; Alanazi, M.M.; Alfardan, A.S.; Attia, S.M.; Algahtani, M.; A Bakheet, S. Dysregulated Nrf2 signaling in response to di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate in neutrophils of children with autism. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 106, 108619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangrazzi, L.; Balasco, L.; Bozzi, Y. Oxidative Stress and Immune System Dysfunction in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Yafee, Y.A.; Ayadhi, L.Y.A.; Haq, S.H.; El-Ansary, A.K. Novel metabolic biomarkers related to sulfur-dependent detoxification pathways in autistic patients of Saudi Arabia. BMC Neurol. 2011, 11, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Gao, S.; Zhao, H. Thioredoxin: A novel, independent diagnosis marker in children with autism. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2014, 40, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshehri, S.; Nadeem, A.; Ahmad, S.F.; Alqarni, S.S.; Al-Harbi, N.O.; Al-Ayadhi, L.Y.; Attia, S.M.; Alqarni, S.A.; Bakheet, S.A. Disequilibrium in the Thioredoxin Reductase-1/Thioredoxin-1 Redox Couple Is Associated with Increased T-Cell Apoptosis in Children with Autism. Metabolites 2023, 13, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Association, Arlington (DSM V): Arlington, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Schopler, E.; Reichler, R.J.; Renner, B.R. The Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS): For Diagnostic Screening and Classification of Autism; Western Psychological Services: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Nadeem, A.; Ahmad, S.F.; Attia, S.M.; Al-Ayadhi, L.Y.; Bakheet, S.A.; Al-Harbi, N.O. Oxidative and inflammatory mediators are upregulated in neutrophils of autistic children: Role of IL-17A receptor signaling. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 90, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauseef, W.M. Isolation of human neutrophils from venous blood. Methods Mol. Biol. 2007, 412, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmood, D.D.F.; Abderrazak, A.; EL Hadri, K.; Simmet, T.; Rouis, M. The Thioredoxin System as a Therapeutic Target in Human Health and Disease. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 1266–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzawa, A. Thioredoxin and redox signaling: Roles of the thioredoxin system in control of cell fate. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 617, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.-I.; Kubota, M.; Shimoda, M.; Hayase, T.; Miyaguchi, M.; Kobayashi, N.; Ikeda, M.; Ishima, Y.; Kawahara, M. Thioredoxin-albumin fusion protein prevents urban aerosol-induced lung injury via suppressing oxidative stress-related neutrophil extracellular trap formation. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, A.; Ahmad, S.F.; Bakheet, S.A.; Al-Harbi, N.O.; Al-Ayadhi, L.Y.; Attia, S.M.; Zoheir, K.M. Toll-like receptor 4 signaling is associated with upregulated NADPH oxidase expression in peripheral T cells of children with autism. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2017, 61, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadeem, A.; Ahmad, S.F.; Attia, S.M.; Al-Ayadhi, L.Y.; Al-Harbi, N.O.; Bakheet, S.A. Dysregulation in IL-6 receptors is associated with upregulated IL-17A related signaling in CD4+ T cells of children with autism. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 97, 109783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napoli, E.; Wong, S.; Hertz-Picciotto, I.; Giulivi, C. Deficits in Bioenergetics and Impaired Immune Response in Granulocytes from Children with Autism. Pediatrics 2014, 133, e1405–e1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauseef, W.M.; Borregaard, N. Neutrophils at work. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, M.F.; Tural Hesapcioglu, S.; Yavas, C.P.; Senat, A.; Erel, O. Serum Ischemia-Modified Albumin Levels, Myeloperoxidase Activity and Peripheral Blood Mononuclear cells in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2021, 51, 2511–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, J.T.; Chana, G.; Abramson, I.; Semendeferi, K.; Courchesne, E.; Everall, I.P. Abnormal microglial–neuronal spatial organization in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in autism. Brain Res. 2012, 1456, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanashiro, A.; Hiroki, C.H.; da Fonseca, D.M.; Birbrair, A.; Ferreira, R.G.; Bassi, G.S.; Fonseca, M.D.; Kusuda, R.; Cebinelli, G.C.M.; da Silva, K.P.; et al. The role of neutrophils in neuro-immune modulation. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 151, 104580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muri, J.; Kopf, M. Redox regulation of immunometabolism. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 21, 363–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mócsai, A. Diverse novel functions of neutrophils in immunity, inflammation, and beyond. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 1283–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Dikshit, M. Metabolic Insight of Neutrophils in Health and Disease. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.-H.; Hong, C.-W.; Kim, E.Y.; Lee, J.M. Current Understanding on the Metabolism of Neutrophils. Immune Netw. 2020, 20, e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novo, J.P.; Martins, B.; Raposo, R.S.; Pereira, F.C.; Oriá, R.B.; Malva, J.O.; Fontes-Ribeiro, C. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms Mediating Methylmercury Neurotoxicity and Neuroinflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, C.M.L.; Chew, E.-H.; Hashemy, S.I.; Lu, J.; Holmgren, A. Inhibition of the Human Thioredoxin System. A molecular mechanism of mercury toxicity. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 11913–11923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, J.; Branco, V.; Lu, J.; Holmgren, A.; Carvalho, C. Toxicological effects of thiomersal and ethylmercury: Inhibition of the thioredoxin system and NADP+-dependent dehydrogenases of the pentose phosphate pathway. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2015, 286, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, V.; Canário, J.; Lu, J.; Holmgren, A.; Carvalho, C. Mercury and selenium interaction in vivo: Effects on thioredoxin reductase and glutathione peroxidase. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 781–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, V.; Godinho-Santos, A.; Gonçalves, J.; Lu, J.; Holmgren, A.; Carvalho, C. Mitochondrial thioredoxin reductase inhibition, selenium status, and Nrf-2 activation are determinant factors modulating the toxicity of mercury compounds. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 73, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, M.; Li, X.; Yin, Z.; Sidoryk-Węgrzynowicz, M.; Jiang, H.; Farina, M.; Rocha, J.B.T.; Syversen, T.; Aschner, M. Comparative study on the response of rat primary astrocytes and microglia to methylmercury toxicity. Glia 2011, 59, 810–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegmann, B.; Tatemoto, P.; Miemczyk, S.; Ludvigsson, J.; Guerrero-Bosagna, C. Identification of potentially relevant metals for the etiology of autism by using a Bayesian multivariate approach for partially censored values. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 12622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaw, Y.M.; Cunningham, C.; Tierney, A.; Sivaguru, M.; Inoue, M. Neutrophil-selective deletion of Cxcr2 protects against CNS neurodegeneration in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Dai, J.; Li, Y.; You, Z.; Zhang, J.; Huang, X.; Nie, S.; Chen, Y.; Xu, L.; Liu, F.; et al. ROS-activated CXCR2+ neutrophils recruited by CXCL1 delay denervated skeletal muscle atrophy and undergo P53-mediated apoptosis. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 1011–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Uribe, N.E.; Bracko, O.; Swallow, M.; Omurzakov, A.; Dash, S.; Uchida, H.; Xiang, D.; Haft-Javaherian, M.; Falkenhain, K.; Lamont, M.E.; et al. Vascular oxidative stress causes neutrophil arrest in brain capillaries, leading to decreased cerebral blood flow and contributing to memory impairment in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. bioRxiv 2023, 2023, 528710. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, E.E. Interplay between cytosolic disulfide reductase systems and the Nrf2/Keap1 pathway. Biochem. Soc Trans. 2015, 43, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suvorova, E.S.; Lucas, O.; Weisend, C.M.; Rollins, M.F.; Merrill, G.F.; Capecchi, M.R.; Schmidt, E.E. Cytoprotective Nrf2 Pathway Is Induced in Chronically Txnrd 1-Deficient Hepatocytes. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebula, M.; Schmidt, E.E.; Arnér, E.S. TrxR1 as a Potent Regulator of the Nrf2-Keap1 Response System. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2015, 23, 823–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrier, M.S.; Zhang, Y.; Trivedi, M.S.; Deth, R.C. Decreased cortical Nrf2 gene expression in autism and its relationship to thiol and cobalamin status. Biochimie 2022, 192, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Connors, S.L.; Macklin, E.A.; Smith, K.D.; Fahey, J.W.; Talalay, P.; Zimmerman, A.W. Sulforaphane treatment of autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 15550–15555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, A.W.; Singh, K.; Connors, S.L.; Liu, H.; Panjwani, A.A.; Lee, L.C.; Diggins, E.; Foley, A.; Melnyk, S.; Singh, I.N.; et al. Randomized controlled trial of sulforaphane and metabolite discovery in children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Mol. Autism 2021, 12, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, J.; Smith, R.C.; Tobe, R.H.; Lin, J.; Arriaza, J.; Fahey, J.W.; Liu, R.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, L.; et al. Efficacy of Sulforaphane in Treatment of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Multi-center Trial. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magner, M.; Thorová, K.; Župová, V.; Houška, M.; Švandová, I.; Novotná, P.; Tříska, J.; Vrchotová, N.; Soural, I.; Jílek, L. Sulforaphane Treatment in Children with Autism: A Prospective Randomized Double-Blind Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alshehri, S.; Ahmad, S.F.; Albekairi, N.A.; Alqarni, S.S.; Al-Harbi, N.O.; Al-Ayadhi, L.Y.; Attia, S.M.; Alfardan, A.S.; Bakheet, S.A.; Nadeem, A. Thioredoxin 1 and Thioredoxin Reductase 1 Redox System Is Dysregulated in Neutrophils of Subjects with Autism: In Vitro Effects of Environmental Toxicant, Methylmercury. Toxics 2023, 11, 739. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11090739
Alshehri S, Ahmad SF, Albekairi NA, Alqarni SS, Al-Harbi NO, Al-Ayadhi LY, Attia SM, Alfardan AS, Bakheet SA, Nadeem A. Thioredoxin 1 and Thioredoxin Reductase 1 Redox System Is Dysregulated in Neutrophils of Subjects with Autism: In Vitro Effects of Environmental Toxicant, Methylmercury. Toxics. 2023; 11(9):739. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11090739
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlshehri, Samiyah, Sheikh F. Ahmad, Norah A. Albekairi, Sana S. Alqarni, Naif O. Al-Harbi, Laila Y. Al-Ayadhi, Sabry M. Attia, Ali S. Alfardan, Saleh A. Bakheet, and Ahmed Nadeem. 2023. "Thioredoxin 1 and Thioredoxin Reductase 1 Redox System Is Dysregulated in Neutrophils of Subjects with Autism: In Vitro Effects of Environmental Toxicant, Methylmercury" Toxics 11, no. 9: 739. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11090739
APA StyleAlshehri, S., Ahmad, S. F., Albekairi, N. A., Alqarni, S. S., Al-Harbi, N. O., Al-Ayadhi, L. Y., Attia, S. M., Alfardan, A. S., Bakheet, S. A., & Nadeem, A. (2023). Thioredoxin 1 and Thioredoxin Reductase 1 Redox System Is Dysregulated in Neutrophils of Subjects with Autism: In Vitro Effects of Environmental Toxicant, Methylmercury. Toxics, 11(9), 739. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11090739







