Arsenic-Induced, Mitochondria-Mediated Apoptosis Is Associated with Decreased Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ Coactivator α in Rat Brains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Animal and Experimental Designs
2.3. Hematoxylin–Eosin (H&E) Staining
2.4. Terminal Deoxynucleoitidyl Transferase-Mediated Nick End Labeling (TUNEL) Assay
2.5. Observation of the Ultrastructure of Neurons in Hippocampus by Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.6. Detection of Total Arsenic in Brain
2.7. Immunohistochemistry
2.8. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.9. Detection of ATP Contents in Brain
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
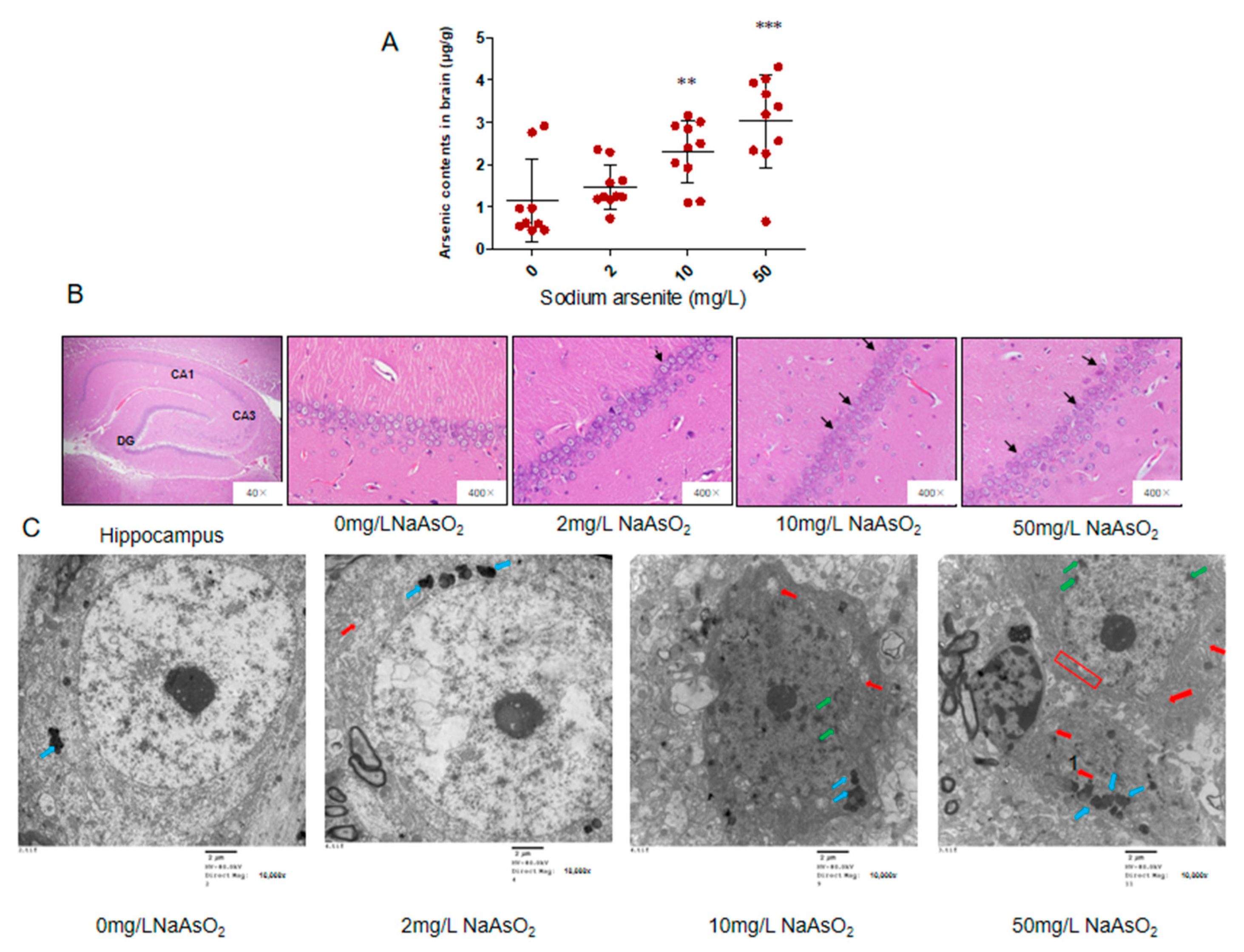
3.1. Arsenic Accumulated in the Brain and Induced Neuronal Apoptosis
3.2. TUNEL Analysis of the Hippocampal CA1 of Rats Exposed to Different Arsenic Concentrations
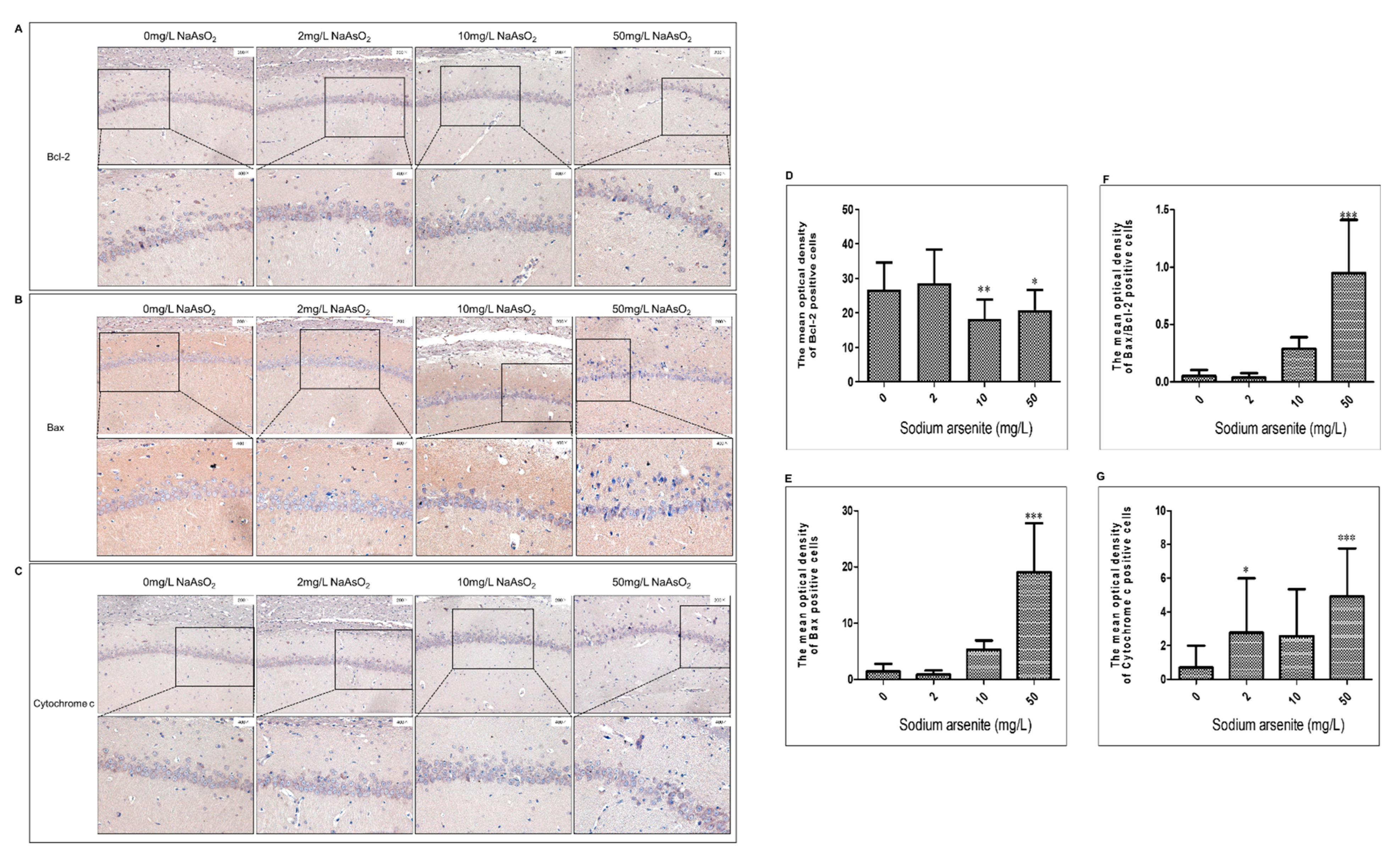
3.3. Bcl-2, Bax, and Cytochrome C Expression in Hippocampal CA1 Region of Rats after Arsenic Exposure
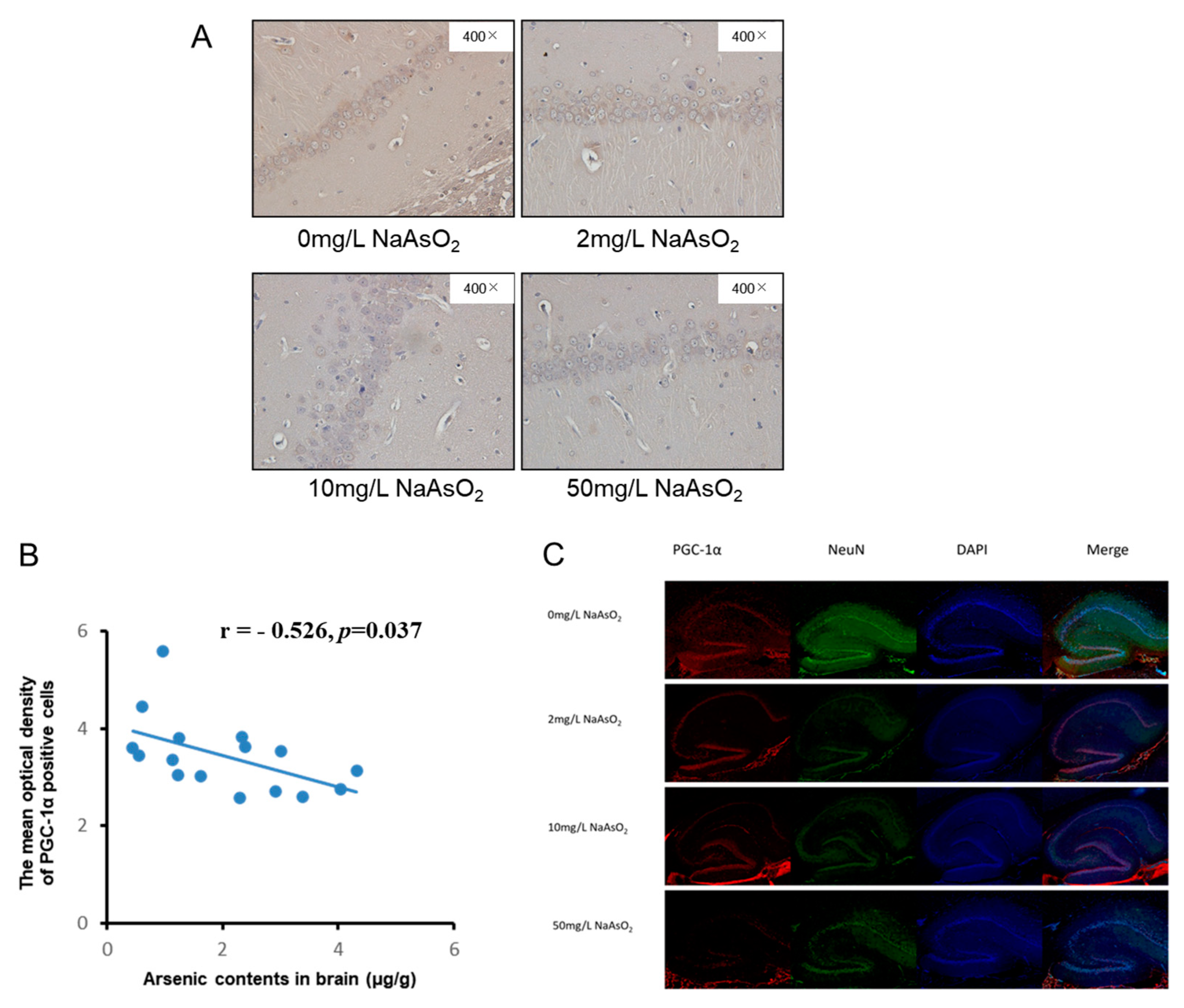
3.4. PGC-1α Expression in Hippocampal CA1 Region of Rats Exposed to Different Arsenic Concentrations
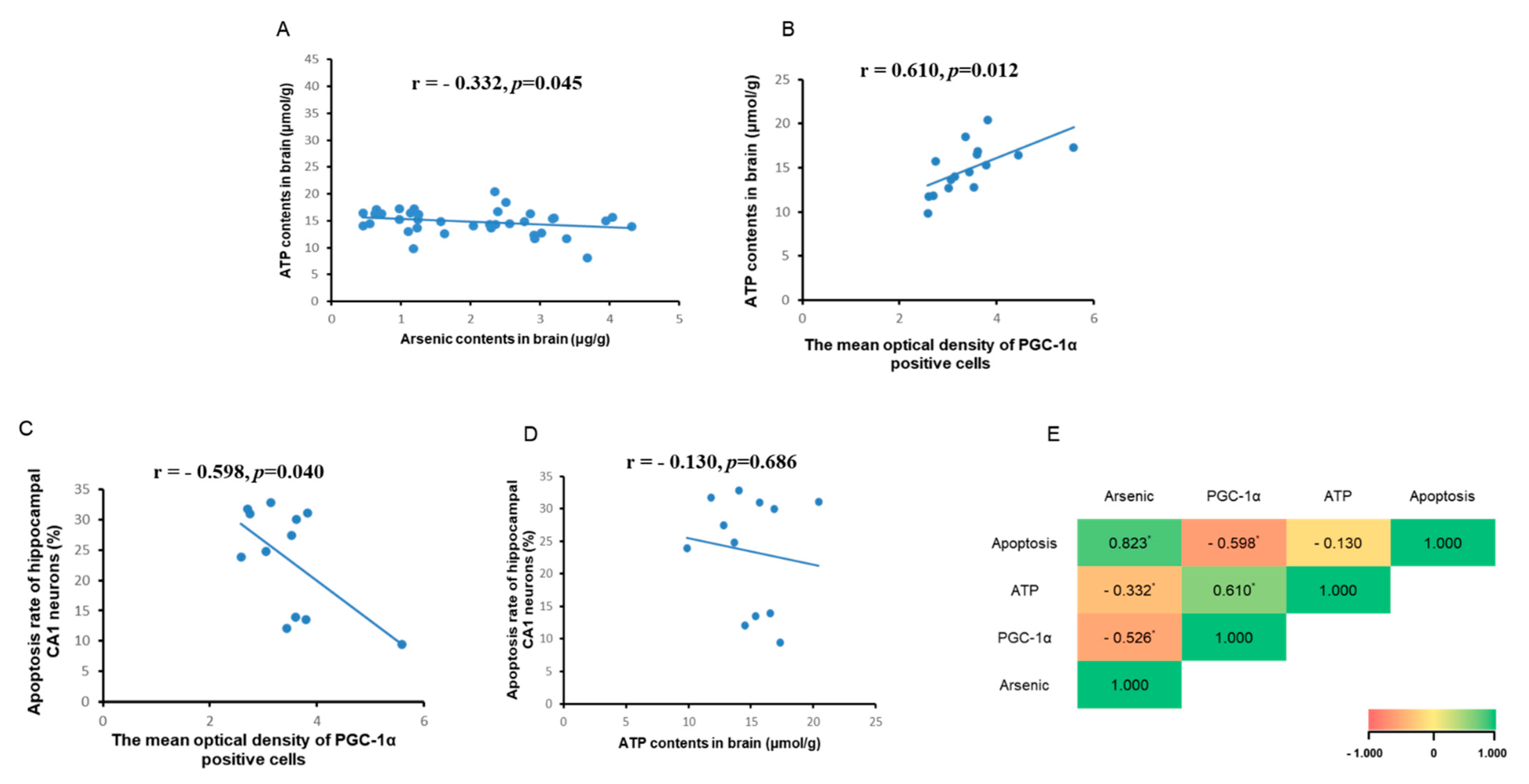
3.5. Correlation Analysis between Brain ATP, Arsenic, and PGC-1α Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hong, Y.S.; Song, K.H.; Chung, J.Y. Health effects of chronic arsenic exposure. J. Prev. Med. Public Health 2014, 47, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raju, N.J. Arsenic in the geo-environment: A review of sources, geochemical processes, toxicity and removal technologies. Environ. Res. 2022, 203, 111782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasserman, G.A.; Liu, X.; Parvez, F.; Ahsan, H.; Factor-Litvak, P.; Geen, A.V.; Slavkovich, V.; Lolacono, N.J.; Cheng, Z.; Hussain, I. Water Arsenic Exposure and Children’s Intellectual Function in Araihazar, Bangladesh. Environ. Health Perspect. 2004, 112, 1329–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Gao, Y.; Liu, H.; Sun, J.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, D.; Sun, D. Assessment of relationship on excess arsenic intake from drinking water and cognitive impairment in adults and elders in arsenicosis areas. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2017, 220, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Yang, Y.; Shao, H.; Sun, W.; Gu, M.; Wang, H.; Jiang, L.; Qu, L.; Sun, D.; Gao, Y. Sodium Arsenite-Induced Learning and Memory Impairment Is Associated with Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Mediated Apoptosis in Rat Hippocampus. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhao, M.; Chen, Z.; Wu, G.; Fujino, M.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, W.; Zhao, M.; Hirano, S.I.; Li, X.K.; et al. Hydrogen Gas Attenuates Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury via Regulation of the MAPK/HO-1/PGC-1a Pathway in Neonatal Rats. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 6978784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bai, C.; Guan, H.; Chen, R.; Wang, X.; Wang, B.; Jin, H.; Piao, F. Subchronic exposure to arsenic induces apoptosis in the hippocampus of the mouse brains through the Bcl-2/Bax pathway. J. Occup. Health 2015, 57, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhou, C.C.; Yang, Y.; Liu, J.W.; Yan, C.H. GM1 Ameliorates Lead-Induced Cognitive Deficits and Brain Damage Through Activating the SIRT1/CREB/BDNF Pathway in the Developing Male Rat Hippocampus. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 190, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Cui, W.; He, J.; Wang, Z.; Yang, X. Olive leaf extract inhibits lead poisoning-induced brain injury. Neural Regen. Res. 2013, 8, 2021–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, W.; Lin, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, F.; Xie, Y. Sulfiredoxin-1 protects spinal cord neurons against oxidative stress in the oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation model through the bax/cytochrome c/caspase 3 apoptosis pathway. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 744, 135615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Yao, Y.; Guo, M.; Li, J.; Yang, P.; Xu, H.; Lin, D. Sevoflurane increases intracellular calcium to induce mitochondrial injury and neuroapoptosis. Toxicol. Lett. 2021, 336, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kass, G.E.; Eriksson, J.E.; Weis, M.; Orrenius, S.; Chow, S.C. Chromatin condensation during apoptosis requires ATP. Biochem. J. 1996, 318 Pt 3, 749–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, H.; Sakamoto, S.; Yoshida, T.; Matsui, Y.; Penuela, S.; Laird, D.W.; Mizukami, S.; Kikuchi, K.; Kakizuka, A. Single-cell dynamics of pannexin-1-facilitated programmed ATP loss during apoptosis. eLife 2020, 9, e61960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luis-García, E.R.; Becerril, C.; Salgado-Aguayo, A.; Aparicio-Trejo, O.E.; Romero, Y.; Flores-Soto, E.; Mendoza-Milla, C.; Montaño, M.; Chagoya, V.; Pedraza-Chaverri, J.; et al. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Alterations in Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore (mPTP) Contribute to Apoptosis Resistance in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nino, S.A.; Morales-Martinez, A.; Chi-Ahumada, E.; Carrizales, L.; Salgado-Delgado, R.; Perez-Severiano, F.; Diaz-Cintra, S.; Jimenez-Capdeville, M.E.; Zarazua, S. Arsenic Exposure Contributes to the Bioenergetic Damage in an Alzheimer’s Disease Model. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dua, T.K.; Dewanjee, S.; Gangopadhyay, M.; Khanra, R.; Zia-Ul-Haq, M.; De Feo, V. Ameliorative effect of water spinach, Ipomea aquatica (Convolvulaceae), against experimentally induced arsenic toxicity. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldissarelli, L.A.; Capiotti, K.M.; Bogo, M.R.; Ghisleni, G.; Bonan, C.D. Arsenic alters behavioral parameters and brain ectonucleotidases activities in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2012, 155, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwivedi, N.; Mehta, A.; Yadav, A.; Binukumar, B.K.; Gill, K.D.; Flora, S.J. MiADMSA reverses impaired mitochondrial energy metabolism and neuronal apoptotic cell death after arsenic exposure in rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2011, 256, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Li, S.; Li, J.; Lv, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, P.; Yang, Q.; Tang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z. Hexavalent chromium induces renal apoptosis and autophagy via disordering the balance of mitochondrial dynamics in rats. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 204, 111061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Yu, A.; Zheng, H.; Wang, S.; He, Y.; Wang, L. Calycosin-7-O-β-D-glucoside Attenuates OGD/R-Induced Damage by Preventing Oxidative Stress and Neuronal Apoptosis via the SIRT1/FOXO1/PGC-1α Pathway in HT22 Cells. Neural Plast. 2019, 2019, 8798069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Teng, F.; Li, J.; Guan, Y.; Xu, J.; Lv, X.; Guan, F.; Zhang, M.; Chen, L. Berberine Improves Cognitive Deficiency and Muscular Dysfunction via Activation of the AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1a Pathway in Skeletal Muscle from Naturally Aging Rats. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2018, 22, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Z.; Hu, X.; Luo, T.; Ming, Z.; Luo, Z. Naturally-occurring spinosyn A and its derivatives function as argininosuccinate synthase activator and tumor inhibitor. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Fu, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Gao, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W. Role of Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor in Arsenic-Induced Vascular Endothelial Dysfunction in a Rat Model. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 190, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Tang, Q.; Zou, Z.; Meng, P.; Tu, B.; Xia, Y.; Cheng, S.; Zhang, L.; Yang, K.; Mu, S.; et al. m6A Demethylase FTO Regulates Dopaminergic Neurotransmission Deficits Caused by Arsenite. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 165, 431–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, K.; Kaur, B.; Pandey, K.K.; Dhar, P.; Kaler, S. Resveratrol protects against inorganic arsenic-induced oxidative damage and cytoarchitectural alterations in female mouse hippocampus. Acta Histochem. 2021, 123, 151792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Wu, R.; Bai, J.; Hou, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Meng, X. Mitochondrial MPTP: A Novel Target of Ethnomedicine for Stroke Treatment by Apoptosis Inhibition. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, C.; Kroemer, G. Apoptosis. Mitochondria--the death signal integrators. Science 2000, 289, 1150–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altznauer, F.; Conus, S.; Cavalli, A.; Folkers, G.; Simon, H.U. Calpain-1 regulates Bax and subsequent Smac-dependent caspase-3 activation in neutrophil apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 5947–5957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binju, M.; Amaya-Padilla, M.A.; Wan, G.; Gunosewoyo, H.; Suryo Rahmanto, Y.; Yu, Y. Therapeutic Inducers of Apoptosis in Ovarian Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cregan, S.P.; MacLaurin, J.G.; Craig, C.G.; Robertson, G.S.; Nicholson, D.W.; Park, D.S.; Slack, R.S. Bax-dependent caspase-3 activation is a key determinant in p53-induced apoptosis in neurons. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 7860–7869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.J.; Kim, D.Y.; Gwag, B.J. Cellular and molecular pathways of ischemic neuronal death. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 35, 67–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Feng, H.; Gao, Y.; Sun, L.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhao, L.; Hu, X.; Sun, H.; et al. Role of pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) in arsenic-induced cell apoptosis of liver and brain in a rat model. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2013, 151, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radajewska, A.; Szyller, J.; Niewiadomska, J.; Noszczyk-Nowak, A.; Bil-Lula, I. Punica granatum L. Polyphenolic Extract as an Antioxidant to Prevent Kidney Injury in Metabolic Syndrome Rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2023, 2023, 6144967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Hang, P.; Pan, Y.; Feng, B.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, T.; Zhao, L.; Du, Z. Inhibition of miR-23a attenuates doxorubicin-induced mitochondria-dependent cardiomyocyte apoptosis by targeting the PGC-1α/Drp1 pathway. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 369, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, N.; Sun, Q.; Su, Q.; Dang, S.; Chen, G. Taurine promotes cognitive function in prenatally stressed juvenile rats via activating the Akt-CREB-PGC1α pathway. Redox Biol. 2016, 10, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, C.; Kumar, V. Arsenic-induced mitochondrial oxidative damage is mediated by decreased PGC-1α expression and its downstream targets in rat brain. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2016, 256, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halling, J.F.; Pilegaard, H. PGC-1α-mediated regulation of mitochondrial function and physiological implications. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2020, 45, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navazani, P.; Vaseghi, S.; Hashemi, M.; Shafaati, M.R.; Nasehi, M. Effects of Treadmill Exercise on the Expression Level of BAX, BAD, BCL-2, BCL-XL, TFAM, and PGC-1α in the Hippocampus of Thimerosal-Treated Rats. Neurotox. Res. 2021, 39, 1274–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tritos, N.A.; Mastaitis, J.W.; Kokkotou, E.G.; Puigserver, P.; Spiegelman, B.M.; Maratos-Flier, E. Characterization of the peroxisome proliferator activated receptor coactivator 1 alpha (PGC 1alpha) expression in the murine brain. Brain Res. 2003, 961, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.D.; Yang, D.I.; Lin, T.K.; Shaw, F.Z.; Liou, C.W.; Chuang, Y.C. Roles of oxidative stress, apoptosis, PGC-1α and mitochondrial biogenesis in cerebral ischemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 7199–7215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szalardy, L.; Zadori, D.; Plangar, I.; Vecsei, L.; Weydt, P.; Ludolph, A.C.; Klivenyi, P.; Kovacs, G.G. Neuropathology of partial PGC-1α deficiency recapitulates features of mitochondrial encephalopathies but not of neurodegenerative diseases. Neurodegener. Dis. 2013, 12, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Pierre, J.; Drori, S.; Uldry, M.; Silvaggi, J.M.; Rhee, J.; Jager, S.; Handschin, C.; Zheng, K.; Lin, J.; Yang, W.; et al. Suppression of reactive oxygen species and neurodegeneration by the PGC-1 transcriptional coactivators. Cell 2006, 127, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Lei, Y.H.; Zhou, J.P.; Hou, Y.Y.; Meng, H. Role of PGC-1α in Mitochondrial Quality Control in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Neurochem. Res. 2019, 44, 2031–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Tao, S.; Li, X.; Yao, Q. Resistin destroys mitochondrial biogenesis by inhibiting the PGC-1α/NRF1/TFAM signaling pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 504, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafa Tork, O.; Ahmed Rashed, L.; Bakr Sadek, N.; Abdel-Tawab, M.S. Targeting Altered Mitochondrial Biogenesis in the Brain of Diabetic Rats: Potential Effect of Pioglitazone and Exendin-4. Rep. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 8, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nasehi, M.; Torabinejad, S.; Hashemi, M.; Vaseghi, S.; Zarrindast, M.R. Effect of cholestasis and NeuroAid treatment on the expression of Bax, Bcl-2, Pgc-1α and Tfam genes involved in apoptosis and mitochondrial biogenesis in the striatum of male rats. Metab. Brain Dis. 2020, 35, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ren, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Z.; Ma, S.; Bao, J.; Li, Z.; Bai, X.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, Z.; et al. PGC-1α/ERRα-Sirt3 Pathway Regulates DAergic Neuronal Death by Directly Deacetylating SOD2 and ATP Synthase β. Antioxid. Redox 2016, 24, 312–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Xiaoqian, Y.E.; You, Y.; Lin, L.; Lian, J.; Juan, L.I.; Yang, S.; Xue, X. The neuroprotection of electro-acupuncture via the PGC-1α/TFAM pathway in transient focal cerebral ischemia rats. Biocell 2022, 46, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, B.; Ma, X.; Liu, Y.; Ni, B.; Lu, S.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W. Arsenic-Induced, Mitochondria-Mediated Apoptosis Is Associated with Decreased Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ Coactivator α in Rat Brains. Toxics 2023, 11, 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11070576
Ding B, Ma X, Liu Y, Ni B, Lu S, Chen Y, Liu X, Zhang W. Arsenic-Induced, Mitochondria-Mediated Apoptosis Is Associated with Decreased Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ Coactivator α in Rat Brains. Toxics. 2023; 11(7):576. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11070576
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Bo, Xinbo Ma, Yang Liu, Bangyao Ni, Siqi Lu, Yuting Chen, Xiaona Liu, and Wei Zhang. 2023. "Arsenic-Induced, Mitochondria-Mediated Apoptosis Is Associated with Decreased Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ Coactivator α in Rat Brains" Toxics 11, no. 7: 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11070576
APA StyleDing, B., Ma, X., Liu, Y., Ni, B., Lu, S., Chen, Y., Liu, X., & Zhang, W. (2023). Arsenic-Induced, Mitochondria-Mediated Apoptosis Is Associated with Decreased Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ Coactivator α in Rat Brains. Toxics, 11(7), 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11070576



