Abstract
Deltamethrin and imidacloprid are commonly used insecticides for controlling sub-sucking insects in greenhouses. However, their application may cause sublethal effects on the aphid coccinellid predator Coccinella septempunctata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Here, we study (i) the toxicity and the effect of two sublethal doses (LD10 and LD30) of deltamethrin and imidacloprid on C. septempunctata in a laboratory microcosm and (ii) the residual toxicity of the two insecticides in a greenhouse. The results showed that both insecticides reduced fecundity, longevity, the intrinsic rate of increase, the finite rate of increase and the net reproductive rate. However, the developmental time of the fourth instar larvae was prolonged by both insecticides at LD10 and LD30. Deltamethrin residues were toxic 21 DAT (days after treatment) to C. septempunctata fourth instar larvae. In contrast, imidacloprid began in the slightly harmful category (75%) 1 DAT and declined to the harmless category (18.33%) 21 DAT. These results indicate that deltamethrin and imidacloprid have potential risks to C. septempunctata. This study provides information to guide the development of integrated pest management (IPM) strategies in greenhouses.
Keywords:
biological control; ecotoxicology; greenhouse; insecticides; IPM; side effect; coccinellids 1. Introduction
Aphids (Hemiptera: Aphididae) comprise an insect group that feeds on a wide range of plant species. In greenhouse crops, aphids are amongst the most dominant and destructive pests, causing significant losses in quality and/or yield [1]. The green peach aphid, Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Hemiptera: Aphididae), is extremely polyphagous, with great efficiency as a virus vector [2]. Myzus persicae can seriously damage crops by feeding on the vascular bundles of plants and/or by transmitting more than 100 plant viruses [3]. Chemical insecticides are widely used to control aphids and especially M. persicae [4]. However, long-term exposure of agricultural systems to insecticides has led to the development of resistance to many classes of insecticides, including pyrethroids and neonicotinoids [5,6]. Concerns about insecticide resistance development and the rapid emergence of insecticide resistance of M. persicae populations to new active ingredients [7] or insecticides with different MoA have increased the interest in integrated pest management (IPM) adoption for aphid control [4,6,8].
Biological control of aphids with parasitoids and/or predators is a critical component of IPM programs. Coccinellid predators are often utilized in greenhouses for aphid management [9], since many species can reduce aphid populations in greenhouses [10,11]. Coccinellid predator release can reduce the aphid population and is considered an alternative to insecticide applications [9,12].
The seven-spotted lady beetle, Coccinella septempunctata L. (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae), is an excellent biological control agent because it preys on more than 20 aphid species of Coccoidea, as well as species of Psylloidea and Tetranychidae, that infest crops both in the fields and in greenhouses [13] and can be found in a wide range of agricultural and/or natural habitats or crops all over the world [14]. Larvae and adults of C. septempunctata preying on aphids pose a major advantage since they could prevent aphid density increases from reaching the economic thresholds (ETs). However, when aphid population density exceeds the ET, the use of selective pesticides is critical for preserving C. septempunctata populations and achieving successful aphid predation rates [15].
Two of the most commonly used classes of insecticides applied to control sap-sucking pests in greenhouses and fields are neonicotinoids and pyrethroid [4,16]. However, in the European Union (EU), the neonicotinoids, imidacloprid, clothianidin and thiamethoxam in 2017 and thiacloprid in 2020 were banned for all outdoor uses [17,18] due to chronic adverse effects on honeybees [19]. In the present study, we aimed to evaluate the toxicity, developmental time, survival and adults’ longevity by examining the pre-oviposition period (APOP), total pre-oviposition period (TPOP), fecundity and population growth parameters of C. septempunctata exposed to lethal and sublethal doses of imidacloprid and deltamethrin. Additionally, in this study, we tried to examine this assumption of differential mortality by directly assessing the residual toxicity of imidacloprid and deltamethrin of C. septempunctata in the greenhouse. The present findings could assist the conservation of C. septempunctata and the regulation of deltamethrin and imidacloprid in IPM programs in greenhouses.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect Rearing
In total, more than 200 adults of C. septempunctata were collected from tobacco and peach fields infested by M. persicae in Katerini, Greece, and transferred to the Laboratory of Agricultural Entomology & Zoology of the University of the Peloponnese (Kalamata City, Greece). The green peach aphid, M. persicae, was used to rear C. septempunctata. Laboratory cultures of C. septempunctata were held on Chinese cabbage Brassica rapa pekinensis Hanelt (Brassicaceae) plants in cylindrical acrylic glass cages (DL: 30 × 50 cm) at 25 ± 1 °C and a relative humidity (RH) of 60–70% with a photoperiod of 16:8 h light: darkness (L:D).
2.2. Insecticides
The experiments were conducted with two commercial insecticides, imidacloprid (Confidor Forte 200SL, Bayer CropScience Hellas, Marousi, Greece) and deltamethrin (Decis 25EC, Bayer CropScience Hellas, Marousi, Greece).
2.3. Dose Response to Topical Application Bioassays
Independent assays were performed to find the acute toxicity of deltamethrin and imidacloprid against 4th instar larvae of C. septempunctata. The assays were carried out by topical application following a modified protocol of the method of [20,21]. Imidacloprid was dissolved in acetone to prepare a concentration gradient of 100, 200, 400, 600, 800, 1000, 1200 and 1600 ng of active ingredient per insect. The corresponding values for deltamethrin were 0.20, 0.40, 0.80, 1.60, 3.20, 4.80 and 6.40 ng of active ingredient per insect. Fourth instar larvae of C. septempunctata (<24 h old) were transferred to a Blackman box [22], and 1 μL of insecticide at each concentration was applied to the mesonotum of C. septempunctata using a 10 μL Hamilton microsyringe. Larvae treated with 1 μL acetone alone were set as control. Each larva was placed separately in a Blackman box with more than five hundred live M. persicae aphids. There were seventeen treatments including control, and every treatment was repeated three times using twenty larvae per treatment. Treated larvae were maintained in a controlled environmental chamber at 23 ± 1 °C, L16:D8 and 50 ± 5% RH. Mortality data for C. septempunctata were scored after 72 h. Larvae were considered dead if they did not move when gently pushed by a fine brush.
2.4. Evaluation of Low and Sublethal Effects on Fourth Instar Larvae
To calculate the life table parameters for C. septempunctata, a total of 361 eggs (12–24 h old) were randomly collected and maintained in Petri dishes (9 cm diameter). We used 65 eggs for the control group, 70 and 75 eggs in the deltamethrin LD10 and LD30 groups, respectively, and 71 and 80 eggs in the imidacloprid LD10 and LD30 groups, respectively. The hatch rate and incubation period of C. septempunctata eggs were recorded daily. After egg hatching, each first instar larva was transferred individually into a Blackman box, at the base of which there was a piece of water-saturated moss. Mortality and development time were recorded daily until the fourth instar larvae. To assess the low and sublethal effects on C. septempunctata population parameters, fourth instar larvae (<24 h old) topically treated (as described in the dose response to topical application bioassays section) to LD10 and LD30 doses of deltamethrin (0.34 ng a.i. and 0.63 ng a.i. per insect, respectively) and to LD10 and LD30 doses of imidacloprid (357.96 ng a.i. and 519.13 ng a.i. per insect, respectively), which were calculated from the toxicity regression equation, and as a control, we used only acetone (65 eggs). One fourth instar larva was released in each Blackman box. Larvae were reared and treated as noted in the topical bioassays section. After exposure to the insecticide, development time and mortality were recorded daily until the emergence of adults. After eclosion, adult females and males of each dose were randomly paired and transferred to a new Blackman box. Each pair was fed ad libitum with M. persicae every 24 h. The survival rate and fecundity were scored daily until all adults were dead. All insects were maintained in a controlled environmental chamber at 23 ± 1 °C, L16:D8 and 50 ± 5% RH.
2.5. Greenhouse Residual Toxicity Test
Seven hundred and twenty plants of Capsicum annuum L. were maintained in a greenhouse at 20 ± 3 °C with additional light (16 h light: 8 h dark) and were grown individually (Supplementary File). Plants at the five-leaf stage were used for the experiment. Pepper plants were sprayed (at the highest dose recommended on the label) until run off with deltamethrin (17.5 mg a.i L−1) or imidacloprid (60 mg a.i L−1) or tap water for control plants using a manual backpack sprayer. Bioassays on pepper plants 1, 3, 10 and 21 days after insecticide application (DAT) were conducted by placing fourth instar larvae (<24 h old) of C. septempunctata. In addition, about more than 300 frozen M. persicae aphids were placed on each plant to assure that all larvae had access to food during the experiment, and each plant–larvae system was covered by muslin to avoid insects’ escape. Each plant counted as a replicate. A total of sixty larvae per treatment were used. Larvae mortality was recorded 3 and 7 days after exposure.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
The predator dose–mortality relationship of LD50 and sublethal (LD10 and LD30), doses of the insecticides, 95% confidence intervals (CI), slopes and chi-square were calculated by probit analysis using SPSS version 25.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). The software two-sex MSChart [23] was used to analyze the life history data of C. septempunctata after exposure to sublethal doses of the insecticides imidacloprid and deltamethrin, based on the age-stage two-sex life table theory [24,25]. The life table parameters (lx), (mx), (exj), (vxj) and (sxj) (age-specific survival rate, age-specific fecundity, age-stage life expectancy, age-stage reproductive value and age-stage survival rate, respectively) were calculated. The pre-adult developmental duration time, pre-oviposition and total pre-oviposition period (APOP and TPOP, respectively) fecundity, male and female duration time, intrinsic rate of increase (r), finite rate of increase (λ), net reproductive rate (R0) and mean generation time (T) were also calculated. The paired bootstrap test was used to analyze the difference among each treatment group for all population parameters [26].
The residual effect of each insecticide on C. septempunctata mortality was compared using the χ2 test. When χ2 was significant, pairwise comparisons were performed using the Bonferroni correction.
3. Results
3.1. Toxicity of Deltamethrin and Imidacloprid to C. septempunctata
The toxicity of deltamethrin and imidacloprid against fourth instar larvae of C. septempunctata was determined after 3 days (Table 1). The LD50, LD10 and LD30 values of deltamethrin were 0.98, 0.337 and 0.633 ng a.i. per insect, respectively. The corresponding values in the case of imidacloprid were 671.56, 519.13 and 357.96 ng a.i per insect, respectively. The LD10 and LD30 values of deltamethrin and imidacloprid obtained were used to calculate the sublethal effects of both insecticides on the population parameters of C. septempunctata.

Table 1.
Toxicity of imidacloprid and deltamethrin to fourth instars larvae of Coccinella septempunctata in lab bioassays after 72 h of treatment.
3.2. Sublethal Effects of Deltamethrin and Imidacloprid on C. septempunctata
The developmental time of fourth instar larvae of C. septempunctata at all doses was significantly longer than that of the control group (Table 2). There were no significant differences between the deltamethrin and imidacloprid LD10 and LD30 groups. Furthermore, the developmental time of pupa did not differ in deltamethrin LD30, two imidacloprid and the control groups, while deltamethrin LD10 resulted in a significantly lower developmental time (4.64 days) than the control group.

Table 2.
Sublethal effects of imidacloprid and deltamethrin on the developmental time (mean ± SE) of C. septempunctata adults exposed to insecticide from the fourth instar larval stage.
Adult longevity was significantly shorter in imidacloprid and deltamethrin treatments than in the control treatment (Table 3). There were no significant differences between imidacloprid and deltamethrin treatments in terms of female adult longevity. In addition, female adult longevity was significantly shorter in the imidacloprid treatments compared with the control treatment. Male adult longevity did not differ significantly between imidacloprid LD10 (61.23 days) and the control treatment (70.11 days). Male adult longevity was significantly lower in the treatments of deltamethrin LD30 and LD10 (52.67 and 50.79 days, respectively) and imidacloprid LD30 (50.33 days) compared to the control treatment (70.11 days). No significant differences were recorded between the imidacloprid, deltamethrin and control group in terms of TPOP and APOP (Table 3). The number of eggs laid by females of C. septempunctata decreased by 52.07% and 69.89% in imidacloprid LD10 and LD30 doses, respectively, and by 57.53% and 31.72% in deltamethrin LD10 and LD30 doses, respectively, when compared with the control treatment. Furthermore, female fecundity did not differ significantly between the deltamethrin LD30 treatment and the control treatment, while imidacloprid treatments (LD10 and LD30 doses) and deltamethrin (LD10 dose) resulted in significantly reduced fecundity compared to the control treatment.

Table 3.
Sublethal effects of imidacloprid and deltamethrin on the life parameters (mean ± SE) of C. septempunctata adults exposed to insecticide from the fourth instar larval stage.
The population growth parameters are shown in Table 4. Treatment with imidacloprid had a significant effect on the finite rate of increase (λ) and intrinsic rate of increase (r) compared to those in the control group. Treatment with deltamethrin and imidacloprid resulted in a significantly smaller net reproductive rate (R0) in comparison to the control group. However, the mean generation time (T) had no significant effect between treatments.

Table 4.
Sublethal effects of imidacloprid and deltamethrin on the population growth parameters (mean ± SE) of C. septempunctata adults exposed to insecticide from the fourth instar larval stage.
Figure 1 presents the fecundity of the total population (mx), age-specific survival rate (lx) and the net maternity (lxmx) of C. septempunctata. The analysis of the age-specific survival rate, lx, demonstrates a more rapid decrease in the deltamethrin and imidacloprid treatment groups than in the control group. The highest mx (16.8) and lxmx (9.1) in the control group occurred on day 41. In comparison, the lowest mx (6.6) peak occurred at age 42 days in the deltamethrin LD10 group, while the lxmx (1.7) peak was recorded at 43 days in the imidacloprid LD30 treatment group.
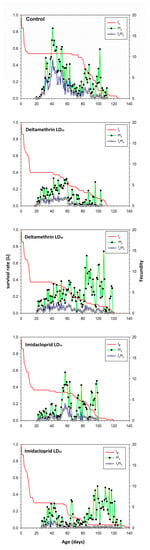
Figure 1.
Age-specific survival rate (lx), age-specific fecundity (mx), and age-specific maternity (lxmx) after fourth instar C. septempunctata larvae exposed to sublethal deltamethrin and imidacloprid doses.
The age-stage life expectancy exj of C. septempunctata is shown in Figure 2. All individuals treated by imidacloprid or deltamethrin have a lower exj than the control group. For example, a newly hatched C. septempunctata egg was supposed to survive 51.67 days in the control group compared to the life expectancies in deltamethrin LD10 and LD30 groups, which were 34.69 and 33.28 days, respectively. The corresponding values for imidacloprid were 34.55 and 27.86 days in the LD10 and LD30 treatments, respectively.
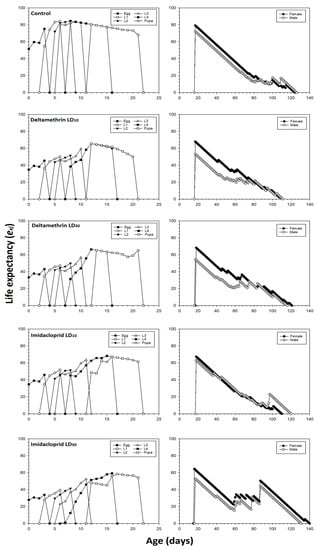
Figure 2.
Life expectancy (exj) values after fourth instar C. septempunctata larvae exposed to sublethal deltamethrin and imidacloprid doses.
The age-stage reproductive value (Vxj) of newly hatched C. septempunctata eggs was significantly lower in the imidacloprid LD10 and LD30 treatments compared to the control and deltamethrin groups (Figure 3). The Vxj began to increase when females started to produce offspring. The peak Vxj value of the untreated control C. septempunctata was 192.58 days−1 at 40 days. In the deltamethrin LD10 and LD30 groups, the peak Vxj values were 83.08 and 105.95 days−1 found at 42 and 85 days, respectively. In the imidacloprid LD10 and LD30 groups, the corresponding values were 118.80 and 106.01 days−1 found at 54 and 94 days, respectively.
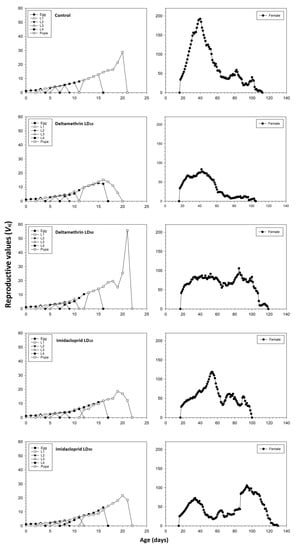
Figure 3.
Age-stage specific reproductive values (Vxj) values after fourth instar C. septempunctata larvae exposed to sublethal deltamethrin and imidacloprid doses.
The age-stage survival rates (Sxj) of C. septempunctata were negatively affected in the deltamethrin and imidacloprid treatment groups compared to the control group (Figure 4). The peak Sxj values for male and female adults in the control group were 0.28 and 0.26, respectively. The peak Sxj values for male and female adults treated with deltamethrin (i.e., LD10: 0.20 for males and females; LD30: 0.20 for males and 0.17 for females) and imidacloprid (i.e., LD10: 0.18 for males and females; LD30: 0.15 for males and females) decreased by increasing the insecticide doses.
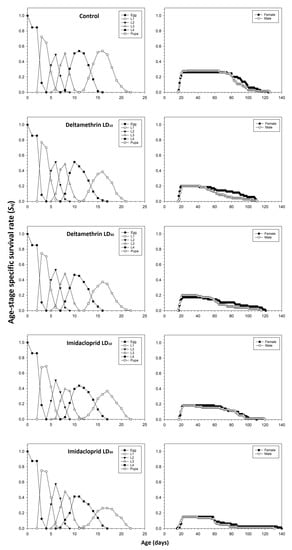
Figure 4.
Age-stage-specific survival rate (Sxj) after fourth instar C. septempunctata larvae exposed to sublethal deltamethrin and imidacloprid doses.
The projection population size of C. septempunctata at 140 days following different insecticide treatments is shown in Figure 5. The population size of C. septempunctata after 140 days in the control group was projected to be 7.6-fold greater than the initial population. The corresponding values for deltamethrin were 6.8 and 6.7 in the LD10 and LD30 groups, respectively. Population size was also affected by imidacloprid at 140 days in the LD10 (5.6-fold) and LD30 (5.0-fold) groups.
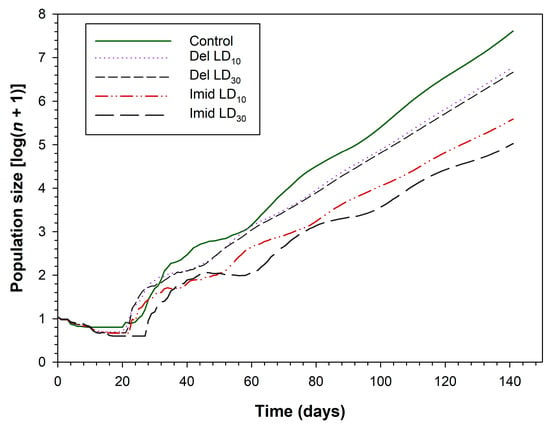
Figure 5.
Population projection for C. septempunctata larvae exposed to LD10 and LD30 doses of deltamethrin and imidacloprid.
3.3. Greenhouse Residual Toxicity Test
The insecticides deltamethrin and imidacloprid affected the mortality of fourth instar larvae of C. septempunctata 1, 3, 10 and 21 DAT (Figure 6). The mortality of fourth instar larvae of C. septempunctata was significantly increased 1 DAT (χ2 = 112.86, df = 2, p < 0.001), 3 DAT (χ2 = 145.12, df = 2, p < 0.001), 10 DAT (χ2 = 45.48, df = 2, p < 0.001) and 3 days after predator exposure to deltamethrin or imidacloprid residues on pepper plants compared to the control. No significant differences were observed at 21 DAT and 3 days after predator exposure to insecticides (χ2 = 2.01, df = 2, p = 0.366). Mortality was significantly higher when exposed for 7 days to insecticide residues at 1 DAT (χ2 = 121.25, df = 2, p < 0.001), 3 DAT (χ2 = 122.58, df = 2, p < 0.001), 10 DAT (χ2 = 132.36, df = 2, p < 0.001) and 21 DAT (χ2 = 138.47, df = 2, p < 0.001). C. septempunctata mortality was significantly higher when exposed to deltamethrin residues on pepper plants for 7 days than the control and the imidacloprid treatments. The mortality of C. septempunctata larvae by deltamethrin 3 days after larvae exposure was 100%, 98.33%, 41.67% and 0% at 1, 3, 10 and 21 DAT, respectively. The corresponding values for imidacloprid were 45%, 11.67%, 6.67% and 1.67%, respectively. In contrast, larvae mortality was 100% when exposed to deltamethrin residues on pepper plants for 7 days at 1, 3, 10 and 21 DAT. The corresponding values for imidacloprid were 75%, 25%, 20% and 18.33% at 1, 3, 10 and 21 DAT, respectively.
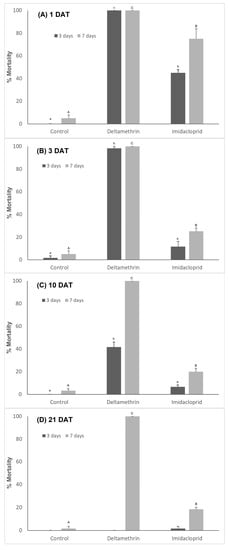
Figure 6.
Mean value (±SE) of mortality of Coccinella septempunctata larvae when exposed to pepper plants previously sprayed with insecticides for 3 and 7 days. Residues were assayed (A) 1 DAT, (B) 3 DAT, (C) 10 DAT and (D) 21 DAT. Means showed by the same letters are not significantly different (p < 0.05) according to Duncan test.
4. Discussion
Combining biological control and insecticide use in IPM programs requires information on how insecticides affect not only the target pest but also their natural enemies [27,28]. In the present study, the toxicity and the sublethal and residual effect of deltamethrin and imidacloprid on the seven-spot ladybeetle, C. septempunctata, were examined. Pyrethroid and neonicotinoid insecticides can have lethal and sublethal effects on coccinellid predators [28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39]. Deltamethrin and imidacloprid, which are frequently used insecticides in greenhouses to control aphids, have direct toxic effects on the fourth instar larvae of C. septempunctata, but among the two insecticides tested, deltamethrin was much more toxic than imidacloprid. Deltamethrin, a widely used pyrethroid, was found to be 685 times more toxic for the fourth instar larvae of C. septempunctata than imidacloprid. This difference in toxicity between the two insecticides was likely due to the resistance development in C. septempunctata to imidacloprid due to its frequent use to control M. persicae in tobacco and peach orchards for more than three decades in northern Greece [5,40], in addition to detoxification enzymes or activity in target site sensitivity by each insecticide [38]. The same toxic results to coccinellid predators by pyrethroids have been reported by many researchers [29,33,41] in Adalia bipunctata (L.) and Ceratomegilla undecimnotata (Schneider, 1792) [37]. Furthermore, residues of the insecticide deltamethrin were more toxic for the fourth instar larvae of C. septempunctata than those of imidacloprid. The mortality of the fourth instar larvae of C. septempunctata for imidacloprid began in the slightly harmful category (75%) 1 DAT and declined to the harmless category (18.33%) 21 DAT. In contrast, deltamethrin was placed in the harmful category (100%) during the entire examined period. Briefly, deltamethrin was toxic to biological control agents for aphid control in greenhouses, and the number of days for release after treatment should be carefully considered when using C. septempunctata in IPM programs.
A sublethal dose of deltamethrin and imidacloprid increased the developmental time of fourth instar larvae of C. septempunctata. Prolonged developmental time has been reported by several authors in C. septempunctata after fourth instar larvae are treated with sublethal doses of imidacloprid [42,43]. Moreover, increased developmental time was caused by imidacloprid in fourth instar larvae of C. undecimnotata and Hippodamia variegata (Goeze) (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) [36,37]. Increased developmental time was caused by bifenthrin to the second instar larvae of C. septempunctata [35]. The prolonged developmental time compared to the control group may be due to the fact that deltamethrin- or imidacloprid-treated larvae groups used their energy to detoxify the insecticides rather than for their development [44] or/and decreased pest consumption and, as a result, reduced their energy supply [30,31,36].
Although the duration of fourth instar larvae was impressively increased by the sublethal doses (LD10 and LD30) of deltamethrin and imidacloprid, the adult total longevity decreased compared to the control group. Furthermore, fecundity was significantly reduced after treatment with the LD10 of imidacloprid and deltamethrin and the LD30 of imidacloprid. These results are similar to those of other studies, where imidacloprid and deltamethrin decreased the adult longevity and fecundity of coccinellid predators [36,37,39,45]. The decreased fecundity could be attributed to the reduced food intake at the fourth instar larvae of C. septempunctata due to the insecticide treatment, which affected adult fitness [38,46]. Decreased fecundity may be based on the direct toxic effect of the insecticide and/or malformations of organs [47]. In addition to fecundity, the developmental time and longevity, value of the intrinsic rate of increase (r), net reproductive rate (R0) and finite rate of increase (λ) can be useful for understanding the predator coccinellid population dynamics. Our results showed that the r, λ and R0 of C. septempunctata decreased under the sublethal doses of imidacloprid compared to the control group. Sublethal doses of deltamethrin decreased the R0 of C. septempunctata compared to the control group. The results indicate that both sublethal doses of imidacloprid and deltamethrin can produce detrimental effects on the physiology of C. septempunctata [34]. Sublethal doses of neonicotinoids have been reported to lower population growth parameters for many coccinellid predators and/or other insects [30,32,36,37,39,47].
Furthermore, in our study, we found that imidacloprid and deltamethrin sublethal doses affected the two-sex life table parameters of C. septempunctata. Values such as mx, lx, lxmx, exj, Vxj and Sxj show a decreasing pattern, indicating that the life table parameters were affected by deltamethrin and imidacloprid at sublethal doses of LD10 and LD30. The reduction in the life table parameters such as mx and lx might be due to the fact that insecticides kill the more sensitive individuals, while the more resistant reduce prey consumption [32,38,46,48]. This result supports the idea that the reduced population parameters of the coccinellid predator verify that sublethal doses of deltamethrin and imidacloprid can reduce the survival and reproduction, thereby minimizing its efficacy as an aphid predator in greenhouse IPM strategies.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, our study showed that the residual toxicity of C. septempunctata varied between imidacloprid and deltamethrin. Imidacloprid had lower residual toxicity than deltamethrin to fourth instar larvae of C. septempunctata. In the present laboratory experiments, deltamethrin and imidacloprid had negative effects on the population parameters and survival of C. septempunctata. These findings indicate that both insecticides should not be preferred for IPM programs of M. persicae and other aphids. In particular, deltamethrin should be avoided due to its extreme toxicity to fourth instar larvae of C. septempunctata, which lasts for up to three weeks after application. These data provide the basis for new studies on the residual toxicity of the insecticides tested on coccinellid predators beyond 21 DAT performed under greenhouse conditions.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/toxics11070584/s1, Figure S1: Variation of temperature and relative humidity in greenhouse during the assessing the residual toxicity of imidacloprid and deltamethrin of C. septempunctata.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.J.S.; methodology, P.J.S.; software, P.J.S.; validation, P.J.S.; formal analysis, P.J.S.; investigation, P.J.S.; resources, P.J.S.; data curation, P.J.S.; writing—original draft preparation, P.J.S., E.K. and I.L.; writing—review and editing, P.J.S., V.D., A.I.D., J.T.M., A.T. and P.C.T.; visualization, A.T.; supervision, G.J.S.; project administration, P.J.S.; funding acquisition, P.J.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is co-financed by Greece and the European Union (European Social Fund-ESF) through the Operational Programme “Human Resources Development, Education and Lifelong Learning” in the context of the project “Reinforcement of Postdoctoral Researchers” (MIS-5001552), implemented by the State Scholarships Foundation (ΙΚΥ).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Available upon request.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Marina Mprokaki for his assistance with the laboratory experiments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Pineda, A.; Angeles Marcos-Garcia, M.J.E. Introducing barley as aphid reservoir in sweet-pepper greenhouses: Effects on native and released hoverflies (Diptera: Syrphidae). Eur. J. Entomol. 2008, 105, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackman, R.L.; Eastop, V.F. Taxonomic Issues. In Aphids as Crop Pests, 2nd ed.; Van Emden, H.F., Harrington, R., Eds.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2017; Chapter 1; pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Goggin, F.L. Plant–aphid interactions: Molecular and ecological perspectives. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2007, 10, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bass, C.; Puinean, A.M.; Zimmer, C.T.; Denholm, I.; Field, L.M.; Foster, S.P.; Gutbrod, O.; Nauen, R.; Slater, R.; Williamson, M.S. The evolution of insecticide resistance in the peach potato aphid, Myzus persicae. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 51, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margaritopoulos, J.T.; Kati, A.N.; Voudouris, C.C.; Skouras, P.J.; Tsitsipis, J.A. Long-term studies on the evolution of resistance of Myzus persicae (Hemiptera: Aphididae) to insecticides in Greece. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2021, 111, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.S.; Cordeiro, E.M.G.; Troczka, B.J.; Pym, A.; Mackisack, J.; Mathers, T.C.; Duarte, A.; Legeai, F.; Robin, S.; Bielza, P.; et al. Global patterns in genomic diversity underpinning the evolution of insecticide resistance in the aphid crop pest Myzus persicae. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umina, P.A.; Bass, C.; van Rooyen, A.; Chirgwin, E.; Arthur, A.L.; Pym, A.; Mackisack, J.; Mathews, A.; Kirkland, L. Spi-rotetramat resistance in Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Hemiptera: Aphididae) and its association with the presence of the A2666V mutation. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 4822–4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overton, K.; Ward, S.E.; Hoffmann, A.A.; Umina, P.A. Lethal impacts of insecticides and miticides on three agriculturally important aphid parasitoids. Biol. Control 2023, 178, 105143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddick, E.W. Identification of Conditions for Successful Aphid Control by Ladybirds in Greenhouses. Insects 2017, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, W.; Pell, J.K. Biological Control. In Aphids as Crop Pests, 2nd ed.; Van Emden, H.F., Harrington, R., Eds.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2017; pp. 469–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Driesche, R.G. An overview of biological control in protected culture. In BioControl in Protected Culture; van Driesche, R., Heinz, K.M., Parrella, M.P., Eds.; Ball Publishing: Batavia, IL, USA, 2004; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Yano, E. Ecological considerations for biological control of aphids in protected culture. Popul. Ecol. 2006, 48, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodek, I.; Honek, A.; Van Emden, H.F. Ecology and Behaviour of the Ladybird Beetles (Coccinellidae); John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.R.; Walters, K.F.A.; Port, G.R.; Northing, P. Consumption rates and predatory activity of adult and fourth instar larvae of the seven spot ladybird, Coccinella septempunctata (L.), following contact with dimethoate residue and contam-inated prey in laboratory arenas. Biol. Control 2004, 30, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Lu, Y.; Chao, W.; Dong, Z.; Ali, A.; Liu, T.X.; Lu, Z. When Does the Prey/Predator Ratio Work for the Effective Biocontrol of Cotton Aphid on Cotton Seedlings? Insects 2022, 13, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, C.; Denholm, I.; Williamson, M.S.; Nauen, R. The global status of insect resistance to neonicotinoid insecticides. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2015, 121, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Authority, E.F.S. Guidance on the risk assessment of plant protection products on bees (Apis mellifera, Bombus spp. and solitary bees). EFSA J. 2013, 11, 3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasman, K.; Hidalgo, S.; Zhu, B.; Rands, S.A.; Hodge, J.J.L. Neonicotinoids disrupt memory, circadian behaviour and sleep. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.C.C.; Cristaldo, P.F.; Araújo, A.P.A.; Melo, C.R.; Lima, A.P.S.; Santana, E.D.R.; de Oliveira, B.M.S.; Oliveira, J.W.S.; Vieira, J.S.; Blank, A.F.; et al. Apis mellifera (Insecta: Hymenoptera) in the target of neonicotinoids: A one-way ticket? Bi-oinsecticides can be an alternative. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 163, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, P.; Budia, F.; Estal, P.D.; Adán, A.; Viñuela, E. Toxicity of Fipronil to the Predatory Lacewing Chrysoperla carnea (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae). Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2004, 14, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.D.; Jepson, P.C.; Mayer, D.F. Limitations to Use of Topical Toxicity Data for Predictions of Pesticide Side Effects in the Field. J. Econ. Entomol. 1995, 88, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackman, R.L. Variation in the photoperiodic response within natural populations of Myzus persicae (Sulz.). Bull. Entomol. Res. 1971, 60, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, H. TWOSEX-MSChart: A Computer Program for the Age-Stage, Two-Sex Life Table Analysis; National Chung Hsing University: Taichung, Taiwan, 2021; Available online: http://140.120.197.173/Ecology/ (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Chi, H. Life-Table Analysis Incorporating Both Sexes and Variable Development Rates Among Individuals. Environ. Entomol. 1988, 17, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.; Liu, H. Two new methods for the study of insect population ecology. Bull. Inst. Zool. Acad. Sin. 1985, 24, 225–240. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, M.; Chi, H.; Guo, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, L.; Ma, R. Demography of Cacopsylla chinensis (Hemiptera: Psyllidae) Reared on Four Cultivars of Pyrus bretschneideri (Rosales: Rosaceae) and P. communis Pears with Estimations of Confidence Intervals of Specific Life Table Statistics. J. Econ. Entomol. 2020, 113, 2343–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desneux, N.; Decourtye, A.; Delpuech, J.-M. The Sublethal Effects of Pesticides on Beneficial Arthropods. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2007, 52, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quesada, C.R.; Sadof, C.S. Residual toxicity of insecticides to Chrysoperla rufilabris and Rhyzobius lophanthae predators as biocontrol agents of pine needle scale. Crop Prot. 2020, 130, 105044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzón, A.; Medina, P.; Amor, F.; Viñuela, E.; Budia, F. Toxicity and sublethal effects of six insecticides to last instar larvae and adults of the biocontrol agents Chrysoperla carnea (Stephens) (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae) and Adalia bipunctata (L.) (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Chemosphere 2015, 132, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Sun, S.; Tan, H.; Sun, X.; Shang, D.; Yao, C.; Qin, C.; Ji, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; et al. Compatibility of chlorantraniliprole with the generalist predator Coccinella septempunctata L. (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) based toxicity, life-cycle development and population parameters in laboratory microcosms. Chemosphere 2019, 225, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zheng, Y.; Desneux, N.; Wu, K. Lethal effect of imidacloprid on the coccinellid predator Serangium japonicum and sublethal effects on predator voracity and on functional response to the whitefly Bemisia tabaci. Ecotoxicology 2012, 21, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, X.; Yu, C.; Liu, F.; Mu, W. Sublethal and transgenerational effects of thiamethoxam on the demo-graphic fitness and predation performance of the seven-spot ladybeetle Coccinella septempunctata L. (Coleoptera: Coc-cinellidae). Chemosphere 2019, 216, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszak, R.W. Influence of some pesticides on mortality and fecundity of the aphidophagous coccinellid Adalia bipunctata L. (Col., Coccinellidae). J. Appl. Entomol. 1999, 123, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, S.; Bandani, A.R. Sublethal concentrations of thiamethoxam adversely affect life table parameters of the aphid predator, Hippodamia variegata (Goeze) (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Crop Prot. 2013, 54, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, M.; Atta, B.; Rizwan, M.; Ashraf, I.; Arshad, M.; Tahir, M.; Ali, M.; Sabir, A.M.; Bilal, M.; Ali, M.Y. Do neonicotinoids better than pyrethroids for Coccinella septempunctata L. (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae)? A comparative sub-lethal indirect age-stage, two-sex life tables laboratory bioassay. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2021, 41, 2811–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skouras, P.J.; Brokaki, M.; Stathas, G.J.; Demopoulos, V.; Louloudakis, G.; Margaritopoulos, J.T. Lethal and sub-lethal effects of imidacloprid on the aphidophagous coccinellid Hippodamia variegata. Chemosphere 2019, 229, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skouras, P.J.; Darras, A.I.; Mprokaki, M.; Demopoulos, V.; Margaritopoulos, J.T.; Delis, C.; Stathas, G.J. Toxicity, sublethal and low dose effects of imidacloprid and deltamethrin on the aphidophagous predator Ceratomegilla undecimnotata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Insects 2021, 12, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhai, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Q.; Ji, X.; Wang, W.; Yuan, H.; Rui, C.; Cui, L. Sulfoxaflor adversely influences the bio-logical characteristics of Coccinella septempunctata by suppressing vitellogenin expression and predation activity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 447, 130787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Zhao, J.; Guo, X.; Chen, H.; Qu, M.; Zhai, W.; Desneux, N.; Biondi, A.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S. Sublethal effects of imidacloprid on the predatory seven-spot ladybird beetle Coccinella septempunctata. Ecotoxicology 2016, 25, 1782–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margaritopoulos, J.T.; Skouras, P.J.; Nikolaidou, P.; Manolikaki, J.; Maritsa, K.; Tsamandani, K.; Kanavaki, O.M.; Bacan-dritsos, N.; Zarpas, K.D.; Tsitsipis, J.A. Insecticide resistance status of Myzus persicae (Hemiptera: Aphididae) populations from peach and tobacco in mainland Greece. Pest Manag. Sci. 2007, 63, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalali, M.A.; Van Leeuwen, T.; Tirry, L.; De Clercq, P. Toxicity of selected insecticides to the two-spot ladybird Adalia bipunctata. Phytoparasitica 2009, 37, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afza, R.; Afzal, A.; Riaz, M.A.; Majeed, M.Z.; Idrees, A.; Qadir, Z.A.; Afzal, M.; Hassan, B.; Li, J. Sublethal and transgener-ational effects of synthetic insecticides on the biological parameters and functional response of Coccinella septempunctata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) under laboratory conditions. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1088712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skouras, P.J.; Stathas, G.J.; Voudouris, C.C.; Darras, A.I.; Tsitsipis, J.A.; Margaritopoulos, J.T. Effect of synthetic insecticides on the larvae of Coccinella septempunctata from Greek populations. Phytoparasitica 2017, 45, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannig, G.T.; Ziegler, M.; Marçon, P.G. Feeding cessation effects of chlorantraniliprole, a new anthranilic diamide in-secticide, in comparison with several insecticides in distinct chemical classes and mode-of-action groups. Pest Manag. Sci. 2009, 65, 969–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Lin, R.; Fu, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zong, F.; Jiang, H.; Lv, N.; Piao, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; et al. Impact of imidacloprid on life-cycle development of Coccinella septempunctata in laboratory microcosms. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 110, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; De Clercq, P.; Pan, C.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Pang, H. Larval nutrition-induced plasticity affects reproduction and gene expression of the ladybeetle, Cryptolaemus montrouzieri. BMC Evol. Biol. 2015, 15, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, D.; Liu, Y.-X.; Liu, X.; Dewer, Y.; Mota-Sanchez, D.; Yang, X.-Q. Exposure to lambda-cyhalothrin and abamectin drives sublethal and transgenerational effects on the development and reproduction of Cydia pomonella. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 252, 114581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, K.; Zhao, Y.; Han, J.; Liu, F.; Mu, W. Effects of Sublethal Concentrations of Cyantraniliprole on the Development, Fecundity and Nutritional Physiology of the Black Cutworm Agrotis ipsilon (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).